Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity and Socioeconomic driving Factors of PM2.5 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
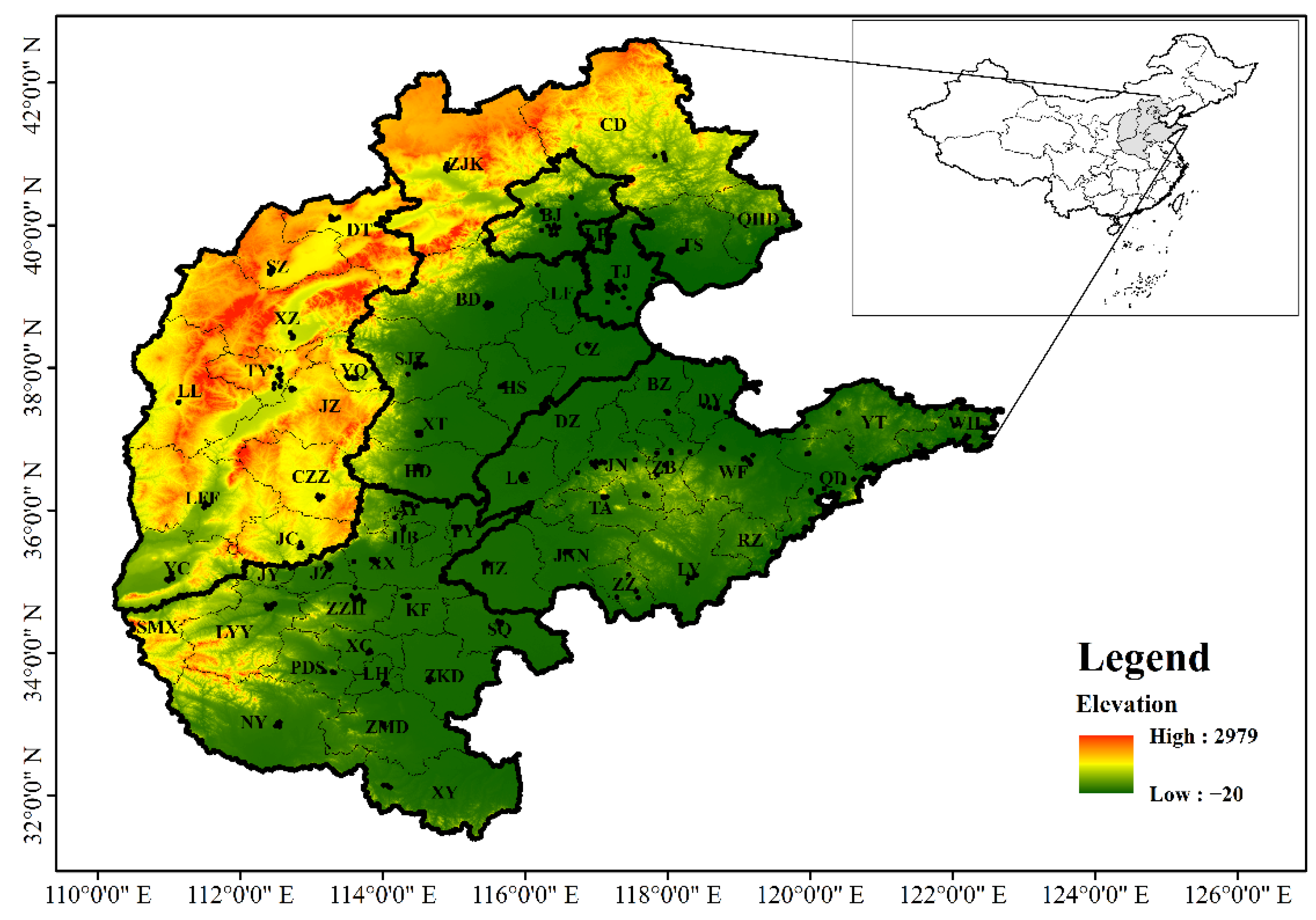
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Validity
2.3. Statistical Methods
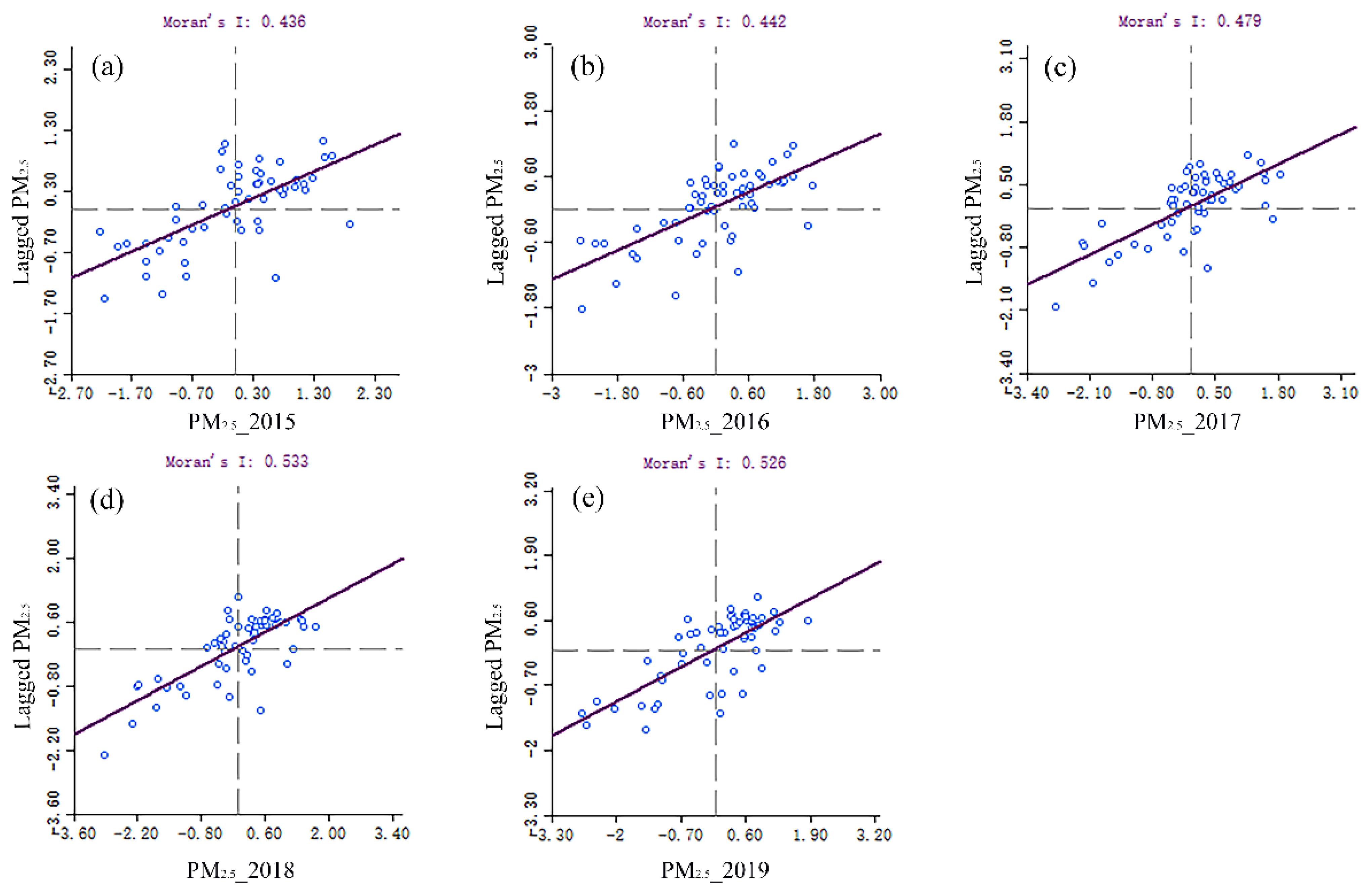
2.3.1. Moran’s I Test
2.3.2. Hot Spot Analysis
2.3.3. Spatial Lag Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5
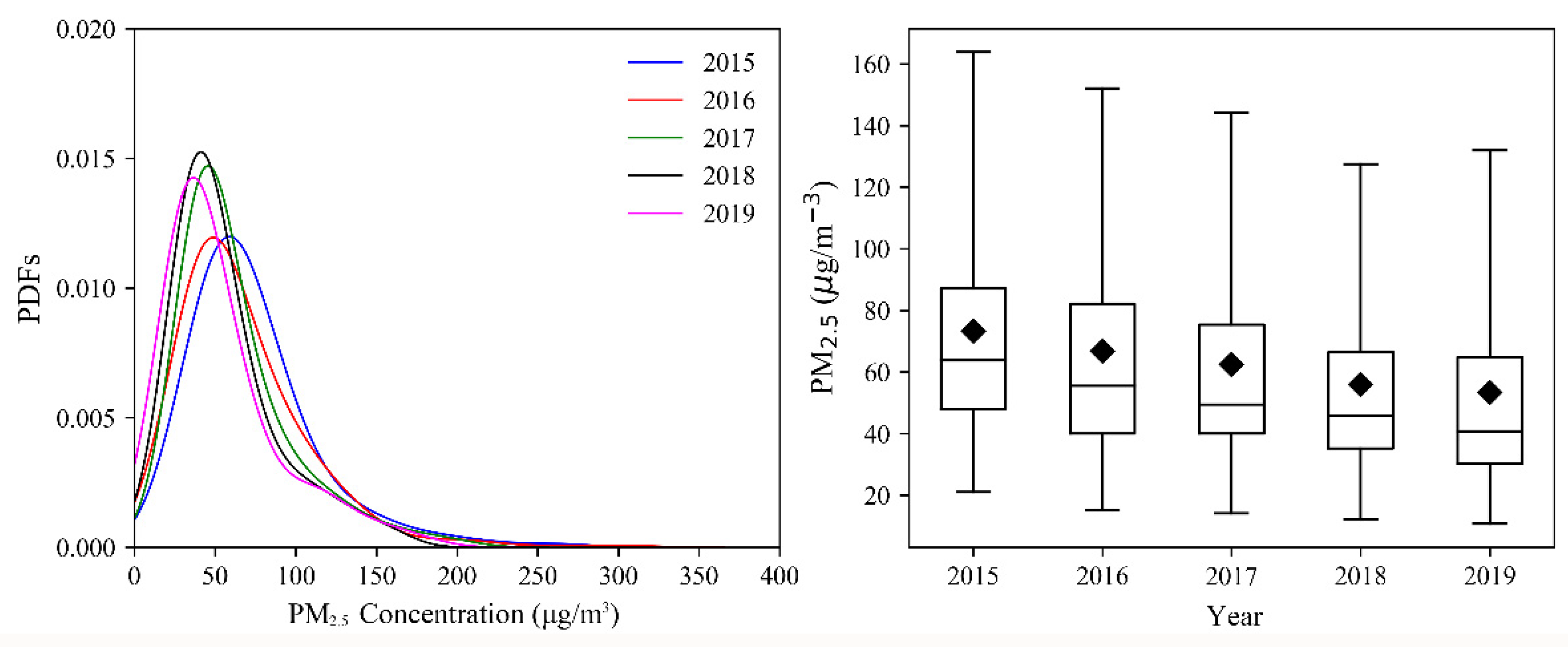
3.1.1. Temporal Variation Trend of PM2.5 Concentration
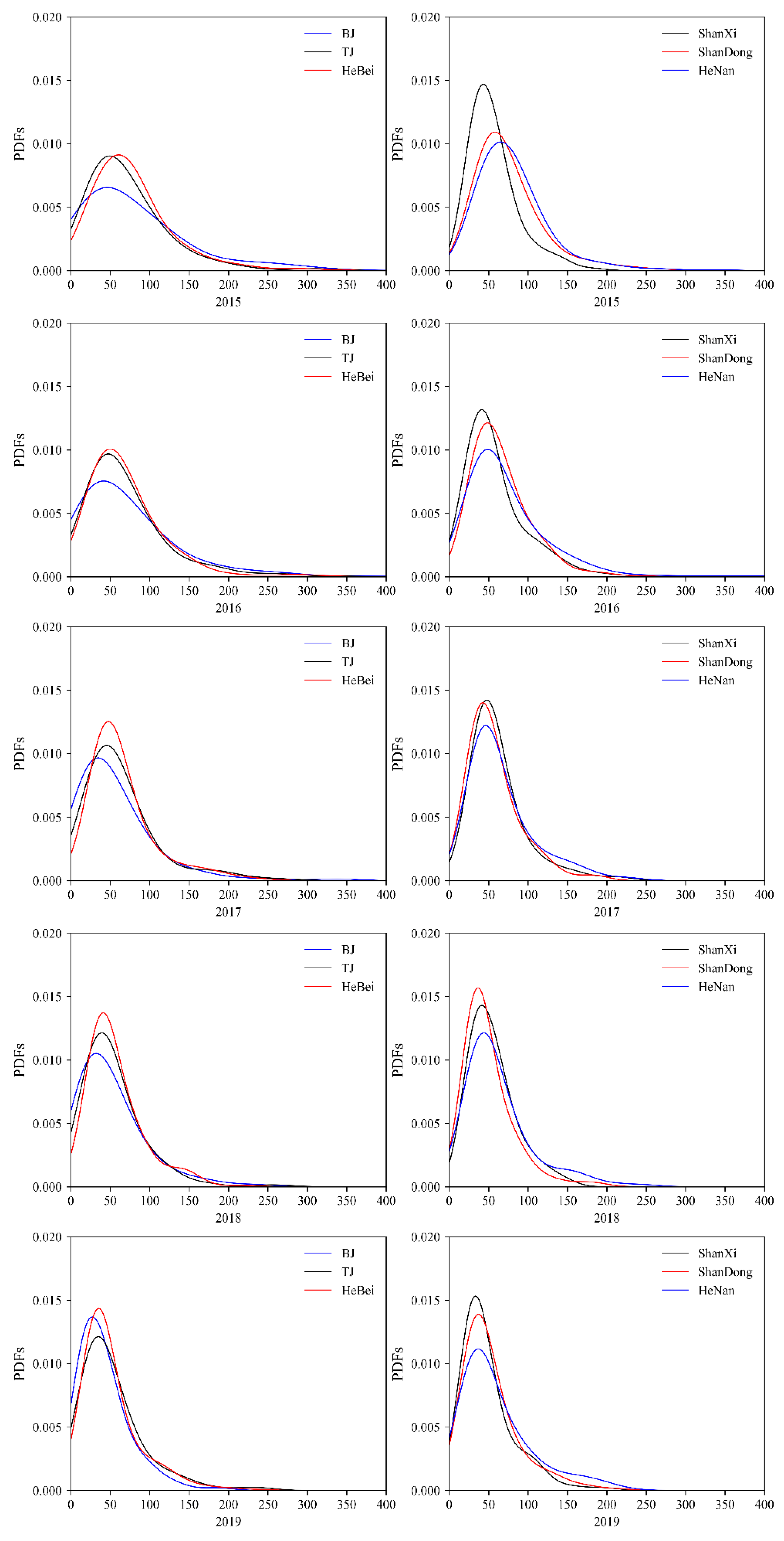
3.1.2. The Spatial Heterogeneity of Temporal Variations
3.2. Spatial Variation Trend of PM2.5
3.3. Analysis of Socioeconomic Influence Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Wilson, J.P.; MacDonald, B.; Zhang, W.; Yu, T. The changing PM2.5 dynamics of global megacities based on long-term remotely sensed observations. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Q.; Wu, G.; Gautam, A.; Jiang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Guan, H. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China, from 2013 to 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, C.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.L. Socioeconomic Drivers of PM2.5 in the Accumulation Phase of Air Pollution Episodes in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pala, K.; Aykac, N.; Yasin, Y. Premature deaths attributable to long-term exposure to PM2.5 in Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 37, 51940–51947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Saari, R.K.; Zhou, G.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Liu, X. Recent trends in premature mortality and health disparities attributable to ambient PM2.5 exposure in China: 2005–2017. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.C.; Jie, Y.; Jun, H.; Xiaogang, Y.; Richard, H.; Dongsheng, J. An investigation into the impact of variations of ambient air pollution and meteorological factors on lung cancer mortality in Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 779, 146427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Fang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J. Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Ren, H.; Cao, J. Impacts of natural and socioeconomic factors on PM2.5 from 2014 to 2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Fang, C. Pollution Characteristics, Transport Pathways, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and PM10 in Changchun City in 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, H.; Tang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.; Yi, H. Transition in air pollution, disease burden and health cost in China: A comparative study of long-term and short-term exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.; Kwan, M.P.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Influence of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A review of methodology and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, W.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Ren, Z.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variation in the impact of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 pollution in China from 2000 to 2017. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, P.; Huang, R.; Ye, B. How do socioeconomic factors influence urban PM2.5 pollution in China? Empirical analysis from the perspective of spatiotemporal disequilibrium. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 761, 143266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. The impact of foreign direct investment on urban PM2.5 pollution in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ren, X.; Kong, Y.; Ye, B.; Liao, Z. The heterogeneous effects of socioeconomic determinants on PM2.5 concentrations using a two-step panel quantile regression. Appl. Energy 2020, 272, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Cheng, C.; Yang, D. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM2.5 and its relationship with urbanization in North China from 2000 to 2017. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 744, 140925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics–Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Ma, M.; Chang, N.B.; Gao, W. Spatiotemporal trend analysis for fine particulate matter concentrations in China using high-resolution satellite-derived and ground-measured PM2.5 data. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Silva, E.A.; Liu, J. A decade of battle against PM2.5 in Beijing. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2018, 50, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.-S.; Wang, J.-H.; Song, W.-D.; Cheng, X.-F. Spatio-temporal Evolution of PM2.5 Concentration During 2000-2019 in China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4832–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, S.; Zhou, H. Spatio-temporal characteristics and convergence trends of PM2.5 pollution: A case study of cities of air pollution transmission channel in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Chang, X.; Ding, D.; Zheng, H. Regional transport in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its changes during 2014-2017: The impacts of meteorology and emission reduction. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 737, 139792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, S.; Long, R.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z. Determinants of haze pollution: An analysis from the perspective of spatiotemporal heterogeneity. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, T. Potential heterogeneity in the relationship between urbanization and air pollution, from the perspective of urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W. Growing Urbanization and the Impact on Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Dynamics. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment—A case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.-M. The influential factors of urban PM2.5 concentrations in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-H.; Wang, J.M.; Hilker, N.; Debosz, J.; Sofowote, U.; Su, Y.; Noble, M.; Healy, R.M.; Munoz, T.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; et al. Temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related PM2.5 sources: Comparison of exhaust and non-exhaust emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, D.Y.H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zuo, Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-B.; Ji, Y.-Q.; Li, S.-L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Characteristics of Elements in PM2.5 and PM10 in Road Dust Fall During Spring in Tianjin. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 39–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qian, X.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, W. Using the geographical detector technique to explore the impact of socioeconomic factors on PM2.5 concentrations in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hong, B.; Jiang, R.; Yan, S.; Zhou, Y. The Effect of Vegetation Enhancement on Particulate Pollution Reduction: CFD Simulations in an Urban Park. Forests 2019, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Category | Variable | Abbreviation | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent variable | PM2.5 concentration | PM2.5 | μg/m3 |
| Dependent variable | Total Population | POP | 104 persons |
| Gross Domestic Product | GDP | 104 CNY | |
| Green Ratio of Built-up Area | GR | % | |
| Output of Second Industry | SI | 104 CNY | |
| Proportion of Urban Population | UP | % | |
| Roads Density | RD | km/km2 | |
| Proportion of Built-up Area | BA | % |
| Year | I | p-Value | Z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 0.372501 | 0.000001 | 4.855292 |
| 2016 | 0.344208 | 0.000006 | 4.532812 |
| 2017 | 0.363731 | 0.000002 | 4.796205 |
| 2018 | 0.389324 | 0.000000 | 5.123085 |
| 2019 | 0.414598 | 0.000000 | 5.429379 |
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Coefficient | Probability | Coefficient | Probability | Coefficient | Probability | Coefficient | Probability | Coefficient | Probability |
| ρ | 0.560 | 0.000 ** | 0.583 | 0.000 ** | 0.739 | 0.000 ** | 0.724 | 0.000 ** | 0.574 | 0.000 ** |
| GDP | −0.405 | 0.005 ** | −0.328 | 0.088 | −0.489 | 0.001 ** | −0.364 | 0.012* | −0.415 | 0.002 ** |
| POP | 0.222 | 0.001 ** | 0.195 | 0.047 * | 0.289 | 0.000 ** | 0.244 | 0.003 ** | 0.243 | 0.002 ** |
| UP | 0.085 | 0.010 * | 0.225 | 0.317 | 0.422 | 0.039 * | 0.351 | 0.091 | 0.339 | 0.080 |
| SI | 0.375 | 0.007 ** | 0.238 | 0.110 | 0.323 | 0.005 ** | 0.202 | 0.062 | 0.248 | 0.018 * |
| RD | 0.337 | 0.000 ** | 0.271 | 0.000 ** | 0.163 | 0.011 * | 0.146 | 0.020 * | 0.218 | 0.001 ** |
| BA | −0.036 | 0.199 | −0.020 | 0.480 | −0.029 | 0.193 | −0.005 | 0.831 | 0.015 | 0.533 |
| GR | 0.217 | 0.332 | −0.112 | 0.560 | −0.132 | 0.631 | −0.166 | 0.582 | −0.163 | 0.595 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Li, R.; Xue, K.; Fang, C. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity and Socioeconomic driving Factors of PM2.5 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101324
Wang J, Li R, Xue K, Fang C. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity and Socioeconomic driving Factors of PM2.5 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(10):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101324
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ju, Ran Li, Kexin Xue, and Chunsheng Fang. 2021. "Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity and Socioeconomic driving Factors of PM2.5 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas" Atmosphere 12, no. 10: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101324
APA StyleWang, J., Li, R., Xue, K., & Fang, C. (2021). Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity and Socioeconomic driving Factors of PM2.5 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas. Atmosphere, 12(10), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101324






