Characteristics of Summer Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Local Environmental Influencing Factors in Beijing under Urbanization Background
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
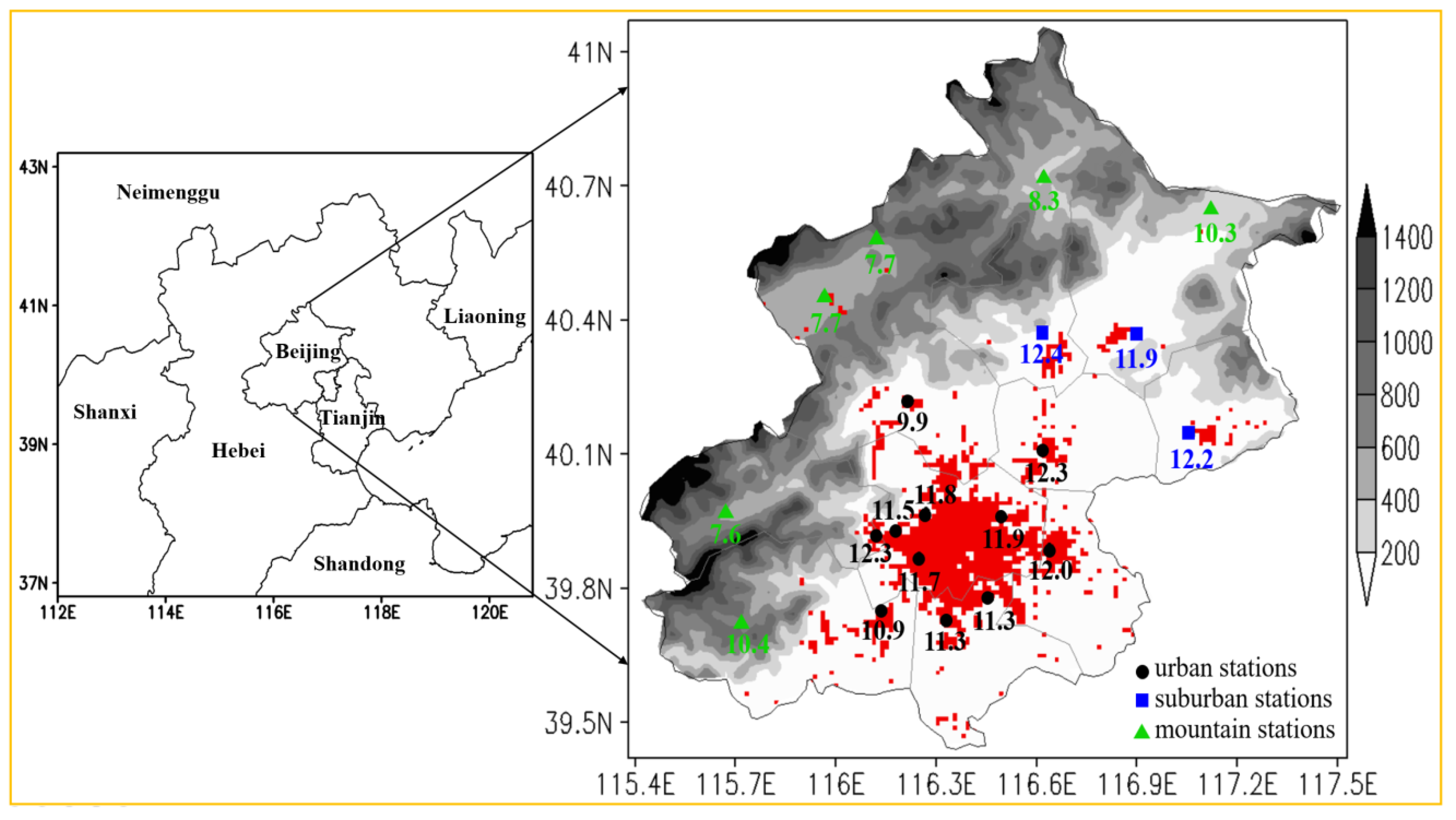
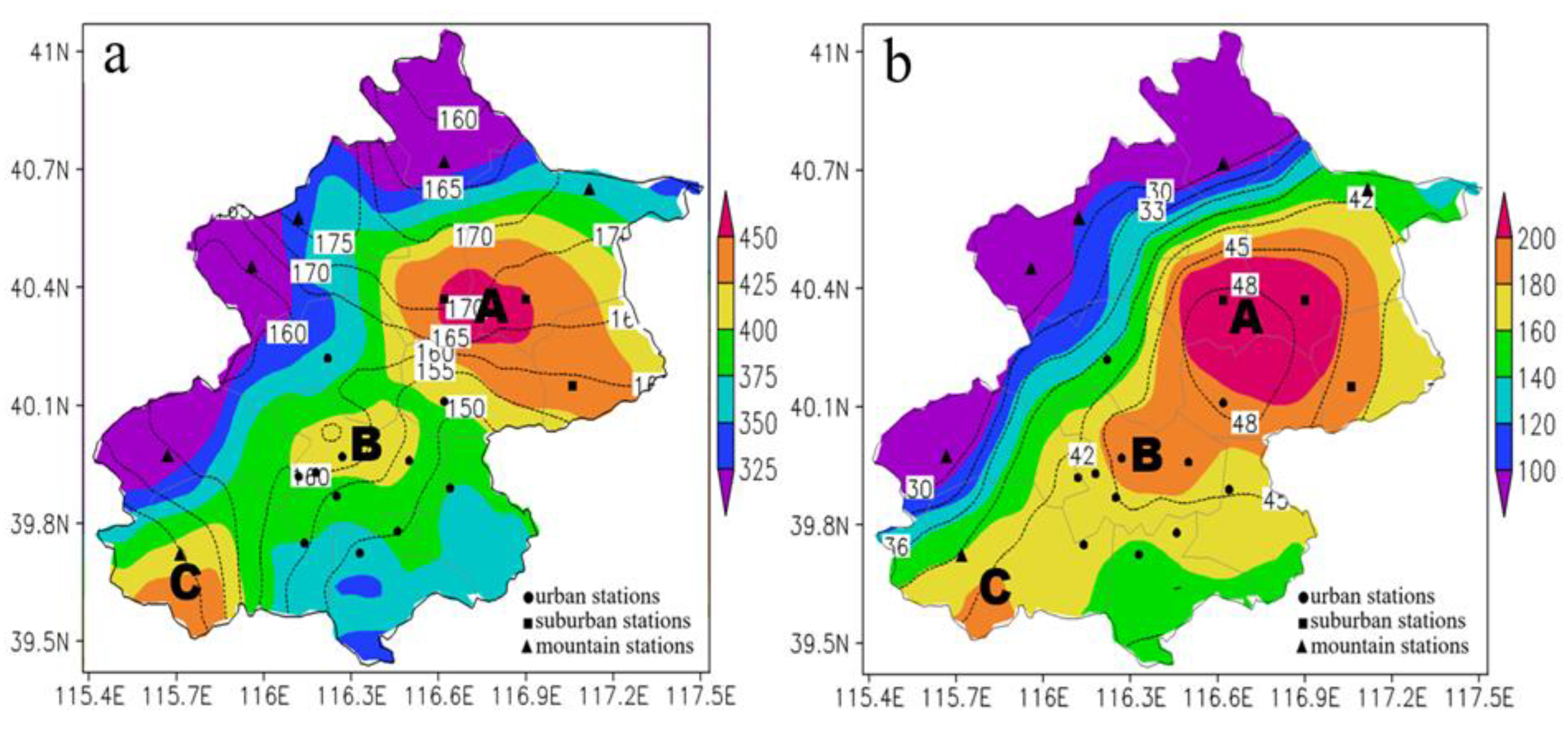
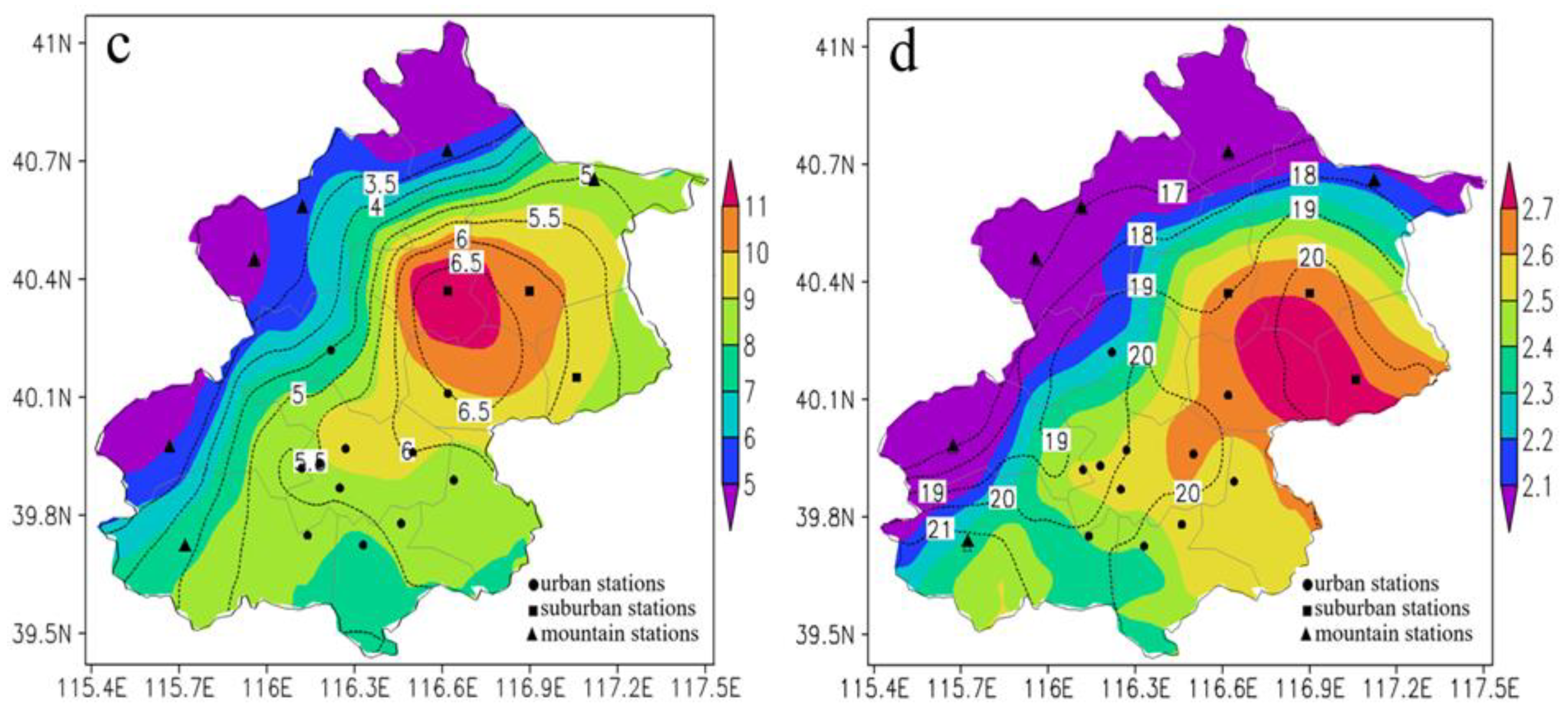
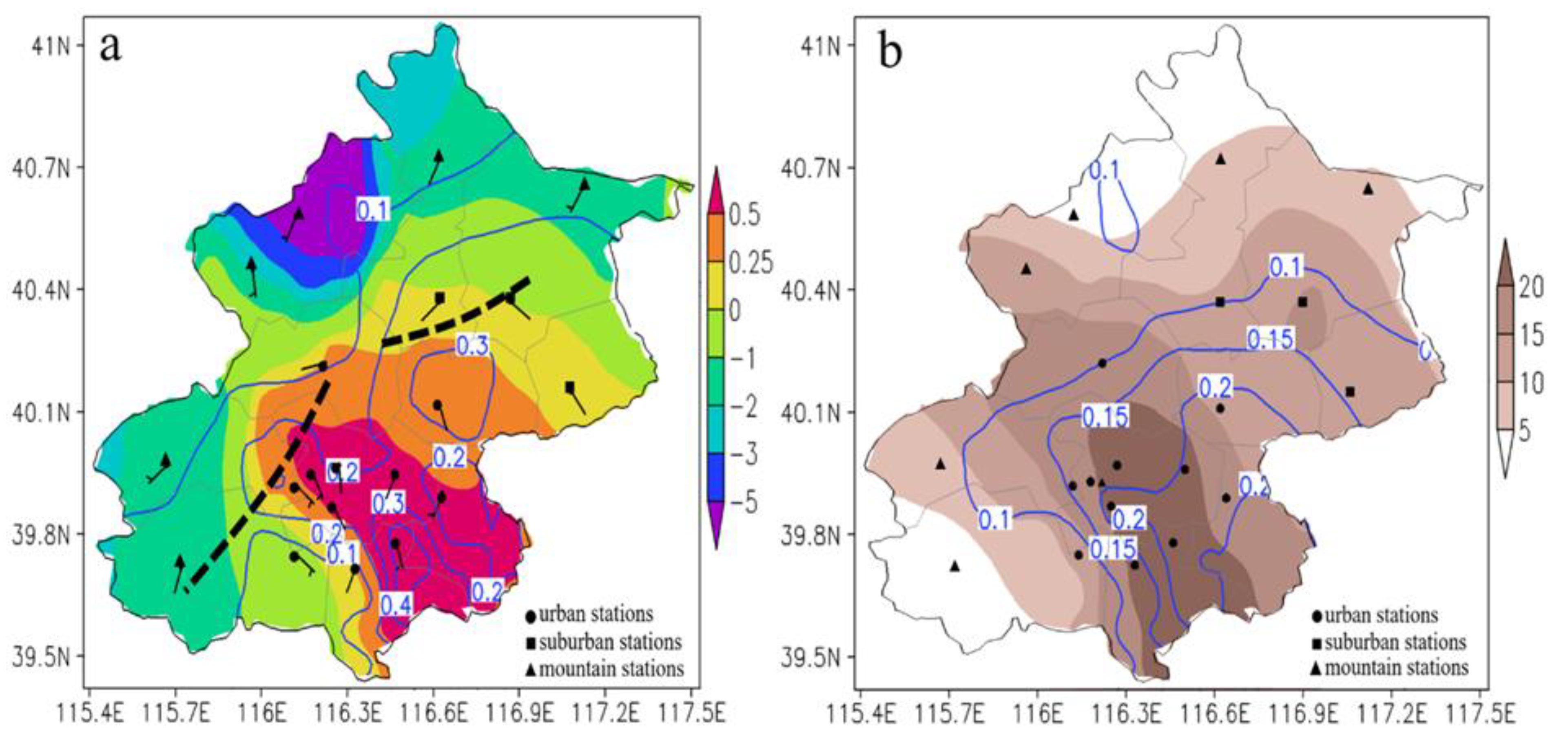
3.1. Spatial Distributions of Summer Precipitation and HEP
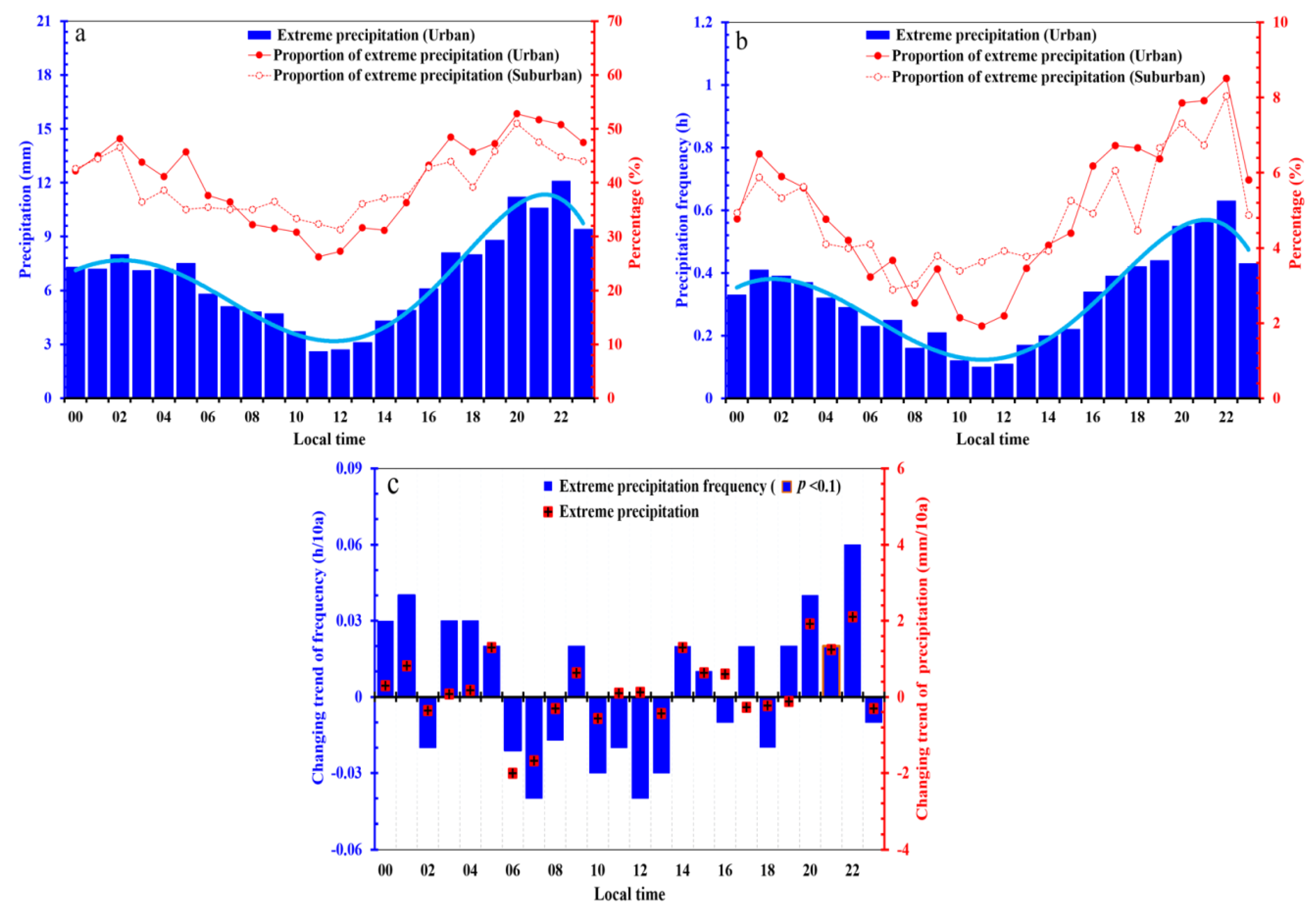
3.2. Temporal Variation of HEP
3.3. Impact of Local Environment on HEP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oki, T.; Musiake, K. Seasonal change of the diurnal cycle of precipitation over Japan and Malaysia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, F.A.; Vogel, J.L. Urban, topographic and diurnal effects on rainfall in the St Louis Region. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1978, 17, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, R.; Lin, Q.L. Urban heat islands and summertime convective thunderstorms in Atlanta: Three case studies. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, O.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of extreme precipitation increases extensively with event rareness under global warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, P.; Arnbjerg, K.; Olsson, J.; Nguyen, V.T.V. Climate change impact assessment on urban rainfall extremes and urban drainage: Methods and shortcomings. Atmos. Res. 2012, 103, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Bardossy, A.; Seidel, J.; Müller, T.; Sanchis, E.F.; Hauser, A. Statistical analysis of sub-daily precipitation extremes in Singapore. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 3, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.C.; Kendon, E.J.; Fowler, H.J.; Blenkinsop, S.; Roberts, N.M. Projected increases in summer and winter UK sub-daily precipitation extremes from high-resolution regional climate models. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Aadhar, S.; Stone, D.; Mishra, V. Increase in extreme precipitation events under anthropogenic warming in India. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2018, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.J. Potentials of meteorological characteristics and synoptic conditions to mitigate urban heat island effects. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Wu, M. Urbanization Enhanced Summertime Extreme Hourly Precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5809–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Lv, L.; Fang, J. Spatiotemporal pattern of hourly heavy rainfall in China and its spatial correlation with urbanization factors during 1991−2010. Clim. Environ. Res. 2017, 22, 355–364. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Zhou, T.J.; Xiong, A.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L01704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Diurnal cycle of the Asian summer monsoon: Air pump of the second kind. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 1747–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Y.; Chen, F.; Wong, W. Observed Link of Extreme Hourly Precipitation Changes to Urbanization over Coastal South China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 1799–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, G. Effect of urban expansion on summer rainfall in the Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Fan, S. Impacts of Urban Processes and Urbanization on Summer Precipitation: A Case Study of Heavy Rainfall in Beijing on 1 August 2006. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 806–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Miao, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Lou, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, D.; Xue, W.; Zhai, P. Synoptic patterns and sounding-derived parameters associated with summertime heavy rainfall in Beijing. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 39, 1476–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zha, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Hourly Extreme Precipitation Changes under the Influences of Regional and Urbanization Effects in Beijing. Int. J. Clim. 2020, 41, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Z.W.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. Impact of urbanization on changes in temperature extremes in Beijing during 1978–2008. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4679–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Deng, M.J.; Lee, S.S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhai, P.M.; Liu, H.; Lv, W.T.; Yao, W. Delaying precipitation and lightning by air pollution over the Pearl River Delta. Part 1: Observational analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6472–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, R.H.; Wang, Y.C. Characteristics of precipitation in Beijing and the precipitation representativeness of Beijing weather observatory. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2012, 23, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molders, N. Landscape changes over a region in East Germany and their impact upon the processes of its atmpospheric water-cycle. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 68, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, L.M.; Shepherd, J.M. An investigation of warm-season spatial rainfall variability in Oklahoma City: Possible Linkages to urbanization and prevailing wind. J. Appl. Meteorol.Clim. 2009, 48, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changnon, S.A. Urban effects on Severe Local Stoms at St.Louis. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1978, 17, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.M.; Pierce, H.; Negri, A.J. Rainfall modification by major urban areas: Observations from spaceborne rain radar on the TRMM satellite. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.M.; Burian, S.J. Detection of urban-induced rainfall anomalies in a major coastal city. Earth Interact. 2003, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomohiko, I.; Takeki, I.; Hiroshima, A. Diagnostic study of the effects of a large city on heavy rainfall as revealed by an ensemble simulation: A case study of central Tokyo, Japan. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2011, 50, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, W.R.; Pielke, R.A. Inadvertent human impacts on regional weather and climate. In Human Impacts on Weather and Climate, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 73–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Surface Convergence Line Features in the Eastern Side of Taihang Mountain. Meteorol. Mon. 2013, 39, 1445–1451. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Grimmond, S.; Cheng, Z.; Miao, S.; Feng, D.; Liao, M. Summertime surface energy balance fluxes at two Beijing sites. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2793–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lolli, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Diurnal variation of summer precipitation modulated by air pollution: Observational evidences in the Beijing metropolitan area. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P.G.; Mote, T.L. Patterns and causes of Atlanta's urban heat island–initiated precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Miao, S.; Zhang, H. Uncertainties in the impact of urbanization on heavy rainfall: Case study of a rainfall event in Beijing on 7 August 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6005–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Sun, A.; Ren, F. Changes of climate extremes in China. Clim. Chang. 1999, 42, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, R. Climate change and sustainable development for cities. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kusaka, H.; Bornstein, R.; Ching, J.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Loridan, T.; Manning, K.; Martilli, A.; Sailor, D.; et al. The integrated WRF/urban modelling system: Development, evaluation, and applications to urban environmental problems. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Deng, M.; Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhai, P.; Dai, Z.; Li, X. Precipitation and air pollution at mountain and plain stations in northern China: Insights gained from observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 4793–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.H.; Xie, Z.H.; Zou, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, S. Future precipitation extremes in China under climate change and their physical quantification based on a regional climate model and CMIP5 model simulations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 460–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Xu, G.; Gao, H. Characteristics of Summer Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Local Environmental Influencing Factors in Beijing under Urbanization Background. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050632
Zheng Z, Xu G, Gao H. Characteristics of Summer Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Local Environmental Influencing Factors in Beijing under Urbanization Background. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050632
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zuofang, Guirong Xu, and Hua Gao. 2021. "Characteristics of Summer Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Local Environmental Influencing Factors in Beijing under Urbanization Background" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050632
APA StyleZheng, Z., Xu, G., & Gao, H. (2021). Characteristics of Summer Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Local Environmental Influencing Factors in Beijing under Urbanization Background. Atmosphere, 12(5), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050632




