Evolution of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in the Air: What Changed after Five Lockdown Weeks at a Southwest Atlantic European Region (Northwest of Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site Details
2.2. Monitoring Techniques and Data Quality
2.3. Meteorological Data, Air Mass Trajectories, Wind Roses, and Biomass Burning Episodes
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
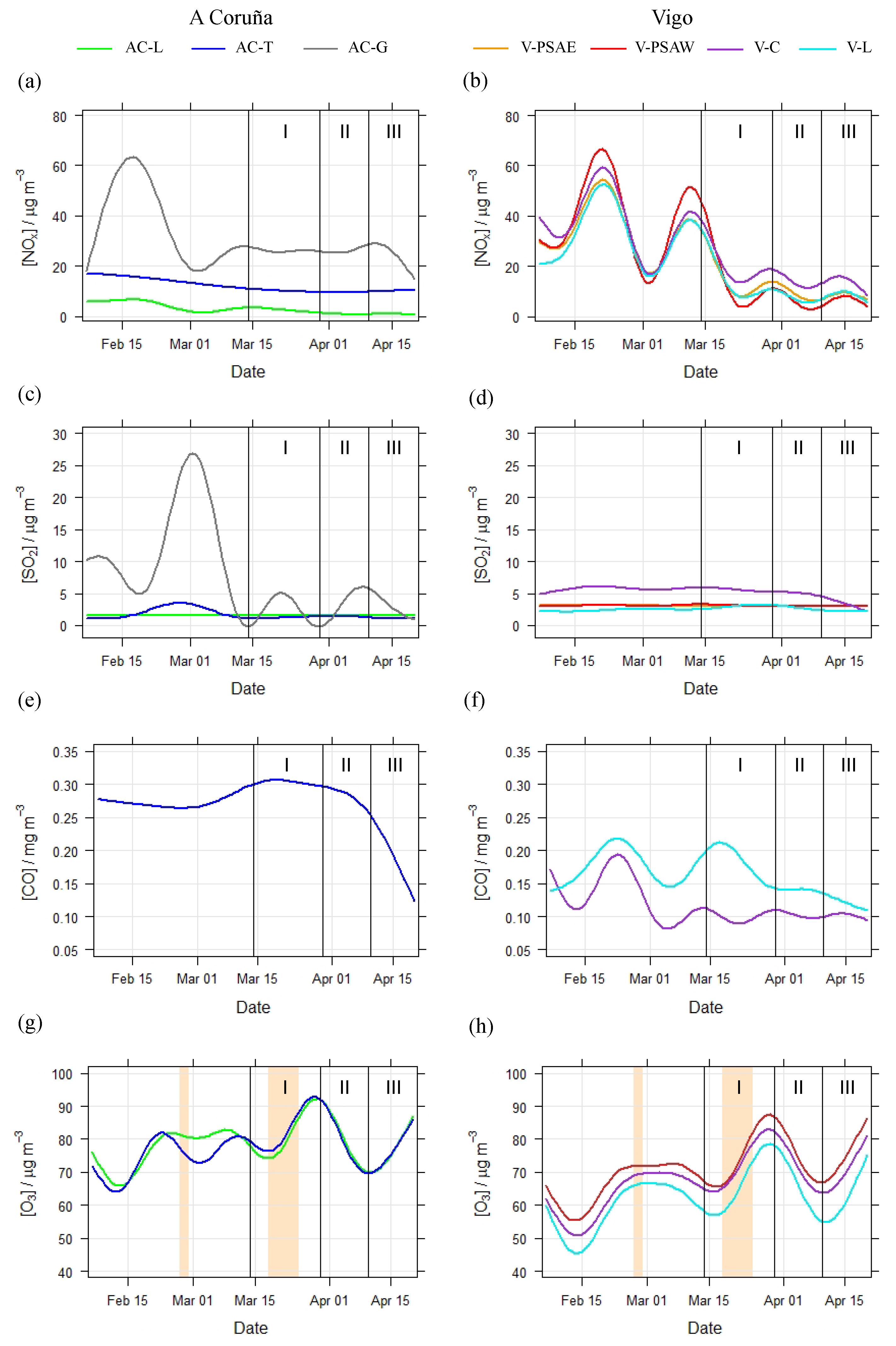
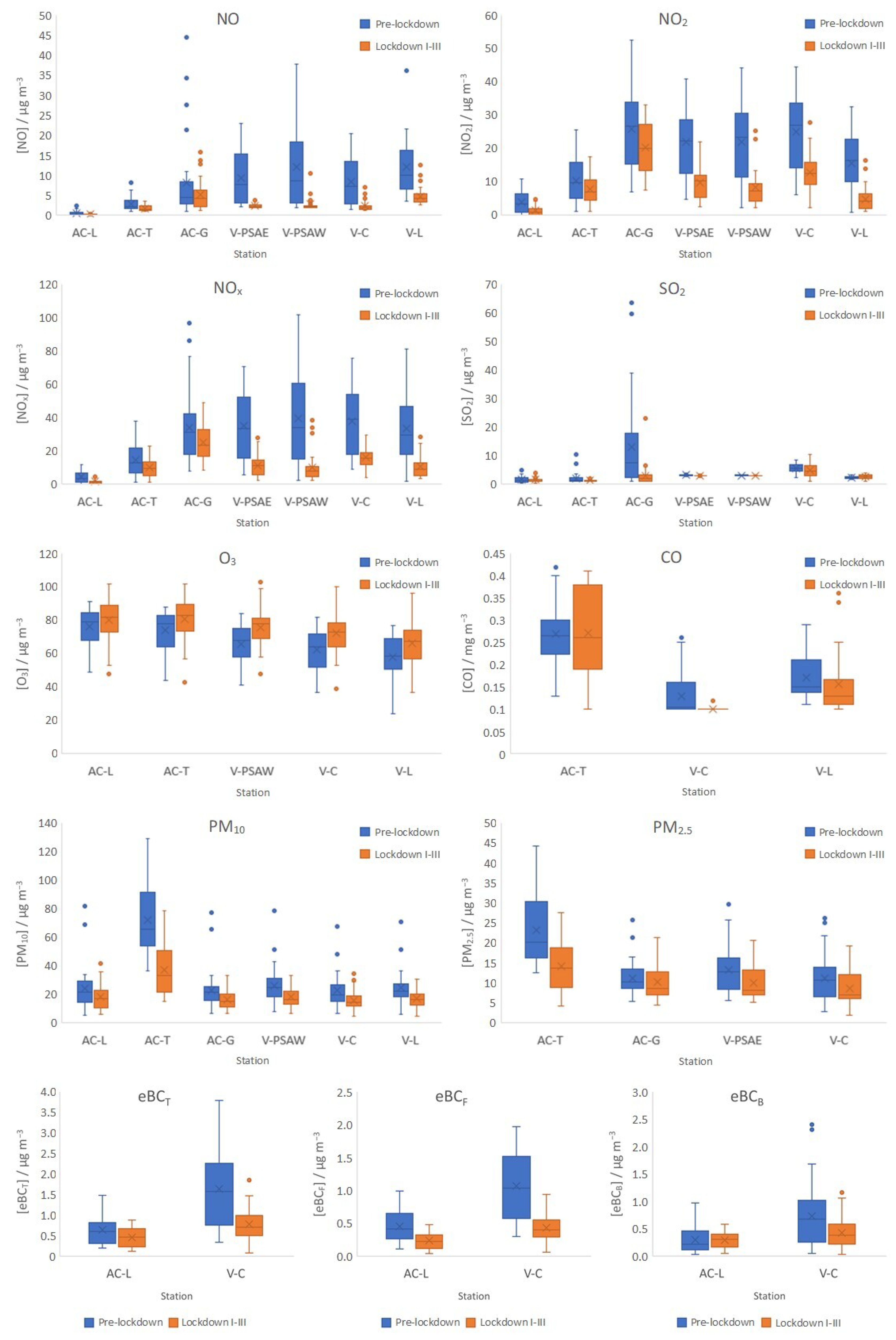
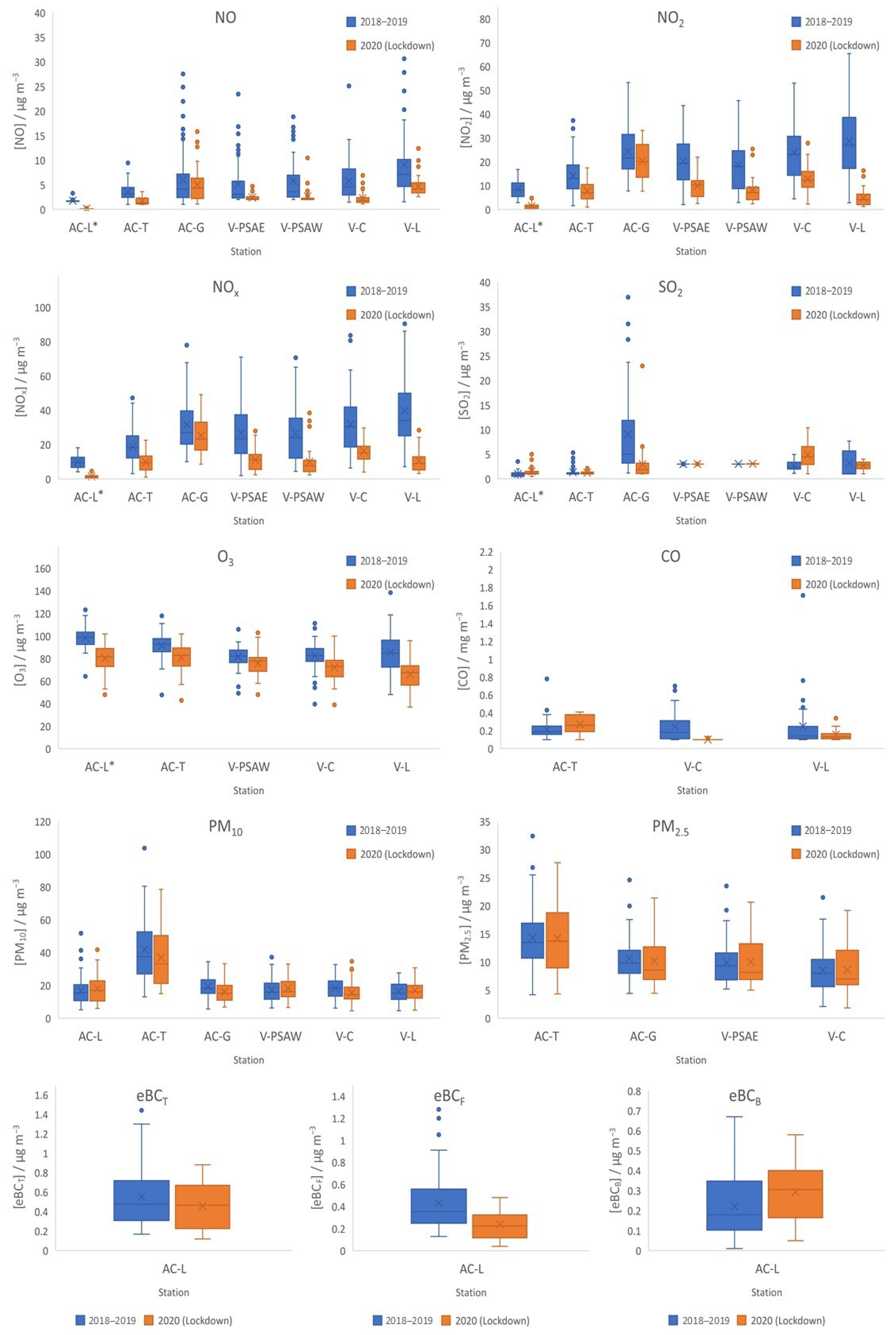
3.1. Decrease in NOx Levels during Lockdown Period
3.2. Decrease in SO2 and CO Levels during Lockdown Period
3.3. Increase in O3 Levels during Lockdown Period
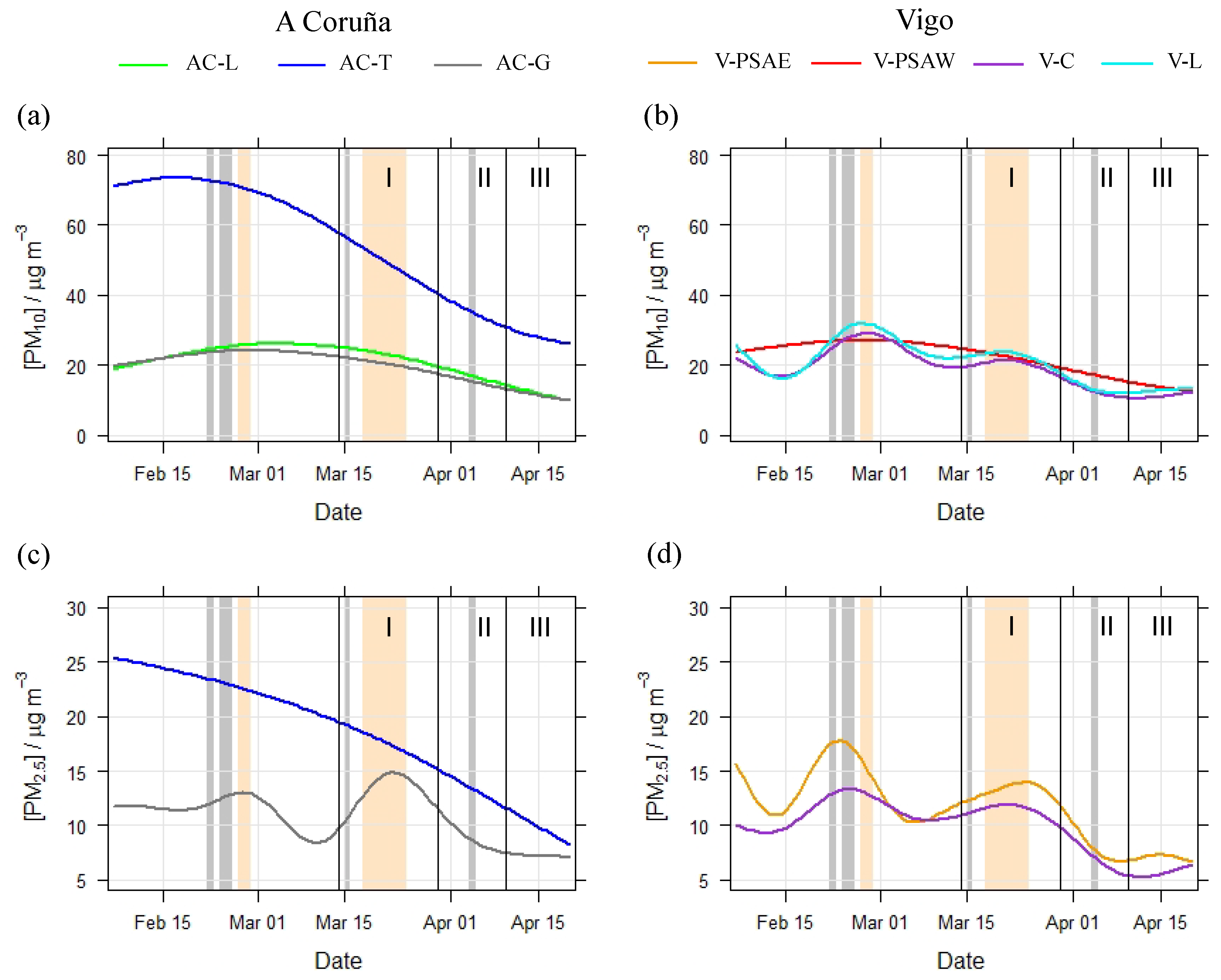
3.4. Decrease in PM10 and PM2.5 Levels during Lockdown Period
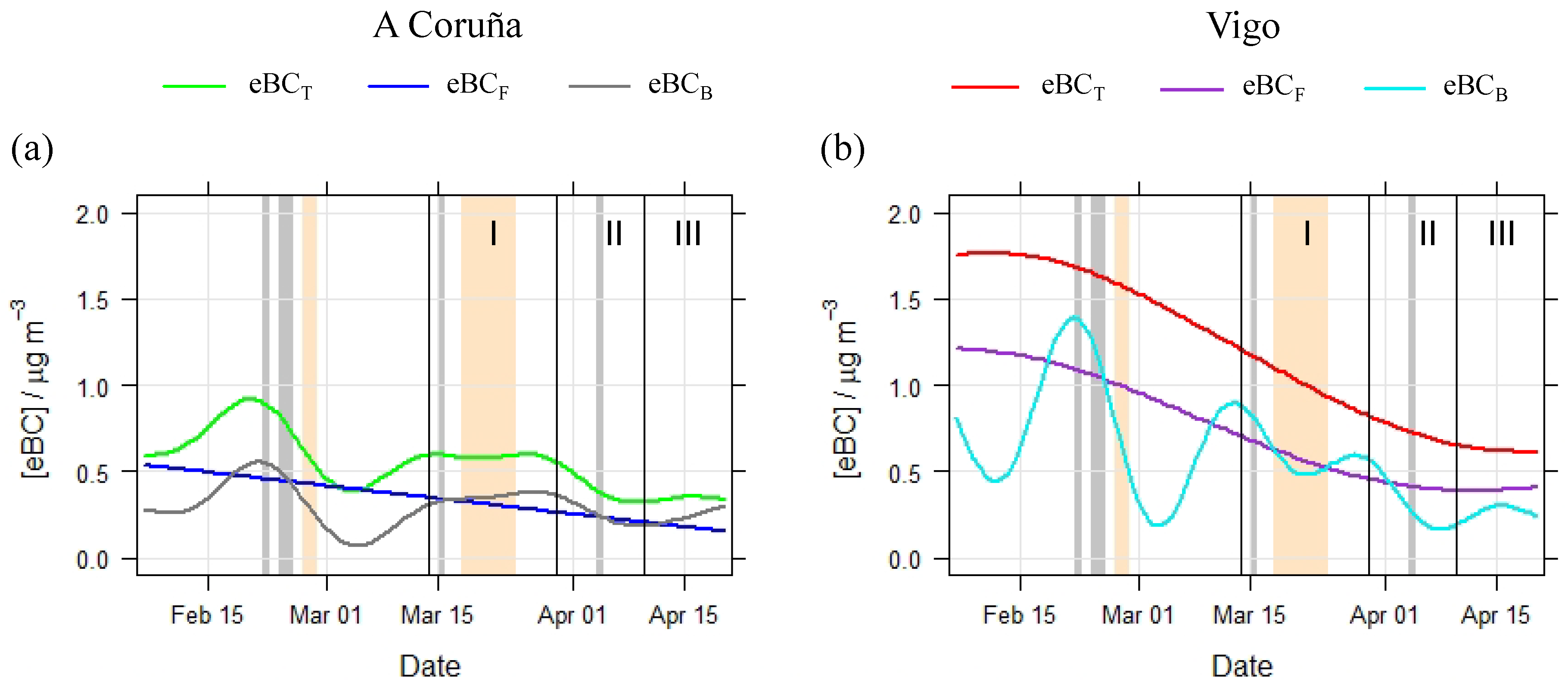
3.5. Decrease in eBC Levels during Lockdown Period
3.6. Meteorological Factors Affecting Pollutants Levels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Virtual Press Conference on COVID-19. 11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/transcripts/who-audio-emergencies-coronavirus-press-conference-full-and-final-11mar2020.pdf?sfvrsn=cb432bb3_2 (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Ministerio de la Presidencia, Relaciones con las Cortes y Memoria Democrática (MPRCMD). Real Decreto 463/2020 de 14 de marzo, por el que se Declara el Estado de Alarma para la Gestión de la Situación de Crisis Sanitaria Ocasionada por el COVID-19. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2020/03/14/463/con (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Ministerio de la Presidencia, Relaciones con las Cortes y Memoria Democrática (MPRCMD). Real Decreto-ley 10/2020, de 29 de marzo, por el que se Regula un Permiso Retribuido Recuperable para las Personas Trabajadoras por Cuenta Ajena que no Presten Servicios Esenciales, con el fin de Reducir la Movilidad de la Población en el Contexto de la Lucha Contra el COVID-19. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=BOE-A-2020-4166 (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Mitjà, O.; Arenas, À.; Rodó, X.; Tobias, A.; Brew, J.; Benlloch, J.M. Experts’ request to the Spanish Government: Move Spain towards complete lockdown. Lancet 2020, 395, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Massagué, J.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, T.; Gangoiti, G.; Mantilla, E.; Duéguez, J.J.; Escudero, M.; Monfort, E.; Pérez García-Pando, C.; et al. Lessons from the COVID-19 air pollution decrease in Spain: Now what? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcel-Carrasco, J.; Pascual-Guillamón, M.; Langa-Sanchis, J. Analysis of the effect of COVID-19 on air pollution: Perspective of the Spanish case. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Donzelli, G.; Cioni, L.; Cancellieri, M.; Llopis-Morales, A.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M. Relations between Air Quality and Covid-19 Lockdown Measures in Valencia, Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briz-Redon, A.; Belenguer-Sapina, C.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Changes in air pollution during COVID-19 lockdown in Spain: A multi-city study. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viteri, G.; Díaz de Mera, Y.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D.; Tajuelo, M.; Escalona, A.; Aranda, A. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 lockdown and de-escalation on air-quality parameters. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell-Marugán, J.; Villatoro-García, J.A.; García-Moreno, A.; López-Domínguez, R.; Requena, F.; Merelo, J.J.; Lacasaña, M.; de Dios Luna, J.; Díaz-Mochón, J.J.; Lorente, J.A.; et al. DatAC: A visual analytics platform to explore climate and air quality indicators associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangeliou, N.; Platt, S.M.; Eckhardt, S.; Myhre, C.L.; Laj, P.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Backman, J.; Brem, B.T.; Fiebig, M.; Flentje, H.; et al. Changes in black carbon emissions over Europe due to COVID-19 lockdowns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2675–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID-19 lockdown effects on air quality by NO2 in the cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobías, A.; Carnerero, C.; Reche, C.; Massagué, J.; Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Changes in air quality during the lockdown in Barcelona (Spain) one month into the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Shahzad, U.; Iqbal, N.; Shahzad, F.; Fareed, Z. Effects of climatological parameters on the outbreak spread of COVID-19 in highly affected regions of Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39657–39666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Sanchez-Alcalde, L. Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinello, S.; Lolli, F.; Gamberini, R. The Impact of the COVID-19 Emergency on Local Vehicular Traffic and It1s Consequences for the Environment: The Case of the City of Reggio Emilia (Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiriene, A.F.; Stasiskiene, Z. COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Bashir, O.; Bilal, M.; Ishaq, A.; Dar, M.U.D.; Kumar, R.; Bhat, R.A.; Sher, F. Impact of COVID-related lockdowns on environmental and climate change scenarios. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, S.K.; Lee, J.D.; Drysdale, W.S.; Lewis, A.C.; Hueglin, C.; Emmenegger, L.; Carslaw, D.C. COVID-19 lockdowns highlight a risk of increasing ozone pollution in European urban areas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 4169–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Statistics Institute (Spain) (INE). Available online: https://www.ine.es/index.htm (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- EN 14211:2013. Ambient Air—Standard Method for the Measurement of the Concentration of Nitrogen Dioxide and Nitrogen Monoxide by Chemiluminescence; The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- EN 14212:2013. Ambient Air—Standard Method for the Measurement of the Concentration of Sulphur Dioxide by Ultraviolet Fluorescence; The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- EN 14626:2013. Ambient Air—Standard Method for the Measurement of the Concentration of Carbon Monoxide by Non-Dispersive Infrared Spectroscopy; The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- EN 14625:2013. Ambient Air—Standard Method for the Measurement of the Concentration of Ozone by Ultraviolet Photometry; The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- EN 16450:2017. Ambient Air—Automated Measuring Systems for the Measurement of the Concentration of Particulate Matter (PM10; PM2.5); The British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). List of Designated Reference and Equivalent Methods. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-08/documents/designated_reference_and-equivalent_methods.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Petzold, A.; Schönlinner, M. Multi-angle absorption photometry—A new method for the measurement of aerosol light absorption and atmospheric black carbon. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkkula, A.; Ahlquist, N.C.; Covert, D.S.; Arnott, W.P.; Sheridan, P.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Coffman, D.J. Modification, Calibration and a Field Test of an Instrument for Measuring Light Absorption by Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, P.M.; Tremper, A.H.; Nicolosi, E.M.G.; Quincey, P.; Fuller, G.W. Estimating particulate black carbon concentrations using two offline light absorption methods applied to four types of filter media. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greilinger, M.; Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Kasper-Giebl, A. Evaluation of measurements of light transmission for the determination of black carbon on filters from different station types. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Recommendations for reporting black carbon measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealo, M.; Alastuey, A.; Ripoll, A.; Pérez, N.; Minguillón, M.C.; Querol, X.; Pandolfi, M. Detection of Saharan dust and biomass burning events using near real-time intensive aerosol optical properties in the northwestern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 12567–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concello da Coruña. Concello Sostenible, Calidad del Aire y Ruido en A Coruña. Available online: http://coruna.es/infoambiental/ (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Meteogalicia. Red Meteorológica de la Xunta de Galicia, Consellería de medio Ambiente, Territorio e Vivenda. Available online: https://www.meteogalicia.gal/observacion/estacions/estacions.action?request_locale=es# (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico (MTERD). Detección de Episodios Naturales de Aportes Transfronterizos de Partículas y Otras Fuentes de Contaminación de Material Particulado, y de Formación de Ozono Troposférico. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/calidad-y-evaluacion-ambiental/temas/atmosfera-y-calidad-del-aire/calidad-del-aire/evaluacion-datos/fuentes-naturales/Prediccion_episodios_2020.aspx (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An r package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. EU Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe; European Environment Agency: København, Denmark, 2008; Available online: https:/www.eur-lrx.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32008L0050 (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Xunta de Galicia. PM10 y PM2,5 en ES1219: Área Metropolitana de A Coruña en 2016 y la Influencia del Aerosol Marino. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/images/es/informe_aerosol_marino_coruna_2016_tcm30-481954.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide—Global Update 2005. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/environment-and-health/air-quality/publications/pre2009/air-quality-guidelines.-global-update-2005.-particulate-matter,-ozone,-nitrogen-dioxide-and-sulfur-dioxide (accessed on 22 May 2020).
| Site | Code | Longitude | Latitude | Monitored Pollutants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Background and Traffic Monitoring Stations | ||||
| A Coruña-Torre | AC-T | 08°24′33″ W | 43°22′58″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, CO, O3, PM10, PM2.5 |
| A Coruña-Liáns | AC-L | 08°21′09″ W | 43°20′12″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, O3, PM10, eBC |
| Vigo-Coia | V-C | 08°44′31″ W | 42°13′08″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, CO, O3, PM10, PM2.5, eBC |
| Vigo-Lope | V-L | 08°42′40″ W | 42°13′21″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, CO, O3, PM10 |
| Industrial Monitoring Stations | ||||
| A Coruña-Grela | AC-G | 08°26′03″ W | 43°20′43″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, PM10, PM2.5 |
| Vigo-PSAE | V-PSAE | 08°44′13″ W | 42°12′37″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, PM2.5 |
| Vigo-PSAW | V-PSAW | 08°44′49″ W | 42°12′10″ N | NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, O3, PM10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Sánchez-Piñero, J.; Fernández-Amado, M.; Costa-Tomé, P.; Gallego-Fernández, N.; Piñeiro-Iglesias, M.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Evolution of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in the Air: What Changed after Five Lockdown Weeks at a Southwest Atlantic European Region (Northwest of Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic? Atmosphere 2021, 12, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050562
Moreda-Piñeiro J, Sánchez-Piñero J, Fernández-Amado M, Costa-Tomé P, Gallego-Fernández N, Piñeiro-Iglesias M, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S. Evolution of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in the Air: What Changed after Five Lockdown Weeks at a Southwest Atlantic European Region (Northwest of Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic? Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050562
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreda-Piñeiro, Jorge, Joel Sánchez-Piñero, María Fernández-Amado, Paula Costa-Tomé, Nuria Gallego-Fernández, María Piñeiro-Iglesias, Purificación López-Mahía, and Soledad Muniategui-Lorenzo. 2021. "Evolution of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in the Air: What Changed after Five Lockdown Weeks at a Southwest Atlantic European Region (Northwest of Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic?" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050562
APA StyleMoreda-Piñeiro, J., Sánchez-Piñero, J., Fernández-Amado, M., Costa-Tomé, P., Gallego-Fernández, N., Piñeiro-Iglesias, M., López-Mahía, P., & Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. (2021). Evolution of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in the Air: What Changed after Five Lockdown Weeks at a Southwest Atlantic European Region (Northwest of Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic? Atmosphere, 12(5), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050562






