Comparison of Inland Ship Emission Results from a Real-World Test and an AIS-Based Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research and Method
2.1. Experimental Section
2.1.1. Test Instruments
2.1.2. Study Area
2.1.3. Test Ships
2.1.4. Test Operating Mode
2.2. AIS-Based Emission Model
2.2.1. Emission Calculation
2.2.2. Emission Factor
2.2.3. Low Load Adjustment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ship Activities Mode Selection
3.2. Characteristic of Instantaneous Emission Rate from a Real-World Test and the AIS-Based Emission Model
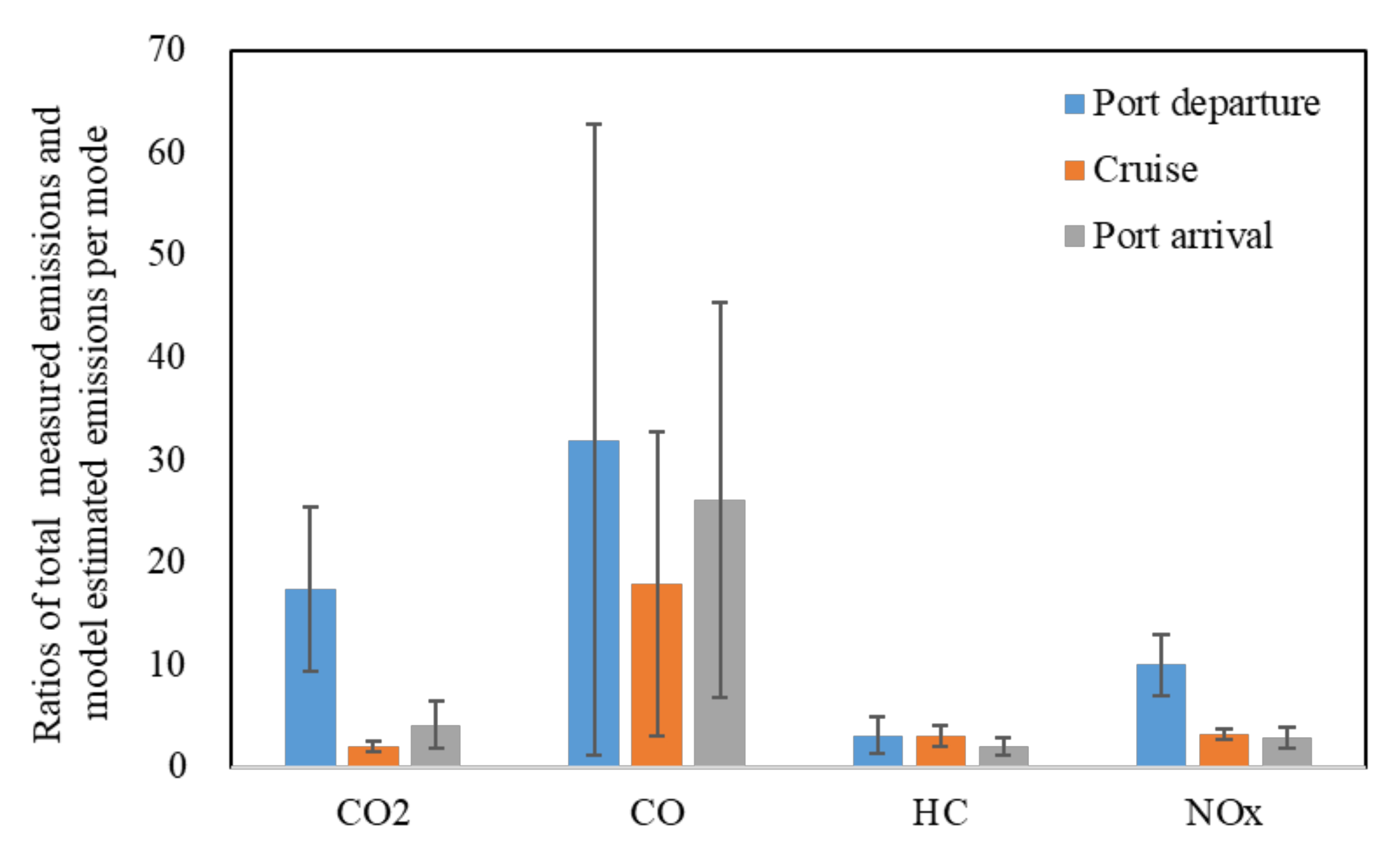
3.3. Comparison of Emissions from Real-World Tests and the AIS-Based Emission Models under Different Engine Loads
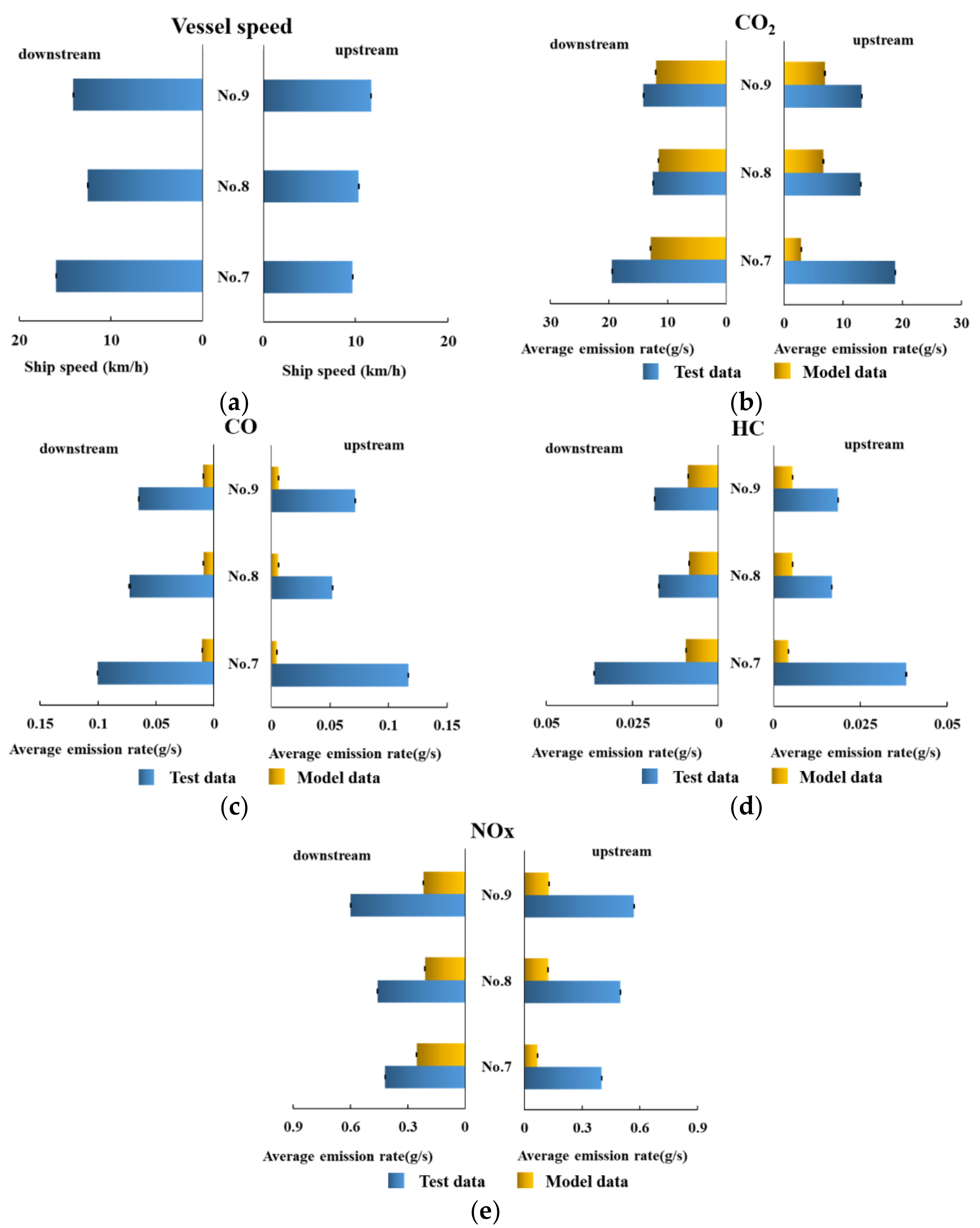
3.4. Analysis of the Emission Rates from the AIS-Based Model under Different Water Flow Directions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Trunk Line of the Yangtze River Carries 2.5 Billion Tons of Cargo Annually. Available online: http://paper.people.com.cn/rmrbhwb/html/2018-01/05/content182787.htm (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Prosperous Jiangsu Port Production. Available online: http://epaper.zgsyb.com/html/2018-02/28/content21728.htm (accessed on 28 February 2018).
- Yi, S. Forecast of Effectiveness and Cost-Benefit Analysis of Chinese Shipping Emission Control Areas. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shang, Y.; Jin, X.; Fu, M. Review of methods and progress on shipping emission inventory studies. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, J.; Tarelko, W. NOx emission from a two-stroke ship engine: Part 2—Laboratory test. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 2160–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yau, P.S.; Lee, S.C.; Corbett, J.J.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ho, K.F. Estimation of exhaust emission from ocean-going vessels in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonati, G.; Cernuschi, S.; Sidi, S. Air quality impact assessment of at-berth ship emissions: Case-study for the project of a new freight port. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 409, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzannatos, E. Ship emissions and their externalities for the port of Piraeus-Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, K.; Setton, E.; McEwen, B.; Hrebenyk, D.; Graham, M.; Keller, P. Impact of cruise ship emissions in Victoria, BC, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Duan, L. Characterization of VOC emissions from construction machinery and river ships in the Pearl River Delta of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 96, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Xiao, H. Air Pollutant Emission Inventory of Marine in China; State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Vehicle Emission Control and Simulation, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Howitt, O.J.A.; Revol, V.G.N.; Smith, I.J.; Rodger, C.J. Carbon emissions from international cruise ship passengers’ travel to and from New Zealand. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2552–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, M.; Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G.; Shindell, C.; He, K. Health and climate impacts of ocean-going vessels in East Asia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tian, X.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B. The impact of ship emissions on PM2.5 and the deposition of nitrogen and sulfur in Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoudou, I.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of PM2.5 from ship emissions and their impacts on the ambient air: A case study in Yangshan Harbor, Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Kukkonen, J. Global assessment of shipping emissions in 2015 on a high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liao, R.; Yan, M.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, G. Accounting the vessels air pollutant emissions in Shenzhen Port. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2016, 35, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q. Shipping emission inventories in China’s Bohai Bay, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta in 2018. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Brown, R.; Yang, L.; Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Fu, Q.; Huang, C. Shipping emissions and their impacts on air quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxian, A.; Eyring, V.; Beer, W.; Sausen, R.; Wright, C. Present-Day and Future Global Bottom-Up Ship Emission Inventories Including Polar Routes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, J.; Ying, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B. Evaluation of different control measures in 2014 to mitigate the impact of ship emissions on air quality in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Huang, C. Development of Monitoring, Forecasting and Evaluation for Fine Ambient Air Quality Management of Major Events in China. Environ. Monit. China 2020, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Kukkonen, J. A comprehensive inventory of ship traffic exhaust emissions in the European sea areas in 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsworthy, B. Spatial and temporal allocation of ship exhaust emissions in Australian coastal waters using AIS data: Analysis and treatment of data gaps. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Lv, J. Ship emission inventory and valuation of eco-efficiency in Xiamen Port. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 2304–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Fu, F.; Zuo, H.; Li, S.; He, H. Ship Emission Inventory and Its Application in Qingdao. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2019, 45, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.-q.; Kwan, S.H.; Lu, T.; Fu, Q.-y.; Cheng, J.-m.; Streets, D.G.; Wu, Y.-m.; Li, J.-j. An Emission Inventory of Marine Vessels in Shanghai in 2003. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5183–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtenbach, R.; Vaupel, K.; Kleffmann, J.; Klenk, U.; Schmidt, E.; Wiesen, P. Emissions of NO, NO2 and PM from inland shipping. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14285–14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, D.; Guiot, B.; Le Cottier, P.; Perret, P.; Tassel, P. Exhaust emissions from in-service inland waterways vessels. In Proceedings of the TAP 2016 21st International Transport and Air Pollution Conference, Lyon, France, 24 May 2016; pp. 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Hulskotte, J.H.J.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C. Fuel consumption and associated emissions from seagoing ships at berth derived from an on-board survey. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesgin, U.; Vardar, N. A study on exhaust gas emissions from ships in Turkish Straits. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, C.; Durmuşoğlu, Y. Estimating shipping emissions in the region of the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecken, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Salo, K.; Ekholm, J.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Johansson, L.; Litvinenko, V.; Volodin, K.; Frank-Kamenetsky, D.A. Emission factors of SO2, NOx and particles from ships in Neva Bay from ground-based and helicopter-borne measurements and AIS-based modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5229–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Nelson, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X. Ship emission inventory and its impact on the PM2.5 air pollution in Qingdao Port, North China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y. High-spatiotemporal-resolution ship emission inventory of China based on AIS data in 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Ding, Y.; Ge, Y.; Yu, L.; Yin, H.; Ye, W.; Liang, B. Real-world emissions of inland ships on the Grand Canal, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Liu, H.; Jin, X.; He, K. National- to port-level inventories of shipping emissions in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Ge, Y.; Tan, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Yin, H.; Ji, Z. Emissions from several in-use ships tested by portable emission measurement system. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 116, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, C.; Huang, L.; Wen, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Effect of Seasonal Flow Field on Inland Ship Emission Assessment: A Case Study of Ferry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wen, Y.; Geng, X.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, C. Integrating multi-source maritime information to estimate ship exhaust emissions under wind, wave and current conditions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pollutant | Measuring Range | Resolution | Measurement Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 0~20% | 0.01% | ±3% |
| CO | 0~8% | 10 ppm | ±50 ppm or ±3% |
| THC | 0~100 ppm | 0.1 ppm | ±5 ppm or ±2% |
| 0~1000 ppm | 1 ppm | ±5 ppm or ±2% | |
| 0~10,000 ppm | 1 ppm | ±25 ppm or ±2% | |
| NO | 0~2500 ppm | 1 ppm | ±15 ppm or ±3% |
| NO2 | 0~500 ppm | 1 ppm | ±10 ppm or ±3% |
| Instrument | Manufacturer | Model |
|---|---|---|
| Generator | YAMAHA | 6800 E |
| Battery | FENGFAN | — |
| ID | Ship Type | Built Year | Engine Rated Power (kw)/Rated Speed (RPM) | Maximum Speed (km/h) | Ship Gross Weight (ton) | Test Route | Departure Time | Arrival Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cargo ship | 2001 | 88.3/500 | 17 | 270 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 10:44 | 12:20 |
| 2 | Cargo ship | 2010 | 136/850 | 18 | 380 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 5:23 | 7:02 |
| 3 | Cargo ship | 2009 | 300/1400 | 18 | 320 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 18:26 | 19:51 |
| 4 | Cargo ship | 2008 | 260/1400 | 18 | 420 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 4:50 | 7:41 a |
| 5 | Cargo ship | 2010 | 145/850 | 18 | 540 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 17:59 | 19:29 |
| 6 | Cargo ship | 2004 | 136/850 | 18 | 560 | Zhenjiang to Danyang | 10:09 | 11:44 |
| 7 | Cargo ship | 2004 | 136/850 | 20 | 380 | Nansha port | 12:39 | 14:38 |
| 8 | Cargo ship | 2007 | 184/1000 | 18 | 350 | Nansha port | 11:53 | 13:00 |
| 9 | Cargo ship | 2007 | 184/1000 | 20 | 350 | Nansha port | 14:30 | 15:30 |
| Operating Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Port arrival | From the slowing down of cruising speed until berthing |
| Cruise | The process of sailing a ship at a constant speed |
| Port departure | From idle state to sailing at cruising speed |
| Berth | Adopting engines to power daily life at berth |
| Engine Type | Fuel Type | Tier | Model Year | NOx | CO | HC | CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD a | MDO/MGO (0.15% Sulfur content) | Tier 0 c | ≤1999 | 17.0 | 0.54 | 0.6 | 607 |
| MSD b | ≤1999 | 13.2 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 670 | ||
| SSD a | Tier 1 | 2000–2010 | 16.0 | 0.54 | 0.6 | 607 | |
| MSD b | 2000–2010 | 12.2 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 670 | ||
| SSD a | Tier 2 | 2011–2015 | 14.4 | 0.54 | 0.6 | 607 | |
| MSD b | 2011–2015 | 10.5 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 670 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Peng, D.; Wang, Y.; Fu, M. Comparison of Inland Ship Emission Results from a Real-World Test and an AIS-Based Model. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121611
Jiang H, Peng D, Wang Y, Fu M. Comparison of Inland Ship Emission Results from a Real-World Test and an AIS-Based Model. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(12):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121611
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Han, Di Peng, Yunjing Wang, and Mingliang Fu. 2021. "Comparison of Inland Ship Emission Results from a Real-World Test and an AIS-Based Model" Atmosphere 12, no. 12: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121611
APA StyleJiang, H., Peng, D., Wang, Y., & Fu, M. (2021). Comparison of Inland Ship Emission Results from a Real-World Test and an AIS-Based Model. Atmosphere, 12(12), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121611







