Sea Surface Temperature Variability over the Tropical Indian Ocean during the ENSO and IOD Events in 2016 and 2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
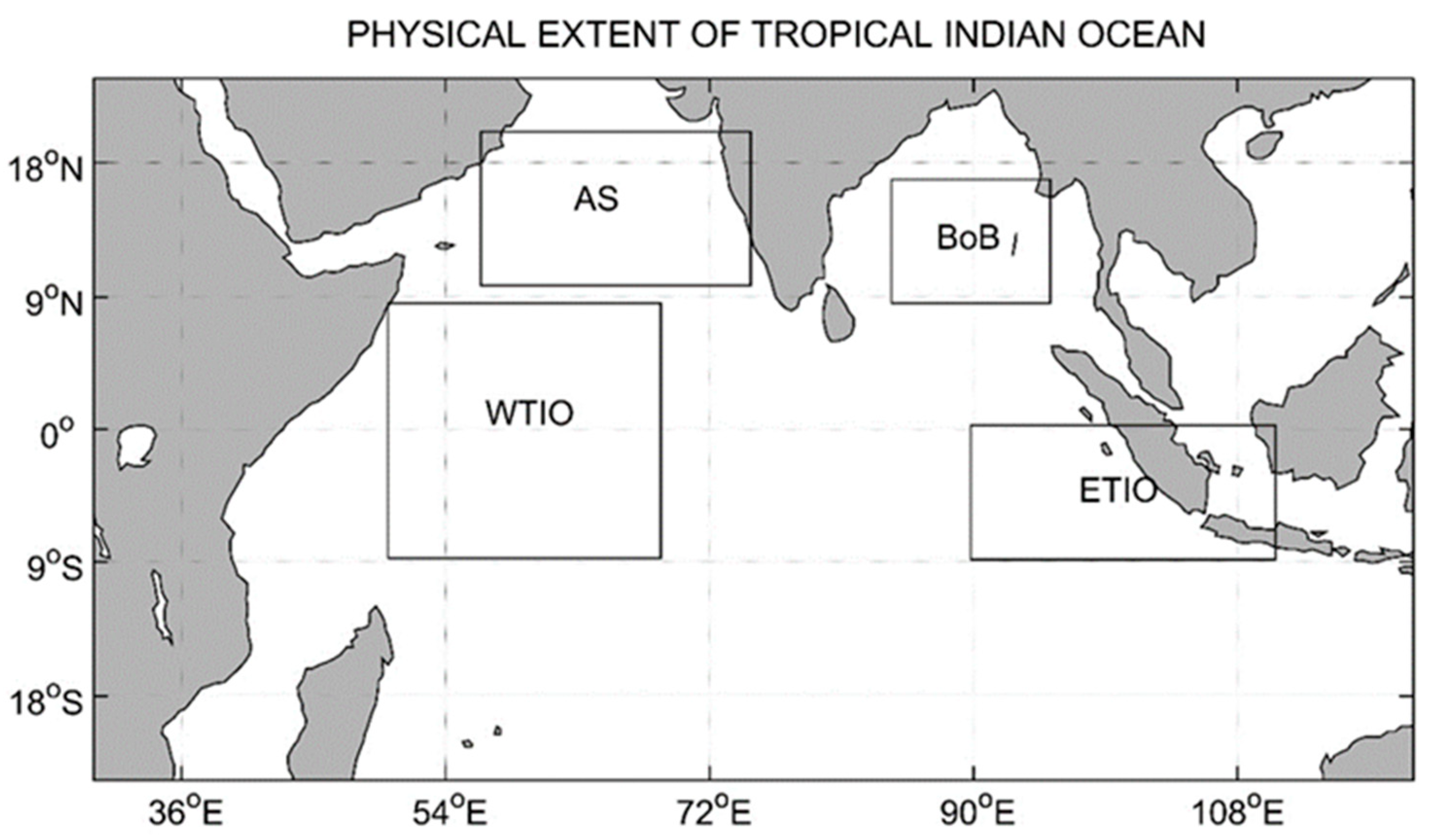
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Analysis
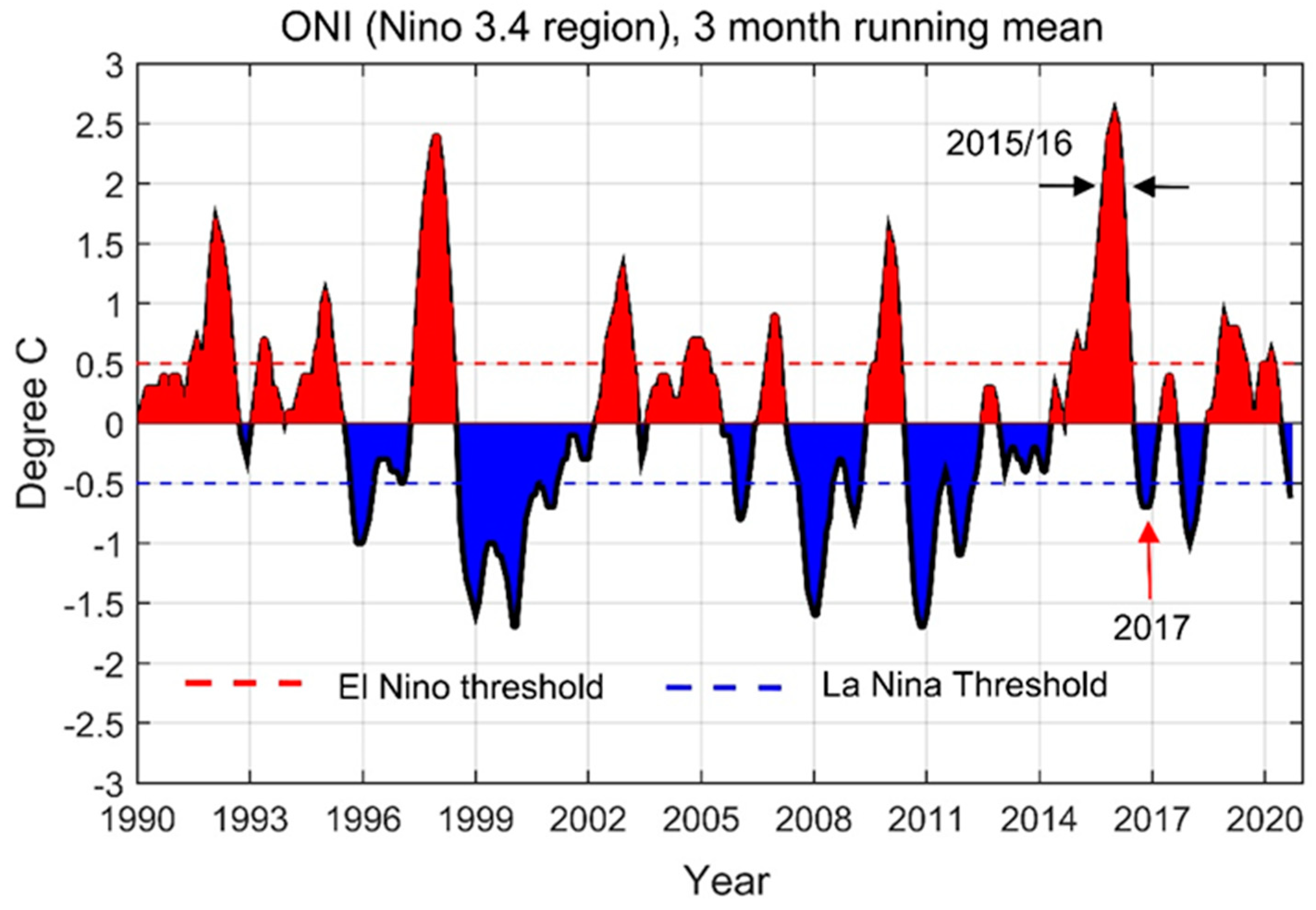
2.3. Measurement of Oceanic Niño Index
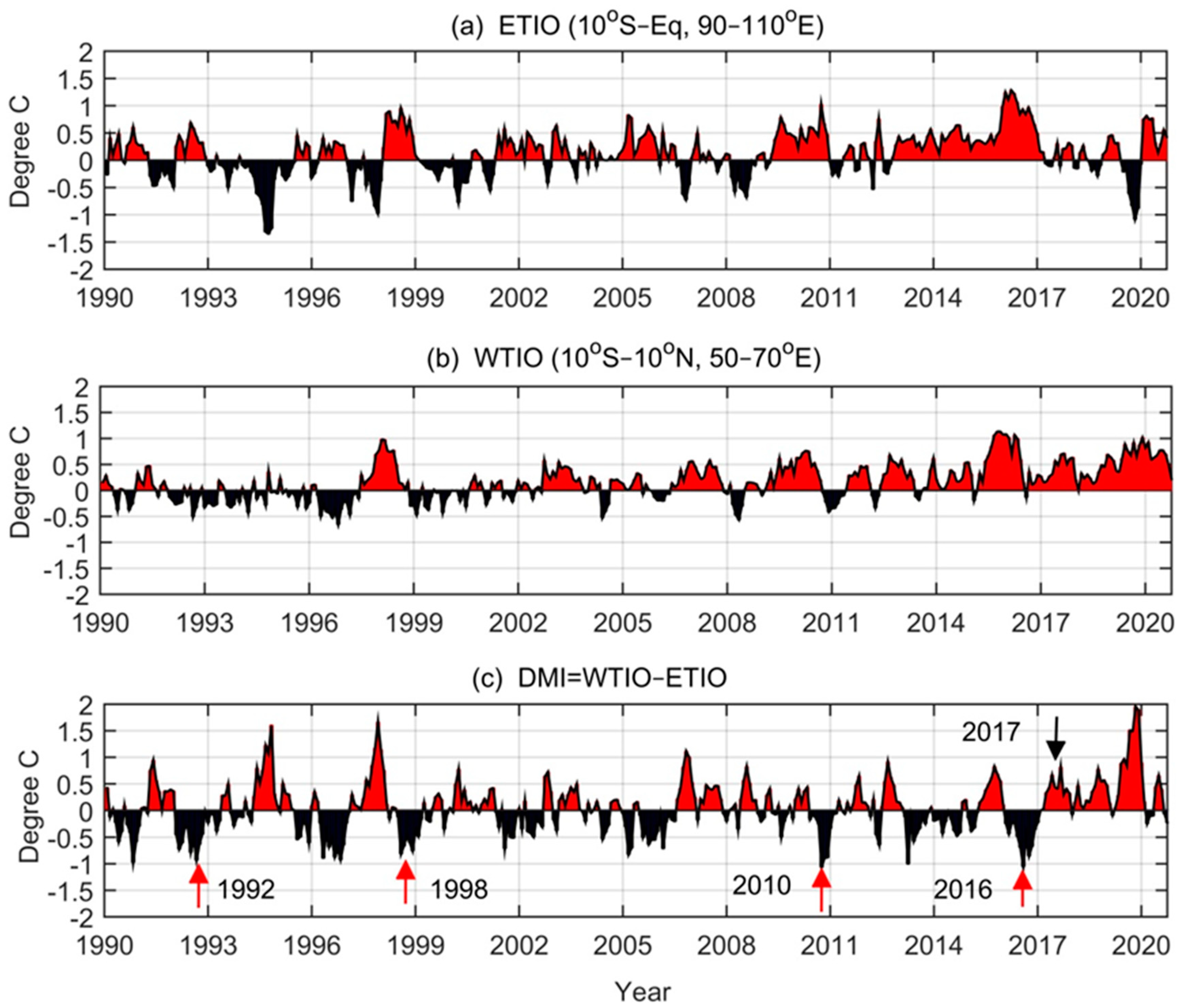
2.4. Measurement of Dipole Mode Index
3. Results and Discussion
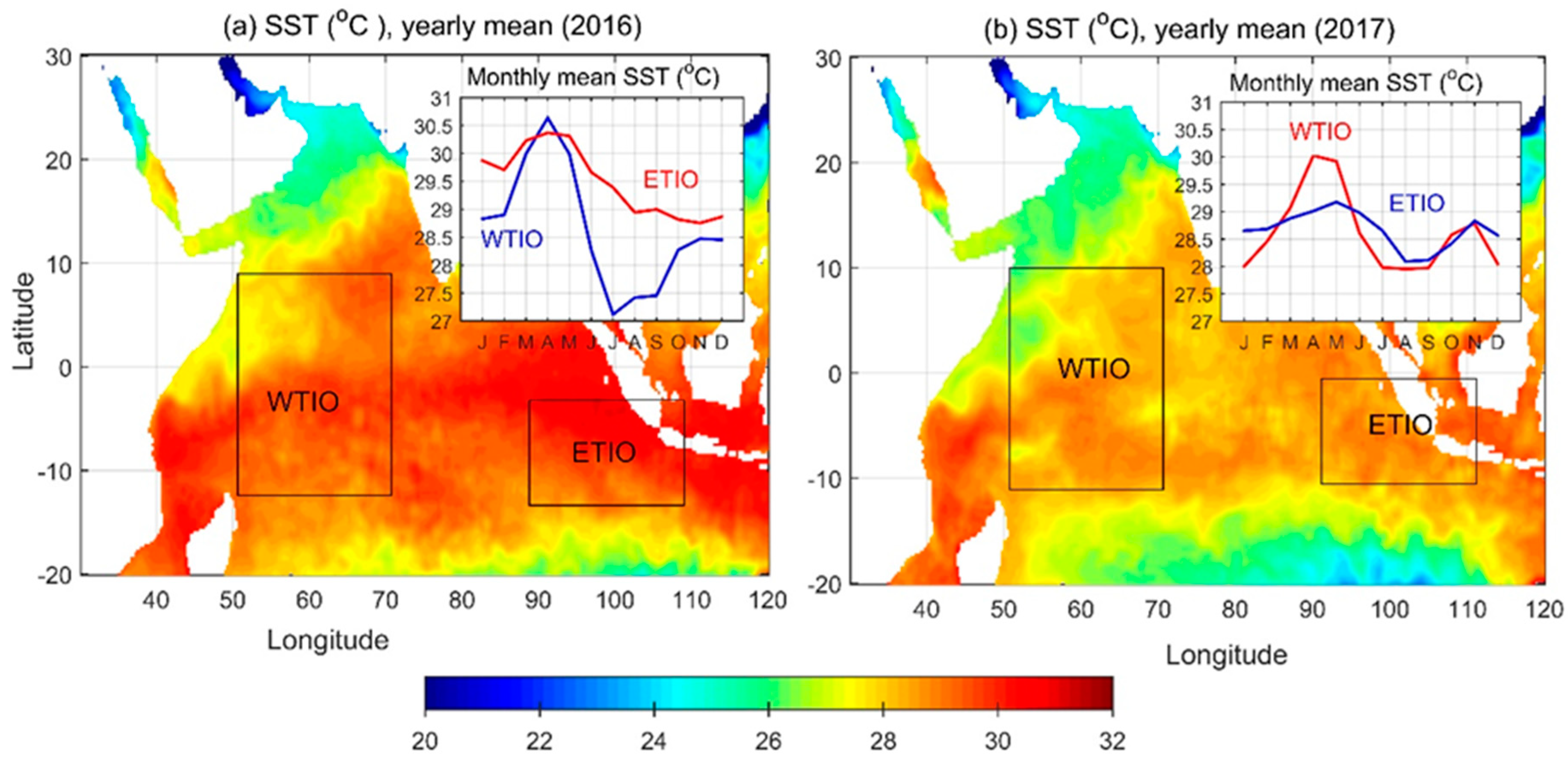
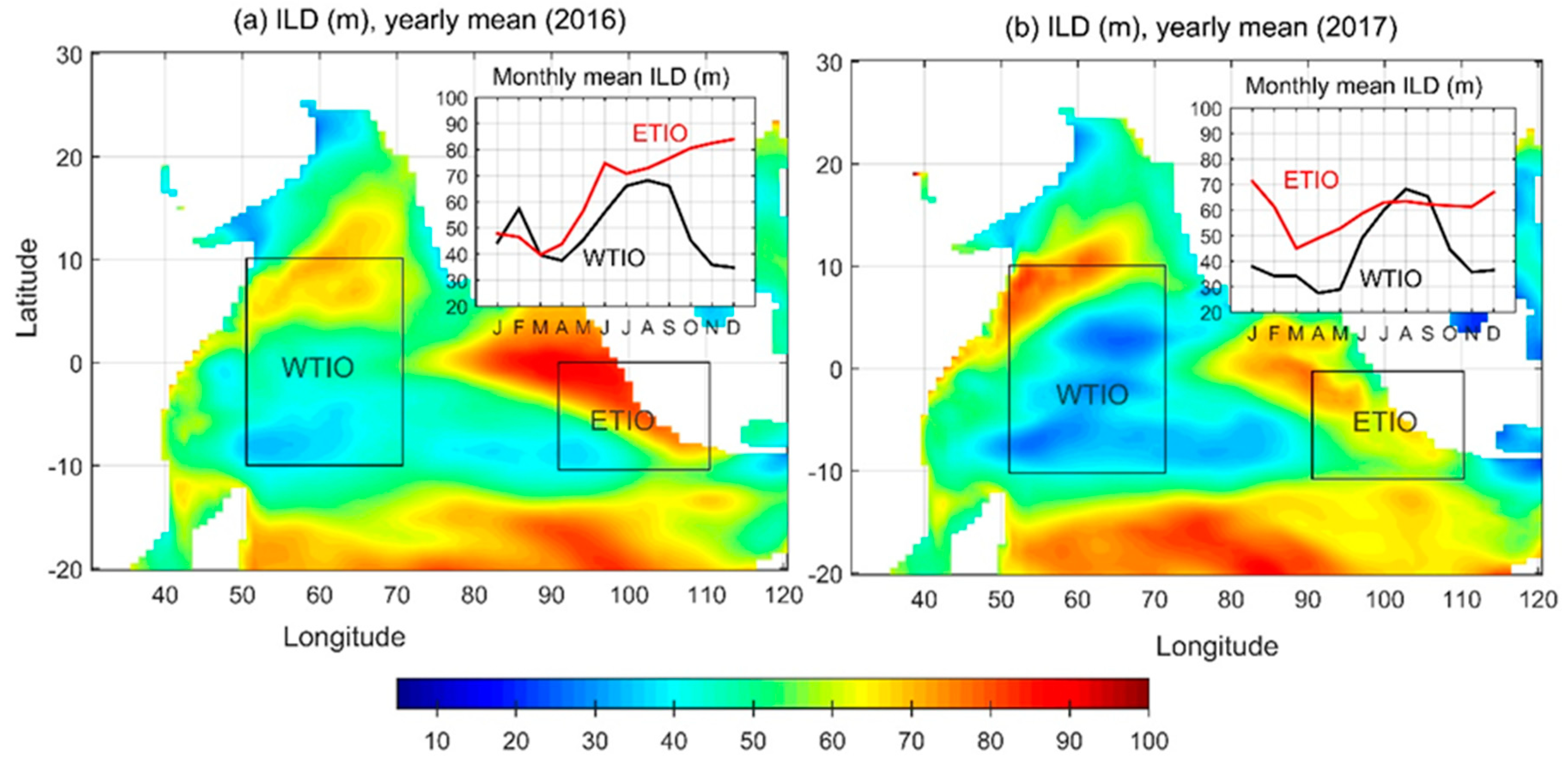
3.1. Evolution of Dipole Structure in 2016 and 2017
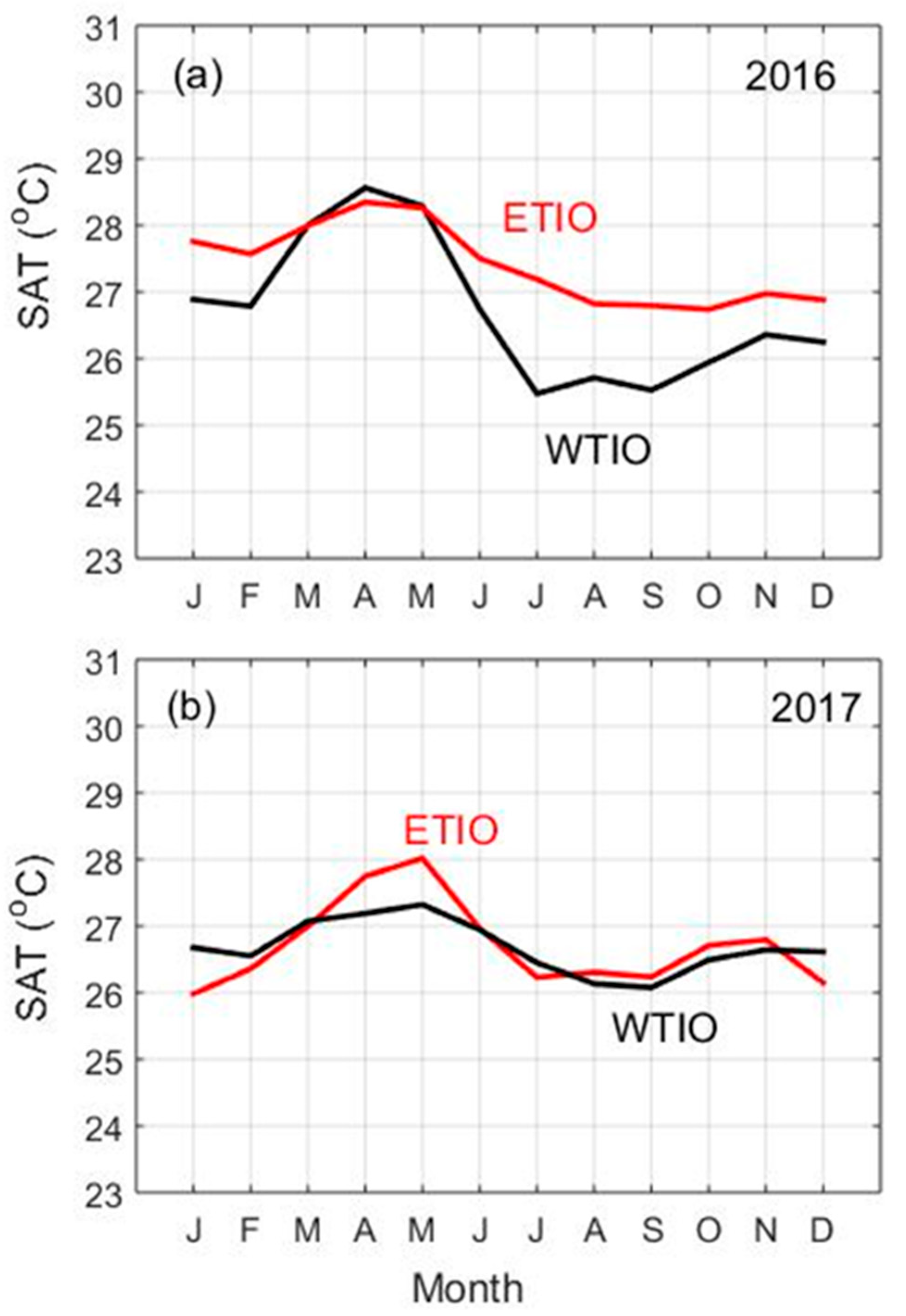
3.2. SST Variability and Associated Mechanisms in the TIO
3.2.1. The Equatorial Indian Ocean Region
3.2.2. The Arabian Sea Region
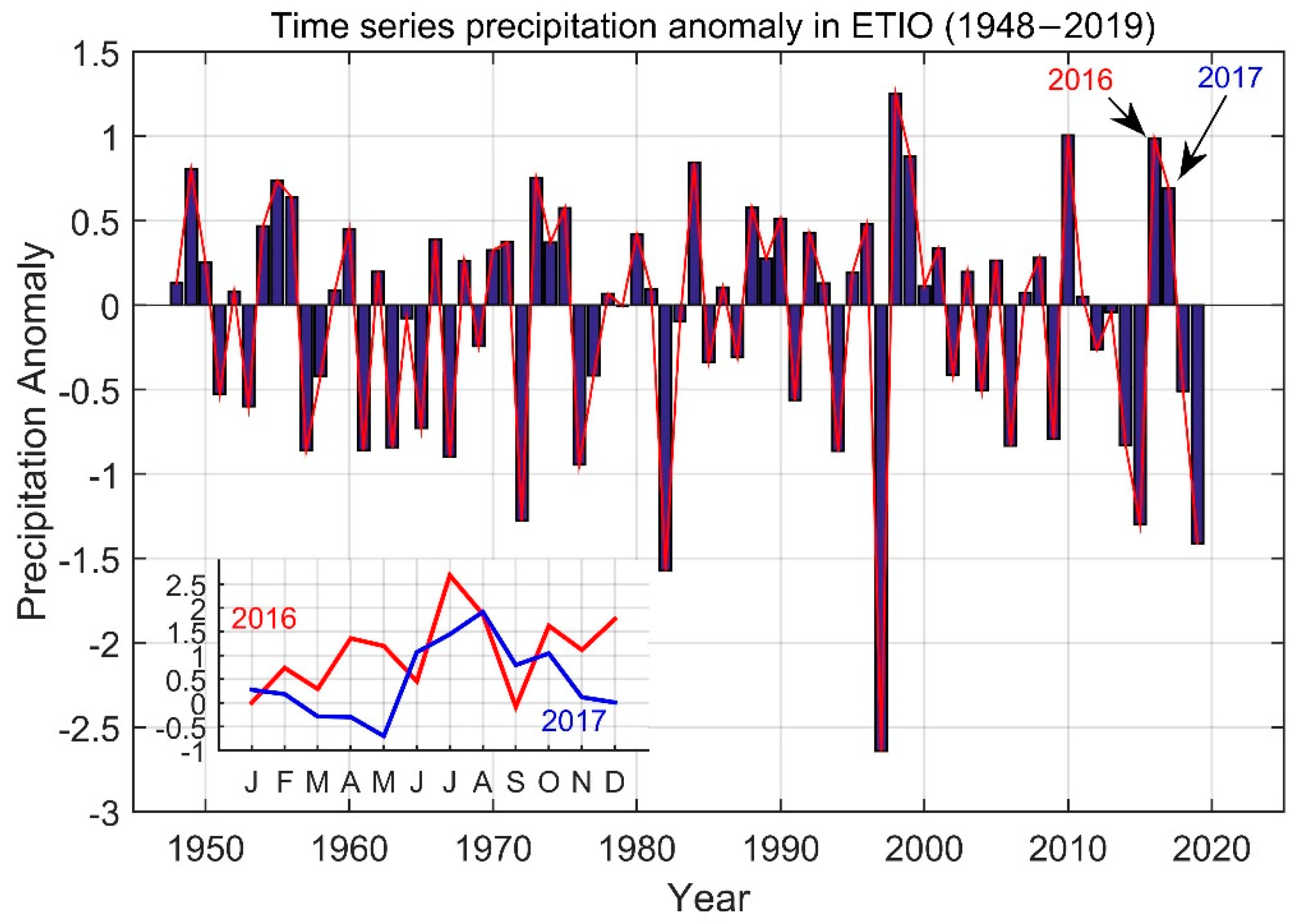
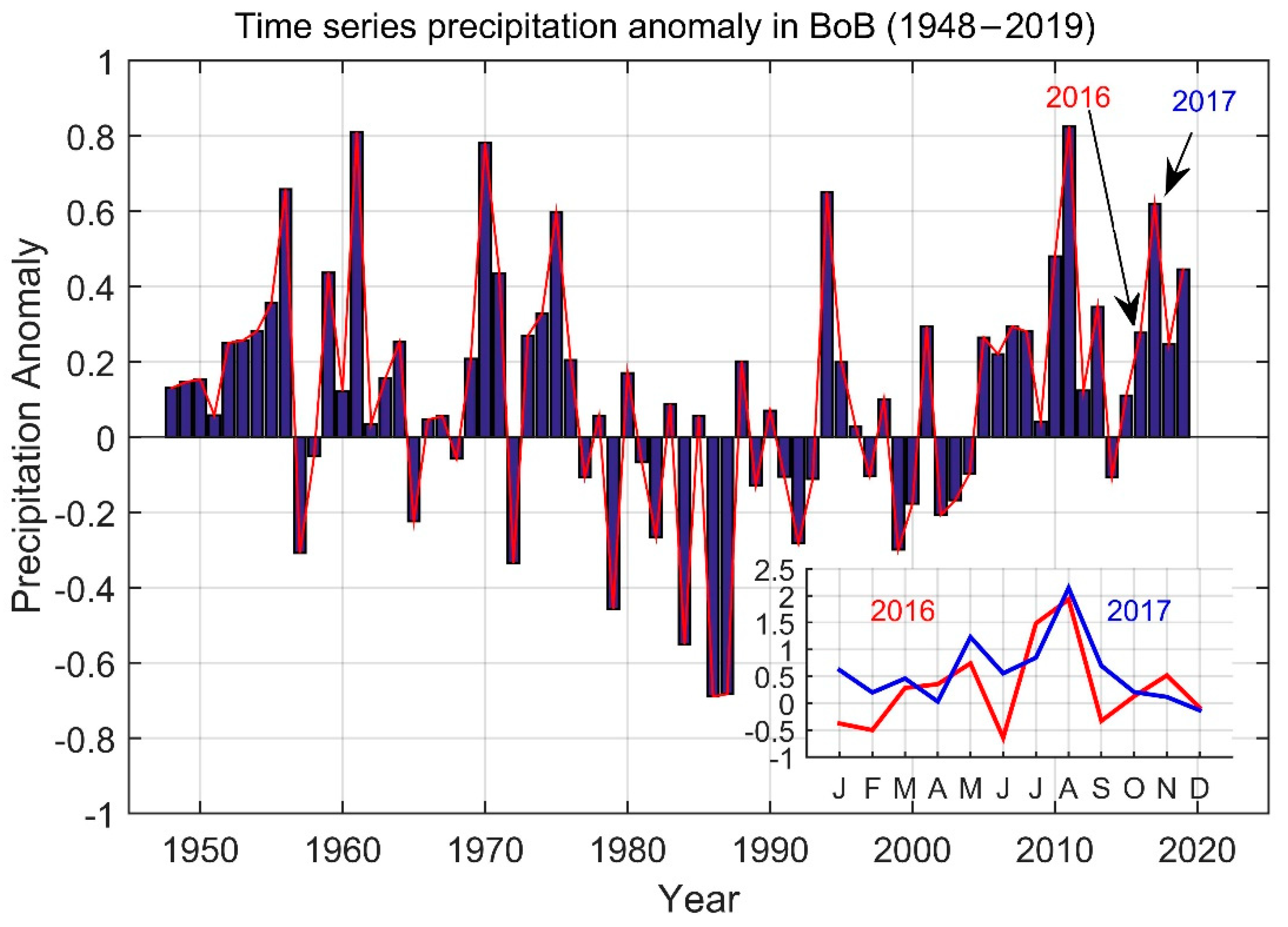
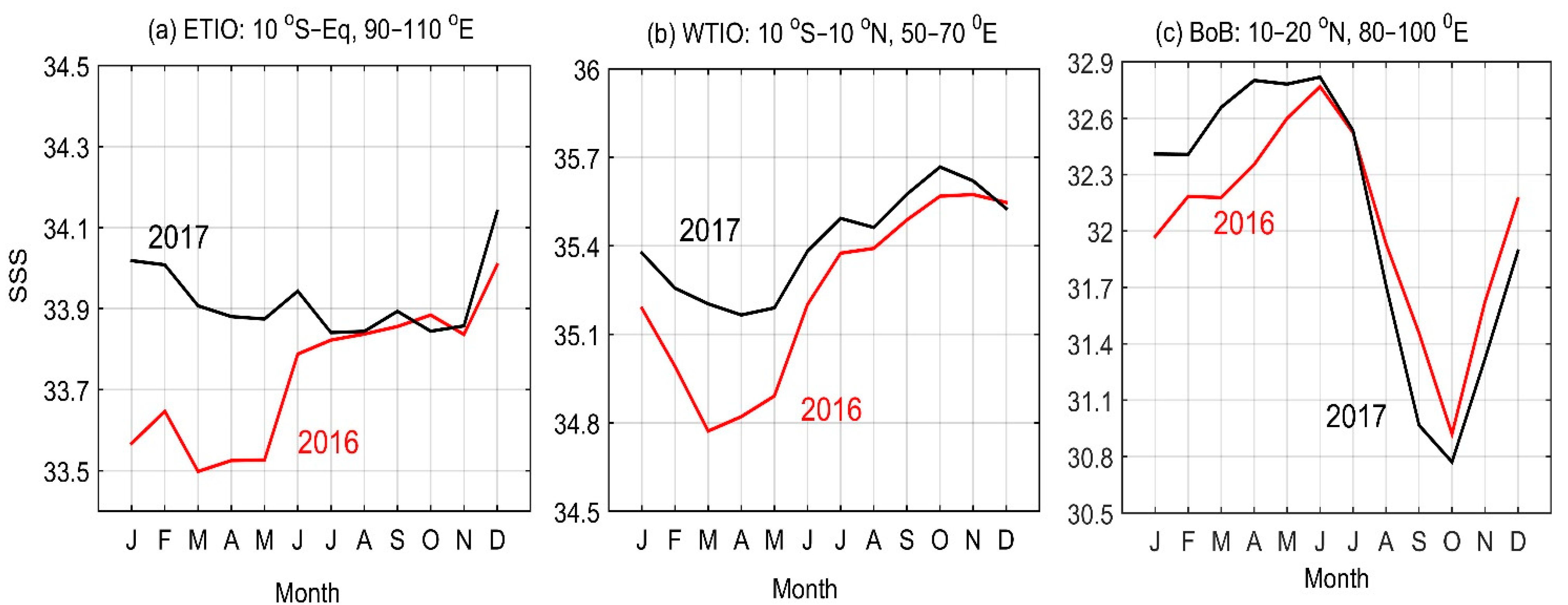
3.3. Precipitation Variability and SSS Circulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, L.; McPhaden, M.J. Unusually warm Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures help to arrest development of El Niño in 2014. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kug, J.S.; Kang, I.S. Interactive feedback between ENSO and the Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1784–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.M.; Deser, C. Asymmetry in the duration of El Niño and La Niña. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5826–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtugudde, R.; Busalacchi, A.J. Interannual variability of the dynamics and thermodynamics of the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2300–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayachandran, P.N.; Iizuka, S.; Yamagata, T. Indian Ocean dipole mode events in an ocean general circulation model. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2002, 49, 1573–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.T. Correlation in seasonal variations of weather. IX. A further study of world weather. Mem. Indian Meteorol. Dep. 1924, 24, 275–332. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, V.; Shukla, J. Intraseasonal and interannual variability of rainfall over India. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4366–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpe, K.; Dümenil, L.; Giorgetta, M.A. Variability of the Indian monsoon in the ECHAM3 model: Sensitivity to sea surface temperature, soil moisture, and the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 1837–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, M.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; de Boyer Montégut, C.; Muraleedharan, P. Interannual variability of the Tropical Indian Ocean mixed layer depth. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverdin, G.; Cadet, D.L.; Gutzler, D. Interannual displacements of convection and surface circulation over the equatorial Indian Ocean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.R. Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtugudde, R.; McCreary, J.P., Jr.; Busalacchi, A.J. Oceanic processes associated with anomalous events in the Indian Ocean with relevance to 1997–1998. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 3295–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.V. Monsoon variability in relation to equatorial trough activity over India and west Pacific Oceans. Mausam 1990, 41, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Niñomiya, K.; Kobayashi, C. Precipitation and moisture balance of the Asian summer monsoon in 1991. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 77, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boyer Montégut, C.; Mignot, J.; Lazar, A.; Cravatte, S. Control of salinity on the mixed layer depth in the world ocean: 1. General description. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C06011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtugudde, R.; Seager, R.; Thoppil, P. Arabian Sea response to monsoon variations. Paleoceanography 2007, 22, PA4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, T.; Montégut, C.B.; Luo, J.J.; Behera, S.K.; Masson, S.; Yamagata, T. The role of the western Arabian Sea upwelling in Indian monsoon rainfall variability. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 5603–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, R. Relationships between Indian Ocean sea surface temperature and the rainfall of Sri Lanka. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1988, 66, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripalani, R.H.; Kumar, P. Northeast monsoon rainfall variability over south peninsular India vis-à-vis the Indian Ocean dipole mode. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 24, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Sahai, A.K.; Goswami, B.N. Eastward propagating MJO during boreal summer and Indian monsoon droughts. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Sahai, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Sharmila, S.; Abhilash, S.; Rajeevan, M.; Mandal, R.; Dey, A.; Borah, N.; Phani, R. Extremes in June rainfall during the Indian summer monsoons of 2013 and 2014: Observational analysis and extended-range prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Jones, P.D.; Ambenje, P.; Bojariu, R.; Easterling, D.; Klein Tank, A.; Parker, D.; Rahimzadeh, F.; Renwick, J.A.; Rusticucci, M.; et al. Chapter 3: Observations: Surface and atmospheric climate change. In Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 235–336. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, T.; Ali, M.M.; Bourassa, M.A.; Zheng, Y.; Goni, G.J.; Foltz, G.R.; Rajeevan, M. Statistical evidence for the role of southwestern Indian Ocean heat content in the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Arblaster, J.M.; Fasullo, J.T.; Hu, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Model-based evidence of deep-ocean heat uptake during surface-temperature hiatus periods. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.T.; Li, W.; Xie, S.-P. Regions of significant influence on unforced global mean surface air temperature variability in climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Fyfe, J.C.; Xie, S.-P.; Dai, X. Decadal modulation of global surface temperature by internal climate variability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Zebiak, S.E.; Glantz, M.H. ENSO as an integrating concept in Earth science. Science 2006, 314, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2016; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Krishnan, R.; Yamagata, T. Unusual ocean-atmosphere conditions in the tropical Indian Ocean during 1994. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, C.; Murtugudde, R.; Allan, T. Indian Ocean climate event brings floods to East Africa’s lakes and the Sudd Marsh. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Ren, H.L.; Scaife, A.A.; Wu, J.; Dunstone, N.; Smith, D.; Wan, J.; Eade, R.; MacLachlan, C.; Gordon, M. An extreme negative Indian Ocean Dipole event in 2016: Dynamics and predictability. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2017; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suthinkumar, P.S.; Babu, C.A.; Varikoden, H. Spatial Distribution of Extreme Rainfall Events during 2017 Southwest Monsoon over Indian Subcontinent. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 5431–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Banzon, V.; Freeman, E.; Graham, G.; Hankins, B.; Smith, T.; Zhang, H.M. Improvements of the Daily Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (DOISST) Version 2.1. J. Clim. 2020, 34, 2923–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzon, V.; Smith, T.M.; Chin, T.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Hankins, W. A long-term record of blended satellite and in situ sea-surface temperature for climate monitoring, modeling and environmental studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.W.; Xue, Y. Evaluation of the global ocean data assimilation system at NCEP: The Pacific Ocean. In Proceedings of the Eighth Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface, AMS 84th Annual Meeting, Washington State Convention and Trade Center, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vissa, N.K.; Satyanarayana, A.N.V.; Prasad Kumar, B. Comparison of mixed layer depth and barrier layer thickness for the Indian Ocean using two different climatologies. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 2855–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G. Improving the global precipitation record: GPCP version 2.1. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Le Vine, D.M. The Salinity Retrieval Algorithms for the NASA Aquarius Version 5 and SMAP Version 3 Releases. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Thorne, P.W.; Banzon, V.F.; Boyer, T.; Chepurin, G.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Menne, M.J.; Smith, T.M.; Vose, R.S.; Zhang, H.M. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature, version 5 (ERSSTv5): Upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8179–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Structure of SST and surface wind variability during Indian Ocean Dipole mode year: COADS observations. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2735–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Behera, S.K.; Masumoto, Y.; Yamagata, T. Interannual subsurface variability in the tropical Indian Ocean with a special emphasis on the Indian Ocean dipole. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 1549–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.J.; Masson, S.; Behera, S.; Yamagata, T. Experimental forecasts of the Indian Ocean Dipole using a coupled OAGCM. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 2178–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Vecchi, G.A.; Rosati, A.J. Predictability of the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomalies in the GFDL coupled model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hendon, H.H.; Alves, O.; Luo, J.J.; Balmaseda, M.; Anderson, D. How predictable is the Indian Ocean Dipole? Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 3867–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, Y.; Chen, D.; Lian, T. Predictability of the Indian Ocean Dipole in the coupled models. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 2005–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Storto, A.; Behera, S.K.; Navarra, A.; Yamagata, T. Improved prediction of the Indian Ocean dipole mode by use of subsurface ocean observations. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 7953–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. Impact of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.J.; Masson, S.; Rao, S.A.; Sakuma, H.; Yamagata, T. A CGCM study on the interaction between IOD and ENSO. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1688–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Rayner, N.A.; Smith, T.M.; Stokes, D.C.; Wang, W. An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weare, B.C. A statistical study of the relationships between ocean surface temperatures and the Indian monsoon. J. Atmos. Sci. 1979, 36, 2279–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.P.; Hendon, H.H. Causes and predictability of the negative Indian Ocean Dipole and its impact on La Niña during 2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantha, L.H.; Clayson, C.A. An improved mixed layer model for geophysical applications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1979, 99, 25235–25266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, J. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1969, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düing, W.; Leetmaa, A. Arabian Sea cooling: A preliminary heat budget. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1980, 10, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J. Effect of Arabian sea-surface temperature anomaly on Indian summer monsoon: A numerical experiment with the GFDL model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1975, 32, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastenrath, S.; Lamb, P. Climatic Atlas of the Indian Ocean. Part I. Surface Circulation and Climate; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1979; p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.R.; Sivakumar, R. Seasonal variability of near-surface thermal structure and heat budget of the mixed layer of the tropical Indian Ocean from a new global ocean temperature climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 995–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Mao, H.L. A theory of upwelling of horizontal extent. J. Mar. Res. 1957, 16, 40–54. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, K. Zonal anomaly of sea surface temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean and its possible effect upon monsoon circulation. Tellus 1970, 22, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, L.; Graham, N.E. Simulation skills of the SST-forced global climate variability of the NCEP-MRF9 and the Scripps-MPI ECHAM3 model. J. Clim. 1999, 13, 3657–3679. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, N. All-India summer monsoon rainfall and sea surface temperatures around northern Australia and Indonesia. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Kim, J. The relationship of the El Niño–Southern oscillation to African rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 17, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, A.; Das, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, A.; Akhand, A.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, T.; Mitra, D.; Hazra, S. Sea surface temperature and rainfall anomaly over the Bay of Bengal during the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the extreme Indian Ocean Dipole events between 2002 and 2016. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 12, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, S.; Piao, S.; Zheng, G.; Khan, I.U.; Bradley, D.; Khan, S.; Song, Y. Sea Surface Temperature Variability over the Tropical Indian Ocean during the ENSO and IOD Events in 2016 and 2017. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050587
Khan S, Piao S, Zheng G, Khan IU, Bradley D, Khan S, Song Y. Sea Surface Temperature Variability over the Tropical Indian Ocean during the ENSO and IOD Events in 2016 and 2017. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050587
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Sartaj, Shengchun Piao, Guangxue Zheng, Imran Ullah Khan, David Bradley, Shazia Khan, and Yang Song. 2021. "Sea Surface Temperature Variability over the Tropical Indian Ocean during the ENSO and IOD Events in 2016 and 2017" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050587
APA StyleKhan, S., Piao, S., Zheng, G., Khan, I. U., Bradley, D., Khan, S., & Song, Y. (2021). Sea Surface Temperature Variability over the Tropical Indian Ocean during the ENSO and IOD Events in 2016 and 2017. Atmosphere, 12(5), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050587





