Abstract
A numerical investigation of aeolian sand particle flow in atmospheric boundary layer is performed with a Eulerian–Eulerian granular pseudofluid model. In this model, the air turbulence is modelled with a large eddy simulation, and a kinetic–frictional constitutive model incorporating frictional stress and the kinetic theory of granular flow is applied to describe the interparticle movement. The simulated profiles of streamwise sand velocity and sand mass flux agree well with the reported experiments. The quantitative discrepancy between them occurs near the sand bed surface, which is due to the difference in sand sample, but also highlights the potential of the present model in addressing near-surface mass transport. The simulated profiles of turbulent root mean square (RMS) particle velocity suggest that the interparticle collision mainly account for the fluctuation of sand particle movement.
1. Introduction
Aeolian sand transport is a leading factor in the geophysical evolution of arid and semiarid regions on earth [1,2,3]. It also causes environmental problems such as air quality deterioration and land degradation [4,5]; the sand transport in atmospheric boundary layer is critical to the latter phenomenon. The interpretation of such gas–particle two-phase flow relies on the understanding of the momentum exchange between the two phases, which is usually specified as the distributions of velocities and mass flux of the sands [6,7].
Intrusive equipment such as ruggedized probes has been used to quantify these distributions at satisfactory temporal resolutions [8,9], which nevertheless inevitably disturb the measured flow fields. The use of nonintrusive measurements, such as particle image velocimetry and high-speed photography [7,10,11,12], avoids this problem. However, they have difficulties in addressing “dense” flow under strong wind or near the sand bed surface.
Numerical simulation has been an indispensable method for accompanying the measurements [2,13]. There are generally two methods for simulating gas–particle flow. One method tracks the information from individual particles in the Lagrangian point of view [14,15]. Such a discrete model constructs the interparticle and gas–particle interactions by virtue of the Newtonian laws; therefore, it would become inefficient in cases of an extremely large numbers of particles. The other method treats moving particles as a continuum in a Eulerian–Eulerian framework. Such a model is suitable for simulating sand flow for two reasons. First, it allows for a uniform format for collectively modelling the air turbulence and particle movement. Second, it requires much less time than the discrete approaches [16]. The Eulerian–Eulerian model has been applied to various cases. These cases include dense spouted or fluidized beds [17,18], granular flow in horizontal pneumatic conveyance and wind-blown dust designated as a suspension [19,20], of which the mechanism is quite different from the near-surface motion of saltation [1,21].
In contrast, the simulation of near-surface sand flow based on the Eulerian–Eulerian model has very rarely been conducted. In this study, a pseudofluid model is introduced and coupled with a large eddy simulation (LES) [22]. In the present coupling model, the LES is applied to simulate wind flows within the turbulent boundary layer. For the solid phase, the sand particles are treated as a kind of continuous pseudofluid. A kinetic theory of granular flow (KTGF) approach [17] is introduced to describe the saltating sand cloud transport. Then the height profiles of the stream-wise velocity and the mass flux of the sand are simulated and compared with the reported experimental data. Finally, some variables that are difficult to measure experimentally are also simulated and analyzed, including the drag between the two phases and the interparticle collision restitution coefficient.
2. Continuum Models for Two Phases
In the Cartesian coordinate system, the filtered equations of motion for the gas phase are given by Chiesa et al. [16] and shown in Equation (1):
where ρg = 1.225 kg/m3 is the gas density; αg, ug,j and pg are the volume fraction, the velocity component in the jth direction and the pressure of the gas phase, respectively; δij is the Kronecker delta, gi is the component of gravity in the ith direction, us,i is the velocity component of the sand phase in the ith direction, β is the drag coefficient between the two phases and μgl = 1.8 × 10−5 kg/(m·s) is the gas viscosity. μgt = ρg(Cg∆)2|Sg| is the gas subgrid-scale eddy viscosity with |Sg| = (2 Sg,ij Sg,ij)1/2, where Cg = 1 is the Smagorinsky model constant, ∆ = (∆x∆y∆z)1/3 is the filter width and Sg,ij = (∂ug,j/∂xi + ∂ug,i/∂xj)/2 is the filtered rate of strain of the gas phase [23,24]. It is undeniable that the Smagorinsky mode does not well model the process of energy backscatter. However, such kind of Smagorinsky LES turbulence model has still successfully and reliably been used in the simulations of aeolian sand transport in equilibrium state [22]. Therefore, considering the emphasis on sand phase analysis and the difficulty of model implementation, the classical Smagorinsky model is adopted.
The filtered equations of motion for the “continuous” sand phase are given by Mathiesen et al. [17] and shown in Equation (2):
where ρs = 2650 kg/m3 is the sand density and αs, ps, μsl, μst and ξs are the volume fraction, the pressure, the shear viscosity, the subgrid-scale eddy viscosity and the bulk viscosity of the sand phase, respectively. In the present simulations, αg + αs = 1.0. A constitutive model is introduced based on the assumption that the interactions between particles can be represented by the sum of the kinetic and frictional stresses [25]. The kinetic stress is based on the kinetic theory of granular flow and the frictional stress is simply reduced to the Coulomb relationship [26,27]. Consequently, the particle pressure and the shear viscosity are formulated as shown in Equation (3):
where e = 0.7 is the interparticle collision restitution coefficient; θ and g0 are the granular pseudotemperature and the radial distribution function, respectively [28]; Fr = 0.05 kg/(m·s2), n = 2.0 and r = 5.0 are the empirical material constants [29]; αs,.max = 0.60 and αs,min = 0.10 are the maximum and the minimum values of the sand volume fraction, respectively [30]. θ = ⟨cs2⟩/3 is a measure of the single particle velocity fluctuation at a small scale, where cs is the fluctuating velocity [31]. g0 = [1 − (αs/αs,max)1/3]−1 is the radial distribution function for the individual particles [32]. φ1 is a transition function that provides a smooth transition between the rapidly shearing viscous regime and the slowly shearing plastic regime [33], which is shown in Equation (4):
The shear viscosity that considers the kinetic and the friction parts is given in Equation (5):
where a smooth function is written as φ2(αs) = arctan[96(αs − αs,min)]/π + 0.5, ds is the average diameter of the sand particles, Ω = 31° is the angle of internal friction of the sand particles and I2D is the second invariant of the strain rate tensor determined by the rate of the strain tensor of the sand phase flow Ss,ij = (∂us,i/∂xj + ∂us,j/∂xi)/2.
Under the Eulerian–Eulerian framework, an eddy viscosity model of the sand phase μst is introduced to take into account the subgrid-scale motion of the sand particles [34]. μst is modelled using an eddy viscosity assumption: μst = αsρs(Cs∆)2(2 Ss,ij Ss,ij)1/2, where Cs = 0.14 [23]. The bulk viscosity is described as ξs = 4αs2ρsds(1 + e)g0(θ/π)1/2/3. Then, the transport equation for turbulent kinetic energy is shown in Equation (6):
Specifically, ks is the conductivity of granular pseudotemperature, as shown in Equation (7):
γs is the dissipation due to inelastic collisions, as shown in Equation (8):
And Φ = −3βθ is the fluctuating energy exchange between the two phases, for which the details are shown in Equation (9):
With Res = αgρgds| ug− us|/μgl as the particle Reynolds number [35,36].
Discretization of the governing equations is performed on a collocate grid using the finite control volume technique. The pressure–velocity coupling is achieved by the SIMPLE method with momentum interpolation [37]. The QUICK scheme is adopted for the convective terms [38]. The second-order central difference scheme is adopted for the diffusion terms. A hybrid of the Adams-Bashforth and Crank-Nicolson schemes is adopted for time advancement of the gas-phase integration [39]. A fully implicit scheme is adopted for the integration of the volume–fraction equation of the sand phase. Due to the strong coupling of drag forces between the two phases, the two-phase partial elimination algorithm is used to decouple the drag [40].
3. Conditions for Simulation
The simulation is conducted in a rectangular domain, as shown in Figure 1a. The coordinates X, Y and Z denote the streamwise, vertical and spanwise directions, respectively. In the X and Z directions, the mesh is uniformly distributed with mesh cell sizes of dx = Lx/Nx = 0.0042 m and dz = Lz/Nz = 0.001563 m, respectively. The periodicity condition is assumed hereby. In the Y direction, the mesh is refined near the bottom, with the mesh cell size of m adopted. The symmetrical boundary conditions are set for both the gas and sand phases at the top of the computational domain: the vertical component of the wind and sand velocities as well as the normal gradients for other variables, including the concentration of gas and sand phases, are assumed to be zero in the Y direction at the top. The nonslip condition and the Werner-Wengle wall function are assumed for the bottom surface [41]. As shown in Equation (10), the boundary conditions are applied to the wall-tangential velocities and the granular pseudotemperature of the sand particles:
where Ψ = 0.01 and ew = 0.45 are the specularity coefficient and the particle–wall collision restitution coefficient, respectively [29]. A logarithmic wind profile is applied for the initial condition, as shown in Equation (11):
where κ = 0.41 is the von Karman constant, Y0 = ds/30 the roughness length, and u∗ is the friction velocity. With regard to the LES simulation, a random fluctuating part of the velocities (ug’,vg’,wg’) is superimposed on the logarithmic profile to generate turbulent flow in the boundary layer. The initial vertical and span wise components of wind velocity are set to vg’ and wg’, respectively. At the initial time t = 0, both the gas pressure and the granular pseudotemperature of the sand are set to zero. An initial sand phase field is adopted by using a random distribution of sand concentration, the total concentration of sand is reasonably set as 1 × 10−4 in the model. The environmental temperature is maintained at a value of 15 °C. When using the Courant–Friedrichs–Lewy (CFL) to determine the limited range of time step, the maximum Courant number can be estimated as . Then, . In order to guarantee the precision of the LES turbulence simulation, the iteration time step can be reasonably set to a value smaller than 8.7 × 10−5 s. On the premise of satisfying CFL criterion, after comprehensive consideration, the final decision to set the time step ∆t for both phases as 1.0 × 10−5 s.
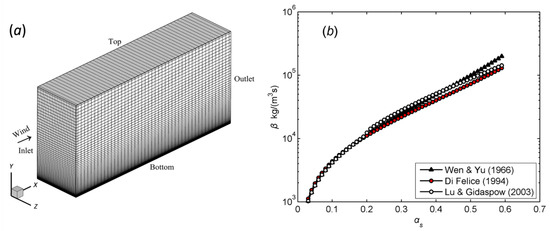
Figure 1.
Preparation for simulation. (a) Rectangular computation domain with a size of LX × LY × LZ = 0.2 m × 0.1 m × 0.05 m. The grid resolution is determined to be NX × NY × NZ = 48 × 64 × 32 as the result of a convergence test. (b) Selection of the model for the drag coefficient, in which three classic models are qualitatively similar to each other.
In the Eulerian–Eulerian granular pseudofluid model, the drag coefficient is a key parameter for simulating the momentum transfer between two phases [42]. For a given slip velocity of 1.50 m/s and a particle diameter of 110 μm, the distribution of the drag coefficient β as a function of the volume fraction of the sand phase αs is given in Figure 1b, which shows that the drag coefficients for three classic models are similar to each other. Therefore, the expression of the drag coefficient by Di Felice is selected for the present simulation [35].
To compare with the simulation, three wind tunnel experiments are introduced with friction velocity u∗ as the unknown [43,44,45]. Equation (11) is used to estimate the values for u∗ in experiments based on half the size of the wind tunnel height and its corresponding freestream velocity. Then, the freestream winds in the simulation are determined so that values of u∗ are produced that are as close to those of in experiments as possible. One of the values for u∗ at ds ≈ 250 μm is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Values for the friction velocity u∗ at ds ≈ 250 μm.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Distribution of Sand Concentration
Figure 2 shows a typical view of the distribution of the sand concentration αs, which is averaged spatially in the Z direction at each time step and then averaged temporally over the entire computation period. It turns out that the sands are inhomogeneously distributed and more than half of their mass is concentrated within a height taking up 20% of the entire thickness of the near-surface sand flow, which is similar to earlier simulations and observation [22,36,46]. The maximum sand concentration is on the order of 10−5, which is consistent with Liu and slightly lower than that observed by Zhang et al. [47,48].
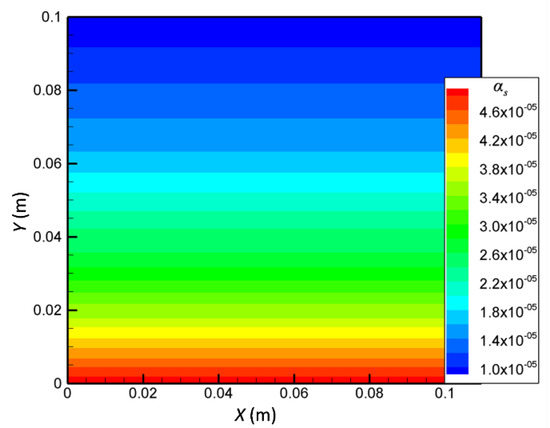
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of the sand concentration on the X–Y plane at u∗ = 0.395 m/s and ds = 250 μm.
4.2. Sand Velocity
The streamwise sand velocity us and mass flux q are averaged spatially along two periodic directions at each time step and then averaged temporally over the entire computation period. Figure 3 shows the simulated height profiles of the streamwise sand velocity. To optimize the comparison, the ensemble average value ⟨us⟩ and Y are normalized by the freestream wind velocity U0 and the thickness of the boundary layer Yb, respectively. In the modeling, the thickness of the boundary layer Yb is set as 0.10 m. This height is basically a representative of the maximum saltating height of blown sand particles, which is consistent with the height measured by the wind tunnel experiments [44,47]. First, as shown in Figure 3a, sand velocity varies logarithmically above a certain height (Y/Yb = 0.2), which is qualitatively consistent with the two experiments and simulations but different from the linear pattern obtained by using a particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurement [10,22,49]. At a given height, the sand velocity (or the interphase momentum transfer) increases with friction velocity. As the height increases, the variation of the sand velocity becomes less sensitive to friction velocity, which can be attributed to the presence of fewer obstacles to the full acceleration of the sand particles in the more “dilute” region. On this issue, the simulation agrees qualitatively well with the two experiments.
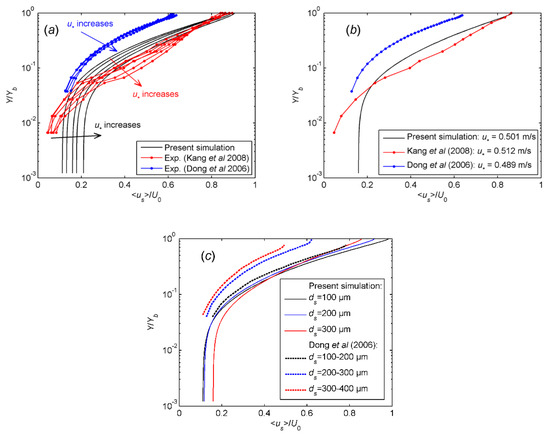
Figure 3.
Variations with height of the average streamwise sand velocity. (a) Profiles vary with friction velocity, where the values for u∗ and ds can be found in Table 1. (b) A specific comparison selected from panel (a), in which ds ≈ 250 μm. (c) The profile varies with particle diameter. u∗ equals 0.395 m/s and 0.407 m/s for the present simulation and Dong, respectively [44].
Figure 3b shows a specific comparison between the height profiles of the present simulation and those of the two experiments that are chosen from the results depicted in Figure 3a. The pattern obtained by the simulation agrees very well with the power function-like result of Dong, which was achieved with a PIV measurement [44]. This is because the PIV technique calculates the Eulerian velocity field by correlating interframe windows that contain continuous grayscale distribution, which is similar to the Eulerian–Eulerian simulation that regards the sand phase as a continuum. The difference between their magnitudes is predictable because the values for the friction velocity of the experiment are rather crudely estimated. Only above a certain height, the logarithmic pattern is shared by the simulation and the result obtained from the phase Doppler particle anemometer (PDPA) measurement by Kang et al. [45]. When approaching the sand bed surface, however, the result from the PDPA technique deviates from the results of the simulation. This is probably because as a point measurement, the PDPA technique is sensitive to the interferences of interparticle motions in the ‘dense’ region.
Figure 3c shows the height profile of the ensemble average streamwise sand velocity varying with particle size. There is a turning point (Y/Yb = 0.2 for the simulation) that divides the profile into two parts. In the upper part, the normalized sand velocity increases with decreasing particle size, which is in contrast to the lower part. This result can be explained as follows: the finer the sand particle, the more easily it is accelerated by wind in the “dilute” region where the momentum transfer from wind to sand is dominant; in contrast, when approaching the sand bed surface, a larger particle becomes superior in retaining momentum after interparticle collisions in the “dense” region. Figure 3c indicates that Dong el al (2006) did not approach down enough to obtain their own turning point, below which we would share the same pattern that particles with bigger diameter suspended lower than the smaller ones. The difference in the height of the turning point is probably due to the fact that sand samples in experiment are mixing sands with nonspherical shapes, which inevitably lead to a vertical shift of the turning point from that in simulation where particles are treated as ideally spherical and with a single diameter. Moreover, as the height increases, the difference between profiles becomes greater, indicating that the variation of the sand velocity becomes more sensitive to particle size. This feature is shared by Dong et al. [44] in the upper layer. Generally, it is not easy for the PIV technique to provide satisfactory near-wall velocity information either because the strong light reflection on the boundary deteriorates the image quality necessary for interframe correlation, or because the size of the interrogation window has to be large enough to guarantee the accuracy of the correlation, which in turn sacrifices the spatial resolution.
4.3. Sand Flux
The height profile of the sand mass flux can be defined in light of the sand concentration and streamwise sand velocity [10,44,50], as shown in Equation (12):
Similar to the definition in Section 4.2, the angle bracket in the above equation is defined as the ensemble average treatment for the quantity. Figure 4 shows the simulated height profile of q(Y) normalized by the reference value q(Y0) at Y0 = 2 × 10−3 m, as previously obtained by Dong et al. [43,44]. One can conclude that (1) all the flux profiles are made up of three parts. The first part is a near-surface layer in which the flux increases with height. The second part refers to the upper layer in which the flux decays rapidly. The third part is a peak of flux around Y/Y0.1 = 0.2 that joins the two layers. Part (2) of the conclusion is that at a given height, the flux increases with the wind velocity shown in Figure 4a and with particle size shown in Figure 4b. These two features can be found in Dong as measured with a segmented sand sampler and Dong as measured by the PIV technique and calculated with Equation (12) [43,44].
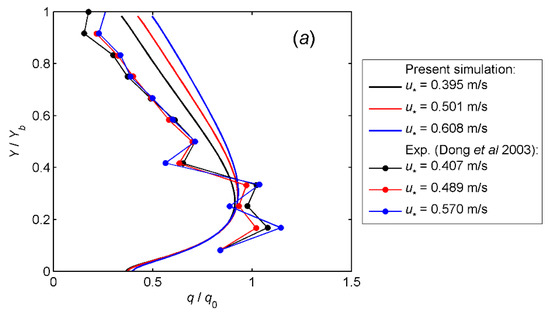
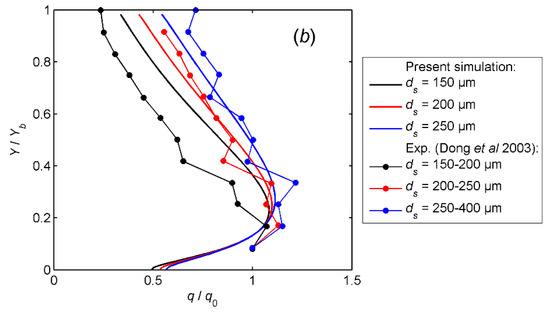
Figure 4.
Variations with height of the average sand mass flux. (a) The profile varies with friction velocity. ds equals 250 μm and 200–250 μm for the present simulation and Dong, respectively [43]. (b) The profile varies with particle size. u∗ equals 0.395 m/s and 0.407 m/s for the present simulation and Dong, respectively [43].
One can also conclude from Figure 4 that the results from Dong and the simulation agree well in the upper layer, but they deviate from each other towards the sand bed surface [43]. This is probably because the segmented sand sampler used in Dong is an intrusive tool that has a drag effect on the sand flow [43]. Such an effect becomes especially evident near the surface where a wind flow with limited strength propels a large number of sand particles. As a result, certain particles obtain momenta and flying heights smaller than they are expected to be, thus resulting in a drop in q above the surface (Y/Y0.1 = 0.4 in this case) and an overestimation of q in the near-surface layer. A nonintrusive measurement technique such as PIV, on the other hand, has to finish two steps to obtain q according to Equation (12). Moreover, it obtains only the relative size of q, because the absolute value of the sand concentration cannot be obtained directly from grayscale images [44].
4.4. Fluctuation of the Sand Phase
In the present numerical model, the pseudotemperature θ directly reflects the characteristics of fluctuation of sand movement. This “temperature” is irrelevant to the thermal one, but is an index of the complex interaction between the viscous and inertial forces asserted on sand particle. Aiming to solve the pseudofluid modelling of granular kinematics, Mathiesen proposed the relation between the turbulent RMS (root mean square) velocity of particle and pseudotemperature: , in which cs2 = us’2 + vs’2 + ws’2), that is, the sum of the squares of components of particle fluctuating velocity in streamwise, vertical and spanwise directions [17]. Based on the isotropic assumption us’2 = vs’2 = ws’2 that is reasonable when particles do not conglomerate, one can obtain ⟨cs2⟩ = 3⟨us’2⟩. In all, the turbulent RMS particle velocity is given as .
Figure 5 shows the variation of the spatially and temporally averaged urms with height by the present simulation and by the PDPA measurement of Kang et al. [45], the latter of which is by far the most detailed experimental data about the turbulent RMS velocity of aeolian sand particles ever found. The friction velocity in experiment is deduced by collectively using the logarithmic law and the mainstream wind. It can be seen that, within the saltation layer, the fluctuation of particle movement increases along with the height and reaches the peak at Y = 0.005 m. As Y > 0.005 m, it drops with the increase of height. Near the sand bed surface, the sand concentration is relatively high, and the above-mentioned fluctuation is supposed to be mainly determined by the intensive interparticle collision. Far away from the saltation layer, on the contrary, the concentration of saltation is relatively low, and the fluctuation can only be determined by the drag of air flow. Now the distribution patterns by simulation and experiment qualitatively agree with each other that, the fluctuation of sand movement near the surface is much higher than that high up in the air. Therefore, the interparticle collision must be the dominating factor accounting for the fluctuation of sand particle movement. It is noteworthy that, close to surface (Y = 0 m) the fluctuation drastically reduces to zero, indicating that the sand movement is inhibited strongly by the sand bed. As shown in Figure 5a, the magnitude of fluctuation increases along with the friction velocity. This is because higher wind energy generates more intensive interparticle colliding activity, thus strengthening the fluctuation of sand particle movement. As shown in Figure 5b, the magnitude of fluctuation increases along with the particle diameter. This is because larger particles result in a higher probability of interparticle collision (or a greater chance of “overlapping in space”). However, on top of the saltation layer, sand particles are so sparse that the above-mentioned probability is quite low. Therefore, either the wind strength or the particle size has very limited influence on the fluctuation.
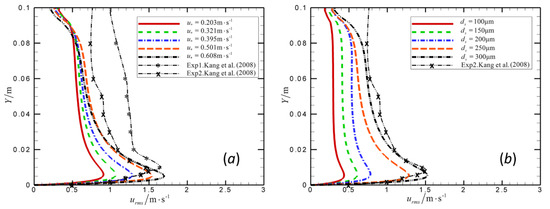
Figure 5.
Variation with height of the fluctuation of sand velocity. (a) The profile varies with friction velocity. ds equals 250 μm and 170–300 μm for the present simulation and Kang, respectively [45]. (b) The profile varies with particle size. u∗ equals 0.395 m/s and 0.353 m/s for the present simulation and Kang, respectively [45].
The reasons for the quantitative discrepancy between simulation and experiment in Figure 5 can be concluded as follows. (1) In simulation the particle diameter is uniform, while for experiment there is a distribution for particle diameter (usually not as symmetric as some classical models like the normal distribution), so the mean diameter is different between simulation and experiment. Furthermore, as concluded above, particle diameter is key to the magnitude of fluctuation. (2) In simulation there are some simplifications, such as the isotropic assumption for the fluctuating components and the assumption to exclude large-scale fluctuation. In experiment the measuring result contains both the large-scale and the small-scale fluctuations, although the small-scale components take the majority [17,51]. (3) The simulation is conducted in space while the PIV measurement is realized on a plane, the latter of which may be a projection of the original 3D information.
4.5. Drag between the Two Phases
The drag is the essential connection of energy transfer between the two phases, affecting significantly the characteristics of sand movement. The average drag that the air phase passed on the sand phase is Fdrag = β∆U∆x∆y∆z, which represents the overall drag in a unit volume. fdrag = β∆U is called the drag density, where ∆U = is defined as the slip velocity between the two phases.
Figure 6 shows the variation of spatially and temporally averaged drag density with height by the present simulation, for which an experimental comparison is very difficult to find. However, according to the above results and discussions, since the velocity, flux and fluctuation of sand phase have been proven to be comparable with those of the experiment, it is sufficient to believe that the simulation result of drag density is instructive (at least qualitatively). It can be seen that, as the height goes up, the drag density increases drastically in the start and reaches the maximum value at Y = 0.005 m. Then it decreases gradually, and finally reduces to zero at the top surface of saltation layer (Y = 0.1 m). Near the sand bed surface, sand particles are propelled by the wind and start to move. Due to the inertia, however, the velocity difference between the two phases is so huge that fdrag has a great potential to increase and finally reach the peak. As the height goes up, there is a continuous momentum transfer between the two phases, so the velocity difference shrinks, leading to the decrease of fdrag. At the sand bed surface, fdrag = 0 due to the nonslip effect. As shown in Figure 1b, with the slip velocity and particle diameter fixed, the drag coefficient β increases along with the sand concentration. Therefore, distribution of fdrag shown in Figure 6 is consistent with that of the sand concentration. As shown in Figure 6a, the slip velocity increases along with the friction velocity, thus lifting the value of fdrag. As shown in Figure 6b, smaller particle leaves a larger room for the drag of air flow, so fdrag increases along with the decrease of particle size. This is especially obvious at the lower part of saltation layer where the sand concentration is higher.
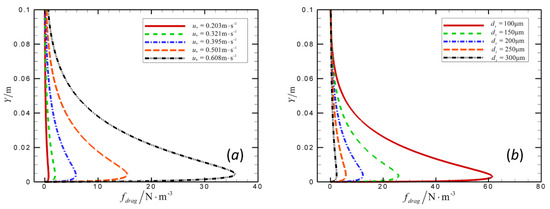
Figure 6.
Variation with height of the drag density. (a) The profile varies with friction velocity (ds = 250 μm). (b) The profile varies with particle size (u∗ = 0.395 m/s).
4.6. Interparticle Collision
The interparticle collision restitution coefficient e is a representative of the elasticity of interparticle collision and defined as the ratio of kinetic energies after and before collision. Du et al. suggest that the pseudotemperature of particle θ is closely related to the interparticle collision coefficient [52]. Therefore, e is critical to the quantitative simulation of fluid driven particle movement. As a matter of fact, due to the shape irregularity of natural quartz sand particles, it is ineffective to use the spherical particles as the substitute in the experiments to measure e. As a result, it is impossible to have a general solution for e among different experiments and simulations. Wang et al. suggest e ∈ [0.428, 0.455] by conducting a wind tunnel experiment using natural sands [11], while Haff and Anderson agree on e ∈ [0.6, 0.8] [14]. Kang and Guo adopted e = 0.87 and e = 0.89 in their DEM simulation of aeolian sand flow [36], while Kang and Liu used e = 0.7 in their simulation [49]. In all, the present work is not looking for a universally effective value (or range) for e, but to investigate the influence of e on the characteristics of fluctuation of particle movement.
Figure 7 shows the variation of the profiles of urms and interparticle collision frequency fc with e. Here, the interparticle collision frequency is based on a kinetic theory of granular flow, which can be calculated by combining the pseudotemperature and sand phase concentration [26]:. It can be seen that, urms and fc increases along with e. This is because as the particles save more energy after the collision, there is a larger opportunity for the subsequent interparticle collision to happen, thus leading to a stronger fluctuation of sand particle movement. The influence of e on the two profiles is more obvious near the sand bed surface than up in the air, which is due to the fact that with a higher sand concentration, the effect of interparticle collision will be magnified to a greater extent. From Figure 7a one can also notice that with e changing from 0.6 to 0.8, the peak RMS velocity varies from 1.124 to 1.555 m/s, corresponding to an increase ratio of 38.3%. Therefore, the fluctuation of particle movement is very sensitive to the interparticle collision restitution coefficient. It is noted that since the experimental verification for the simulation results in Figure 7 cannot be obtained at present and the e value used in some modeling studies based on DEM is not within the range of [0.6, 0.8] [36]. Therefore, it is speculated that the classical statement such as e ∈ [0.6, 0.8] mentioned above may not be an optimal condition for the quantitative simulation of turbulent aeolian sand transport.
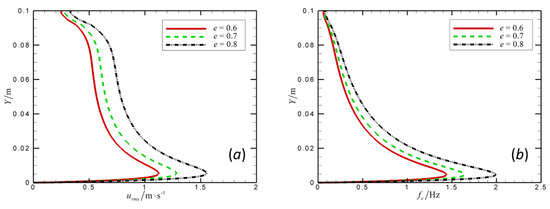
Figure 7.
Influence of the interparticle collision restitution coefficient on the fluctuation of sand movement. (a) Variation with height of the turbulent RMS sand velocity. (b) Variation with height of the interparticle collision frequency. In both panels, the interparticle collision restitution coefficient increases from 0.6 to 0.8 with an increment of 0.1, with the conditions ds = 250 μm and u∗ = 0.395 m/s.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the aeolian sand transport within a turbulent atmospheric boundary layer was simulated using a Eulerian–Eulerian model coupling the granular pseudofluid optimization and the gas-phase large eddy simulation. This continuum model is efficient in simulating a dense particle flow and makes it possible to avoid determining the specific modes of near-surface particle motion, i.e., saltation or creep, for which distinct laws of motion must be applied [1,2].
The simulated profiles of streamwise mean sand velocity and sand mass flux qualitatively agree with the reported experiments. The discrepancy between them occurs near the sand bed surface. This highlights the potential of the present model in addressing the near-surface sand transport layer, which is problematic for nonintrusive measurement techniques with limited spatial resolution. The simulated profiles of turbulent RMS particle velocity indicate that the interparticle collision is mainly responsible for the fluctuation of sand particle movement. Therefore, the interparticle collision restitution coefficient should be carefully chosen in simulation. The above conclusions may be helpful as reference in developing the Euler–Euler fluid driving particle transport. To fully achieve geophysical significance, the next step is to simulate the sand flow in nature rather than in a wind tunnel. For this effort, it is necessary to develop more reasonable constitutive relations to deal with a wider range of particle sizes, and it is also necessary to reproduce the fluid turbulence as appropriate for the typical spectra of wild gusts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and X.Z.; methodology, X.Z.; software, C.W.; validation, C.W. and Y.H.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, Y.H. and B.Y.; resources, Y.Z.; data curation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.W.; visualization, X.Z.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration, Y.W. and B.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (11402190) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M552443).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes, 1st ed.; Methuen: London, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burr, D.M.; Bridges, N.T.; Marshall, J.R.; Smith, J.K.; White, B.R.; Emery, J.P. Higher-than-predicted saltation threshold wind speeds on Titan. Nature 2015, 517, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.W.; Kellogg, C.A.; Shinn, E.A. Dust in the wind: Long range transport of dust in the atmosphere and its implications for global public and ecosystem health. Glob. Chang. Hum. Health 2001, 2, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettke, T.; Halliday, A.N.; Hall, C.M.; Rea, D.K. Dust production and deposition in Asia and the north Pacific Ocean over the past 12 Myr. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 178, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, B.; Claudin, P.; Douady, S. Selection of dune shapes and velocities. Part 1: Dynamics of sand, wind and barchans. Eur. Phys. J. B 2002, 28, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Dong, Z.B.; Qian, G.Q.; Luo, W.Y.; Wang, H.T. Height profile of the mean velocity of an aeolian saltating cloud: Wind tunnel measurements by Particle Image Velocimetry. Geomorphology 2007, 89, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Blumberg, D.G.; Williams, S.H. Field measurements of the flux and speed of wind-blown sand. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Houser, C.A.; Nickling, W.G. Analysis of velocity profile measurements from wind-tunnel experiments with saltation. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creyssels, M.; Dupont, P.; El Moctar, A.O.; Valance, A.; Cantat, I.; Jenkins, J.T.; Pasini, J.M.; Rasmussen, K.R. Saltating particles in a turbulent boundary layer: Experiment and theory. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 625, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Statistical analysis of sand grain/bed collision process recorded by high-speed digital camera. Sedimentology 2007, 55, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, P. Measuring the kinetic parameters of saltating sand grains using a high-speed digital camera. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, B.; Claudin, P.; Douady, S. Selection of dune shapes and velocities. Part 2: A two dimensional modelling. Eur. Phys. J. B 2002, 28, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haff, P.K.; Anderson, R.S. Particle scale simulations of loose sedimentary beds: The example of particle-bed impacts in aeolian saltation. Sedimentology 1993, 40, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.V.; Pahtz, T.; Herrmann, H.J. Jump at the onset of saltation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 098001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, M.; Mathiesen, V.; Melheim, J.A.; Halvorsen, B. Numerical simulation of particulate flow by the Eulerian-Lagrangian and the Eulerian-Eulerian approach with application to a fluidized bed. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2005, 29, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, V.; Solberg, T.; Hjertager, B.H. An experimental and computational study of multiphase flow behavior in a circulating fluidized bed. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2000, 26, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Lu, H.L.; Wang, S.A.; Xu, P.F.; Wei, L.X.; He, Y.R. Flow of gas and particles in a bubbling fluidized bed with a filtered two-fluid model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2664–2679. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, W.H.; Zhao, C.S.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Liang, C.; Chen, X.P.; Lu, P.; Fan, C.L. Numerical simulation on dense phase pneumatic conveying of pulverized coal in horizontal pipe at high pressure. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2500–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Guo, Y. Numerical simulation of aeolian dusty sand transport in a marginal desert region at the early entrainment stage. Geomorphology 2008, 100, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. On aeolian transport: Grain-scale interactions, dynamical mechanisms and scaling laws. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A numerical study of particle motion and two-phase interaction in aeolian sand transport using a coupled large eddy simulation-discrete element method. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. I. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Ohba, M.; Yoshie, R. CFD modelling of unsteady cross ventilation flows using LES. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 1692–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Sundaresan, S. Analysis of a frictional-kinetic model for gas-particle flow. Powder Technol. 2003, 129, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaspow, D. Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions, 1st ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.C.; Nott, P.; Jackson, R. Frictional-collisional equations of motion for particulate flows and their application to chutes. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 210, 501–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Lu, H.L.; Yu, L.; Sun, D.; He, Y.R.; Ding, Y.L. Numerical simulations of flow behavior of gas and particles in spouted beds using frictional-kinetic stresses model. Powder Technol. 2009, 196, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Jackson, R. Frictional-collisional constitutive relations for granular materials, with application to plane shearing. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 176, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parteli, E.J.R.; Duran, O.; Herrmann, H.J. Minimal size of a barchan dune. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, C.K.K.; Savage, S.B.; Jeffrey, D.J.; Chepurniy, N. Kinetic theories for granular flow–inelastic particles in Couette-flow and slightly inelastic particles in a general flowfield. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 140, 223–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, J.L.; Jackson, R. Gas-particle flow in a vertical pipe with particle-particle interactions. AICHE J. 1989, 35, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, D.G. Instability in the evolution equations describing incompressible granular flow. J. Differ. Equ. 1987, 66, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Bergametti, G.; Marticorena, B.; Simoens, S. Modeling saltation intermittency. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 7109–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, R.D. The voidage function for fluid-particle interaction systems. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1994, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Q.; Guo, L.J. Eulerian-Lagrangian simulation of aeolian sand transport. Powder Technol. 2006, 162, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhie, C.M.; Chow, W.L. A numerical study of the turbulent flow past an isolated airfoil with trailing edge separation. AIAA J. 1983, 21, 1525–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, B.P. Order of accuracy of QUICK and related convection-diffusion schemes. Appl. Math. Model. 1995, 19, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejoan, A.; Schiestel, R. LES of unsteady turbulence via a one-equation subgrid-scale transport model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 2002, 23, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboreiro, J.; Joseph, G.G.; Hrenya, C.M. Revisiting the standard drag law for bubbling, gas-fluidized beds. Powder Technol. 2008, 183, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, H.; Wengle, H. Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over and around a cube in a plate channel. In Proceedings of the The 8th Symposium on Turbulent Shear Flows, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 9–11 September 1991; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.L.; Gidaspow, D. Hydrodynamics of binary fluidization in a riser: CFD simulation using two granular temperatures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.B.; Liu, X.P.; Wang, H.T.L.; Zhao, A.G.; Wang, X.M. The flux profile of a blowing sand cloud: A wind tunnel investigation. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Qian, G.Q.; Luo, W.Y.; Wang, H.T. Analysis of the mass flux profiles of an aeolian saltating cloud. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos 2006, 111, D16111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Q.; Guo, L.J.; Gu, Z.M.; Liu, D.Y. Wind tunnel experimental investigation of sand velocity in aeolian sand transport. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.J. Simultaneous PIV and PTV measurements of wind and sand particle velocities. Exp. Fluids 2008, 45, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Dong, Z. Experimental investigation of the concentration profile of a blowing sand cloud. Geomorphology 2004, 60, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.J. Two-phase measurements of wind and saltating sand in an atmospheric boundary layer. Geomorphology 2007, 88, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Q.; Liu, D.Y. Numerical investigation of particle velocity distributions in aeolian sand transport. Geomorphology 2010, 115, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, L.Q.; Zou, X.Y. Theoretical analysis of particle number density in steady aeolian saltation. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wan, X.T.; Qian, Z.; Wei, F.; Jin, Y. Numerical simulation of the gas-particle turbulent flow in riser reactor based on k-epsilon-k(p)-epsilon(p)-Theta two-fluid model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 6813–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Bao, X.J.; Xu, J.; Wei, W.S. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling of spouted bed: Influence of frictional stress, maximum packing limit and coefficient of restitution of particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 4558–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).