Drop Size Distribution Measurements in Outer Rainbands of Hurricane Dorian at the NASA Wallops Precipitation-Research Facility
Abstract
1. Introduction
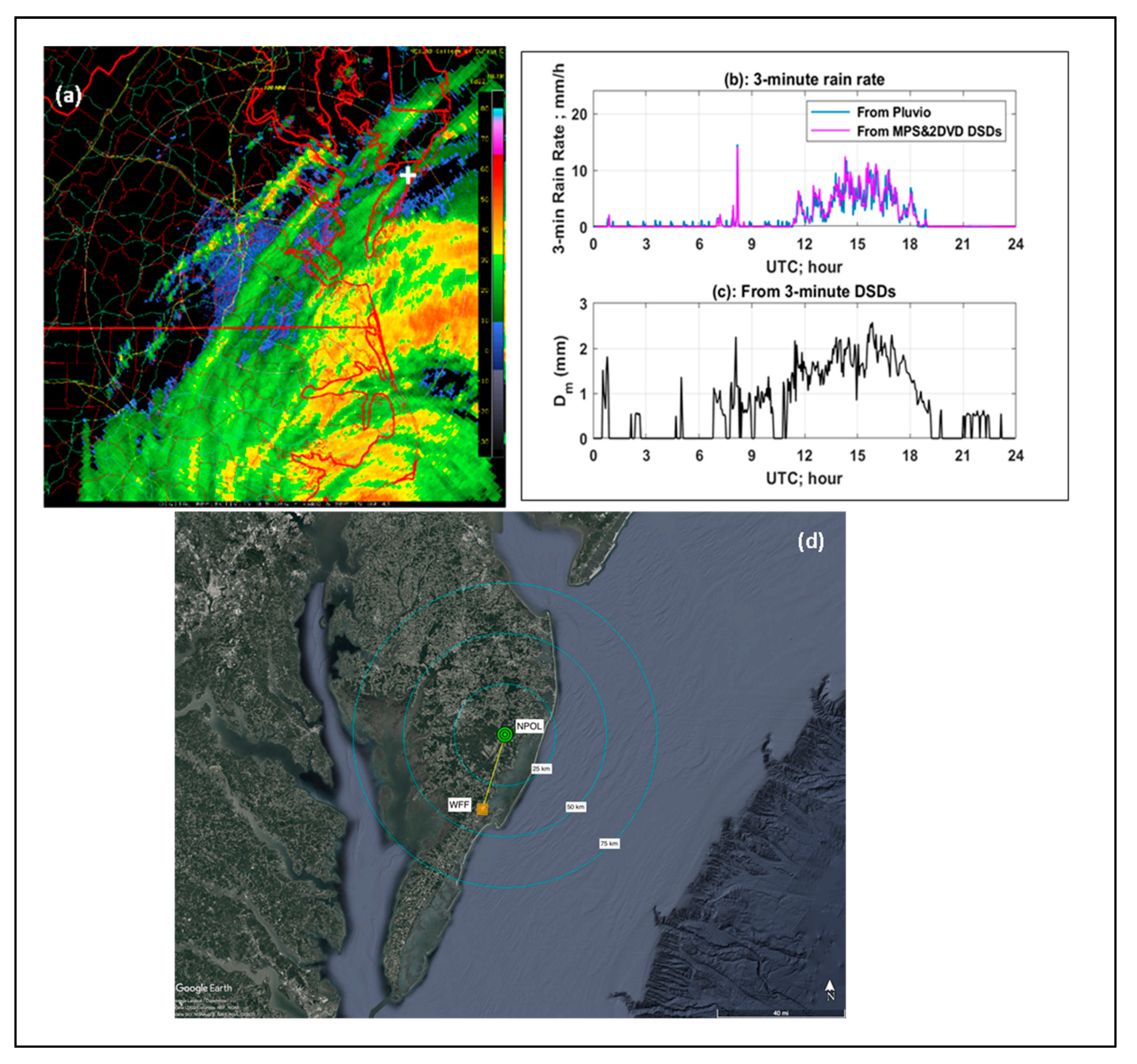
2. Instrumentation
3. DSD Analysis
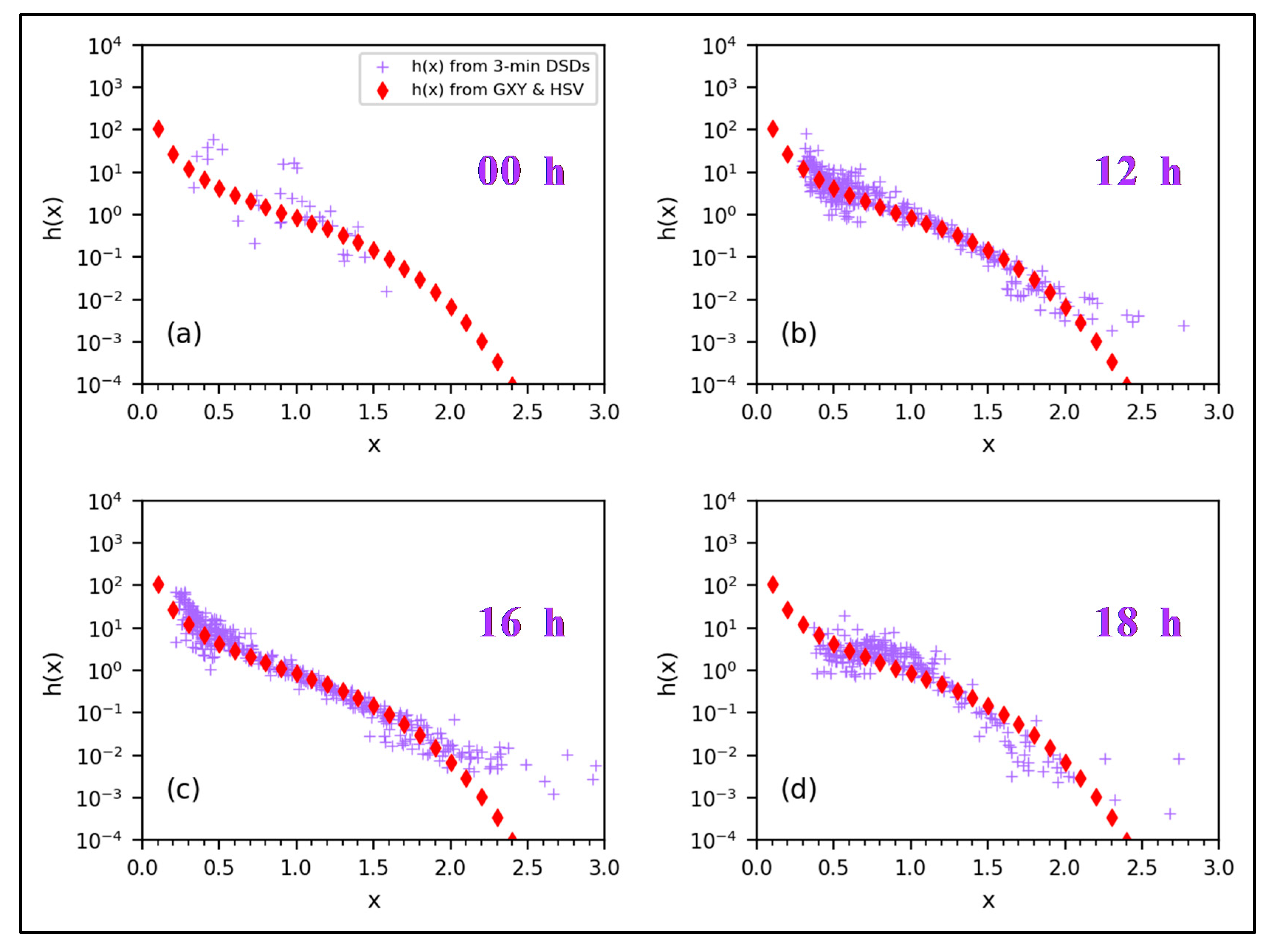
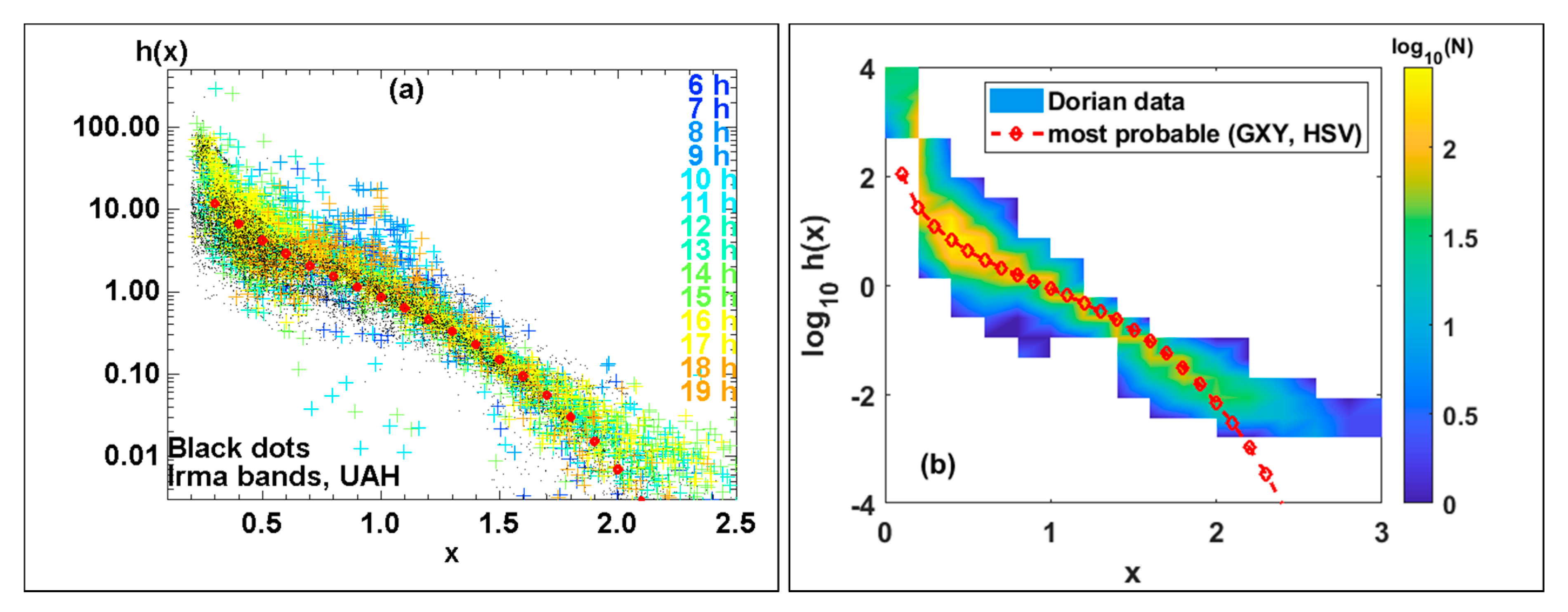
3.1. Double-Moment Normalization
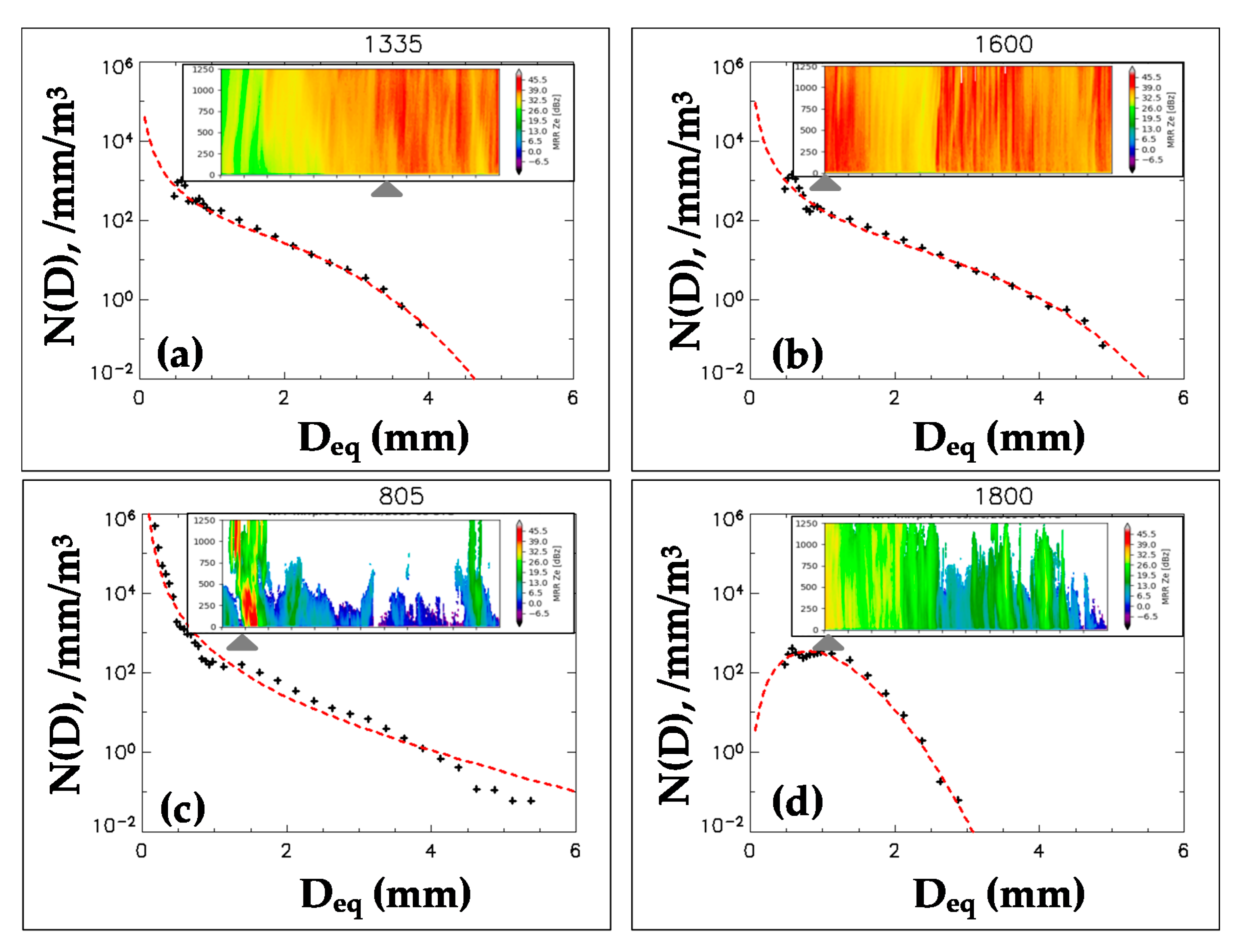
3.2. Generalized Gamma Fits
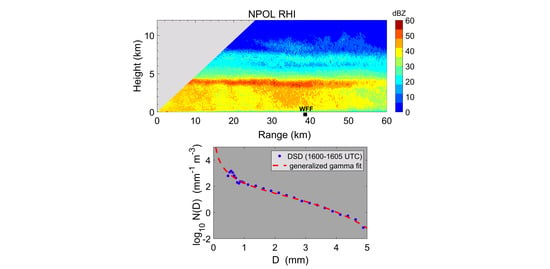
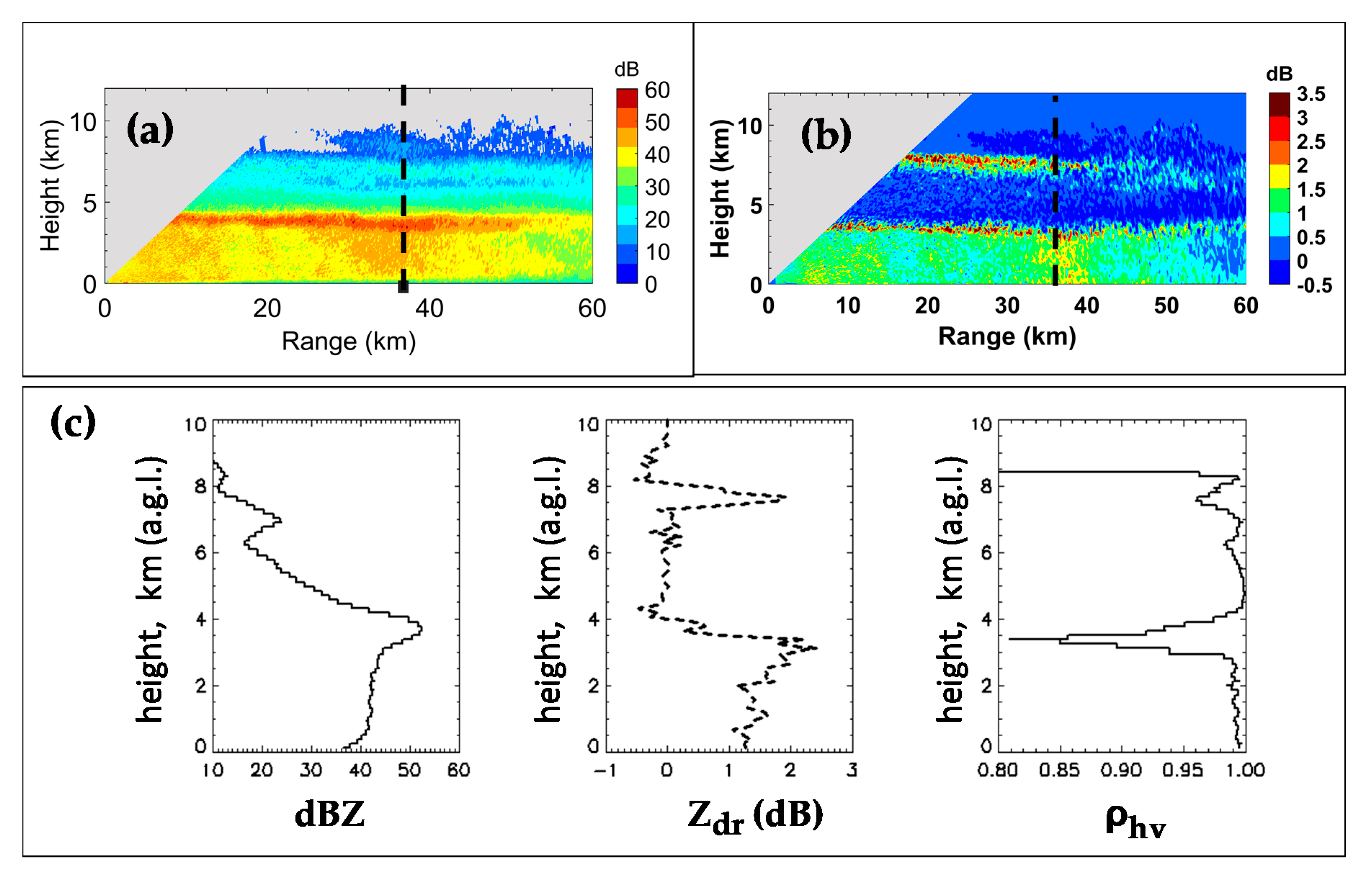
4. NPOL Radar Observations
5. Radar Data and DSDs
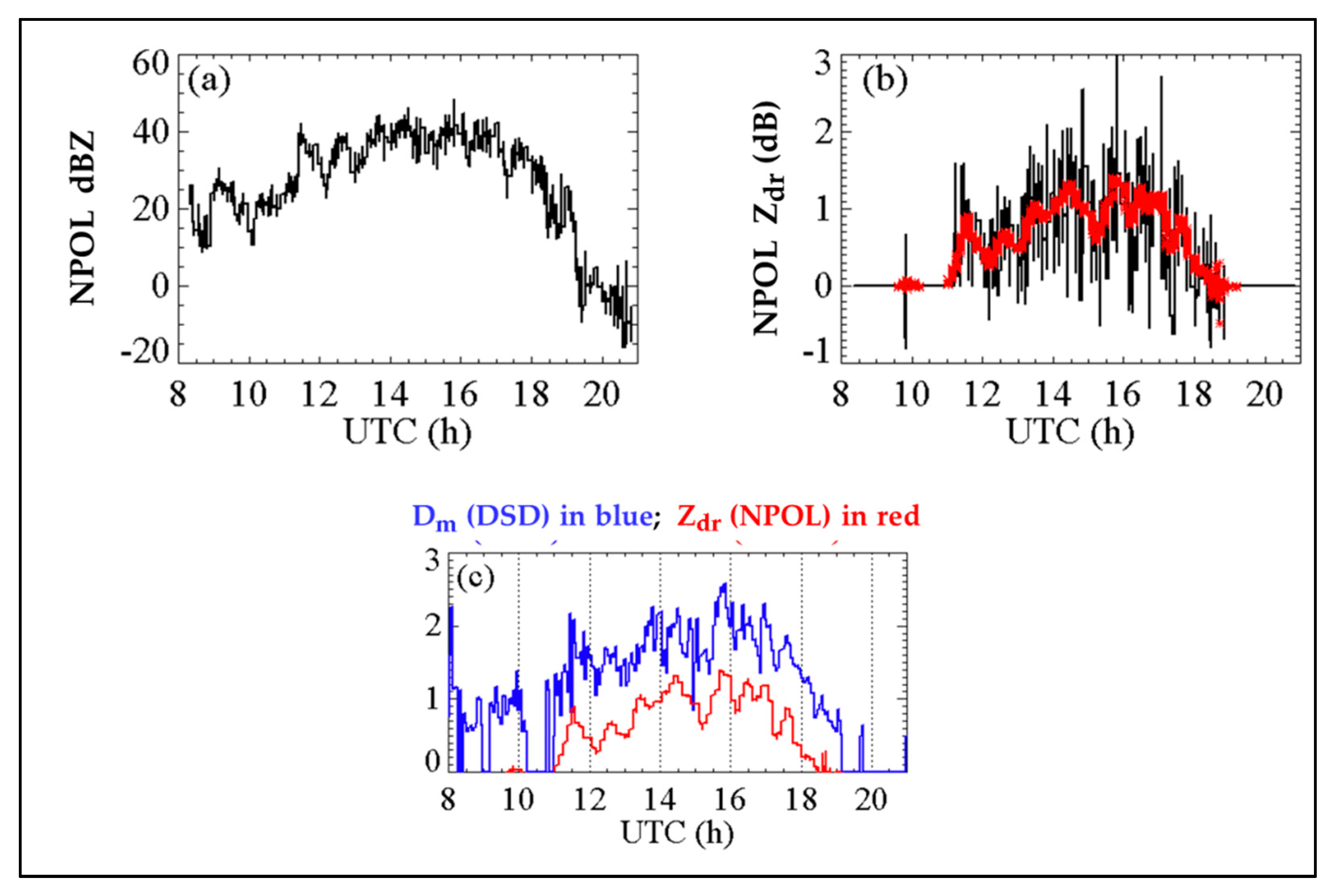
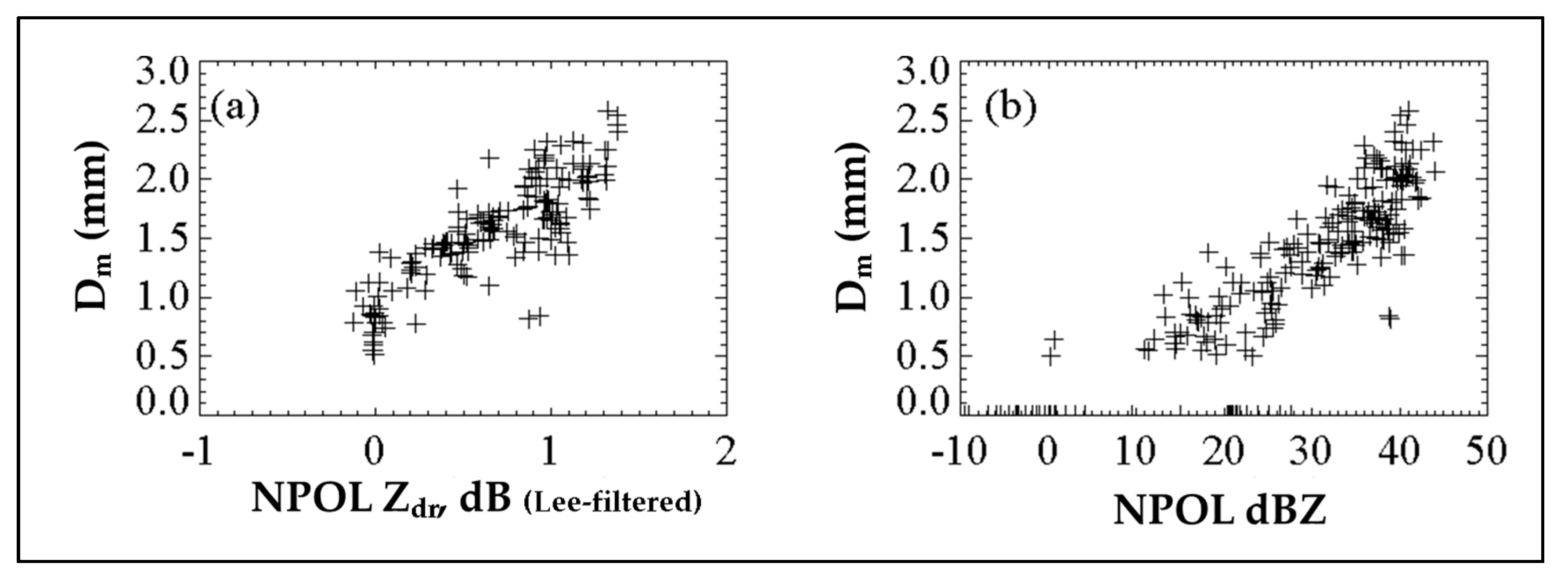
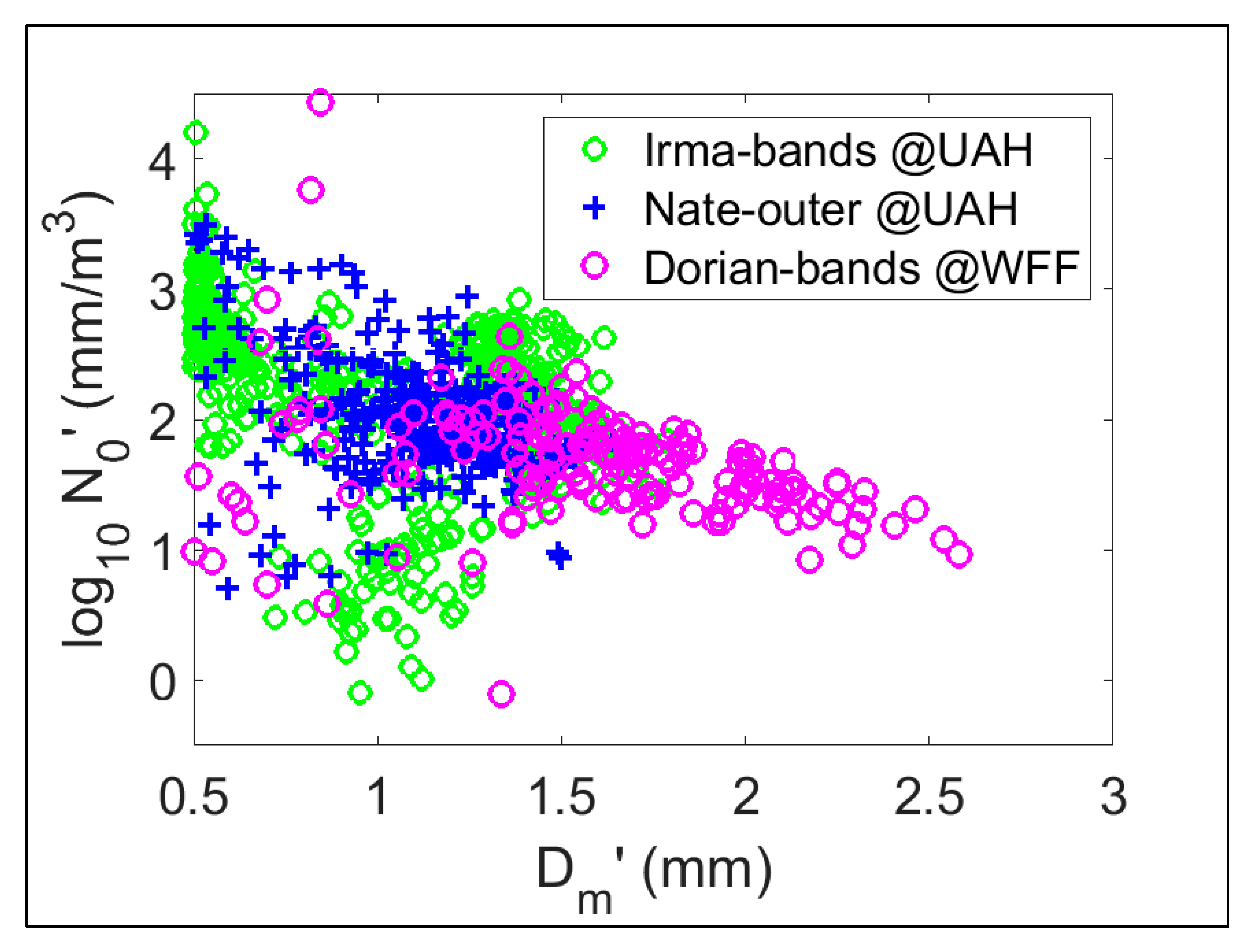
6. Comparisons of DSD Characteristics
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolff, D.B.; Marks, D.A.; Petersen, W.A. 2015: General Application of the Relative Calibration Adjustment (RCA) Technique for Monitoring and Correcting Radar Reflectivity Calibration. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merceret, F.J. On the Size Distribution of Raindrops in Hurricane Ginger. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1974, 102, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jorgensen, D.P.; Willis, P.T. A Z–R relationship for hurricanes. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1982, 21, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarquhar, G.M.; Black, R.A. Observations of particle size and phase in tropical cyclones: Implications for mesoscale modeling of microphysical processes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Bashor, P.G.; Habib, E.; Kasparis, T. Raindrop Size Distribution Measurements in Tropical Cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-C.; Bell, M.M. Microphysical Characteristics of an Asymmetric Eyewall in Major Hurricane Harvey. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 46, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didlake, A.C.; Kumjian, M.R. Examining Polarimetric Radar Observations of Bulk Microphysical Structures and Their Relation to Vortex Kinematics in Hurricane Arthur (2014). Mon. Wea. Rev. 2017, 145, 4521–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.R.; Bell, M.M.; Frambach, A.J. Validation of simulated hurricane drop size distributions using polarimetric radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A.; Tokay, A.; Marks, D.A.; Pippitt, J.L. Assessing Dual-Polarization Radar Estimates of Extreme Rainfall during Hurricane Harvey. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 2501–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural Variations in the Analytical Form of the Raindrop Size Distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; Bringi, V.N.; Carey, L.D.; Chandrasekar, V.; Gatlin, P.N.; Haddad, Z.S.; Meneghini, R.; Munchak, S.J.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Petersen, W.A. Describing the Shape of Raindrop Size Distributions Using Uncorrelated Raindrop Mass Spectrum Parameters. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnic, D.S. Radar Polarimetry for Weather Observations; Springer: Chaim, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sempere-Torres, D.; Porrà, J.M.; Creutin, J.-D. Experimental evidence of a general description for raindrop size distribution properties. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.A.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X. The concept of “normalized” distribution to describe raindrop spectra: A tool for cloud physics and cloud remote sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Zawadzki, I.; Szyrmer, W.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Uijlenhoet, R. A General Approach to Double-Moment Normalization of Drop Size Distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Delrieu, G.; Boudevillain, B.; Hazenberg, P.; Uijlenhoet, R. Unified Formulation of Single- and Multimoment Normalizations of the Raindrop Size Distribution Based on the Gamma Probability Density Function. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auf der Maur, A.N. Statistical tools for drop size distribution: Moments and generalized gamma. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, G.W.; Huang, W. The modified gamma size distribution applied to inhomogeneous and non-spherical particles: Key relationships and conversions. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 1460–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, T.H.; Berne, A. Retrieval of the raindrop size distribution from polarimetric radar data using double-moment normalization. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2573–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.A.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission for science and society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 98, 1679–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knollenberg, R. The optical array: An alternative to scattering or extinction for airborne particle size determination. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1970, 9, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Kok, G.; Dawson, W.; O’Connor, D.; Newton, R. A new ground-based precipitation spectrometer: The Meteorological Particle Sensor (MPS). In Proceedings of the 11th Conference on Cloud Physics, Ogden, UT, USA, 3–7 June 2002. paper 8.6. [Google Scholar]
- Bringi, V.N.; Thurai, M.; Baumgardner, D. Raindrop fall velocities from an optical array probe and 2-D video disdrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenhuber, M.; Lammer, G.; Randeu, W.L. One decade of imaging precipitation measurement by 2D-video-distrometer. Adv. Geosci. 2007, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhuber, M.; Lammer, G.; Randeu, W.L. The 2D-Video-Distrometer. In Precipitation: Advances in Measurement, Estimation and Prediction; Michaelides, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 3–31. ISBN 978-3-540-77654-3. [Google Scholar]
- OTT Hydromet GmbH. Operating Instructions: OTT Pluvio2 Precipitation Gauge; OTT Hydromet: Loveland, CO, USA, 2010; p. 60. Available online: http://www.ott.com/en-us/products/download/operating-instructions-precipitation-gauge-ott-pluvio2/ (accessed on 14 April 2015).
- Rasmussen, R.; Baker, B.; Kochendorfer, J.; Meyers, T.; Landolt, S.; Fischer, A.P.; Black, J.; Thériault, J.M.; Kucera, P.; Gochis, D.; et al. How Well Are We Measuring Snow: The NOAA/FAA/NCAR Winter Precipitation Test Bed. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.; Gatlin, P.N.; Petersen, W.A.; Wingo, M.T. Measurements and Modeling of the Full Rain Drop Size Distribution. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, T.H.; Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; Berne, A. Reconstructing the Drizzle Mode of the Raindrop Size Distribution Using Double-Moment Normalization. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2019, 58, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Blackman, T.M. The Need to Represent Raindrop Size Spectra as Normalized Gamma Distributions for the Interpretation of Polarization Radar Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N. Application of the Generalized Gamma Model to Represent the Full Rain Drop Size Distribution Spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.; Fischer, B.; Münster, H.; Clemens, M.; Wagner, A. Profiles of Raindrop Size Distributions as Retrieved by Microrain Radars. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; Gatlin, P.N.; Petersen, W.A.; Wingo, M. Why the Generalized Gamma? - An Answer Based on Measurements with Meteorological Particle Spectrometer and 2D Video Disdrometer. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology (ERAD 2018) 2018, extended abstract, 051, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trömel, S.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Hickman, B.; Mühlbauer, K.; Simmer, C. Polarimetric Radar Variables in the Layers of Melting and Dendritic Growth at X Band—Implications for a Nowcasting Strategy in Stratiform Rain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 2497–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, P.N.; Petersen, W.A.; Knupp, K.R.; Carey, L.D. Observed Response of the Raindrop Size Distribution to Changes in the Melting Layer. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Caylor, I.J. Polarization Radar Estimates of Raindrop Size Spectra and Rainfall Rates. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1989, 6, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zrnić, D.S.; Raghavan, R.; Chandrasekar, V. Observations of Copolar Correlation Coefficient through a Bright Band at Vertical Incidence. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.T.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Estimation of Melting-Layer Cooling Rate from Dual-Polarization Radar: Spectral Bin Model Simulations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 1485–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.C.; Rutledge, S.A. S-Band Dual-Polarization Radar Observations of Winter Storms. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, J.; Bringi, V.N. An Iterative Filtering Technique for the Analysis of Copolar Differential Phase and Dual-Frequency Radar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, 2, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; Carey, L.D.; Gatlin, P.; Schultz, E.; Petersen, W.A. Estimating the Accuracy of Polarimetric Radar–Based Retrievals of Drop Size Distribution Parameters and Rain Rate: An Application of Error Variance Separation Using Radar-Derived Spatial Correlations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop Size Distribution in Different Climatic Regimes from Disdrometer and Dual-Polarized Radar Analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Prat, O.P. The Impact of Raindrop Collisional Processes on the Polarimetric Radar Variables. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3052–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; Wolff, D.B.; Marks, D.A.; Pabla, C.S. Drop Size Distribution Measurements in Outer Rainbands of Hurricane Dorian at the NASA Wallops Precipitation-Research Facility. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060578
Thurai M, Bringi VN, Wolff DB, Marks DA, Pabla CS. Drop Size Distribution Measurements in Outer Rainbands of Hurricane Dorian at the NASA Wallops Precipitation-Research Facility. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060578
Chicago/Turabian StyleThurai, Merhala, Viswanathan N. Bringi, David B. Wolff, David A. Marks, and Charanjit S. Pabla. 2020. "Drop Size Distribution Measurements in Outer Rainbands of Hurricane Dorian at the NASA Wallops Precipitation-Research Facility" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060578
APA StyleThurai, M., Bringi, V. N., Wolff, D. B., Marks, D. A., & Pabla, C. S. (2020). Drop Size Distribution Measurements in Outer Rainbands of Hurricane Dorian at the NASA Wallops Precipitation-Research Facility. Atmosphere, 11(6), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060578