Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution and Its Impacts on the Vertical Distributions of Pollutant Particulate Matter
Abstract
1. Introduction
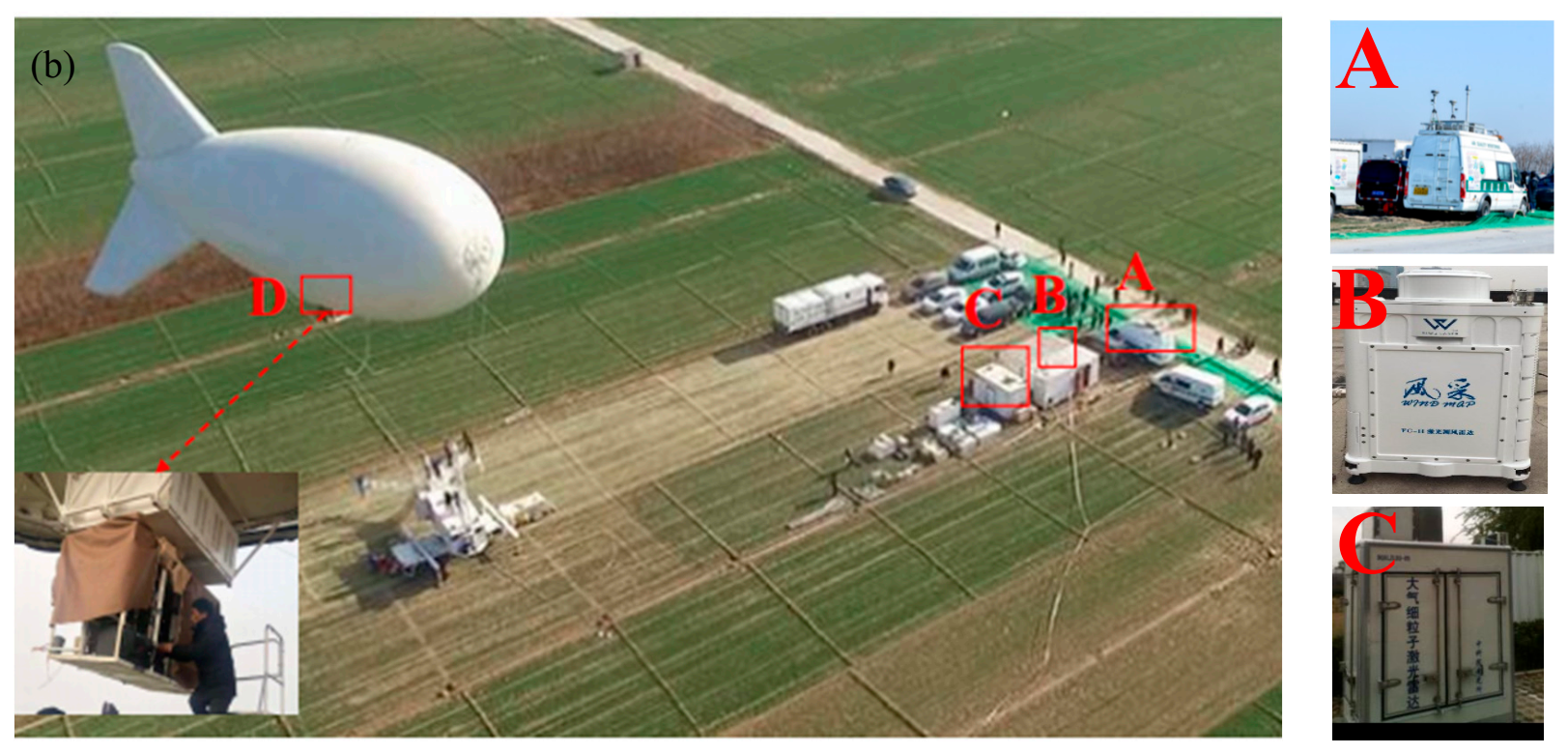
2. Measurement Site and Instrumentation
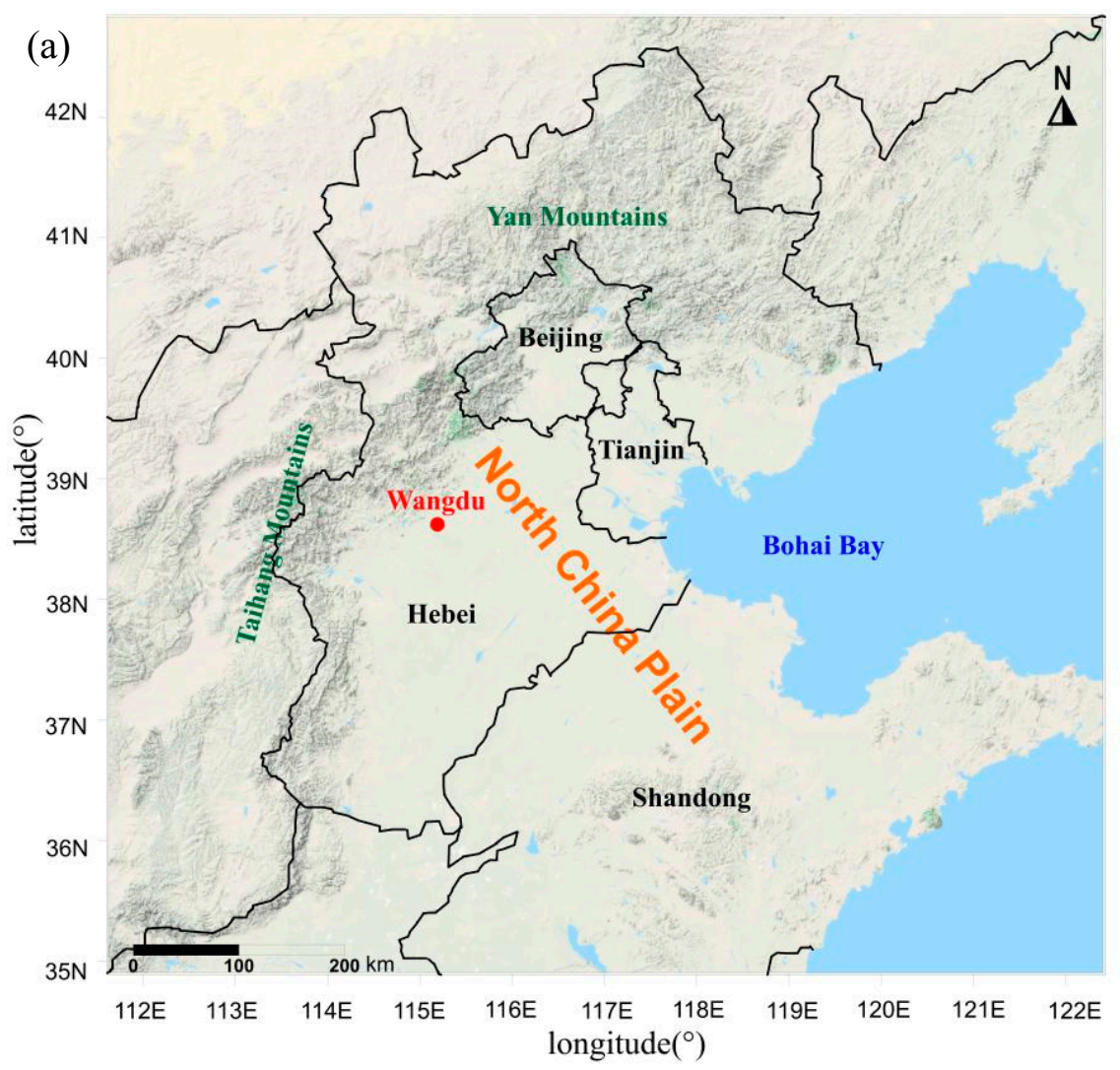
2.1. Field Experiment
2.2. Ascending Times and Altitude Records from the Large Tethered balloon
3. Results
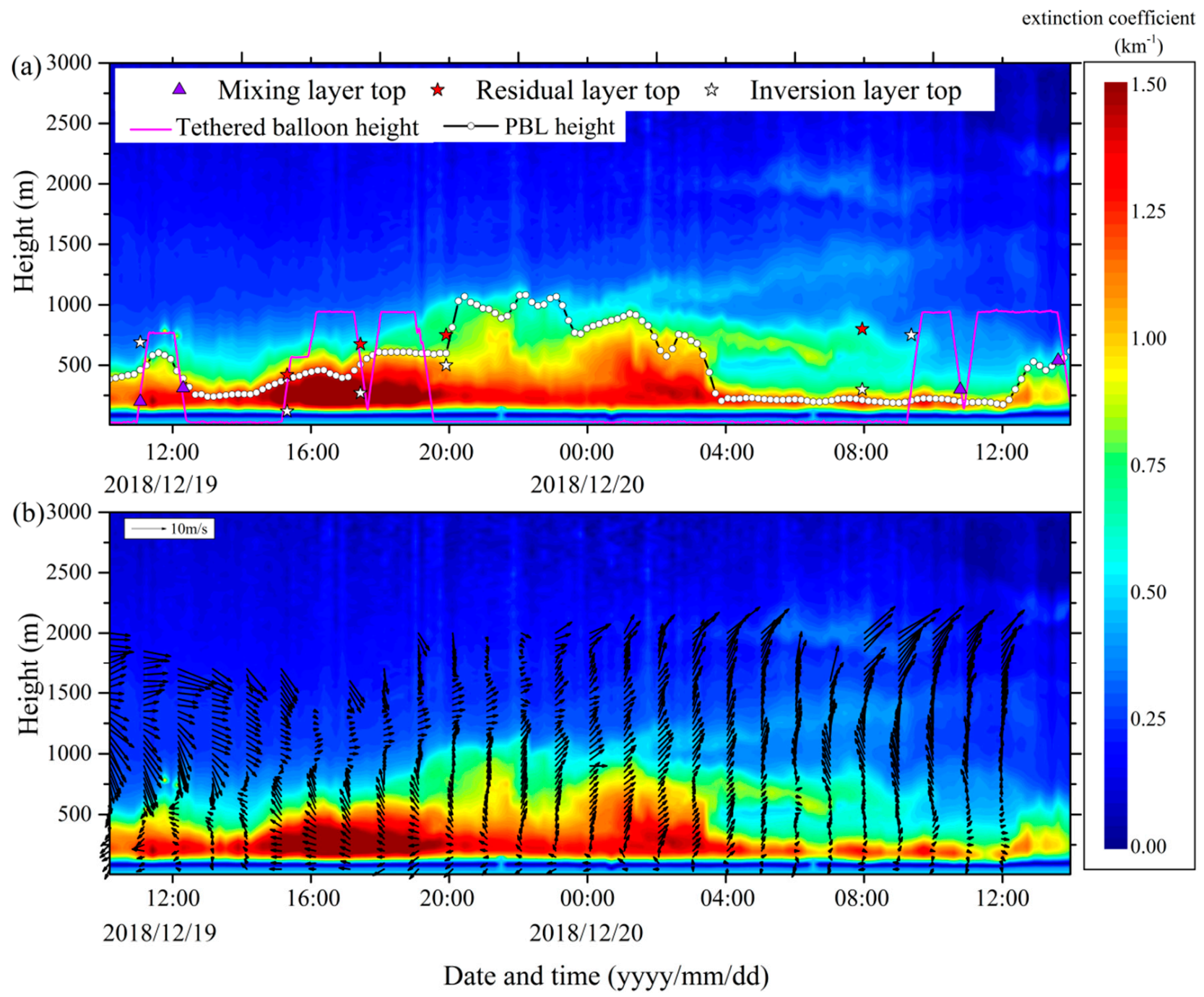
3.1. Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution Observed by Ground-Based Aerosol Lidar and Doppler Wind Lidar
3.2. Identification of the Vertical Structure of Nocturnal Boundary Layer Observed by the Tethered Balloon
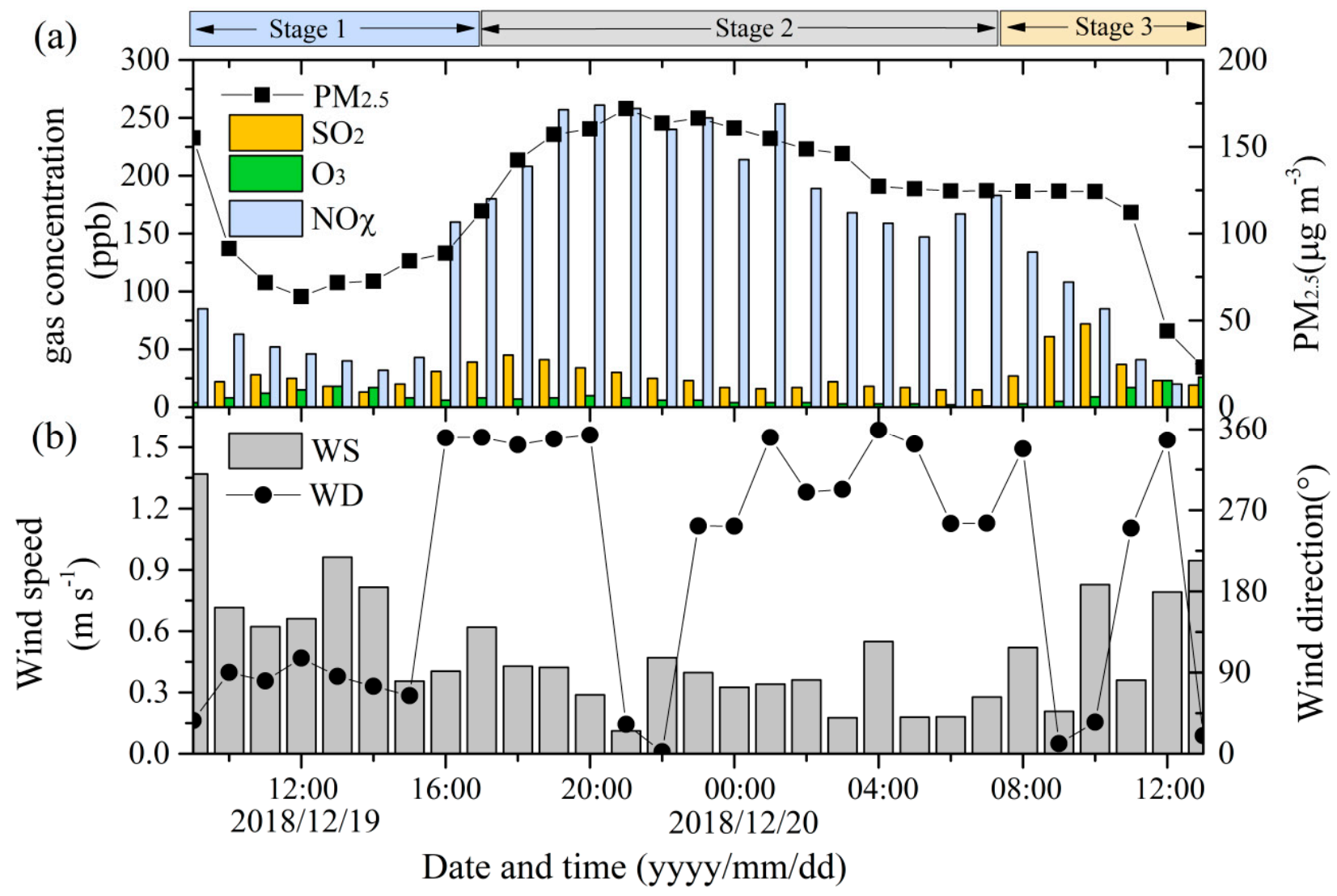
3.3. The Correlation between the Richardson Number and the Vertical Distribution of PM2.5
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quan, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Ding, D.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Anthropogenic pollution elevates the peak height of new particle formation from planetary boundary layer to lower free troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7537–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, T.; Liang, Y.; Kang, L.; Xia, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yun, H.; et al. Characterization of organic aerosols and their precursors in southern China during a severe haze episode in January 2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lu, C.; Chan, P.W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.L.; Lan, Z.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Liu, Y.W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, L. Tower observed vertical distribution of PM2.5, O-3 and NOx in the Pearl River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, A.; Takami, A.; Hara, K.; Nishita-Hara, C.; Hayashi, M.; Kaneyasu, N. Contribution of Local and Transboundary Air Pollution to the Urban Air Quality of Fukuoka, Japan. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Glickman, T.S.; Zenk, W. Glossary of Meteorology; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Blay-Carreras, E.; Pino, D.; Arellano, J.V.-G.d.; Boer, A.V.d.; Coster, O.d.; Darbieu, C.; Hartogensis, O.K.; Lohou, F.; Lothon, M.; Pietersen, H.P. Role of the residual layer and large-scale subsidence on the development and evolution of the convective boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4515–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.A.; McKendry, I.G. A review of turbulence in the very stable nocturnal boundary layer and its implications for air quality. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2005, 29, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, C.; Hong, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. Using Hourly Measurements to Explore the Role of Secondary Inorganic Aerosol in PM 2.5 during Haze and Fog in Hangzhou, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Ding, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J. Atmospheric circulation and dynamic mechanism for persistent haze events in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Tang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Vertical characteristics of VOCs in the lower troposphere over the North China Plain during pollution periods. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 236, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, B.; Zhang, X. Winter haze over North China Plain from 2009 to 2016: Influence of emission and meteorology. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, F.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z. Multiple technical observations of the atmospheric boundary layer structure of a red-alert haze episode in Beijing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4887–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Klein, P.M.; Xue, M.; Zhang, F.; Doughty, D.C.; Forkel, R.; Joseph, E.; Fuentes, J.D. Impact of the vertical mixing induced by low-level jets on boundary layer ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, F.; Summa, D.; Girolamo, P.D.; Marra, F.; Wang, Y.; Rosoldi, M. Assessment of Trends and Uncertainties in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimated using Radiosounding Observations over Europe. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; D’Amico, G.; Summa, D.; Lolli, S.; Amodeo, A.; Bortoli, D.; Pappalardo, G. Atmospheric Boundary Layer height estimation from aerosol lidar: A new approach based on morphological image processing techniques. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 21, 4249–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Yan, P.; Ding, G.A.; Wang, M.L.; Sun, J.; Lelieveld, J. The IPAC-NC field campaign: A pollution and oxidization pool in the lower atmosphere over Huabei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3883–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rao, S.T. The Role of Vertical Mixing in the Temporal Evolution of Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 1674–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.A.; Ford, B.; Rappenglück, B.; Thompson, A.M.; Mefferd, A.; Ngan, F.; Lefer, B. An evaluation of the interaction of morning residual layer and afternoon mixed layer ozone in Houston using ozonesonde data. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4024–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Schäfer, K. Remote Sensing Methods to Investigate Boundary-layer Structures relevant to Air Pollution in Cities. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 121, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blary, F.; Ziad, A.; Borgnino, J.; Fanteï-Caujolle, Y.; Aristidi, E.; Lanteri, H. Monitoring atmospheric turbulence profiles with high vertical resolution using PML/PBL instrument. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Montréal, QC, Canada, 22–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Yuan, R.; Wang, Z. Lidar-based remote sensing of atmospheric boundary layer height over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.; Smalikho, I.; Falits, A. Estimation of the height of the turbulent mixing layer from data of Doppler lidar measurements using conical scanning by a probe beam. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kiselev, A.V.; Kovadlo, P.G.; Kolobov, D.Y.; Lukin, V.P.; Tomin, V.E. Method for Estimating the Altitudes of Atmospheric Layers with Strong Turbulence. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2020, 33, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, A.; Shamanaeva, L.; Kulagina, V. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Kinetic Energy in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer from Minisodar Measurements. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovadlo, P.; Shikhovtsev, A.; Kopylov, E.; Kiselev, A.; Russkikh, I. Study of the Optical Atmospheric Distortions using Wavefront Sensor Data. Russ. Phys. J. 2021, 63, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Beyrich, F.; Gryning, S.-E.; Joffre, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Tercier, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Notholt, J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, B. Lidar measurement of planetary boundary layer height and comparison with microwave profiling radiometer observation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.; Cao, J.; Han, S.; Meng, J.; Chen, P.; Zhao, D. Evolution of planetary boundary layer under different weather conditions, and its impact on aerosol concentrations. Particuology 2013, 11, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of four different types of planetary boundary layer heights during a haze episode in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacesaria, V.; Marenco, F.; Balis, D.; Papayannis, A.; Zerefos, C. Lidar observations of the Planetary Boundary Layer above the city of Thessaloniki, Greece. Nuovo Cimento 1998, 21, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Wuebbles, D.J. Chemical competition in nitrate and sulfate formations and its effect on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Siebert, H.; Ansmann, A.; Ditas, F.; Seifert, P.; Stratmann, F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Apituley, A.; Shaw, R.A.; Manninen, H.E.; et al. Observations of turbulence-induced new particle formation in the residual layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4319–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, H.; Wehner, B.; Hellmuth, O.; Stratmann, F.; Boy, M.; Kulmala, M. New-particle formation in connection with a nocturnal low-level jet: Observations and modeling results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, G.; Ferrero, L.; Perrone, M.G.; Bolzacchini, E.; Duane, M.; Larsen, B.R. Vertical distribution of hydrocarbons in the low troposphere below and above the mixing height: Tethered balloon measurements in Milan, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3545–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, L.; Fu, Q.; Yan, L.; Bian, Q.; Wang, D.; Xiu, G. Vertical distribution of ozone over Shanghai during late spring: A balloon-borne observation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Li, Y.S.; Wong, K.H.; Ding, G.A.; Chan, L.Y.; Cheng, X.H. Characteristics of vertical profiles and sources of PM2.5, PM10 and carbonaceous species in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5113–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.; Yue-si, W.; Jie, J.; Fang-kun, W.; Mingxing, W. The vertical distributions of VOCs in the atmosphere of Beijing in autumn. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Vertical structures of physical and chemical properties of urban boundary layer and formation mechanisms of atmospheric pollution. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1374–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, U.; Künzle, T.; Wanner, H. On the relation between ozone storage in the residual layer and daily variation in near-surface ozone concentration: A case study. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1994, 69, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappenglück, B.; Perna, R.; Zhong, S.; Morris, G.A. An analysis of the vertical structure of the atmosphere and the upper-level meteorology and their impact on surface ozone levels in Houston, Texas. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, F. Impacts of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Vertical Structure on Haze Pollution Observed by Tethered Balloon and Lidar. J. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 35, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, S.A.; Angevine, W.M. Boundary Layer Height and Entrainment Zone Thickness Measured by Lidars and Wind-Profiling Radars. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding Boundary Layer Top: Application of a Wavelet Covariance Transform to Lidar Backscatter Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.; Madronich, S.; Wu, F.; Olson, J.B.; Ramos, R.; Retama, A.; Muñoz, R. Weekly patterns of México City’s surface concentrations of CO, NOx, PM10 and O3 during 1986–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5313–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Tse, L.A.; Zhao, Z.; Kan, H. Combined atmospheric oxidant capacity and increased levels of exhaled nitric oxide. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 74014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeron, Y.; Staquet, C. Persistent inversion dynamics and wintertime PM10 air pollution in Alpine valleys. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 135, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkamer, R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Martini, F.S.; Dzepina, K.; Zhang, Q.; Salcedo, D.; Molina, L.T.; Worsnop, D.R.; Molina, M.J. Secondary organic aerosol formation from anthropogenic air pollution: Rapid and higher than expected. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, B.M.; Rappenglück, B.; Clements, C.B.; Tucker, S.C.; Brewer, W.A. Nocturnal boundary layer characteristics and land breeze development in Houston, Texas during TexAQS II. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4014–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.B.; Neuman, J.A.; Bahreini, R.; Brock, C.A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Wollny, A.G.; Holloway, J.S.; Peischl, J.; Ryerson, T.B.; Fehsenfeld, F.C. Airborne observations of ammonia and ammonium nitrate formation over Houston, Texas. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.W. Comments on the oxidation of NO2 to nitrate—Day and night. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Liu, X.; Yu, T.; Cachier, H. Identification and estimate of biomass burning contribution to the urban aerosol organic carbon concentrations in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.A.; Stull, R.B. Subsidence in the Nocturnal Boundary Layer. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Summa, D.; Girolamo, P.D.; Stelitano, D.; Cacciani, M. Characterization of the planetary boundary layer height and structure by Raman lidar: Comparison of different approaches. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjernström, M.; Balsley, B.B.; Svensson, G.; Nappo, C.J. The Effects of Critical Layers on Residual Layer Turbulence. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilitinkevich, S.S.; Elperin, T.; Kleeorin, N.; Rogachevskii, I. Energy- and flux-budget (EFB) turbulence closure model for stably stratified flows. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 125, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L. Variability and Maintenance of Turbulence in the Very Stable Boundary Layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2010, 135, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschinski, A.; Frehlich, R.G.; Balsley, B.B. Small-scale and large-scale intermittency in the nocturnal boundary layer and the residual layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 515, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

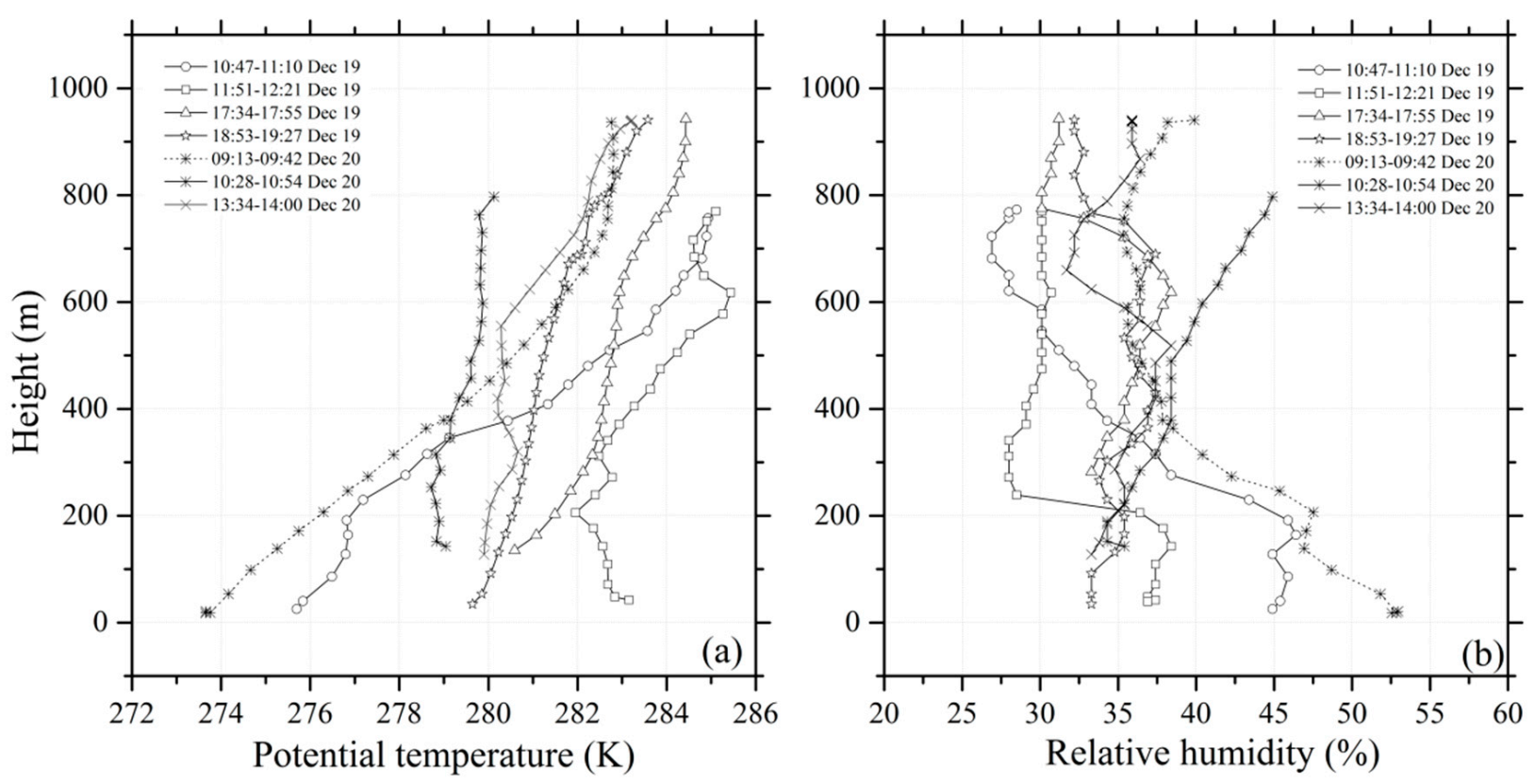
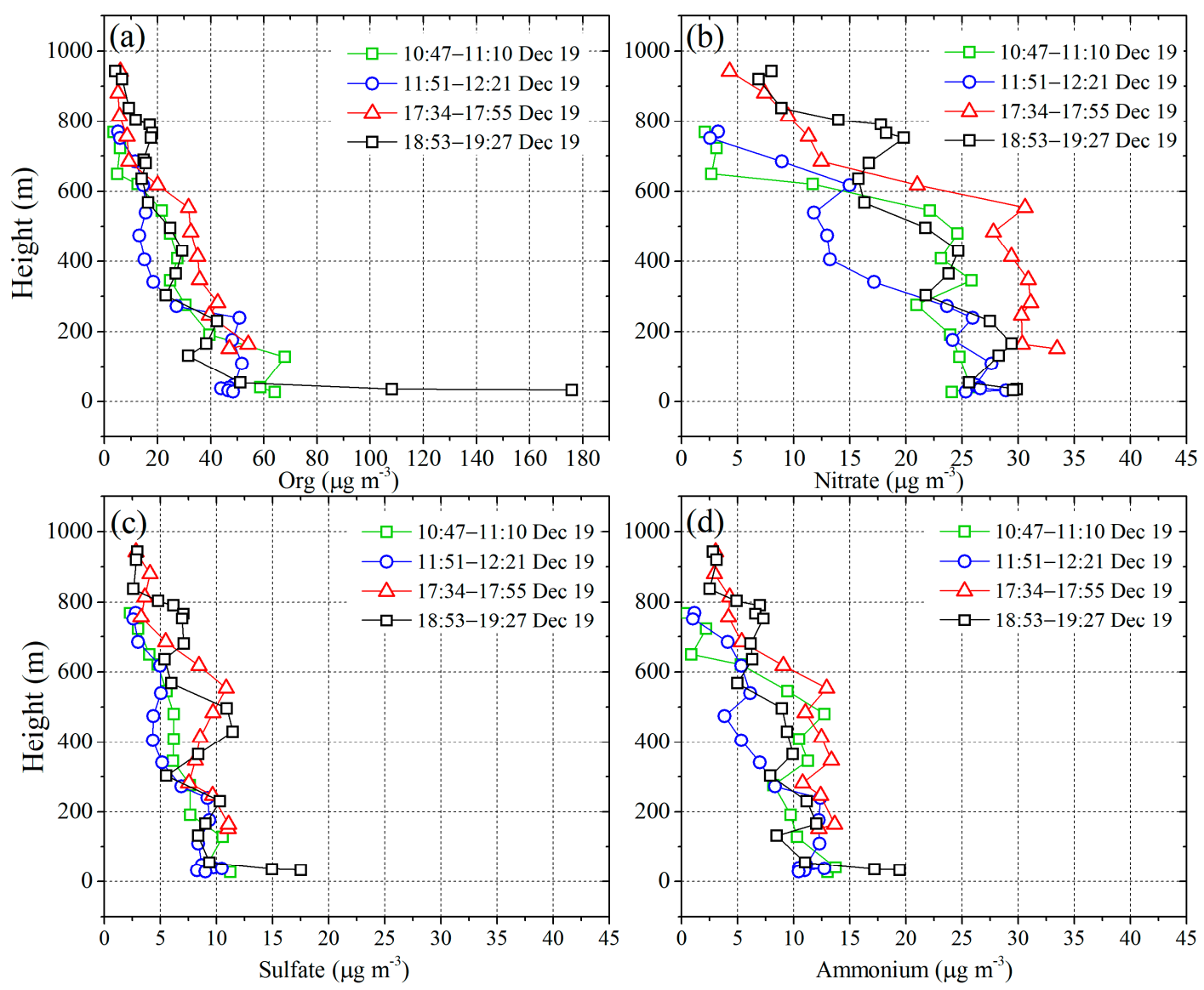

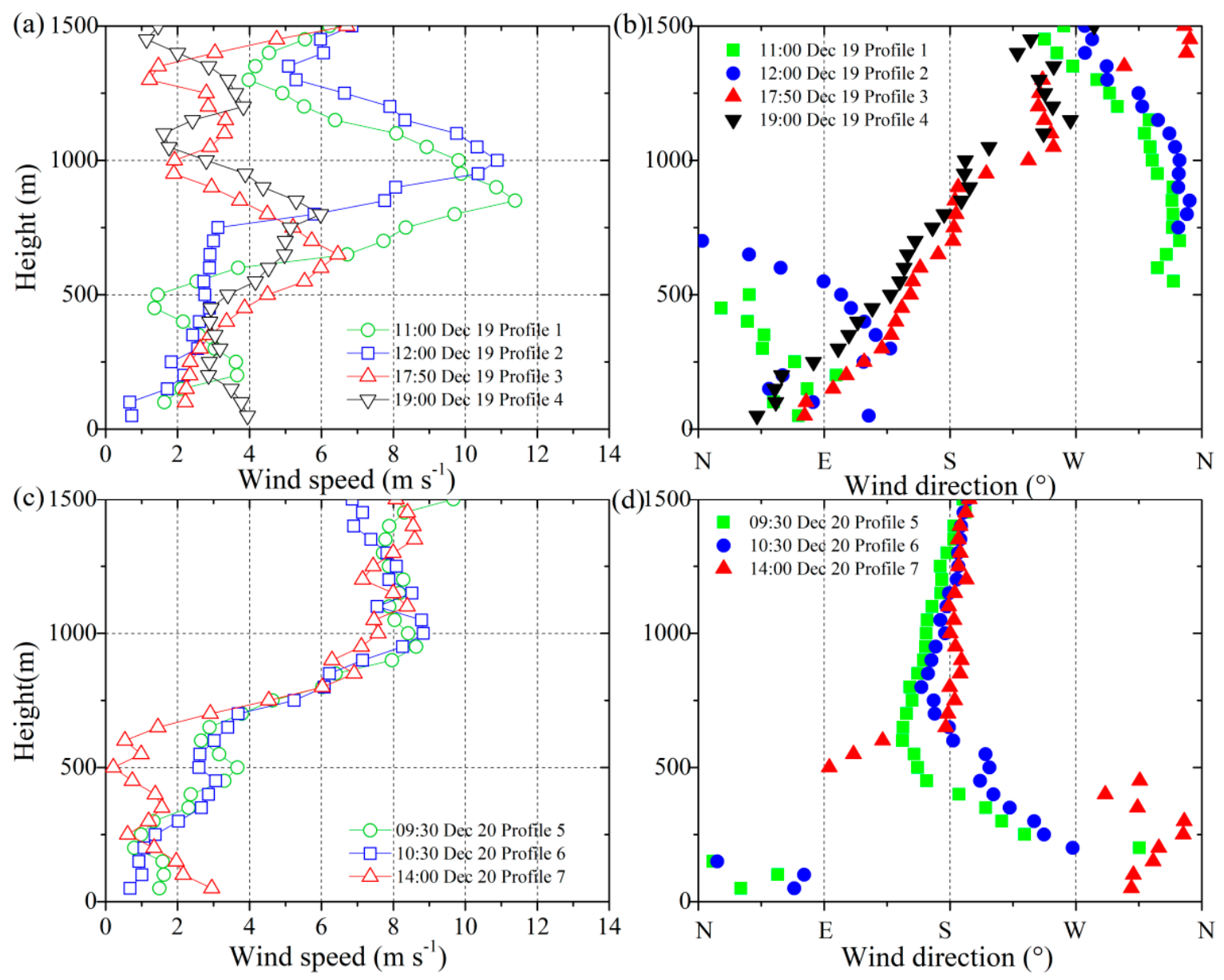
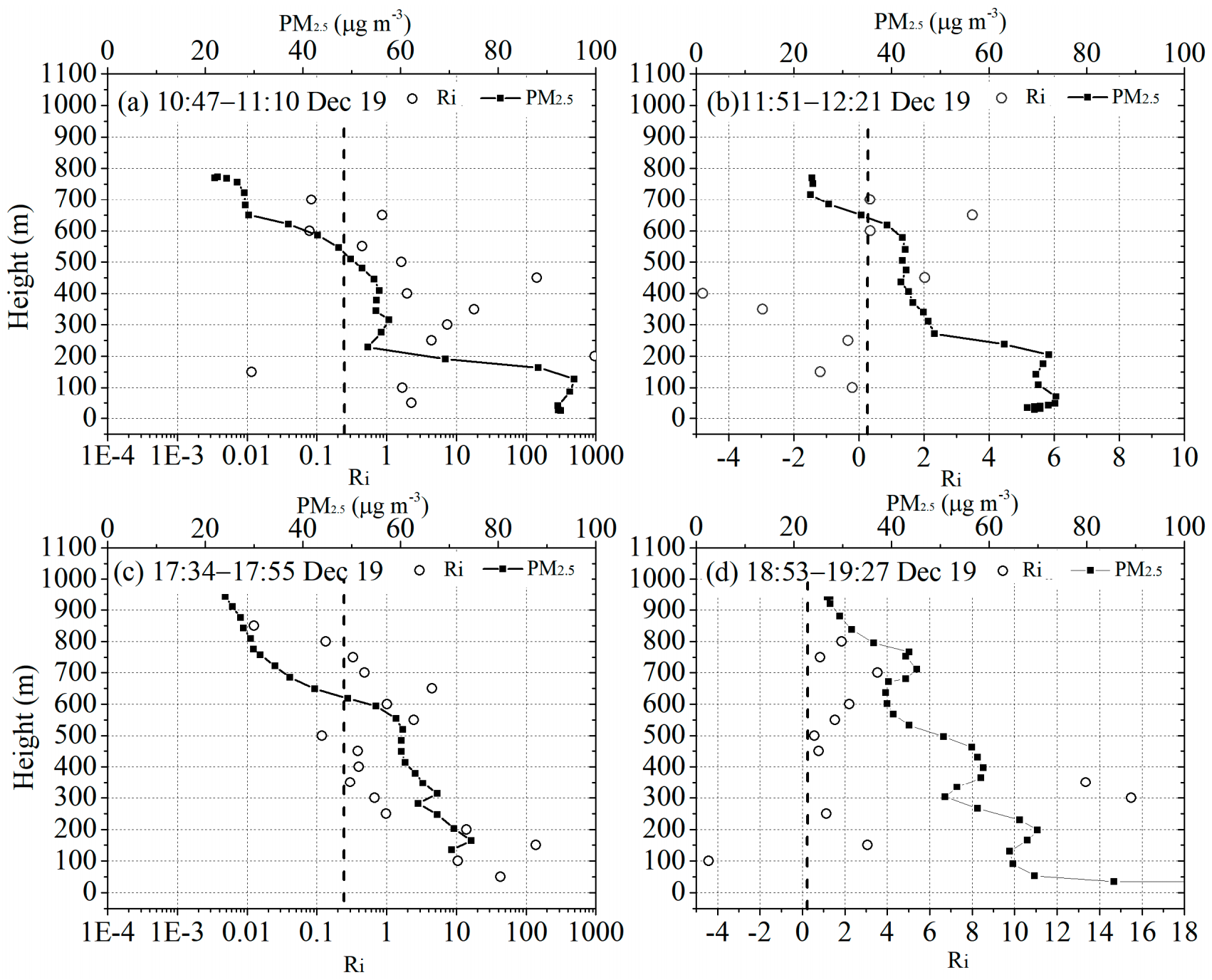
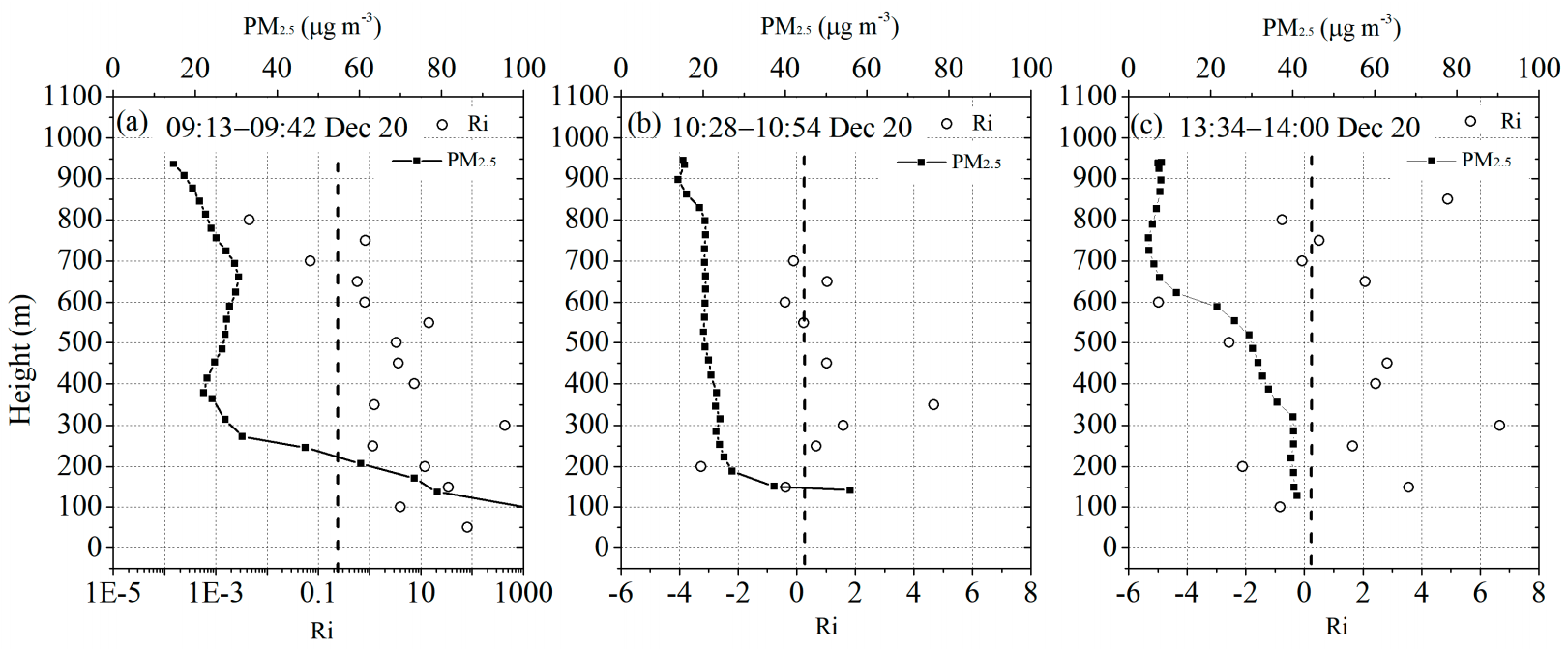
| Detection | Profile 1 | Profile 2 | Profile 3 | Profile 4 | Profile 5 | Profile 6 | Profile 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height | 250–772 m | 769–27 m | 246–942 m | 940–34 m | 17–937 m | 946–142 m | 940–149 m |
| Time | 10:47–11:10 | 11:51–12:21 | 17:34–17:55 | 18:53–19:27 | 09:13–09:42 | 10:28–10:54 | 13:34–14:00 |
| Date | 19 December | 19 December | 19 December | 19 December | 20 December | 20 December | 20 December |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.; Fan, G.; Huo, J. Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution and Its Impacts on the Vertical Distributions of Pollutant Particulate Matter. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050610
Shi Y, Liu L, Hu F, Fan G, Huo J. Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution and Its Impacts on the Vertical Distributions of Pollutant Particulate Matter. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050610
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yu, Lei Liu, Fei Hu, Guangqiang Fan, and Juntao Huo. 2021. "Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution and Its Impacts on the Vertical Distributions of Pollutant Particulate Matter" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050610
APA StyleShi, Y., Liu, L., Hu, F., Fan, G., & Huo, J. (2021). Nocturnal Boundary Layer Evolution and Its Impacts on the Vertical Distributions of Pollutant Particulate Matter. Atmosphere, 12(5), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050610






