The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Optical Properties of Aerosol
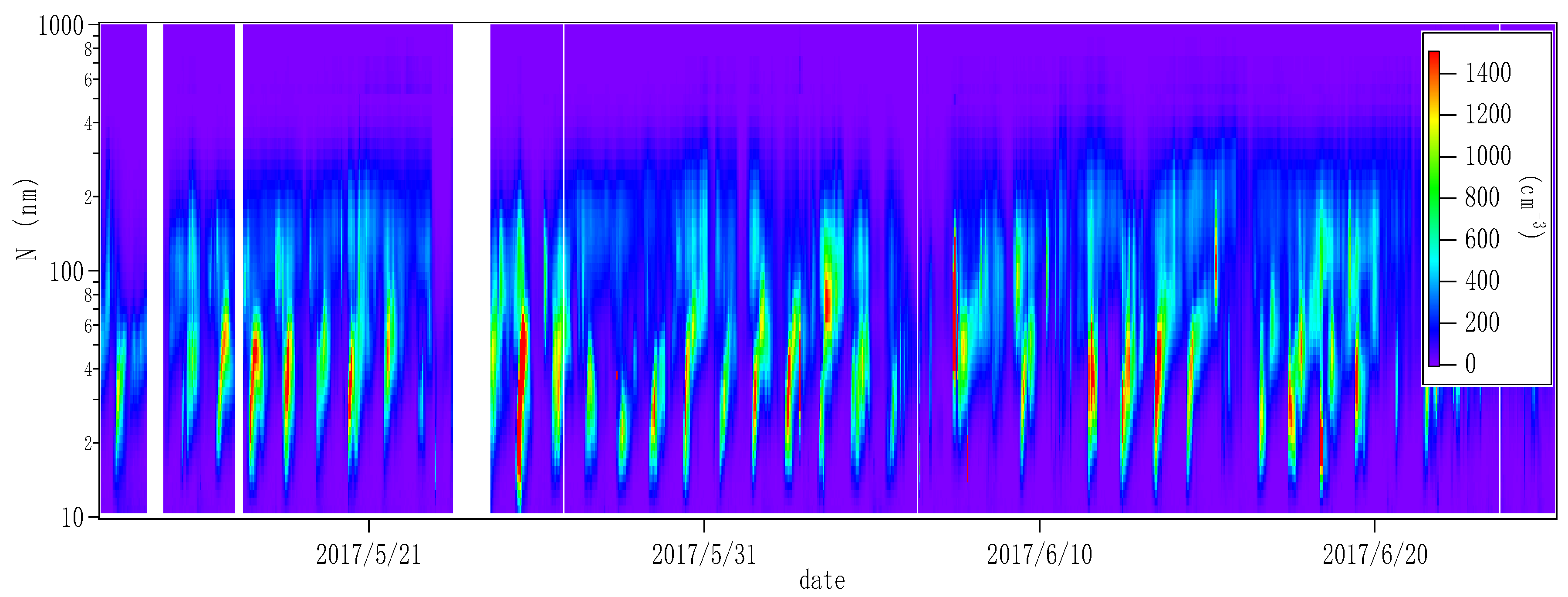
2.1. Sources and Processing of Optical Data
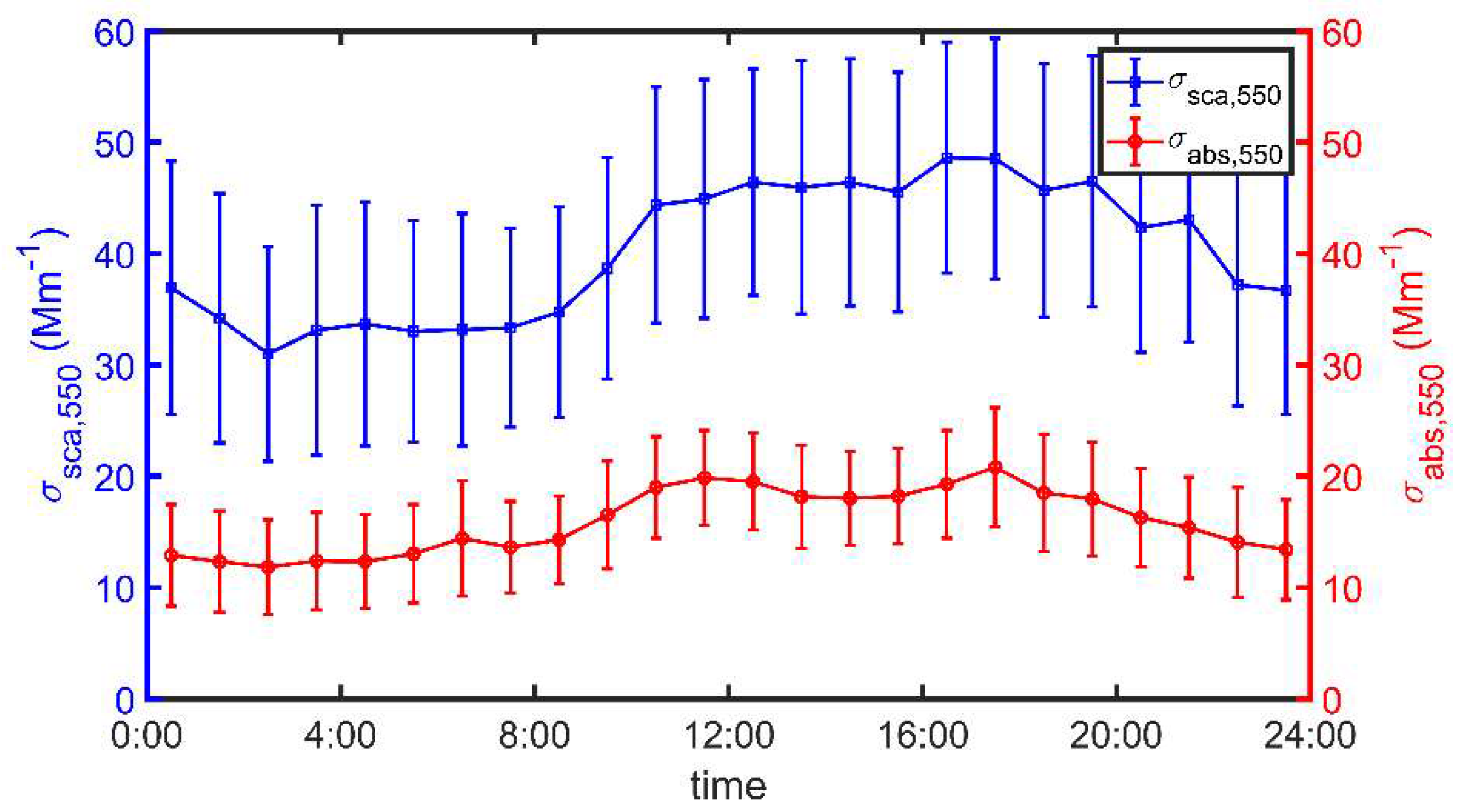
2.2. Results and Analysis of the Optical Properties of Aerosols
3. The Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index
3.1. Inversion Method of the Complex Refractive Index
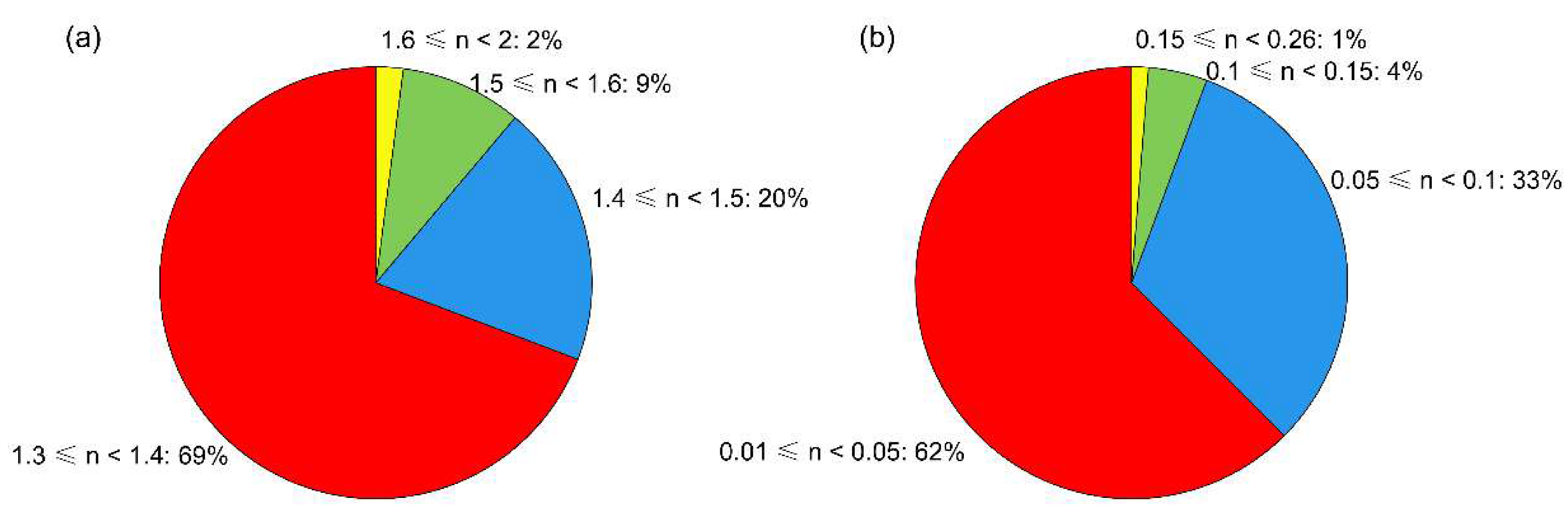
3.2. Inversion Results and Analysis of the Complex Refractive Index
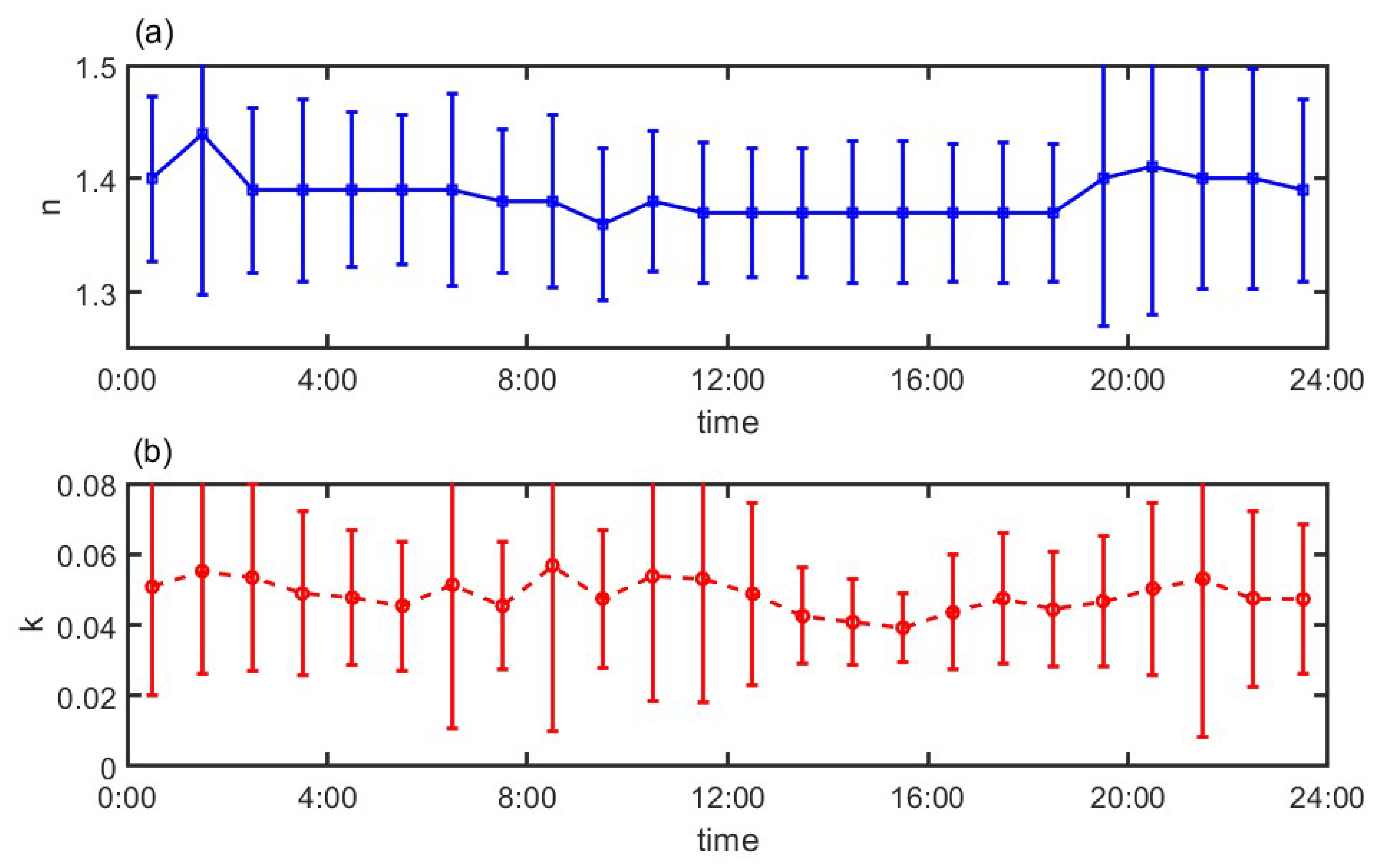
3.3. Diurnal Variation in the Complex Refractive Index
3.4. Correlation Analysis between the Complex Refractive Index and Meteorological Elements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. J. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, F. Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth validation of the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, D3, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yu, X.; Hao, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, C. A closure study of aerosol optical properties at a regional background mountainous site in Eastern China. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Liu, L.; Fan, S.; Li, F.; Yin, Y.; Cai, M.; Chan, P.W. Aerosol optical properties and mixing state of black carbon in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wehner, B.; Nowak, A.; Tuch, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X. First long-term study of particle number size distributions and new particle formation events of regional aerosol in the North China Plain. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1565–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Seinfeld, J. Radiative forcing by mineral dust aerosols: Sensitivity to key variables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 31637–31645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Liousse, C. A case study of optical and chemical ground apportionment for urban aerosols in Thessaloniki. J. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumlin, B.J.; Heinson, W.R.; Chakrabarty, R.K. Retrieving the aerosol complex refractive index using PyMieScatt: A Mie computational package with visualization capabilities. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 205, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mätzler, C. MATLAB functions for Mie scattering and absorption, version 2. J. IAP Res. Rep. 2002, 8, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Kolgotin, A.; Müller, D.; Chemyakin, E.; Romanov, A. Perspectives of the explicit retrieval of the complex refractive index of aerosols from optical data taken with lidar. In EPJ Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2016; Volume 119, p. 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, C.; Riziq, A.A.; Rudich, Y. Retrieval of aerosol complex refractive index by combining cavity ring down aerosol spectrometer measurements with full size distribution information. J. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.E.; Peters, D.M.; McPheat, R.; Grainger, R. The complex refractive index of volcanic ash aerosol retrieved from spectral mass extinction. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiles, M.; Painter, T.; Okin, G. A Method to Retrieve the Complex Refractive Index and Single Scattering Optical Properties of Dust Deposited in Mountain Snow Cover. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Ajtai, T.; Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Linke, C.; Müller, T.; Schnaiter, M.; Vragel, M. Complex refractive indices of Saharan dust samples at visible and near UV wavelengths: A laboratory study. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2491–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Xing-Na, Y.U.; Shen, L.; Chao, Y.U.; Zhu, J.; Xia, H. Aerosol optical properties in spring over urban Beijing. J. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Huang, Y.B.; Xu, C.D.; Wei, H.L.; Hu, H.L. Measurement of refractive index for aerosol particle in Xiamen. J. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2008, 16, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, M.; Li, X.; Qin, W.; Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Dai, C.; Miao, X.; Weng, N. Research on the characteristics of aerosol size distribution and complex refractive index in typical areas of China. J. Infrared Laser Eng. 2018, 47, 311001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Mao, J.; Deng, X.; Tie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Li, F.; Tan, H.; Bi, X.; Huang, X. Black carbon aerosols and their radiative properties in the Pearl River Delta region. J. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessler, R.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Adaptation of dry nephelometer measurements to ambient conditions at the Jungfraujoch. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delene, D.J.; Ogren, J.A. Variability of aerosol optical properties at four North American surface monitoring sites. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Wu, Y.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Yan, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, L. Observation and analysis of near-surface atmospheric aerosol optical properties in urban Beijing. J. Particuol. 2015, 18, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, T.; Leng, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Measurements of surface aerosol optical properties in winter of Shanghai. J. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ma, J.; Kumar, K.R.; Zhu, B.; An, J.; He, J.; Li, M. Measurement and analysis of surface aerosol optical properties over urban Nanjing in the Chinese Yangtze River Delta. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Hagino, R.; Matsumi, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kawasaki, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Uchiyama, A.; Kudo, R.; Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y. Measurements of aerosol optical properties in central Tokyo during summertime using cavity ring-down spectroscopy: Comparison with conventional techniques. J. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.; Singh, S.; Bano, T.; Tanwar, R.; Nath, S.; Arya, B. Variations in single scattering albedo and Angstrom absorption exponent during different seasons at Delhi, India. J. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4355–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, R.; Schmid, O.; Nowak, A.; Achtert, P.; Wiedensohler, A.; Gunthe, S.; Takegawa, N.; Kita, K.; Kondo, Y.; Hu, M. Aerosol optical properties observed during Campaign of Air Quality Research in Beijing 2006 (CAREBeijing-2006): Characteristic differences between the inflow and outflow of Beijing city air. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D00G04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyamani, H.; Olmo, F.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Light scattering and absorption properties of aerosol particles in the urban environment of Granada, Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2630–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; He, Z.; Kim, Y.J. Physicochemical characteristics and radiative properties of Asian dust particles observed at Kwangju, Korea, during the 2001 ACE-Asia intensive observation period. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D19S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.; Cass, G.; Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.; Yu, T.; Salmon, L.; Kiang, C.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol radiative, physical, and chemical properties in Beijing during June 1999. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17969–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.; Covert, D.; Wheeler, J.; Harris, J.; Perry, K.; Trost, B.; Jaffe, D.; Ogren, J. Aerosol backscatter fraction and single scattering albedo: Measured values and uncertainties at a coastal station in the Pacific Northwest. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 26793–26807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, T.P.; Toon, O.B. Absorption of visible radiation in atmosphere containing mixtures of absorbing and nonabsorbing particles. J. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3661–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Cui, Z.L.; Han, S.Q.; Cai, Z.Y.; Yao, Q. The Retrieval of Aerosol Complex Refractive Index and the Contribution Rate Analyses of Extinction Coefficient in Urban Tianjin City. J. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Liou, K.N.; Takano, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zamora, M.L.; Yang, P.; Leung, L.R. Variation of the radiative properties during black carbon aging: Theoretical and experimental intercomparison. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11967–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Scarnato, B.; Owen, R.C.; Zhang, B.; Ampadu, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Dzepina, K.; Dziobak, M.P.; Fialho, P.; Perlinger, J.A. Morphology and mixing state of aged soot particles at a remote marine free troposphere site: Implications for optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpong, E.; Smith, D.; Pokhrel, R.; Fiddler, M.N.; Bililign, S. Refractive indices of biomass burning aerosols obtained from African biomass fuels using rdg approximation. J. Atmos. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Fiddler, M.N.; Smith, D.; Flurchick, K.M.; Bililign, S. Optical properties of biomass burning aerosols: Comparison of experimental measurements and T-matrix calculations. J. Atmos. 2017, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumlin, B.J.; Pandey, A.; Walker, M.J.; Pattison, R.S.; Williams, B.J.; Chakrabarty, R.K. Atmospheric Photooxidation Diminishes Light Absorption by Primary Brown Carbon Aerosol from Biomass Burning. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.C.; Chazette, P. Vertical profiles of urban aerosol complex refractive index in the frame of ESQUIF airborne measurements. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Ortner, H.M. The chemical composition and complex refractive index of rural and urban influenced aerosols determined by individual particle analysis. J. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6531–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, J.L.; Kreidenweis, S.M. A new method for retrieving particle refractive index and effective density from aerosol size distribution data. J. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, W.W.; Nagy, A.; Czitrovszky, A.; Jani, P. A new method for the simultaneous measurement of aerosol particle size, complex refractive index and particle density. J. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Yin, Y.; Schnaiter, M.; Yung, Y.L. Black carbon aggregates: An optical property database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2019, 222–223, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yin, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, C.; Xu, X. Can the aerosol absorption Ångström exponent represent aerosol color in the atmosphere: A numerical study. J. Atmos. 2020, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Liu, C.; Schnaiter, M.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Liu, F. Accounting for the effects of nonideal minor structures on the optical properties of black carbon aerosol. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2917–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Shi, S. Size Distributions of Aerosol During the Summer at the Summit of Mountain Taishan (1534 m) in Central East China. J. Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhen, Z.; He, C. Characteristics and sources of WSI in North China Plain: A simultaneous measurement at the summit and foot of Mount Tai. J. Environ. Sci. China 2020, 92, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | (Mm−1) | (Mm−1) | Data Time | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mt. Tai, China | 40.3 | 16.0 | 0.67 | 2017.5–2017.6 | This study |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Mt. Tai, China | 142.9 | 13.0 | 0.88 | 2010.7–2011.12 | [6] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Mt. Huang | 62.6 | 5.5 | 0.89 | 2011.6–2011.8 | [4] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Shangdianzi, China | 174.6 | 17.5 | 0.88 | 2003.9–2005.1 | [21] |
| (525 nm) | (525 nm) | (525 nm) | |||
| Bondville, USA | 48.7 | 3.9 | 0.92 | 1996.9–2000.9 | [24] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Beijing, China | 360 | 64 | 0.82 | 2009.6–2010.5 | [25] |
| (525 nm) | (525 nm) | (525 nm) | |||
| Shanghai, China | 292.8 | 65.8 | 0.81 | 2010.12–2011.3 | [26] |
| (532 nm) | (532 nm) | (532 nm) | |||
| Nanjing, China | 303.3 | 28.0 | 0.89 | 2011.3–2011.4 | [27] |
| (532 nm) | (532 nm) | (532 nm) | |||
| Tokyo, Japan | 130.8 | 113.6 | 0.88 | 2007.8–2007.9 | [28] |
| (532 nm) | (532 nm) | (532 nm) | |||
| Delhi, India | 110.5 | 62.5 | 0.69 | 2008.4–2008.6 | [29] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Guangzhou, China | 151.0 | 34.3 | 0.82 | 2006.7 | [30] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Granada, Spain | 84.0 | 28.8 | 0.66 | 2005.12–2006.2 | [31] |
| (550 nm) | (670 nm) | (670 nm) | |||
| Kwangju, Korea | 319.0 | 42.0 | 0.88 | 2001.4 | [32] |
| (520 nm) | (880 nm) | (550 nm) | |||
| Beijing, China | 488 | 83 | 0.79 | 1999.6 | [33] |
| (530 nm) | (530 nm) | (530 nm) | |||
| North American continent | 10.8 | 1.4 | 0.88 | 1997.3–1997.4 | [34] |
| (550 nm) | (550 nm) | (550 nm) |
| Site | Aerosol Type | n | k | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mt. Tai, China | mountain atmosphere | 1.38 (550 nm) | 0.049 (550 nm) | This study |
| Mt. Tai, China | black carbon | 1.80 (550 nm) | 0.54 (550 nm) | [6] |
| no-optical absorption components | 1.50 (550 nm) | 10−7 (550 nm) | ||
| water | 1.33 (550 nm) | 0 (550 nm) | ||
| Mt. Huang, China | sulfate | 1.54 (550 nm) | 10−7 (550 nm) | [4] |
| nitrate | 1.54 (550 nm) | 10−7 (550 nm) | ||
| organics | 1.55 (550 nm) | 0.001 (550 nm) | ||
| dust | 1.52 (550 nm) | 0.0034 (550 nm) | ||
| Sahara, Africa | dust | 1.53 (305–955 nm) | 0.016–0.50 (305 nm) | [17] |
| Tianjin, China | urban aerosols | 1.64 (550 nm) | 0.015 (550 nm) | [36] |
| Paris, France | urban aerosols | 1.51–1.59 (530 nm) | 0.017–0.040 (530 nm) | [42] |
| Eastern Germany | urban aerosols | 1.60 (530 nm) | 0.04 (530 nm) | [43] |
| America | clean atmosphere | 1.45 (500 nm) | 0 | [44] |
| Japan | urban aerosols | 1.6 | 0.04 | [45] |
| Part of the m | Wind Speed (m·s−1) | T (°C) | RH (%) | Pressure (hPa) | Visibility (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 0.185 ** | −0.167 ** | −0.04 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| k | 0.353 ** | −0.257 ** | −0.220 ** | 0.07 | 0.332 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shi, S. The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060655
Zhao D, Yin Y, Zhang M, Wang H, Lu C, Yuan L, Shi S. The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060655
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dapeng, Yan Yin, Min Zhang, Honglei Wang, Chunsong Lu, Liang Yuan, and Shuangshuang Shi. 2020. "The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060655
APA StyleZhao, D., Yin, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, H., Lu, C., Yuan, L., & Shi, S. (2020). The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index. Atmosphere, 11(6), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060655






