Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
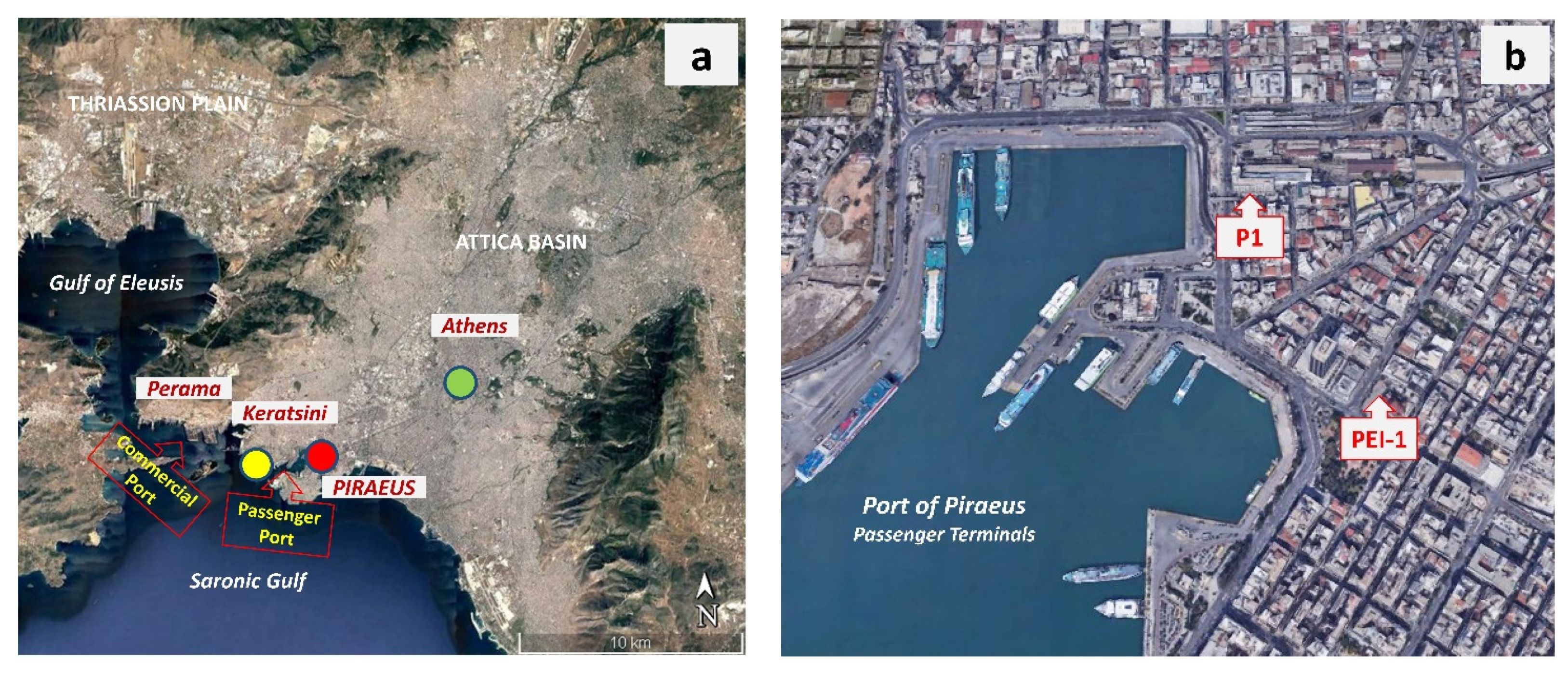
2.1. Study Area and Measurement Site
2.2. Online Measurements
2.3. Offline Measurements and Auxiliary Data
2.4. Source Apportionment of Organic Aerosol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of ACSM Data with Filter-Based Analyses
3.2. Composition of Submicron Aerosol and Black Carbon
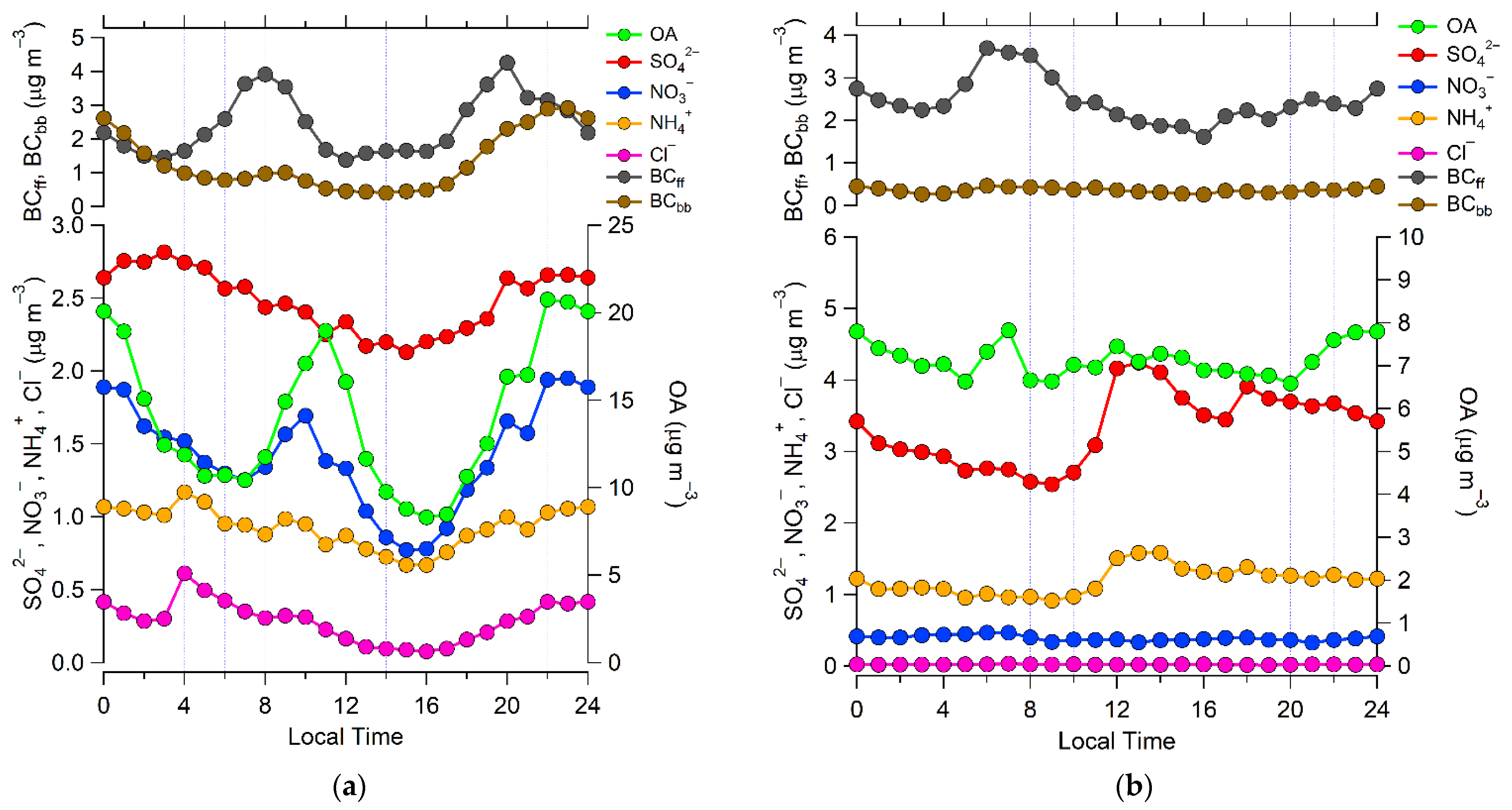
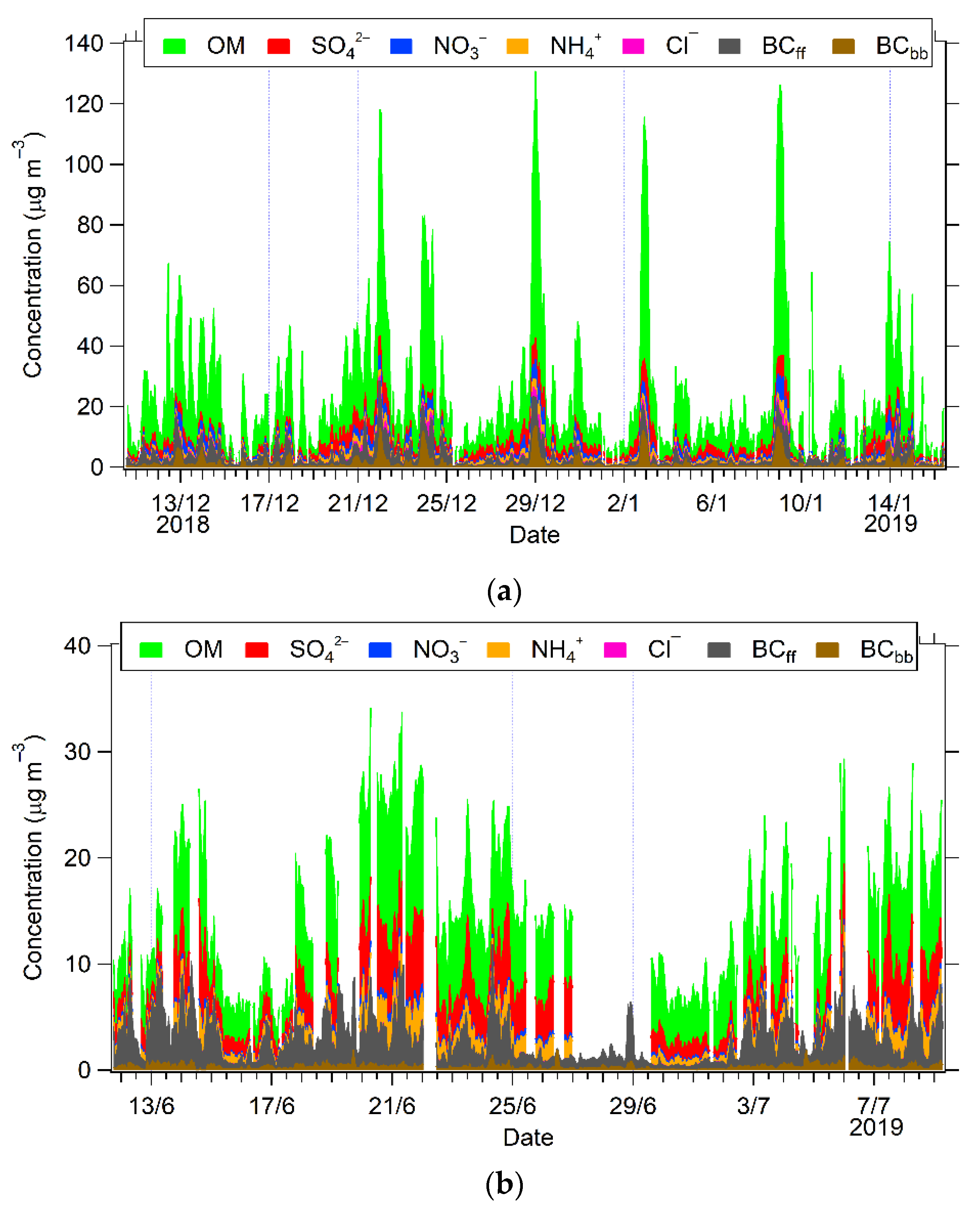
3.2.1. Winter Period
3.2.2. Summer Period
3.3. Sources of Organic Aerosol
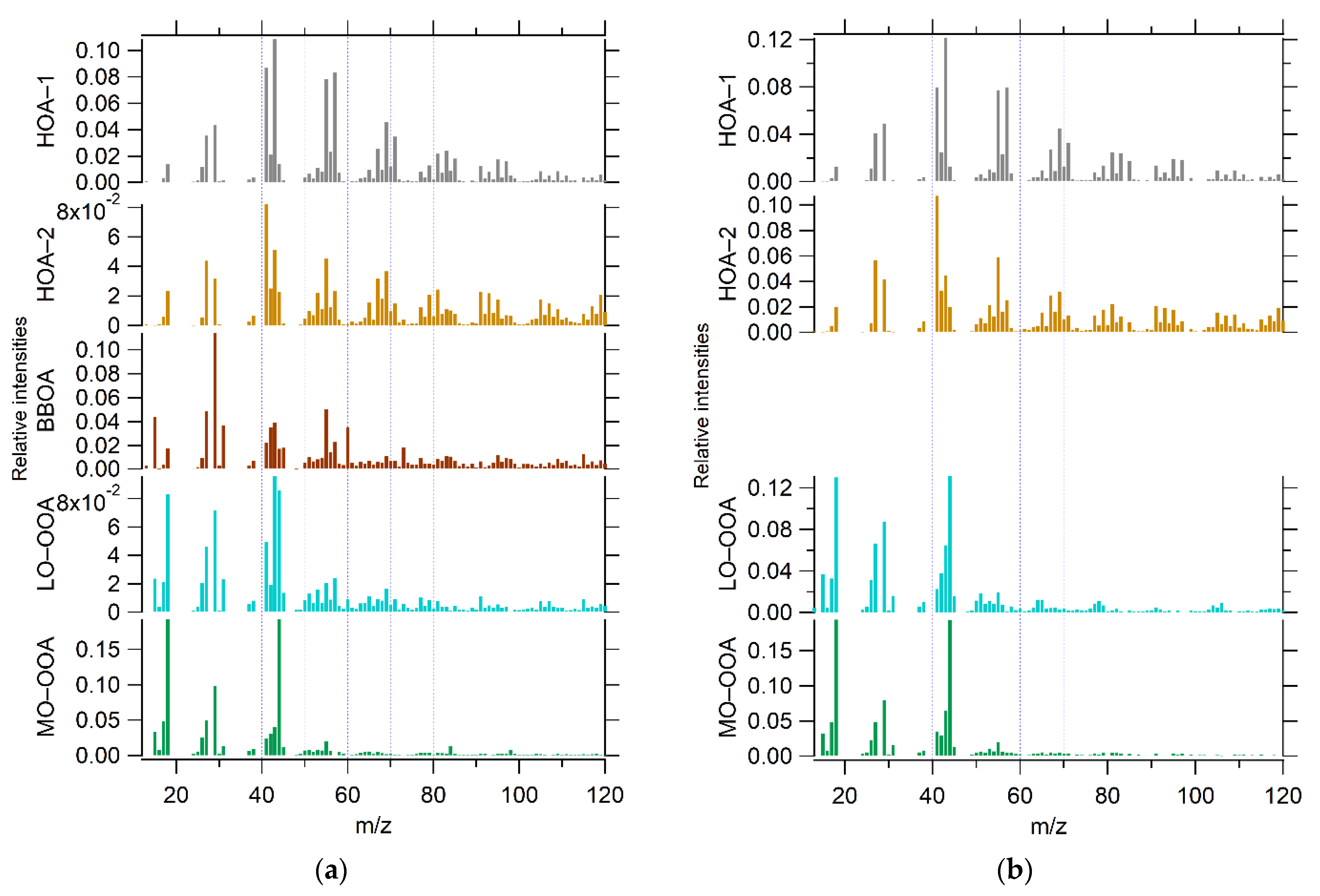
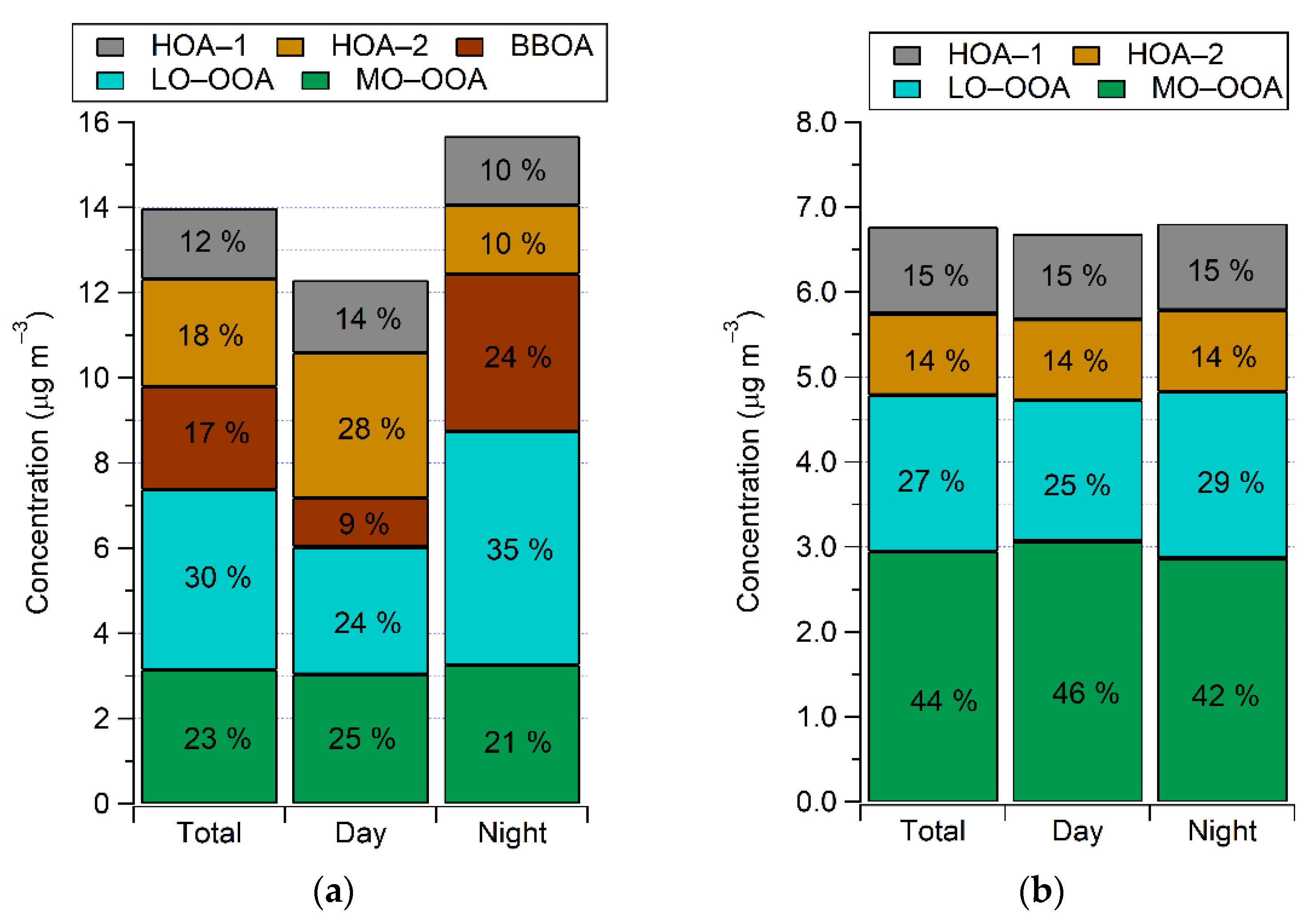
3.3.1. Winter Period
3.3.2. Summer Period
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, R.W.; Kang, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Mills, I.C.; Walton, H.A. Epidemiological time series studies of PM2.5 and daily mortality and hospital admissions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2014, 69, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zanobetti, A.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Choirat, C.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Air pollution and mortality in the medicare population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Air Quality in Europe—2020 Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2020; ISBN 978-92-9480-292-7.
- Hammer, M.S.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Li, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Garay, M.J.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Kahn, R.A.; et al. Global Estimates and Long-Term Trends of Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations (1998–2018). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7879–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, M.; Chen, L.C.; Gordon, T.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G. National Particle Component Toxicity (NPACT) Initiative: Integrated epidemiologic and toxicologic studies of the health effects of particulate matter components. Res. Rep. Health. Eff. Inst. 2013, 177, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Basagaña, X.; Jacquemin, B.; Karanasiou, A.; Ostro, B.; Querol, X.; Agis, D.; Alessandrini, E.; Alguacil, J.; Artiñano, B.; Catrambone, M.; et al. Short-term effects of particulate matter constituents on daily hospitalizations and mortality in five South-European cities: Results from the MED-PARTICLES project. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Dutton, S.J.; Sheppard, L.; Hannigan, M.P.; Miller, S.L.; Milford, J.B.; Peel, J.L.; Vedal, S. The short-term association of selected components of fine particulate matter and mortality in the Denver Aerosol Sources and Health (DASH) study. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2015, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostro, B.; Malig, B.; Hasheminassab, S.; Berger, K.; Chang, E.; Sioutas, C. Associations of Source-Specific Fine Particulate Matter with Emergency Department Visits in California. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 184, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirbek, I.; Wheeler, K.; Walters, S.; Kass, D.; Matte, T. PM2.5 and ozone health impacts and disparities in New York City: Sensitivity to spatial and temporal resolution. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martenies, S.E.; Milando, C.W.; Williams, G.O.; Batterman, S.A. Disease and Health Inequalities Attributable to Air Pollutant Exposure in Detroit, Michigan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burwell-Naney, K.; Wilson, S.M.; Tarver, S.L.; Svendsen, E.; Jiang, C.; Ogunsakin, O.A.; Zhang, H.; Campbell, D.; Fraser-Rahim, H. Baseline Air Quality Assessment of Goods Movement Activities before the Port of Charleston Expansion: A Community-University Collaborative. Environ. Justice 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenbaum, A.; Hartley, S.; Holder, C. Analysis of Diesel Particulate Matter Health Risk Disparities in Selected US Harbor Areas. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, S217–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.; Krudysz, M.; Winer, A. Diesel Truck Traffic in Low-Income and Minority Communities Adjacent to Ports: Environmental Justice Implications of Near-Roadway Land Use Conflicts. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008, 2067, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredrickson, A. The California Coastal Act and Ports: The Unintended Environmental Justice Implications of Preserving California’s Coastline. Coast. Manage. 2013, 41, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; Vlieger, I.D.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of maritime transport emissions on coastal air quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donateo, A.; Gregoris, E.; Gambaro, A.; Merico, E.; Giua, R.; Nocioni, A.; Contini, D. Contribution of harbour activities and ship traffic to PM2.5, particle number concentrations and PAHs in a port city of the Mediterranean Sea (Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9415–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merico, E.; Conte, M.; Grasso, F.M.; Cesari, D.; Gambaro, A.; Morabito, E.; Gregoris, E.; Orlando, S.; Alebić-Juretić, A.; Zubak, V.; et al. Comparison of the impact of ships to size-segregated particle concentrations in two harbour cities of northern Adriatic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Cheristanidis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Mihalopoulos, N. Elemental Composition and Source Apportionment of Fine and Coarse Particles at Traffic and Urban Background Locations in Athens, Greece. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorte, S.; Rodrigues, V.; Borrego, C.; Monteiro, A. Impact of harbour activities on local air quality: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merico, E.; Cesari, D.; Gregoris, E.; Gambaro, A.; Cordella, M.; Contini, D. Shipping and Air Quality in Italian Port Cities: State-of-the-Art Analysis of Available Results of Estimated Impacts. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbra, R.M.; Wooldridge, C.; Puig, M. ESPO Environmental Report 2020 EcoPortsinSights 2020; ESPO: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Tzannatos, E. Ship emissions and their externalities for the port of Piraeus-Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Bougiatioti, A.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Measuring the spatial variability of black carbon in Athens during wintertime. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Grivas, G.; Borge, R.; Lumbreras, J. Study of PM10 and PM2.5 levels in three European cities: Analysis of intra and inter urban variations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodosi, C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Lianou, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Multi-year chemical composition of the fine-aerosol fraction in Athens, Greece, with emphasis on the contribution of residential heating in wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14371–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Dumka, U.C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; et al. Long-term variability, source apportionment and spectral properties of black carbon at an urban background site in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Chaloulakou, A.; Kassomenos, P. An overview of the PM10 pollution problem, in the Metropolitan Area of Athens, Greece. Assessment of controlling factors and potential impact of long range transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.; Vardoulakis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Grivas, G.; Borge, R.; Lumbreras, J. Levels, sources and seasonality of coarse particles (PM10–PM2.5) in three European capitals-Implications for particulate pollution control. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomaidis, N.S.; Bakeas, E.B.; Siskos, P.A. Characterization of lead, cadmium, arsenic and nickel in PM2.5 particles in the Athens atmosphere, Greece. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskos, P.A.; Bakeas, E.B.; Lioli, I.; Smirnioudi, V.N.; Koutrakis, P. Chemical characterization of PM2.5 Aerosols in Athens-Greece. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, M.; Gonzalez-Castanedo, Y.; Alastuey, A.; de la Rosa, J.D.; Mantilla, E.; de la Campa, A.S.; Querol, X.; Pey, J.; Amato, F.; Moreno, T. Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 at multiple sites in the strait of Gibraltar by PMF: Impact of shipping emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, N.; Pey, J.; Reche, C.; Cortés, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Impact of harbour emissions on ambient PM10 and PM2.5 in Barcelona (Spain): Evidences of secondary aerosol formation within the urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, D.; Genga, A.; Ielpo, P.; Siciliano, M.; Mascolo, G.; Grasso, F.M.; Contini, D. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in the harbour–industrial area of Brindisi (Italy): Identification and estimation of the contribution of in-port ship emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.; Decarlo, P.F.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Slowik, J.G.; Richter, R.; Reche, C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Seco, R.; et al. Identification and quantification of organic aerosol from cooking and other sources in Barcelona using aerosol mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chazeau, B.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Gille, G.; Mesbah, B.; D’Anna, B.; Wortham, H.; Marchand, N. Measurement report: Fourteen months of real-time characterisation of the submicronic aerosol and its atmospheric dynamics at the Marseille-Longchamp supersite. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7293–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Brook, J.R.; Rami Alfarra, M.; Anlauf, K.; Richard Leaitch, W.; Sharma, S.; Wang, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Phinney, L. Identification and characterization of inland ship plumes over Vancouver, BC. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2767–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Hellebust, S.; Healy, R.M.; Connor, I.P.; Kourtchev, I.; Sodeau, J.R.; Ovadnevaite, J.; Ceburnis, D.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Wenger, J.C. Apportionment of urban aerosol sources in Cork (Ireland) by synergistic measurement techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, B.C.; Wallace, H.W.; Bui, A.T.; Flynn, J.H.; Erickson, M.H.; Alvarez, S.; Dai, Q.; Usenko, S.; Sheesley, R.J.; Griffin, R.J. The impacts of regional shipping emissions on the chemical characteristics of coastal submicron aerosols near Houston, TX. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14217–14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Naiema, I.M.; Hettiyadura, A.P.S.; Wallace, H.W.; Sanchez, N.P.; Madler, C.J.; Karakurt Cevik, B.; Bui, A.A.T.; Kettler, J.; Griffin, R.J.; Stone, E.A. Source apportionment of fine particulate matter in Houston, Texas: Insights to secondary organic aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15601–15622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.U.; Robinson, E.S.; Gu, P.; Robinson, A.L.; Apte, J.S.; Presto, A.A. High-spatial-resolution mapping and source apportionment of aerosol composition in Oakland, California, using mobile aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16325–16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manalis, N.; Grivas, G.; Protonotarios, V.; Moutsatsou, A.; Samara, C.; Chaloulakou, A. Toxic metal content of particulate matter (PM10), within the Greater Area of Athens. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallos, G.; Kassomenos, P.; Pielke, R.A. Synoptic and mesoscale weather conditions during air pollution episodes in Athens, Greece. Bound. -Layer Meteorol. 1993, 62, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.; Flocas, H.A.; Lykoudis, S.; Petrakis, M. Analysis of Mesoscale Patterns in Relation to Synoptic Conditionsover an Urban Mediterranean Basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1998, 59, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S.; Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Maggos, T.; Vasilakos, C. Particulate matter levels in a suburban Mediterranean area: Analysis of a 53-month long experimental campaign. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.S.K.; Deng, R.; Smith, K.A.; Williams, L.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Moore, K.; Onasch, T.B.; Worsnop, D.R.; Deshler, T. Transmission Efficiency of an Aerodynamic Focusing Lens System: Comparison of Model Calculations and Laboratory Measurements for the Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrook, A.M.; Bahreini, R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R. Evaluation of Composition-Dependent Collection Efficiencies for the Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer using Field Data. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freney, E.; Zhang, Y.; Croteau, P.; Amodeo, T.; Williams, L.; Truong, F.; Petit, J.-E.; Sciare, J.; Sarda-Esteve, R.; Bonnaire, N.; et al. The second ACTRIS inter-comparison (2016) for Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitors (ACSM): Calibration protocols and instrument performance evaluations. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.L.; Herndon, S.C.; Trimborn, A.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Croteau, P.L.; Onasch, T.B.; Sueper, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. An Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) for Routine Monitoring of the Composition and Mass Concentrations of Ambient Aerosol. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources and processes that control the submicron organic aerosol composition in an urban Mediterranean environment (Athens): A high temporal-resolution chemical composition measurement study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weingartner, E.; Saathoff, H.; Schnaiter, M.; Streit, N.; Bitnar, B.; Baltensperger, U. Absorption of light by soot particles: Determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, J.R.; Jaffe, D.A.; Sedlacek, A.J. Comparison of Filter-based Absorption Measurements of Biomass Burning Aerosol and Background Aerosol at the Mt. Bachelor Observatory. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Lanz, V.A.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using Aerosol Light Absorption Measurements for the Quantitative Determination of Wood Burning and Traffic Emission Contributions to Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D. Impact of brown and clear carbon on light absorption enhancement, single scatter albedo and absorption wavelength dependence of black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4207–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, T.; Ni, H.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Characterization of the light-Absorbing properties, chromophore composition and sources of brown carbon aerosol in Xi’an, northwestern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5129–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, T.A.; Ramachandran, S.; Dhaker, V.K. Black carbon aerosols: Relative source strengths of vehicular emissions and residential/open wood burning over an urban and a semi-urban environment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Liakakou, E.; Dumka, U.C.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Apportionment of black and brown carbon spectral absorption sources in the urban environment of Athens, Greece, during winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J.P. Toward a standardised thermal-optical protocol for measuring atmospheric organic and elemental carbon: The EUSAAR protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Theodosi, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Long-term characterization of organic and elemental carbon in the PM2.5 fraction: The case of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13313–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Doraiswamy, P.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Park, K.; Arnott, W.P.; Motallebi, N. Aerosol light absorption, black carbon, and elemental carbon at the Fresno Supersite, California. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A.-P.; Kolmonen, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Virkkula, A.; Leskinen, A.; Komppula, M.; Hatakka, J.; Burkhart, J.; Stohl, A.; Aalto, P.; et al. Aerosol black carbon at five background measurement sites over Finland, a gateway to the Arctic. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Sciare, J.; Crenn, V.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Bonnaire, N.; Močnik, G.; Dupont, J.C.; Haeffelin, M.; Leoz-Garziandia, E. Two years of near real-time chemical composition of submicron aerosols in the region of Paris using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) and a multi-wavelength Aethalometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2985–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uria-Tellaetxe, I.; Carslaw, D.C. Conditional bivariate probability function for source identification. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. Aerosol contributions at an urban background site in Eastern Mediterranean–Potential source regions of PAHs in PM10 mass. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Albinet, A.; Canonaco, F. A user-friendly tool for comprehensive evaluation of the geographical origins of atmospheric pollution: Wind and trajectory analyses. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 88, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paatero, P. The Multilinear Engine—A Table-Driven, Least Squares Program for Solving Multilinear Problems, Including the n-Way Parallel Factor Analysis Model. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2012, 8, 854–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonaco, F.; Crippa, M.; Slowik, J.G.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. SoFi, an IGOR-based interface for the efficient use of the generalized multilinear engine (ME-2) for the source apportionment: ME-2 application to aerosol mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allan, J.D.; Delia, A.E.; Coe, H.; Bower, K.N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Drewnick, F.; Onasch, T.B.; Canagaratna, M.R.; et al. A generalised method for the extraction of chemically resolved mass spectra from Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer data. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, I.M.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jimenez, J.L. Interpretation of organic components from Positive Matrix Factorization of aerosol mass spectrometric data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2891–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crippa, M.; Canonaco, F.; Lanz, V.A.; Äijälä, M.; Allan, J.D.; Carbone, S.; Capes, G.; Ceburnis, D.; Dall’Osto, M.; Day, D.A.; et al. Organic aerosol components derived from 25 AMS data sets across Europe using a consistent ME-2 based source apportionment approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6159–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cubison, M.J.; Ortega, A.M.; Hayes, P.L.; Farmer, D.K.; Day, D.; Lechner, M.J.; Brune, W.H.; Apel, E.; Diskin, G.S.; Fisher, J.A.; et al. Effects of aging on organic aerosol from open biomass burning smoke in aircraft and laboratory studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12049–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crippa, M.; El Haddad, I.; Slowik, J.G.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Mohr, C.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Marchand, N.; Sciare, J.; Baltensperger, U.; et al. Identification of marine and continental aerosol sources in Paris using high resolution aerosol mass spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1950–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, N.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Worsnop, D.R. Real-time methods for estimating organic component mass concentrations from aerosol mass spectrometer data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florou, K.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Pikridas, M.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Louvaris, E.; Gkatzelis, G.I.; Patoulias, D.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Pandis, S.N. The contribution of wood burning and other pollution sources to wintertime organic aerosol levels in two Greek cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3145–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fröhlich, R.; Crenn, V.; Setyan, A.; Belis, C.A.; Canonaco, F.; Favez, O.; Riffault, V.; Slowik, J.G.; Aas, W.; Aijälä, M.; et al. ACTRIS ACSM intercomparison-Part 2: Intercomparison of ME-2 organic source apportionment results from 15 individual, co-located aerosol mass spectrometers. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2555–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pateraki, S.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kouvarakis, G.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Vasilakos, C. Carbonaceous and ionic compositional patterns of fine particles over an urban Mediterranean area. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Wang, X.; Watson, J.G. Mass reconstruction methods for PM2.5: A review. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanatta, M.; Gysel, M.; Bukowiecki, N.; Müller, T.; Weingartner, E.; Areskoug, H.; Fiebig, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kouvarakis, G.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology-5: Climatology of black carbon optical properties at 9 regional background sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Yin, Y. Investigation of the sources and evolution processes of severe haze pollution in Beijing in January 2013. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 4380–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Suresh, S.; Guo, H.; Weber, R.J.; Ng, N.L. Aerosol characterization over the southeastern United States using high-resolution aerosol mass spectrometry: Spatial and seasonal variation of aerosol composition and sources with a focus on organic nitrates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7307–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barreira, L.M.F.; Helin, A.; Aurela, M.; Teinila, K.; Friman, M.; Kangas, L.; Niemi, J.V.; Portin, H.; Kousa, A.; Pirjola, L.; et al. In-depth characterization of submicron particulate matter inter-annual variations at a street canyon site in northern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6297–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Favez, O.; Petit, J.E.; Canonaco, F.; Truong, F.; Bonnaire, N.; Crenn, V.; Amodeo, T.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Sciare, J.; et al. Six-year source apportionment of submicron organic aerosols from near-continuous highly time-resolved measurements at SIRTA (Paris area, France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14755–14776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Fu, P.Q.; Yang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, H.B.; Li, J.; Jia, J.J. Aerosol composition, sources and processes during wintertime in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4577–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qin, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.; Ding, A.; Wu, J.; et al. Chemical composition, sources and evolution processes of aerosol at an urban site in Yangtze River Delta, China during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Cheristanidis, S.; Chaloulakou, A. Elemental and organic carbon in the urban environment of Athens. Seasonal and diurnal variations and estimates of secondary organic carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Sowlat, M.H.; Lovett, C.; Rauber, M.; Szidat, S.; Boffi, R.; Borgini, A.; De Marco, C.; Ruprecht, A.A.; Sioutas, C. Source apportionment of black carbon (BC) from fossil fuel and biomass burning in metropolitan Milan, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrough, S.; Hanley, T.; Hagler, G.; Baldauf, R.; Snyder, M.; Brantley, H. Influential factors affecting black carbon trends at four sites of differing distance from a major highway in Las Vegas. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguillón, M.C.; Pérez, N.; Marchand, N.; Bertrand, A.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Agrios, K.; Szidat, S.; Van Drooge, B.; Sylvestre, A.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Secondary organic aerosol origin in an urban environment: Influence of biogenic and fuel combustion precursors. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumka, U.C.; Tiwari, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Soni, V.K.; Safai, P.D.; Attri, S.D. Aerosol and pollutant characteristics in Delhi during a winter research campaign. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 3771–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilley, L.R.; Bloss, W.J.; Yin, J.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Allan, J.D.; Young, D.E.; Flynn, M.; Williams, P.; Zotter, P.; et al. Sources and contributions of wood smoke during winter in London: Assessing local and regional influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3149–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costabile, F.; Alas, H.; Aufderheide, M.; Avino, P.; Amato, F.; Argentini, S.; Barnaba, F.; Berico, M.; Bernardoni, V.; Biondi, R.; et al. First Results of the “Carbonaceous Aerosol in Rome and Environs (CARE)” Experiment: Beyond Current Standards for PM10. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briggs, N.L.; Long, C.M. Critical review of black carbon and elemental carbon source apportionment in Europe and the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiou, A.G.; Bakeas, E.; Evangelidou, E.; Kontogiorgi, C.; Lagkadinou, E.; Sebos, I. Air pollutant emissions from Piraeus port: External costs and air quality levels. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 91, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ceburnis, D.; Xu, W.; Heffernan, E.; Hellebust, S.; Gallagher, J.; Huang, R.J.; O’Dowd, C.; Ovadnevaite, J. The impact of traffic on air quality in Ireland: Insights from the simultaneous kerbside and suburban monitoring of submicron aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10513–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titos, G.; del Águila, A.; Cazorla, A.; Lyamani, H.; Casquero-Vera, J.A.; Colombi, C.; Cuccia, E.; Gianelle, V.; Močnik, G.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Spatial and temporal variability of carbonaceous aerosols: Assessing the impact of biomass burning in the urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Healy, R.M.; Sofowote, U.; Su, Y.; Debosz, J.; Noble, M.; Jeong, C.H.; Wang, J.M.; Hilker, N.; Evans, G.J.; Doerksen, G.; et al. Ambient measurements and source apportionment of fossil fuel and biomass burning black carbon in Ontario. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiodra, I.; Grivas, G.; Tavernaraki, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; Apostolaki, M.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Gogou, A.; Parinos, C.; Oikonomou, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; et al. Annual exposure to PAHs in urban environments linked to wintertime wood-burning episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17865–17883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Brunner, D.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Changes in domestic heating fuel use in Greece: Effects on atmospheric chemistry and radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10597–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodosi, C.; Grivas, G.; Zarmpas, P.; Chaloulakou, A.; Mihalopoulos, N. Mass and chemical composition of size-segregated aerosols (PM1, PM2.5, PM10) over Athens, Greece: Local versus regional sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11895–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Tison, E.; Dusanter, S.; Beaugard, C.; Gengembre, C.; Augustin, P.; Fourmentin, M.; Delbarre, H.; Riffault, V. Near real-time PM1 chemical composition measurements at a French urban background and coastal site under industrial influence over more than a year: Temporal variability and assessment of sulfur-containing emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budisulistiorini, S.H.; Baumann, K.; Edgerton, E.S.; Bairai, S.T.; Mueller, S.; Shaw, S.L.; Knipping, E.M.; Gold, A.; Surratt, J.D. Seasonal characterization of submicron aerosol chemical composition and organic aerosol sources in the southeastern United States: Atlanta, Georgia, and Look Rock, Tennessee. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5171–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Yang, T.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, P.; Jayne, J.T. Characterization of summer organic and inorganic aerosols in Beijing, China with an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, M.; Cavalli, F.; Putaud, J.P.; Fröhlich, R.; Petit, J.E.; Aas, W.; Äijälä, M.; Alastuey, A.; Allan, J.D.; Aurela, M.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology-7: High-time resolution chemical characteristics of submicron particulate matter across Europe. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 10, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yan, H.; Xiang, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, R.; Wang, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H. Characteristics, evolution, and potential source regions of submicron aerosol in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougiatioti, A.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Stavroulas, I.; Weber, R.; Nenes, A.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. The effects of biomass burning on fine aerosol acidity, liquid water content and nitrogen partitioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Aerosol Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 27 August–1 September 2017; p. T209N57B. [Google Scholar]
- Kassomenos, P.; Kotroni, V.; Kallos, G. Analysis of climatological and air quality observations from Greater Athens Area. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenidou, E.; Florou, K.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Tsiflikiotou, M.; Vratolis, S.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Pandis, S.N. Sources and chemical characterization of organic aerosol during the summer in the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11355–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Na, K.; Sawant, A.A.; Song, C.; Cocker, D.R., III. Primary and secondary carbonaceous species in the atmosphere of Western Riverside County, California. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, J.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Núñez, L.; Pujadas, M.; Artíñano, B. Estimation of secondary organic aerosol formation from semi-continuous OC-EC measurements in a Madrid suburban area. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellini, L.H.; Adam, M.G.; Kasthuriarachchi, N.; Lee, A.K.Y. Characterization of carbonaceous aerosols in Singapore: Insight from black carbon fragments and trace metal ions detected by a soot particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5977–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougiatioti, A.; Stavroulas, I.; Kostenidou, E.; Zarmpas, P.; Theodosi, C.; Kouvarakis, G.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N.; et al. Processing of biomass-burning aerosol in the eastern Mediterranean during summertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4793–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becerril-Valle, M.; Coz, E.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Močnik, G.; Pandis, S.N.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Díaz, E.; Pérez, R.M.; Artíñano, B. Characterization of atmospheric black carbon and co-pollutants in urban and rural areas of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helin, A.; Niemi, J.V.; Virkkula, A.; Pirjola, L.; Teinilä, K.; Backman, J.; Aurela, M.; Saarikoski, S.; Rönkkö, T.; Asmi, E.; et al. Characteristics and source apportionment of black carbon in the Helsinki metropolitan area, Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. Development of a road transport emission inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area: Effects of important parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gobbi, G.P.; Di Liberto, L.; Barnaba, F. Impact of port emissions on EU-regulated and non-regulated air quality indicators: The case of Civitavecchia (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 134984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin Sun, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Deng, T.; Yu, J.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Amplification of black carbon light absorption induced by atmospheric aging: Temporal variation at seasonal and diel scales in urban Guangzhou. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2445–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Canagaratna, M. A case study of urban particle acidity and its influence on secondary organic aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3213–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y. Analysis of Chemical Composition, Source and Processing Characteristics of Submicron Aerosol during the Summer in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, S.; Agrawal, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Padró, L.T.; Gates, H.; Hersey, S.; Welch, W.A.; Jung, H.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R., III; et al. Comprehensive simultaneous shipboard and airborne characterization of exhaust from a modern container ship at sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4626–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanellopoulos, P.G.; Verouti, E.; Chrysochou, E.; Koukoulakis, K.; Bakeas, E. Primary and secondary organic aerosol in an urban/industrial site: Sources, health implications and the role of plastic enriched waste burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanavaraha, W.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Budisulistiorini, S.H.; Croteau, P.L.; Baumann, K.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Edgerton, E.S.; Zhang, Z.; Jayne, J.T.; et al. Source apportionment of submicron organic aerosol collected from Atlanta, Georgia, during 2014–2015 using the aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ACSM). Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, S.; Cai, M.; Zhao, J.; Song, W.; Zhao, W.; Hu, W.; Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, C.; et al. Characterization of submicron particles by time-of-flight aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ToF-ACSM) during wintertime: Aerosol composition, sources, and chemical processes in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7595–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, D.; Alvarez-Ospina, H.; Peralta, O.; Castro, T. PM1 Chemical Characterization during the ACU15 Campaign, South of Mexico City. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aurela, M.; Saarikoski, S.; Niemi, J.V.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Frey, A.; Carbone, S.; Kousa, A.; Hillamo, R. Chemical and Source Characterization of Submicron Particles at Residential and Traffic Sites in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area, Finland. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfarra, M.R.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Sandradewi, J.; Weimer, S.; Lanz, V.A.; Schreiber, D.; Mohr, M.; Baltensperger, U. Identification of the mass spectral signature of organic aerosols from wood burning emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5770–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, B.; Liu, C.; Xu, R.; Li, T. A comprehensive ammonia emission inventory with high-resolution and its evaluation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodros, J.K.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Paglione, M.; Masiol, M.; Squizzato, S.; Florou, K.; Skyllakou, K.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N. Rapid dark aging of biomass burning as an overlooked source of oxidized organic aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33028–33033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorga, S.D.; Florou, K.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Kodros, J.K.; Vasilakopoulou, C.; Cirtog, M.; Fouqueau, A.; Picquet-Varrault, B.; Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N. Nighttime chemistry of biomass burning emissions in urban areas: A dual mobile chamber study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 15337–15349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lee, B.P.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.J.; Schurman, M.I.; Louie, P.K.K.; Luk, C.; Chan, C.K. Continuous measurements at the urban roadside in an Asian megacity by Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM): Particulate matter characteristics during fall and winter seasons in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1713–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; Dumka, U.C.; Dimitriou, K.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. In situ identification of aerosol types in Athens, Greece, based on long-term optical and on online chemical characterization. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Bhandari, S.; Gani, S.; Campmier, M.J.; Kumar, P.; Habib, G.; Apte, J.; Hildebrandt Ruiz, L. Sources and Dynamics of Submicron Aerosol during the Autumn Onset of the Air Pollution Season in Delhi, India. ACS Earth Sp. Chem. 2021, 5, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Favez, O.; Petit, J.-E.; Zhang, Y.; Sofowote, U.M.; Hopke, P.K.; Bonnaire, N.; Perraudin, E.; Gros, V.; Villenave, E.; et al. Speciation of organic fractions does matter for aerosol source apportionment. Part 3: Combining off-line and on-line measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, M.D.; D’Anna, B.; Même, A.; Chiara Bove, M.; Cassola, F.; Pace, G.; Desboeufs, K.; Di Biagio, C.; Doussin, J.F.; Maille, M.; et al. Summertime surface PM1 aerosol composition and size by source region at the Lampedusa island in the central Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11123–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sage, A.M.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M. Evolving mass spectra of the oxidized component of organic aerosol: Results from aerosol mass spectrometer analyses of aged diesel emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, S.; Saarikoski, S.; Frey, A.; Reyes, F.; Reyes, P.; Castillo, M.; Gramsch, E.; Oyola, P.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R.; et al. Chemical Characterization of Submicron Aerosol Particles in Santiago de Chile. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Kokkalis, P.; Eleftheratos, K.; Andreae, M.O.; Andreae, T.W.; El-Askary, H.; Zerefos, C.S. Three-year ground based measurements of aerosol optical depth over the Eastern Mediterranean: The urban environment of Athens. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Reche, C.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Increase in secondary organic aerosol in an urban environment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8323–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struckmeier, C.; Drewnick, F.; Fachinger, F.; Paolo Gobbi, G.; Borrmann, S. Atmospheric aerosols in Rome, Italy: Sources, dynamics and spatial variations during two seasons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15277–15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Bougiatioti, A.; Stavroulas, I.; Fang, T.; Lianou, M.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Weber, R.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N. Yearlong variability of oxidative potential of particulate matter in an urban Mediterranean environment. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillón, M.C.; Ripoll, A.; Pérez, N.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Canonaco, F.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Chemical characterization of submicron regional background aerosols in the western Mediterranean using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Pey, J.; Cusack, M.; Pérez, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Theodosi, C.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Kubilay, N.; Koçak, M. Variability in regional background aerosols within the Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4575–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Pérez, N.; Reche, C.; Castro, I.; Shatalov, V.; Querol, X. Trends analysis of PM source contributions and chemical tracers in NE Spain during 2004–2014: A multi-exponential approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11787–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Total | Day | Night | Weekday | Weekend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | |||||
| OM | 13.88 (0.41–89.56) | 12.21 (1.10–58.90) | 15.57 (0.41–89.56) | 14.30 (0.41–89.56) | 12.80 (1.10–88.03) |
| SO42− | 2.48 (0.01–9.19) | 2.33 (0.01–7.14) | 2.63 (0.11–9.19) | 2.51 (0.01–9.19) | 2.40 (0.01–7.60) |
| NO3− | 1.40 (0.01–7.97) | 1.19 (0.01–5.92) | 1.62 (0.01–7.97) | 1.44 (0.01–7.97) | 1.31 (0.05–7.00) |
| NH4+ | 0.92 (0.14–4.56) | 0.83 (0.14–3.74) | 1.02 (0.14–4.56) | 0.94 (0.14–4.46) | 0.88 (0.14–4.56) |
| Cl− | 0.28 (0.01–6.13) | 0.21 (0.01–4.07) | 0.35 (0.01–6.13) | 0.29 (0.01–6.13) | 0.26 (0.01–4.49) |
| BC | 3.72 (0.17–28.52) | 2.96 (0.32–17.24) | 4.47 (0.17–28.52) | 3.73 (0.17–28.47) | 3.66 (0.34–28.52) |
| BCff | 2.43 (0.01–18.63) | 2.31 (0.22–13.92) | 2.56 (0.01–18.63) | 2.48 (0.16–18.63) | 2.30 (0.01–15.49) |
| BCbb | 1.28 (0.01–13.65) | 0.65 (0.04–3.56) | 1.91 (0.01–13.65) | 1.25 (0.01–13.38) | 1.36 (0.01–13.65) |
| PM1 | 22.75 (1.11–130.69) | 19.76 (2.28–78.51) | 25.76 (1.11–130.69) | 23.29 (1.11–126.19) | 21.33 (2.28–130.69) |
| Summer | |||||
| OM | 7.14 (1.70–15.94) | 7.11 (1.70–15.94) | 7.16 (1.71–15.25) | 7.63 (1.70–15.94) | 6.15 (1.74–14.67) |
| SO42− | 3.32 (0.13–10.91) | 3.29 (0.13–10.91) | 3.35 (0.68–8.50) | 3.47 (0.13–10.91) | 2.95 (0.68–9.75) |
| NO3− | 0.46 (0.04–1.69) | 0.52 (0.04–1.69) | 0.41 (0.05–1.32) | 0.51 (0.04–1.69) | 0.33 (0.05–1.22) |
| NH4+ | 1.20 (0.14–3.82) | 1.22 (0.14–3.82) | 1.18 (0.14–3.29) | 1.26 (0.14–3.82) | 1.04 (0.14–3.14) |
| Cl− | 0.03 (0.01–0.21) | 0.04 (0.01–0.21) | 0.02 (0.01–0.10) | 0.03 (0.01–0.21) | 0.02 (0.01–0.06) |
| BC | 2.81 (0.28–11.82) | 2.88 (0.39–11.82) | 2.74 (0.28–11.71) | 3.10 (0.37–11.82) | 2.05 (0.28–11.71) |
| BCff | 2.45 (0.04–10.39) | 2.51 (0.04–10.39) | 2.39 (0.14–10.36) | 2.71 (0.04–10.39) | 1.79 (0.23–10.36) |
| BCbb | 0.36 (0.01–1.90) | 0.37 (0.01–1.90) | 0.35 (0.01–1.86) | 0.40 (0.01–1.90) | 0.26 (0.03–1.35) |
| PM1 | 14.78 (3.37–34.11) | 14.69 (3.37–34.11) | 14.84 (3.62–29.33) | 16.02 (3.72–34.11) | 12.26 (3.37–29.33) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Kalkavouras, P.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Lianou, M.; Papoutsidaki, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; et al. Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121686
Stavroulas I, Grivas G, Liakakou E, Kalkavouras P, Bougiatioti A, Kaskaoutis DG, Lianou M, Papoutsidaki K, Tsagkaraki M, Zarmpas P, et al. Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(12):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121686
Chicago/Turabian StyleStavroulas, Iasonas, Georgios Grivas, Eleni Liakakou, Panayiotis Kalkavouras, Aikaterini Bougiatioti, Dimitris G. Kaskaoutis, Maria Lianou, Kyriaki Papoutsidaki, Maria Tsagkaraki, Pavlos Zarmpas, and et al. 2021. "Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece" Atmosphere 12, no. 12: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121686
APA StyleStavroulas, I., Grivas, G., Liakakou, E., Kalkavouras, P., Bougiatioti, A., Kaskaoutis, D. G., Lianou, M., Papoutsidaki, K., Tsagkaraki, M., Zarmpas, P., Gerasopoulos, E., & Mihalopoulos, N. (2021). Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece. Atmosphere, 12(12), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121686










