Modulated Responses of East Asian Winter Climate to Anthropogenic Aerosols by Urban Cover in Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Data and Model Simulations
2.2. Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Aerosol Column Burdens and the Modulating Role of Urban Cover
3.2. Responses of East Asian Winter Climate
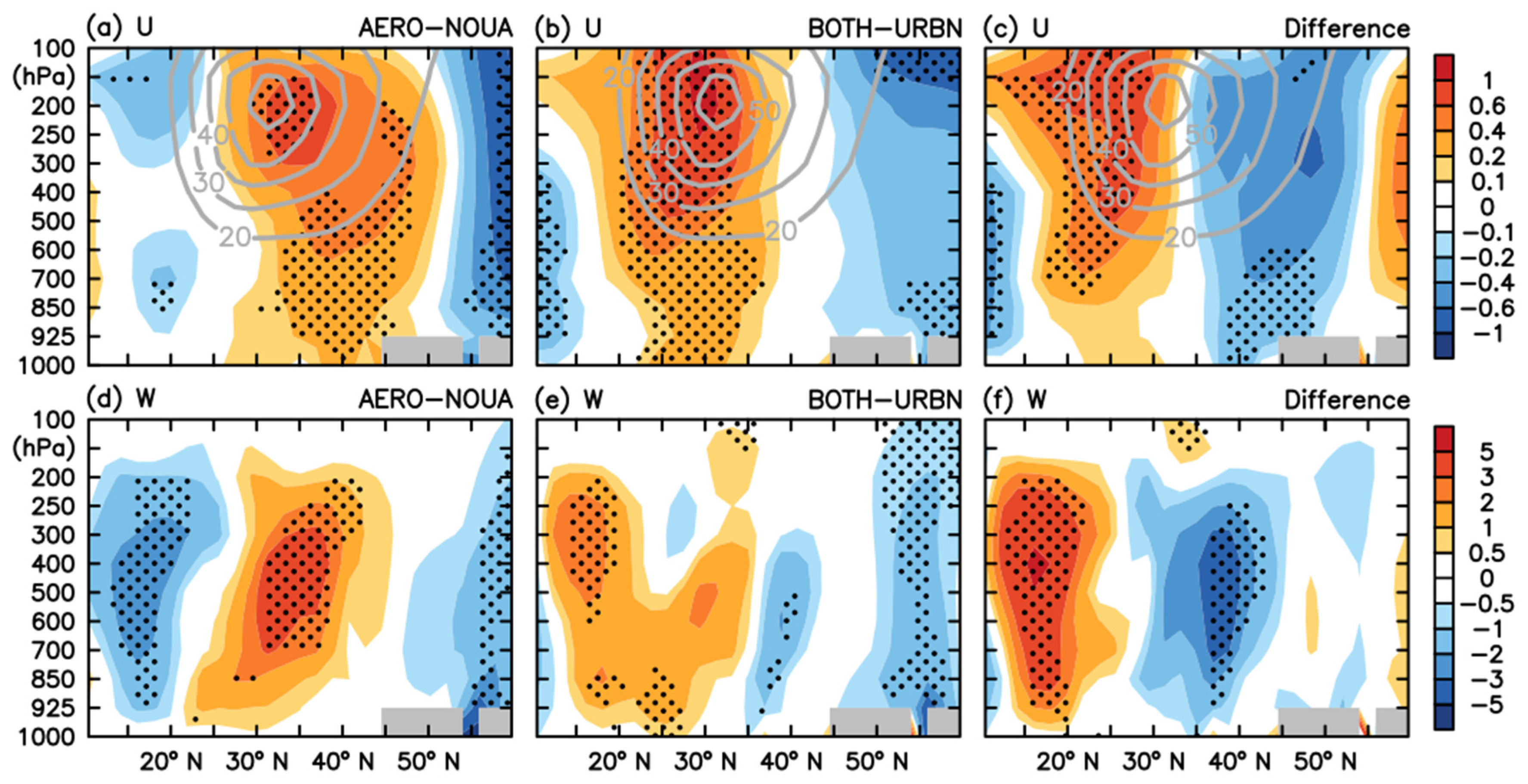
3.2.1. Atmospheric Circulation
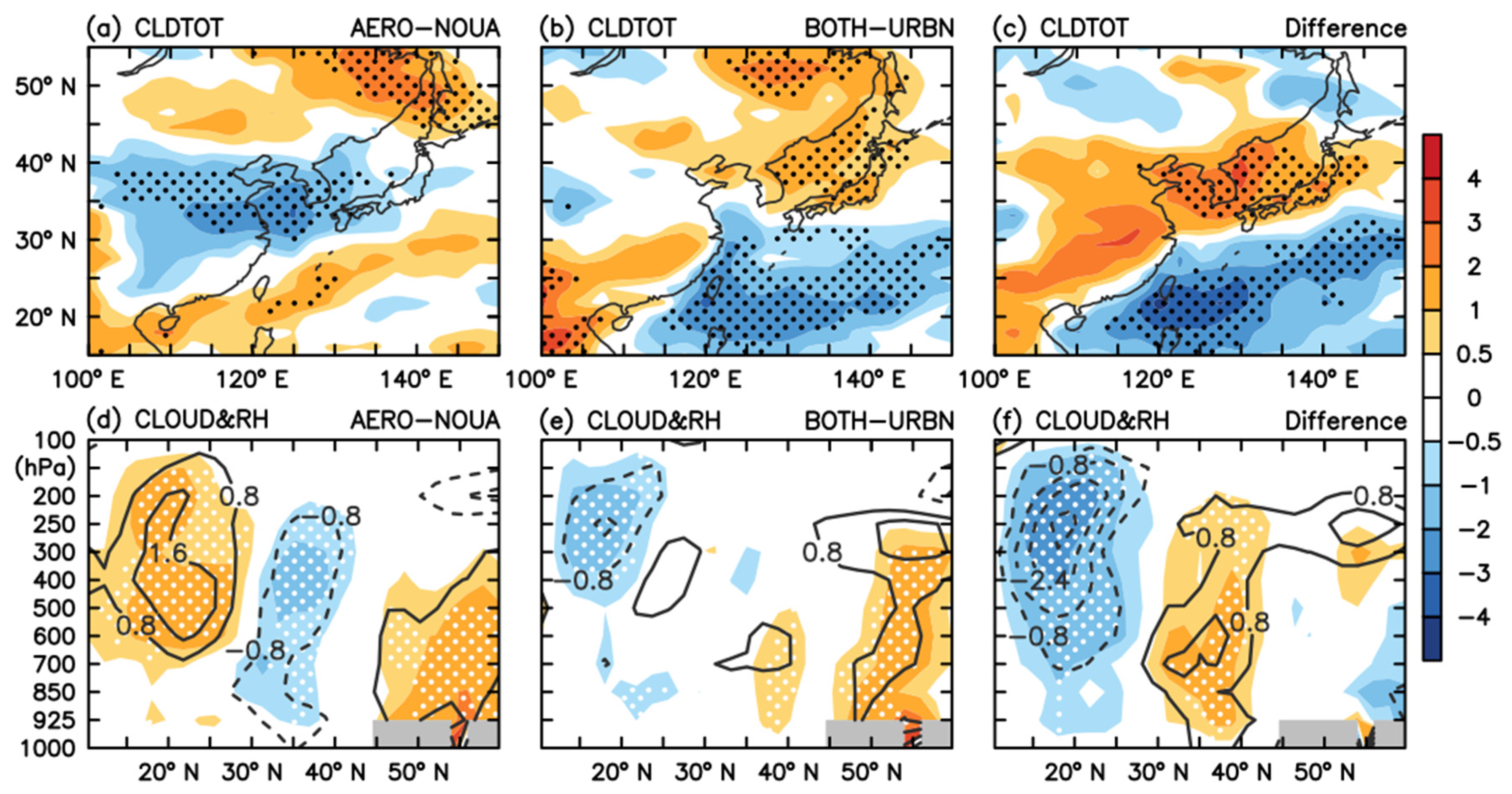
3.2.2. Cloud Properties and Surface Radiation Budget
3.2.3. Air Temperature
3.2.4. Precipitation
4. Summary and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Qian, Y. Indirect vs. Direct Effects of Anthropogenic Sulfate on the Climate of East Asia as Simulated with a Regional Coupled Climate-chemistry/Aerosols Model. Clim. Chang. 2003, 58, 345–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G. Consistency between Satellite-derived and Modeled Estimates of the Aerosol Effect. Science 2009, 325, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The Influence of Pollution on the Shortwave Albedo of Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B. Aerosols, Cloud Microphysics, and Fractional Cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, Y.; Ramaswamy, V. A Model Investigation of Aerosol-induced Changes in Tropical Circulation. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5125–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, Q. Comparison of Climate Response to Anthropogenic Aerosol vs. Greenhouse Gas Forcing: Distinct Patterns. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 5175–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ming, Y. The Influence of Aerosol Absorption on the Extratropical Circulation. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 5961–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dai, A.; Xu, H. Nonlinear Climate Responses to Increasing CO2 and Anthropogenic Aerosols Simulated by CESM1. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, B. The Effects of Black Carbon and Sulphate Aerosols in China Regions on East Asia Monsoons. Tellus B 2009, 61, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, M. A Numerical Study of the Effect of Different Aerosol Types on East Asian Summer Clouds and Precipitation. Atmos. Res. 2013, 70, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, I.B.; Ramaswamy, V.; Ming, Y. Contrasting Climate Responses to the Scattering and Absorbing Features of Anthropogenic Aerosol Forcings. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5329–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Chin, M.; Kim, K.M.; Sud, Y.C.; Walker, G.K. Atmospheric Teleconnection over Eurasia Induced by Aerosol Radiative Forcing during Boreal Spring. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4700–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Ramaswamy, V.; Chen, G. A Model Investigation of Aerosol Induced Changes in Boreal Winter Extratropical Circulation. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 6077–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, D.; Rasch, P.J.; Wang, H.L.; Yoon, J. Fast and Slow Responses of the South Asian Monsoon System to Anthropogenic Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L18804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.P.; Kosaka, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y. Dynamics of Asian summer monsoon response to anthropogenic aerosol forcing. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhou, T.; Qian, Y. Responses of East Asian Summer Monsoon to Natural and Anthropogenic Forcings in the 17 Latest CMIP5 Models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, W.S. A GCM Study of Effects of Radiative Forcing of Sulfate Aerosol on Large Scale Circulation and Rainfall in East Asia during Boreal Spring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L24701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H.; Ma, H.; Jiang, Z. Numerical Study of the Effect of Anthropogenic Aerosols on Spring Persistent Rain over Eastern China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J. Interdecadal Weakening of the East Asian Winter Monsoon in the Mid-1980s: The Roles of External Forcings. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8985–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Han, T. Quantifying the Contribution of Anthropogenic Influence to the East Asian Winter Monsoon in 1960–2012. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9903–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Sun, X.; Wang, M.; Ding, A.; Wang, T.; Fu, C. Anthropogenic Aerosol Effects on East Asian Winter Monsoon: The Role of Black Carbon-induced Tibetan Plateau Warming. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5883–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, P.L.; Li, M.M.; Xie, M. Interaction between the Black Carbon Aerosol Warming Effect and East Asian Monsoon Using RegCM4. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 9367–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ming, Y.; Wang, L.; Bollasina, M.; Luo, M.; Lau, N.C.; Yim, S.H.L. A Model Investigation of Aerosol-induced Changes in the East Asian Winter Monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10186–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Smith, S.J.; Qian, Y.; Rasch, P.J. Black Carbon Amplifies Haze over the North China Plain by Weakening the East Asian Winter Monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of Urbanization and Land-use Change on Climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chu, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, A.; Guo, J.; Liu, X. Urbanization Effects on Observed Surface Air Temperature Trends in North China. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Hou, Y.L.; Chen, B.D. Observed Surface Warming Induced by Urbanization in East China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Zhang, Y. Sensitivity Experiments of Impacts of Large-scale Urbanization in East China on East Asian Winter Monsoon. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Song, J.; Ma, H. Sensitivity of the East Asian Summer Monsoon Circulation and Precipitation to an Idealized Large-scale Urban Expansion. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 91, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H. Atmospheric Responses to Idealized Urban Land Surface Forcing in Eastern China during the Boreal Spring. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10022–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Jiang, Z.; Song, J.; Dai, A.; Yang, X.; Fei, H. Effects of Urban Land-use Change in East China on the East Asian Summer Monsoon Based on the CAM5.1 Model. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Hua, W.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Gao, C. Large-scale Urbanization Effects on Eastern Asian Summer Monsoon Circulation and Climate. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.K.; Liou, Y.-A. Influence of Land Use and Land Cover Change on the Formation of Local Lightning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Yang, X.Q. A Case Study of Urbanization Impact on Summer Precipitation in the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area: Urban Heat Island vs. Aerosol Effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10903–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Fan, J.; Yan, H.; Yang, X.Q. Urbanization-induced Urban Heat Island and Aerosol Effects on Climate Extremes in the Yangtze River Delta Region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5439–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, C.; Tripathi, S.N.; Qian, Y.; Kumar, S.; Leung, L.R. Aerosol and Urban Land Use Effect on Rainfall Around Cities in Indo-Gangetic Basin from Observations and Cloud Resolving Model Simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3645–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Rosenfeld, D. Urbanization-induced Land and Aerosol Impacts on Sea-breeze Circulation and Convective Precipitation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14163–14182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huo, F.; Ma, H.; Song, J.; Dai, A. Impact of Chinese Urbanization and Aerosol Emissions on the East Asian Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H. Nonlinear Effect on the East Asian Summer Monsoon Due to Two Coexisting Anthropogenic Forcing Factors in Eastern China: An AGCM Study. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 3767–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Nonlinear Effects of Anthropogenic Aerosol and Urban Land Surface Forcing on Spring Climate in Eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4581–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neale, R.B.; Chen, C.-C.; Gettelman, A.; Lauritzen, P.H.; Park, S.; Williamson, D.L.; Conley, A.J.; Garcia, R.; Kinnison, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. Description of the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM5.0). NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN-4861STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CL, USA, 2012; p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Oleson, K.W.; Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Thornton, P.E.; Lawrence, P.J.; Stöckli, R.; Dickinson, R.E.; Bonan, G.B.; Levis, S.; et al. Improvements to the Community Land Model and Their Impact on the Hydrological Cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, G01021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, J.W.; Holland, M.M.; Gent, P.R.; Ghan, S.; Kay, J.E.; Kushner, P.J.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Large, W.G.; Lawrence, D.; Lindsay, K.; et al. The Community Earth System Model: A Framework for Collaborative Research. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2013, 94, 1339–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Easter, R.C.; Ghan, S.J.; Zaveri, R.; Rasch, P.; Shi, X.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Gettelman, A.; Morrison, H.; Vitt, F.; et al. Toward a Minimal Representation of Aerosols in Climate Models: Description and Evaluation in the Community Atmosphere Model CAM5. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 709–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettelman, A.; Liu, X.; Ghan, S.J.; Morrison, H.; Park, S.; Conley, A.J.; Klein, S.A.; Boyle, J.; Mitchell, D.L.; Li, J.-L.F.; et al. Global Simulations of Ice Nucleation and Ice Supersaturation with an Improved Cloud Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D18216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Razzak, H.; Ghan, S.J. A Parameterization of Aerosol Activation: 2. Multiple Aerosol Types. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 6837–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Penner, J.E.; Ghan, S.J.; Wang, M. Inclusion of Ice Microphysics in the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model Version 3 (CAM3). J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4526–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, J.F.; Bond, T.C.; Eyring, V.; Granier, C.; Heil, A.; Klimont, Z.; Lee, D.; Liousse, C.; Mieville, A.; Owen, B.; et al. Historical (1850–2000) Gridded Anthropogenic and Biomass Burning Emissions of Reactive Gases and Aerosols: Methodology and Application. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7017–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.E.; Bright, E.A.; Coleman, P.R.; Durfee, R.C.; Worley, B.A. LandScan: A Global Population Database for Estimating Populations at Risk. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.L.; Feddema, J.J.; Oleson, K.W.; Bonan, G.B.; Bauer, J.T. Parameterization of Urban Characteristics for Global Climate Modeling. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2010, 100, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Beckert, J.C.; Reilly, T.H.; Bruegge, C.J.; Conel, J.E.; Kahn, R.A.; Martonchik, J.V.; Ackerman, T.P.; Davies, R.; Gerstl, S.A.W.; et al. Multi-angle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) Instrument Description and Experiment Overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Liu, X. Seasonality in Anthropogenic Aerosol Effects on East Asian Climate Simulated with CAM5. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10837–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, M.; Lu, Z.; Wu, C.; Murphy, S.; Pokhrel, R. Radiative Effect and Climate Impacts of Brown Carbon with the Community Atmosphere Model (CAM5). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17745–17768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Liu, X.; Pokhrel, R.; Murphy, S.; Lu, Z.; Saleh, R.; Mielonen, T.; Kokkola, H.; Bergman, T.; Myhre, G.; et al. Biomass Burning Aerosols in Most Climate Models are too Absorbing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavelle, F.F.; Haywood, J.M.; Field, P.R.; Hill, A.A.; Abel, S.J.; Lock, A.P.; Shipway, B.J.; McBeath, K. A Method to Represent Subgrid-scale Updraft Velocity in Kilometer-scale Models: Implication for Aerosol Activation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4149–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, H. Relationship between Middle Stratiform Clouds and Large-scale Circulation over Eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L09706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Christensen, M.W.; Stephens, G.L.; Seinfeld, J.H. Satellite-based Estimate of Global Aerosol–cloud Radiative Forcing by Marine Warm Clouds. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryspeerdt, E.; Goren, T.; Sourdeval, O.; Quaas, J.; Mülmenstädt, J.; Dipu, S.; Unglaub, C.; Gettelman, A.; Christensen, M. Constraining the Aerosol Influence on Cloud Liquid Water Path. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5331–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Impact of Anthropogenic Aerosols from Global, East Asian, and Non-East Asian Sources on East Asian Summer Monsoon System. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhou, W.; Huang, R. Interannual Variations of East Asian trough Axis at 500 hPa and Its Association with the East Asian Winter Monsoon Pathway. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Fan, J.; Wu, D.L.; Molina, M.J. Intensification of Pacific Storm Track Linked to Asian Pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5295–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Ghan, S.J.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Pan, B.; Levy, M.; Jiang, J.H.; Molina, M. Assessing the Effects of Anthropogenic Aerosols on Pacific Storm Track Using a Multiscale Global Climate Model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6894–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Bréon, F.M. Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 659–740. [Google Scholar]










| Signal | AOD × 100 | SO4 Burden | BC Burden | POM Burden |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AERO−NOUA | 5.14 (79.72%) | 4.02 (156.22%) | 0.88 (402.53%) | 2.34 (180.14%) |
| BOTH−URBN | 5.15 (79.88%) | 4.09 (159.03%) | 0.87 (399.62%) | 2.31 (177.94%) |
| Difference | 0.01 (0.16%) | 0.07 (2.81%) | −0.01 (−2.87%) | −0.03 (−2.20%) |
| Signal | CCN0.1 | CDNC | Reff | LTS | RH700 | LWP | SWCF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AERO−NOUA | 155.13 | 5.42 | −0.22 | 0.26 | −0.46 | 23.42 | −2.64 |
| BOTH−URBN | 158.20 | 5.91 | −0.16 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 28.35 | −4.06 |
| Difference | 3.07 | 0.49 | 0.06 | −0.07 | 1.20 | 4.93 | −1.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Chyi, D. Modulated Responses of East Asian Winter Climate to Anthropogenic Aerosols by Urban Cover in Eastern China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040471
Deng J, Zhang L, Ma J, Chyi D. Modulated Responses of East Asian Winter Climate to Anthropogenic Aerosols by Urban Cover in Eastern China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(4):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040471
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Jiechun, Leying Zhang, Jing Ma, and Dorina Chyi. 2021. "Modulated Responses of East Asian Winter Climate to Anthropogenic Aerosols by Urban Cover in Eastern China" Atmosphere 12, no. 4: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040471
APA StyleDeng, J., Zhang, L., Ma, J., & Chyi, D. (2021). Modulated Responses of East Asian Winter Climate to Anthropogenic Aerosols by Urban Cover in Eastern China. Atmosphere, 12(4), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040471






