Model Details, Parametrization, and Accuracy in Daily Scale Green Roof Hydrological Conceptual Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
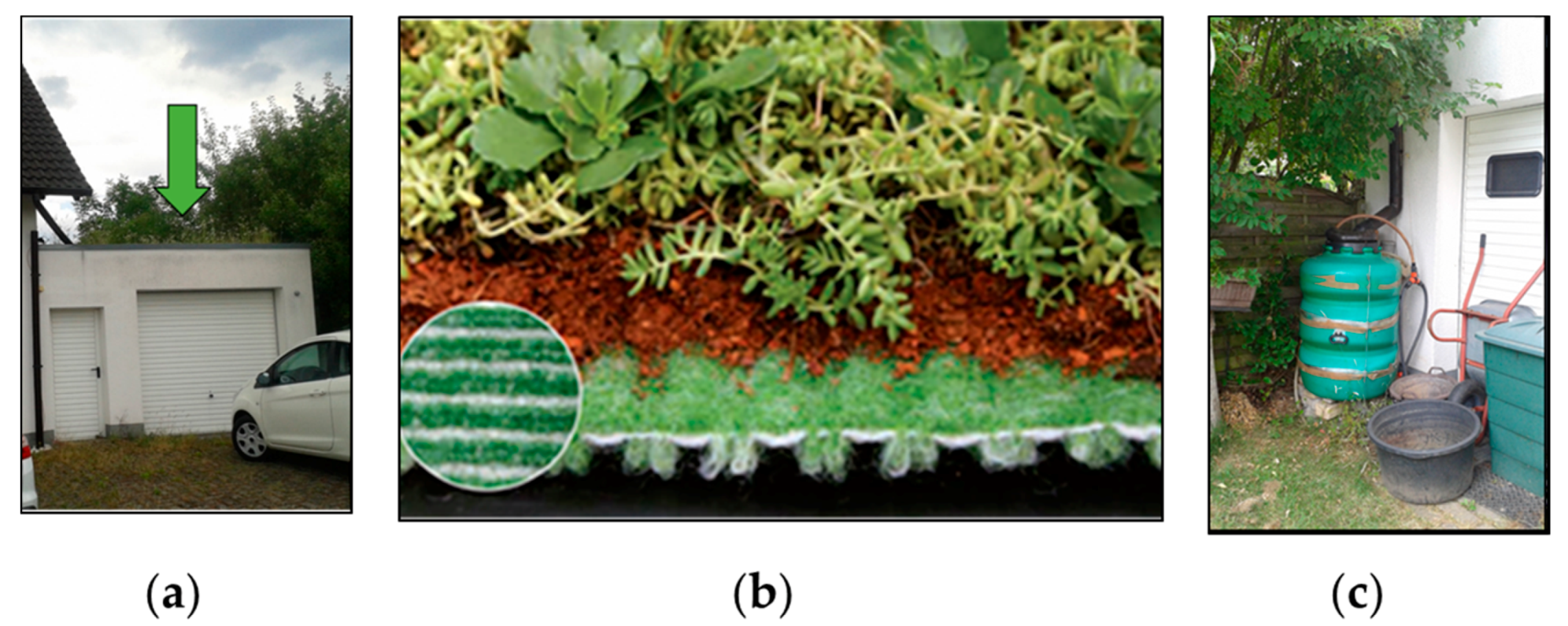
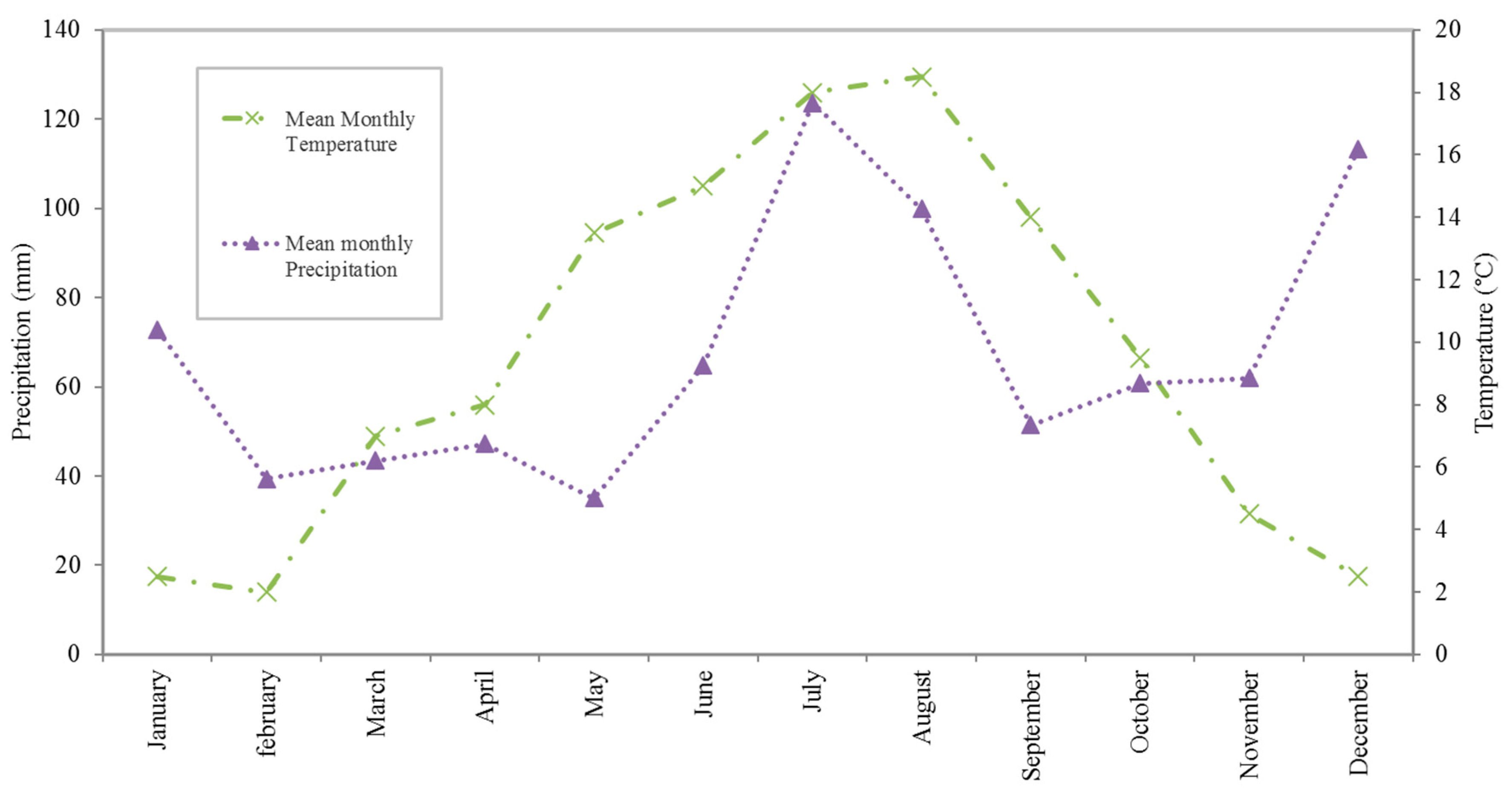
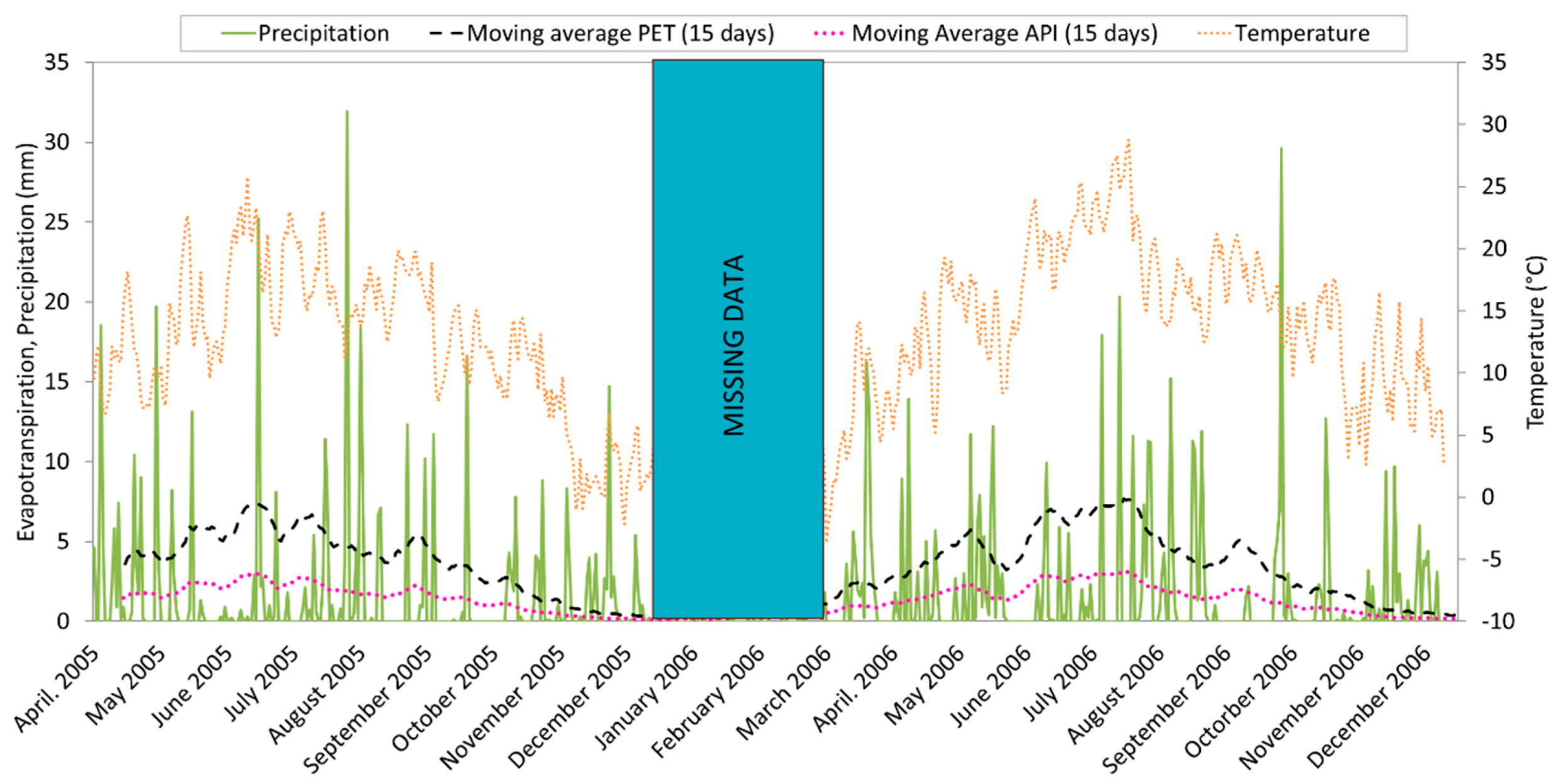
2.1. The Study Site and Data
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. The Governing Equations
2.2.2. Models Selection for Potential and Actual Evapotranspiration Assessment
3. Results
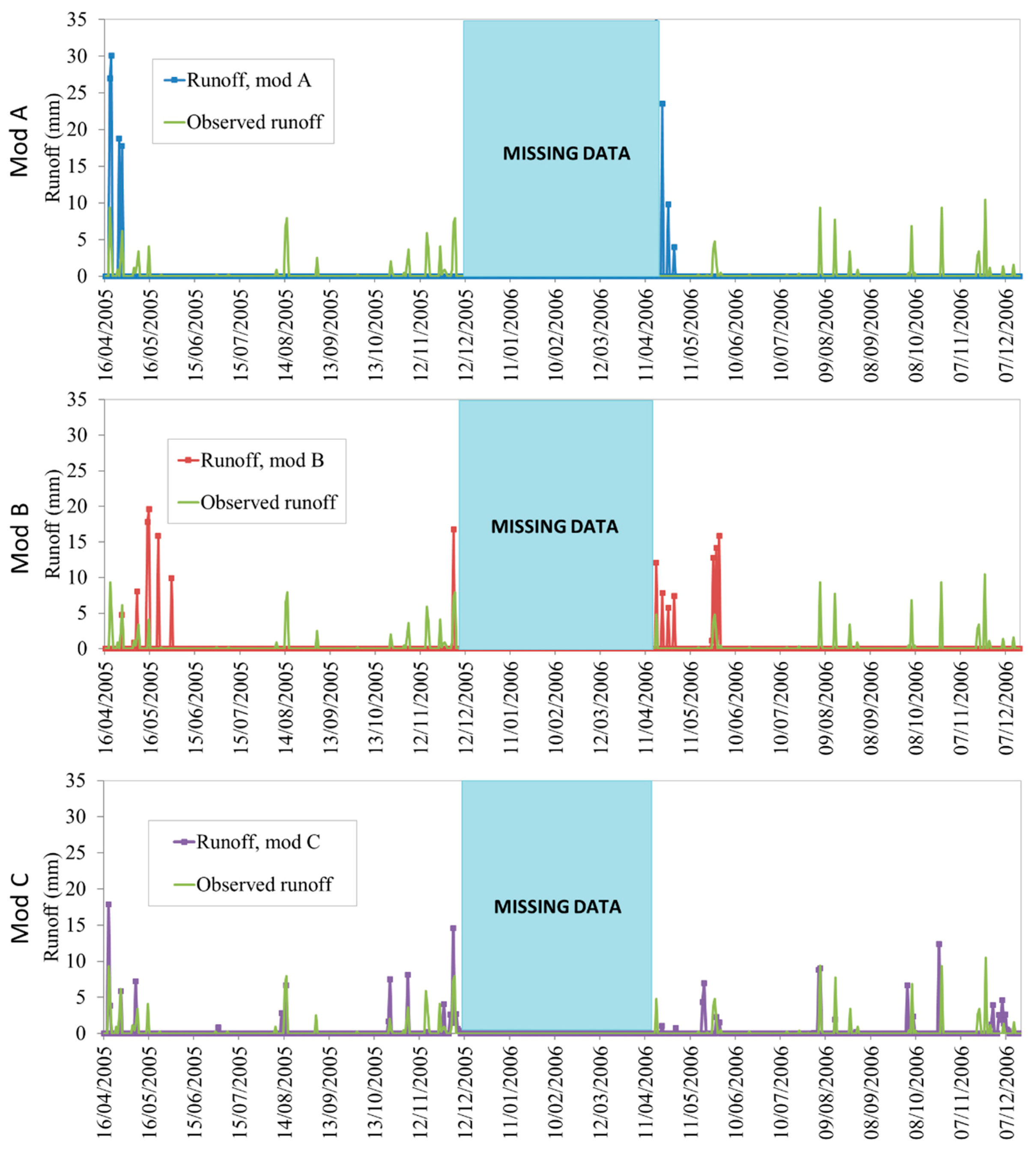
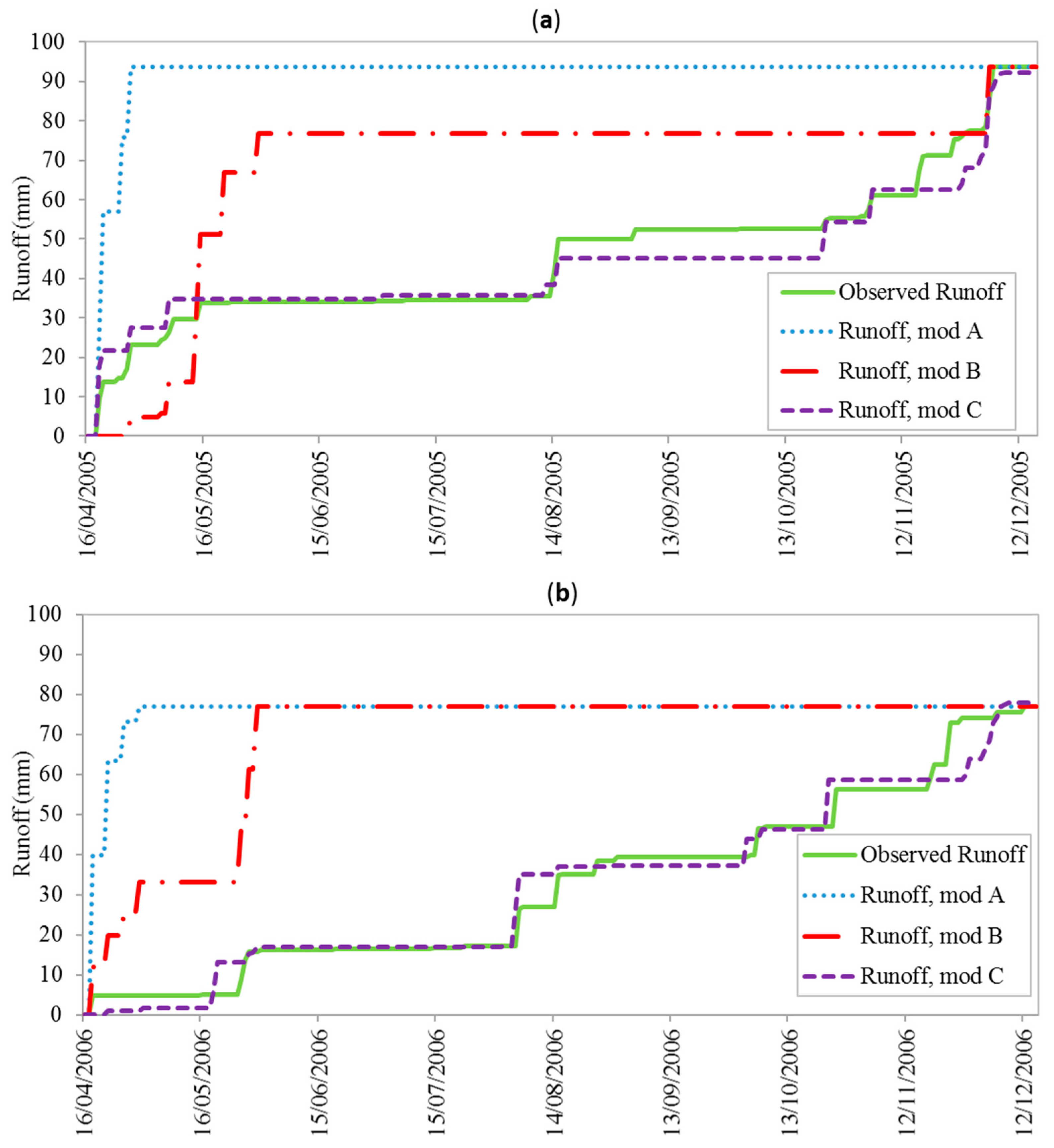
3.1. Models Evaluation
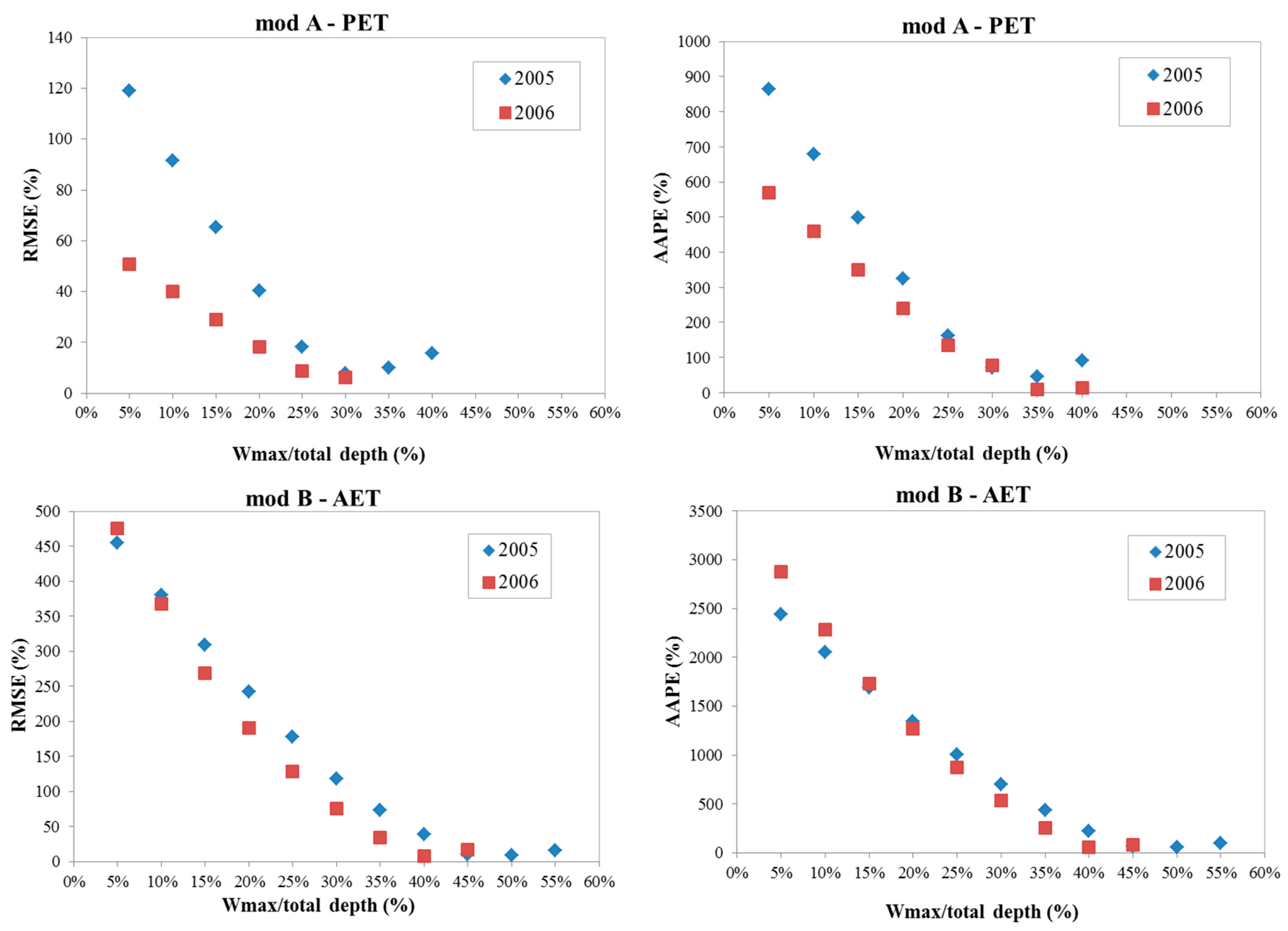
3.2. Impact of Maximum Water Holding Capacity Threshold
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cettner, A.; Ashley, R.; Hedström, A.; Viklander, M. Sustainable development and urban stormwater practice. Urban Water J. 2013, 11, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharuddin, A.; Noorazuan, M.H.; Yaakob, M.J. Green roofs as best management practices for heat reduction and stormwater flow mitigation. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 13, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sartor, J.; Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Results and findings from 15 years of sustainable urban storm water management. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 2018, 8, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Smart stormwater management in urban areas by roofs greening. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2017, 10406, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versini, P.-A.; Jouve, P.; Ramier, D.; Berthier, E.; De Gouvello, B. Use of green roofs to solve storm water issues at the basin scale—Study in the Hauts-de-Seine County (France). Urban Water J. 2015, 13, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnogorskaya, N.; Longobardi, A.; Mobilia, M.; Khasanova, L.F.; Shchelchkova, A.I. Hydrological modeling of green roofs runoff by Nash cascade model. Open Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 13, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibler, M.R. Comprehensive benefits of green roofs. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2015: Floods, Droughts, and Ecosystems, Austin, TX, USA, 17–21 May 2015; pp. 2244–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Stovin, V.; Vesuviano, G.; De-Ville, S. Defining green roof detention performance. Urban Water J. 2015, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentens, J.; Raes, D.; Hermy, M. Green roofs as a tool for solving the rainwater runoff problem in the urbanized 21st century? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teemusk, A.; Mander, Ü. Rainwater runoff quantity and quality performance from a greenroof: The effects of short-term events. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, A.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Mobilia, M. Predicting stormwater retention capacity of green roofs: An experimental study of the roles of climate, substrate soil moisture, and drainage layer properties. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovin, V.; Vesuviano, G.; Kasmin, H. The hydrological performance of a green roof test bed under UK climatic conditions. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poë, S.; Stovin, V.; Berretta, C. Parameters influencing the regeneration of a green roof’s retention capacity via evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starry, O.; Lea-Cox, J.; Ristvey, A.; Cohan, S. Parameterizing a water-balance model for predicting stormwater runoff from green roofs. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04016046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, R.C.; Wilkinson, S.J. Modelling green roof stormwater response for different soil depths. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 153, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyde, E.; Fassman, E.; Simcock, R.; Wells, J.; Fassman-Beck, E. Quantifying evapotranspiration rates for new zealand green roofs. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burszta-Adamiak, E.; Mrowiec, M. Modelling of green roofs’ hydrologic performance using EPA’s SWMM. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, T.; Keeley, M.; Marasco, D.E.; McGillis, W.; Culligan, P. Assessing methods for predicting green roof rainfall capture: A comparison between full-scale observations and four hydrologic models. Urban Water J. 2015, 14, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Impact of rainfall properties on the performance of hydrological models for green roofs simulation. Water Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A.; Sartor, J.F. Including a-priori assessment of actual evapotranspiration for green roof daily scale hydrological modelling. Water 2017, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawdsley, J.A.; Ali, M.F. Estimating nonpotential evapotranspiration by means of the equilibrium evaporation concept. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass, proceedings of the royal society of London. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Linsley, R.K.; Kohler, M.A. Variations in storm rainfall over small areas. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1951, 32, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogawski, P.; Bednorz, E. Comparison and validation of selected evapotranspiration models for conditions in Poland (Central Europe). Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 5021–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, D.E.; Culligan, P.J.; McGillis, W.R. Evaluation of common evapotranspiration models based on measurements from two extensive green roofs in New York City. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; Goulden, M.L.; Famiglietti, J. Ground heat flux: An analytical review of 6 models evaluated at 88 sites and globally. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 3045–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.A.; Allen, C.D. Equilibrium, potential and actual evaporation from cropped surfaces in Southern Ontario. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1973, 12, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-H.; Altunkaynak, A. Comparative case study of rainfall-runoff modeling between SWMM and fuzzy logic approach. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I.; Lanza, L.G. Compared performance of a conceptual and a mechanistic hydrologic models of a green roof. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haowen, X.; Yawen, W.; Luping, W.; Weilin, L.; Wenqi, Z.; Hong, Z.; Yichen, Y.; Jun, L. Comparing simulations of green roof hydrological processes by SWMM and HYDRUS-1D. Water Supply 2019, 20, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | ET | Wmax |
|---|---|---|
| mod A | PET | Constant |
| mod B | AET | Constant |
| mod C | AET | Variable |
| Year | Method | Rmod (mm) | RMSE (mm) | AAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 Robs(mm) = 93.6 | mod A | 93.64 | 13.15 | 126.40 |
| mod B | 93.64 | 5.83 | 48.17 | |
| mod C | 92.34 | 1.75 | 13.08 | |
| 2006 Robs(mm) = 77.0 | mod A | 77.05 | 146.50 | 9.79 |
| mod B | 77.05 | 89.87 | 8.71 | |
| mod C | 77.91 | 15.64 | 1.53 |
| Year | Mod A (%) | Mod B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 26.6 | 46.1 |
| 2006 | 24.3 | 38.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Model Details, Parametrization, and Accuracy in Daily Scale Green Roof Hydrological Conceptual Simulation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060575
Mobilia M, Longobardi A. Model Details, Parametrization, and Accuracy in Daily Scale Green Roof Hydrological Conceptual Simulation. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060575
Chicago/Turabian StyleMobilia, Mirka, and Antonia Longobardi. 2020. "Model Details, Parametrization, and Accuracy in Daily Scale Green Roof Hydrological Conceptual Simulation" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060575
APA StyleMobilia, M., & Longobardi, A. (2020). Model Details, Parametrization, and Accuracy in Daily Scale Green Roof Hydrological Conceptual Simulation. Atmosphere, 11(6), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060575






