Applying a Delphi-Type Approach to Estimate the Adaptation Cost on Agriculture to Climate Change in Cyprus
Abstract
1. Introduction
- reduced inflows to dams and wetlands
- reduced water for irrigation
- unsatisfactory recharge of the aquifers
- reduced domestic water supply risking the quality of life and citizens’ sanitation
- adverse effects on biodiversity
- social, economic, and environmental adverse effects
- threat of fires due to drylands
- uncontrolled fires and environmental disasters
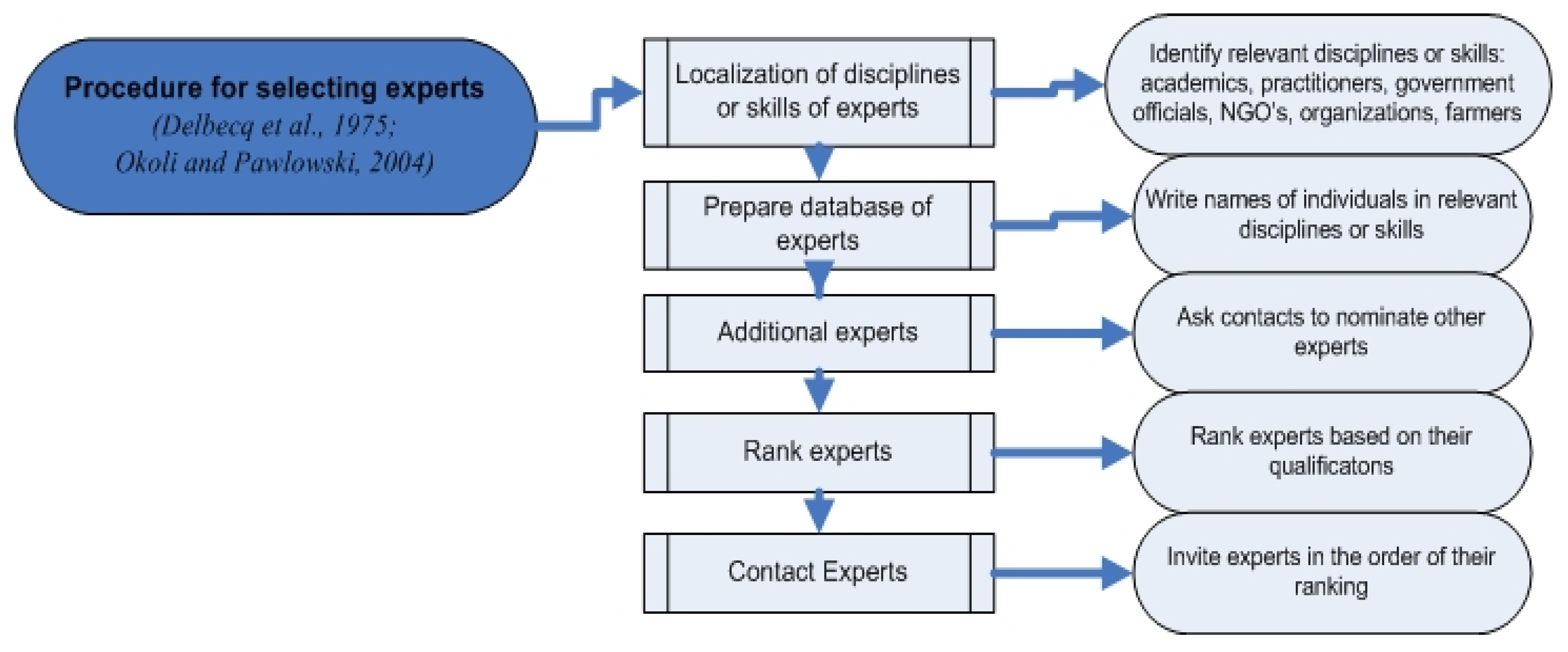
2. Methodology
- there is no need for a physical meeting of experts
- there is no requirement for a large number of experts, but for a small number of the most specialized ones
- it’s an appropriate method to rank climate change impacts
- it can be used additionally to evaluate climate change impacts (using WTP values)
- a deeper understanding of the complex research question has been allowed
- it’s a flexible method to follow-up interviews
- it’s a compatible method for complex study questions that require deep knowledge
- it’s a compatible method for compound concerns that need practical experience from experts, who deeply understand several dimensions of climate change (economic, environmental, agronomical, social and political).
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hadjinicolaou, P.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Zerefos, C.; Lange, M.A.; Pashiardis, S.; Lelieveld, J. Mid-21st century climate and weather extremes in Cyprus as projected by six regional climate models. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA-European Environmental Agency. Water Resources across Europe-Confronting Water Scarcity and Drought; EEA Report No 2/2009; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Tateishi, R. A water index for rapid mapping of shoreline changes of five East African Rift Valley lakes: An empirical analysis using Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3153–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasozomenou, R.; Zikos, D. Linking perceptions and water management: Reflections from cyprus. Wseas Trans. Environ. Dev. 2009, 5, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiouris, N.X. Cyprus-Water Resources, Planning and Climate Change Adaptation; Mediterranean Regional Roundtable: Athens, Greece, 2002; pp. 4–21. [Google Scholar]
- Alston, M.; Whittenbury, K. Does climatic crisis in Australia’s food bowl create a basis for change in agricultural gender relations? Agric. Hum. Values 2013, 30, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.D.; Ghahramani, A. Climate change and broad-acre livestock production across southern Australia: Adaptation options via livestock genetic improvement. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastis, S.A.; Michailidis, A.; Chatzitheodoridis, F. Climate change and agricultural productivity. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 4885–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Development Indicators: Agricultural Methane Emissions. 2016. Available online: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.METH.KT.CE (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Kusin, F.M.; Akhir, N.I.M.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Awang, M. The impact of nitrogen fertilizer use on greenhouse gas emissions in an oil palm plantation associated with land use change. Atmosfera 2015, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IFAD; WHO; WFP; UNICEF. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2019: Safeguarding Against Economic Slowdowns and Downturns; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P. Agricultural greenhouse gas mitigation potential globally, in Europe and in the UK: What have we learnt in the last 20 years? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, M.; Stylianou, A.; Bruggeman, A.; Zoumides, C.; Pashiardis, S.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Lange, M.A.; Zachariadis, T.; Michaelides, A. Economic Impact of Climate Change on the Cypriot Agricultural Sector; Working Paper: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, T.; Holzkämper, A.; Calanca, P.; Fuhrer, J. Adaptation options under climate change for multifunctional agriculture: A simulation study for western Switzerland. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, A.; Rehdanz, K.; Betts, R.; Falloon, P.; Wiltshire, A.; Tol, R.S.J. Climate change impacts on global agriculture. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadavid, G.; Hadjimitsis, D.; Fedra, K.; Michaelides, S. Smart management and irrigation demand monitoring in Cyprus, using remote sensing and water resources simulation and optimization. Adv. Geosci. 2011, 30, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papadaskalopoulou, C.; Katsou, E.; Valta, K.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Dodou, M. Review and assessment of the adaptive capacity of the water sector in Cyprus against climate change impacts on water availability Resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariadis, T. The Costs of Residential Water Scarcity in Cyprus: Impact of Climate Change and Policy Options. Econ. Policy Pap. 2010, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Thierfelder, C.; Rusinamhodzi, L.; Ngwira, A.R.; Mupangwa, W.; Nyagumbo, I.; Kassie, G.T.; Cairns, J.E. Conservation agriculture in Southern Africa: Advances in knowledge. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 328–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Hu, W.; Maynard, L.J.; Goddard, E. A Taste for Safer Beef? How Much Does Consumers’ Perceived Risk Influence Willingness to Pay for Country-of-Origin Labeled Beef. Agribusiness 2014, 30, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, B.W.; Russo, M.V.; Meza, C.E.B.; Tilleman, S.G. An exploratory study of environmental attitudes and the willingness to pay for environmental certification in Mexico. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastis, S.A.; Mattas, K. Income elasticity of willingness-to-pay for a carbon tax in Greece. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2018, 14, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.I.; Liou, J.L.; Hsu, S.H. Economic Valuation of Public Meteorological Information Services-A Case Study of Agricultural Producers in Taiwan. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkey, N.C.; Helmer, O. An experimental application of the Delphi method to the use of experts. Manag. Sci. 1963, 9, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Sandford, B.A. The Delphi Technique: Making Sense of Consensus. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2007, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Linstone, H.A.; Turoff, M. Delphi: A brief look backward and forward. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2011, 78, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Pina, V. E-participation perspectives. A Delphi study applied to climate change policies. In Proceedings of the IADIS Int. Conf. ICT, Society and Human Beings 2011, Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference e-Democracy, Equity and Social Justice, Part of the IADIS, MCCSIS, Rome, Italy, 20–26 July 2011; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Doria, M.; Boyd, E.; Tompkins, E.L.; Adger, W.N. Using expert elicitation to define successful adaptation to climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changnon, S.A., Jr. Views of climate change: A Delphi experiment in the Midwest. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1160–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McMillan, S.S.; King, M.; Tully, M.P. How to use the nominal group and Delphi techniques. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 38, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, C.; Pawlowski, S.D. The Delphi method as a research tool: An example, design considerations and applications. Inf. Manag. 2004, 42, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.C. Managing Delphi surveys using nonparametric statistical techniques. Decis. Sci. 1997, 28, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, F.; Keeney, S.; McKenna, H. Research guidelines for the Delphi survey technique. J. Adv. Nurs. 2000, 32, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.A.; Lovell, K.; Harris, N.; Campbell, M. Multidisciplinary consensus of best practice for pro re nata (PRN) psychotropic medications within acute mental health settings: A Delphi study. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2007, 14, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantel, K. Comprehensiveness of strategic planning: The importance of heterogeneity of a top team. Psychol. Rep. 1993, 73, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulkedid, R.; Abdoul, H.; Loustau, M.; Sibony, O.; Alberti, C. Using and reporting the Delphi method for selecting healthcare quality indicators: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbecq, A.L.; Van de Ven, A.H.; Gustafson, D.H. Group Techniques for Program Planning: A Guide to Nominal Group and Delphi Processes; Scott, Foresman and Company: Glenview, IL, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridou, D.; Michailidis, A. Valuing users’ willingness to pay for improved water quality in the context of the water framework directive. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, D.; Michailidis, A.; Mattas, K. Evaluating the willingness to pay for using recycled water for irrigation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, D.; Michailidis, A.; Trigkas, M. Socio-economic factors influencing farmers’ willingness to undertake environmental responsibility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14732–14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charatsari, C.; Papadaki-Klavdianou, A.; Michailidis, A.; Partalidou, M. Great expectations? Antecedents of women farmers’ willingness to participate in agricultural education programmes. Outlook Agric. 2013, 42, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSSC-National Statistical Service of Cyprus. Analytical Tables. 2020. Available online: https://www.mof.gov.cy/mof/cystat/statistics.nsf/populationcondition_21main_en/populationcondition_21main_en?OpenForm&sub=1&sel=1 (accessed on 22 April 2020).

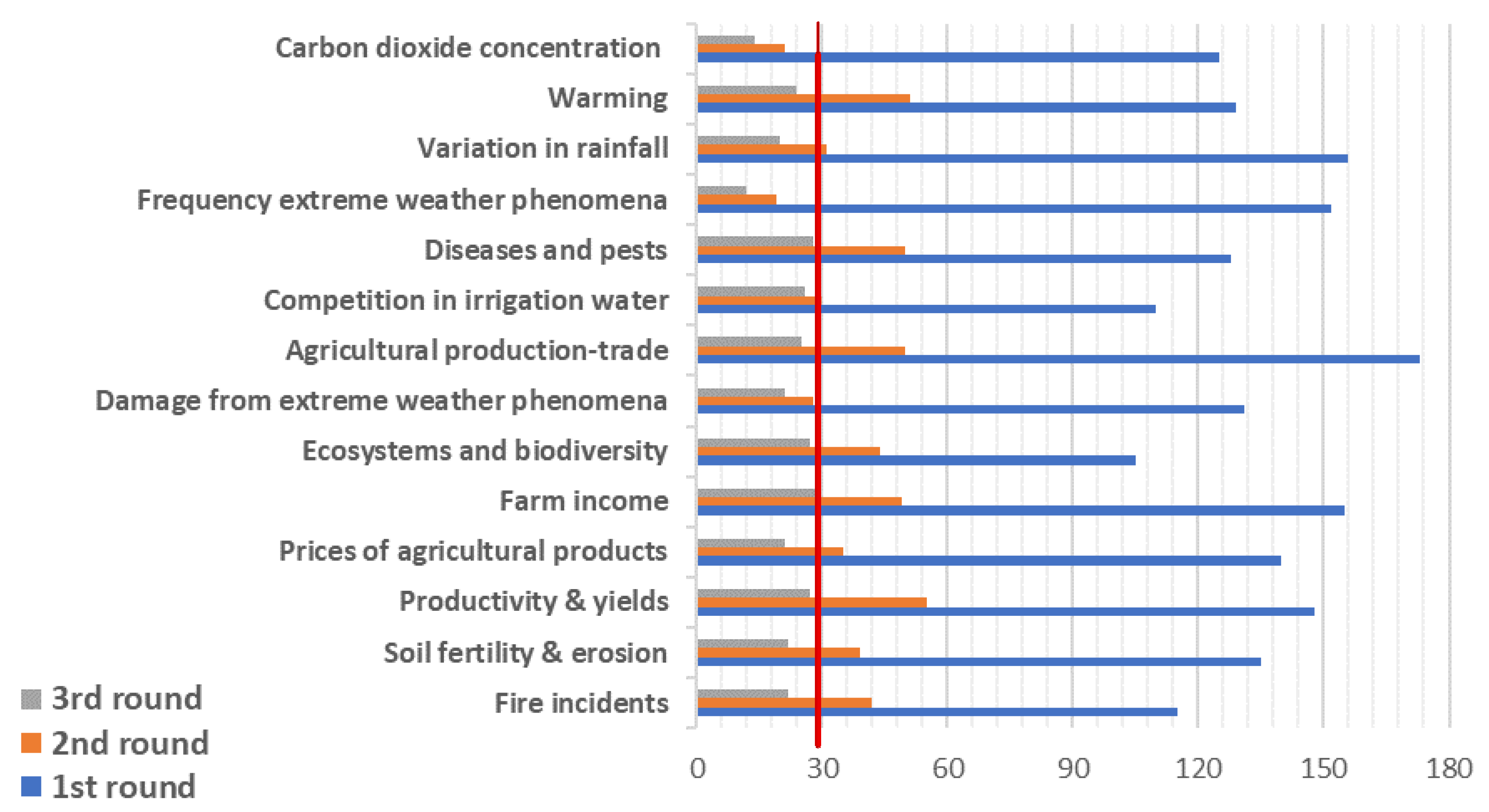
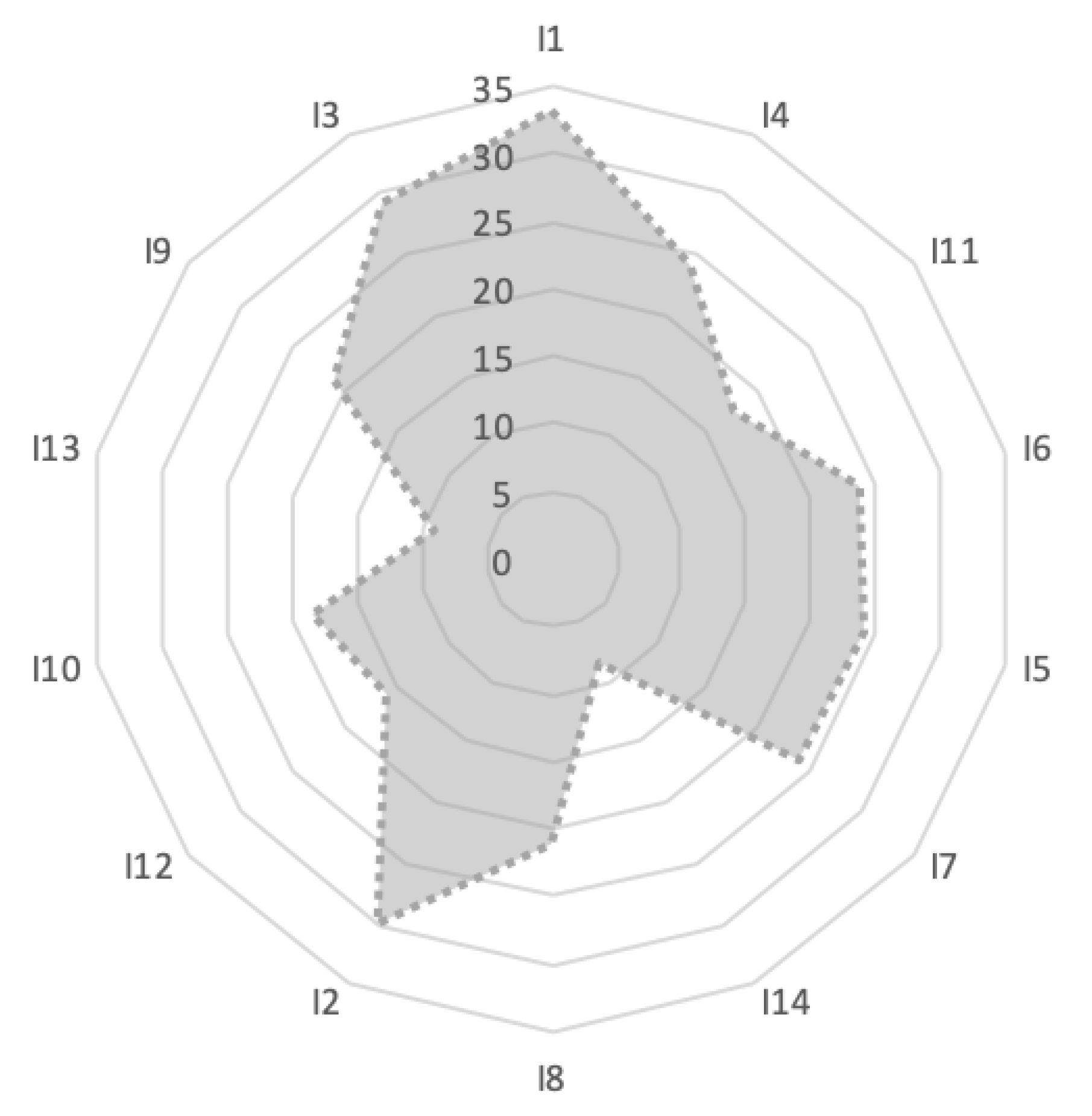
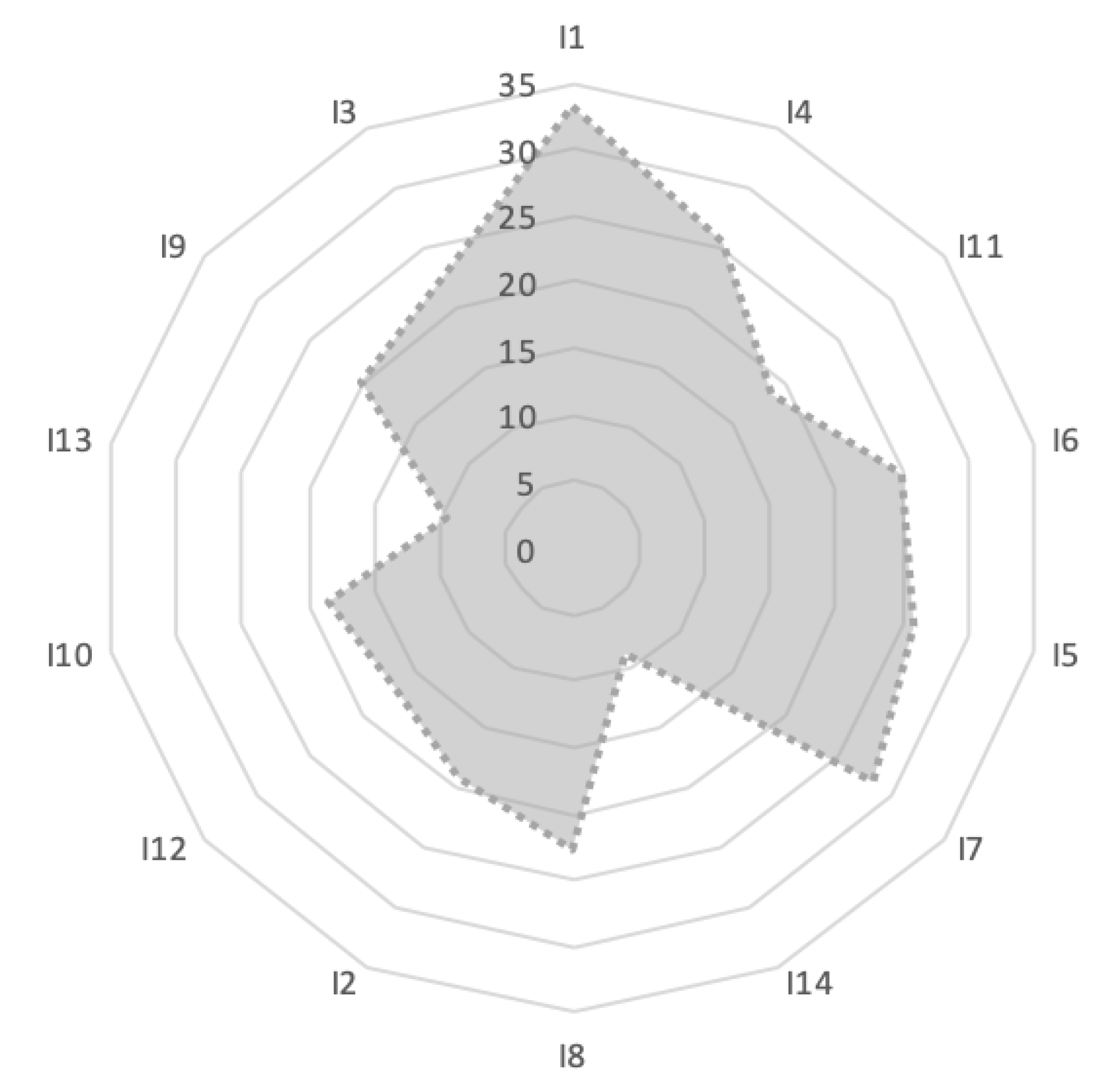
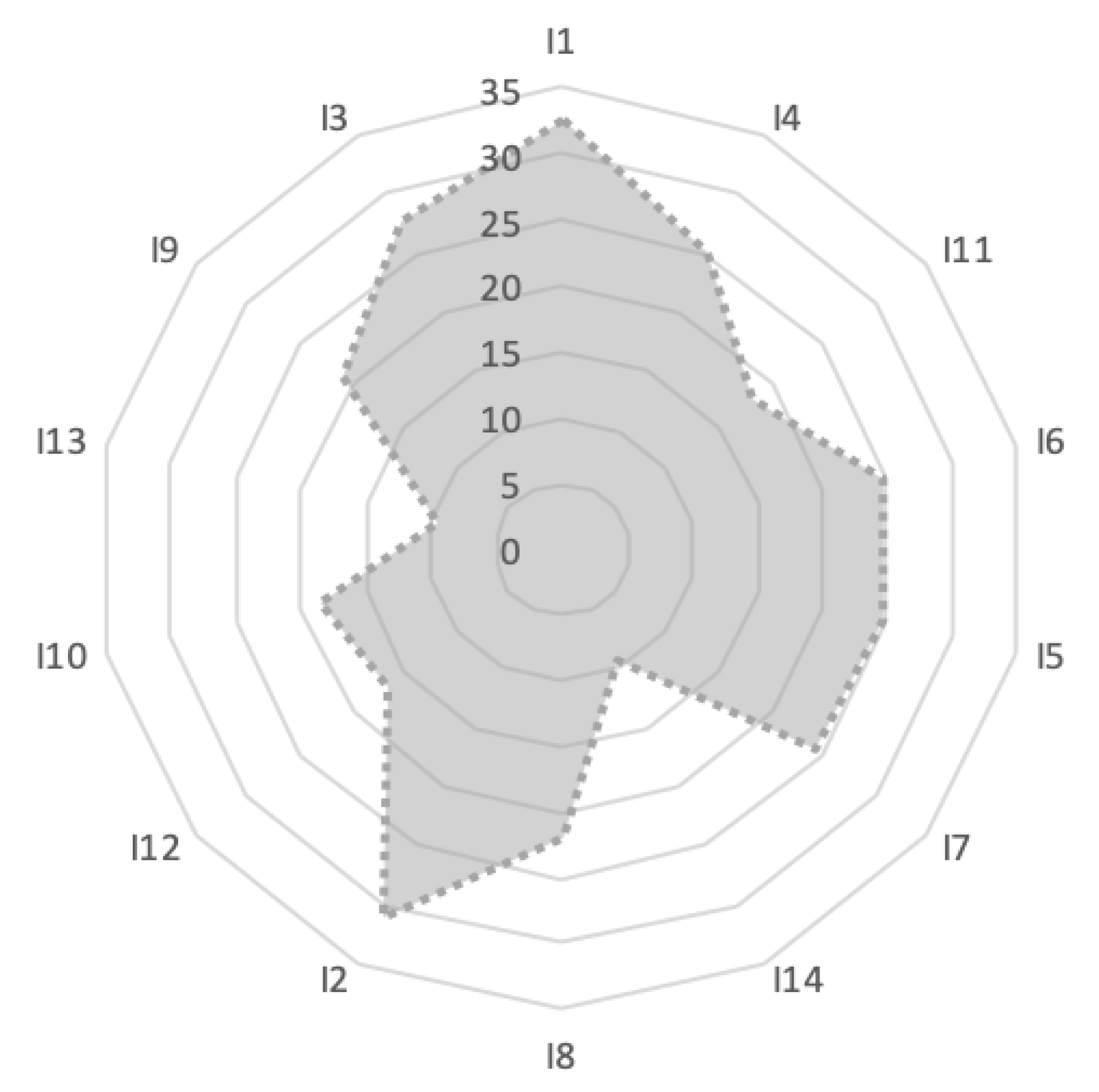
| Impacts of Climate Change | First Round’s Results | Second Round’s Results | Third Round’s Results | |||||||||
| Max | Mean | Min | Standard Deviation | Max | Mean | Min | Standard Deviation | Max | Mean | Min | Standard Deviation | |
| I1 | 71.17 | 33.16 | 0.00 | 38.01 | 41.17 | 33.08 | 26.18 | 7.50 | 37.14 | 32.66 | 28.17 | 4.49 |
| I2 | 60.55 | 30.00 | 0.00 | 30.55 | 46.11 | 31.00 | 17.89 | 14.11 | 39.34 | 31.11 | 22.88 | 8.23 |
| I3 | 59.68 | 29.15 | 1.38 | 29.15 | 35.99 | 25.56 | 15.13 | 10.43 | 34.47 | 27.52 | 20.56 | 6.96 |
| I4 | 54.82 | 24.42 | 0.00 | 30.61 | 38.92 | 25.57 | 12.21 | 13.36 | 32.19 | 25.01 | 17.82 | 7.19 |
| I5 | 55.00 | 24.12 | 0.00 | 30.79 | 39.22 | 25.77 | 12.31 | 13.46 | 31.14 | 24.63 | 18.11 | 6.52 |
| I6 | 49.14 | 23.89 | 0.00 | 36.30 | 29.13 | 24.89 | 20.64 | 4.25 | 30.09 | 24.62 | 19.14 | 5.48 |
| I7 | 49.01 | 23.79 | 0.00 | 25.24 | 34.18 | 26.42 | 18.65 | 7.77 | 27.13 | 24.41 | 21.68 | 2.73 |
| I8 | 48.32 | 21.25 | 0.00 | 27.26 | 29.14 | 22.72 | 16.30 | 6.42 | 26.75 | 22.00 | 17.24 | 4.76 |
| I9 | 48.72 | 21.05 | 0.00 | 27.67 | 27.32 | 20.03 | 12.73 | 7.30 | 25.51 | 20.84 | 16.17 | 4.67 |
| I10 | 44.30 | 18.42 | 0.00 | 25.88 | 25.13 | 18.55 | 11.97 | 6.58 | 22.17 | 18.66 | 15.14 | 3.52 |
| I11 | 44.66 | 17.47 | 0.00 | 27.19 | 24.55 | 18.66 | 12.77 | 5.89 | 22.48 | 18.46 | 14.44 | 4.02 |
| I12 | 40.36 | 15.79 | 0.00 | 24.57 | 29.18 | 19.31 | 9.44 | 9.87 | 21.71 | 16.82 | 11.93 | 4.89 |
| I13 | 22.24 | 8.95 | 0.00 | 13.29 | 14.89 | 9.59 | 4.29 | 4.63 | 11.80 | 9.52 | 7.23 | 2.29 |
| I14 | 23.07 | 8.47 | 0.00 | 14.60 | 13.60 | 8.97 | 4.34 | 4.63 | 12.19 | 9.50 | 6.80 | 2.70 |
| Index | ||||||||||||
| I1. Increasing of CO2 concentration | I8. Increased spending on tackling the cost of irrigation water, appropriate propagation material, special fertilizers and damage from extreme weather phenomena | |||||||||||
| I2. Burden on the environment, ecosystems and of biodiversity (loss of native species) | I9. Burden of soil fertility and erosion | |||||||||||
| I3. Increased fire incidents | I10. Increase in price of agricultural products | |||||||||||
| I4. Warming | I11. Variation in rainfall | |||||||||||
| I5. Increased occurrence of diseases and pests | I12. Reduction of farm income | |||||||||||
| I6. Increased frequency of extreme weather events | I13. Change in productivity and yields | |||||||||||
| I7. Intensity of competition in water use in agriculture | I14. Diversification of agricultural production and agricultural trade | |||||||||||
| Impacts of Climate Change | Reduction to the Agricultural Population | Reduction to the Whole Population |
|---|---|---|
| 2,679,426 | 39,145,460 |
| 2,552,264 | 37,287,699 |
| 2,257,741 | 32,984,839 |
| 2,051,820 | 29,976,436 |
| 2,020,645 | 29,521,001 |
| 2,019,825 | 29,509,040 |
| 2,002,596 | 29,257,362 |
| 1,804,880 | 26,368,804 |
| 1,709,714 | 24,978,470 |
| 1,530,866 | 22,365,577 |
| 1,514,458 | 22,125,879 |
| 1,379,913 | 20,160,217 |
| 781,021 | 11,410,548 |
| 779,380 | 11,386,586 |
| National level | 25,084,550 | 366,477,917 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markou, M.; Michailidis, A.; Loizou, E.; Nastis, S.A.; Lazaridou, D.; Kountios, G.; Allahyari, M.S.; Stylianou, A.; Papadavid, G.; Mattas, K. Applying a Delphi-Type Approach to Estimate the Adaptation Cost on Agriculture to Climate Change in Cyprus. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050536
Markou M, Michailidis A, Loizou E, Nastis SA, Lazaridou D, Kountios G, Allahyari MS, Stylianou A, Papadavid G, Mattas K. Applying a Delphi-Type Approach to Estimate the Adaptation Cost on Agriculture to Climate Change in Cyprus. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkou, Marinos, Anastasios Michailidis, Efstratios Loizou, Stefanos A. Nastis, Dimitra Lazaridou, Georgios Kountios, Mohammad S. Allahyari, Andreas Stylianou, George Papadavid, and Konstadinos Mattas. 2020. "Applying a Delphi-Type Approach to Estimate the Adaptation Cost on Agriculture to Climate Change in Cyprus" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050536
APA StyleMarkou, M., Michailidis, A., Loizou, E., Nastis, S. A., Lazaridou, D., Kountios, G., Allahyari, M. S., Stylianou, A., Papadavid, G., & Mattas, K. (2020). Applying a Delphi-Type Approach to Estimate the Adaptation Cost on Agriculture to Climate Change in Cyprus. Atmosphere, 11(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050536













