Concentration and Physical Characteristics of Black Carbon in Winter Snow of Beijing in 2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Time
2.2. Sample Analysis
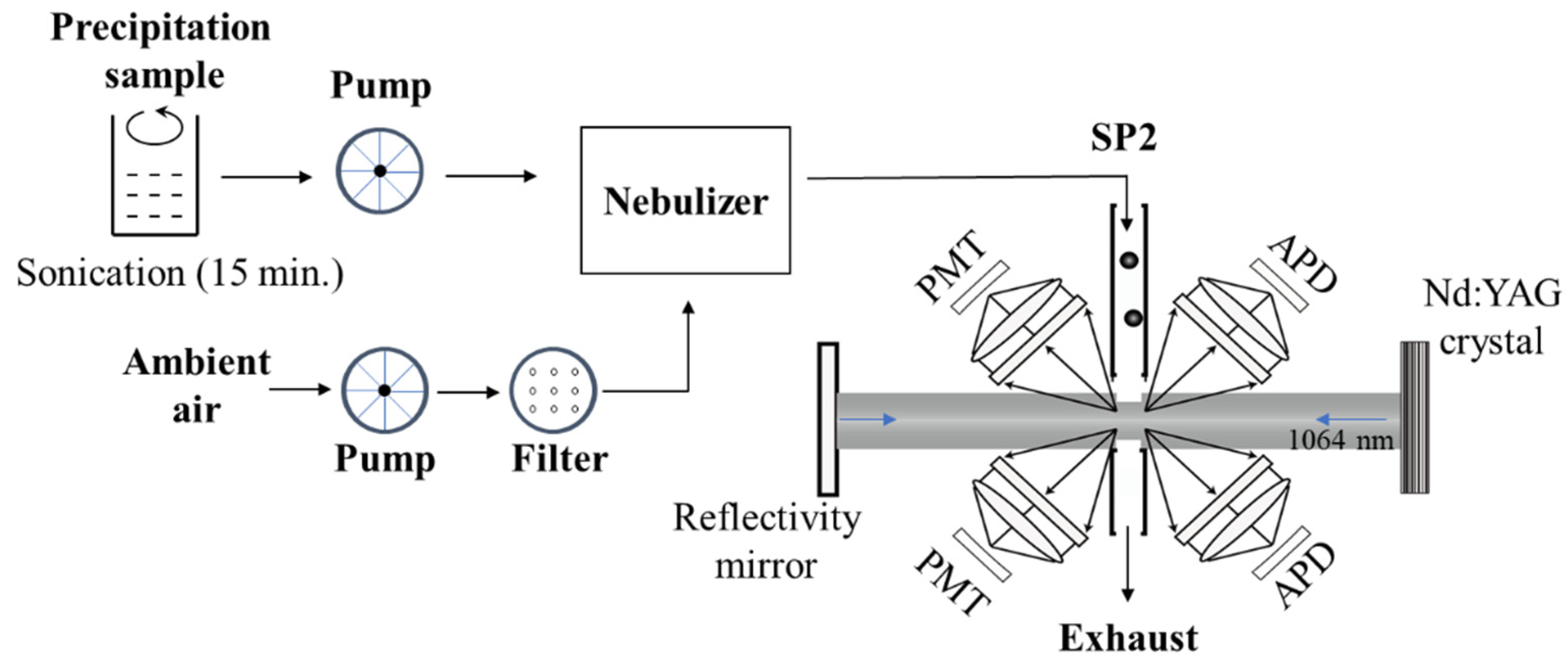
2.3. Single Particle Soot Photometer (SP2)
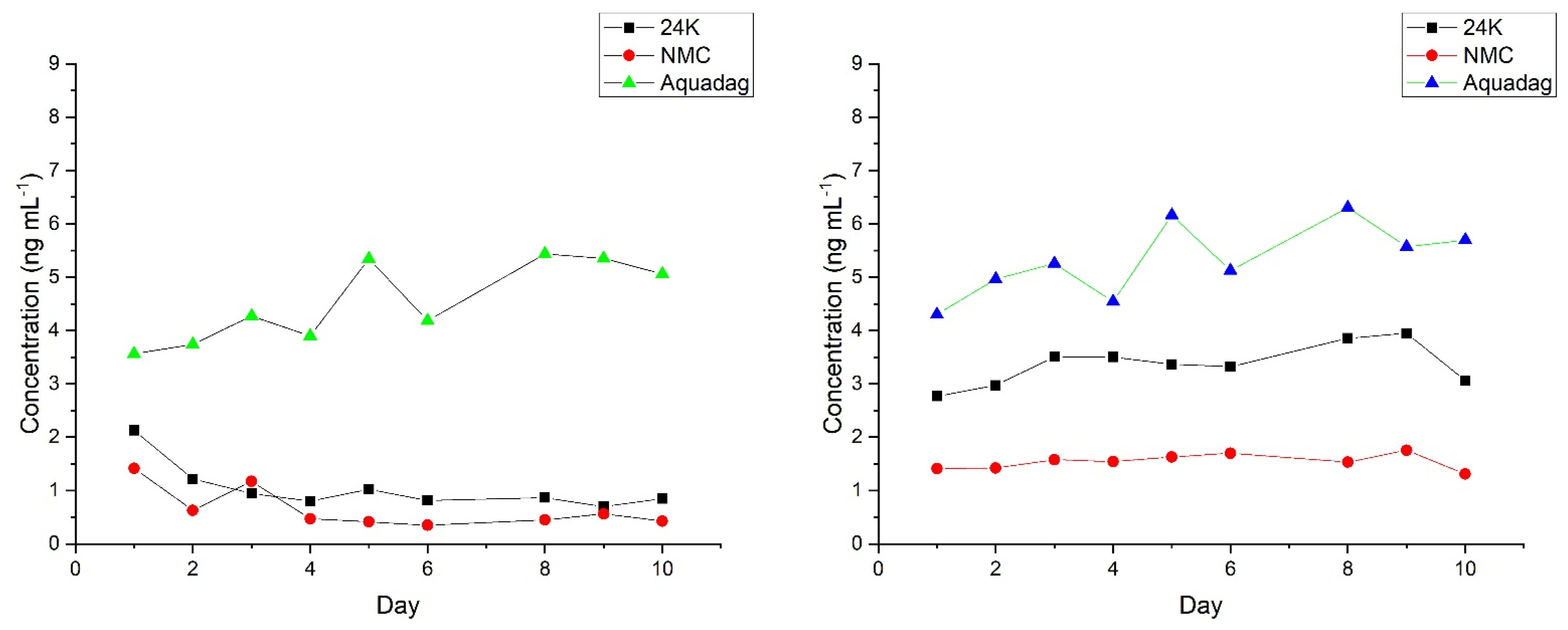
2.4. Effects of Different Treatment Methods on Measurement
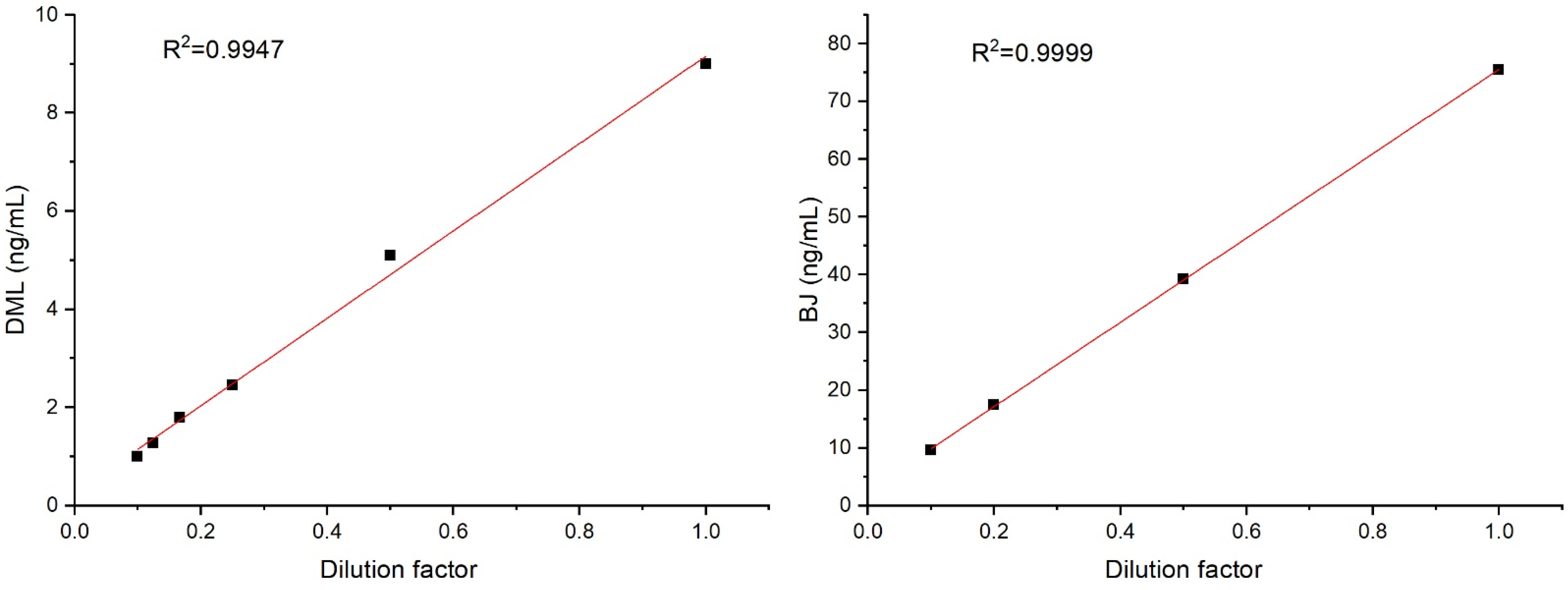
2.5. The Effect of Sample Dilution on Measuring Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass Concentration of BC in Snow
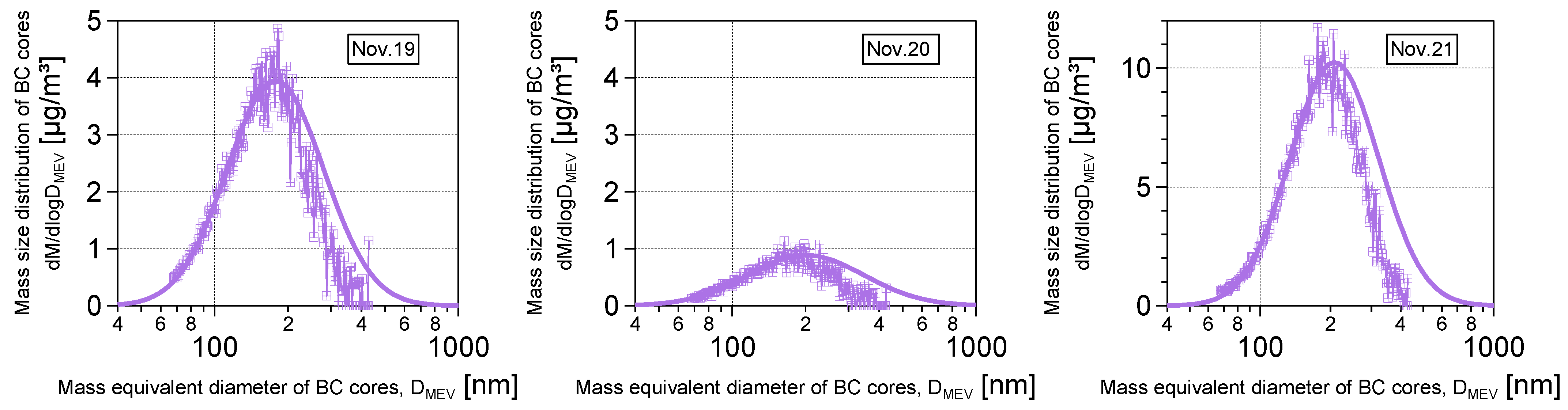
3.2. Size Distribution of BC in Snow
3.3. Meteorological Effects on Day-to-Day Variation in BC Concentration in Snow
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujitani, Y.; Fushimi, A.; Saitoh, K.; Sato, K.; Takami, A.; Kondo, Y.; Tanabe, K.; Kobayashi, S. Mid carbon (C6+-C29+) in refractory black carbon aerosols is a potential tracer of open burning of rice straw: Insights from atmospheric observation and emission source studies. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, J. Characterization of black carbon aerosol at the summit of Mount Tai (1534 m) in central east China: Temporal variation, source appointment and transport. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Bai, D.; Liu, A.; Shi, S.; Dai, Q. Impact of Black Carbon on Surface Ozone in the Yangtze River Delta from 2015 to 2018. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, B.; Guo, S.; Wu, Z.; Song, Z.; Yin, Y.; et al. Annual variations of black carbon over the Yangtze River Delta from 2015 to 2018. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 96, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Bréon, F.-M.; Collins, W.; Fuglestvedt, J.; Huang, J.; Koch, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lee, D.; Mendoza, B.; et al. Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Can the direct and semi-direct aerosol effect compete with the indirect effect on a global scale? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoose, C.; Kristjánsson, J.; Burrows, S. How important is biological ice nucleation in clouds on a global scale? Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 024009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohy, C.H.; DeMott, P.J.; Pratt, K.A.; Subramanian, R.; Kok, G.L.; Murphy, S.M.; Lersch, T.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Wang, Z.; Prather, K.A.; et al. Relationships of Biomass-Burning Aerosols to Ice in Orographic Wave Clouds. J. Atmospheric Sci. 2010, 67, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallavardin, S.J.; Froyd, K.D.; Lohmann, U.; Moehler, O.; Murphy, D.M.; Cziczo, D.J. Single particle laser mass spectrometry applied to differential ice nucleation experiments at the AIDA chamber. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X. Can cirrus cloud seeding be used for geoengineering? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8775–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadley, O.L.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Black-carbon reduction of snow albedo. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegg, D.A.; Warren, S.G.; Grenfell, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Larson, T.V.; Clarke, A.D. Source Attribution of Black Carbon in Arctic Snow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4016–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Perring, A.; Spackman, J.R.; Fahey, D.W. Black carbon aerosol size in snow. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H. A review of black carbon in snow and ice and its impact on the cryosphere. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Wang, S.-H.; Lin, N.-H.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.-T.; Thepnuan, D. Black carbon over an urban atmosphere in northern peninsular Southeast Asia: Characteristics, source apportionment, and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; Van Bree, L.; ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Black Carbon as an Additional Indicator of the Adverse Health Effects of Airborne Particles Compared with PM10and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Dai, J.; Liu, R.; Zhai, Y.; Yue, D.; Hu, Q. Integrated assessment of health risk and climate effects of black carbon in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Flanner, M.G.; Chen, F.; Barlage, M.; Liou, K.N.; Kang, S.; Ming, J.; Qian, Y. Black carbon-induced snow albedo reduction over the Tibetan Plateau: Uncertainties from snow grain shape and aerosol–snow mixing state based on an updated SNICAR model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11507–11527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, S.G. Can black carbon in snow be detected by remote sensing? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skiles, S.M.; Painter, T. Daily evolution in dust and black carbon content, snow grain size, and snow albedo during snowmelt, Rocky Mountains, Colorado. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, S.; Zhu, B. Characterization of black carbon aerosol in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Seasonal variation and source apportionment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Kennedy, D.; Miller, R.L.; Cowin, J.P.; Jung, K.-H.; Perzanowski, M.; Balletta, M.; Perera, F.P.; Kinney, P.L.; Chillrud, S.N. Validating a nondestructive optical method for apportioning colored particulate matter into black carbon and additional components. Atmospheric Environ. 2011, 45, 7478–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, G.A.; Lawrence, J.; Koutrakis, P. Field validation of a semi-continuous method for aerosol black carbon (aethalometer) and temporal patterns of summertime hourly black carbon measurements in southwestern PA. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Che, H.; Ming, J.; Yi, Z. Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Aerosol in China Based on Revised Aethalometer Monitoring Data. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Li, C.; Gao, T.; Cong, Z.; Sprenger, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Sillanpää, M.; et al. Characteristics of black carbon in snow from Laohugou No. 12 glacier on the northern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 607, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zheng, F. Inventory of black carbon and organic carbon emissions from China. Atmospheric Environ. 2006, 40, 6516–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Bond, T.C.; Lehmann, C.M.B.; Subramanian, R.; Hadley, O.L. Measuring Organic Carbon and Black Carbon in Rainwater: Evaluation of Methods. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hao, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, F. Real-time geochemistry of urban aerosol during a heavy dust episode by single-particle aerosol mass spectrometer: Spatio-temporal variability, mixing state and spectral distribution. Particuology 2020, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, J.F.; Guillemette, F.; Berggren, M.; Del Giorgio, A. Increases in terrestrially derived carbon stimulate organic carbon processing and CO2 emissions in boreal aquatic ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Miao, Q.; Shen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wei, H. Air pollutant variations in Suzhou during the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) lockdown of 2020: High time-resolution measurements of aerosol chemical compositions and source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Cao, J.; Hansen, J.; Yao, T.; Joswia, D.R.; Wang, N.; Wu, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, W.; et al. Black soot and the survival of Tibetan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22114–22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, A.; Zhen, Z.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, J. Vertical Structures of Meteorological Elements and Black Carbon at Mt. Tianshan Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle System. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.J.; Warren, S.G.; Grenfell, T.C.; Clarke, A.D.; Brandt, R.E. Light-absorbing impurities in Arctic snow. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 11647–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.L.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Pochanart Akimoto, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Dong, H.B.; Li, J.; Irie, H.; Takigawa, M. Correlation of black carbon aerosol and carbon monoxide in the high-altitude environment of Mt. Huang in Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9735–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grenfell, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Clarke, A.D.; Warren, S.G. Light absorption from particulate impurities in snow and ice determined by spectrophotometric analysis of filters. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, M.; Brun, E.; Picard, G.; Michou, M.; Libois, Q.; Petit, J.-R.; Geyer, M.; Morin, S.; Josse, B. Contribution of light-absorbing impurities in snow to Greenland’s darkening since 2009. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Yan, X.; Pu, T.; He, Y. Distribution of light-absorbing impurities in snow of glacier on Mt. Yulong, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Cong, Z.; Wu, G.; Ji, M. Quantifying Light Absorption of Iron Oxides and Carbonaceous Aerosol in Seasonal Snow across Northern China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.; Doherty, S.J.; Li, F.; Ruggiero, S.T.; Tanner, C.E.; Perring, A.E.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W. Assessing recent measurement techniques for quantifying black carbon concentration in snow. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2012, 5, 3771–3795. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Doherty, S.J.; Huang, J. Black carbon and other light-absorbing impurities in snow across Northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Hegg, D.A. Quantifying light absorption by organic carbon in Western North American snow by serial chemical extractions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, J.R.; Edwards, R.; Kok, G.L.; Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.; Saltzman, E.S.; Banta, J.R.; Pasteris, D.R.; Carter, M.M.; Kahl, J.D.W. 20th-Century Industrial Black Carbon Emissions Altered Arctic Climate Forcing. Science 2007, 317, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Spackman, J.R.; Gao, R.S.; Perring, A.; Cross, E.; Onasch, T.B.; Ahern, A.; Wrobel, W.; Davidovits, P.; Olfert, J.; et al. The Detection Efficiency of the Single Particle Soot Photometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, M.; Mertes, P.; Zieger, P.; Dommen, J.; Baltensperger, U.; Gysel, M. Sensitivity of the Single Particle Soot Photometer to different black carbon types. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wendl, I.A.; Menking, J.A.; Färber, R.; Gysel, M.; Kaspari, S.D.; Laborde, M.J.G.; Schwikowski, M. Optimized method for black carbon analysis in ice and snow using the Single Particle Soot Photometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Faïn, X.; Zanatta, M.; Cozic, J.; Jaffrezo, J.-L.; Ginot, P.; Laj, P. Refractory black carbon mass concentrations in snow and ice: Method evaluation and inter-comparison with elemental carbon measurement. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3307–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adachi, K.; Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y.; Igarashi, Y. Mixing states of light-absorbing particles measured using a transmission electron microscope and a single-particle soot photometer in Tokyo, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9153–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbin, J.C.; Gysel-Beer, M. Detection of tar brown carbon with a single particle soot photometer (SP2). Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 15673–15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.; Perring, A.; Markovic, M.; Gao, R.; Ohata, S.; Langridge, J.; Law, D.; McLaughlin, R.; Fahey, D. Technique and theoretical approach for quantifying the hygroscopicity of black-carbon-containing aerosol using a single particle soot photometer. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 81, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P. Extrapolation of single particle soot photometer incandescent signal data. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Gupta, S.; Waldhoff, S.T.; Wang, M.Q.; Bond, T.C.; Yiyun, B. Black carbon emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4281–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black Carbon Emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xia, X.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S. Black carbon (BC) in urban and surrounding rural soils of Beijing, China: Spatial distribution and relationship with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemosphere 2011, 82, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Schleicher, N.; Fricker, M.; Cen, K.; Liu, X.-L.; Kaminski, U.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.-F.; Norra, S. Long-term variation of black carbon and PM2.5 in Beijing, China with respect to meteorological conditions and governmental measures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, R.; et al. Chemical composition, water content and size distribution of aerosols during different development stages of regional haze episodes over the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Kang, S.; He, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Gao, S.; Li, C. Carbonaceous matter in glacier at the head-waters of the Yangtze River: Concentration, sources and fractionation during the melting process. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A. Impact of aerosol-PBL interaction on haze pollution: Multiyear observational evidences in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8596–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; Chen, H. Spatial-temporal features of intense snowfall events in China and their possible change. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, D. Measuring black carbon in snow and ice in the Tibetan Plateau by single particle soot photometer. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspari, S.; Painter, T.H.; Gysel, M.; Skiles, S.M.; Schwikowski, M. Seasonal and elevational variations of black car-bon and dust in snow and ice in the Solu-Khumbu, Nepal and estimated radiative forcings. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8089–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Liou, K.-N.; Takano, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zamora, M.L.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Leung, L.R. Variation of the radiative properties during black carbon aging: Theoretical and experimental intercomparison. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 11967–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanner, M.G.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Penner, J.; Jiao, C. Enhanced solar energy absorption by internally-mixed black carbon in snow grains. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 4699–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Takano, Y.; Liou, K.-N.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Chen, F. Impact of Snow Grain Shape and Black Carbon–Snow Internal Mixing on Snow Optical Properties: Parameterizations for Climate Models. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 10019–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liou, K.; Takano, Y. Resolving Size Distribution of Black Carbon Internally Mixed With Snow: Impact on Snow Optical Properties and Albedo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2697–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Doherty, S.J.; Li, F.; Ruggiero, S.T.; Tanner, C.; Perring, A.; Gao, R.S.; Fahey, D.W. Assessing Single Particle Soot Photometer and Integrating Sphere/Integrating Sandwich Spectrophotometer measurement techniques for quantifying black carbon concentration in snow. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Rasch, P.J. Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Zhu, H.; Gan, W.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Occurrence of nitrogenous and carbonaceous disinfection byproducts in drinking water distributed in Shenzhen, China. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. | No. of Samples | Concentration (ng/mL) | Actual Concentration (ng/mL) | Weather |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19-1 | 15.3995 | 76.9975 | Light snow |
| 2 | 19-2 | 16.0576 | 80.288 | Light snow |
| 3 | 19-3 | 12.8519 | 64.2595 | Light snow |
| 4 | 19-4 | 12.5724 | 62.862 | Light snow |
| 5 | 20-1 | 3.63763 | 18.18815 | Moderate snow |
| 6 | 20-4 | 2.89438 | 14.4719 | Moderate snow |
| 7 | 21-1 | 42.1161 | 210.5805 | Heavy snow |
| 8 | 21-4 | 29.7629 | 148.8145 | Heavy snow |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Sheng, J.; Du, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, F.; Xiao, W.; Ding, D. Concentration and Physical Characteristics of Black Carbon in Winter Snow of Beijing in 2015. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070816
Zhao D, Sheng J, Du Y, Zhou W, Wang F, Xiao W, Ding D. Concentration and Physical Characteristics of Black Carbon in Winter Snow of Beijing in 2015. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(7):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070816
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Delong, Jiujiang Sheng, Yuanmou Du, Wei Zhou, Fei Wang, Wei Xiao, and Deping Ding. 2021. "Concentration and Physical Characteristics of Black Carbon in Winter Snow of Beijing in 2015" Atmosphere 12, no. 7: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070816
APA StyleZhao, D., Sheng, J., Du, Y., Zhou, W., Wang, F., Xiao, W., & Ding, D. (2021). Concentration and Physical Characteristics of Black Carbon in Winter Snow of Beijing in 2015. Atmosphere, 12(7), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070816





