Abstract
In 2018, 3.8 million premature deaths were attributed to exposure to biomass burning nanoparticles from wood combustion. The objective of this study was to investigate and compare the toxic effect of wood-combustion-related biomass burning nanoparticles from three different combustion stages (i.e., flaming, smoldering, and pyrolysis) on alveolar lung cells, by studying cell proliferation, and structural and behavioral parameters. A549 lung epithelial cells were treated with 31, 62, 125, 250, and 500 µg/mL of water-soluble particulate pollutants from wood burning, and measured by means of real-time cell analysis, cell imaging, and phase imaging microscopy. At low concentrations (31 and 62 µg/mL), all three types of wood burning samples exhibited no toxicity. At 125 µg/mL, they caused decreased cell proliferation compared to the control. Exposure to higher concentrations (250 and 500 µg/mL) killed the cells. Cell physical parameters (area, optical volume, eccentricity, perimeter, and optical thickness) and behavioral parameters (migration, motility, and motility speed) did not change in response to exposure to wood burning materials up to a concentration of 125 µg/mL. Exposure to higher concentrations (250 and 500 µg/mL) changed cell perimeter, optical thickness for smoldering and flaming particles, and led to decreased migration, motility, and motility speed of cells. In conclusion, all three of the combustion water-soluble organic pollutants were identified as equally toxic by real-time cell analysis (RTCA) results. The parameters describing cell structure suggest that pyrolysis particles were slightly less toxic than others.
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization (2018) estimates that 3.8 million premature deaths per year are due to exposure to environmental pollution, especially particulate matter (PM) [1]. These nanoparticles (NPs) arise from household air pollution, industrial and traffic sources, and wildfires. In fact, around 3 billion people still cook or heat their houses using solid fuels due to economic conditions, and wood is the main fuel used for domestic biomass combustion [2]. While wood is often considered as a renewable fuel, its combustion produces primary nanoparticles more efficiently than oil or natural gas burning systems [3]. As of 2005, domestic biomass combustion was responsible for more than 45% of PM2.5 over Europe [4]. Such particulate pollution causes not only lung-related diseases, such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, lung cancer, and cardiovascular diseases, but also negatively affects cognitive functioning among the elderly [5,6].
Under the changing climate and land use change, the frequency of wildfires gradually increased worldwide. Large fires are frequently reported in countries such as Canada and the USA, Australia, Brazil, and Indonesia [7,8,9]. These fires can exert impacts ranging from regional to global on climate and air quality, in contrast to household pollution. Global exposure to wood-related aromatic compounds is inevitable. These compounds have a short lifetime in the atmosphere (several hours up to a few days) and they are ubiquitously present in fog and precipitation [10,11]. In addition, two different subfractions (water-soluble vs. organic-soluble) of wood fuel pyrolysis brown carbon (BrC) were tested and shown to be toxic to epithelial lung cells [12,13,14].
Wood burning can be described by three identified combustion stages: flaming, smoldering, and pyrolysis. Flaming is defined by the burning of wood with flames or complete combustion, while smoldering is the slow and incomplete burning of wood, with low-temperatures, and is flameless. Pyrolysis is an intricate process that is not yet fully understood, but it is the genesis for both flaming and smoldering conditions [15,16,17,18,19,20].
In vitro studies have been performed with lung cell lines, demonstrating that wood-burning biomass NP is toxic, due to the presence of phenolic compounds, organic peroxides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH). PAH are considered as human carcinogens, with well-documented mechanisms of action that involve the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [21,22]. In addition, in vivo studies were performed to establish which burning condition produces the most toxic outcome, but the results were inconclusive, with different studies highlighting different combustion conditions [14,18,19].
Forest fires are unexpected, and smoke can be transported over large distances. Hence, it is almost impossible not to be exposed to smoke particles and gaseous species. It is critical to understand what the most toxic mechanisms of action of biomass burning particles are, in order to prevent their adverse health effects. Three different but complementary methods were used to determine the cytotoxicity of particles. All three methods are without labelling, and are conducted in real-time. First, real-time cell analysis (RTCA) allows for the monitoring of cell proliferation and viability. It analyzes cell viability using electrical impedance. Second, the quantitative phase microscope Holomonitor produces 3D reconstructive images of cells, and measures the structural and behavioral parameters of cells, such as their area and migration. Third, the multi-mode brightfield microscope Cytation 3 provides images of cells, allowing the visualization of cell division and death [23,24,25]. All three, flaming, smoldering and pyrolysis stages, can occur during wood fires. In this study, we focused on their effects on cell proliferation, which is an important feature of the maintenance of epithelia, and on the effects on the cell structure and cell behavior of epithelial lung cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
Human carcinoma A549 cells (ATCC) were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium with low glucose (1 g/L), supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (DMEM 10% FCS, PAA Laboratories, Etobicoke, ON, Canada) and streptomycin–penicillin solution (100 units/mL; Sigma Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France). After trypsinization by 0.05% trypsin (Sigma Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), cell concentration was measured using an automated cell counter (Sceptor Millipore, Danvers, MA, USA). Cells were used from passage 3 to 7.
2.2. Water-Soluble Particulate Pollutants from Biomass Burning
Wood pellets (Hallingdal Trepellets; water content 6.55 wt.%; length 2~3 cm, diameter 0.2–0.3 cm) were used for the production of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning. For pyrolysis, the wood pellets were pyrolyzed at 535 °C without any air; for smoldering, 1.6 LPM oxygen-poor air (O2 <~5.0 Vol.%) was supplied to sustain smoldering of wood pellets maintained at 535 °C; for flaming 1.6 LPM high-purity air (O2 ~21.0 Vol.%) was supplied to sustain flaming combustion of wood pellets that were ignited at above 530 °C. The particulate emissions from specific burning conditions were collected as tar emulsions using a water-cooled trap. Then, the water-soluble fraction of the respective tar emulsions was extracted with MilliQ water (18 MΩ, sterilized by 185 nm UVA irradiation) and filtered using 0.45 μm and 0.2 μm syringe filters in sequence (polytetrafluoroethylene [PTFE] membrane, Pall Corporation) to remove impurities and PM. Subsequently, the filtered solutions were further centrifuged to remove any suspended colloidal particles (2500 rps for 4 min at −2 °C). Finally, the extracts were freeze-dried to obtain the water-soluble tar material in a semisolid, viscous form. The dry water-soluble extracts were termed FWS, SWS, and PWS, corresponding to the water-soluble extracts from flaming combustion, smoldering burning, and pyrolysis-related smoke particles, respectively. The chemical composition of processed wood tar extracts was extensively characterized by Pardo et al. [12]. All three water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning were tested at the concentrations of 31, 62, 125, 250 and 500 µg/mL.
2.3. Measurements of Cytotoxicity
2.3.1. Real-Time Cell Analysis
The real-time cell analysis (RTCA) (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) system measures cell index, taking cell number, cell size, and adhesion force into consideration. In the case of cytotoxicity, a decrease in cell index can result from a decreased cell number (cell death), a decrease in cell adhesion, or a decrease in cell surface. During cell proliferation, cell index mainly represents cell number, since cell size is homogenous in non-differentiating cells, and adhesion is a constant for a given cell line. In order to measure the cytotoxic response of A549 cells in real-time, 2500 cells/well were seeded on gold microelectrodes embedded at the bottom of 96-well microplates (E-plates; Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland). The gold microelectrodes emit a flow of electrons when cells are present in the wells and attached to the microelectrodes, an impedance of electron flow is created and translated into cell index. The impedance was recorded at 15 min intervals for time sequences of 72 h under control conditions, 24 h incubation with particle addition, and 24 h particle wash-out incubation. The wash-out period allows for measurement of the capacity of cells to recover after particle-exposure treatment. The RTCA system was placed in a standard 37 °C cell culture incubator with 5% CO2. The EC50 of all compounds was calculated using the RTCA system.
Data are presented as delta cell indices, calculated by the difference between final and initial cell index, for the time of treatment and wash-out periods. In particle-exposure experiments, the initial time was established as the moment of particle addition, while the final time was set at particle wash-out. For the wash-out, the initial time was fixed at the moment in which the culture with particles was replaced by the control culture medium, while the final time was 24 h afterward. Cells were also monitored for 20 h in a 96-well plate in the Cytation 3 microscope.
2.3.2. Quantitative Phase Imaging
Quantitative phase imaging was performed using the Holomonitor M4 digital holographic cytometer (DHC) from Phase Holographic Imaging (PHI, Lund, Sweden). The microscope was placed in a standard 37 °C cell culture incubator with 5% CO2. The microscope measured eight parameters obtained from 3D reconstructed images, every 10 min for 10 h: area, perimeter length, optical thickness, optical volume, eccentricity, migration, motility, and motility speed.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The figures presented here depict three experiments performed independently. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM for RTCA and Holomonitor (each value represents the average of eight wells). Statistical analysis was performed with Stat View 4.5 software (Abacus Corporation, Baltimore, MD, USA) for Windows; the data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s protected least significance difference (PLSD), post hoc test. Differences were considered to be significant at a probability level of p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Water-Soluble Particulate Pollutants from Biomass Burning on A549 Cell Index
A549 cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning, in order to determine their toxicity. The particle types used were FWS, SWS and PWS, at concentrations of 31, 62, 125, 250, and 500 µg/mL.
Figure 1 shows the evolution of the cell index provided by RTCA for A549 cells in response to increasing concentrations of SWS, PWS, and FWS particles. All three particle types showed similar results, in which cell exposure to the two smallest concentrations, 31 and 62 µg/mL, were not significantly different from the control, while exposure to 125 µg/mL decreased the cell index compared to the control (p < 0.001), and exposures of 250 and 500 µg/mL decreased the cell index of cells to 0 (Figure 1).
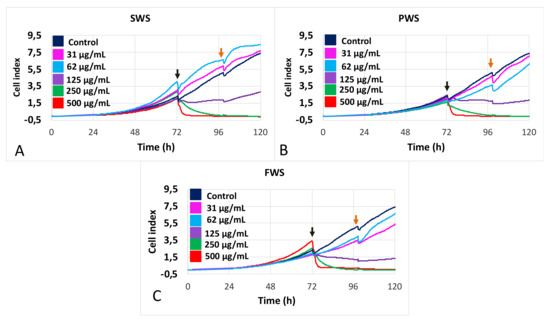
Figure 1.
Dose–response curves of A549 cell proliferation in response to stimulations by increasing concentrations of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning obtained for various burning conditions: (A): smoldering (SWS); (B): pyrolysis (PWS); and (C): flaming (FWS). Color code: dark blue: control, pink: 31 µg/mL; light blue: 62 µg/mL; purple: 125 µg/mL; green: 250 µg/mL; and red: 500 µg/mL. Black arrows indicate time of treatment addition; orange arrows indicate time of wash-out.
Figure 2 represents the EC50 for each type of water-soluble particulate pollutant from varied biomass burning conditions. They were calculated from the mean of delta cell indices obtained from the treatment time for three independent experiments. The resulting EC50 are 188.3 ± 43.3 µg/mL for FWS; 188.7 ± 24.3 µg/mL for SWS; and 202 ± 20.9 µg/mL for PWS. Statistical significance was not found between the toxicities of the three particle types.
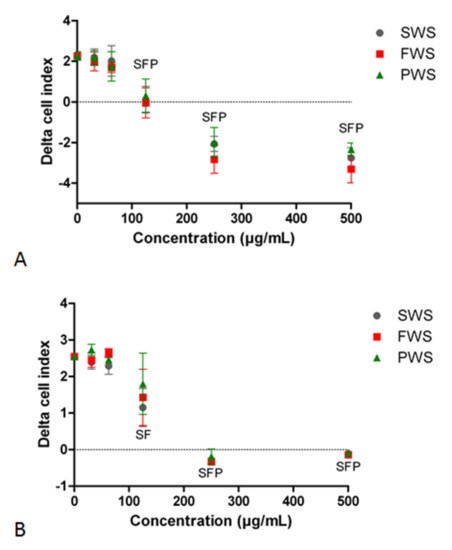
Figure 2.
Delta cell index of A549 cells. (A): Delta cell index for the time of treatment with increasing concentrations of three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning: flaming (FWS), smoldering (SWS), and pyrolysis (PWS). (B): Delta cell index for the time of wash-out after removal of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning. Means of three independent experiments are presented. Significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 between the particles and the control are represented by F for FWS, S for SWS, and P for PWS.
The two lowest concentrations of all three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning did not significantly alter the cell index compared to the control (Figure 2A). The concentration of 125 µg/mL froze the cell index, inducing a static condition for cells. Exposure to higher concentrations of 250 and 500 µg/mL resulted in a highly negative delta cell index (Figure 2A).
Figure 2B shows the effect of wash-out on the cell index for cells previously treated with FWS, SWS, and PWS particles from biomass burning. For the two lowest concentrations, i.e., 31 and 62 µg/mL, the cells did not exhibit any difference from the control (Figure 2B). At a concentration of 125 µg/mL, an improvement in the cell index was observed for all three types of particles, showing that the cells were able to proliferate after the removal of particles, although at a much lower rate than the control, with the exception of PWS, which did not exhibit any statistical difference compared to the control, mainly due to a higher standard error (Figure 2B). Since the effect of the wash-out is calculated as the difference between 24h after the removal of particles and the time of removal for particles, dead cells have a delta cell index equal to 0, as observed for cells exposed to 250 and 500 µg/mL.
Photomicrographs taken with Cytation enable a more detailed observation of the effect of biomass burning particles. Figure 3 represents the initial (Figure 3A,C,E,G) and final time (Figure 3B,D,F,H) of treatment with the particles at different concentrations (control, FSW, SWS, and PWS at 125, 250, and 500 µg/mL). As particle concentration of 125 µg/mL did not cause any changes in the delta cell index, leading to a static condition in the cells (Figure 2A), Figure 3D shows that, after 20h of treatment, some cells were still dividing (red arrows), but not all the dividing cells survived (yellow arrows). The full movies for 250 µg/mL are available as Supplementary Data as S1 (SWS), S2 (FWS), S3 (PWS) and S4 (Control).
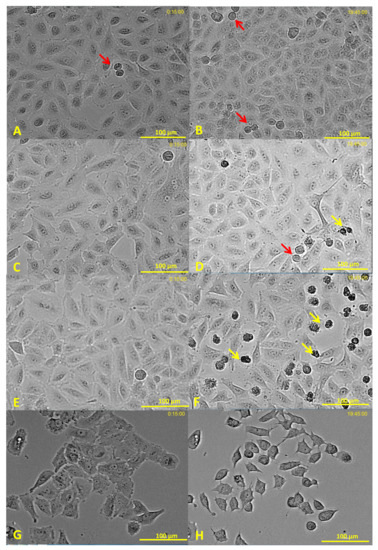
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of cells treated with SWS water-soluble particle pollutants from biomass burning. (A,B): Control; (C,D): 125 µg/mL; (E,F): 250 µg/mL; and (G,H): 500 µg/mL. (A,C,E, and G): photomicrography at the beginning of the time-lapse. (B,D,F, and H): photomicrography after 19 h 45 min of treatment. Yellow arrows point to dying cells. Red arrows mark cells during division. Cells treated with FWS and PWS exhibited similar results. The full movies for 250 µg/mL are available in the Supplementary Data.
All three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning caused a strongly negative cell index at 250 and 500 µg/mL exposures (Figure 2A). However, cells treated with all three particles at 250 µg/mL started cell division, and died during the division process (Figure 3E,F), while cells treated with particles at a concentration of 500 µg/mL shrank and remained fixed during the rest of the experiment (Figure 3G,H).
3.2. Effects of Water-Soluble Particulate Pollutants from Biomass Burning on A549 Behavioral and Structural Parameters
Cells were monitored with a Holomonitor, a quantitative phase contrast microscopy for non-invasive analysis of cellular events by long-term digital phase imaging, allowing for the quantification of behavioral and structural parameters. The analyses were performed for 10 h, and results are presented as the mean of the last two hours.
The area and optical volume of cells were not affected by any of the three types of particles in any of the tested concentrations (Figure 4A,D). SWS and FWS caused a decrease in the perimeter of cells at 500 µg/mL, while PWS had no effect (Figure 4B). The optical thickness of cells increased after treatment with FWS and SWS at 500 µg/mL, but did not change after treatment with PWS (Figure 4C).
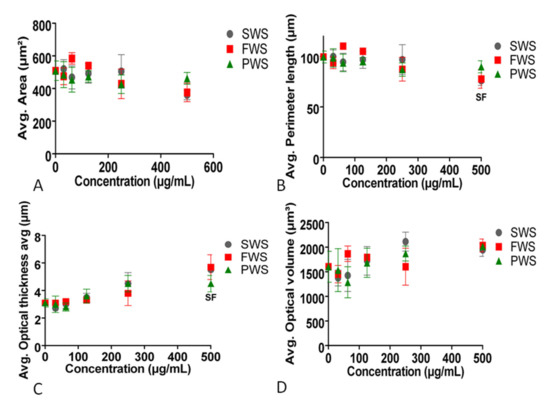
Figure 4.
Effects of three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning on (A): area, (B): perimeter length, (C): optical thickness, and (D): optical volume of A549 cells. Significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 between the particles and the control are represented by F for FWS and S for SWS.
The eccentricity of the cells was not affected by any of the three types of particles in any of the tested concentrations (Figure 5A). FWS, SWS, and PWS caused a decrease in the migration and motility speed of cells at 250 and 500 µg/mL, further validating the results obtained with Cytation (Figure 5B,D). The cells’ motility decreased when treated with FWS, SWS, and PWS particles at 500 µg/mL, but only with FWS and PWS at 250 µg/mL (Figure 5C).
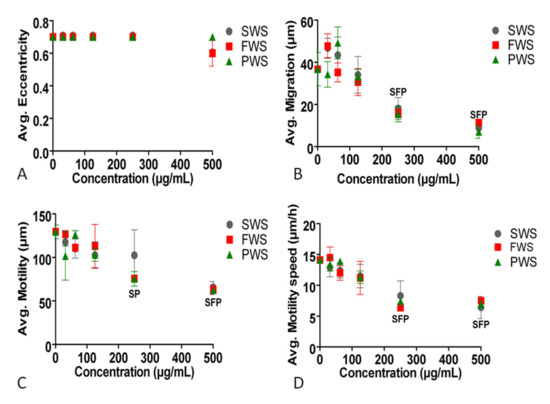
Figure 5.
Effects of three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning on: (A): eccentricity, (B): migration, (C): motility, and (D): motility speed of A549 cells. Significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 between the particles and the control are represented by F for FWS, S for SWS, and P for PWS.
4. Discussion
Water-soluble organics constitute the major and most environmentally relevant fraction of biomass burning smoke particles. However, the health effect and toxicity mechanisms of these water-soluble carbonaceous pollutants are not fully constrained, due to their inherent complexity, which arises from the varying burning conditions and particle compositions. The present study investigated the cytophysics-based toxicity of the water-soluble fraction of biomass burning particles emitted from almost all combustion processes, including FWS, SWS, and PWS. The main finding of the present study is that water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning are toxic at high concentrations (higher than 125 µg/mL). Cell division, or mitosis, is a complex succession of sophisticated rearrangements of all cell components, and is critical for epithelium renewal. Mitosis is rather easily perturbed in response to cell environmental changes. For these reasons, it is a reliable parameter for testing the toxicity of chemical compounds. There is no major difference between the three types of biomass burning particulates, SWS, PWS and FWS, since their EC50 for the inhibition of cell proliferation was similar. The effects of biomass burning particles can be tested by analyzing the structural effect they exert on cells, such as area, perimeter, and optical thickness. Only cell perimeter and optical thickness were affected by the water-soluble fraction of smoke particles, at the highest concentrations tested (500 µg/mL) for smoldering and flaming, but not for pyrolysis. Another approach for analyzing the toxicity of chemicals is to study their effects on cell behavior, such as migration, motility, and motility speed. These three behavioral parameters decreased at 250 µg/mL for the three particle subtypes that were tested. As expected, the materials altered the cell behavior at concentrations lower than those required to produce cell structure modifications (250 vs. 500 µg/mL). Surprisingly, cell division was more sensitive than behavioral changes, as a concentration of 125 µg/mL was sufficient to significantly alter cell division. This is most likely related to the fact that cell division is highly complex and finely regulated and, therefore, more sensitive to chemicals.
Previous studies have indicated that exposure to biomass burning particles in indoor air and from wildfires may impact human health [26,27]. Regarding in vitro toxicity, studies with A549 cells have demonstrated that PWS biomass burning particles were toxic to cells at 200 µg/mL [12]. Biomass burning particles generate ROS and induce DNA damage [12,28]. In the present study, all three types of particles caused cell death at 250 and 500 µg/mL, and stopped cell proliferation at 125 µg/mL (Figure 1 and Figure 2A). To investigate whether the toxic effects induced by the particles continued even after their removal from the cells, the culture medium in which the particles were maintained was replaced by a clean culture medium, allowing for the investigation of the recovery of the cell properties by real-time cell analysis, a procedure never previously reported in the literature. Cells treated with 125 µg/mL had partially recovered; however, their speed of cell proliferation was significantly lower compared to the control (Figure 2B). This observation suggests that exposure caused permanent cell damage. Cells treated with 250 and 500 µg/mL did not restart proliferation for all three types of particles from biomass burning.
Pardo et al. [12], while working with similar materials from the SWS phase, described the toxicity of these NPs by the reduction in the cellular antioxidant activity, characterized by a decreased Nrf2 factor, and an inflammatory response, characterized by an increase in IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-8. The decrease in the Nrf2 factor and the increase in IL-1β and TNF-α are corroborated by de Oliveira Alves et al. [27] and Mondal et al. [29]. Additionally, de Oliveira Alves et al. [27] stated that biomass burning caused cell death by autophagy, apoptosis, and necrosis. Ko et al. [30] observed that the suppression of Nrf2 in A549 cells inhibited cell migration and invasion, and shrunk cell size due to decreased focal adhesions via inhibition of the RhoA–ROCK1 pathway. In this study, the results show that water-soluble particle pollutants from biomass burning did not alter the area, optical volume, or eccentricity (how elongated the cells are) of cells for any of the three combustion types, a result that can also be observed by time-lapse microscopy (Figure 3). However, the particles did alter the cell structure by increasing their optical thickness and decreasing their perimeter (for FWS and SWS) (Figure 4). PWS did not change any of the cells’ structural parameters. Related to the behavioral parameters, all three extract types decreased the migration and motility speed of cells at 250 µg/mL (Figure 5), in agreement with the decreased expression of Nrf2 [12] and its effect on cell migration [30].
Differences in toxicity due to combustion conditions have rarely been investigated in the literature. Moreover, the few studies that investigated the effects of the combustion process are controversial, as Hargrove et al. (2019) stated that SWS particles induce more respiratory effects than FWS particles, while Kim et al. [17] stated the opposite, with both citing the emission factor as a determinant factor in the toxicity of biomass burning particles. In our study, SWS, and FWS particles exhibited the same overall toxicity. PWS, however, was less toxic than FWS and SWS and did not induce changes in the structural parameters, while inducing changes in two (migration and motility speed) out of three behavioral parameters (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
The present study is also an opportunity to compare three different methods for cell analysis: RTCA, phase imaging microscopy, and time-lapse microscopy. The three methods provide real-time monitoring of the cells without labelling. Each process has its own advantages and drawbacks. RTCA is based on impedance measurements, which are affected by the surface of electrodes covered by the cells and the adhesion strength of the specific cell line. Cell size is rather constant and homogeneous during cell proliferation. Adhesion strength is a characteristic of the cell line. Under normal conditions, it is not expected to change; however, the possibility that adhesion may be altered by various chemicals cannot be excluded. For this reason, the results obtained from RTCA were cross-checked using phase imaging microscopy (Holomonitor), which measures numerous cell parameters, such as cell volume and mobility, which are normally difficult to measure. The results showed that cell surface did not change in response to particles, and the decrease in cell index cannot be explained by a reduction in cell size, which strengthens the conclusion that these results from a decrease in cell proliferation. Interestingly, time-lapse microscopy showed that cells were still capable of division in response to the 250 µg/mL treatment, but this invariably ended with cell death (Figure 3).
All tests were performed in A549 cells, a commonly used tumorigenic cell line. Pardo et al. [13] compared the toxicity of wood tar materials in both A549 and BEAS-2B cells, finding that BEAS-2B were slightly less responsive to the toxic effects of biomass burning than A549. Other studies, however, stated that BEAS-2B is more responsive to toxicity than A549 [31,32]. Pardo et al. [13] justify the use of A549 cells by stating that BEAS-2B cells are immortalized by integrated SV40 virus and present a low sensitivity, suggesting that the choice of BEAS-2B over A549 is disputable.
5. Conclusions
Materials extracted from biomass burning particles from three combustion processes did not exhibit differences in toxicity with respect to the cell index of A549 cells, exerting toxic effects on cells at 125, 250, and 500 µg/mL. All three types of water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning caused a decrease in the migration, motility, and motility speed at 250 and 500 µg/mL, with the exception of PWS, which did not cause a decrease in motility for 250 µg/mL, as measured by a Holomonitor for 10 h. Overall, the particles from FWS and SWS were the only ones that affected cell structure by increasing the cell optical thickness (FWS and SWS 500 µg/mL, Figure 4) and decreasing the perimeter length (FWS and SWS 500 µg/mL). Furthermore, the different real-time and label-free methods, used here to study the toxicity of these particles, shared an essential complementarity to properly assert toxicity studies of atmospheric pollutants. Our results demonstrate that a short but intense exposure to water-soluble particulate pollutants from biomass burning may exert long-term, persistent, deleterious effects.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos12081023/s1, Video S1: Effect of SWS at 250 µg/mL on A549 cells; Video S2: Effect of FWS at 250 µg/mL on A549 cells; Video S3: Effect of PWS at 250 µg/mL on A549 cells; Video S4: A549 cells without treatment (Control).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L.d.A., C.G., Y.R. and A.G.; methodology, Y.L.d.A., E.B., C.L., Y.R. and A.G.; validation, C.G., Y.R. and A.G.; formal analysis, Y.L.d.A. and A.G.; investigation, Y.L.d.A., E.B. and A.G.; resources, E.B., C.L., M.P., C.G., Y.R. and A.G.; data curation, Y.L.d.A. and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.d.A. and A.G.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.d.A., C.L., M.P., C.G., Y.R. and A.G.; visualization, Y.L.d.A. and A.G.; supervision, C.G., Y.R. and A.G.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, C.G. and A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Lyon through the Breakthrough Grant, WANTED, call IDEXLYON-SBP-2018. Y.R. acknowledges support by the NSFC-ISF joint research program (grant NO. 3205/19).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Household Air Pollution and Health. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/household-air-pollution-and-health (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Straif, K.; Cohen, A.; Samet, J. Air Pollution and Cancer; IARC Scientific Publications; International Agency for Reseach on Cancer; WHO: Lyom, France, 2013; p. 161. [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski, R.; Fthenakis, V. Nanoparticle emissions from residential wood combustion: A critical literature review, characterization, and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Comission. Clean Air Outlook. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/air/clean_air/outlook.htm (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Saenz, J.L.; Wong, R.; Ailshire, J.A. Indoor air pollution and cognitive function among older Mexican adults. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2017, 72, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.M. Household Air Pollution from Cooking Fires Is a Global Problem. Am. J. Nurs. 2019, 119, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, C. Indonesian forest fires raise concerns about health. Lancet 2019, 394, 1699–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.A. To save Brazil’s rainforest, boost its science. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 574, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossiello, M.R.; Szema, A. Health Effects of Climate Change-induced Wildfires and Heatwaves. Cureus 2019, 11, e4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; He, Q.; Fang, Z.; Brown, S.S.; Laskin, A.; Cohen, S.R.; Rudich, Y. Laboratory Insights into the Diel Cycle of Optical and Chemical Transformations of Biomass Burning Brown Carbon Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11827–11837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desyaterik, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.; Lee, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Collett, J. Speciation of “brown” carbon in cloud water impacted by agricultural biomass burning in eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7389–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Li, C.; He, Q.; Levin-Zaidman, S.; Tsoory, M.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Rudich, Y. Mechanisms of lung toxicity induced by biomass burning aerosols. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pardo, M.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Levin-Zaidman, S.; Dezorella, N.; Czech, H.; Martens, P.; Käfer, U.; Gröger, T.; Rüger, C.P.; et al. Toxicity of Water- and Organic-Soluble Wood Tar Fractions from Biomass Burning in Lung Epithelial Cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1588–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwi, K.; Mondal, A.; Pant, J.; Cheng, Z.; El Hajj, O.; Ijeli, I.; Handa, H.; Saleh, R. Physicochemical properties and cytotoxicity of brown carbon produced under different combustion conditions. Atmospheric Environ. 2021, 244, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Sullivan, A.P.; Mack, L.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Onasch, T.B.; Worsnop, D.R.; Malm, W.; Wold, C.E.; Hao, W.M.; et al. Chemical Smoke Marker Emissions During Flaming and Smoldering Phases of Laboratory Open Burning of Wildland Fuels. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bathia, S.C. Advanced Renewed Energy Systems; Part 1; Woodhead Publishing India: New Delhi, India, 2014; p. 775. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Warren, S.H.; Krantz, Q.T.; King, C.; Jaskot, R.; Preston, W.T.; George, B.J.; Hays, M.D.; Landis, M.; Higuchi, M.; et al. Mutagenicity and Lung Toxicity of Smoldering vs. Flaming Emissions from Various Biomass Fuels: Implications for Health Effects from Wildland Fires. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; King, C.; Krantz, T.; Hargrove, M.M.; George, I.J.; McGee, J.; Copeland, L.; Hays, M.D.; Landis, M.; Higuchi, M.; et al. The role of fuel type and combustion phase on the toxicity of biomass smoke following inhalation exposure in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargrove, M.M.; Kim, Y.H.; King, C.; Wood, C.E.; Gilmour, M.I.; Dye, J.A.; Gavett, S.H. Smoldering and flaming biomass wood smoke inhibit respiratory responses in mice. Inhal. Toxicol. 2019, 31, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, M.A.; Christensen, E.G.; Yang, J.; Rein, G. Review of the Transition From Smouldering to Flaming Combustion in Wildfires. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, W.M.; Hooven, L.A.; Mahadevan, B. Carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts and mechanism of action. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2005, 45, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilger, M.; Orasche, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Paur, H.-R.; Diabaté, S.; Weiss, C. Toxicity of wood smoke particles in human A549 lung epithelial cells: The role of PAHs, soot and zinc. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 3029–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mölder, A.; Sebesta, M.; Gustafsson, M.; Gisselson, L.; Wingren, A.G.; Alm, K. Non-invasive, label-free cell counting and quantitative analysis of adherent cells using digital holography. J. Microsc. 2008, 232, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Abassi, Y.A. The xCELLigence System for Real-Time and Label-Free Monitoring of Cell Viability. Assay Guid. Man. 2011, 740, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Albuquerque, Y.L.; Berger, E.; Tomaz, S.; George, C.; Géloën, A. Evaluation of the Toxicity on Lung Cells of By-Products Present in Naphthalene Secondary Organic Aerosols. Life 2021, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzati, M.; Kammen, D.M. Indoor air pollution from biomass combustion and acute respiratory infections in Kenya: An exposure-response study. Lancet 2001, 358, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.D.O.; Vessoni, A.; Quinet, A.; Fortunato, R.S.; Kajitani, G.S.; Peixoto, M.S.; Hacon, S.D.S.; Artaxo, P.; Saldiva, P.; Menck, C.F.; et al. Biomass burning in the Amazon region causes DNA damage and cell death in human lung cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bølling, A.K.; Totlandsdal, A.I.; Sallsten, G.; Braun, A.; Westerholm, R.; Bergvall, C.; Boman, J.; Dahlman, H.J.; Sehlstedt, M.; Cassee, F.; et al. Wood smoke particles from different combustion phases induce similar pro-inflammatory effects in a co-culture of monocyte and pneumocyte cell lines. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mondal, N.K.; Saha, H.; Mukherjee, B.; Tyagi, N.; Ray, M.R. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and higher expression levels of Nrf2 and NQO1 proteins in the airways of women chronically exposed to biomass fuel smoke. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 447, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.; Kim, D.; Min, D.W.; Kwon, S.-H.; Lee, J.-Y. Nrf2 regulates cell motility through RhoA–ROCK1 signalling in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biola-Clier, M.; Beal, D.; Caillat, S.; Libert, S.; Armand, L.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Carriere, M. Comparison of the DNA damage response in BEAS-2B and A549 cells exposed to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mutagenesis 2016, 32, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankoff, A.; Brzóska, K.; Czarnocka, J.; Kowalska, M.; Lisowska, H.; Mruk, R.; Øvrevik, J.; Wegierek-Ciuk, A.; Zuberek, M.; Kruszewski, M. A comparative analysis of in vitro toxicity of diesel exhaust particles from combustion of 1st- and 2nd-generation biodiesel fuels in relation to their physicochemical properties—the FuelHealth project. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19357–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).