Relationships among Indoor Radon, Earthquake Magnitude Data and Lung Cancer Risks in a Residential Building of an Apulian Town (Southern Italy)
Abstract
1. Background
1.1. Indoor Exposure to Radon
1.2. Earthquakes and Radon
1.3. Aims
- to validate a model of indoor radon measurements,
- to apply our radon software for the estimation of lung cancer cases attributable to radon and
- to study the relationship between radon and earthquakes.
2. Methods
2.1. Environmental Radon Measurements
Radon Detectors Used in This Study Technical Characteristics
2.2. Web Cloud System and Access with a Smartphone App
2.3. Software Used for Estimating Radon-Attributable Lung Cancer
- (1)
- the population of the municipality;
- (2)
- C (the average annual concentration (Bq/m3));
- (3)
- F (the equilibrium factor);
- (4)
- N (the number of hours recorded in a year);
- (5)
- EEC (the equilibrium equivalent radon concentration at 1 WLM (working level month));
- (6)
- P (the probability of lung cancer in excess).
- (1)
- the annual cumulative concentration (Bq/m3);
- (2)
- EEC1;
- (3)
- 210Po (Ca);
- (4)
- 214Pb (CB);
- (5)
- 214Bi (Cc);
- (6)
- WLM;
- (7)
- estimates of the annual number of lung cancer cases attributable to radon.
- the probability of excess lung tumors resulting from annual exposure to 1 WLM (18–64 years) = 2.83/10,000;
- F (equilibrium factor) = EEC × C−1;
- CA (210Po unstable decay product of radon); CB (214Bi unstable decay product of Radon);
- Cc (214Pb stable decay product of radon);
- C (average annual concentration);
- Ccum (average annual cumulative exposure);
- EEC (radon concentration equivalent to equilibrium) = C × F (in this study, this value is estimated to be 6.3 × 105 Bqh/m3).
2.4. Earthquake Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
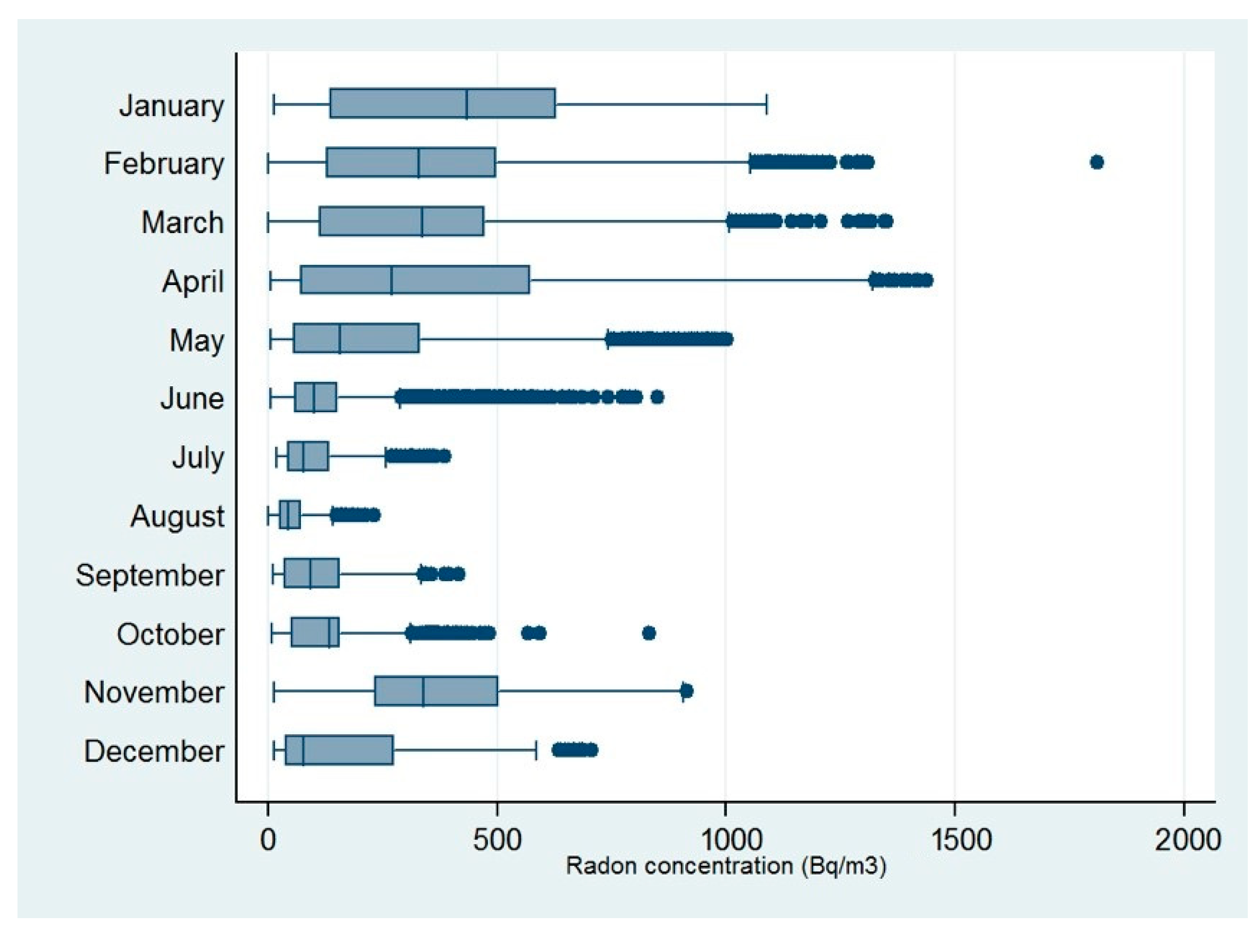
3.1. Radon Measurements
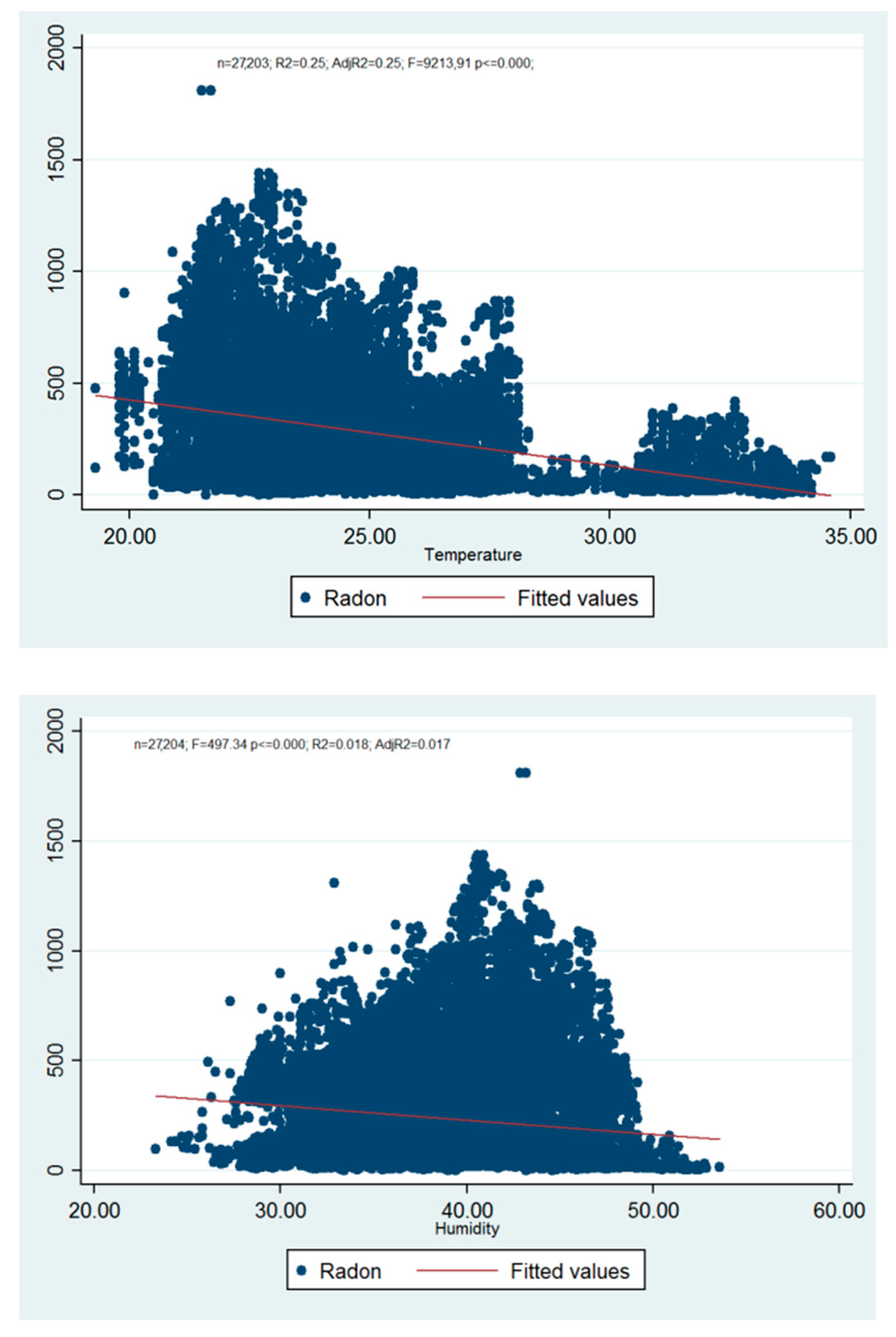
3.2. Temperature and Humidity
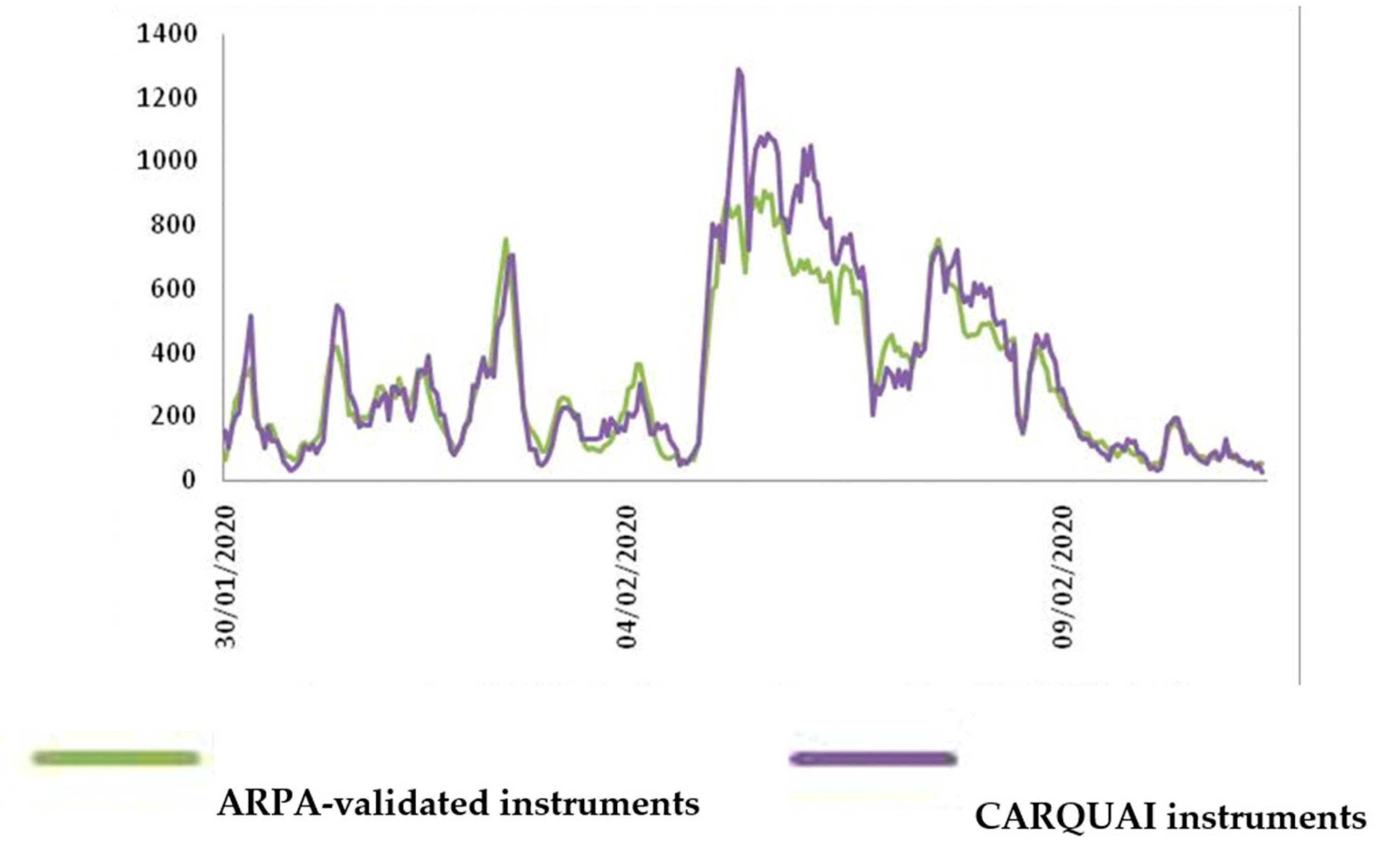
3.3. Radon Data Measurement Evaluation
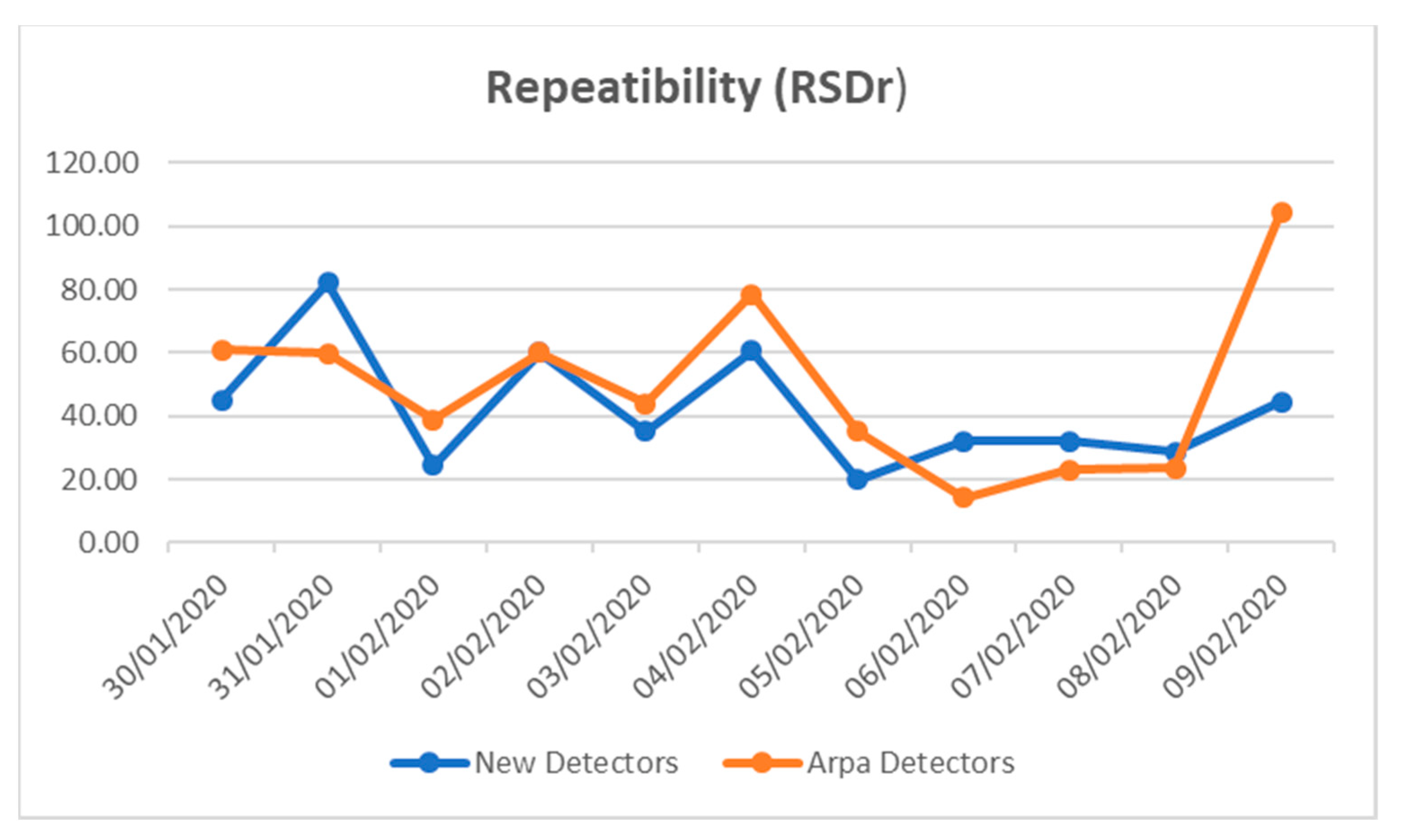
3.4. Validation of the New Radon Detectors Used Herein
3.5. Annual Radon-Attributed Lung Cancer Estimates
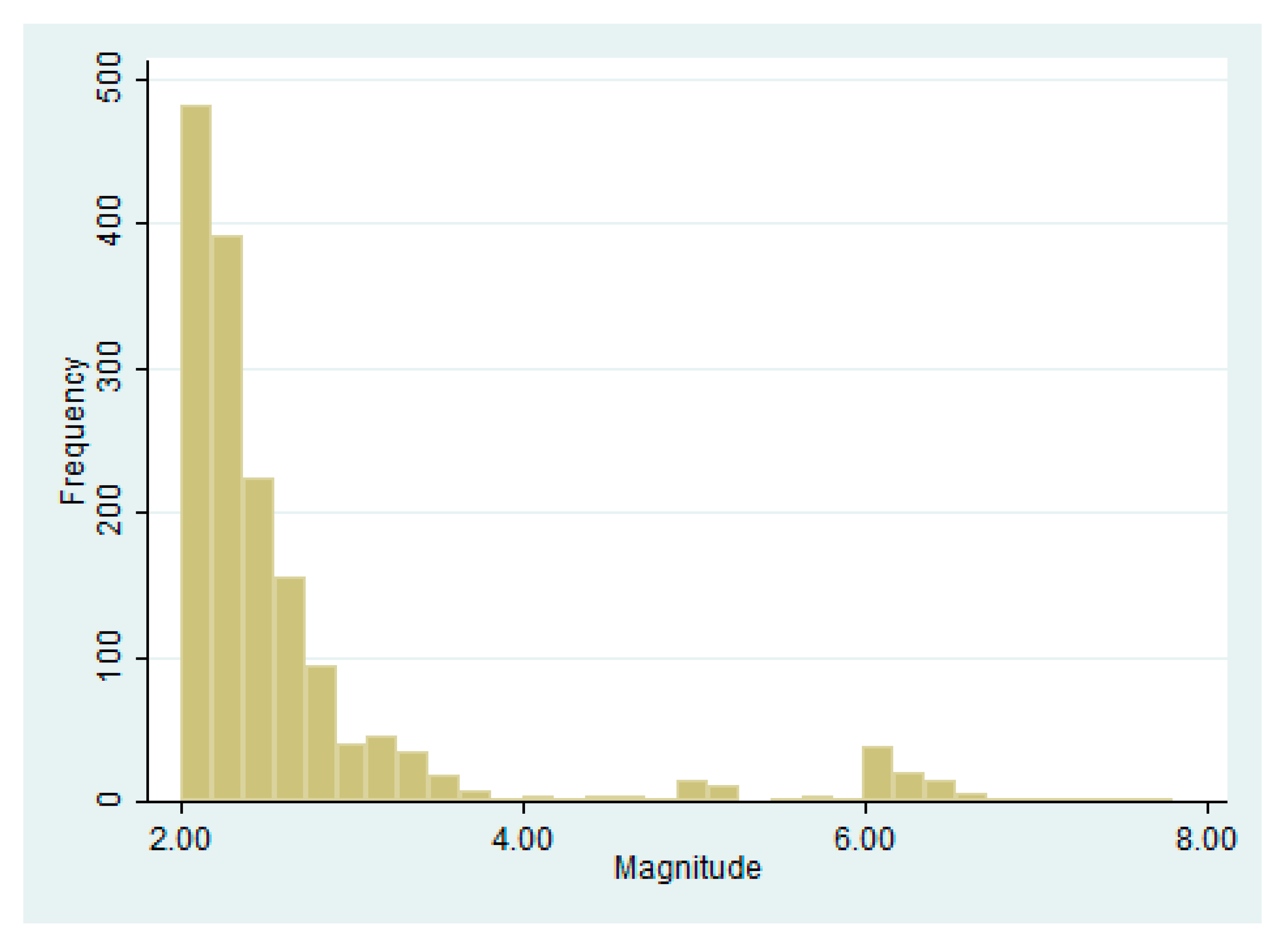
3.6. Earthquake Data Distribution
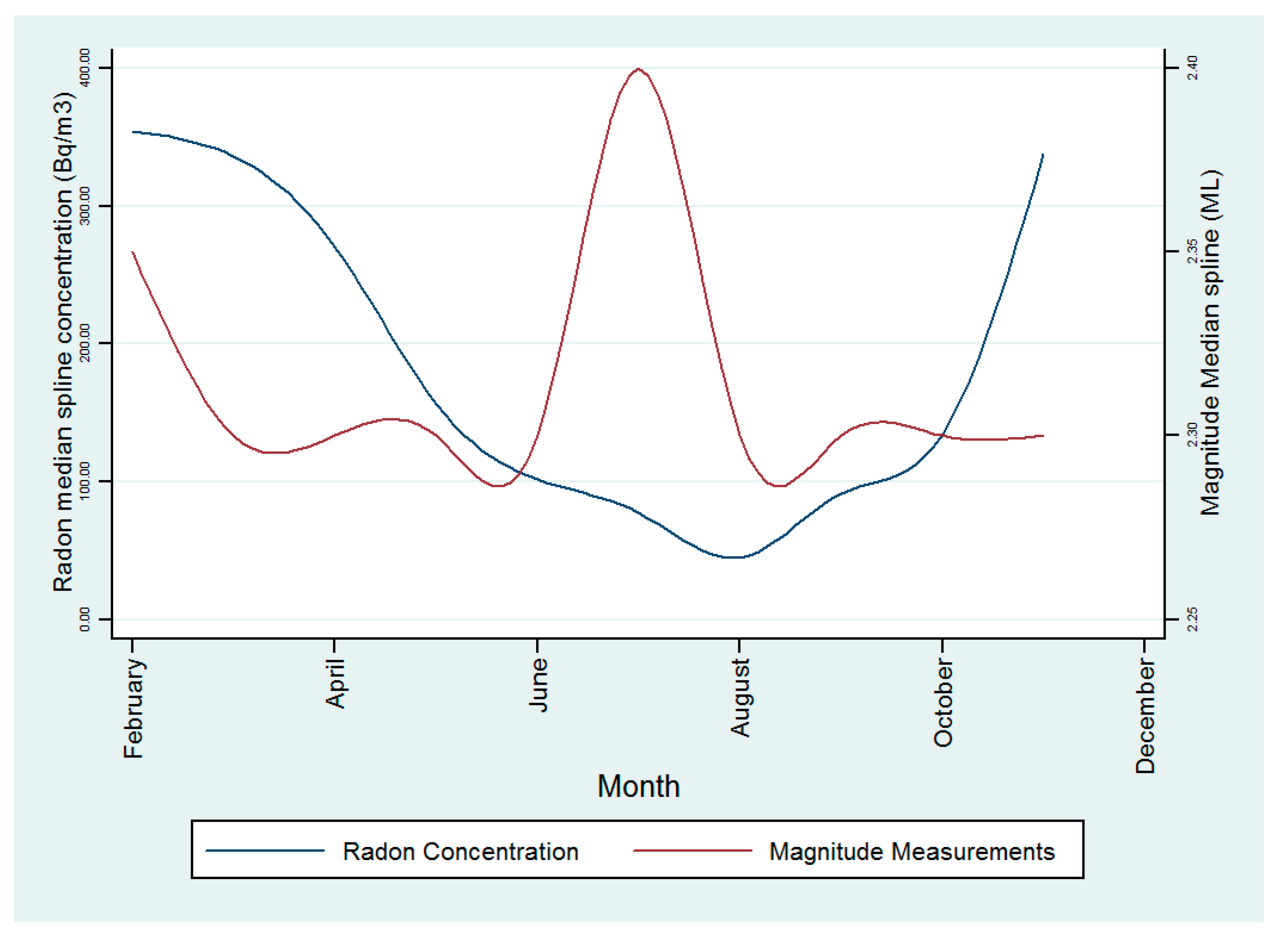
3.7. Relationship between Radon and Earthquake Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Radon Monitoring and Measurement Validations
4.2. Radon-Attributable Lung Cancer Risk
4.3. Radon and Earthquakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements. Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of the United States; NCRP Report 160; National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Health Effects of Exposure to Radon. BEIR VI; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monograph on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk to Human. Man-made Mineral Fibers and Radon; IARC: Lyon, France, 1988; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]
- Eidy, M.; Tishkowski, K. Radon Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ćujić, M.; Mandić, L.J.; Petrović, J.; Dragović, R.; Đorđević, M.; Đokić, M.; Dragović, S. Radon-222: Environmental behavior and impact to (human and non-human) biota. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 65, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp. Oncol. (Pozn) 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Hwang, W.J.; Cho, J.-S.; Kang, D.R. Attributable risk of lung cancer deaths due to indoor radon exposure. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.; Jang, H.; Cho, J.; Kang, D.R.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, D.C.; Kim, C. Estimating the disease burden of lung cancer attributable to residential radon exposure in Korea during 2006–2015: A socio-economic approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponciano-Rodríguez, G.; Gaso, M.I.; Armienta, M.A.; Trueta, C.; Morales, I.; Alfaro, R.; Segovia, N. Indoor radon exposure and excess of lung cancer mortality: The case of Mexico—An ecological study. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 43, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Gonzalez, M.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Torres-Duran, M.; Kelsey, K.T.; Provencio, M.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Piñeiro-Lamas, M.; Varela-Lema, L.; Perez-Rios, M.; Fernandez-Villar, A.; et al. Lung cancer risk and residential radon exposure: A pooling of case-control studies in northwestern Spain. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Durán, M.; Casal-Mouriño, A.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Provencio, M.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Hernández-Hernández, J.; Vidal-García, I.; Varela-Lema, L.; Cuadrado, L.V.; Fernández-Villar, A.; et al. Residential radon and lung cancer characteristics at diagnosis. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2021, 97, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Osorio, A.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Varela-Lema, L.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Pérez-Ríos, M. Residential Radon in Central and South America: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Shang, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.-B.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q. Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in thyroid nodules with calcification. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, N.H. Potential lung cancer risk from indoor radon exposure. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1990, 40, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samet, J.M. Indoor radon and lung cancer. Estimating the risks. West. J. Med. 1992, 156, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. BMJ 2004, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojo, K.; Kurttio, P. Indoor Radon Measurements in Finnish Daycare Centers and Schools-Enforcement of the Radiation Act. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serio, G.; Vimercati, L.; Pennella, A.; Gentile, M.; Cavone, D.; Buonadonna, A.L.; Scattone, A.; Fortarezza, F.; De Palma, A.; Marzullo, A. Genomic changes of chromosomes 8p23.1 and 1q21: Novel mutations in malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2018, 126, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano-Ravina, A.; Pereyra, M.F.; Castro, M.T.; Pérez-Ríos, M.; Abal-Arca, J.; Barros-Dios, J.M. Genetic Susceptibility, Residential Radon, and Lung Cancer in a Radon Prone Area. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, A.; Hung, R.; Christiani, D.C.; Caporaso, N.E.; Liu, G.; Bojesen, S.E.; Le Marchand, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Albanes, D.; Aldrich, M.C.; et al. Genetic modifiers of radon-induced lung cancer risk: A genome-wide interaction study in former uranium miners. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2018, 91, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.L.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Torres-Durán, M.; Kelsey, K.T.; Provencio, M.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Leiro-Fernández, V.; Vidal-García, I.; Castro-Añón, O.; Martínez, C.; et al. Residential radon, genetic polymorphisms in DNA damage and repair-related. Lung Cancer 2019, 135, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkilä, A.; Arvela, H.; Mehtonen, J.; Raitanen, J.; Heinäniemi, M.; Lohi, O.; Auvinen, A. Predicting residential radon concentrations in Finland: Model development, validation, and application to childhood leukemia. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2019, 46, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal-Mouriño, A.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Torres-Durán, M.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Provencio-Pulla, M.; Castro-Añón, O.; Vidal-García, I.; Pena-Álvarez, C.; Abal-Arca, J.; Piñeiro-Lamas, M.; et al. Lung cancer survival in never-smokers and exposure to residential radon: Results of the LCRINS study. Cancer Lett. 2020, 487, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; ISBN 978-92-4-154767-3. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/201612/documents/2016_a_citizens_guide_to_radon.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Grundy, A.; Brand, K.; Khandwala, F.; Poirier, A.; Tamminen, S.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Brenner, D.R. Lung cancer incidence attributable to residential radon exposure in Alberta in 2012. CMAJ Open 2017, 5, E529–E534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-S.; Koh, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, J. Radon exposure and lung cancer: Risk in nonsmokers among cohort studies. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 28, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, J.H.; Boice, J.D.; Edling, C.; Hornung, R.W.; Howe, G.R.; Kunz, E.; Kusiak, R.A.; Morrison, H.I.; Radford, E.P.; Samet, J.M.; et al. Lung Cancer in Radon-Exposed Miners and Estimation of Risk From Indoor Exposure. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.C.; Whitely, E.; Howe, G.R.; Hutchings, S.J.; Kusiak, R.A.; Lubin, J.H.; Morrison, H.I.; Tirmarche, M.; Tomásek, L.; Radford, E.P.; et al. Radon and Cancers Other Than Lung Cancer in Underground Miners: A Collaborative Analysis of 11 Studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirmarche, M.; Harrison, J.; Laurier, D.; Blanchardon, E.; Paquet, F.; Marsh, J. Risk of lung cancer from radon exposure: Contribution of recently published studies of uranium miners. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi, A.; Adelikhah, M.; Imani, M.; Kovács, T. A brief radiological survey and associated occupational exposure to radiation in an open pit slate mine in Kashan, Iran. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer, M.; Deffner, V.; Schnelzer, M.; Fenske, N. Mortality in underground miners in a former uranium ore mine. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2021, 118, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojo, K.; Laine, J.-P.; Turtiainen, T.; Kurttio, P. Radon in Finnish underground mines 2011–2019. J. Radiol. Prot. 2021, 41, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Reif, K.; Sandler, D.P.; Shore, D.; Schubauer-Berigan, M.K.; Troester, M.A.; Nylander-French, L.; Richardson, D.B. Radon and cancer mortality among underground uranium miners in the Příbram region of the Czech Republic. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2020, 63, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowska-Lichwa, L.; Przylibski, T.A. Assessment of occupational exposure from radon in the newly formed underground tourist route under Książ castle, Poland. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2021, 60, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K. Health Effects of High Radon Environments in Central Europe: Another Test for the LNT Hypothesis? Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2003, 1, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.E.; Nelson, D.F.; Popkin, J.H.; Popkin, Z. Case-Control Study of Lung Cancer Risk from Residential Radon Exposure in Worcester County, Massachusetts. Health Phys. 2008, 94, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornalski, K.W.; Adams, R.; Allison, W.; Corrice, L.E.; Cuttler, J.M.; Davey, C.; Dobrzyński, L.; Esposito, V.J.; Feinendegen, L.E.; Gomez, L.S.; et al. The assumption of radon-induced cancer risk. Cancer Causes Control. 2015, 26, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyński, L.; Fornalski, K.; Reszczyńska, J. Meta-analysis of thirty-two case–control and two ecological radon studies of lung cancer. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 59, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.R. Epidemiologic Studies Cannot Reveal the True Shape of the Dose–Response Relationship for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer. Dose-Response 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pylak, M.; Fornalski, K.W.; Reszczyńska, J.; Kukulski, P.; Waligórski, M.P.R.; Dobrzyński, L. Analysis of Indoor Radon Data Using Bayesian, Random Binning, and Maximum Entropy Methods. Dose-Response 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 December 2013. Laying down Basic Safety Standards for Protection against the Dangers Arising from Exposure to Ionising Radiation, and Repealing Directives 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/ Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom1. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/sites/ener/files/documents/CELEX- 32013L0059-EN-TXT.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Vimercati, L.; Cavone, D.; Caputi, A.; Delfino, M.C.; De Maria, L.; Ferri, G.M.; Serio, G. Malignant mesothelioma in construction workers: The Apulia regional mesothelioma register, Southern Italy. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavacci, S.J.; Shapiro, C.D.; Pindilli, E.J.; Casey, C.F.; Rayens, M.K.; Wiggins, A.T.; Andrews, W.M., Jr.; Hahn, E.J. Economic valuation of health benefits from using geologic data to communicate radon risk potential. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossew, P.; Cinelli, G.; Ciotoli, G.; Crowley, Q.G.; De Cort, M.; Medina, J.E.; Gruber, V.; Petermann, E.; Tollefsen, T. Development of a Geogenic Radon Hazard Index—Concept, History, Experiences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann, E.; Bossew, P. Mapping indoor radon hazard in Germany: The geogenic component. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 780, 146601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelić, G.; Čeliković, I.; Živanović, M.; Vukanac, I.; Nikolić, J.K.; Cinelli, G.; Gruber, V. Literature Review of Indoor Radon Surveys in Europe; JRC Technical Reports; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, G.M.; Intranuovo, G.; Cavone, D.; Corrado, V.; Birtolo, F.; Tricase, P.; Fuso, R.; Vilardi, V.; Sumerano, M.; L’Abbate, N.; et al. Estimates of the Lung Cancer Cases Attributable to Radon in Municipalities of Two Apulia Provinces (Italy) and Assessment of Main Exposure Determinants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legge Regionale n. 30 del 3/11/2016: “Norme in Materia di Riduzione Dalle Esposizioni alla Radioattività Naturale Derivante dal gas ‘Radon’ in Ambiente Chiuso”, Modificata dall’art. 25 Legge Regionale 36/2017 del 09/08/2017 e Dall’art.12 Della Legge Regionale 18/2019. Available online: http://www.arpa.puglia.it/web/ guest/agentifisici_radon_normativa (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Legislative Decree 31 July 2020, n. 101 “Implementation of Directive 2013/59 / Euratom” (GU General Series n.201 of 12-08-2020–Ordinary Suppl. N. 29). Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/08/12/20G00121/sg (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Goto, M.; Yasuoka, Y.; Nagahama, H.; Muto, J.; Omori, Y.; Ihara, H.; Mukai, T. Anomalous changes in atmospheric radon concentration before and after the 2011 northern Wakayama Earthquake (Mj 5.5). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 174, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muhammad, S.; Ullah, R.; Turab, S.A.; Khan, M.Y.; Khattak, N.U.; Khan, M.A. Radon concentration in drinking water and soil after the September 24, 2019, Mw 5.8 earthquake, Mirpur, Azad Jammu, and Kashmir: An evaluation for potential risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32628–32636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, Y.; Nagahama, H.; Yasuoka, Y.; Muto, J. Radon degassing triggered by tidal loading before an earthquake. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Cannelli, V.; Piersanti, A. Monitoring soil radon during the 2016–2017 central Italy sequence in light of seismicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccimei, P.; Mollo, S.; Soligo, M.; Scarlato, P.; Castelluccio, M. Real-time setup to record radon emission during rock de-formation: Implications for geochemical surveillance. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. Discuss. 2015, 5, 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- Piersanti, A.; Cannelli, V.; Galli, G. The Pollino 2012 seismic sequence: Clues from continuous radon monitoring. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Içhedef, M.; Giammanco, S.; Neri, M.; Catalano, R.; Immé, G.; Morelli, D.; Muré, F.; Giudice, N. In soil radon anomalies and volcanic activity on Mt. Etna (Italy). J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 218, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, D.; Nagahama, H.; Muto, J.; Yasuoka, Y. Non-parametric detection of atmospheric radon concentration anomalies related to earthquakes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, J.; Yasuoka, Y.; Miura, N.; Iwata, D.; Nagahama, H.; Hirano, M.; Ohmomo, Y.; Mukai, T. Preseismic atmospheric radon anomaly associated with 2018 Northern Osaka earthquake. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Casal-Guisande, M.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B. Design and Development of a New Methodology Based on Expert Systems Applied to the Prevention of Indoor Radon Gas Exposition Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studnička, F.; Štěpán, J.; Šlégr, J. Low-Cost Radon Detector with Low-Voltage Air-Ionization Chamber. Sensors 2019, 19, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarellos, A.; Gestal, M.; Dorado, J.; Rabuñal, J.R. Developing a Secure Low-Cost Radon Monitoring System. Sensors 2020, 20, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Brewster, M.S.; Schwartz, G.G. Communicating radon risk via a smartphone app: A pilot intervention study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterweck, G.; Schmidt, V.; Buchröder, H.; Hügi, R.; Hohmann, E.; Foerster, E.; Mayer, S. Reference instruments based on spectrometric measurement with Lucas Cells. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 167, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbady, A.; Michel, R. Indoor radon measurement with The Lucas cell technique. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloy, K.B.; James, D.S.; Mohs, K.; Kornfeld, V. Lung Cancer in a Nonsmoking Underground Uranium Miner. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Abbate, N.; Marcuccio, P.; Dipace, C.; Carbonara, M.; Carioggia, E.; Martucci, V.; Salamanna, S.; Simeone, G.; Vitucci, L. Contaminazione da radon indoor nelle abitazioni pugliesi e valutazione della probabilità di insorgenza di tumore polmonare nella popolazione residente [Indoor radon pollution in houses in the Apulian Region of Italy and evaluation of the probability of lung cancer in the population]. Med. Lav. 2002, 93, 527–539. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, N.; Muirhead, C.; Bochicchio, F.; Haylock, R.G.E. Calculation of lifetime lung cancer risks associated with radon exposure, based on various models and exposure scenarios. J. Radiol. Prot. 2015, 35, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, F.; Campos Venuti, G.; Piermattei, S.; Torri, G.; Nuccetelli, C.; Risica, S.; Tommasino, L. Results of the national survey on radon indoors in the all the 21 Italian Regions. In Proceedings of the “Radon in the Living Environment” Workshop, Athens, Greece, 19–23 April 1999; pp. 997–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Loffredo, F.; Savino, F.; Amato, R.; Irollo, A.; Gargiulo, F.; Sabatino, G.; Serra, M.; Quarto, M. Indoor Radon Concentration and Risk Assessment in 27 Districts of a Public Healthcare Company in Naples, South Italy. Life 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienneau, D.; Boz, S.; Forlin, L.; Flückiger, B.; de Hoogh, K.; Berlin, C.; Bochud, M.; Bulliard, J.-L.; Zwahlen, M.; Röösli, M. Residential radon—Comparative analysis of exposure models in Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 271, 116356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignani, S.; Venoso, G.; Ampollini, M.; Caprio, M.; Carpentieri, C.; Di Carlo, C.; Caccia, B.; Hunter, N.; Bochicchio, F. A 10-year follow-up study of yearly indoor radon measurements in homes, review of other studies and implications on lung cancer risk estimates. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 762, 144150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, P.; Dowdall, A.; Long, S.; Curtin, B.; Fenton, D. Estimating population lung cancer risk from radon using a resource efficient stratified population weighted sample survey protocol—Lessons and results from Ireland. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 233, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimercati, L.; Fucilli, F.; Cavone, D.; De Maria, L.; Birtolo, F.; Ferri, G.M.; Soleo, L.; Lovreglio, P. Radon Levels in Indoor Environments of the University Hospital in Bari-Apulia Region Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.M.; Chreim, S. Residents’ perceptions of radon health risks: A qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, J.; Coyle, D.; Whyte, J.; Krewksi, D. Global Estimate of Lung Cancer Mortality Attributable to Residential Radon. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 057009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.C.; Sheen, S.S.; Koh, S.B.; Park, K.S.; Cho, N.H.; Lee, C.-M.; Kang, D.R. Residential Radon Exposure and Cigarette Smoking in Association with Lung Cancer: A Matched Case-Control Study in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdoraghi, M.; Einor, D.; Asghari, F.B.; Esrafili, A.; Heidari, N.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Yousefi, M. Assess the annual effective dose and contribute to risk of lung cancer caused by internal radon 222 in 22 regions of Tehran, Iran using geographic information system. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.B.; Kim, J.; Labrèche, F.; Heer, E.; Song, C.; Arrandale, V.H.; Pahwa, M.; Peters, C.E.; Demers, P.A. Estimating the burden of lung cancer in Canada attributed to occupational radon exposure using a novel exposure assessment method. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2020, 93, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.S.; Egger, S.; Hughes, S.; Weber, M.; Steinberg, J.; Rahman, B.; Worth, H.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Rawstorne, P.; Yu, X.Q. Systematic review and meta-analysis of residential radon and lung cancer in never-smokers. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, W.; Shi, T. Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowski, A.; Shemiakina, E.; Güthlin, D.; Becker, J.; Preston, D.; Apostoaei, A.I.; Hoffman, F.O.; Jacob, P.; Kaiser, J.C.; Eidemüller, M. ProZES: The methodology and software tool for assessment of assigned share of radiation in probability of cancer occurrence. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2020, 59, 601–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.D. Lung cancer risk and effective dose coefficients for radon: UNSCEAR review and ICRP conclusions. J. Radiol. Prot. 2021, 41, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Evaluation of occupational radon exposure and comparison with residential radon exposure in Canada—A population-level assessment. J. Radiol. Prot. 2020, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.S.D.; Tomášek, L.; Zablotska, L.B.; Rage, E.; Momoli, F.; Little, J. Low radon exposures and lung cancer risk: Joint analysis of the Czech, French, and Beaverlodge cohorts of uranium miners. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2019, 92, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, M.; Sobotzki, C.; Schnelzer, M.; Fenske, N. Factors Modifying the Radon-Related Lung Cancer Risk at Low Exposures and Exposure Rates among German Uranium Miners. Radiat. Res. 2017, 189, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, G.; De Filippis, G.; Totaro, T.; Tamborino, B.; Idolo, A.; Serio, F.; Castorini, I.F.; Valenzano, B.; Riccio, A.; Miani, A.; et al. Evaluation of radon exposure risk and lung cancer incidence/mortality in South-eastern Italy. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2020, 61, E31–E38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Chauhan, V.; Kumar, N.; Hazarika, D. Assessment of Rn-222 continuous time series for the identification of anomalous changes during moderate earthquakes of the Garhwal Himalaya. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 166, 109327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Katlamudi, M.; Barman, C.; Lakshmi, G.U. Identification of earthquake precursors in soil radon-222 data of Kutch, Gujarat, India using empirical mode decomposition based Hilbert Huang Transform. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 222, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, F.; Thinová, L.; Briestenský, M.; Giudicepietro, F.; Roca, V.; Sabbarese, C. Analysis of geophysical and meteorological parameters influencing 222Rn activity concentration in Mladeč caves (Czech Republic) and in soils of Phlegrean Fields caldera (Italy). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 160, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Radon Residential LOCOROTONDO (Ground Floor) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Number of Samples | Median | Min | Max | Mean | St.Dev. | St.Err. | Var. Coef. (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis |
| January | 1824 | 434.01 | 11 | 1087 | 412.59 | 274.58 | 6.43 | 66.55 | 0.18 | 1.92 |
| February | 2780 | 329.12 | 0 | 1811 | 358.06 | 269.44 | 5.11 | 75.25 | 0.95 | 3.89 |
| March | 2996 | 336.33 | 0 | 1350 | 324.37 | 232.30 | 4.24 | 71.62 | 0.78 | 3.90 |
| April | 2805 | 270.84 | 4 | 1438 | 366.01 | 323.21 | 6.10 | 88.31 | 0.87 | 3.01 |
| May | 2350 | 156.51 | 4 | 1001 | 222.06 | 206.35 | 4.26 | 92.93 | 1.35 | 4.59 |
| June | 2879 | 101.38 | 4 | 849 | 137.01 | 124.04 | 2.31 | 90.53 | 1.90 | 7.04 |
| July | 2336 | 40.60 | 30 | 48 | 95.80 | 68.62 | 1.42 | 71.63 | 1.37 | 4.58 |
| August | 2976 | 44.77 | 0 | 232 | 58.02 | 42.53 | 0.78 | 73.29 | 1.72 | 4.16 |
| September | 2880 | 91.39 | 9 | 417 | 118.91 | 92.40 | 1.72 | 77.71 | 0.83 | 2.62 |
| October | 2980 | 134.68 | 8 | 833 | 162.97 | 165.91 | 3.04 | 101.81 | 2.67 | 10.81 |
| November | 2873 | 338.18 | 13 | 914 | 366.23 | 198.80 | 3.71 | 54.28 | 0.42 | 2.56 |
| December | 429 | 75.85 | 11 | 706 | 162.92 | 169.76 | 8.20 | 104.20 | 1.34 | 3.99 |
| Annual | 30,078 | 134.68 | 0 | 1811 | 232.72 | 232.73 | 1.34 | 100.00 | 1.49 | 5.14 |
| Temperature Residential (Ground Floor) | Humidity Residential (Ground Floor) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Number of Samples | Mean | St.Dev. | St.Err. | Var. Coef. (%) | Number of Samples | Mean | St.Dev. | St.Err. | Var. Coef. (%) |
| January | 1824 | 21.77 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 3.50 | 1824 | 43.75 | 2.41 | 0.06 | 5.51 |
| February | 2782 | 23.00 | 1.15 | 0.02 | 5.02 | 2780 | 37.27 | 4.66 | 0.09 | 12.50 |
| March | 2966 | 23.10 | 1.23 | 0.02 | 5.32 | 2966 | 36.33 | 3.39 | 0.06 | 9.32 |
| April | 2085 | 23.95 | 1.14 | 0.03 | 4.77 | 2805 | 37.90 | 3.92 | 0.07 | 10.35 |
| May | 2350 | 26.42 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 2.64 | 2350 | 40.39 | 3.47 | 0.07 | 8.59 |
| June | 2879 | 27.39 | 1.32 | 0.02 | 4.83 | 2879 | 45.79 | 2.98 | 0.06 | 6.52 |
| July | 2336 | 31.43 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 2.33 | 2336 | 40.92 | 2.50 | 0.05 | 6.12 |
| August | 2976 | 33.34 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 2.23 | 2976 | 42.27 | 2.64 | 0.05 | 6.24 |
| September | 2880 | 31.59 | 1.31 | 0.02 | 4.14 | 2880 | 43.63 | 3.71 | 0.07 | 8.50 |
| October | 2980 | 26.81 | 1.19 | 0.02 | 4.43 | 2980 | 45.57 | 3.33 | 0.06 | 7.31 |
| November | 427 | 26.16 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 428 | 45.65 | 1.08 | 0.05 | 2.36 |
| December | Data not available | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Annual | 27,205 | 27.02 | 3.95 | 0.02 | 14.62 | 27,207 | 41.41 | 4.74 | 0.03 | 11.45 |
| New Detectors (CARQUAI) | Arpa Detectors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Mean | Sd | RSDr | Mean | Sd | RSDr | |
| 30/01/2020 | 214.63 | 96.44 | 44.93 | 143.00 | 87.06 | 60.87 | * |
| 31/01/2020 | 191.26 | 157.16 | 82.17 | 177.08 | 106.05 | 59.88 | |
| 01/02/2020 | 251.55 | 61.62 | 24.50 | 208.18 | 81.09 | 38.95 | * |
| 02/02/2020 | 319.68 | 191.84 | 60.01 | 340.00 | 203.76 | 59.95 | * |
| 03/02/2020 | 149.05 | 52.42 | 35.17 | 104.44 | 45.86 | 43.90 | * |
| 04/02/2020 | 179.03 | 108.52 | 60.62 | 139.17 | 109.00 | 78.32 | * |
| 05/02/2020 | 943.14 | 188.03 | 19.77 | 659.52 | 231.57 | 35.11 | * |
| 06/02/2020 | 720.02 | 230.17 | 31.97 | 596.67 | 85.16 | 14.27 | |
| 07/02/2020 | 498.07 | 159.32 | 31.99 | 361.54 | 82.95 | 22.94 | |
| 08/02/2020 | 440.03 | 125.91 | 28.61 | 465.83 | 109.91 | 23.59 | |
| 09/02/2020 | 138.03 | 61.58 | 44.62 | 107.65 | 112.52 | 104.52 | * |
| Total | 368.17 | 287.72 | 78.15 | 328.63 | 243.22 | 74.01 | |
| Data Input | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Locorotondo | |||
| Province | Bari | |||
| Population | 14,500 | |||
| Annual Mean concentration (Bq/m3) | 233 | |||
| F | 0.50 | |||
| Number of hours a year | 7000 | |||
| EEC D 1WLM | 6.30 | |||
| Probability of lung cancer in eccess | 2.83 | |||
| Data Output | ||||
| Annual Cumulative Exposure | 16.29 | |||
| EEC1 | 8.15 | |||
| 210Po (CA) | 2.12 | Annual cases of Radon attributable lung cancer | 3.66 | |
| 214Pb (CB) | 2.12 | |||
| 214Bi (Cc) | 18.00 | |||
| WLM | 1.29 | |||
| Radon Residential (Ground Floor) | Magnitude | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Number of Samples | Median | Min | Max | Number of Measurements | Median | Min | Max |
| January | 1824 | 434.01 | 11 | 1087 | 120 | 2.40 | 2.00 | 7.80 |
| February | 2780 | 329.12 | 0 | 1811 | 188 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 6.90 |
| March | 2966 | 336.33 | 0 | 1350 | 187 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 7.60 |
| April | 2805 | 270.84 | 4 | 1438 | 185 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 6.40 |
| May | 2350 | 156.51 | 4 | 1001 | 196 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 6.70 |
| June | 2879 | 101.38 | 4 | 849 | 138 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 7.60 |
| July | 2336 | 40.60 | 30 | 48 | 91 | 2.40 | 2.00 | 7.70 |
| August | 2976 | 44.77 | 0 | 232 | 154 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 7.10 |
| September | 2880 | 91.39 | 9 | 417 | 168 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 6.80 |
| October | 2980 | 134.68 | 8 | 833 | 196 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 7.40 |
| November | 2873 | 338.18 | 13 | 914 | 17 | 2.10 | 2.00 | 6.10 |
| December | 429 | 75.85 | 11 | 706 | Not available | - | - | - |
| Annual | 30,078 | 134.68 | 0 | 1811 | 1640 | 2.30 | 2.00 | 7.80 |
| Magnitude | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radon conc. | (≥2.7 mL) | (<2.7 mL) | Total | |
| (≥557 Bq/m3) | 43 | 114 | 157 | |
| (<557 Bq/m3) | 345 | 1138 | 1483 | |
| Total | 388 | 1252 | 1640 | |
| Odds Ratio | 95% LCL | 95% UCL | χ2 | p |
| 1.240 | 0.860 | 1.800 | 1.340 | 0.240 |
| Magnitude | Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | Z | p > Z | (95% Conf. Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radon | 1.231 * | 0.113 | 2.260 | 0.024 | 1.028 | 1.474 |
| Humidity | 1.008 | 0.062 | 0.130 | 0.894 | 0.894 | 1.137 |
| Temperature | 1.436 * | 0.099 | 5.230 | 0.000 | 1.254 | 1.645 |
| Season | 0.993 | 0.035 | −0.200 | 0.842 | 0.926 | 1.065 |
| _cons | 13.545 * | 1.035 | 34.110 | 0.000 | 11.662 | 15.733 |
| Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | Z | p > Z | (95% Conf. Interval) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | 1.227 * | 0.112 | 2.230 | 0.026 | 1.025 | 1.468 |
| Spring | 1.235 * | 0.113 | 2.320 | 0.021 | 1.033 | 1.477 |
| Summer | 1.252 * | 0.114 | 2.460 | 0.014 | 1.047 | 1.497 |
| Autumn | 1.221 * | 0.112 | 2.190 | 0.029 | 1.021 | 1.461 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vimercati, L.; Cavone, D.; Delfino, M.C.; De Maria, L.; Caputi, A.; Sponselli, S.; Corrado, V.; Bruno, V.; Spalluto, G.; Eranio, G.; et al. Relationships among Indoor Radon, Earthquake Magnitude Data and Lung Cancer Risks in a Residential Building of an Apulian Town (Southern Italy). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101342
Vimercati L, Cavone D, Delfino MC, De Maria L, Caputi A, Sponselli S, Corrado V, Bruno V, Spalluto G, Eranio G, et al. Relationships among Indoor Radon, Earthquake Magnitude Data and Lung Cancer Risks in a Residential Building of an Apulian Town (Southern Italy). Atmosphere. 2021; 12(10):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101342
Chicago/Turabian StyleVimercati, Luigi, Domenica Cavone, Maria Celeste Delfino, Luigi De Maria, Antonio Caputi, Stefania Sponselli, Vincenzo Corrado, Vito Bruno, Gianfranco Spalluto, Giorgia Eranio, and et al. 2021. "Relationships among Indoor Radon, Earthquake Magnitude Data and Lung Cancer Risks in a Residential Building of an Apulian Town (Southern Italy)" Atmosphere 12, no. 10: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101342
APA StyleVimercati, L., Cavone, D., Delfino, M. C., De Maria, L., Caputi, A., Sponselli, S., Corrado, V., Bruno, V., Spalluto, G., Eranio, G., & Ferri, G. M. (2021). Relationships among Indoor Radon, Earthquake Magnitude Data and Lung Cancer Risks in a Residential Building of an Apulian Town (Southern Italy). Atmosphere, 12(10), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101342









