Multi-Model Ensemble Sub-Seasonal Forecasting of Precipitation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Summer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models, Data, and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Construction of MME
2.3. Forecasting Skill Metrics
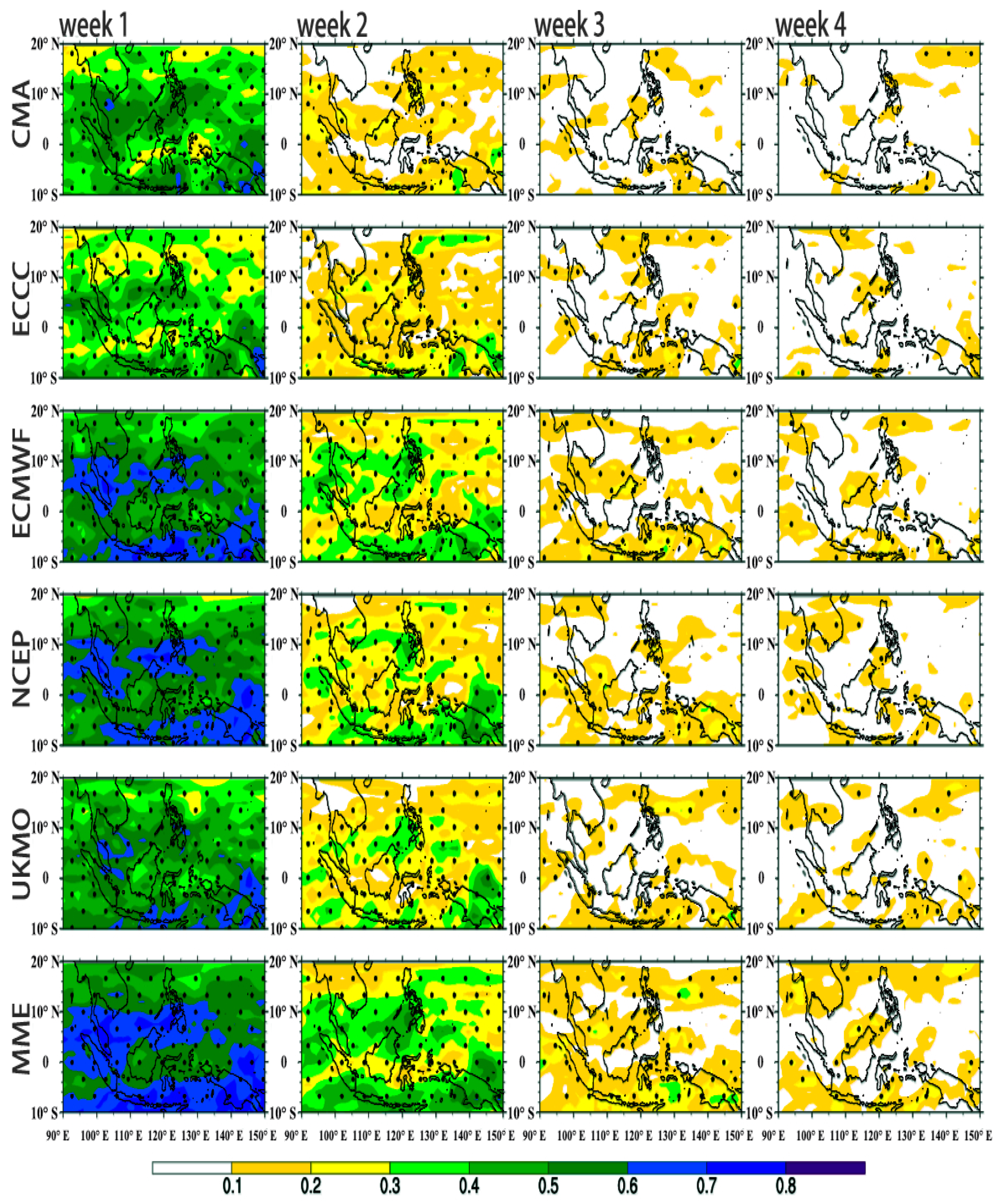
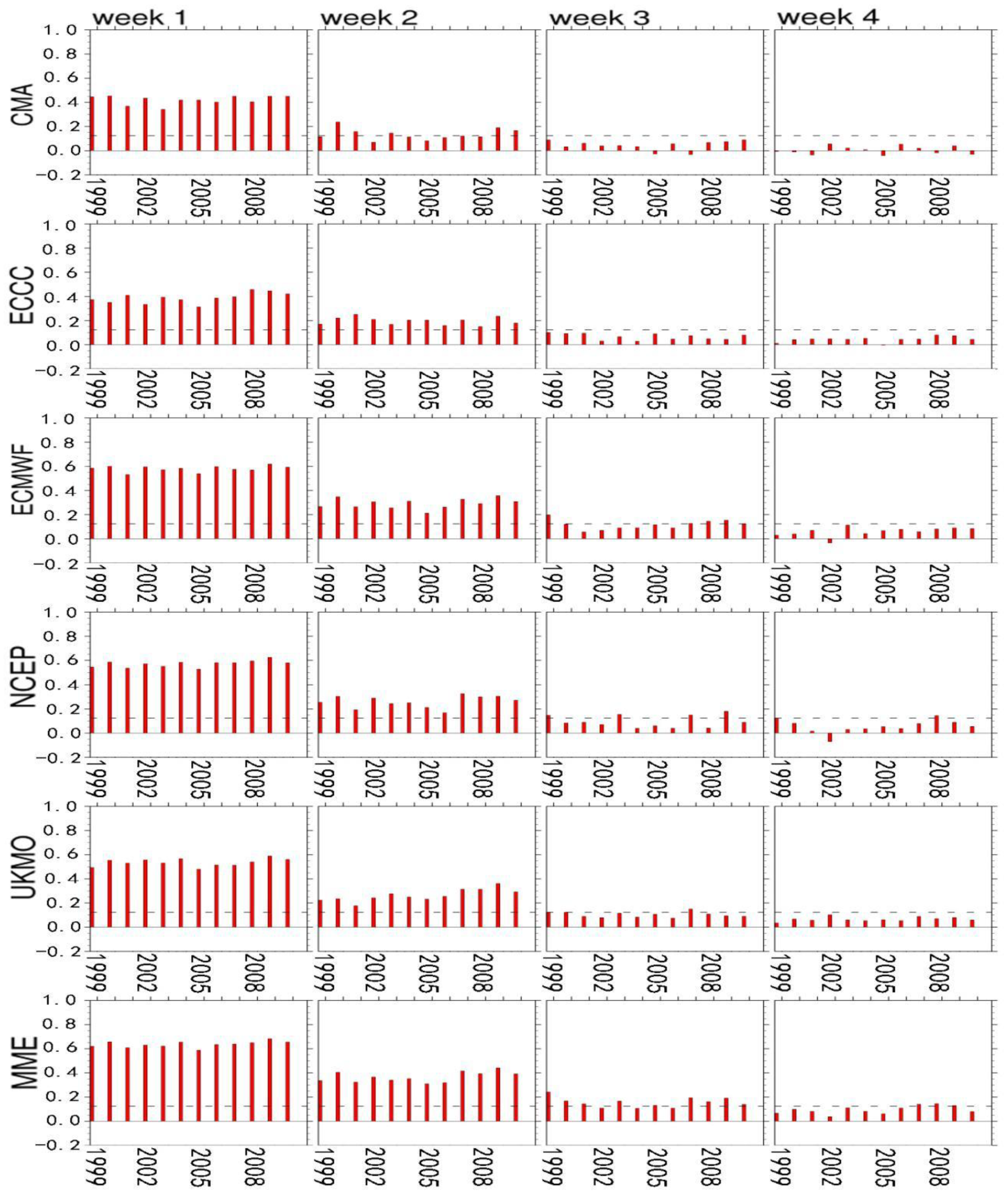
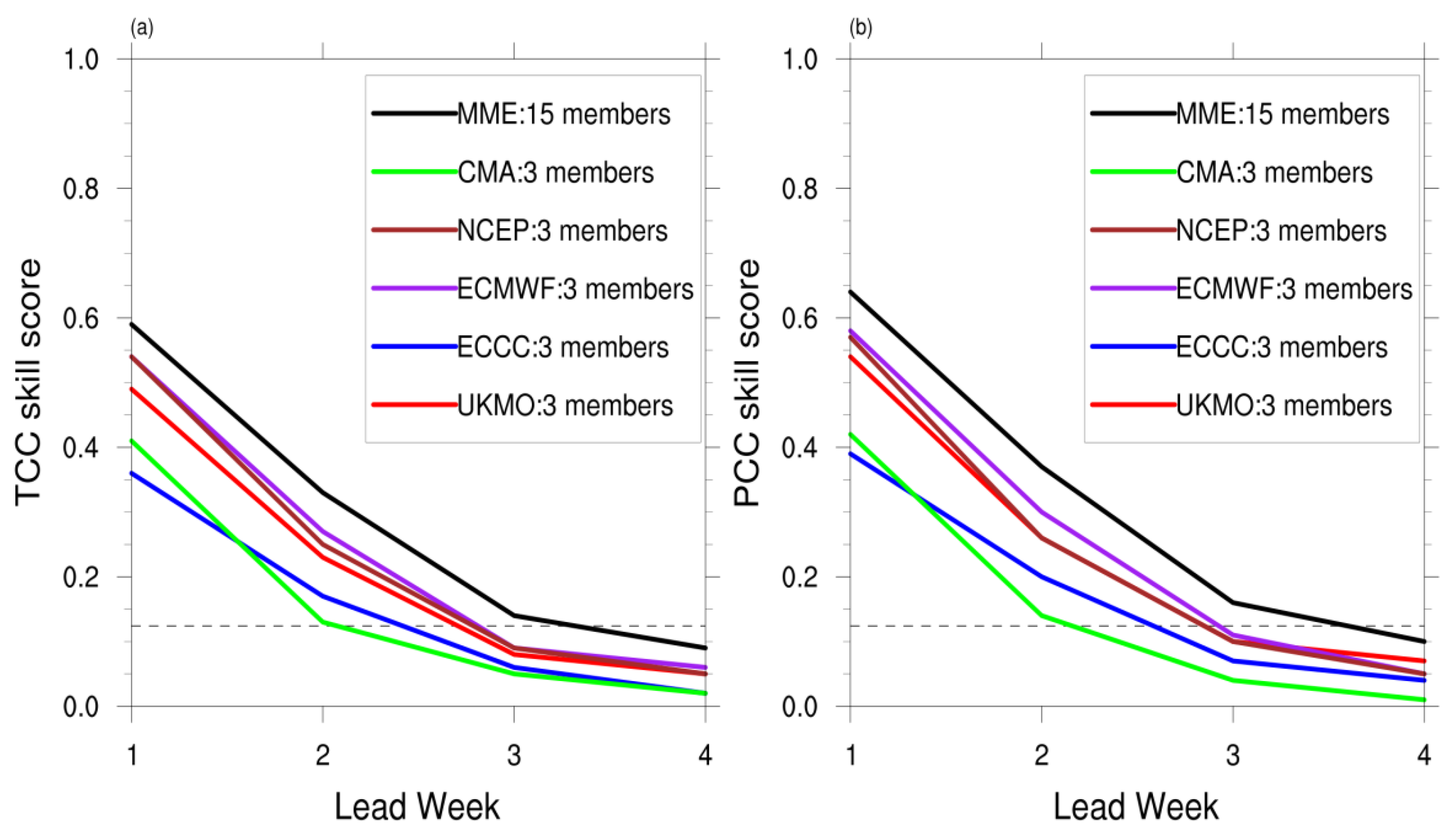
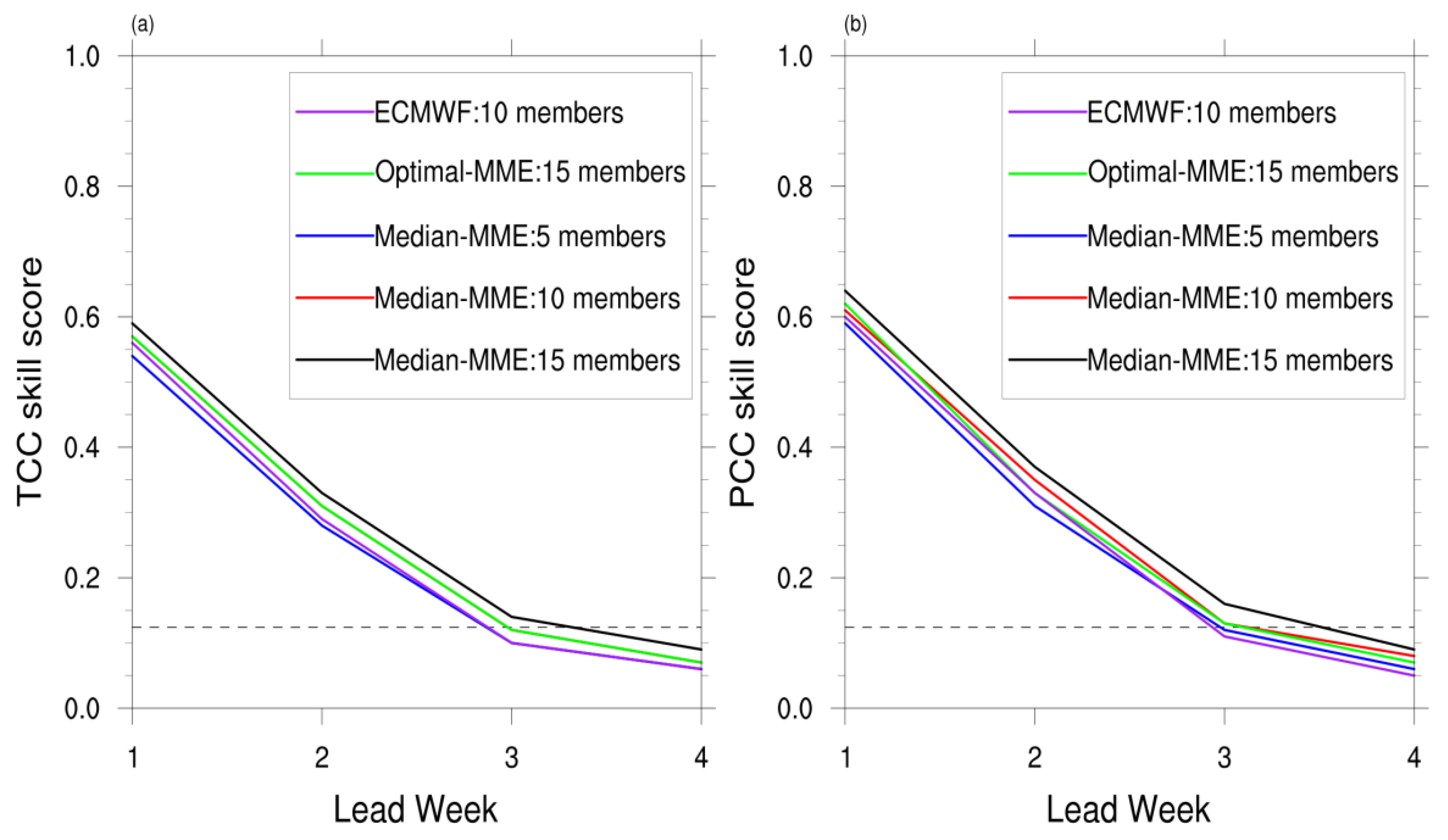
3. Prediction Skills of Individual Models and MME
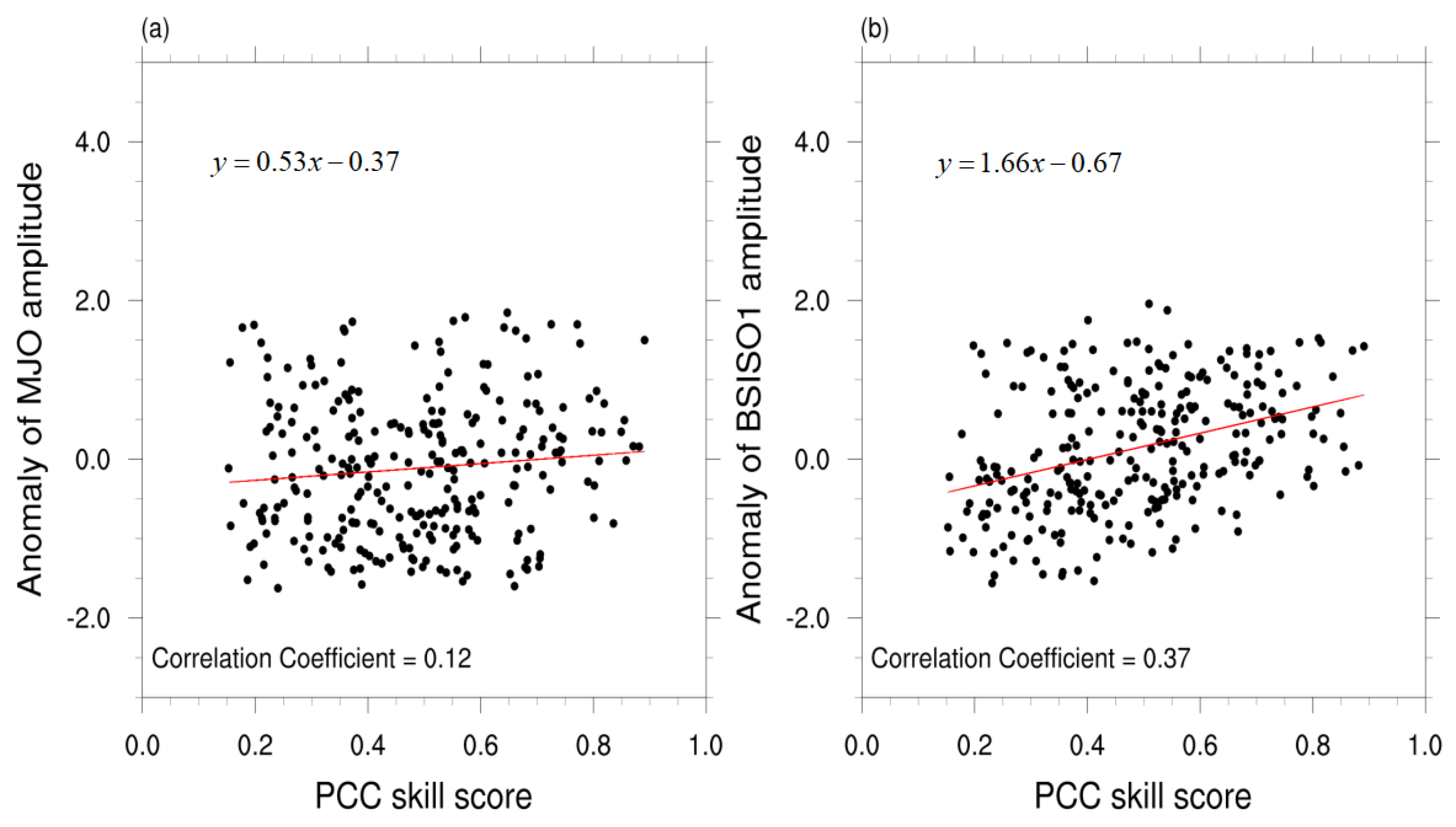
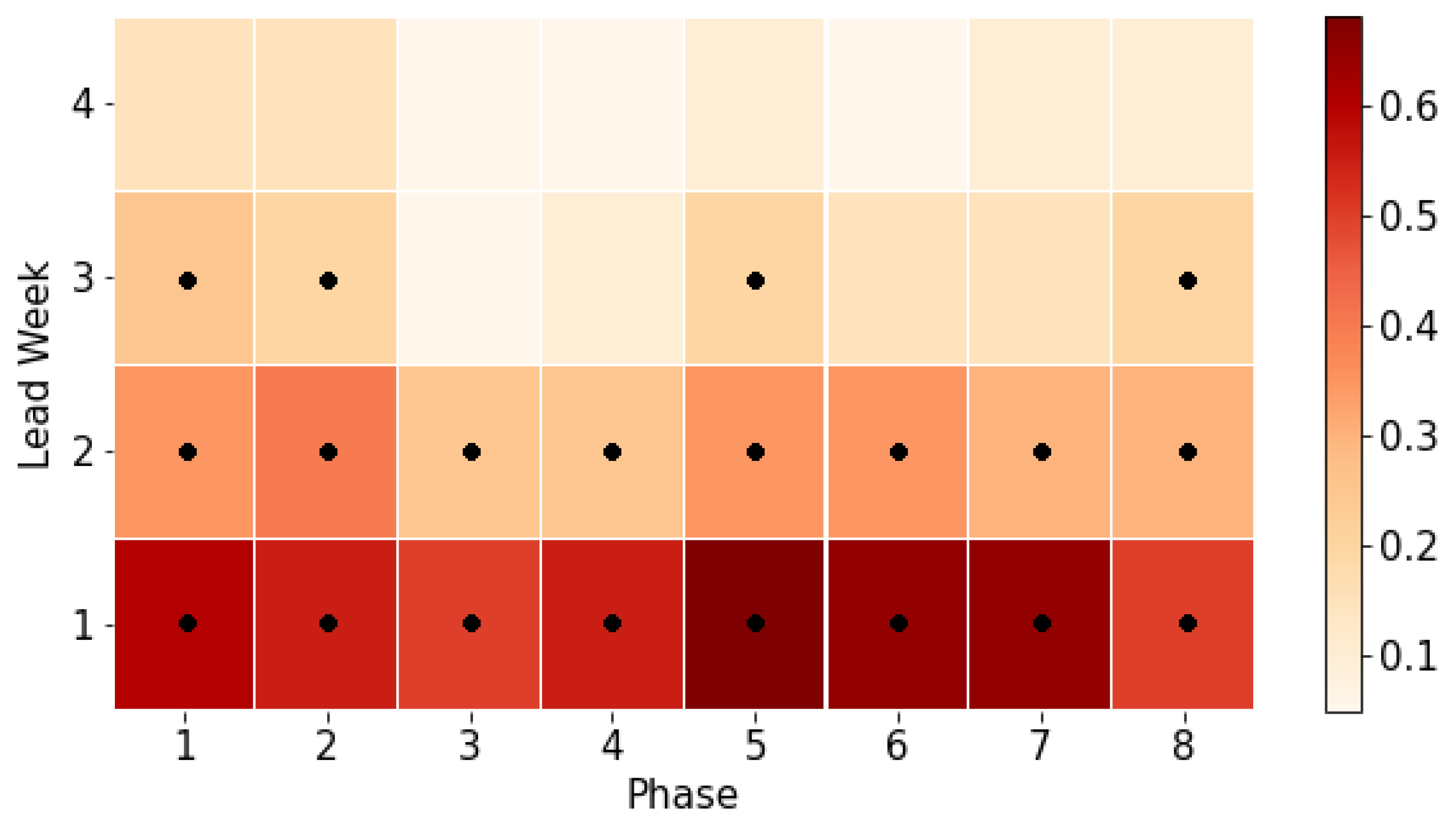
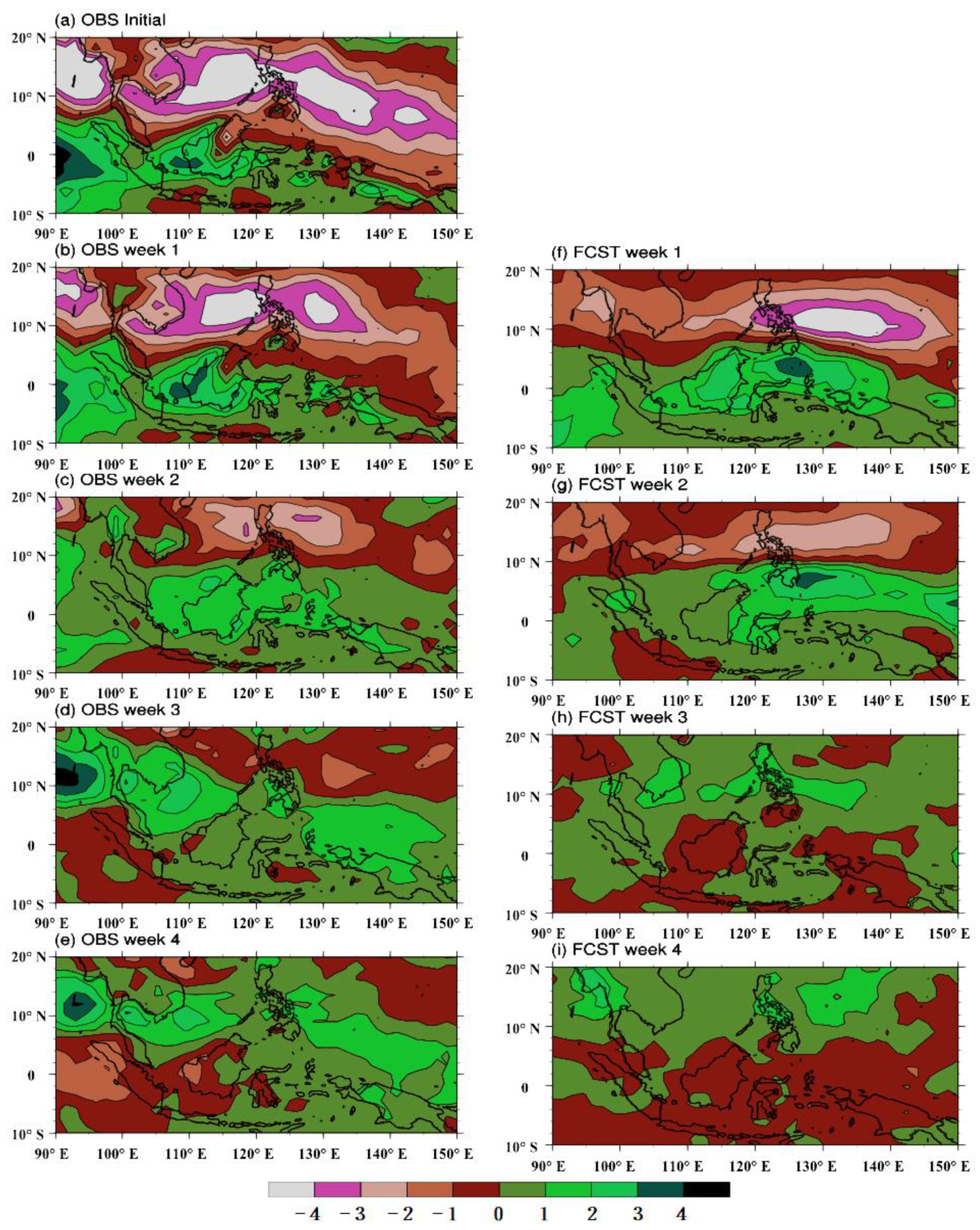
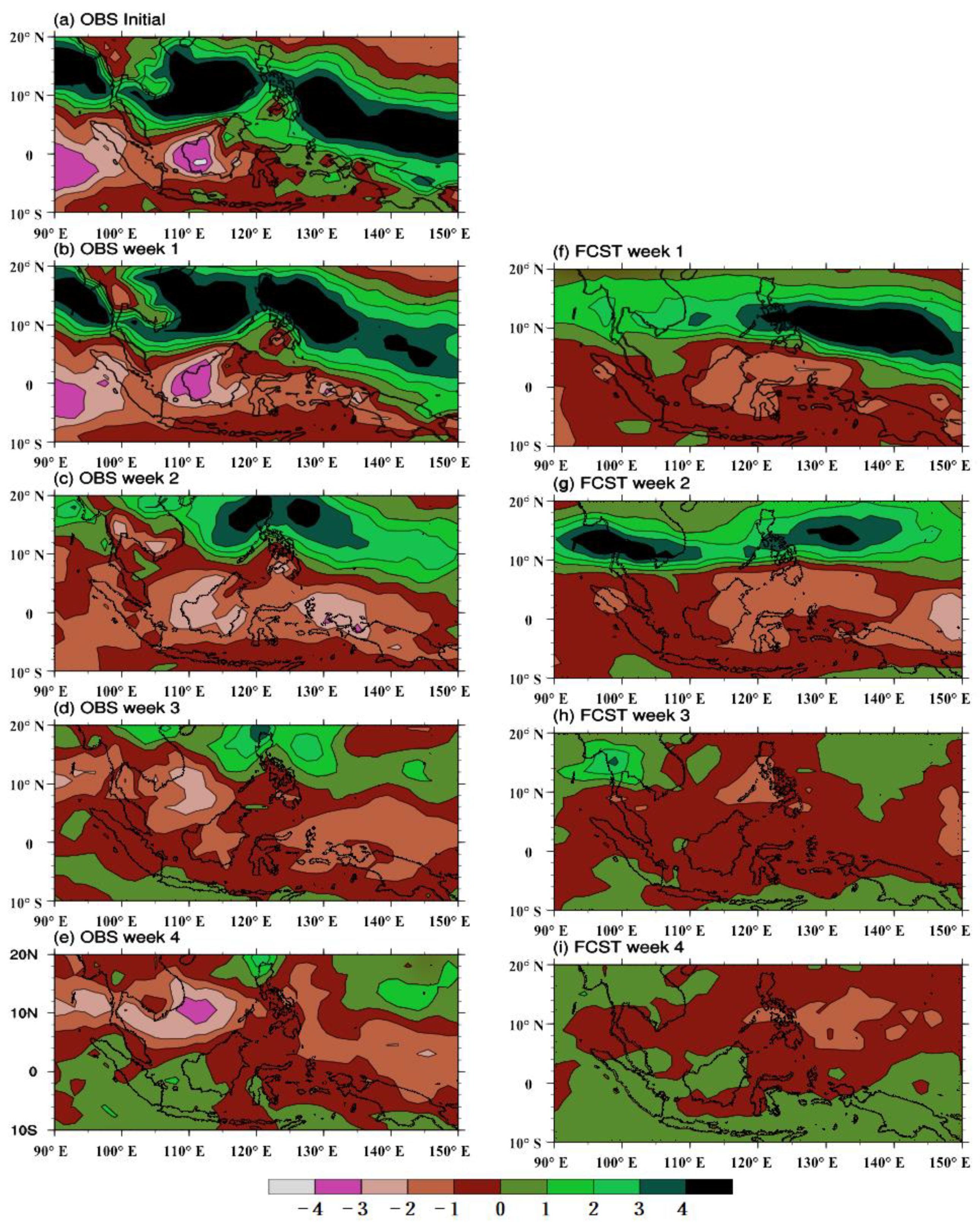
4. Association of MME Prediction with MJO and BSISO
5. Summary and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramage, C.S. Role of tropical “Maritime Continent” in the atmospheric circulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.L. Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and tropical Australia: The southern hemisphere monsoon, in meteorology of the Southern Hemisphere. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 27, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, R.; Slingo, J. The Maritime continent and its role in the global climate: A GCM study. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A. The annual cycle and interannual variability in the tropical Pacific and Indian ocean regions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.L.; Haylock, M.R.; Nicholls, N. Relationships between the Maritime Continent heat source and the EI Nino-Southern Oscillation phenomenon. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Harr, P.A.; Chen, H.J. Synoptic disturbances over the equatorial South China sea and Western Maritime Continent during boreal winter. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.H.; Lee, D.K. Seasonal march of Asian summer monsoon. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.H. Why precipitation is mostly concentrated over islands in the Maritime Continent. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q.H. Global monsoon: Dominant mode of annual variation in the tropics. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2008, 44, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materia, S.; Muñoz, Á.G.; Álvarez-Castro, M.C.; Mason, S.J.; Vitart, F.; Gualdi, S. Multimodel Subseasonal Forecasts of Spring Cold Spells: Potential Value for the Hazelnut Agribusiness. Weather. Forecast. 2020, 35, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Atmospheric Sciences and Climate; Committee on Assessment of Intraseasonal to Interannual Climate Prediction and Predictability. Assessment of Intraseasonal to Interannual Climate Prediction and Predictability; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, B.; Waliser, D.; Tao, L. Impact of atmosphere-ocean coipling on the predictability of monsoon intraseasonal oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Yang, B.; Bao, Q.; Wang, B. Sea surface temperature feedback extends the predictability of tropical intraseasonal oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, B.; Bao, Q.; Liu, P.; Lee, J.Y. Impacts of initial conditions on monsoon intraseasonal forecasting. Geo. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L08801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Robertson, A.W.; S2S Steering Group. Sub-Seasonal to Seasonal Prediction: Linking Weather and Climate. Seamless Prediction of the Earth System: from Minutes to Months (WMO-No. 1156); WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Waliser, D.E.; Sperber, K.; Hendon, H.; Kim, D.; Maloney, E.; Wheeler, M.; Weickmann, K.; Zhang, C.; Donner, L.; Gottschalck, J.; et al. MJO simulation diagnostics. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3006–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Mahanama, S.; Yamada, T.; Balsamo, G.; Berg, A.A.; Boisserie, M.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Drewitt, G.; Gordon, C.T.; et al. The Contribution of Land Surface Initialization to Subseasonal Forecast Skill: First Results from a multi-model experiment. Geo. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L02402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deser, C.; Tomas, R.A.; Peng, S. The transient atmospheric circulation response to North Atlantic SST and sea ice anomalies. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4751–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Bailey, D.A.; Vavrus, S. Inherent sea ice predictability in the rapidly changing Arctic environment of the Community Climate System Model, version 3. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Dunkerton, T.J. Stratospheric harbingers of anomalous weather regimes. Science 2001, 244, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, B. A review on the Western North Pacific monsoon: Synoptic-to-interannual variabilities. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2005, 16, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, W.; Li, T.; Murty, V.S.N.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Adi, T.R.; Budi, S. Structures and mechanisms of the first-branch northward-propagating intraseasonal oscillation over the tropical Indian Ocean. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E. Predictability and Forecasting. In Intraseasonal variability of the Atmosphere-Ocean Climate System, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 433–468. [Google Scholar]
- Suhas, E.; Neena, J.M.; Goswami, B.N. An Indian monsoon intraseasonal oscillations (MISO) index for real time monitoring and forecast verification. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Wang, B.; Wheeler, M.C.; Fu, X.; Waliser, D.E.; Kang, I.-S. Real-time multivariate indices for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation over the Asian summer monsoon region. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homepage of S2S Project. Available online: http://www.s2sprediction.net (accessed on 18 October 2019).
- Vitart, F.; Ardilouze, C.; Bonet, A.; Brookshaw, A.; Chen, M.; Codorean, C.; Déqué, M.; Ferranti, L.; Fucile, E.; Fuentes, M.; et al. The Subseasonal to Seasonal (S2S) Prediction Project Database. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F. Madden-Julian oscillation prediction and teleconnections in the S2S database. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.L.; Zuo, J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, L.; Li, Q. MJO prediction skill, predictability, and teleconnection impacts in the beijing climate centeratmospheric general circulation model. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2016, 75, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Son, S.W.; Kim, D. MJO Prediction Skill of the Subseasonal-to-Seasonal Prediction Models. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4075–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyan, E.; Adefisan, E.A.; Oni, F.; Afiesimama, E.; Balogun, A.A.; Lawal, K.A.A. Evaluation of the ECMWF Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Precipitation Forecasts during the Peak of West Africa Monsoon in Nigeria. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Robertson, A.W. The sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction project (S2S) and the Prediction of extreme events. Clim. Atmospheric Sci. 2018, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Camargo, S.J.; Vitart, F.; Sobel, A.H.; Tippett, M.K. Subseasonal Tropical Cyclone Genesis Prediction and MJO in the S2S Dataset. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.F.; Wang, W. Multi-week prediction of South-East Asia rainfall variability during boreal summer in CFSv2. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.H.; Vitart, F.; Wu, T.; Liu, X. Simulations of the Asian summer monsoon in the sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction project (S2S) database. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 2282–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Ren, H.L.; Zhou, F.; Li, S.; Fu, J.-X.; Li, G. Multi-pentad Prediction of Precipitation Variability over Southeast Asia during Boreal Summer Using BCC_CSM1.2. Dynam. Atmos. Ocean. 2018, 82, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ren, H.L.; Song, L.; Wu, J. Madden-Julian oscillation simulated in BCC climate models. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2015, 72, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.L.; Lu, B.; Zhang, P.Q.; Zhao, C.B.; Liu, X.W. Effects of moisture initialization on MJO and its teleconnection prediction in BCC subseasonal coupled model. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2019JD031537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chang, E.K.; Colle, B.A.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, Y. Applying fuzzy clustering to a multimodel ensemble for US East Coast winter storms: Scenario identification and forecast verification. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 881–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chang, E.K.; Colle, B.A. Evaluating US East Coast Winter Storms in a Multimodel Ensemble Using EOF and Clustering Approaches. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 967–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, T.N.; Kishtawal, C.M.; LaRow, T.E.; Bachiochi, D.R.; Zhang, Z.; Williford, C.E.; Gadgil, S.; Surendran, S. Improved weather and seasonal climate forecasts from multimodel superensemble. Science 1999, 285, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N.; Branković, Č.; Richardson, D.S. A probability and decision-model analysis of PROVOST seasonal multi-model ensemble integrations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 2013–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.T.; Kumar, A.; Dool, H.V.D.; Barnston, A.G. An analysis of multimodel ensemble predictions for seasonal climate anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Hagedorn, R.; Palmer, T.N. The rationale behind the success of multi-model ensembles in seasonal forecasting-II. Calibration and combination. Tellus A 2005, 57, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, C.D. The ENSEMBLES project: Providing ensemble-based predictions of climate changes and their impacts. EGGS Newslett. 2005, 13, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kirtman, B.P.; Min, D.; Infanti, J.M.; Kinter, J.L.; Paolino, D.A.; Zhang, Q.; van den Dool, H.; Saha, S.; Mendez, M.P.; Becher, E.; et al. The North American Multimodel Ensemble: Phase-1 Seasonal-to-Interannual Prediction; Phase-2 toward Developing Intraseasonal Prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Bao, Q.; Ma, J.; Liu, C.; Wan, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, B.; et al. The China Multi-Model Ensemble Prediction System and Its Application to Flood-Season Prediction in 2018. J. Meteor. Res. 2019, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, T.N.; Kishtawal, C.M.; Zhang, Z.; LaRow, T.; Bachiochi, D.; Williford, E.; Gadgil, S.; Surendran, S. Multimodel Ensemble Forecasts for Weather and Seasonal Climate. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4196–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotal, S.D.; Bhowmik, S.K.R. A multimodel ensemble (MME) technique for cyclone track prediction over the North Indian Sea. Geofizika 2011, 28, 275–291. [Google Scholar]
- Kirtman, B.P.; Min, D. Multimodel ensemble ENSO prediction with CCSM and CFS. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 2908–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeault, P.; Burridge, D.; Chen, D.H.; Ebert, B.; Mylne, K.; Nicolau, J.; Park, Y.-Y.; Raoult, B.; Schuster, D.; Dias, P.S.; et al. The THORPEX Interactive Grand Global Ensemble. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigaud, N.; Robertson, A.W.; Tippett, M.K. Multimodel Ensembling of Subseasonal Precipitation Forecasts over North America. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 3913–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathy, P.; Ben, P.K.; Emily, B.; Dan, C.C.; Emerson, L.; Robert, B.; Ray, B.; Timothy, D.; Dughong, M.; Yuejian, Z.; et al. The Subseasonal Experiment (SubX): A Multimodel Subseasonal Prediction Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 2043–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specq, D.; Batte, L.; Déqué, M.; Ardilouze, C. Multimodel forecasting of precipitation at subseasonal timescales over the southwest tropical Pacific. Earth Space Sci. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homepage of NEWS. Available online: http://precip.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 20 October 2019).
- Wheeler, M.C.; Hendon, H.H. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO Index: Development of an Index for monitoring and prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MJO Monitoring. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/#tabs=MJO~%20phase (accessed on 21 October 2019).
- BSISO Monitoring. Available online: http://www.apcc21.org/ser/moni.do?lang=en (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- WMO. Standardised Verification System (SVS) for Long-Range Forecasts (LRF): New Attachment II-8 to the Manual on the GDPFS (WMO-No. 485); WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Robertson, A.W. Evaluation of submonthly precipitation forecast skill from global ensemble prediction systems. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2015, 143, 2871–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40-50 Day Oscillation in the Zonal Wind in the Tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of global-scale circulation cells in tropics with a 40-50 day period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, X. A model for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, H.L. Revision of convection and vertical diffusion schemes in the NCEP global forecast system. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, B.; Lee, J.Y. Sensitivity of Dynamical Intraseasonal Prediction Skills to Different Initial Conditions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 2572–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendon, H.H.; Wheeler, M.C.; Zhang, C.D. Seasonal Dependence of the MJO ENSO Relationship. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddersen, H.; Andersen, U. A method for statistical downscaling of seasonal ensemble predictions. Tellus A 2005, 57, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; An, K.H.; Park, C.K.; Solis, A.L.S.; Stitthichivapak, K.; Kang, H. Multimodel output statistical downscaling prediction of precipitation in the Philippines and Thailand. Geo. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Park, C.K.; Hameed, S.N.; Ashok, K. Statistical downscaling of precipitation in Korea using multimodel output variables as predictors. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, H.L. A hybrid statistical downscaling model for prediction of winter precipitation in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, H.L. Improving ENSO prediction in CFSv2 with an analogue-based correction method. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 5035–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Resolution | Model Top | Time Range | Reforecast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Period | Frequency | Size | ||||
| CMA | 1° × 1° L40 | 0.5 hPa | Day 1–60 | Fix | 1994–2014 | Daily | 4 |
| UKMO | 0.5° × 0.8° L85 | 85 km | Day 1–60 | On the fly | 1993–2015 | 4/month | 3 |
| ECMWF | 0.25° × 0.25°/0.5° × 0.5° L91 | 0.01 hPa | Day 1–46 | On the fly | 1996–2015 | 2/week | 11 |
| ECCC | 0.45° × 0.45° L40 | 2h Pa | Day 1–32 | On the fly | 1995–2014 | Weekly | 4 |
| NCEP | 1° × 1° L64 | 0.02 Pa | Day 1–44 | Fix | 1999–2010 | Daily | 4 |
| Model | Start Date | Lead Days | Target Week 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMA | 1 May | Lead 5 to 11 | 6–12 May |
| UKMO | 1 May | Lead 5 to 11 | 6–12 May |
| ECMWF | 30 April | Lead 6 to 12 | 6–12 May |
| ECCC | 5 May | Lead 1 to 7 | 6–12 May |
| NCEP | 1 May | Lead 5 to 11 | 6–12 May |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Zhou, F.; Fu, J.-X.; Chen, Q.-L.; Wu, J.; Jie, W.-H.; Zhang, P.-Q. Multi-Model Ensemble Sub-Seasonal Forecasting of Precipitation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Summer. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050515
Wang Y, Ren H-L, Zhou F, Fu J-X, Chen Q-L, Wu J, Jie W-H, Zhang P-Q. Multi-Model Ensemble Sub-Seasonal Forecasting of Precipitation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Summer. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan, Hong-Li Ren, Fang Zhou, Joshua-Xiouhua Fu, Quan-Liang Chen, Jie Wu, Wei-Hua Jie, and Pei-Qun Zhang. 2020. "Multi-Model Ensemble Sub-Seasonal Forecasting of Precipitation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Summer" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050515
APA StyleWang, Y., Ren, H.-L., Zhou, F., Fu, J.-X., Chen, Q.-L., Wu, J., Jie, W.-H., & Zhang, P.-Q. (2020). Multi-Model Ensemble Sub-Seasonal Forecasting of Precipitation over the Maritime Continent in Boreal Summer. Atmosphere, 11(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050515







