Abstract
In order to investigate the seasonal variations in the chemical characteristics of PM2.5 at the plateau slope of a mountain city in southwest China, 178 PM2.5 filters (89 quartz and 89 Teflon samples for PM2.5) were collected to sample the urban air of Wenshan in spring and autumn 2016 at three sites. The mass concentrations, water-soluble inorganic ions, organic and inorganic carbon concentrations, and inorganic elements constituting PM2.5 were determined, principal component analysis was used to identify potential sources of PM2.5, and the backward trajectory model was used to calculate the contribution of the long-distance transmission of air particles to the Wenshan area. The average concentration of PM2.5 in spring and autumn was 44.85 ± 10.99 μg/m3. Secondary inorganic aerosols contributed 21.82% and 16.50% of the total PM2.5 in spring and autumn, respectively. The daily mean value of OC/EC indicated that the measured SOC content was generated by the photochemical processes active during the sampling days. However, elements from anthropogenic sources (Ti, Si, Ca, Fe, Al, K, Mg, Na, Sb, Zn, P, Pb, Mn, As and Cu) accounted for 99.38% and 99.24% of the total inorganic elements in spring and autumn, respectively. Finally, source apportionment showed that SIA, dust, industry, biomass burning, motor vehicle emissions and copper smelting emissions constituted the major components in Wenshan. This study is the first to investigate the chemical characterizations and sources of PM2.5 in Wenshan, and it provides effective support for local governments formulating air pollution control policies.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, with rapid economic development, industrialization and urbanization in China, the number of motor vehicles and the total energy consumption have increased, and atmospheric particulate matter (PM) has become one of the most significant air contaminants [1,2,3]. PM, particularly PM2.5 (aerodynamic diameter ≤2.5 mm), can exist in the atmosphere for a long time, which is conducive to its long-distance transport through the atmosphere and deposition towards remote areas. During long-range transport, PM2.5 carries abundant anthropogenic pollutants and has a serious impact on the global and regional climate, the visibility and composition of the atmosphere, the global biogeochemical cycle and the activation of cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) [4,5,6].
PM2.5 has been widely studied in recent years in China due to its potential impacts on air quality and human health. Water-soluble inorganic ions (WSIIs), organic carbon (OC) particles, inorganic carbon (EC) particles, and inorganic elements (IEs), as the main chemical components of PM2.5, have been extensively studied in China [7,8,9]. WSIIs are dominated by secondary inorganic aerosols (SIAs), including NH4+, NO3−, and SO42−. OC is composed of thousands of organic compounds and contains many toxic substances. Heavy metals are an important part of the inorganic elements comprising PM2.5, such as Fe, Zn, Cu and Pb [10,11,12].
Whether worldwide or only in China, it is essential to reduce PM2.5 concentrations to control their sources. The key point in formulating policies for the government to control PM2.5 pollution is the result of source apportionment and reliable source quantification [13,14]. In fact, PM2.5 is usually sourced by the emission of pollutants, and its classification is very complex, including its anthropogenic and natural sources and gas and particle phases [15,16]. In addition, PM2.5 forms secondary pollutants from primary emissions through photochemical reactions after being released from pollution sources, making it difficult to quantify its impacts [17,18,19]. The contribution levels of different sources in the air can be quantitatively estimated by using the receptor model. Generally, researchers have identified the possible sources of PM2.5 as traffic and industrial, coal combustion, biomass burning and secondary inorganic aerosol sources [20,21].
In recent years, most studies have generally focused on the Jing-Jin-Ji region and its coastal areas with severely degraded atmospheric environments in China [22,23,24]. Only a few researchers have investigated PM2.5 pollution in Yunnan Province, which is a remote southwestern region. More research has been conducted in areas such as Kunming and Yuxi [25,26,27]. Despite the economic backwardness of the remote southwestern mountains, there are still cases of PM2.5 exceeding the standard every year [28,29,30]. Therefore, we should pay more attention to these areas to improve their air quality.
Wenshan, a developing industrialized city in southwest China, has a high degree of air pollution, mainly resulting from the presence of PM2.5 in the atmosphere. Furthermore, Wenshan is located in the basin valley on the plateau, and the urban area is surrounded by high mountains, which aggravate particulate pollution. Wenshan is chosen as the study area to conduct PM2.5 sampling during the spring and autumn seasons at three monitoring sites. The concentrations of PM2.5, WSIIs, OC, EC and IEs are analyzed and discussed in the current study. Principal component analysis (PCA) is used for PM2.5 source apportionment to analyze the pollution sources. Potential major contributors were identified on the basis of PCA and local environmental background information. The details of the pollution characteristics and the results of PM2.5 source apportionment in this study can provide the local government with reasonable and effective measures to slow down atmospheric pollution with PM2.5.
2. Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Sample Collection
Wenshan is a developing industrialized city with half a million inhabitants in an urban area of 75 km2. With a longitude of 103°43′–104°27′ E and a latitude of 23°06′–23°44′ N, Wenshan lies in southwest China (Figure 1), which is the transition zone of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and Vietnam Basin.
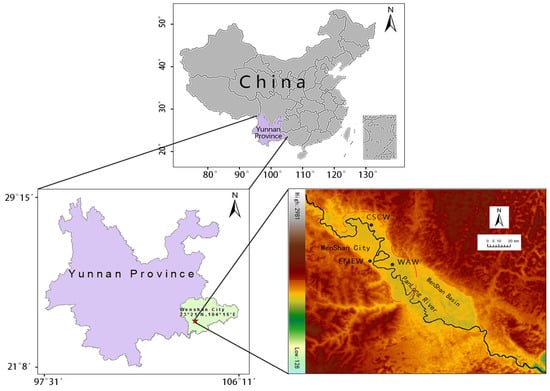
Figure 1.
Location of the sampling site in Wenshan, China.
Wenshan lies in a small basin valley on the plateau and is surrounded by mountains on three sides. The terrain inclines from northwest to southeast, and the mountain range runs almost from north to south. Therefore, a corridor topography consisting of high points on both sides and low points in the middle is formed. The relative altitude difference is 1751.2 m, with the highest altitude of 2991.2 m in Bozhu Mountain and the lowest of 1240 m in the urban area. Wenshan is dominated by a subtropical monsoon climate, which is characterized by a long spring and autumn, no bitter cold in winter, no brutal heat in summer and delightful weather in all seasons. Airflow near the ground can only enter the urban area from the southeast. The cold air in Siberia from the north is obstructed by mountains, and the monsoon of the Beibu Gulf and the Bay of Bengal traveling from the southeast flows right into the urban area, which forms comfortable temperatures, low wind speeds and high ultraviolet (UV) light conditions throughout the year. Strong ultraviolet light is conducive to the formation of photochemical atmospheric effects, and the conditions of low pressure and low oxygen can lead to the incomplete combustion of fuel and can increase the resulting pollution emissions. The conditions of low wind speed (<3 m/s) and the large diurnal temperature variation readily form an inversion layer, hindering the diffusion of pollutants.
Measurement campaigns of PM2.5 sampling at three sites at the Convenience Service Center of Wenshan (CSCW), Water Authority of Wenshan (WAW) and Environmental Monitoring Station of Wenshan (EMSW) in Wenshan city (Figure 1), were carried out in two periods in 2016, i.e., 19 April to 3 May and 12 October to 26 October. Daily measurements of 22 ± 1 h with an intelligent mid-volume atmospheric particulate sampler (TH-150F, Tianhong, China) were conducted at a 100 L/min sample flow. Teflon filters (China, 90 mm) were used to analyze IEs, and quartz filters (PALL Inc., USA, 90 mm) were used to analyze OC particles, EC components and WSIIs. A total of 178 PM2.5 samples and 12 blank samples were collected. After sampling, the filters were individually placed into plastic boxes and put into a freezer at −20°C until transport and subsequent analysis.
2.2. Chemical Analysis and Quality Control
2.2.1. WSII Analysis
The anion (i.e., F−, Cl−, SO42− and NO3−) and cation (i.e., K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and NH4+) concentrations were measured by ion chromatography (DX-600, Dionex, USA). This system was outfitted with a separation column (Dionex AS-14A for anions and CS-12A for cations) and a guard column (Dionex AG14A for anions and CG12A for cations). A gradient weak base eluent (3.5 mmol/L Na2CO3; 1 mmol/L NaHCO3) was used for anion detection, while a weak acid eluent (18 mmol/L methanesulfonic acid) was used for cation detection. The measurement error of each ion in a standard solution is within 10%, and the average relative standard deviations of anions and cations are 3.0% and 4.0%, respectively. For quality assurance, two blank spaces were detected in each batch of samples, and the test was carried out at 10%. At least six standard solution concentrations needed to be mixed for each ion component.
2.2.2. Elements Analysis
Li, Be, P, Cr, Mn, Bi, Co, Ni, Cu, Sr, Mo, Cs, Cd, Tl, Pb, Th, Sc, V, As, Rb, Y, Zr, Sn, Sb, La, Ce, U, Sm and W were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Mg, Ca, K, Fe, Al, Ba, Zn, Na and Si were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES).
2.2.3. OC and EC Analysis
The concentrations of OC and EC were analyzed by DRI Model 2001 OC/EC Analyser, which was developed by the American Desert Institute (DRI). The main testing principle of this method is as follows: the sample is heated and converted into CO2 under different temperature gradients and gas environments. CO2 is reduced to CH4 by catalyzing MnO2 and is detected by using a flame ion detector (FID). Then, using a 633 nm helium/neon laser to detect the anti-light intensity of filter paper to detect the production of organic pyrolysis carbon (OPC), eight different carbon components (OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4, OPC, EC1, EC2, and EC2) were obtained. IMPROVE (Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments) defines OC as OC1+OC2+OC3+OC4+OCPyro and EC as EC1+EC2+EC3-OCPyro. The detection limits were 0.82 (OC), 0.19 (EC) and 0.93 (TC) μg/cm2, and the measuring range was 0.2~750 μg/cm2.
2.2.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Modeling
PCA is an important multivariate statistical tool that can reduce the dimensionality of large datasets and extract the number of principal components needed to explain all the variance of such datasets, which is much less than the original number of variables [31,32]. PCA extracts new variables by the correlation between all variables, which contain most of the information about the data, called principal components. Each variable has the same significance, and each topic has the same weight. The first component extracted explains the maximum amount of data variance. The maximum amount of remaining data variance will be further explained by successive components [33,34,35]. This process sets up the orthogonal distribution of components to each other, and the result of the regression adjustment of factors is simple and stable, regardless of how large a dataset is and how many variables are included in the study [36].
2.2.5. HYSPLIT4 Model
The HYSPLIT4 model is a professional model jointly developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) in the past 20 years to calculate and analyze the transport and diffusion trajectories of atmospheric pollutants. The model has a relatively complete transport, diffusion and sedimentation model that can handle multiple meteorological element input fields, multiple physical processes, and different types of pollutant emission sources. It is widely used in the study of the transmission and diffusion of multiple pollutants in various regions. In this study, the independent version of the backward trajectory model was used, the auxiliary software package was used (GUI; Ghostscript; ImageMagick), and the meteorological data were obtained through NCEP (National Centers for Environmental Prediction) and GDAS (Global Data Assimilation System).
2.2.6. Quality Control
The quartz filters were baked at 450 °C for 5 h in a muffle furnace before sampling to identify the possible presence of organics. All filters were placed in a clean room (temperature of 25 °C ± 5; relative humidity of 50 ± 5%) for 48 h and weighed by a high-precision electronic balance (EX125ZH) with an accuracy of 10 mg before and after sampling. Each filter was weighed twice, with the difference between the two results not exceeding 0.2 mg for quartz filters and 0.02 mg for Teflon filters, to guarantee the precision of the weighting results. All filters were stored in a freezer at −20 °C before analysis to prevent the loss of volatile components.
In the sample analysis process, the instrument was calibrated with standard gas before and after the sample analysis. Then, one sample was randomly selected from every 10 samples for parallel analysis, and the standard sample was measured twice a week. The recovery rate of the standard sample was 98%~102%. Finally, the system blank of the instrument and the blank of the laboratory system were measured every week. The results showed no contamination during sample handling and collection, as assured by the quality assurance and control (QC/QA) procedures.
3. Results and Analyses
3.1. Concentration Characteristics of PM2.5
During the two sampling campaigns, the mass concentrations (from Telfon filters) of PM2.5 ranged from 29.11 μg/m3 to 62.03 μg/m3 in spring and from 24.46 μg/m3 to 60.08 μg/m3 in autumn (Figure 2). The overall concentration of PM2.5 is higher in spring than that in autumn. The concentration on individual days in autumn is higher than that in spring, which may be related to changes in meteorological conditions. The daily concentration levels of PM2.5 were all within Chinese National Ambient Air Quality Standards II (75 μg/m3). In addition, the total average concentration of PM2.5 in spring and autumn (44.85 ± 10.99 μg/m3) was higher than Standard II (35.00 μg/m3) (GB3095-2012), and was 3.0 times higher than the annual standard concentration in the USA (15 μg/m3). These values are lower than those of developed cities in the plains of China, such as Beijing, Tianjing and Shanghai [37,38]. Furthermore, the concentration of PM2.5 in Wenshan was lower than that in some plateau cities, such as Guiyang and Kunming [39]. In our previous research, we found that the dust emission volume of Wenshan was 1164 t, accounting for 52.9% of the total emissions. PM2.5 pollution may be associated with city construction, and the floor space of buildings under construction was 5.48 × 106 m2 during 2016 in Wenshan. The mean concentrations of PM2.5 decreased from spring (48.00 ± 11.01 μg/m3) to autumn (41.64 ± 10.10 μg/m3). There were 10 and 5 days in spring and autumn, respectively, that exceeded the total average concentration, which means that were 62.5% of the days in spring exceeded the total average concentration, and it was twice that in autumn. This seasonal mean concentration variation is attributed to the primary influence of meteorological characteristics and source emissions.
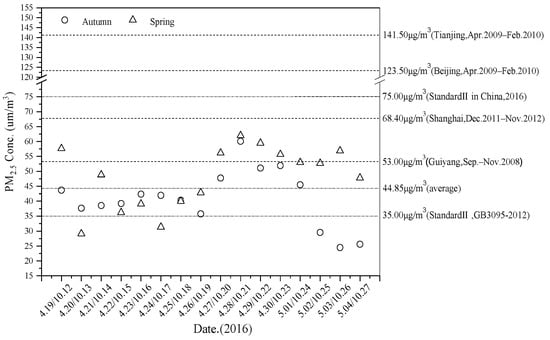
Figure 2.
The daily mass concentration of PM2.5 during sampling.
3.2. Chemical Composition Characteristic of PM2.5
3.2.1. WSIIs Levels
The concentrations of WSIIs were 11.75 ± 3.25 and 12.50 ± 3.40 μg/m3 in spring and autumn, respectively. In PM2.5, the concentrations of K+, NH4+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, F−, NO3− and SO42− were 0.67, 2.54, 1.28, 0.07, 0.24, 0.16, 1.25 and 5.53 μg/m3 in spring and 0.59, 3.17, 0.78, 0.07, 0.38, 0.22, 0.77 and 6.53 μg/m3 in autumn, respectively. The annual concentration of WSIIs was 12.15 μg/m3 and occupied 26.91% of the total PM2.5. This result indicated that WSIIs were one of the main components of PM2.5. The mass concentrations of sulfate occupied 49.67% of the total WSIIs, followed by NH4+ (23.50%), Ca2+ (8.60%), NO3− (8.37%), K+ (5.21%), Cl− (2.52%), F− (1.56%), and Mg2+ (0.57%). The dominant compounds were secondary inorganic aerosols (SIAs, including NO3−, SO42− and NH4+), with concentrations accounting for more than 80% of the total WSII mass of PM2.5. The concentrations of WSIIs in Wenshan are shown in Table 1 and compared to other typical cities, such as Kunming [30] and Guiyang [40] on the plateau and Beijing [41] and Nanjing [42] on the plain. Compared to other Chinese studies, most of the ionic species identified in research are found to be on the lower side. Compared with Kunming and Guiyang, the concentration of SO42− was lowest, which is consistent with the lagged industrial development of Wenshan. These results show that the WSII concentrations at Wenshan were impacted more by local pollution sources (e.g., biomass burning, agricultural dust, construction dust, etc.) [43].

Table 1.
Mean concentrations of WSIIs sampled in Wenshan in 2016 compared with data from other sites (μg/m3).
SIAs were the dominant ions in the PM2.5 component in both autumn and spring. The spring and autumn concentrations of SIAs follow the order SO42− ˃ NH4+ ˃ NO3− (Figure 3). One of the reasons is that industrial production leads to the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, which increases the emission of the gaseous precursor SO2 [44,45]. Moreover, the geographical structure of urban areas is not favorable to pollutant diffusion in the atmosphere. Another reason is the high conversion rate of SO2 to PM2.5, which may be due to the relatively high humidity in autumn [46,47]. In addition, NH4+ was the most dominant cation in PM2.5 in the two seasons, and the emission of NH4+ originated from the nitrogen fertilizers used in agriculture [48,49]. The observed NO3− levels were related to the synthetic action of various influencing factors, i.e., precursor NOX emissions, complex photochemical and heterogeneous reactions and gas-aerosol equilibrium [50,51].
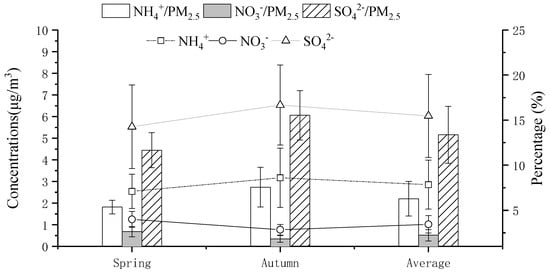
Figure 3.
Seasonal variations in SIAs and their ratios in PM2.5 in Wenshan.
To discuss the relative importance of mobile and stationary sources of SO2 and NOX, the mass concentration ratio of NO3−/SO42− was used as an indicator [52]. The seasonal variation in NO3−/SO42− in PM2.5 ranged from 0.16 to 0.32 and from 0.09 to 0.18 in spring and autumn, respectively, with an annual mean of 0.18 ± 0.07, which was lower than the values measured in Shanghai (0.43) [53], Qingdao (0.35) [54] and Taiwan (0.20) [55]. Therefore, with the increasing number of motor vehicles, the contribution of mobile sources is more important than before.
Ion balance calculations are frequently used to investigate the acid base balance of ions in PM2.5. The correlation of CE and AE and the variation in CE/AE in the two seasons were calculated. According to the electroneutrality of solutions, AE must be equal to CE [56]. The correlation coefficient between CE and AE for spring (R2 = 0.92) was higher than that for autumn (R2 = 0.85), showing that cations and anions maintained better equilibrium during neutralization in spring. The average CE/AE ratios for autumn (1.72) were higher than those for spring (1.54), which indicates the basic nature of aerosols in which PM2.5 is alkaline in the two seasons in Wenshan [57,58].
3.2.2. IEs Levels
The concentrations of IEs in PM2.5 in the two seasons are shown in Figure 4. The concentrations of IEs in PM2.5 were 4.82 μg/m3 and 4.10 μg/m3 in spring and autumn, respectively. Fifteen main elements, Ti, Si, Ca, Fe, Al, K, Mg, Na, Sb, Zn, P, Pb, Mn, As and Cu, account for 99.38% and 99.24% of the total inorganic elements in spring and autumn, respectively. These fifteen elements play a key role in the estimation of emission sources and are associated with human activity (such as industrial processes, residential activities, and traffic patterns).
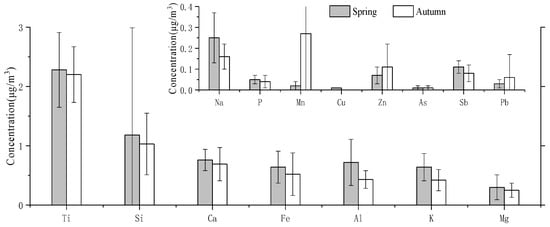
Figure 4.
Mean concentrations of inorganic elements in PM2.5 sampled at Wenshan.
In the PM2.5 samples, the relatively high concentrations of elements are in the order of Ti>Si>Ca>Al>Fe>K>Mg>Na>Sb>Zn>P>Pb>Mn>As>Cu (spring) and Ti>Si>Ca>Fe>Al>K>Mn>Mg>Na>Zn>Sb>Pb>P>As>Cu (autumn). The fifteen main IE concentrations accounted for 14.88% of the total PM2.5 in spring and 14.89% in autumn. The concentrations of the identified elements of soil dust (Ti, Si, Al, Ca, Mg) were 5.24 μg/m3 in spring and 4.29 μg/m3 in autumn, which showed that surface dust was the main source of PM2.5. The concentrations of the industrial discharge elements (As, Zn, and Mn) were 0.10 μg/m3 in spring and 0.38 μg/m3 in autumn. The concentration of Pb was 0.03 μg/m3 in spring and 0.06 μg/m3 in autumn, and it may be due to motor vehicle exhaust emissions. The concentrations of K accounted for 1.35% of PM2.5 in spring and 0.99% in autumn, which may be due to biomass burning [59,60,61].
3.2.3. OC and EC Levels
The mean concentrations of OC were 12.03 ± 2.24 μg/m3 and 9.32 ± 2.13 μg/m3 in spring and autumn, respectively (Figure 5). The mean EC concentrations were 3.66 ± 0.47 μg/m3 and 2.88 ± 0.61 μg/m3 in spring and autumn, respectively. Wenshan is located in the basin valley on the plateau, with wind speeds that are too low to be conducive to pollutant spreading during the two seasons. During the two sampling campaigns, the daily mean value of OC/EC was 2.64–4.17 in spring and 2.74–3.65 in autumn, all of which exceeded 2.0, which indicated that Wenshan experienced secondary organic carbon (SOC) pollution in both seasons. Moreover, OC and EC in Wenshan had a better correlation in autumn (R = 0.86) than in spring (R = 0.69), which showed that the measured OC and EC were derived from similar sources during autumn and from complex sources during spring. The possible reason is that the spring is affected by the long-distance transmission of biomass combustion sources in Southeast Asia due to climatic conditions.
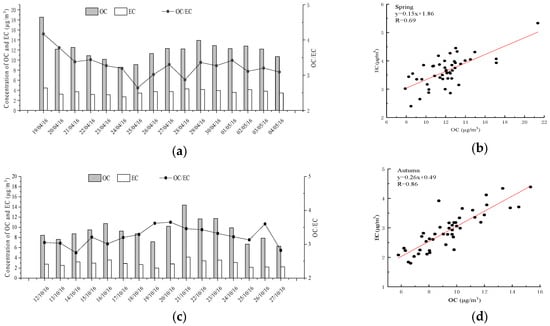
Figure 5.
Concentrations of OC and EC, the value of OC/EC and the relevance of OC and EC in PM2.5 during the sampling period. (a) Concentrations of OC and EC in spring. (b) Concentrations of OC and EC in autumn. (c) The value of OC/EC and the relevance of OC and EC in PM2.5 during the spring sampling period. (d) The value of OC/EC and the relevance of OC and EC in PM2.5 during the autumn sampling period.
Since there is no simple and direct calculation method for SOC, this study estimates the content of SOC considering the lowest value of the OC/EC ratio in the two seasons [62,63,64]. The principle of this method is the use of the lowest value of OC/EC rather that of the OC/EC of the primary pollutant in every season. SOC=TOC, EC×(OC/EC)min, and TOC and EC are the concentrations of OC and EC in PM2.5, respectively [65,66]. The average values of SOC in PM2.5 are 2.36 ± 1.00 μg/m3 and 1.41 ± 0.46 μg/m3 in spring and autumn, respectively. The values of SOC/OC in the two seasons are 19.65% and 15.14% in spring and autumn, respectively. The radiation and temperature in autumn were higher than those in spring, which represented more favorable photochemical conditions for the formation of SOC in autumn. However, there was more rain in autumn in Wenshan, which could limit the formation of SOC. The order of OC, SOC and SOC/EC was the same pattern as spring ˃ autumn, which meant that the impact of radiation and temperature was less than that of rainfall, and rainfall was the main influencing factor and had a greater impact on SOC [67,68].
3.3. Source Apportionment of PM2.5
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The sample quantity is crucial for good PCA. The PCA of the study was performed considering the chemical constituents of 90 PM2.5 samples. The outliers (those beyond 2SD) were removed, and the dataset was normalized prior to the operation [69]. When the value of KMO is close to 1, it indicates that there is a strong correlation between these variables (KMO indicates the amount of variance shared among the items designed to measure a latent variable when compared to that shared with the error), and these variables are more suitable for PCA [70]. In this study, the SPSS software package (IBM, version 24.0) was used to conduct PCA research on substances in PM2.5 to obtain the emission characteristics of its pollution sources. For this study, the species of Li, Na, K, Mn, Cu, Zn, As, Pb, Al, Mg, Ca, Fe, Ba, Si, Ti, NH4+, NO3−, SO42−, OC and EC had strong correlations in the two seasons, and the PCA results are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Matrix of loading factors of PCA in spring and autumn.
From Table 2, we know that PCA resolved six components explaining 80.5% of the variance in spring.
Factor 1: The first factor contributes 18.15% to the total factor contributions and is characterized by a high concentration of SIAs, which indicates that Wenshan was greatly affected by secondary inorganic aerosol pollution in spring. SIAs are mainly generated by the photochemical reactions of precursor gases (SO2, NH3, and NOx), which are emitted from specific identified sources of human activity (coal combustion, vehicle exhaust emission, and biomass burning). Therefore, the strict control of precursor gases is conducive to reducing PM2.5 levels.
Factor 2: The second factor contributed 16.28% of the total PM2.5, and mostly originated from natural sources, such as the lifting of dust or mechanical abrasion processes, which was identified by high concentrations of Al, Fe, Si and Ti, indicating the leading contribution of dust [71]. Si and Ti are the key tracers of soil dust caused by winds. The extra Ba is emitted from brake linings and tire tread wear. These results can be explained as a consequence of dust persisting in the atmosphere longer because of calm and low-speed winds.
Factor 3: The third factor resolved 14.15%, and represents the factor contribution from industrial emissions. The elements are related to the industrial metal smelting process and represent anthropogenic emissions from various industries near the sampling site [72].
Factor 4: This source provided 11.55% of PM2.5. OC and EC are considered to be tracers of motor vehicle emissions, and EC is an indicator of primary emissions of OC [73]. The presence of K also deserved our attention, directly indicating emissions from biomass burning.
Factor 5: Cu and Na were apportioned to this factor, which suggests that the effect of this factor was manifold, such as copper smelting and sea salt [74]. The contribution of this factor towards PM2.5 was 10.83%, as revealed by PCA. In addition, Na might travel long distances from the Indian Ocean, and Cu could have come from the nearby industrial area in Honghe Prefecture.
Factor 6: This factor is construction cement dust, which is represented by high concentrations of Ca and Mg [75]. This finding indicates that construction and demolition activities were prevalent in the urban areas in Wenshan during the sampling period, without effective measures for dust control. More precise and effective policies are needed for the local government to improve PM2.5 pollution.
In addition, PCA resolved five components explaining 78.7% of the variance in autumn. Different from spring, Factor 1 represent biomass burning and industry sources, contributing 29.40% of PM2.5. Factor 2 includes secondary inorganic aerosols and motor vehicle exhaust emissions, which resolved 18.73% of the factor contribution. Factor 3 represents metal smelting, with remarkable representative Al, Fe and Mg features, which can be attributed to the smelting production activities around the site. Factor 4 and Factor 5 are soil dust and construction dust, which resolved 9.30% and 8.91% of the factor contributions, respectively.
3.3.2. The Long-Range Transport
To better understand the transport of airborne particles from distant sources, the 72 h backward trajectories starting at a height of 100 m at the sampling site were calculated using the Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory 4.0 (HYSPLIT4) model with a 12 h period (meteorological data from the Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS)). The back trajectories were classified into three clusters using TrajStat in this study.
In spring, the trajectories were grouped into three clusters (Figure 6). Cluster 1 (blue line), from the southwestern direction, was associated with slower and lower air mass trajectories and accounted for 57%. The other two trajectory clusters (green line and red line) came from the north and southwestern directions, accounting for 24% and 19%, respectively. Cluster 1 came from central Myanmar and passed through during spring sampling in northern Vietnam and the Honghe Prefecture in Yunnan Province, China, which explains the effect of Factor 3. At the same time, Cluster 2 (green line) came from the industrial region in Chongqing, which explained the source of biomass burning in Factor 1 and the industrial impact in Factor 3. Figure 6b shows that wind mainly originated from the south during the sampling period, which prevented the diffusion and great accumulation of NOX and SO2. Then, they formed secondary pollution through photochemical reaction transformation, which conforms to the SIA pollution in Factor 1. The higher wind speeds were also consistent with the contribution of Factor 2.
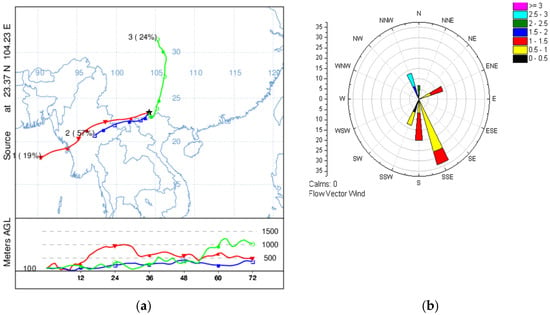
Figure 6.
(a) Mean 72 h backward trajectories of each trajectory cluster during spring and the percentage of allocation to each cluster. (b) Wind roses of Wenshan during spring sampling.
In autumn, the trajectories were grouped into three clusters from the southeastern direction (Figure 7). Cluster 1 (red line) came from Guangxi Province and passed through the industrial region in Baise, which explains the presence of industrial elements in Factor 1. The other two trajectory clusters (blue line and green line) accounted for 33% and 8%, respectively. Figure 7b also shows that the wind mainly originated from the south during the sampling period and resulted in the impossibility of the diffusion and dilution of pollutants, which was also the reason for the SIA pollution in Factor 2.
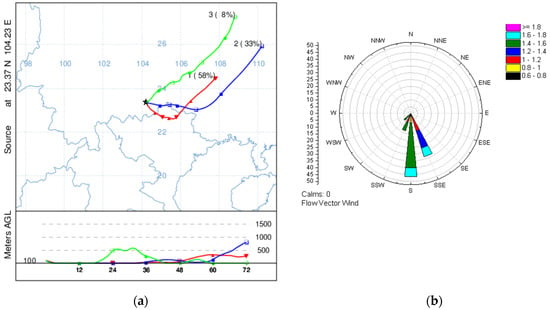
Figure 7.
(a) The mean 72 h backward trajectories of each trajectory cluster during autumn and the percentage of allocation to each cluster. (b) Wind roses of Wenshan during autumn sampling.
4. Conclusions
In this study, PM2.5 samples were collected in Wenshan, and their mass concentration, chemical composition and source apportionment characteristics were analyzed in spring and autumn. The mean concentrations of PM2.5 were 48.00 ± 11.01 μg/m3 and 41.64 ± 10.10 μg/m3 in spring (sampled on 19 April–3 May) and autumn (sampled on 12 October–26 October). The annual mean concentration of PM2.5 at the three sites was 44.85 ± 10.99 μg/m3, which was lower than that in Standard II (75.00 μg/m3) and higher than that in Standard II (35.00 μg/m3). This means that the air quality in Wenshan is better than that in most cities in China.
WSIIs and OC were the main components of PM2.5, accounting for 26.91% and 23.80% of PM2.5, respectively. SIAs were the major contributors to WSIIs, due to the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and the slathering of nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture. Wenshan was greatly affected by secondary inorganic aerosol pollution in the two seasons, which contributed 21.82% and 16.50% to the total factor contributions in spring and autumn, respectively. The ratio of NO3−/SO42− implied that the contribution of mobile sources was not significantly different from that of other developed areas. The daily mean value of OC/EC was 2.64–4.17 in spring and 2.74–3.65 in autumn, which indicates that the SOC was generated by the photochemical process during the sampling days in Wenshan. Moreover, the OC and EC concentrations in Wenshan had a better correlation in autumn (R = 0.86) than in spring (R = 0.69), which shows that OC and EC were derived from similar sources during autumn and from complex sources during spring. However, elements from anthropogenic sources (Ti, Si, Ca, Fe, Al, K, Mg, Na, Sb, Zn, P, Pb, Mn, As and Cu) accounted for 99.38% and 99.24% of the total inorganic element concentration in spring and autumn, respectively.
Source apportionment showed that SIAs (18.15%), the lifting of dust or mechanical abrasion processes (16.28%), industrial sources (14.15%), motor vehicle emissions (11.55%), copper smelting and sea salt pathways (10.83%), and construction cement dust emissions (9.58%) were the main pollution sources in PM2.5 in spring. Furthermore, source apportionment showed that biomass burning and industry (29.40%), SIAs and motor vehicle exhaust (18.73%), metal smelting (12.33%), soil dust (9.30%) and construction dust (8.91%) emissions were the main pollution sources of PM2.5 in autumn. Different source contributions were found in spring and autumn. According to the research results, the pollution prevention and control suggestions are as follows: (1) Exert related effective management for artificial sources, such as industry and construction sites, to accelerate industrial transformation and upgrading. (2) Adopt emission control measures, such as motor vehicle restrictions and the promotion of new energy transportation methods.
The results of cluster analysis indicate that the long-range transport of air pollutants has a profound effect on local air quality in Wenshan. Wenshan is mainly affected by long-distance atmospheric transmission from the southwest and the northeast in spring and autumn, respectively.
In this paper, chemical composition and source characteristics of PM2.5 in a plateau slope city were first studied, and the main sources of PM2.5 in Wenshan City are resolved. The results can provide scientific data to support PM2.5 pollution control in local and similar cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and X.H.; investigation, Y.Z. and L.R.; resources, X.H.; data curation, Y.F.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, J.S. and X.H.; supervision, P.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Projects of China (grant number 2019YFC0214405) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 21966016 and 21667014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper can be provided by Jianwu Shi (Shijianwu@kust.edu.cn).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Projects of China (No. 2019YFC0214405), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21966016, 21667014).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests that could inappropriately influence the contents of this manuscript.
Nomenclature
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter with aerodynamic equivalent diameter less than or equal to 2.5 microns in ambient air |
| NOx | Refers to the sum of NO and NO2 |
| CCN | cloud condensation nuclei |
| WSIIs | Water-soluble inorganic ions |
| OC | organic carbon |
| EC | inorganic carbon |
| IEs | inorganic elements |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| CSCW | Convenience Service Center of Wenshan |
| WAW | Water Authority of Wenshan |
| EMSW | Environmental Monitoring Station of Wenshan |
| ICP-AES | inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry |
| DRI | Desert Institute |
| FID | Flame ion detector |
| OPC | Organic pyrolysis carbon |
| IMPROVE | Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments |
| SIAs | Secondary inorganic aerosols (including NO3−, SO42− and NH4+) |
| CE/AE | Cation/Anion concentration ratio |
| NCEP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| GDAS | Global Data Assimilation System |
| QC/QA | Quality control and Quality assurance |
References
- Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Qu, L.; Ji, L.; Zhi, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Source apportionment of PM2.5 at a regional background site in North China using PMF linked with radiocarbon analysis: Insight into the contribution of biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11249–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, W.; Feng, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Gu, Z.; Wang, B.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Composition source mass closure of PM2.5 aerosols for four forests in eastern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J. Spatio-temporal variation and influence factors of PM2.5 concentrations in China from 1998 to 2014. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samresh, K.; Ramya, S.R. Inorganic ions in ambient fine particles over a National Park in central India: Seasonality, dependencies between SO42−, NO3− and NH4+, and neutralization of aerosol acidity. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Andreae, M.O.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosol–cloud–precipitation interactions. Part 1. The nature and sources of cloud-active aerosols. Earth Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turap, Y.; Talifu, D.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A.; Maihemuti, M.; Tursun, Y.; Ding, X.; Aierken, T.; Rekefu, S. Temporal distribution and source apportionment of PM2.5 chemical composition in Xinjiang, NW-China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Chen, Y.; Tian, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Luo, Q.; Ding, S. Characterization of water soluble inorganic ions and their evolution processes during PM2.5 pollution episodes in a small city in southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2605–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Lv, B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W.; Geng, C.; Han, B. Chemical Compositions and Source Analysis of PM2.5 during Autumn and Winter in a Heavily Polluted City in China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Long, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, N.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, H. Seasonal Control of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 from Nanning, a Subtropical Monsoon Climate City in Southwestern China. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tong, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Dai, X.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Seasonal variation and size distributions of water-soluble inorganic ions and carbonaceous aerosols at a coastal site in Ningbo, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Su, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Observation of chemical components of PM2.5 and secondary inorganic aerosol formation during haze and sandy haze days in Zhengzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golly, B.; Waked, A.; Weber, S.; Samake, A.; Jacob, V.; Conil, S.; Rangognio, J.; Chrétien, E.; Vagnot, M.-P.; Robic, P.-Y.; et al. Organic markers and OC source apportionment for seasonal variations of PM2.5 at 5 rural sites in France. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Fang, X.; Wen, B.; Shan, A. Spatio-temporal variations of PM2.5 emission in China from 2005 to 2014. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siudek, P.; Frankowski, M. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements at urban and forest sites in central Poland–Insight into seasonal variability and sources. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, F. Variation in PM2.5 source over megacities on the ancient Silk Road, northwestern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Martínez, L.F.; Carbajal, N.; Campos-Ramos, A.; Aragón-Piña, A.; García, A.R. Dispersion of atmospheric coarse particulate matter in the San Luis Potosí, Mexico, urban area. Atmósfera 2014, 27, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dai, Q.; Bi, X.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Ding, J.; Song, W.; Bi, S.; Schulze, B.C.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Chemical nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in Xi’an, China: Insights into primary emissions and secondary particle formation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Cui, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, G. Chemical characteristics, sources, and formation mechanisms of PM2.5 before and during the Spring Festival in a coastal city in Southeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wen, T.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, R.; Hu, B.; et al. Characteristics of chemical composition and seasonal variations of PM2.5 in Shijiazhuang, China: Impact of primary emissions and secondary formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto-Oliveira, C.E.; Babinski, M.; Araújo, D.F.; Weiss, D.J.; Ruiz, I.R. Multi-isotope approach of Pb, Cu and Zn in urban aerosols and anthropogenic sources improves tracing of the atmospheric pollutant sources in megacities. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hardy, R.; Zhang, W.; Reinbold, G.L.; Strachan, S.M. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in a Nonattainment Rocky Mountain Valley. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Qiao, L.P.; Lou, S.R.; Zhou, M.; Ding, A.J.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, Q.; Tao, S.K.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Chemical composition of PM2.5 and meteorological impact among three years in urban Shanghai, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; He, L. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric submicron particles on the western coast of Taiwan Strait, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, X.; Zheng, J.; Yan, P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W. The characteristics of abnormal wintertime pollution events in the Jing-Jin-Ji region and its relationships with meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bi, L.; Han, X.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Shi, Z.; Ning, P. Characteristics and source apportionment of the water soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 of Kunming. J. Yunnan Univ. 2017, 39, 63–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bi, L.; Hao, J.; Ning, P.; Shi, J.; Shi, Z.; Xu, X. Characteristics and sources apportionment of PM2.5-bound PAHs in Kunming. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 659–667. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Yan, K.; Han, X.Y.; Shi, Z.; Bi, L.M.; Xiang, F.; Ning, P.; Shi, J.W. Physico-chemical Characteristic Analysis of PM2.5 in the Highway Tunnel in the Plateau City of Kunming. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 4968–4975. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Huang, J.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.; Ning, P. Characteristics and Sources of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric PM2.5 Research during the Dry Season in Kunming. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2019, 44, 99–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.-R.; Ji, Z.-Y.; Han, X.-Y.; Shi, J.-W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.-N.; Ning, P. Spatial and temporal characteristics of atmospheric VOCs and other pollutants concentrations in urban air of Yuxi City. J. Yunnan Univ. 2018, 40, 705–715. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Bi, L.; Shi, J.; Xiang, F.; Qian, L.; Ning, P. Characterization and Source Identification of PM2.5 in Ambient Air of Kunming in Windy Spring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 143–147, 153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, S.; Mandal, T.; Saxena, M. Source apportionment of PM10 in Delhi, India using PCA/APCS, UNMIX and PMF. Particuology 2018, 37, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallarosa, J.; Teixeira, E.C.; Meira, L.; Wiegand, F. Study of the chemical elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particles of PM10 and PM2.5 in the urban and rural areas of South Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.; Artaxo, P.; Martinelli, L.; Victoria, R.; Camargo, P.; Krusche, A.; Ayers, G.; Ferraz, E.; Ballester, M. Chemical composition of rainwater and anthropogenic influences in the Piracicaba River Basin, Southeast Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4937–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, N.S. Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.W.; Mozurkewich, M. Application of absolute principal component analysis to size distribution data: Identification of particle origins. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2007, 7, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gadi, R.; Sharma, S.; Mandal, T. Characterization and source apportionment of organic compounds in PM10 using PCA and PMF at a traffic hotspot of Delhi. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.S.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yao, Q.; Liu, H.Y. Characteristics of concentrations and chemical compositions for PM2.5 in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, Z.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiu, G.; Yu, J. Chemical characterization, the transport pathways and potential sources of PM2.5 in Shanghai: Seasonal variations. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Feng, X.; Matthew, L.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, G. Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 in Guiyang and Its Influence on Meteorological Parameters. Earth Environ. 2014, 42, 311–315. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Tang, X.; Hu, Y. Initial interpretation on the source of atmospheric PM2.5 in Guiyang city. Environ. Prot. Technol. 2014, 5, 1–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L. Seasonal variations and size distributions of water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols in Beijing, 2012. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, H.L. Size Distributions and Source Apportionment of Soluble Ions in Aerosol in Nanjing. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 1633–1643. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Influence of PRD Industrial Emission Variation on Concentrations of SO2, NOx and their Secondary Pollutants. Res. Environ. Sci. 2009, 22, 207–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; An, J.; Cheng, M.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Sullivan, A.; Xia, L. One year online measurements of water-soluble ions at the industrially polluted town of Nanjing, China: Sources, seasonal and diurnal variations. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, K.; Xu, C.; Tang, A.; Chen, J.; An, Z. The ion chemistry, seasonal cycle, and sources of PM2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yan, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Characterization and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ionic species in PM2.5 in Taiyuan city, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, R.; Sudheer, A.K.; Sarin, M.M. Wintertime PM2.5 and PM10 carbonaceous and inorganic constituents from urban site in western India. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favez, O.; Cachier, H.; Sciare, J.; Alfaro, S.C.; El-Araby, T.M.; Harhash, M.A.; Abdelwahab, M.M. Seasonality of major aerosol species and their transformations in Cairo megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, J.; Guo, H.; Yu, W. Characteristics and sources apportionment of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 in autumn and winter of Wuhan. Environ. Pollut. Prev. 2015, 37, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Guo, J.; Dan, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Z. The air-borne particulate pollution in Beijing—concentration, composition, distribution and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5991–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.; Tie, X.; Shen, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Ho, K.; Qiang, J.; et al. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in Xi’an, China: Seasonal variations and sources. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.-J.; Shen, Z.-X.; Han, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.-S.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Xu, H.-M.; Huang, R.-J. Spatial and seasonal variations of PM2.5 mass and species during 2010 in Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Fang, M.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.; He, K.; Ye, B. The water-soluble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; He, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, M.; Kim, Y.P.; Moon, K. Seasonal variation of ionic species in fine particles at Qingdao, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5853–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.-C.; Chang, C.-N.; Wu, Y.-S.; Fu, P.P.-C.; Yang, C.-J.; Chen, C.-D.; Chang, S.-C. Ambient suspended particulate matters and related chemical species study in central Taiwan, Taichung during 1998–2001. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, P.; Deka, P.; Prakash, A.; Balachandran, S.; Hoque, R.R. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of aerosol over mid Brahmaputra Valley, India. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wei, Z.; Ma, S.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. Characteristics of concentrations and water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Handan City, Hebei province, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, W. Size-resolved aerosol water-soluble ions at a regional background station of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, North China. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, G. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric particles during heating period in Harbin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2475–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Shao, L.; Wu, M. Characteristics of Chemical Elements in Beijing PM10 and Their Source Apportionment. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2006, 35, 685–688. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pakkanen, T.A.; Loukkola, K.; Korhonen, C.H.; Aurela, M.; Mäkelä, T.; Hillamo, R.E.; Aarnio, P.; Koskentalo, T.; Kousa, A.; Maenhaut, W. Sources and chemical composition of atmospheric fine and coarse particles in the Helsinki area. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 5381–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.H. Stable estimate of primary OC/EC ratios in the EC tracer method. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Nie, W.; Gao, J.; Xue, L.K.; Gao, X.M.; Wang, X.F.; Qiu, J.; Poon, C.N.; Meinardi, S.; Blake, D.; et al. Air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympics: Secondary pollutants and regional impact. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7603–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotivit, L.; Jacobsen, D. Temperature increase and respiratory performance of macroinvertebrates with different tolerances to organic pollution. Limnologica 2013, 43, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Liu, C.; Han, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, C. Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Organic Carbon and Elemental Carbon in PM2.5 During the Heating Season in Beijing. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2014, 40, 586–591. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Duan, J.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 during a typical haze episode in Guangzhou. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Zhai, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Fu, Q.; Sha, F.; Jin, J. Insights into the formation of secondary organic carbon in the summertime in urban Shanghai. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sarkar, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Mao, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Jia, S. Evaluation of factors influencing secondary organic carbon (SOC) estimation by CO and EC tracer methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusack, M.; Perez, N.; Pey, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Source apportionment of fine PM and sub-micron particle number concentrations at a regional background site in the western Mediterranean: A 2.5 year study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 5173–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Salmon, L.G.; Zheng, M. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing using principal component analysis/absolute principal component scores and UNMIX. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morera-Gómez, Y.; Elustondo, D.; Lasheras, E.; Alonso-Hernández, C.M.; Santamaría, J.M. Chemical characterization of PM10 samples collected simultaneously at a rural and an urban site in the Caribbean coast: Local and long-range source apportionment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Duan, L.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Chai, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yun, Y. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Lanzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yin, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, P.; Zhang, R.; Tang, X. Characteristics of mass concentration, chemical composition, source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 and health risk assessment in the emerging megacity in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenhaut, W.; Karnieli, A.; Andreae, M.O. Ten-year study of fine aerosol at Sde Boker, Israel, using PIXE: Time trends, seasonal variation, correlations, and source areas for anthropogenic elements. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2014, 318, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, D.; Wen, T.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the size-segregated water-soluble inorganic ions in the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration: Spatial/temporal variability, size distribution and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).