Evaluation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave Simulated by CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Gridded Datasets
2.2. Taylor Analysis
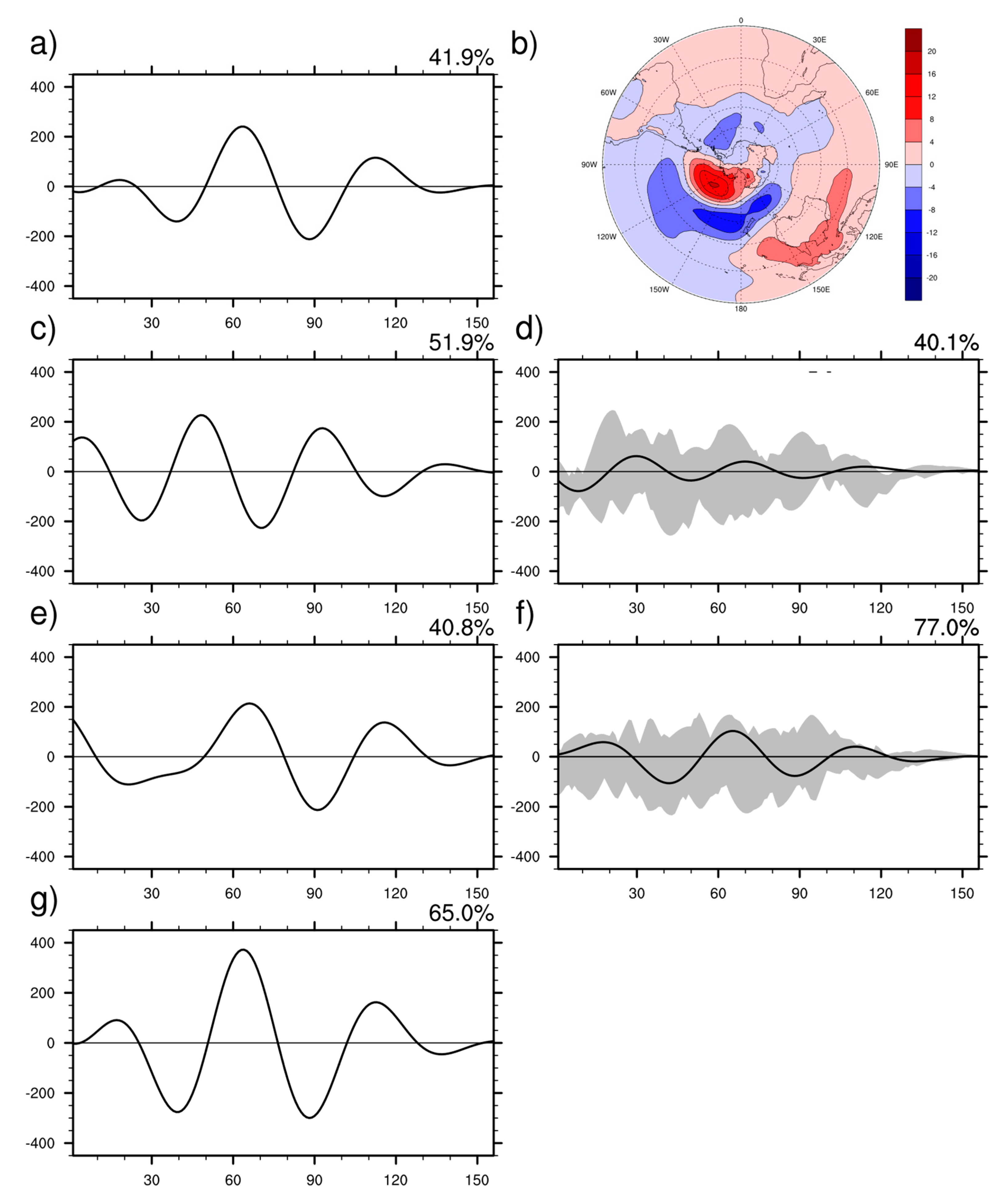
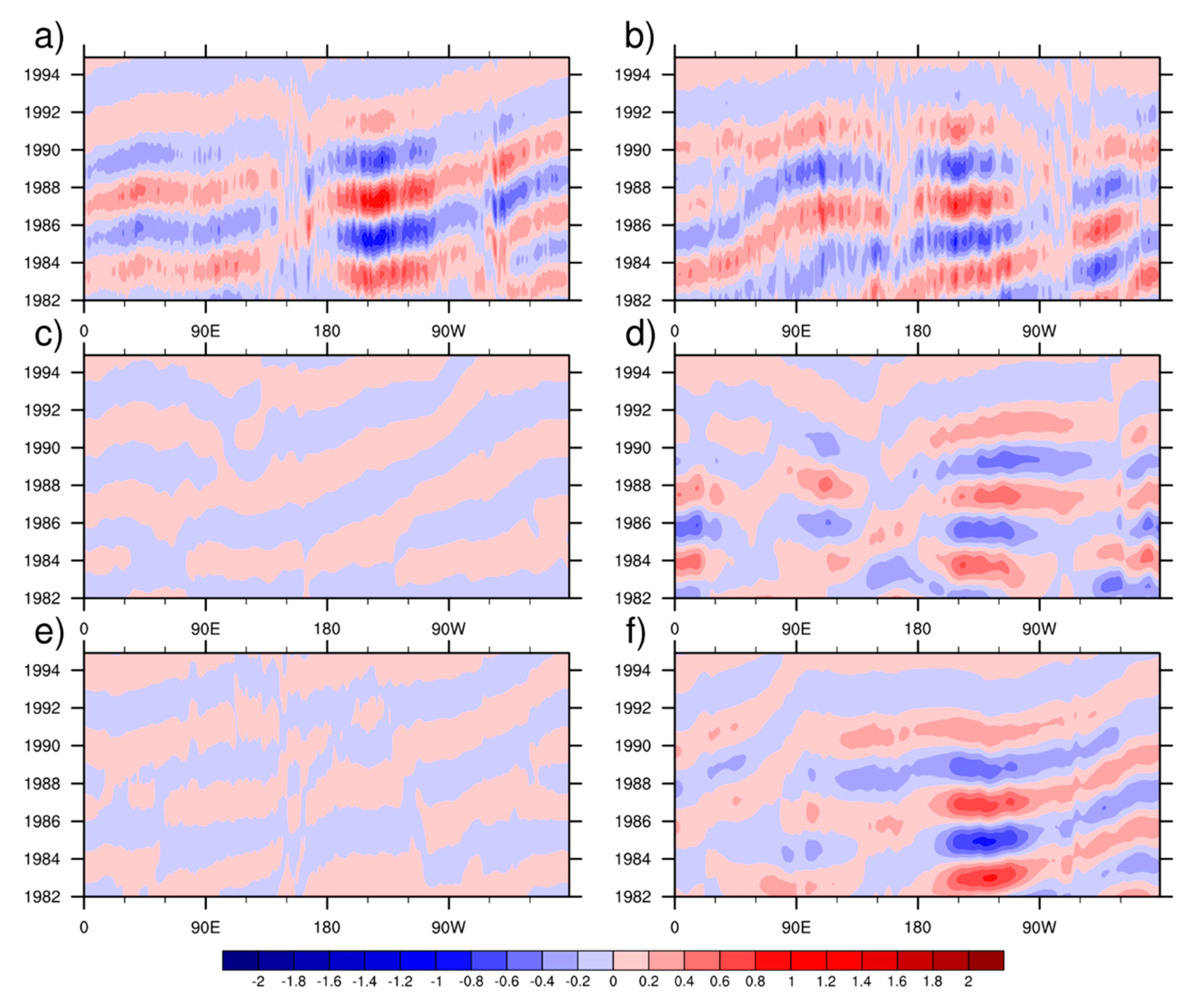
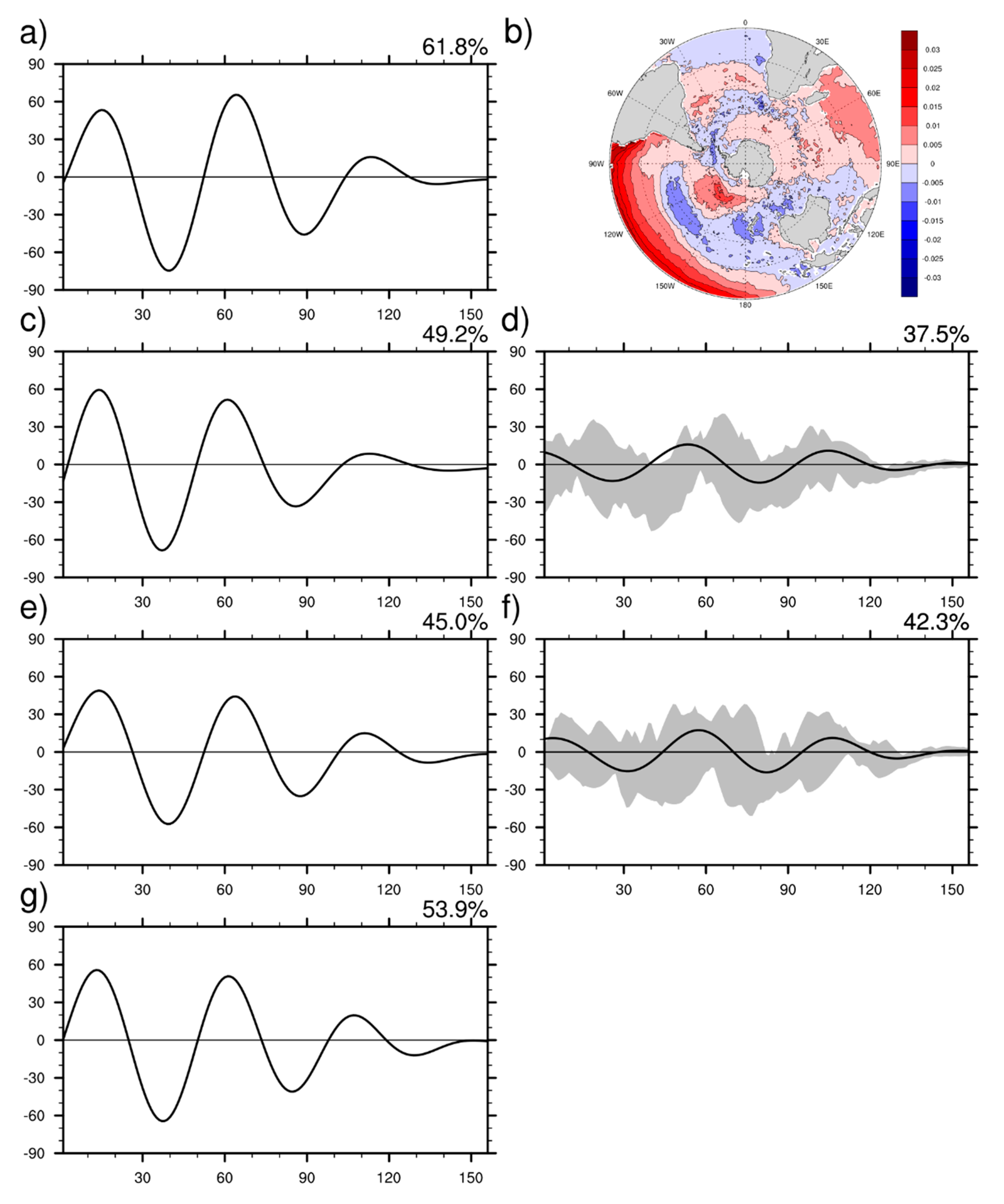
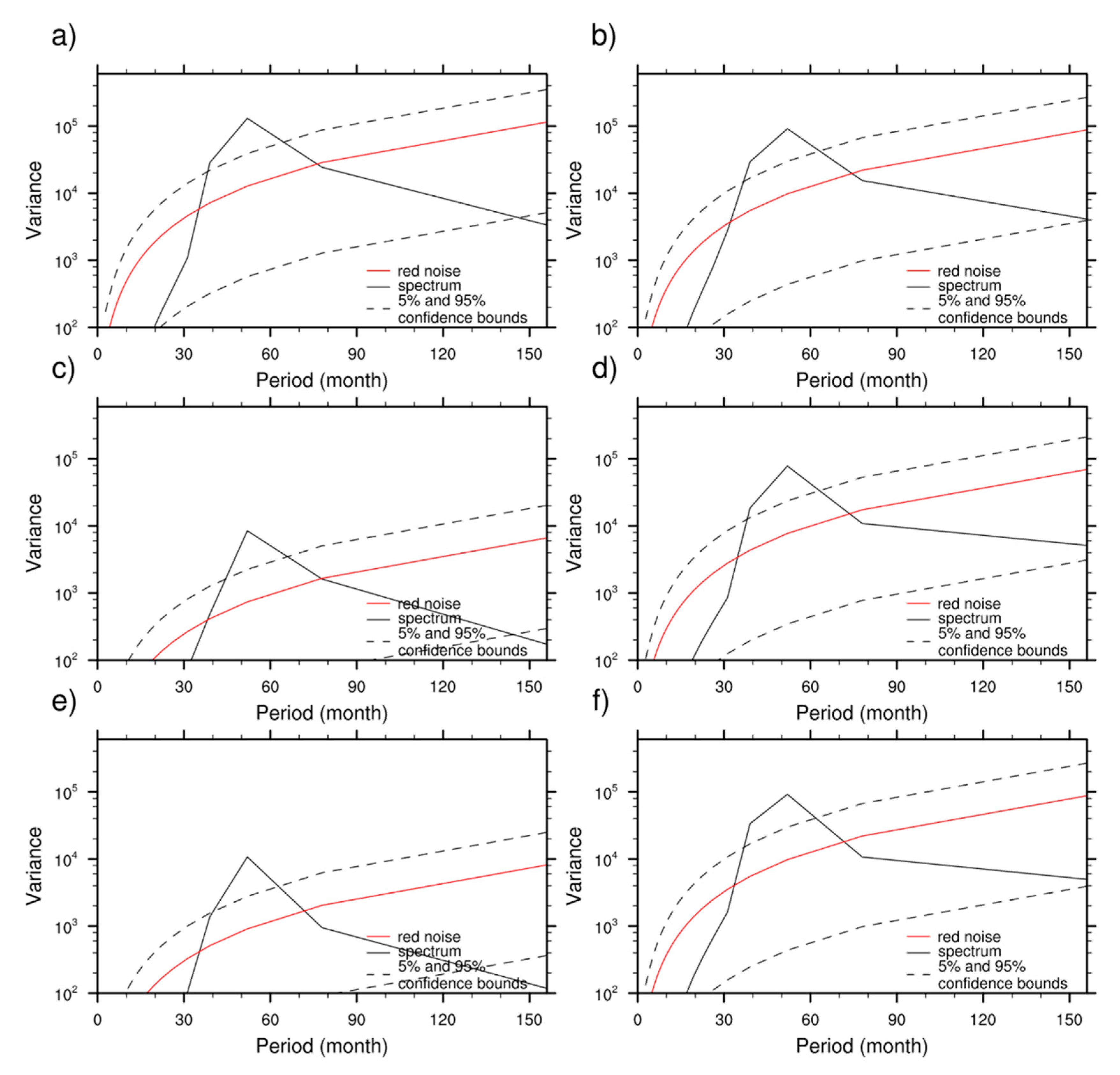
2.3. ACW Extraction
3. Results
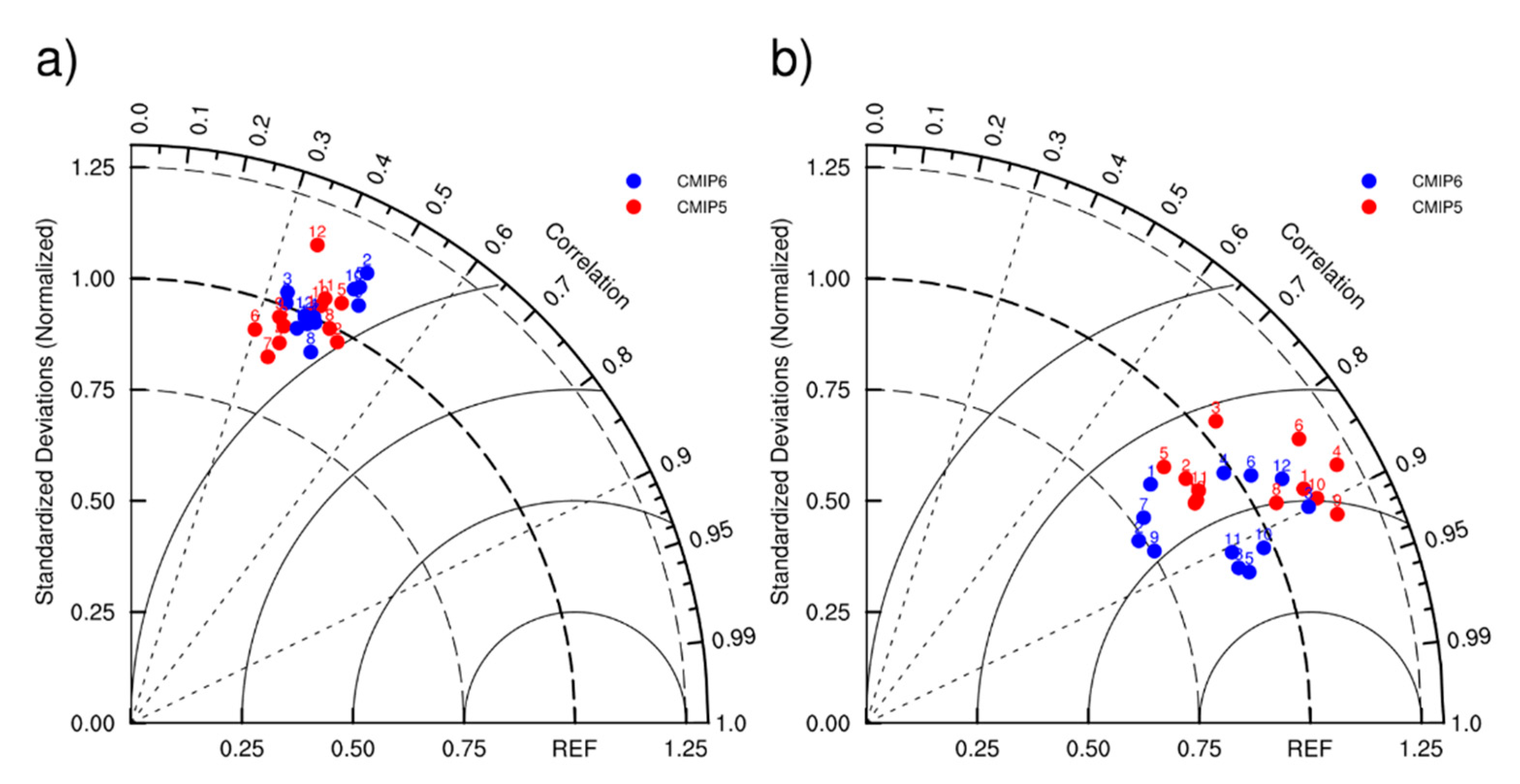
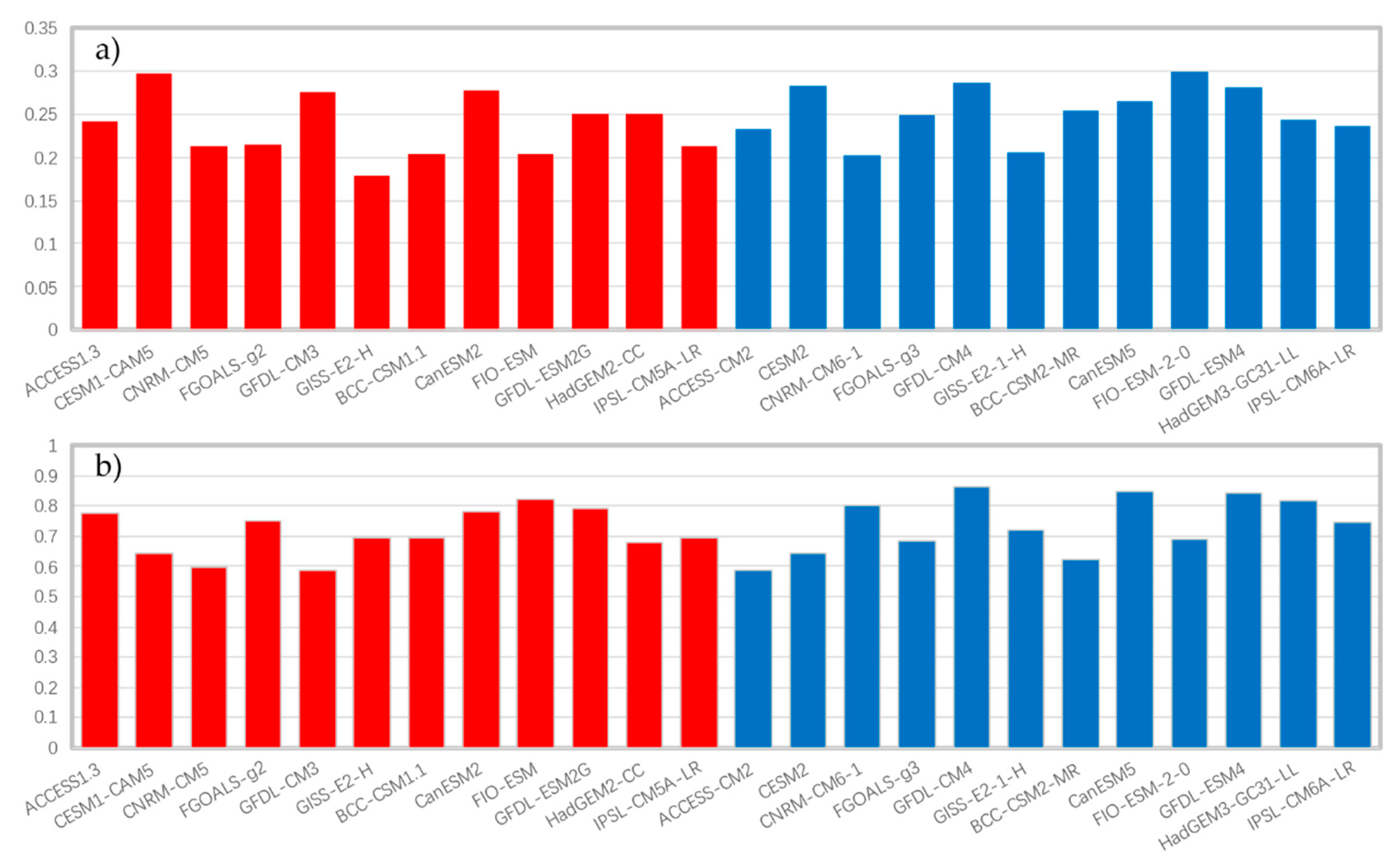
3.1. Taylor Analysis of Model Simulations
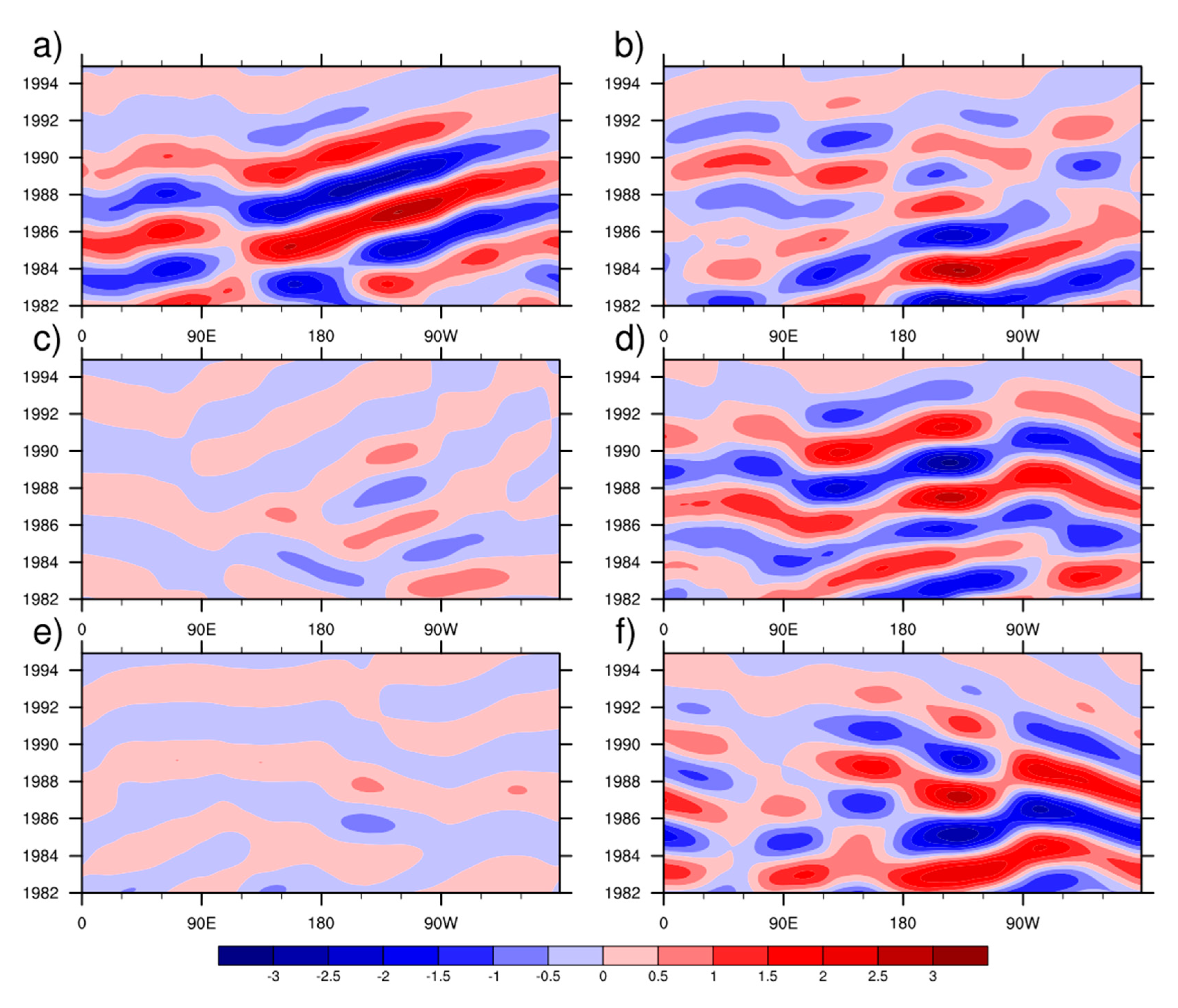
3.2. Evaluation of Model-Simulated SLP
3.3. Evaluation of Model-Simulated SST
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- For SLP simulation, models had low correlations with the reanalysis data. The CMIP6 models show a slightly better performance than the CMIP5 models. Three models, namely, the FIO-ESM model from CMIP5 and the CanESM5 and GFDL-ESM4 models from CMIP6, performed well. Models with an atmospheric chemistry module had better simulations.
- (2)
- For SST simulation, the CMIP6 models reproduced weaker but more reliable signals than the CMIP5 models. Five models, the ACCESS1.3 and CNRM-CM5 models from CMIP5 and the CESM2, GFDL-CM4 and CanESM5 models from CMIP6, performed well. Models with a carbon cycle process and a chemistry module tended to produce better simulations.
- (3)
- When both SLP and SST were taken into consideration, most CMIP6 models show an improvement compared with the CMIP5 version. Models simulated SST better than SLP. The best simulation was produced by the CanESM5 model. Most models could capture the 50-month period of SLP and SST signals in the ACW. The main problem remained in generating the correct phase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, W.B.; Peterson, R.G. An Antarctic circumpolar wave in surface pressure, wind, temperature and sea-ice extent. Nature 1996, 380, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Chen, S.-C.; Peterson, R.G. The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave: A Beta Effect in Ocean-Atmosphere Coupling over the Southern Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 2345–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonekamp, H.; Sterl, A.; Komen, G.J. Interannual variability in the Southern Ocean from an ocean model forced by European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts reanalysis fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 13317–13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Simmonds, I. Sea surface temperature-induced cyclogenesis in the Antarctic circumpolar wave. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.A.; Mitchell, J.L. Ocean circulation variations associated with the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 2947–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Cherry, N.J. Influence of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave upon New Zealand Temperature and Precipitation during Autumn-Winter. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélice, J.L.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Goosse, H.; Fichefet, T.; Reason, C.J.C. Evidence for the Antarctic circumpolar wave in the sub-Antarctic during the past 50 years. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloersen, P.; Huang, N.E. In search of an elusive Antarctic circumpolar wave in sea ice extents: 1978–1996. Polar Res. 1999, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Martinson, D.G. Antarctic Sea Ice Extent Variability and Its Global Connectivity. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1697–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarolla, E.; Matano, R.P. The Low-Frequency Variability of the Southern Ocean Circulation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6081–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cerrone, D.; Fusco, G.; Cotroneo, Y.; Simmonds, I.; Budillon, G. The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave: Its Presence and Interdecadal Changes during the Last 142 Years. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6371–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Kim, S.; Lim, K.; Kim, S.Y. Time series analysis of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave via symbolic transfer entropy. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 499, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuncio, M.; Luis, A.J.; Yuan, X. Topographic meandering of Antarctic Circumpolar Current and Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in the ice-ocean-atmosphere system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, J.; He, Y. Review of Studies of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 19, 761–766. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Jin, F.-F. Antarctic circumpolar waves: An Indication of ocean-atmosphere coupling in the extratropics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2585–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Baines, P.G. Forcing of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave by El Niño-Southern Oscillation teleconnections. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 9019–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.G.; White, W.B. Slow oceanic teleconnections linking the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave with the tropical El Niño-Southern Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 24573–24583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Jeffrey, A. Influence of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave on El Niño and its multidecadal changes from 1950 to 2001. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, S.A. The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave: A Combination of Two Signals? J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2509–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Chen, S.-C. Thermodynamic Mechanisms Responsible for the Tropospheric Response to SST Anomalies in the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2577–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B. Influence of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave on Australian Precipitation from 1958 to 1997. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2125–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Gloersen, P.; Simmonds, I. Tropospheric Response in the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave along the Sea Ice Edge around Antarctica. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2765–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.; Mahajan, P.N.; Khaladkar, R.M.; Chipade, M.D. Role of Antarctic circumpolar wave in modulating the extremes of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.; Lu, L.; Li, Z.; Qin, D.; Zhou, X. Signals of Antarctic Circumpolar Wave over the Southern Indian Ocean as recorded in an Antarctica ice core. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Lin, X. Interdecadal change of the Atlantic oscillation and the Antarctic circumpolar wave. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 33, 251–260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bian, L.; Lin, X. Interdecadal change in the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave during 1951–2010. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Koide, H. Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. Ann. Glaciol. 1998, 27, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, M.; Barnett, T.P.; Roeckner, E. The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in a Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere GCM. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarsma, R.J.; Selten, F.M.; Opsteegh, J.D. On the Mechanism of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1461–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsland, S.J.; Latif, M.; Legutke, S. Antarctic circumpolar modes in a coupled ocean? Atmosphere model. Ocean Dyn. 2003, 53, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cai, W.; Baines, P.G.; Gordon, H.B. Southern Mid- to High-Latitude Variability, a Zonal Wavenumber-3 Pattern, and the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in the CSIRO Coupled Model. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 3087–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.J. Trends in the Southern Annular Mode from Observations and Reanalyses. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zou, L.; Wu, B.; Jin, C.; Song, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Development of earth/climate system models in China: A review from the coupled model intercomparison project perspective. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 762–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.P.; Guo, P.W.; Wang, Y.L. Antarctic Circumpolar Waves and Its Association with the Abnormality of Summer Rainfall over China. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 2005, 28, 376–383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J. A study on the Antarctic circumpolar wave mode-A coexistence system of standing and traveling wave. Chin. J. Polar Sci. 2006, 17, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Connolley, W.M. Long-term variation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, SOV 3-1–SOV 3-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Bian, L. Characteristics of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave during Recent 100 Years. Clim. Environ. Res. 2015, 20, 21–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, J.; He, Y. Low-frequency variability of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current sea level detected from TOPEX/Poseidon satellite altimeter. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2003, 34, 256–266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Project | No. | Model Name | Institution and Country | SLP Spatial Grids | SST Spatial Grids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIP5 | 1 | ACCESS1.3 | CSIRO-BOM, Australia | 192 × 145 | 192 × 145 |
| CMIP5 | 2 | CESM1-CAM5 | NSF-DOE-NCAR, USA | 288 × 192 | 384 × 320 |
| CMIP5 | 3 | CNRM-CM5 | CNRM-CERFACS, France | 256 × 128 | 362 × 292 |
| CMIP5 | 4 | FGOALS-g2 | LASG-CESS, China | 128 × 60 | 360 × 196 |
| CMIP5 | 5 | GFDL-CM3 | NOAA GFDL, USA | 144 × 90 | 360 × 200 |
| CMIP5 | 6 | GISS-E2-H | NASA GISS, USA | 144 × 90 | 144 × 90 |
| CMIP5 | 7 | BCC-CSM1.1 | BCC, China | 128 × 64 | 360 × 232 |
| CMIP5 | 8 | CanESM2 | CCCMA, Canada | 128 × 64 | 256 × 192 |
| CMIP5 | 9 | FIO-ESM | FIO, China | 128 × 64 | 320 × 384 |
| CMIP5 | 10 | GFDL-ESM2G | NOAA GFDL, USA | 144 × 90 | 360 × 210 |
| CMIP5 | 11 | HadGEM2-CC | MOHC, UK | 192 × 145 | 360 × 216 |
| CMIP5 | 12 | IPSL-CM5A-LR | IPSL, France | 96 × 96 | 182 × 149 |
| CMIP6 | 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | CSIRO-ARCCSS, Australia | 192 × 144 | 360 × 300 |
| CMIP6 | 2 | CESM2 | NCAR, USA | 288 × 192 | 320 × 384 |
| CMIP6 | 3 | CNRM-CM6-1 | CNRM-CERFACS, France | 256 × 128 | 362 × 294 |
| CMIP6 | 4 | FGOALS-g3 | CAS, China | 180 × 80 | 360 × 218 |
| CMIP6 | 5 | GFDL-CM4 | NOAA-GFDL, USA | 360 × 180 | 1440 × 1080 |
| CMIP6 | 6 | GISS-E2-1-H | NASA-GISS, USA | 144 × 90 | 360 × 180 |
| CMIP6 | 7 | BCC-CSM2-MR | BCC, China | 320 × 160 | 360 × 232 |
| CMIP6 | 8 | CanESM5 | CCCMA, Canada | 128 × 64 | 360 × 291 |
| CMIP6 | 9 | FIO-ESM-2-0 | FIO-QLNM, China | 192 × 288 | 320 × 384 |
| CMIP6 | 10 | GFDL-ESM4 | NOAA-GFDL, USA | 288 × 180 | 720 × 576 |
| CMIP6 | 11 | HadGEM3-GC31-LL | MOHC NERC, UK | 192 × 144 | 360 × 330 |
| CMIP6 | 12 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | IPSL, France | 144 × 143 | 362 × 332 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, W. Evaluation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave Simulated by CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090931
Lu Z, Zhao T, Zhou W. Evaluation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave Simulated by CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Zhichao, Tianbao Zhao, and Weican Zhou. 2020. "Evaluation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave Simulated by CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090931
APA StyleLu, Z., Zhao, T., & Zhou, W. (2020). Evaluation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave Simulated by CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models. Atmosphere, 11(9), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090931






