Particulate PAH Transport Associated with Adult Chronic Cough Occurrence Closely Connected with Meteorological Conditions: A Modelling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Emission Inventory
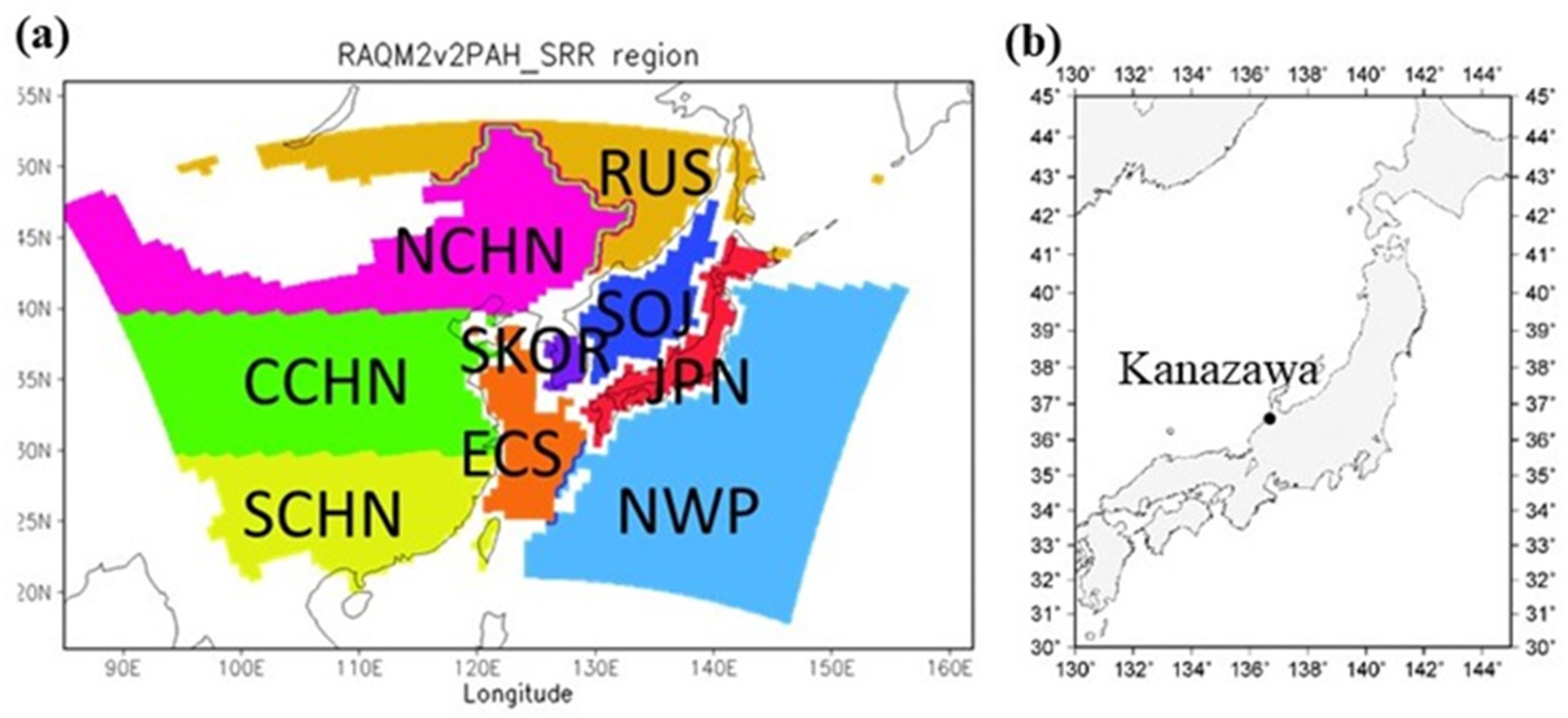
2.3. Source-Receptor Relationship Analysis Method
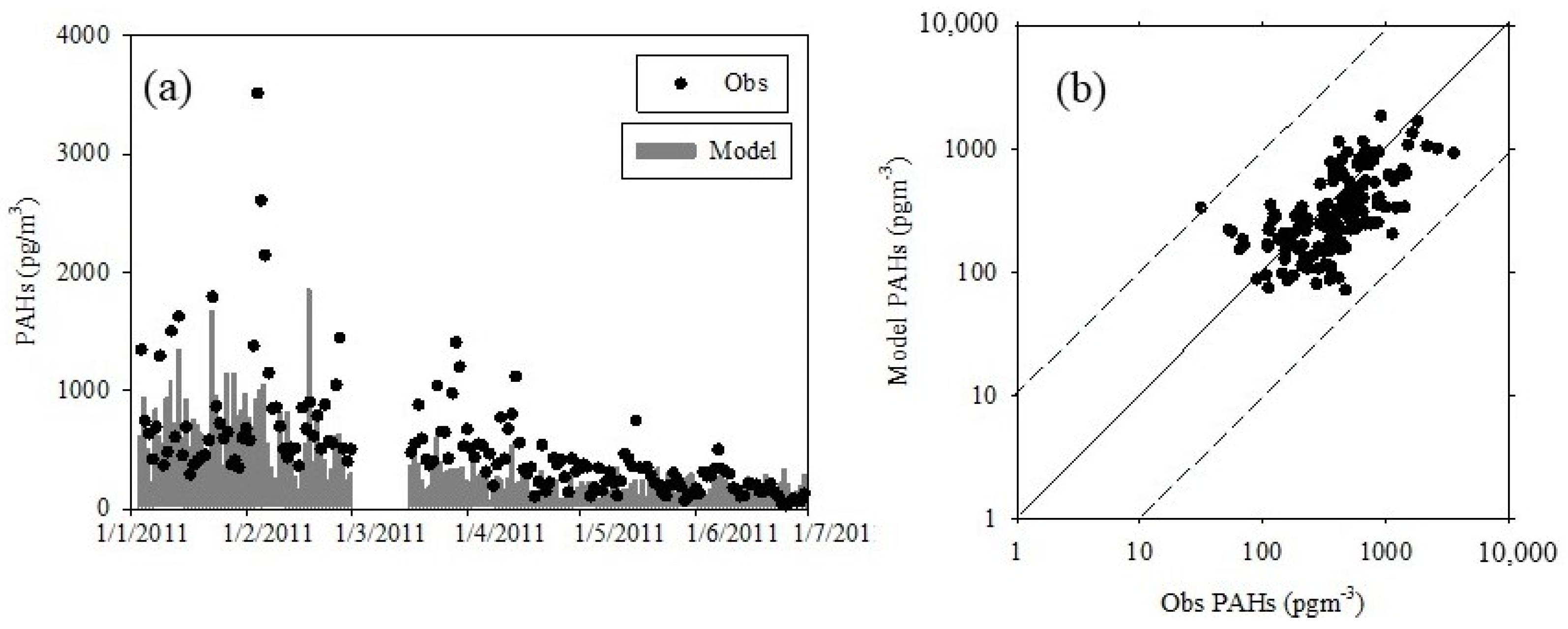
2.4. Model Validation Using the Observed Data
2.5. Observations of the p-PAH Concentration and Epidemiological Analysis
2.5.1. Analysis of the Ambient p-PAHs
2.5.2. Epidemiological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Relation of the Daily Cough Occurrence and p-PAH Concentration
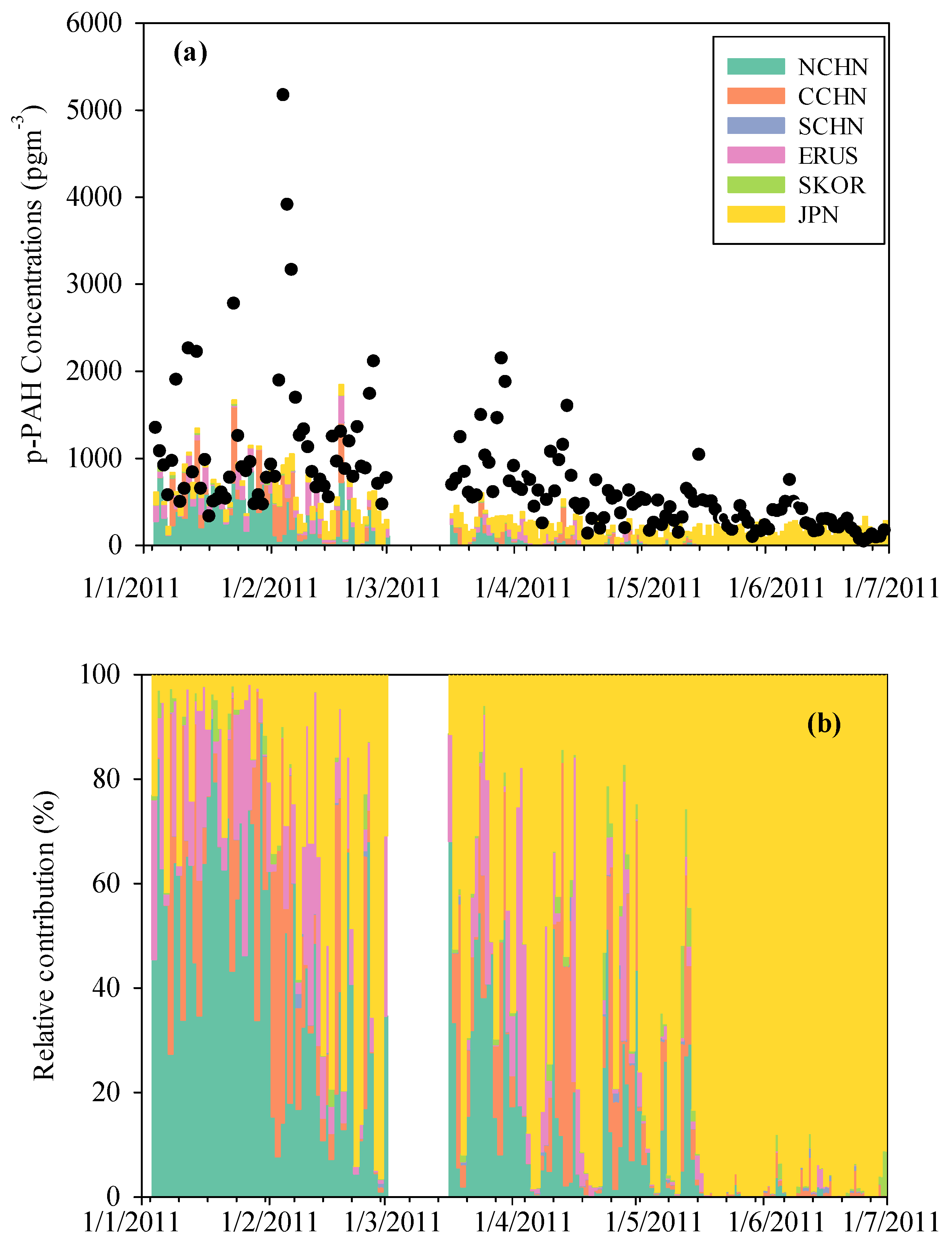
3.2. SRR Analysis of the Simulated p-PAH Concentration
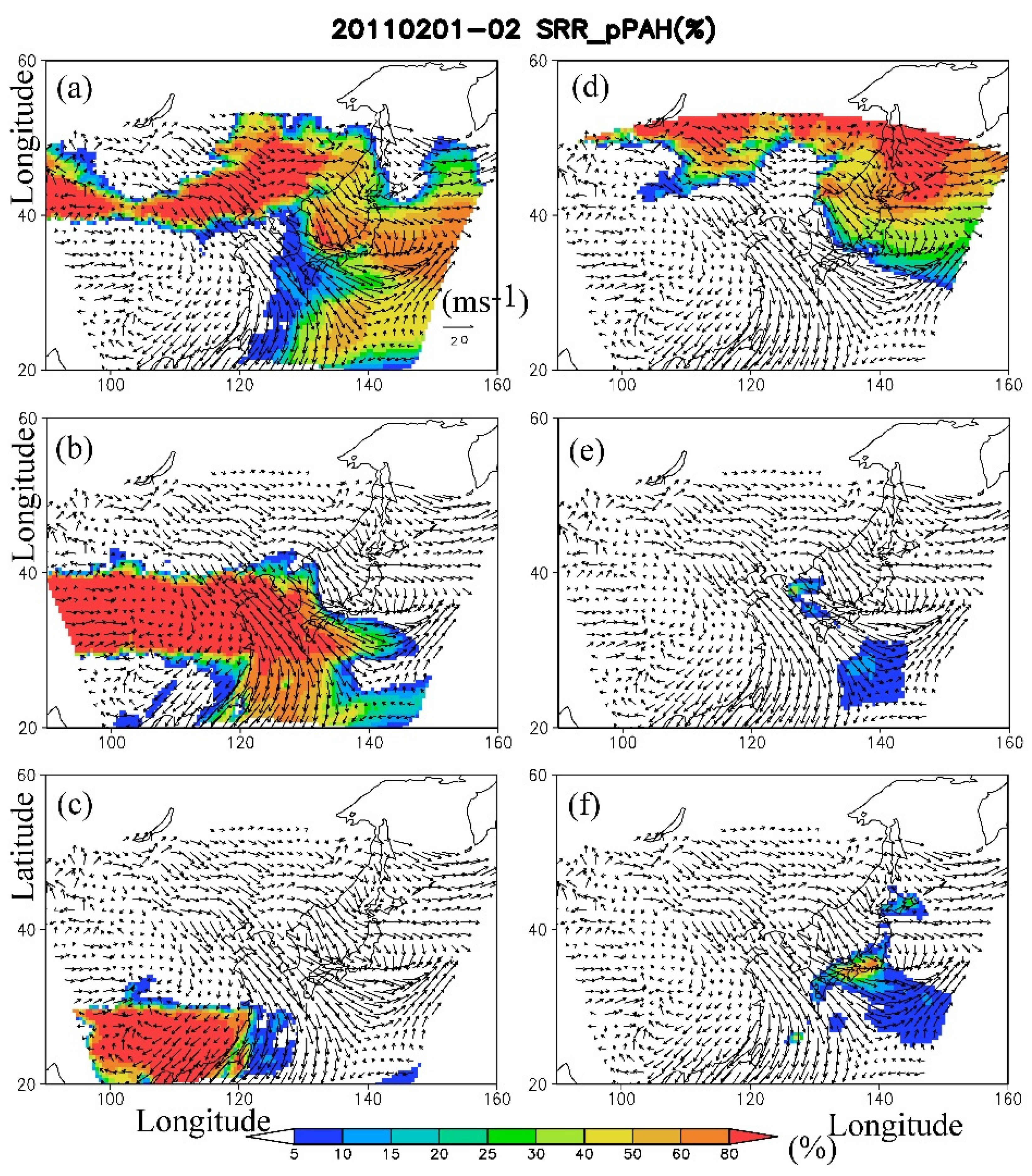
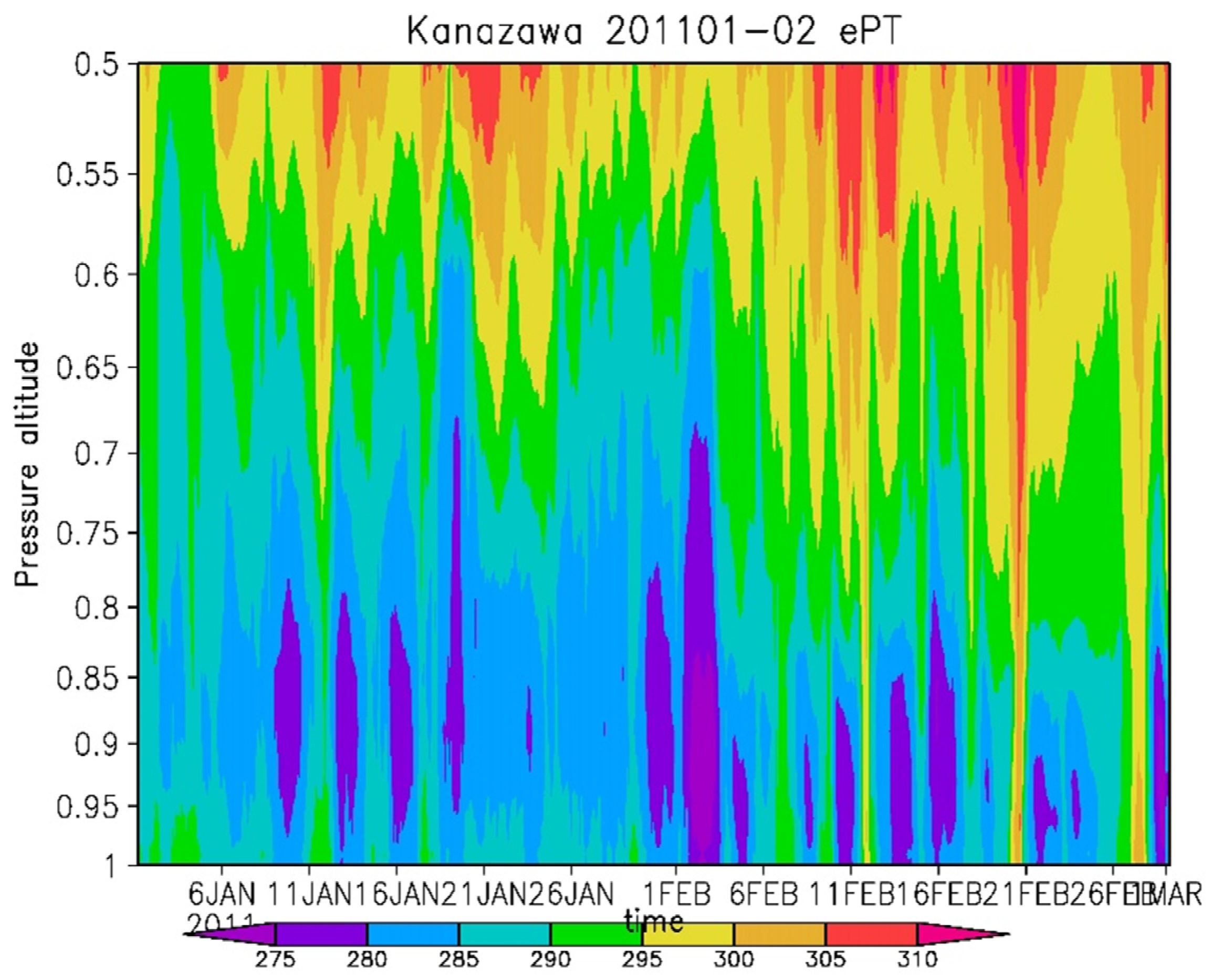
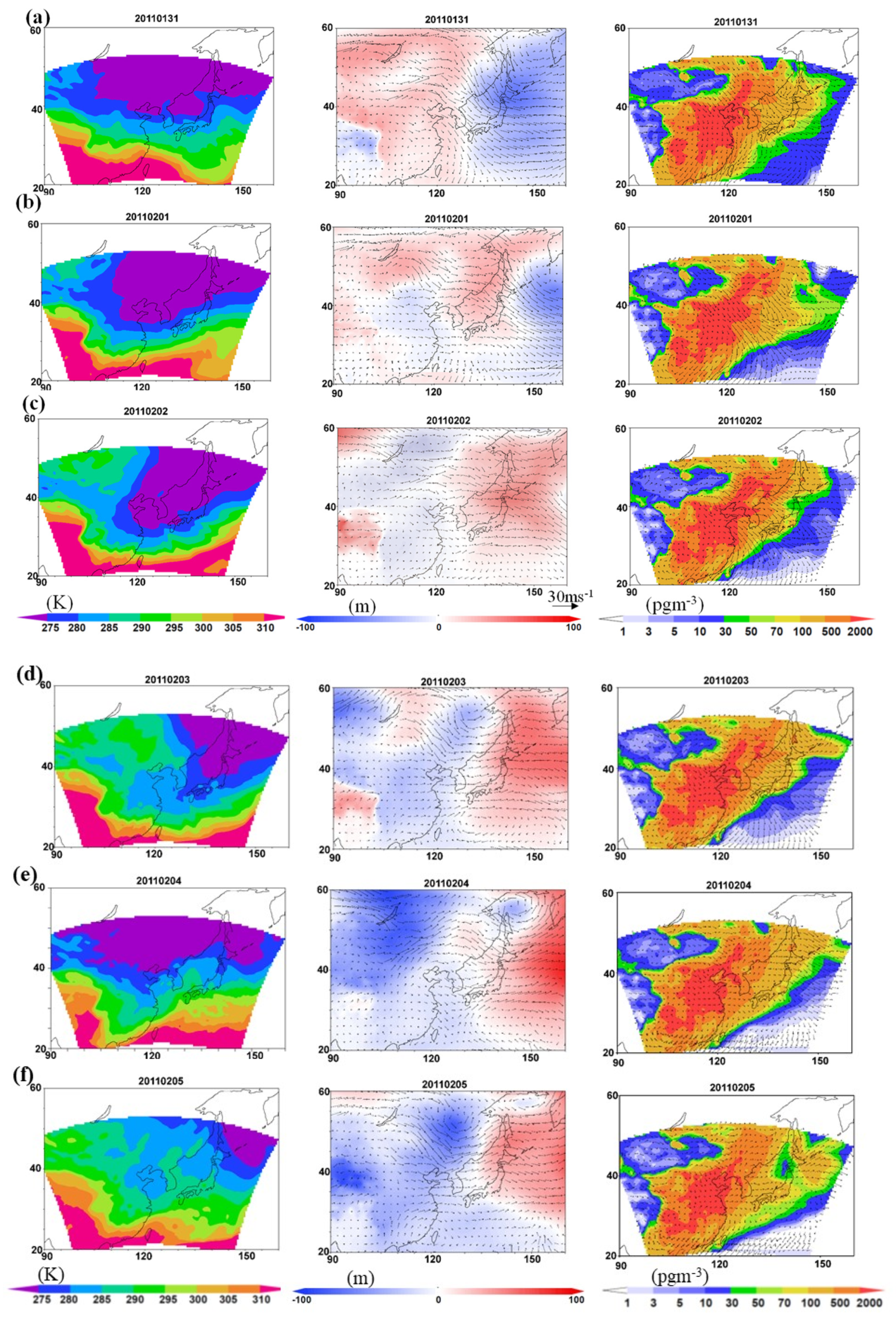
3.3. Transport of High Concentrations of p-PAHs near the Surface under Cold Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeFlorio-Barker, S.; Lobdell, D.T.; Stone, S.L.; Boehmer, T.; Rappazzo, K.M. Acute effects of short-term exposure to air pollution while being physically active, the potential for modification: A review of the literature. Prev. Med. 2020, 139, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.; Toro, A.; Manzano, C.; Canepari, S.; Massimi, L.; Leiva-Guzmán, M. Airborne Aerosols and Human Health: Leapfrogging from Mass Concentration to Oxidative Potential. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almetwally, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Allam, A. Ambient air pollution and its influence on human health and welfare: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24815–24830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guercio, V.; Pojum, I.C.; Leonardi, G.S.; Shrubsole, C.; Mac Gowers, A.; Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Exley, K.S. Exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution from solid fuel combustion and respiratory outcomes in children in developed countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 755, 142187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cori, L.; Donzelli, G.; Gorini, F.; Bianchi, F.; Curzio, O. Risk Perception of Air Pollution: A Systematic Review Focused on Particulate Matter Exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Toxicity of airborne particles-established evidence, knowledge gaps and emerging areas of importance. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiotiu, A.I.; Novakova, P.; Nedeva, D.; Chong-Neto, H.J.; Novakova, S.; Steiropoulos, P.; Kowal, K. Impact of Air Pollution on Asthma Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhvidi, M.J.Z.; Lequy, E.; Goldberg, M.; Jacquemin, B. Air pollution exposure and bladder, kidney and urinary tract cancer risk: A systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. In Some Non-Herocycloc Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Some Related Exposures; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 92.
- Jung, K.H.; Yan, B.; Chillrud, S.N.; Perera, F.P.; Whyatt, R.; Camann, D.; Kinney, P.L.; Miller, R.L. Assessment of benzo(a)pyrene-equivalent carcinogenicity and mutagenicity of residential indoor versus outdoor polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposing young children in New York City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Garfinkel, R.; Horton, M.; Camann, D.; Perera, F.P.; Whyatt, R.M.; Kinney, P.L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Environmental Tobacco Smoke, and Respiratory Symptoms in an Inner-city Birth Cohort. Chest 2004, 126, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyenda, E.O.; Higashi, T.; Kambayashi, Y.; Thao, N.T.T.; Michigami, Y.; Fujimura, M.; Hara, J.; Tsujiguchi, H.; Kitaoka, M.; Asakura, H.; et al. Exposure to daily ambient particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cough occurrence in adult chronic cough patients: A longitudinal study. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, Y.; Kajino, M.; Sato, K.; Ohara, T.; Kurokawa, J.-I.; Ueda, H.; Tang, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Ohizumi, T.; Akimoto, H. Emission and Atmospheric Transport of Particulate PAHs in Northeast Asia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4941–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, Y.; Kajino, M.; Sato, K.; Ohara, T.; Kurokawa, J.-I.; Ueda, H.; Tang, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Ohizumi, T.; Akimoto, H. Source contribution analysis of surface particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations in northeastern Asia by source–receptor relationships. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, M.; Inomata, Y.; Sato, K.; Ueda, H.; Han, Z.; An, J.; Katata, G.; Deushi, M.; Maki, T.; Oshima, N.; et al. Development of the RAQM2 aerosol chemical transport model and predictions of the Northeast Asian aerosol mass, size, chemistry, and mixing type. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 11833–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, Y.; Kajino, M.; Sato, K.; Kurokawa, J.; Tang, N.; Ohara, T.; Hayakawa, K.; Ueda, H. Source-Receptor Relationship Analysis of the Atmospheric Deposition of PAHs Subject to Long-Range Transport in Northeast Asia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7972–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, M.; Sato, K.; Inomata, Y.; Ueda, H. Source–receptor relationships of nitrate in Northeast Asia and influence of sea salt on the long-range transport of nitrate. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF, Version 3; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gusev, A.; Mantseva, E.; Shatalov, V.; Strukov, B. Regional Multicompartment Model MSCE-POP; MSC-E Technical Report; Meteorological Synthesizing Centre-East: Moscow, Russia, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Pankow, J.F. Review and comparative analysis of the theories on partitioning between the gas and aerosol particulate phases in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1987, 21, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankow, J.F. Application of common y-intercept regression parameters for log kpvs lit for predicting gas-particle partitioning in the urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 1992, 26, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008; Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) Version. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Randerson, J.T.; van der Werf, G.R.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Collatz, G.J.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S. Assessing variability and long-term trends in burned area by merging multiple satellite fire products. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Oki, T.; Bengtsson, M.; Kanae, S.; Holloway, T.; Streets, D.G. Long-range transport of acidifying substances in East Asia—Part IISource–receptor relationships. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5956–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Aherne, J.; Wentworth, G.R. Impacts and Effects Indicators of Atmospheric Deposition of Major Pollutants to Various Ecosystems-A Review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1953–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Akiyama, K.; Adachi, M.; Ichinose, M.; Takahashi, K.; Nishimuta, T.; Morikawa, A.; Nishima, S. Japanese Guideline for Adult Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2011, 60, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, M.; Ogawa, H.; Nishizawa, Y.; Nishi, K. Comparison of atopic cough with cough variant asthma is atopic cough a precursor of asthma? Thorax 2003, 58, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Kamio, Y.; Matsuda, T. Effects of methacholine induced bronchoconstriction and procaterol induced bronchodilation on cough receptor sensitivity to inhaled capsaicin and tartaric acid. Thorax 1992, 47, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Japanese Respiratory Society The committee for the Japanese Respiratory Society guidelines for management of cough, Concept and use of the guide line. Respirology 2006, 11 (Suppl. 4), S135–S186.
- Fujimura, M.; Abo, M.; Ogawa, H.; Nishi, K.; Kibe, Y.; Hirose, T.; Nakatsumi, Y.; Iwasa, K. Importance of atopic cough, cough variant asthma and sinobronchial syndrome as causes of chronic cough in the Hokuriku area of Japan. Respirology 2005, 10, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T.; Kambayashi, Y.; Ohkura, N.; Fujimura, M.; Nakai, S.; Honda, Y.; Saijoh, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Kobayashi, F.; Michigami, Y.; et al. Reprint of: Effects of Asian dust on daily cough occurrence in patients with chronic cough: A panel study. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ballinger, G.A. Using Generalized Estimating Equations for Longitudinal Data Analysis. Organ. Res. Methods 2004, 7, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfield, J.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]


| Total (N = 88) | Atshma (N = 54) | Non-Asthma (N = 34) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Kanazawa | |||
| Periods | 4 January–30 June 2011 * | |||
| PAH measuremetnt | Daily | |||
| Analysis data | 12,473 | 144.2 | 152 | 131.8 |
| Time periods (days) | 130.2 | 135.7 | 121.5 | |
| Number of recorded days | 36.1% (10–178) | 23.0% (10–178) | 60.2% (57–178) |
| Participants | Classification | Total (N = 88) % | Asthma (N = 54) % | Non-Ashma (N = 34) % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Asthma(Adult bronchial asthma) | 49 (56) | 49 (91) | - |
| Cough Variant Asthma (CVA) | 8 (9) | - | 8 (24) | |
| Atopic Cough (AC) | 16 (18) | - | 16 (47) | |
| Asthma and AC | 5 (6) | 5 (9) | - | |
| AC and CVA | 10 (11) | - | 10 (29) | |
| Record days | 130.2 | 135.7 | 121.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inomata, Y.; Takeda, M.; Thao, N.; Kajino, M.; Seto, T.; Nakamura, H.; Hayakawa, K. Particulate PAH Transport Associated with Adult Chronic Cough Occurrence Closely Connected with Meteorological Conditions: A Modelling Study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091163
Inomata Y, Takeda M, Thao N, Kajino M, Seto T, Nakamura H, Hayakawa K. Particulate PAH Transport Associated with Adult Chronic Cough Occurrence Closely Connected with Meteorological Conditions: A Modelling Study. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091163
Chicago/Turabian StyleInomata, Yayoi, Masato Takeda, Nguyen Thao, Mizuo Kajino, Takafumi Seto, Hiroyuki Nakamura, and Kazuichi Hayakawa. 2021. "Particulate PAH Transport Associated with Adult Chronic Cough Occurrence Closely Connected with Meteorological Conditions: A Modelling Study" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091163
APA StyleInomata, Y., Takeda, M., Thao, N., Kajino, M., Seto, T., Nakamura, H., & Hayakawa, K. (2021). Particulate PAH Transport Associated with Adult Chronic Cough Occurrence Closely Connected with Meteorological Conditions: A Modelling Study. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091163







