Variational Assimilation of the Impervious Surfaces Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Land Model
2.3. Data
2.4. Variational Assimilation Method
3. Results and Discussions
4. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dickinson, R.E.; Tian, Y.; Fang, J.Y.; Li, Q.X.; Robert, K.; Kaufmann, C.; Tucker, J.; Ranga, B. Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9540–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, E.G.; Bockstael, N.E. The evolution of urban sprawl: Evidence of spatial heterogeneity and increasing land fragmentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 672–20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.G. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; He, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.F.; Sun, Z.X. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban impervious surfaces in China: An improved assessment using nighttime light data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, P.; Bou-Zeid, E. Contribution of impervious surfaces to urban evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, W.F.; Schienke, E.; Wang, X.K. Spatial pattern of impervious surfaces and their impacts on land surface temperature in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. China 2007, 19, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, W.; van der Kwast, J.; Verbeiren, B.; Batelaan, O. Downscaling of thermal images over urban areas using the land surface temperature-impervious percentage relationshop. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2013, 23, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jia, G.; Hou, M.; Zhang, X.X.; Zheng, F.X.; Liu, Y.H. The cumulative effects of urban expansion on land surface temperature in metropolitan Jingjintang China. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 9932–9943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhan, Q.; Guo, H.; Jin, Z.C. Characterizing the spatial dynamics of land surface temperature-impervious surface fraction relationshop. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 45, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liao, W.; Rigden, A.J.; Liu, X.P.; Wang, D.G.; Malyshev, S. Urban heat island: Aerodynamics or imperviousness? Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, Z.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhang, A.Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.F. Urbanization effects on observed surface air temperature trends in north China. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C. A numerical forecast model for road meteorology. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.J.; Grimmond, C.S.B. Key Conclusions of the First International Urban Land Surface Model Comparison Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Warner, T.; Basara, J. Verification of a mesoscale data-assimilation and forecasting system for the Okalahoma city area during the joint urban 2003 field project. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 912–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C. The integrated urban land model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, H.; Demuzere, M.; Blahak, U.; Keith, W.; Gordon, B. The efficient urban canopy dependency parameterization (SURY) v1.0 for atmospheric modelling: Description and application with the COSMO-CLM model for a Belgian summer. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3027–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V. A physically-based scheme for the urban energy budget in atmospheric models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 357–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kikegawa, Y.; Kimura, F. A simple single-layer urban canopymodel for atmospheric models: Comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2001, 101, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martilli, A.; Clappier, A.; Rotach, M.W. An urban surface exchange parameterization for mesoscale models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2002, 104, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleson, K.W.; Bonan, G.B.; Feddema, J.; Vertenstein, M.; Grimmond, C.S.B. An urban parameterization for a global climate model. Part I: Formulation and evaluation for two cities. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 1038–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Manning, K.W.; LeMone, M.A.; Trier, S.B.; Alfieri, J.G.; Roberts, R.D.; Blanken, P.D. Description and evaluation of the characteristics of the NCAR high-resolution land data assimilation system. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 694–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, F.; Entekhabi, D.; Caporali, E. Estimation of surface heat flux and an index of soil moisture using adjoint-state surface energy balance. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrini, F.; Castelli, F.; Entekhabi, D. Variational estimation of soil and vegetation turbulent transfer and heat flux parameters from sequences of multisensor imagery. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Li, Z.; Zhan, X.; Shi, J.C.; Liu, C.Y. Land surface temperature data assimilation and its impact on evapotranspiration estimates from the Common Land Model. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W02421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, S.M.; Entekhabi, D.; Jeng, D.S. Variational assimilation of land surface temperature and the estimation of surface energy balance components. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, C.; Tang, R. Variational estimation of land-atmosphere heat fluxes and land surface parameters using MODIS remote sensing data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; He, X.; Bateni, S.M.; Auligne, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhou, J.; Mao, K. Mapping regional turbulent heat fluxes via variational assimilation of land surface temperature data from polar orbiting satellites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zeng, X.; Dickinson, R.E.; Baker, I.; Bonan, G.; Bosilovich, M.; Denning, S.; Dirmeyer, P.; Houser, P.; Niu, G. The common land model. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, K.; Mitchell, C.-J.; Meng, K.; Arsenault, B.; Cosogrove, J.; Radakovich, M.; Entin, J. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrini, F.; Castelli, F.; Entekhabi, D. Mapping of land-atmosphere heat fluxes and surface parameters with remote sensing data. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2003, 107, 605–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

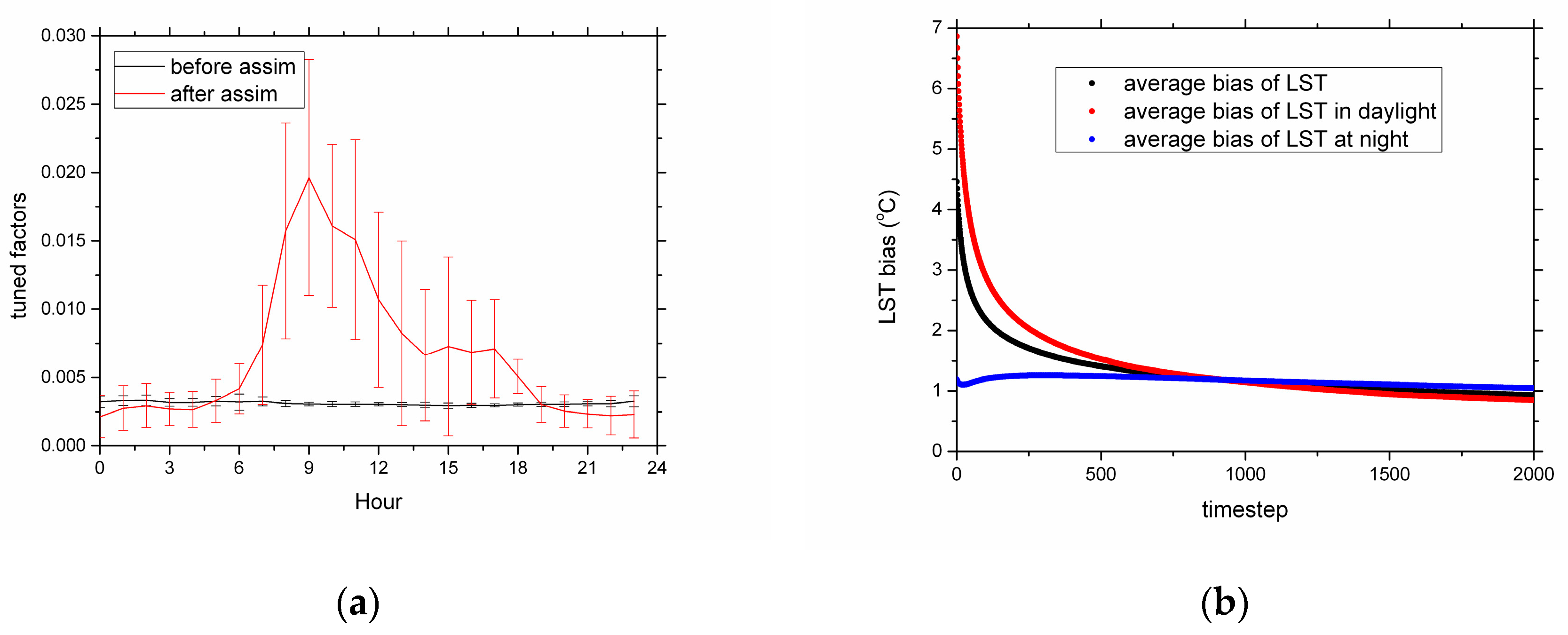
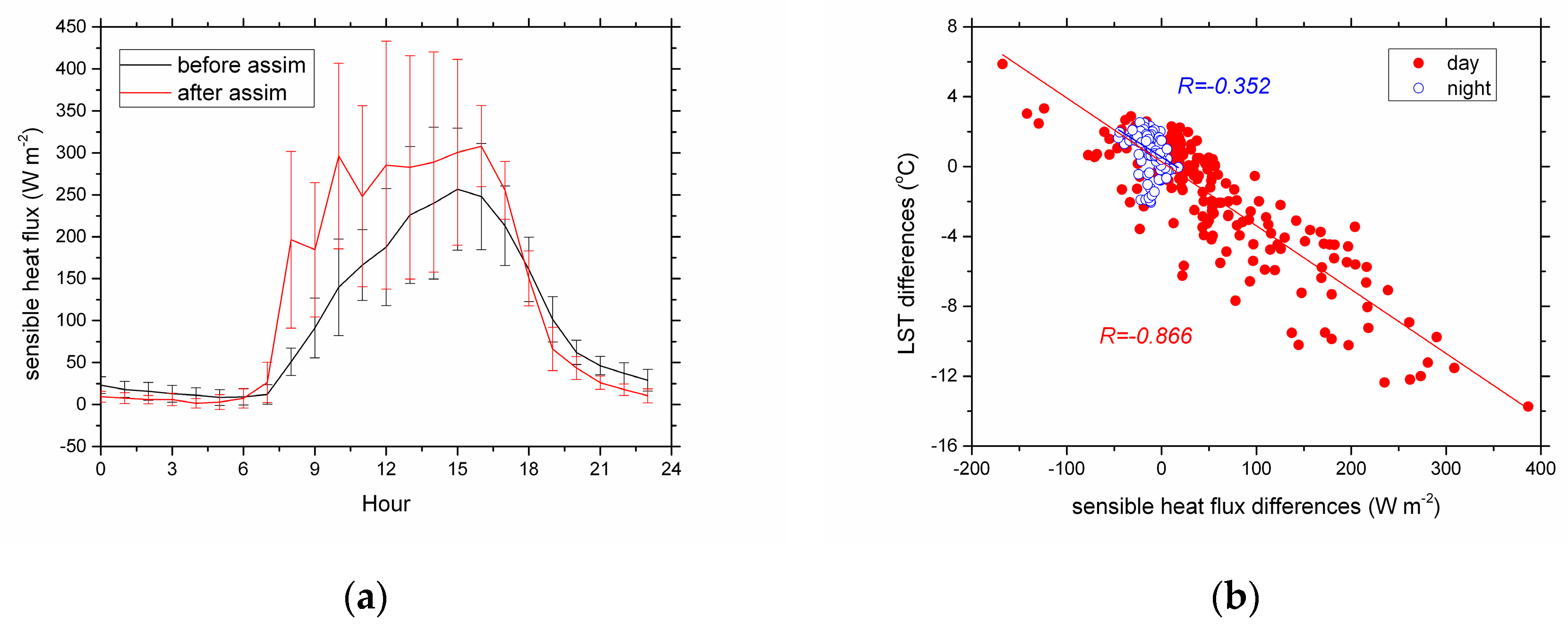
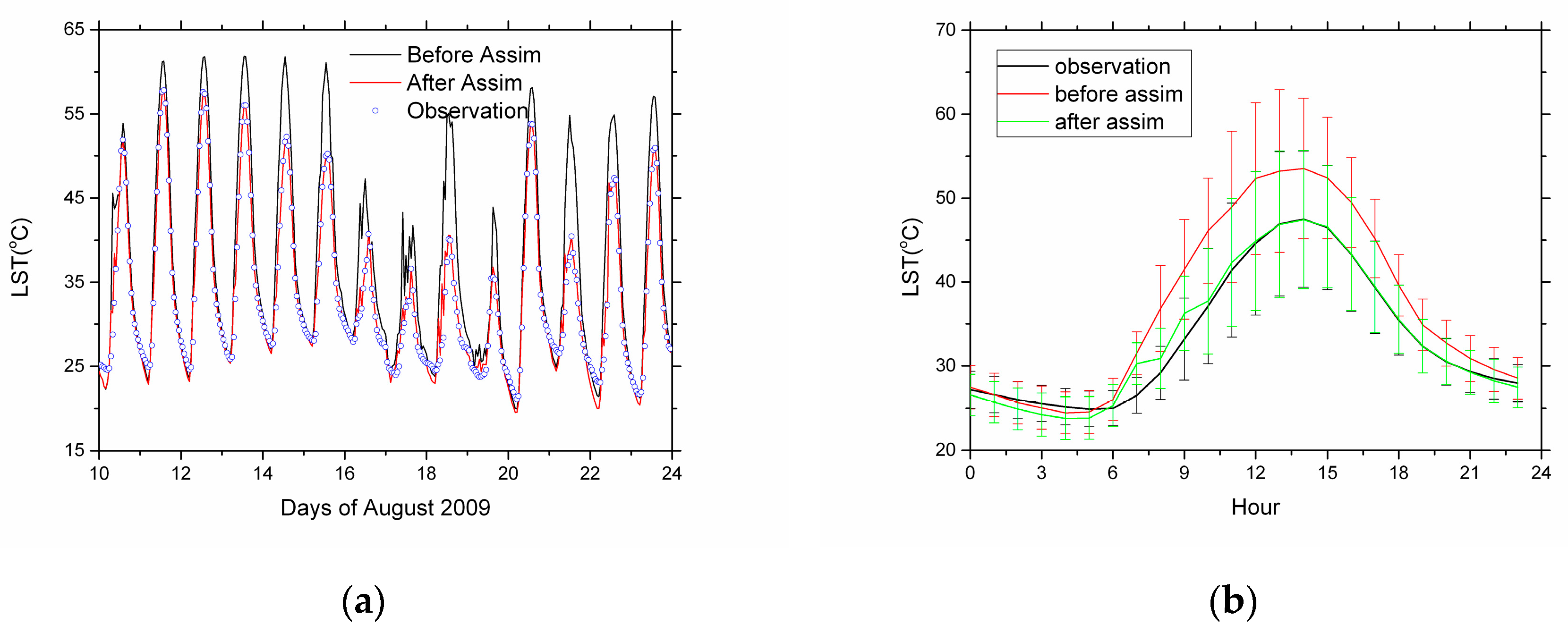
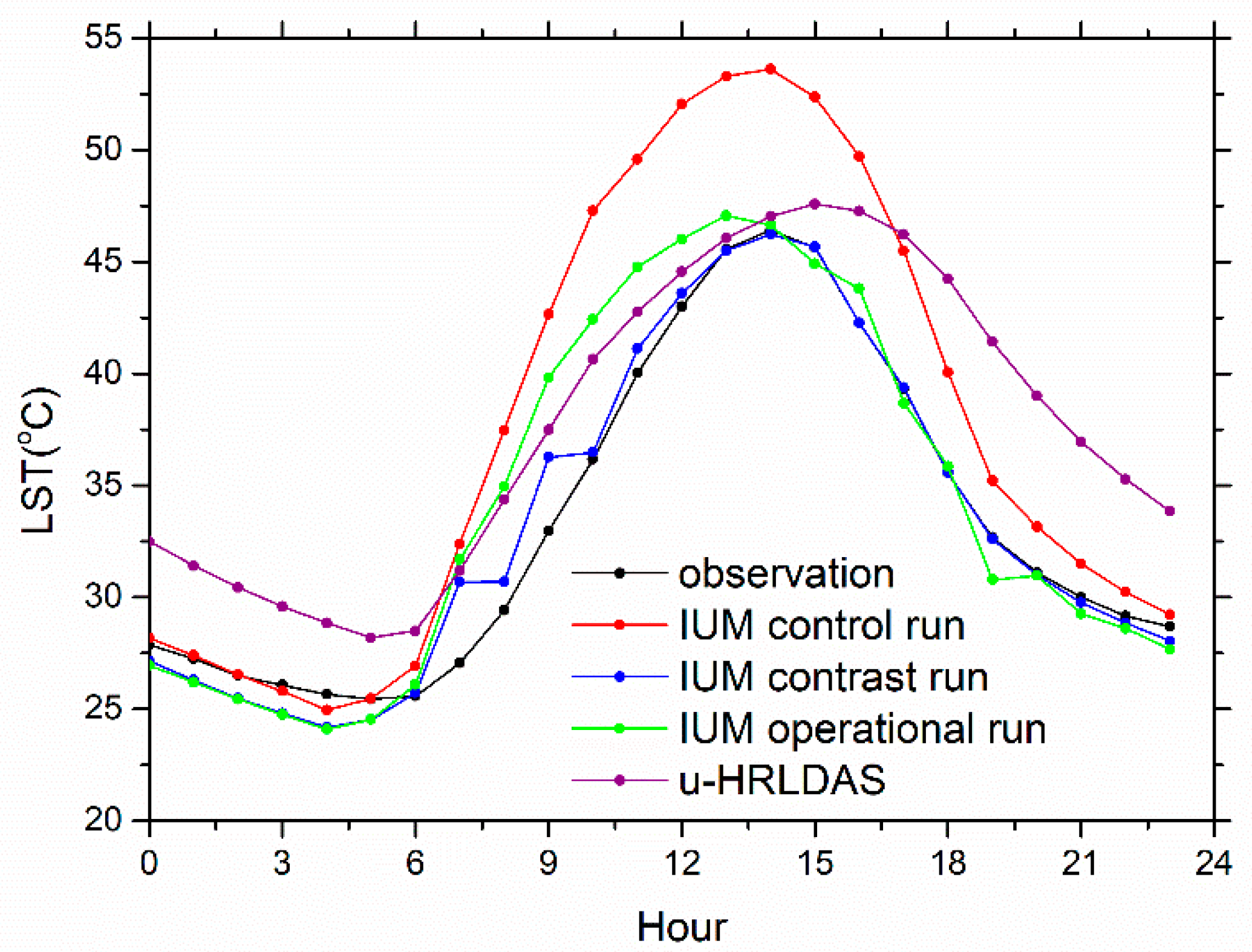
| Items | Bias (K) | ME (K) | RMSE (K) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before assim | 3.63 | 3.93 | 5.53 | 0.947 |
| After assim | 0.15 | 0.81 | 1.46 | 0.988 |
| Before assim (day) | 5.48 | 5.51 | 6.44 | 0.945 |
| After assim (day) | 0.78 | 0.85 | 1.7 | 0.989 |
| Before assim (night) | 0.58 | 1.11 | 1.44 | 0.941 |
| After assim (night) | −0.69 | 0.75 | 1.05 | 0.981 |
| Items | Bias (K) | ME (K) | RMSE (K) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control run | 4.22 | 4.52 | 6.31 | 0.936 |
| Contrast run | 0.11 | 0.88 | 1.63 | 0.982 |
| Operational run | 0.94 | 2.92 | 4.33 | 0.896 |
| u-HRLDAS | 4.41 | 4.95 | 5.73 | 0.902 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, C. Variational Assimilation of the Impervious Surfaces Temperature. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040380
Meng C. Variational Assimilation of the Impervious Surfaces Temperature. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Chunlei. 2020. "Variational Assimilation of the Impervious Surfaces Temperature" Atmosphere 11, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040380
APA StyleMeng, C. (2020). Variational Assimilation of the Impervious Surfaces Temperature. Atmosphere, 11(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040380




