The Climatological Analysis of Typhoon Tracks, Steering Flow, and the Pacific Subtropical High in the Vicinity of Taiwan and the Western North Pacific
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Establishing the Typhoon (Ty) Category
3.2. Calculating Steering Flow
4. Results
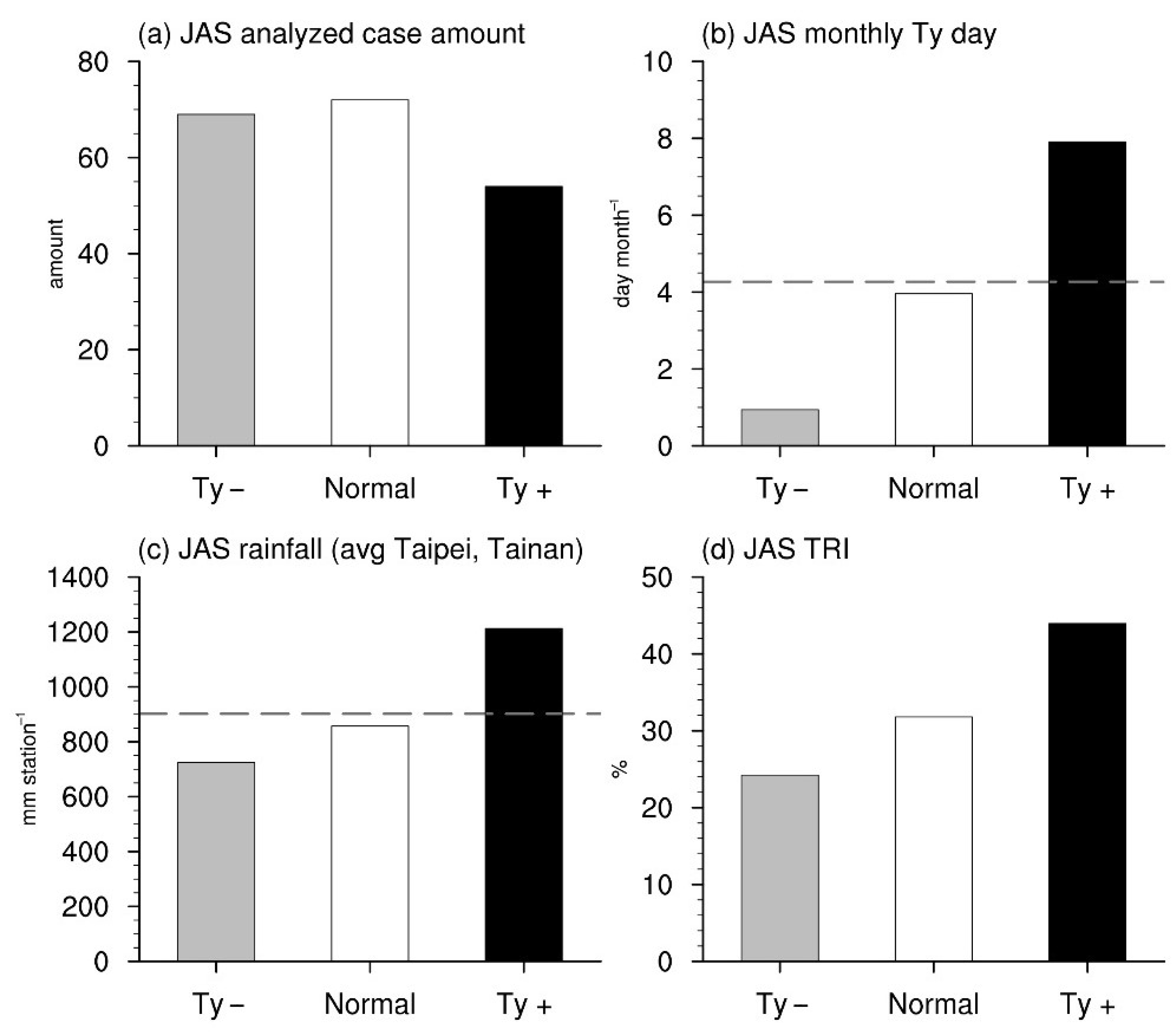
4.1. The Ty Categories
4.2. Typhoon Paths and Corresponding Large-Scale Environmental Fields
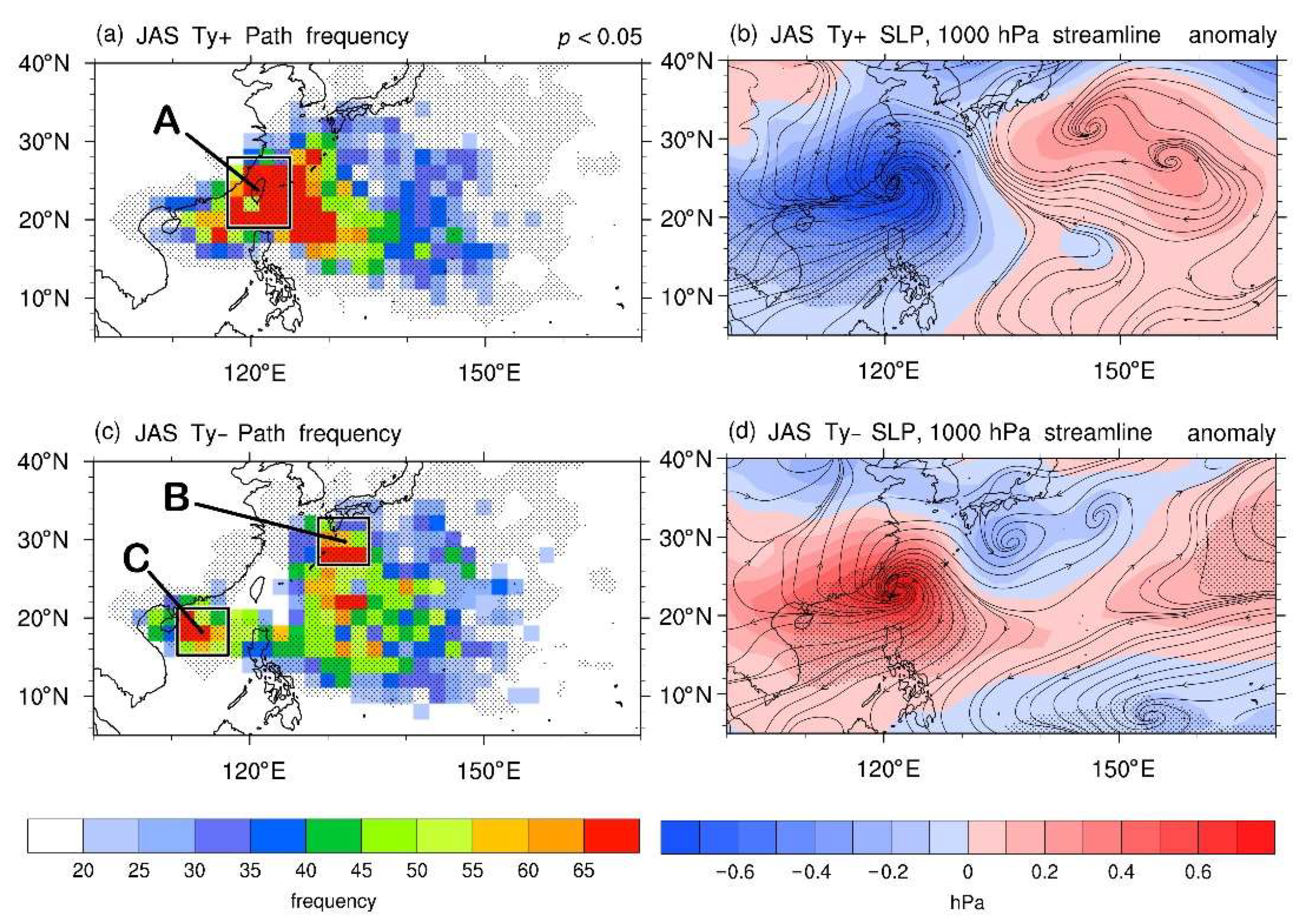
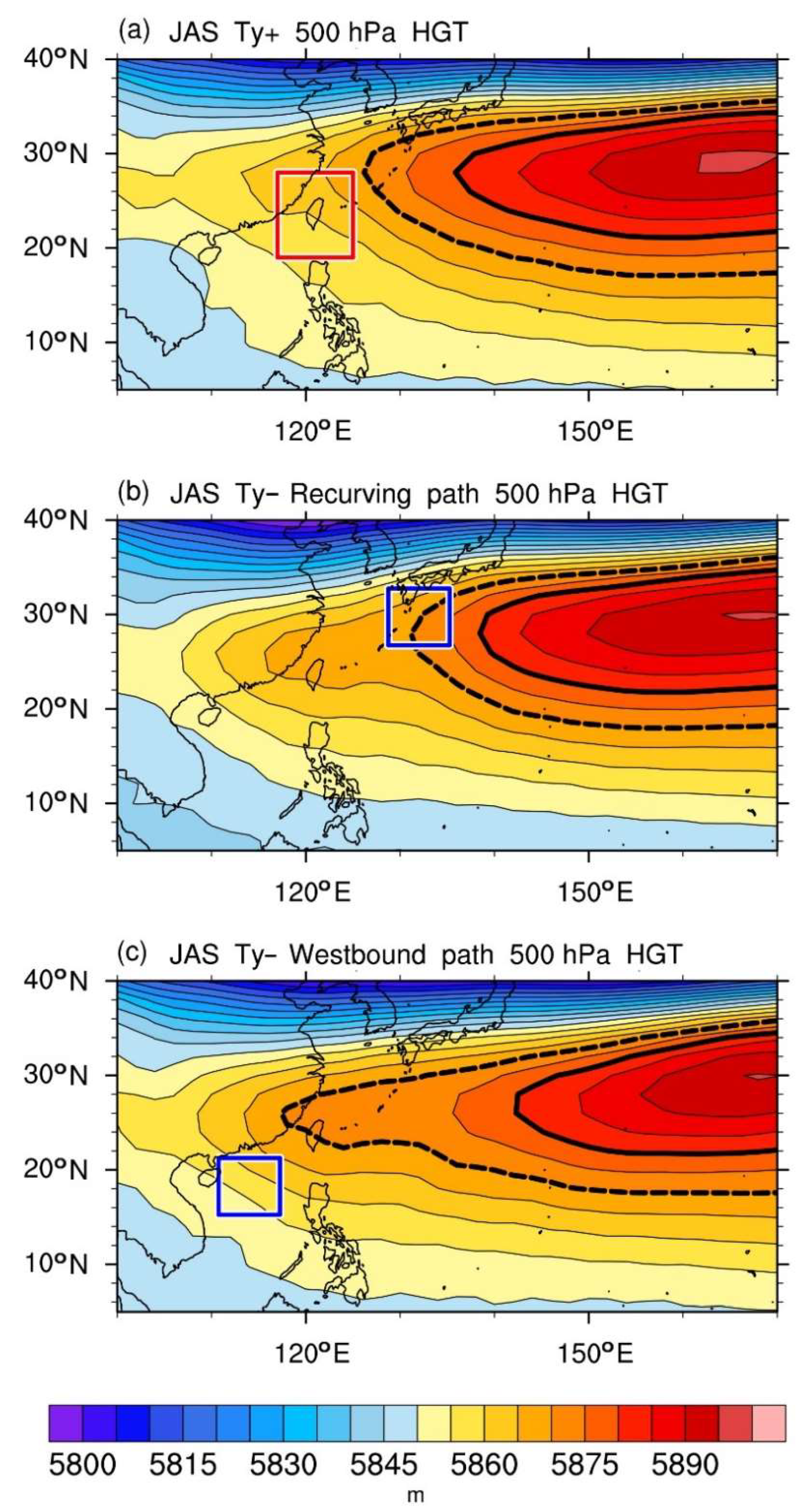
4.2.1. The Ty+ and Ty− Categories
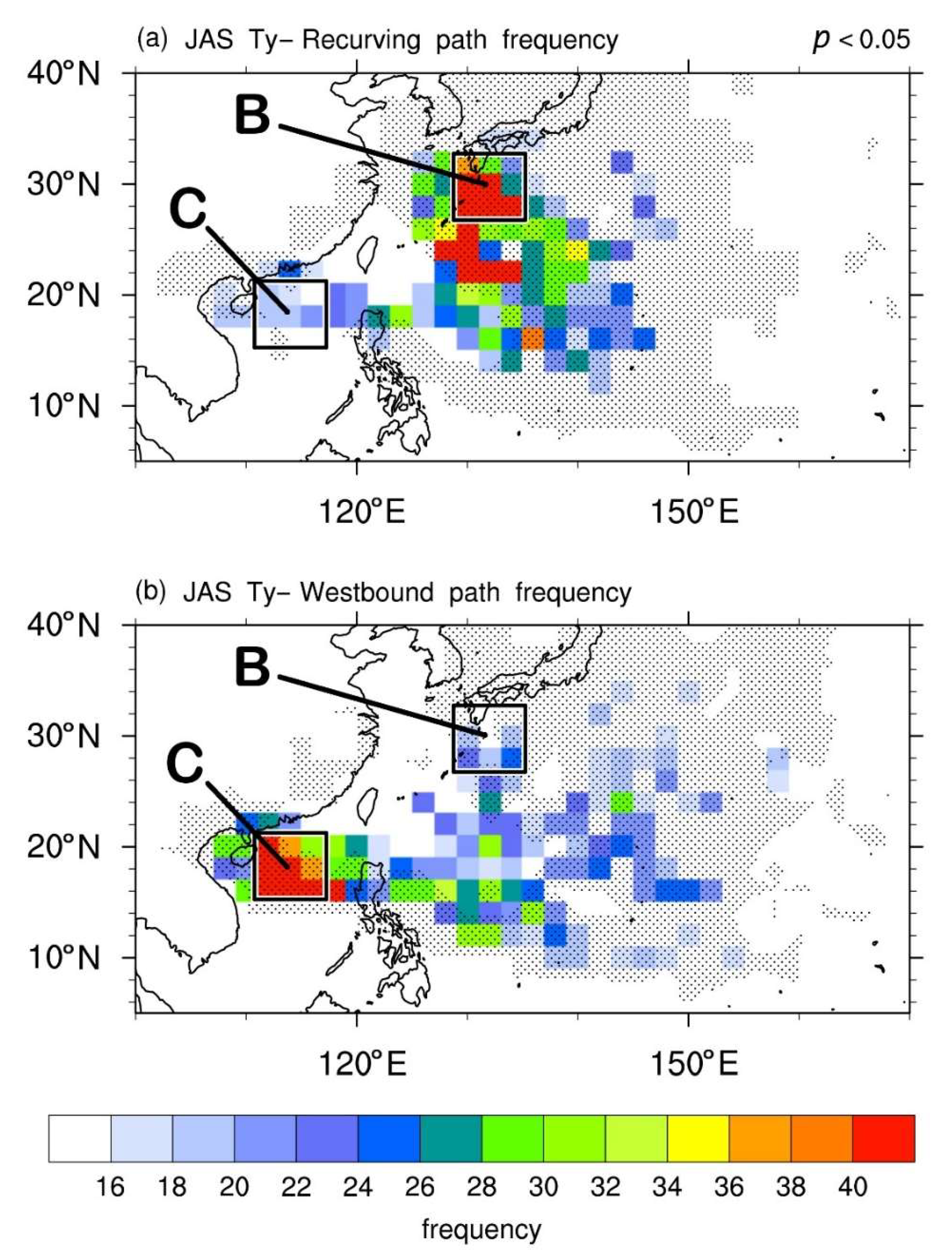
4.2.2. The Recurving and Westbound Paths
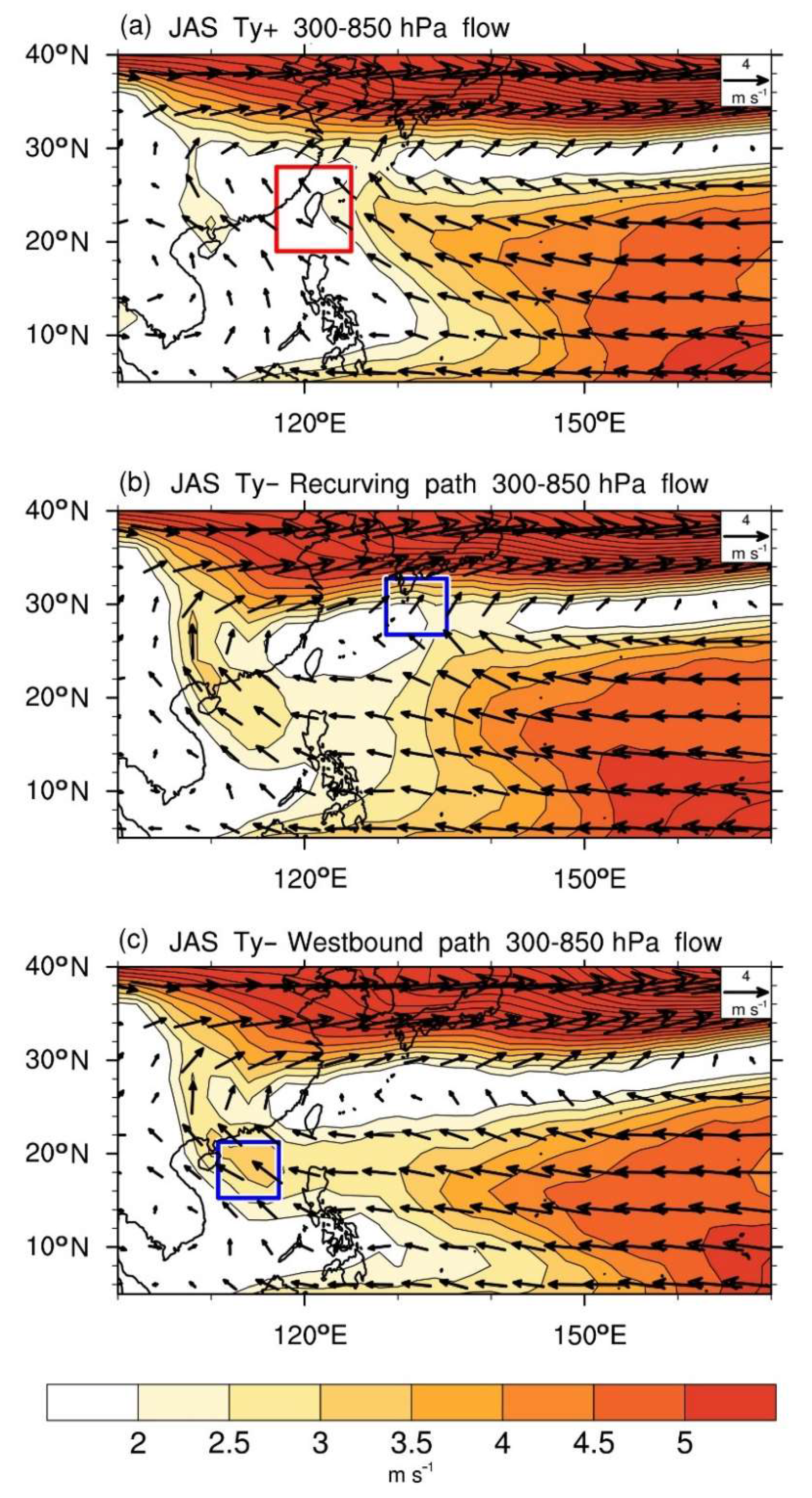
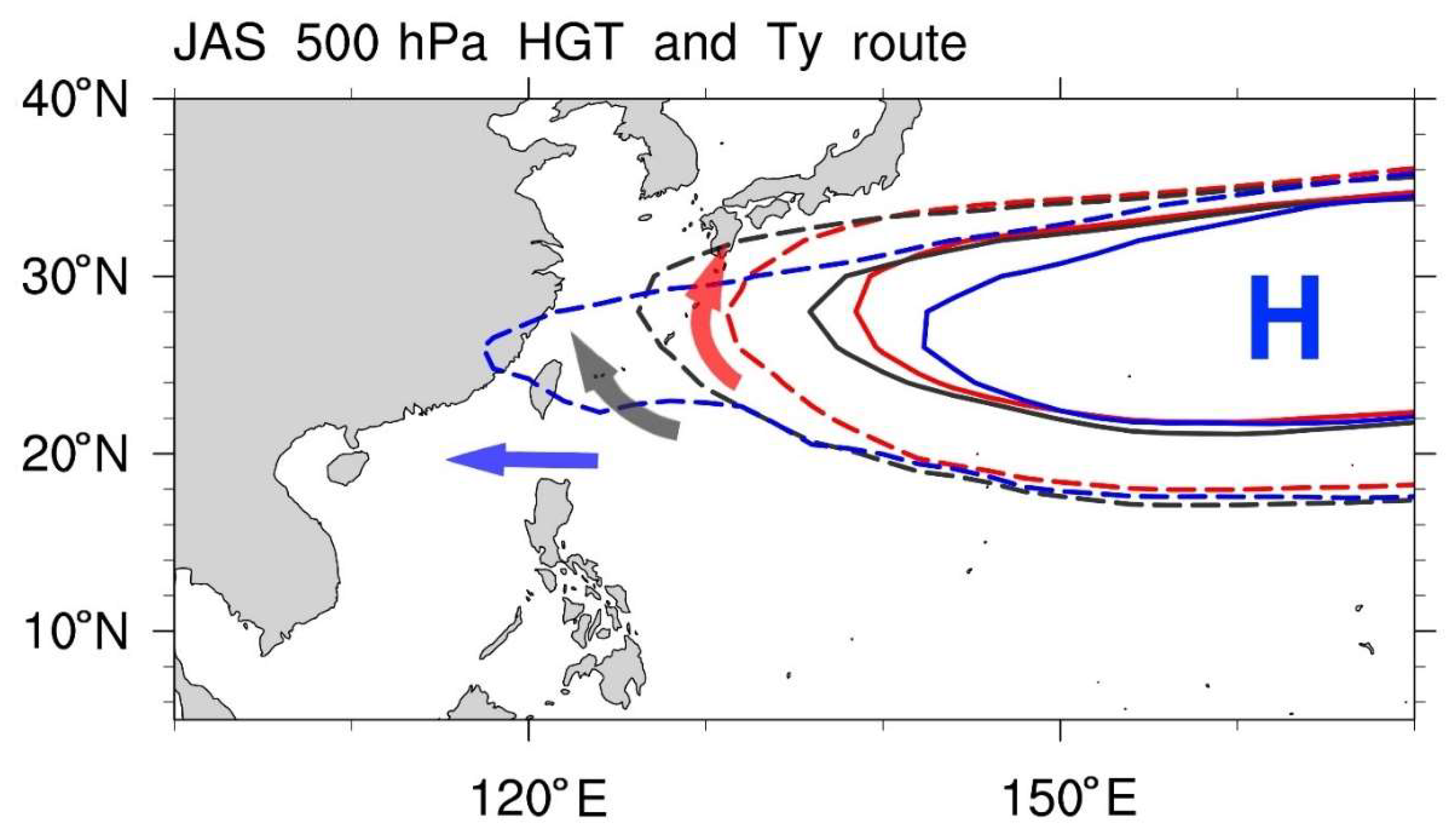
4.2.3. Corresponding Large-Scale Circulations
4.2.4. Typhoon Paths and the Position of the Pacific Subtropical High
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yumoto, M.; Matsuura, T. Interdecadal variability of tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.-C.; Kuo, H.-C. On the extreme rainfall of Typhoon Morakot (2009). J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D05104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Wu, I.-H.; Feng, L. A numerical investigation of the convective systems in the vicinity of southern Taiwan associated with Typhoon Fanapi (2010): Formation mechanism of double rainfall peaks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12647–12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Hsu, L.-H.; Yang, Y.-T. Temporal and spatial characteristics of typhoon extreme rainfall in Taiwan. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Wang, B. How much do tropical cyclones affect seasonal and interannual rainfall variability over the Western North Pacific? J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5495–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.W.; Hsu, H.H. Contribution of typhoons to the rainfall in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Geography in Taiwan, NTNU, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–23 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-M.; Li, T.; Shih, C.-F. Tropical cyclone and monsoon-induced rainfall variability in Taiwan. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-M.; Chen, H.-S. Interdecadal variability of summer rainfall in Taiwan associated with tropical cyclones and monsoon. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5786–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-M.; Fan, H.-L. Interannual Variability of the South China Sea Summer Rainfall and Typhoon Invading Taiwan. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 31, 221–238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.-Y.; Chen, J.-M. Large-scale indices for assessing typhoon activity around Taiwan. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, T. Quasi-geostrophic motions in the equatorial area. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 44, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T. Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 65, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-R. Have steering flows over the western North Pacific and the South China Sea changed over the last 50 years? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.-Y.; Chou, C. Changes in precipitation frequency and intensity in the vicinity in Taiwan: Typhoon vs. non-typhoon events. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-P.; Yang, Y.-T.; Kuo, H.-C. Large increasing trend of tropical cyclone rainfall in Taiwan and the role of terrain. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4138–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Wang, Y. The Influence of Island Topography on Typhoon Track Deflection. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2011, 139, 1708–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.; Hsiao, L.F.; Chen, D.S.; Huang, K.N. A study on terrain-induced tropical cyclone looping in East Taiwan: Case study of Typhoon Haitang in 2005. Nat. Hazards 2012, 63, 1497–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hung, C.W. The Construction of TCCIP Taiwan Rainfall Index (TRI) and its Applications. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 67, 73–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Physical Sciences Laboratory. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/ (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Tu, J.-Y.; Chou, C.; Chu, P.-S. The abrupt shift of typhoon activity in the vicinity of Taiwan and its association with western North Pacific-East Asian climate change. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3617–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlain, T.B.; Breman, M.J. Chapter 3: Tropical cyclone motion. In Global Guide to Tropical Cyclone Forecasting, 2nd ed.; Guard, C.C., Ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 63–125. ISBN 978-92-63-11194-4. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, G.J. Chapter 3: Tropical cyclone motion. In Global Guide to Tropical Cyclone Forecasting, 1st ed.; Holland, G.J., Ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; pp. 3.1–3.48. ISBN 978-92-63-11194-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.S.; Kuo, Y.S.; Lai, W.C.; Tsai, Y.J.; Lee, S.P.; Chen, K.T.; Shieh, C.L. Reflection of typhoon morakot―The challenge of compound disaster simulation. J. Mt. Sci. 2011, 8, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Russell, E.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Dynamics in tropical cyclone motion. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 22, 416–434. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wu, L.; Wang, C. Typhoon track changes associated with global warming. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3748–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Leung, Y.; Chan, J.C. The analysis of tropical cyclone tracks in the western North Pacific through data mining. Part I: Tropical cyclone recurvature. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1394–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Leung, Y.; Chan, J.C. The analysis of tropical cyclone tracks in the western North Pacific through data mining. Part II: Tropical cyclone landfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Robertson, A.W.; Gaffney, S.J.; Smyth, P.; Ghil, M. Cluster analysis of typhoon tracks. Part I: General properties. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3635–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J. Tropical Cyclone Formation. Available online: https://www.hurricanezone.net/articles/tropicalcycloneformation.html (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Wu, L.; Wang, B.; Geng, S. Growing typhoon influence on east Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L18703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horse Latitudes. Available online: http://www.worldwidewords.org/qa/qa-hor3.htm (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Zehnder, J.A. Tropical cyclone. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/tropical-cyclone/Life-of-a-cyclone (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40-50 day period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Observations of the 40-50-day tropical oscillation-A review. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 814–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Waliser, D.E.; Lau, K.M.; Stern, W. Global occurrences of extreme precipitation and the Madden-Julian oscillation: Observations and predictability. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4575–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, RG2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.; Meinke, H.; Power, B.; Maia, A.D.; Wheeler, M.C.; White, N.; Stone, R.C.; Ribbe, J. Near-global impact of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L09704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T. Cloudiness fluctuations associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 57, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T. A quasi-stationary appearance of 30 to 40 day period in the cloudiness fluctuations during the summer monsoon over India. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 58, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T. Structure of an Indian summer monsoon system with around 40-day period. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 59, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Sui, C.H.; Park, S.K. Systematic variation of summertime tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific in relation to the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1171–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Zhou, W. Modulation of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity by the ISO. Part I: Genesis and intensity. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2904–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chou, C. Joint Contribution of multiple equatorial waves to tropical cyclogenesis over the western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.W.; Lin, H.J.; Kao, P.K.; Shih, M.F.; Fong, W.Y. Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation Impact on Western North Pacific Typhoons and Rainfall in Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2016, 27, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elsner, J.B.; Liu, K.B. Examining the ENSO-typhoon hypothesis. Clim. Res. 2003, 25, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Sobel, A.H. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Intensity and ENSO. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H. Variability of typhoon tracks and genesis over the Western North Pacific. In Cyclones: Formation, Triggers and Control; Oouchi, K., Fudeyasu, H., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Weng, H.; Yamagata, T. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; McPhaden, M.J. Increasing intensity of El Niño in the central-equatorial Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L14603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Graf, H.; Leung, Y.; Herzog, M. Different El Niño Types and Tropical Cyclone Landfall in East Asia. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6510–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.-H.; Chung, P.-H.; Li, T. Interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western North Pacific subtropical high. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| July | August | September | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ty+ | Ty− | Ty+ | Ty− | Ty+ | Ty− |
| 1952 | 1950 | 1960 | 1950 | 1956 | 1950 |
| 1961 | 1951 | 1961 | 1951 | 1957 | 1954 |
| 1962 | 1953 | 1962 | 1952 | 1959 | 1955 |
| 1966 | 1954 | 1972 | 1954 | 1963 | 1958 |
| 1968 | 1955 | 1974 | 1956 | 1966 | 1960 |
| 1972 | 1956 | 1982 | 1957 | 1974 | 1965 |
| 1973 | 1957 | 1986 | 1958 | 1977 | 1967 |
| 1977 | 1958 | 1990 | 1963 | 1989 | 1972 |
| 1979 | 1959 | 1992 | 1964 | 1990 | 1975 |
| 1987 | 1960 | 1994 | 1967 | 1991 | 1976 |
| 1990 | 1970 | 1995 | 1969 | 1992 | 1979 |
| 1998 | 1974 | 1997 | 1970 | 1993 | 1981 |
| 2000 | 1975 | 2003 | 1971 | 2001 | 1984 |
| 2001 | 1976 | 2004 | 1983 | 2008 | 1988 |
| 2002 | 1978 | 2005 | 1987 | 2010 | 1996 |
| 2004 | 1983 | 2007 | 1988 | - | 1997 |
| 2006 | 1985 | 2008 | 2001 | - | 2003 |
| 2008 | 1986 | 2010 | 2002 | - | 2007 |
| 2013 | 1988 | 2012 | 2014 | - | 2009 |
| - | 1989 | 2013 | - | - | 2011 |
| - | 1992 | - | - | - | 2012 |
| - | 1993 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 1995 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 1997 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 1999 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 2003 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 2007 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 2010 | - | - | - | - |
| - | 2011 | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, C.-w.; Shih, M.-F.; Lin, T.-Y. The Climatological Analysis of Typhoon Tracks, Steering Flow, and the Pacific Subtropical High in the Vicinity of Taiwan and the Western North Pacific. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050543
Hung C-w, Shih M-F, Lin T-Y. The Climatological Analysis of Typhoon Tracks, Steering Flow, and the Pacific Subtropical High in the Vicinity of Taiwan and the Western North Pacific. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050543
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Chih-wen, Ming-Fu Shih, and Te-Yuan Lin. 2020. "The Climatological Analysis of Typhoon Tracks, Steering Flow, and the Pacific Subtropical High in the Vicinity of Taiwan and the Western North Pacific" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050543
APA StyleHung, C.-w., Shih, M.-F., & Lin, T.-Y. (2020). The Climatological Analysis of Typhoon Tracks, Steering Flow, and the Pacific Subtropical High in the Vicinity of Taiwan and the Western North Pacific. Atmosphere, 11(5), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050543




