A Collaborative Training Program to Assess Mercury Pollution from Gold Shops in Guyana’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sector
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Mercury Problem in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining
1.2. ASGM in Guyana
1.3. ASGM and the Minamata Convention on Mercury
1.4. Training Program for Monitoring of Hg0 in Air in ASGM Communities
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of Training
3.2. Phase I: Training in Georgetown
Field Training in Georgetown
3.3. Phase II: Training in Bartica
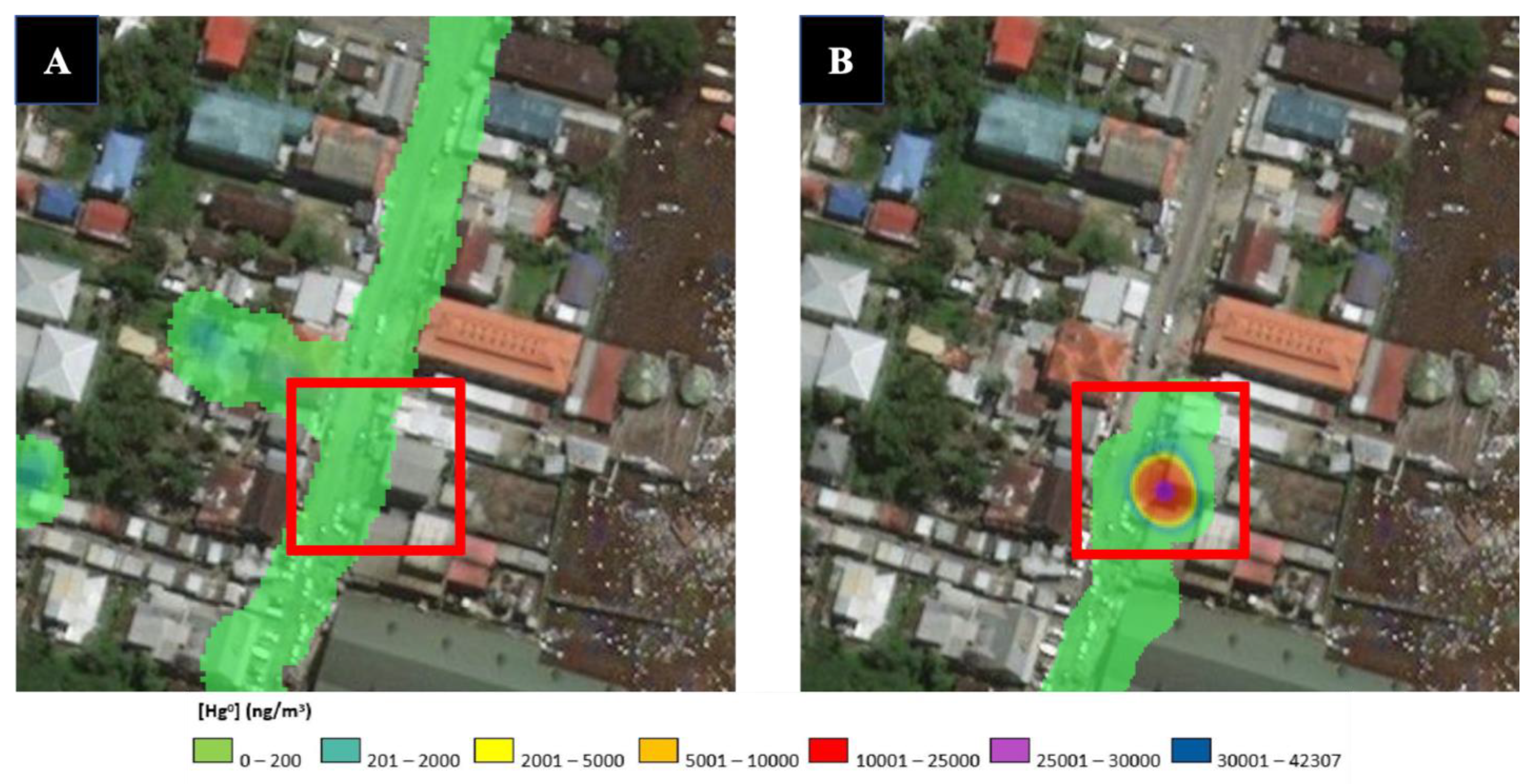
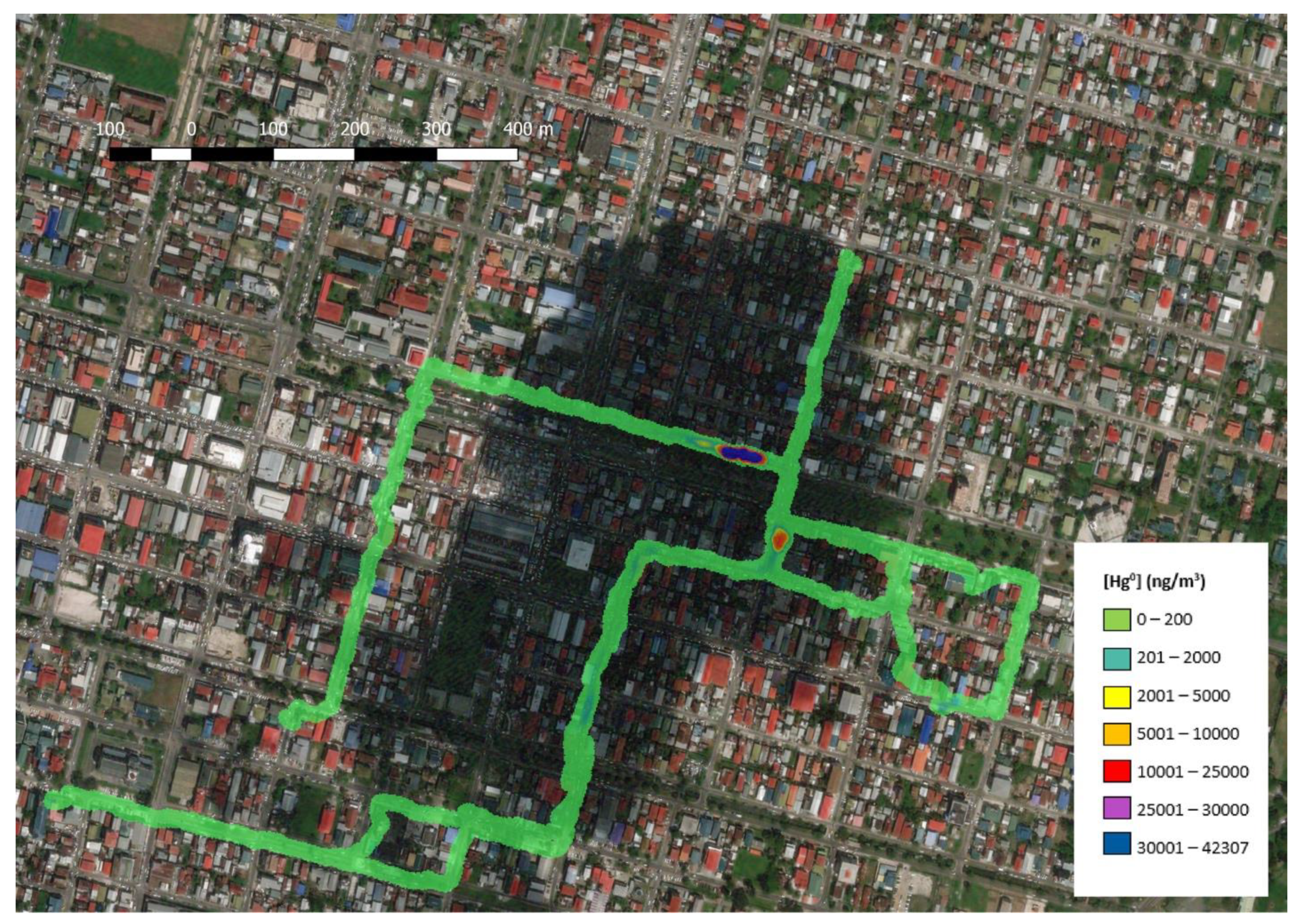
3.3.1. Mapping of Central Bartica
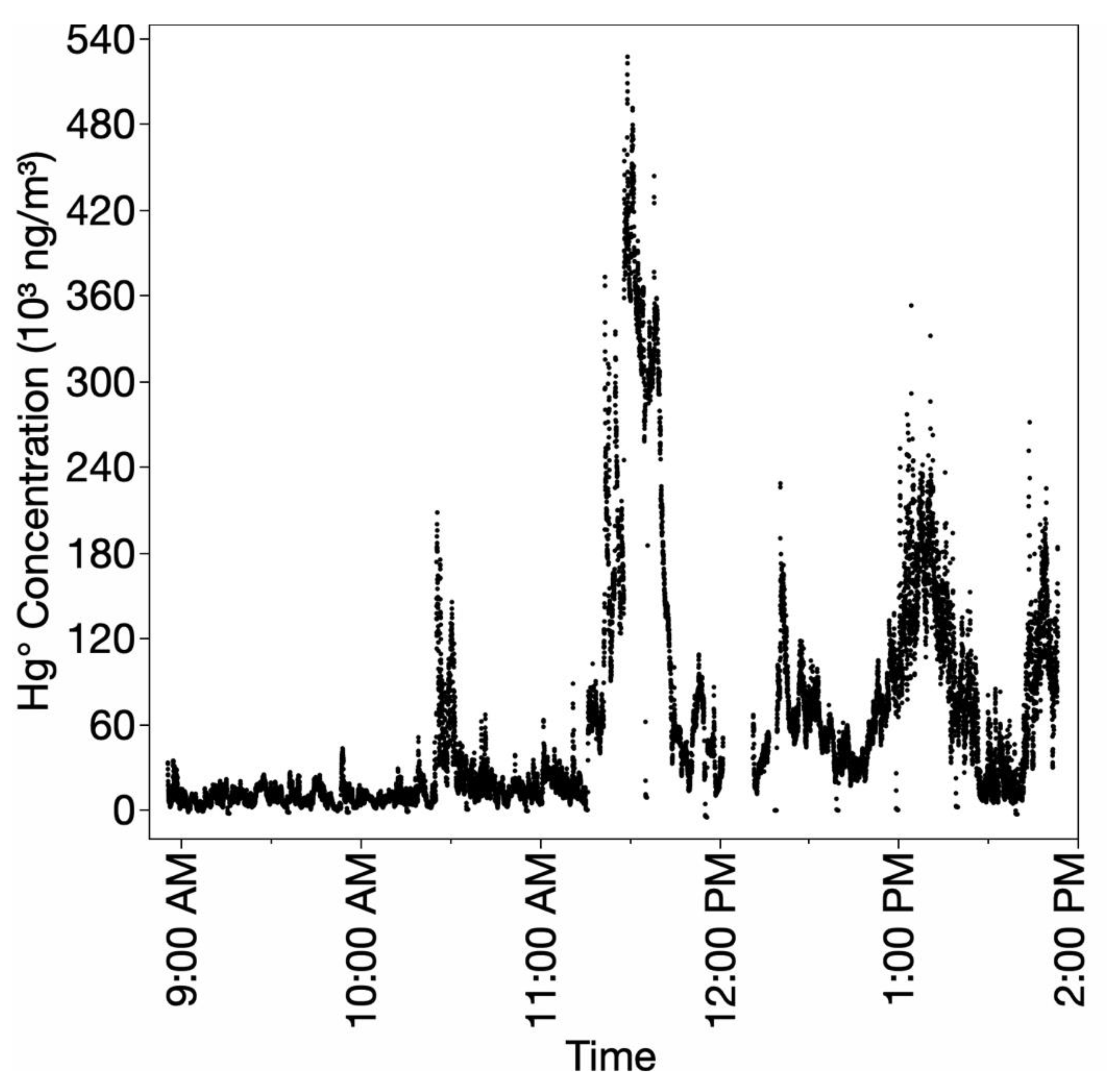
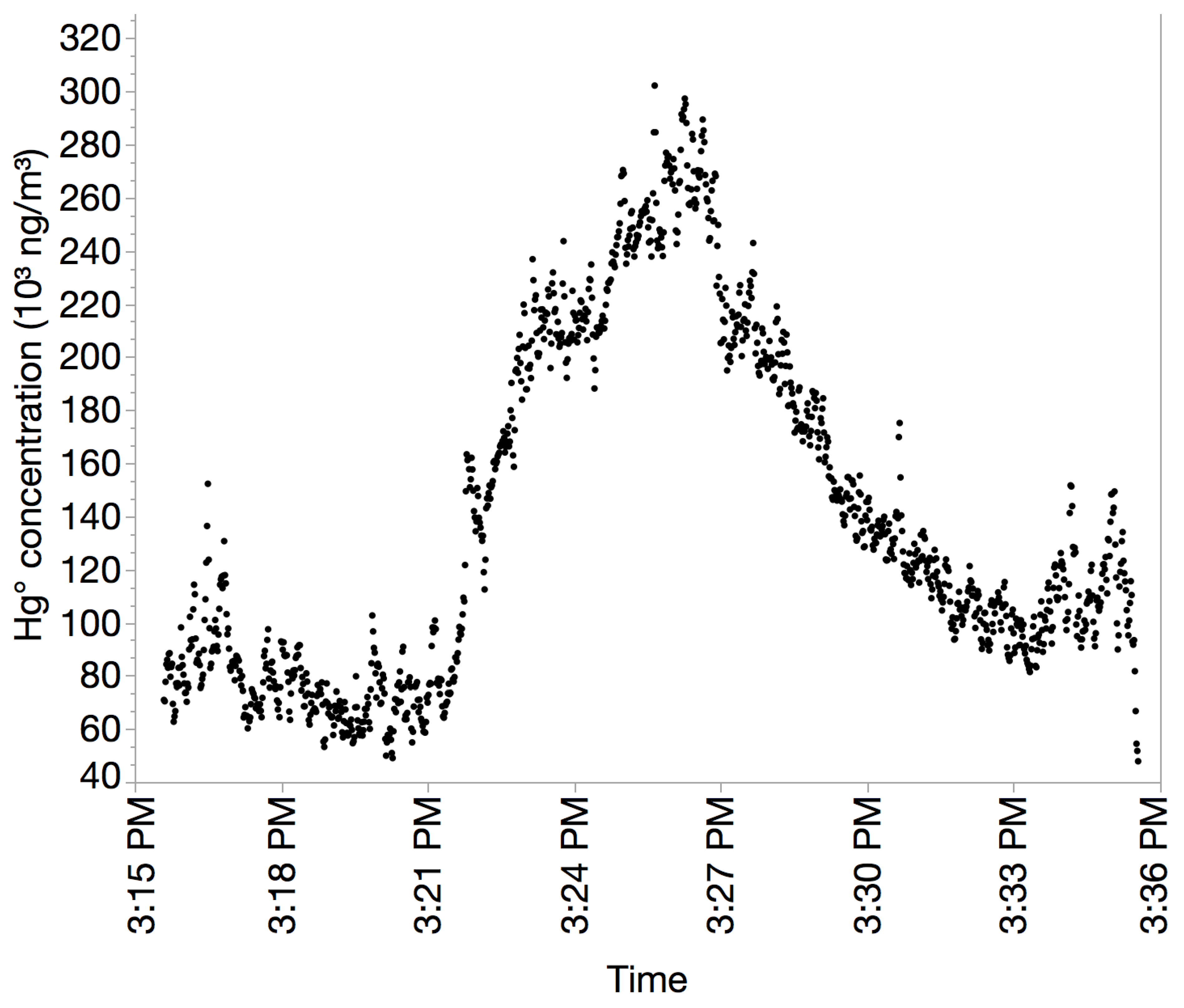
3.3.2. Monitoring Hg0 Concentrations During Burning/Smelting Operations at Gold Shops
3.3.3. The Relationship Between Gold Shops and Hg0 Contamination in Bartica
3.4. Phase III: Analysis and Dissemination of Results
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seccatore, J.; Veiga, M.; Origliasso, C.; Marin, T.; De Tomi, G. An Estimation of the Artisanal Small-Scale Production of Gold in the World. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-McPherson, D. Expansion of Small-Scale Gold Mining in Madre de Dios: ‘Capital Interests’ and the Emergence of a New Elite of Entrepreneurs in the Peruvian Amazon. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, T.; Hruschka, F.; Priester, M. Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining: Challenges and Opportunities; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hilson, G.; Zolnikov, T.R.; Ortiz, D.R.; Kumah, C. Formalizing Artisanal Gold Mining under the Minamata Convention: Previewing the Challenge in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 85, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.; Pardie, S. Mercury: An Agent of Poverty in Ghana’s Small-Scale Gold-Mining Sector? Resour. Policy 2006, 31, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.M. (Ed.) The Socio-Economic Impacts of Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining in Developing Countries; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hruschka, F.; Echavarria, C. Rock Solid Chances for Responsible Artisanal Mining; Series on Responsible ASM; Alliance for Responsible Mining: Medellin, Columbia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jønsson, J.B.; Charles, E.; Kalvig, P. Toxic Mercury versus Appropriate Technology: Artisanal Gold Miners’ Retort Aversion. Resour. Policy 2013, 38, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, E.R. The Case of Artisanal Mining in Bolivia: Local Participatory Development and Mining Investment Opportunities. Nat. Resour. Forum 2002, 26, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, S.J. Socioeconomic Dimensions of Mercury Pollution Abatement: Engaging Artisanal Mining Communities in Sub-Saharan Africa. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 3072–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero Espejo, J.; Messinger, M.; Román-Dañobeytia, F.; Ascorra, C.; Fernandez, L.E.; Silman, M. Deforestation and Forest Degradation Due to Gold Mining in the Peruvian Amazon: A 34-Year Perspective. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezécache, C.; Faure, E.; Gond, V.; Salles, J.-M.; Vieilledent, G.; Hérault, B. Gold-Rush in a Forested El Dorado: Deforestation Leakages and the Need for Regional Cooperation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 034013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deikumah, J.P.; McAlpine, C.A.; Maron, M. Mining Matrix Effects on West African Rainforest Birds. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 169, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, A.; Garber, P.A.; Chaudhary, A. Expanding Global Commodities Trade and Consumption Place the World’s Primates at Risk of Extinction. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, A.R.; Piquero, A.R.; Accetturo, P.W. Insights into the Nature and Spatial Distribution of Guyanese Crime. Deviant Behav. 2018, 39, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.; Laing, T. Gold Mining, Indigenous Land Claims and Conflict in Guyana’s Hinterland. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 50, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calys-Tagoe, B.N.L.; Ovadje, L.; Clarke, E.; Basu, N.; Robins, T. Injury Profiles Associated with Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Tarkwa, Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7922–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calys-Tagoe, B.N.L.; Clarke, E.; Robins, T.; Basu, N. A Comparison of Licensed and Un-Licensed Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Miners (ASGM) in Terms of Socio-Demographics, Work Profiles, and Injury Rates. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esdaile, L.J.; Chalker, J.M. The Mercury Problem in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6905–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, H.; O’Leary, K.G. Mercury Exposure and Health Impacts among Individuals in the Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Community: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylander, L.D. Gold and Amalgams: Environmental Pollution and Health Effects; Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, K.E.; Sangermano, F. Evaluating Wildlife Vulnerability to Mercury Pollution from Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Madre de Dios, Peru. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.; McCord, S.A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Todorova, S.; Wu, S.; Araújo, J.F.; Vega, C.M.; Fernandez, L.E. Mercury Contamination in Riverine Sediments and Fish Associated with Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Madre de Dios, Peru. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Brush, M.; McLagan, D.S.; Biester, H. Fate of Mercury from Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Tropical Rivers: Hydrological and Biogeochemical Controls. A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 437–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckling, N.; Tobollik, M.; Plass, D.; Hornberg, C.; Ericson, B.; Fuller, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S. Global Burden of Disease of Mercury Used in Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining. Ann. Glob. Health 2017, 83, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, N.; Horvat, M.; Evers, D.C.; Zastenskaya, I.; Weihe, P.; Tempowski, J. A State-of-the-Science Review of Mercury Biomarkers in Human Populations Worldwide between 2000 and 2018. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Lettmeier, B.; Gothe, R.M.; Beinhoff, C.; Siebert, U.; Drasch, G. Mercury as a Serious Health Hazard for Children in Gold Mining Areas. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Environmental Program. Global Mercury Assessment 2013: Sources, Emissions, Releases and Environmental Transport; United Nations Pubns: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Environment, U.N. Global Mercury Assessment. 2018. Available online: http://www.unenvironment.org/resources/publication/global-mercury-assessment-2018 (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Risher, J.; World Health Organization; United Nations Environment Programme; International Labour Organisation; Inter-Organization Programme for the Sound Management of Chemicals; International Program on Chemical Safety. Elemental Mercury and Inorganic Mercury Compounds: Human Health Aspects; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eisler, R. Health Risks of Gold Miners: A Synoptic Review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2003, 25, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes Azevedo, B.; Barros Furieri, L.; Peçanha, F.M.; Wiggers, G.A.; Frizera Vassallo, P.; Ronacher Simões, M.; Fiorim, J.; Rossi de Batista, P.; Fioresi, M.; Rossoni, L.; et al. Toxic Effects of Mercury on the Cardiovascular and Central Nervous Systems. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2012/949048/citations/ (accessed on 14 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, T.W.; Magos, L. The Toxicology of Mercury and Its Chemical Compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 609–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N.E. A Review of Global Environmental Mercury Processes in Response to Human and Natural Perturbations: Changes of Emissions, Climate, and Land Use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.J. Pork Knocking in the Land of Many Waters: Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM) in Guyana. Resour. Policy 2011, 36, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrol, D. Gold Board Wants to Buy “All Gold” Directly from Miners. Available online: https://demerarawaves.com/2019/02/25/gold-board-wants-to-buy-all-gold-directly-from-miners/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Laws of Guyana. Chapter 66:01 Guyana Gold Board Act. Available online: http://www.guyaneselawyer.com/lawsofguyana/Laws/cap6601.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Pasha, S.; Wenner, M.D.; Clarke, D. Toward the Greening of the Gold Mining Sector of Guyana: Transition Issues and Challenges; Technical Note IDB-TN-1290; Inter-American Development Bank. Available online: https://publications.iadb.org/publications/english/document/Toward-the-Greening-of-the-Gold-Mining-Sector-of-Guyana-Transition-Issues-and-Challenges.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Staff Editor. Around 15,000 Ozs Gold Smuggled Each Week—Trotman. Available online: https://www.stabroeknews.com/2016/01/06/news/guyana/around-15000-ozs-gold-smuggled-week-trotman/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Canterbury, D.C. Natural Resources Extraction and Politics in Guyana. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2016, 3, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.; Laing, T. Guyana Gold: A Unique Resource Curse? J. Dev. Stud. 2017, 53, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordy, P.; Veiga, M.; Crawford, B.; Garcia, O.; Gonzalez, V.; Moraga, D.; Roeser, M.; Wip, D. Characterization, Mapping, and Mitigation of Mercury Vapour Emissions from Artisanal Mining Gold Shops. Environ. Res. 2013, 125, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa Rosa, R.M.; Müller, R.C.; Alves, C.N.; Sarkis, J.E.D.S.; Bentes, M.H.D.S.; Brabo, E.; de Oliveira, E.S. Determination of Total Mercury in Workers’ Urine in Gold Shops of Itaituba, Pará State, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 261, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wip, D.; Warneke, T.; Petersen, A.K.; Notholt, J.; Temme, C.; Kock, H.; Cordy, P. Urban Mercury Pollution in the City of Paramaribo, Suriname. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2011, 6, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordy, P.; Veiga, M.M.; Salih, I.; Al-Saadi, S.; Console, S.; Garcia, O.; Mesa, L.A.; Velásquez-López, P.C.; Roeser, M. Mercury Contamination from Artisanal Gold Mining in Antioquia, Colombia: The World’s Highest per Capita Mercury Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacerda, L.D.; Salomons, W. Mercury from Gold and Silver Mining: A Chemical Time Bomb? Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lilis, R.; Miller, A.; Lerman, Y. Acute Mercury Poisoning with Severe Chronic Pulmonary Manifestations. Chest 1985, 88, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; Jacobs, J.; Polos, P.G. Acute Mercury Poisoning and Mercurial Pneumonitis from Gold Ore Purification. Chest 1988, 94, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Treaty Collection. Minamatata Convention on Mercury. Available online: https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=IND&mtdsg_no=XXVII-17&chapter=27&clang=_en (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- United Nations Environmental Programme. Mercury Convention Texts and Annexes. Available online: http://www.mercuryconvention.org/Convention/Text/tabid/3426/language/en-US/Default.aspx (accessed on 22 April 2019).
- Clifford, M.J. Future Strategies for Tackling Mercury Pollution in the Artisanal Gold Mining Sector: Making the Minamata Convention Work. Futures 2014, 62, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, H.H.; Perrez, F.X. The Minamata Convention: A Comprehensive Response to a Global Problem. Rev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2014, 23, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, D.C.; Keane, S.E.; Basu, N.; Buck, D. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Minamata Convention on Mercury: Principles and Recommendations for next Steps. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S.; Evers, D.C.; Bank, M.S.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Pierce, A.; Basu, N.; Blum, J.; Bustamante, P.; Chen, C.; Driscoll, C.T.; et al. Importance of Integration and Implementation of Emerging and Future Mercury Research into the Minamata Convention. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2767–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, H.; Keane, S.E.; Wang, S.; Selin, N.E.; Davis, K.; Bally, D. Linking Science and Policy to Support the Implementation of the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Ambio 2018, 47, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selin, H. Global Environmental Law and Treaty-Making on Hazardous Substances: The Minamata Convention and Mercury Abatement. Glob. Environ. Politics 2014, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnikov, T.R.; Ramirez Ortiz, D. A Systematic Review on the Management and Treatment of Mercury in Artisanal Gold Mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R. X-ray Techniques: Overview. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; American Cancer Society: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, R.M. The Quest for a Fundamental Algorithm in X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis and Calibration. Open Spectrosc. J. 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, R.; Boivin, J.A. The Fundamental Algorithm: A Natural Extension of Sherman Equation. Rigaku J. 1998, 15, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Van Sprang, H.A. Fundamental Parameter Methods in XRF Spectroscopy. Adv. X-ray Anal. 2000, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, V. Basic Fundamental Parameters in X-Ray Fluorescence. Spectroscopy 2007, 22, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ohio Lumex Co., Inc. RA-915M Mercury Analyzer Operation Manual B0100-00-00-00-00 OM.; Ohio Lumex Co., Inc.: Twinsburg, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, K.H.; Hasan, K.M.; Aljic, S.; Blakeman, V.M.; Hicks, L.P.; Loving, D.C.; Moore, M.E.; Hammett, B.S.; Silva-González, M.; Seney, C.S.; et al. Mercury Emissions from Peruvian Gold Shops: Potential Ramifications for Minamata Compliance in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Communities. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drace, K.; Kiefer, A.M.; Veiga, M.M.; Williams, M.K.; Ascari, B.; Knapper, K.A.; Logan, K.M.; Breslin, V.M.; Skidmore, A.; Bolt, D.A.; et al. Mercury-Free, Small-Scale Artisanal Gold Mining in Mozambique: Utilization of Magnets to Isolate Gold at Clean Tech Mine. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 32, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, V.W.L.; Lockhart, K.; Spiegel, S.J.; Yassi, A. Occupational Health Programs for Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining: A Systematic Review for the WHO Global Plan of Action for Workers’ Health. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, P.W.U.; Na-Oy, L.D. Mercury-Free Gold Extraction Using Borax for Small-Scale Gold Miners. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistema Nacional de Informacíon Ambiental. Aprueban Estándares de Calidad Ambiental (ECA) para Aire y establecen Disposiciones Complementarias. Available online: https://sinia.minam.gob.pe/normas/aprueban-estandares-calidad-ambiental-eca-aire-establecen-disposiciones (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Norma Técnica Peruano 900.068 (NTP 900.068). Monitoreo de Calidad Ambiental. Calidad del Aire. Método Normalizado Para la Determinación del Mercurio Gaseoso Total; Dirección de Normalización—INACAL: Lima, Peru, 2016.
- Kiefer, A.M.; Seney, C.S.; Boyd, E.A.; Smith, C.; Shivdat, D.S.; Matthews, E.; Hull, M.W.; Bridges, C.C.; Castleberry, A. Chemical Analysis of Hg0-Containing Hindu Religious Objects. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, K. Parad Items Readily Emit Mercury Vapor. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vV3fSXpt0-Q (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. ATSDR-Toxicological Profile: Mercury. Available online: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=115&tid=24 (accessed on 26 June 2015).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Action Levels for Elemental Mercury Spills: Chemical-Specific Health Consultation for Joint EPA/ATSDR National Mercury Cleanup Policy Workgroup; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012.
- Plataforma Digital Única del Estado Peruano. Decreto Supremo N° 10-2019-MINAM. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/minam/normas-legales/363557-10-2019-minam (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- United States Department of Labor: Occupational Safety and Health Administration. OSHA Annotated PELs. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/dsg/annotated-pels/tablez-2.html (accessed on 26 June 2015).
- US EPA. Mercury Vapor Results-AEGL Program. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/aegl/mercury-vapor-results-aegl-program (accessed on 7 April 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. CDC-Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH): Mercury Compounds [Except (Organo) Alkyls] (as Hg)-NIOSH Publications and Products. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7439976.html (accessed on 26 June 2015).
- Hacon, S.; Rochedo, E.R.; Campos, R.; Rosales, G.; Lacerda, L.D. Risk Assessment of Mercury in Alta Floresta. Amazon Basin-Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 97, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, P.L.; Rojas, M.; Reh, C.M.; Mueller, C.A.; Jenkins, F.M. Occupational Exposure to Airborne Mercury during Gold Mining Operations near El Callao, Venezuela. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2001, 74, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, A.M. Mercury Toxicity Due to the Smelting of Placer Gold Recovered by Mercury Amalgam. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 1998, 48, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyana Gold and Diamond Miners Association. Authorized Gold Dealers of the Guyana Gold Board. Available online: https://ggdma.com/pressnews/authorized-gold-dealers-of-the-guyana-gold-board/ (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- McLagan, D.S.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Huang, H.; Lei, Y.D.; Cole, A.S.; Steffen, A.; Hung, H.; Wania, F. A High-Precision Passive Air Sampler for Gaseous Mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLagan, D.S.; Mazur, M.E.E.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Wania, F. Passive Air Sampling of Gaseous Elemental Mercury: A Critical Review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLagan, D.S.; Monaci, F.; Huang, H.; Lei, Y.D.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Wania, F. Characterization and Quantification of Atmospheric Mercury Sources Using Passive Air Samplers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Cizdziel, J.V. Can the MerPAS Passive Air Sampler Discriminate Landscape, Seasonal, and Elevation Effects on Atmospheric Mercury? A Feasibility Study in Mississippi, USA. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Topic | Content Delivery |
|---|---|
| Introduction to the chemical properties of Hg0 | Lecture |
| Mercury in the environment: Myths vs. Realities | Lecture, discussion |
| Mercury Pollution from ASGM: processing ore vs. processing amalgams | Lecture, discussion |
| Monitoring Hg0 pollution in the environment | Lecture, discussion |
| Human health effects of Hg0: safety in the field | Lecture, discussion |
| Techniques for soil analysis: XRF screening of metals in the field, laboratory analysis | Lecture, discussion, hands-on training |
| Techniques for monitoring Hg in the air: Hg0 vs. total gaseous mercury (TGM) | Lecture, discussion, hands-on training |
| Case study on Peruvian ASGM mercury emissions: science vs. policy | Lecture, discussion |
| Introduction to operating principles of XRF and portable spectrometers | Lecture |
| Closing discussion: Hg0 use in Guyana | Discussion |
| [Hg0] (ng/m3) | Agency | Description/Potential Health Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | ATSDR a | Minimum risk level (MRL) | [73] |
| 1000 | ATSDR a | Recommended action level, residential setting | [74] |
| 2000 | Government of Peru | Air quality standards, Total gaseous mercury (TGM), not to exceed value over 24 h. | [69,75] |
| 10,000 | ATSDR a | Isolation of residential setting (evacuation, restricted access, etc.) | [74] |
| 20,000 | WHO b | Chronic exposure greater than or equal to this value can result in damage to the central nervous system | [30] |
| 25,000 | ACGIH c | Threshold limit value (TLV) | [76] |
| 50,000 | NIOSH d | Recommended exposure limit (REL), 10 h time-weighted average | [76] |
| 100,000 | NIOSH d/OSHA e | Acceptable ceiling concentration | [76] |
| 670,000 | USEPA f | Acute exposure guideline limit (AEGL) 2; 1 h, irreversible, serious, and/or long-lasting health effects may occur | [77] |
| 2,200,000 | USEPA f | Acute exposure guideline limit (AEGL) 3; 4 h, life-threatening effects or death | [77] |
| 3,100,000 | USEPA f | Acute exposure guideline limit (AEGL) 2; 10 min, irreversible, serious, and/or long-lasting health effects may occur | [77] |
| 10,000,000 | NIOSH d | Immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) | [78] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, S.T.; Bandoo, L.L.; Agard, S.S.; Thom, S.T.; Gilhuys, T.E.; Mudireddy, G.K.; Eechampati, A.V.; Hasan, K.M.; Loving, D.C.; Seney, C.S.; et al. A Collaborative Training Program to Assess Mercury Pollution from Gold Shops in Guyana’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sector. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070719
Brown ST, Bandoo LL, Agard SS, Thom ST, Gilhuys TE, Mudireddy GK, Eechampati AV, Hasan KM, Loving DC, Seney CS, et al. A Collaborative Training Program to Assess Mercury Pollution from Gold Shops in Guyana’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sector. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(7):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070719
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Samantha T., Lloyd L. Bandoo, Shenelle S. Agard, Shemeiza T. Thom, Tamara E. Gilhuys, Gautham K. Mudireddy, Arnith V. Eechampati, Kazi M. Hasan, Danielle C. Loving, Caryn S. Seney, and et al. 2020. "A Collaborative Training Program to Assess Mercury Pollution from Gold Shops in Guyana’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sector" Atmosphere 11, no. 7: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070719
APA StyleBrown, S. T., Bandoo, L. L., Agard, S. S., Thom, S. T., Gilhuys, T. E., Mudireddy, G. K., Eechampati, A. V., Hasan, K. M., Loving, D. C., Seney, C. S., & Kiefer, A. M. (2020). A Collaborative Training Program to Assess Mercury Pollution from Gold Shops in Guyana’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sector. Atmosphere, 11(7), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070719





