Multi-Sensor Observation of a Saharan Dust Outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Instruments and Method
2.1. Cimel CE 318 Sun Photometer
2.2. Multi-Wavelength Raman and Depolarization Lidar
2.3. MODIS Retrievals
2.4. Modelling Tools
2.5. In-Situ Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
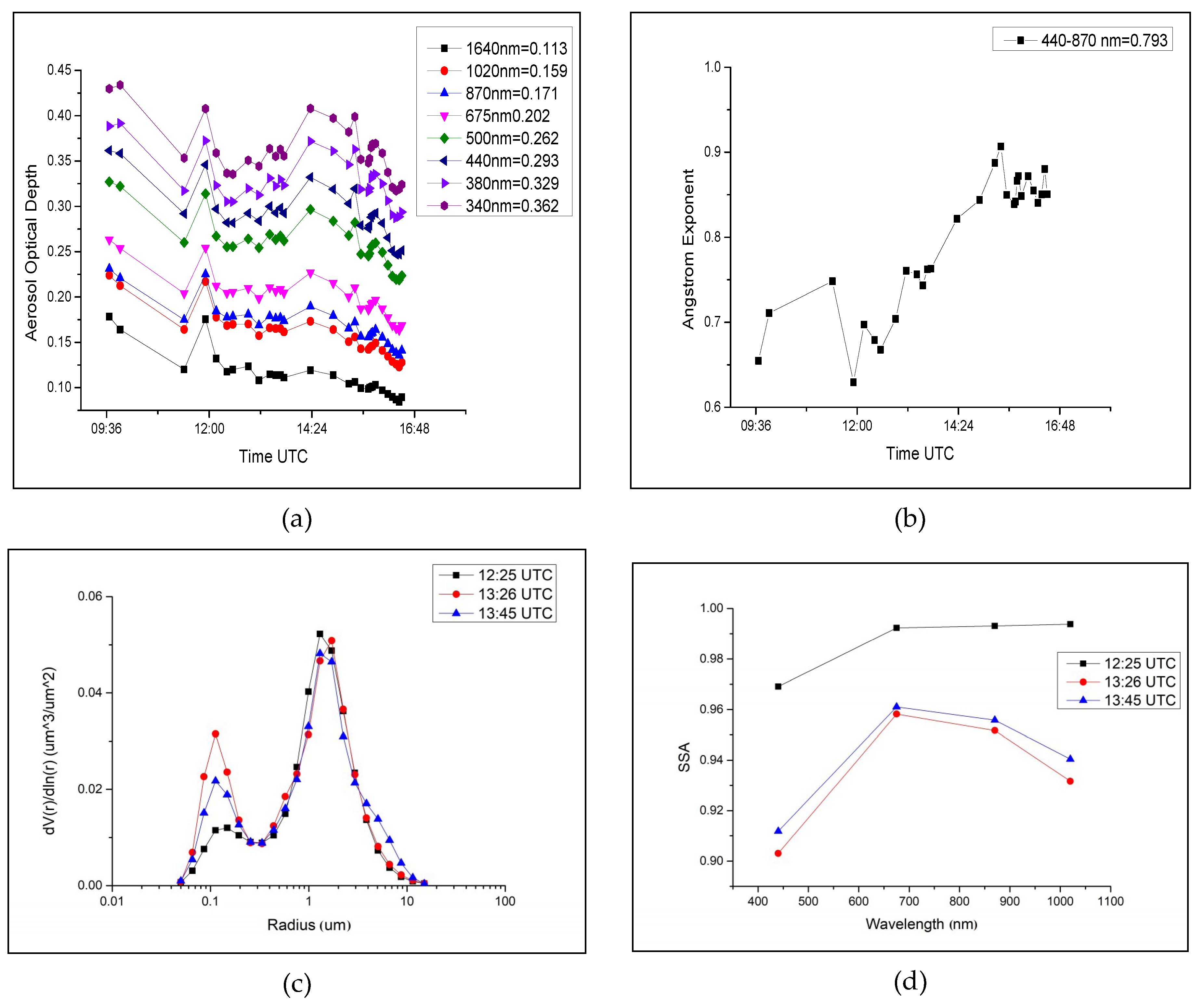
3.1. Sun Photometer Data Analysis
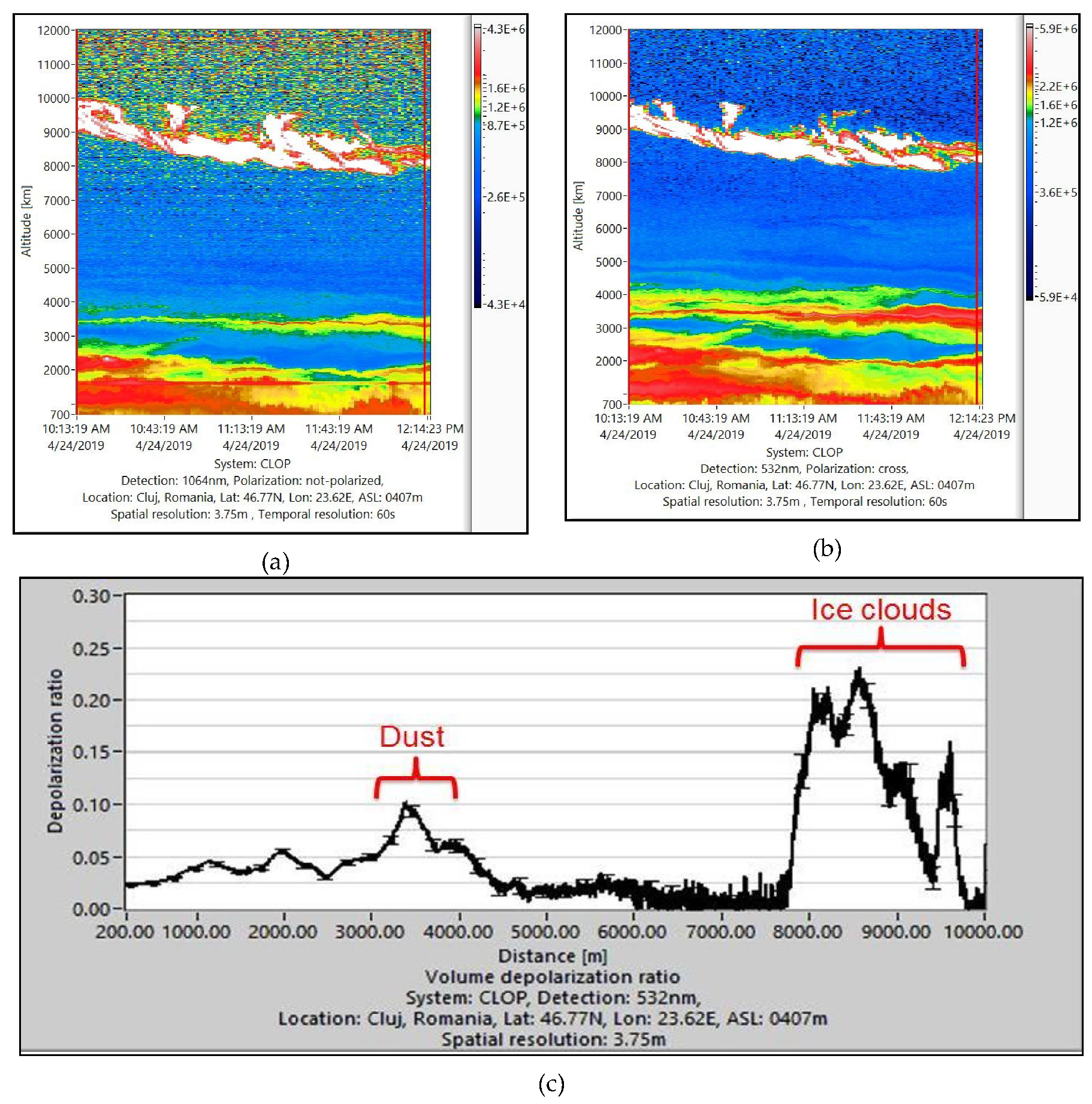
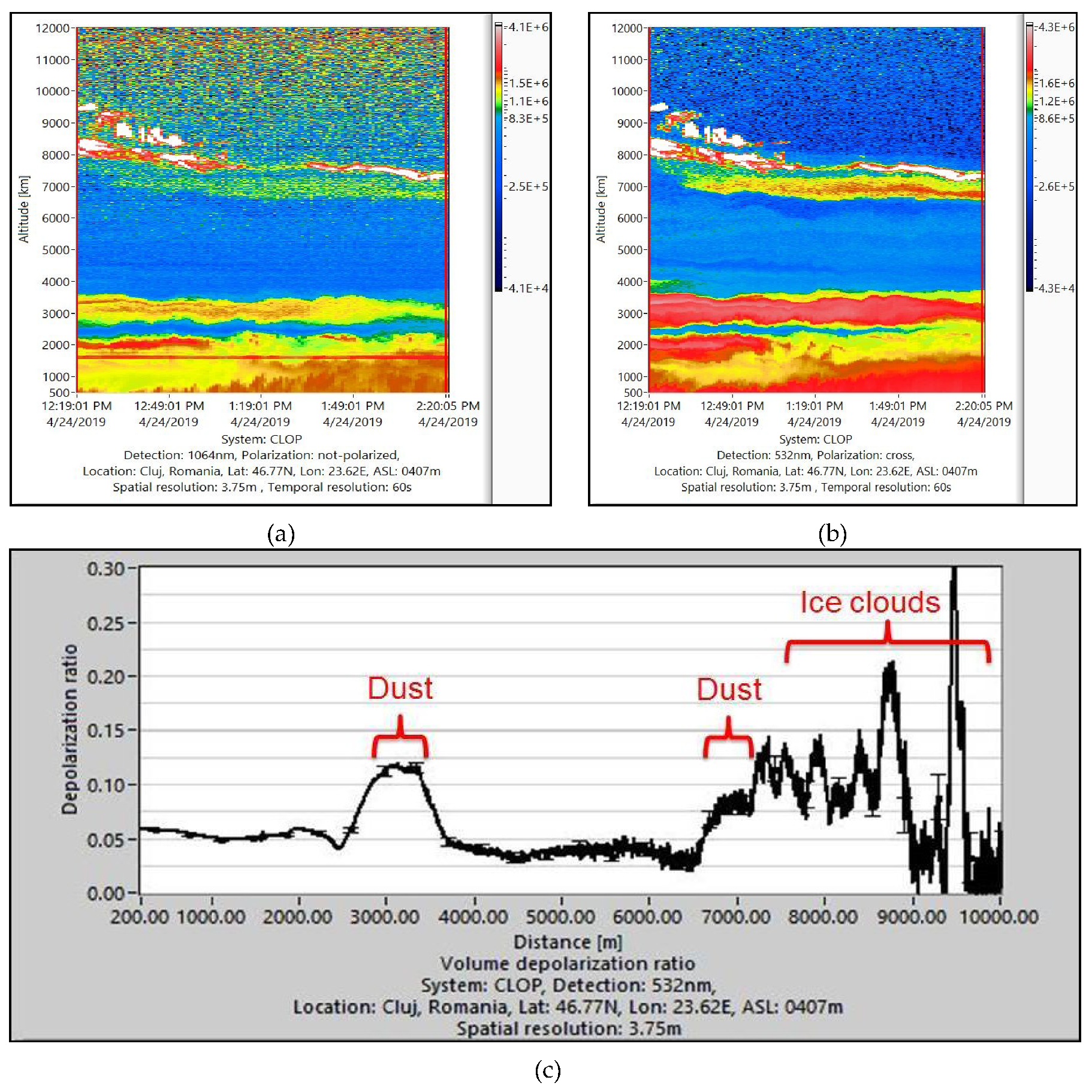
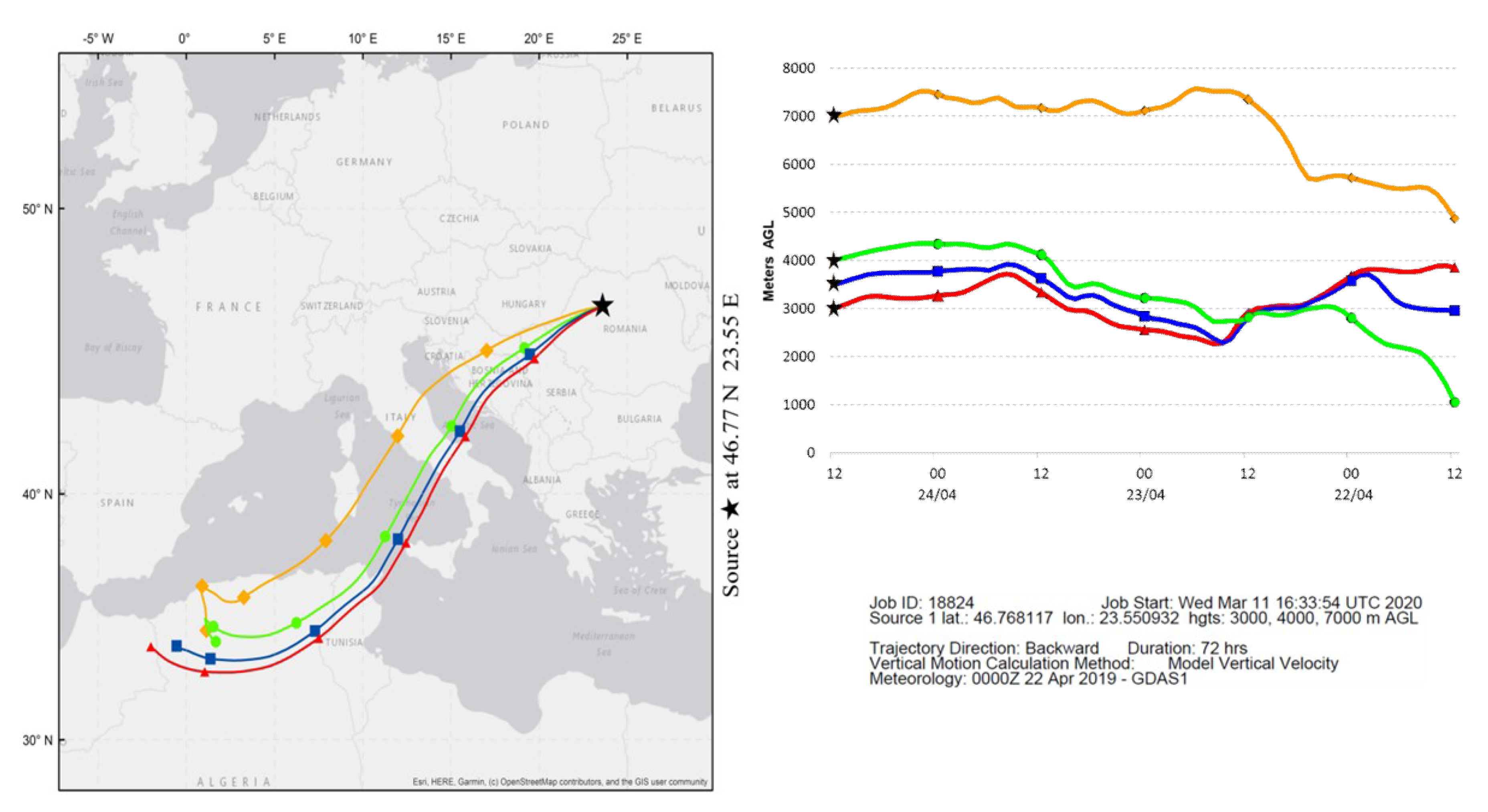
3.2. Lidar Data Analysis
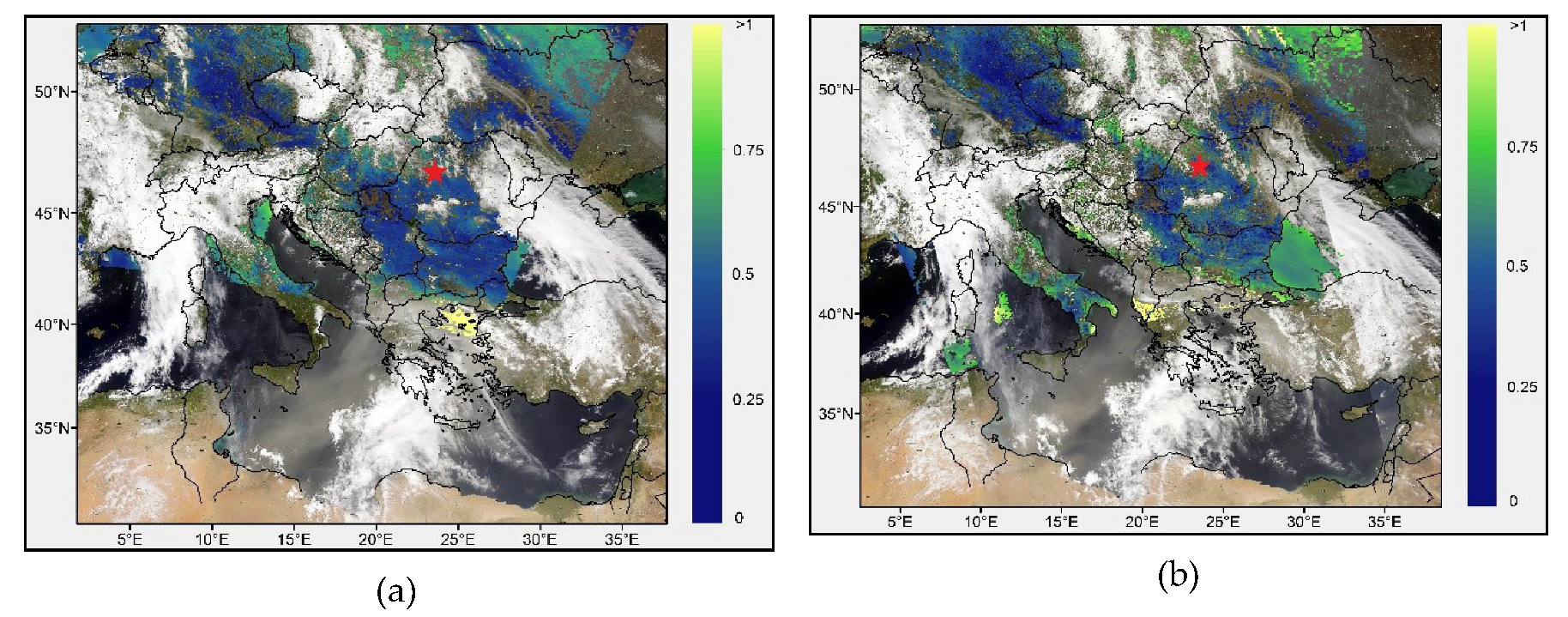
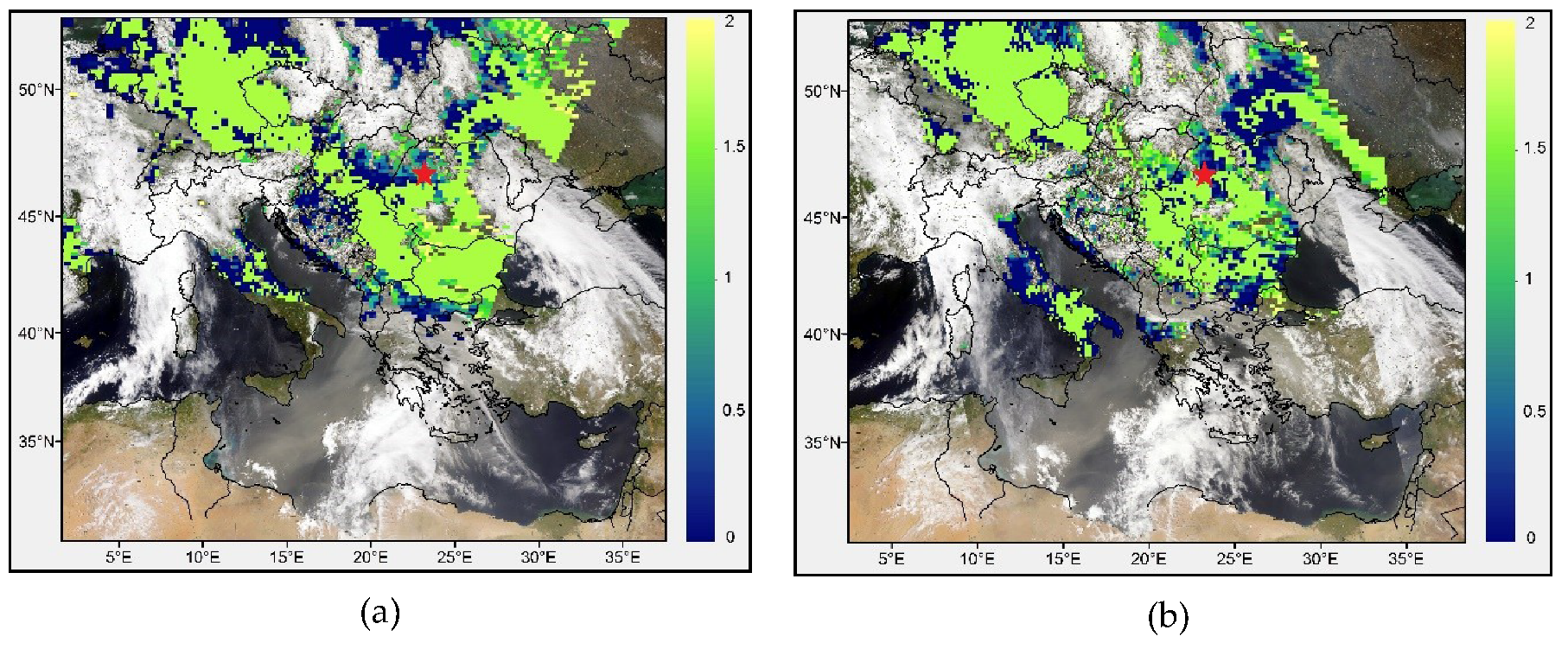
3.3. MODIS Data Analysis
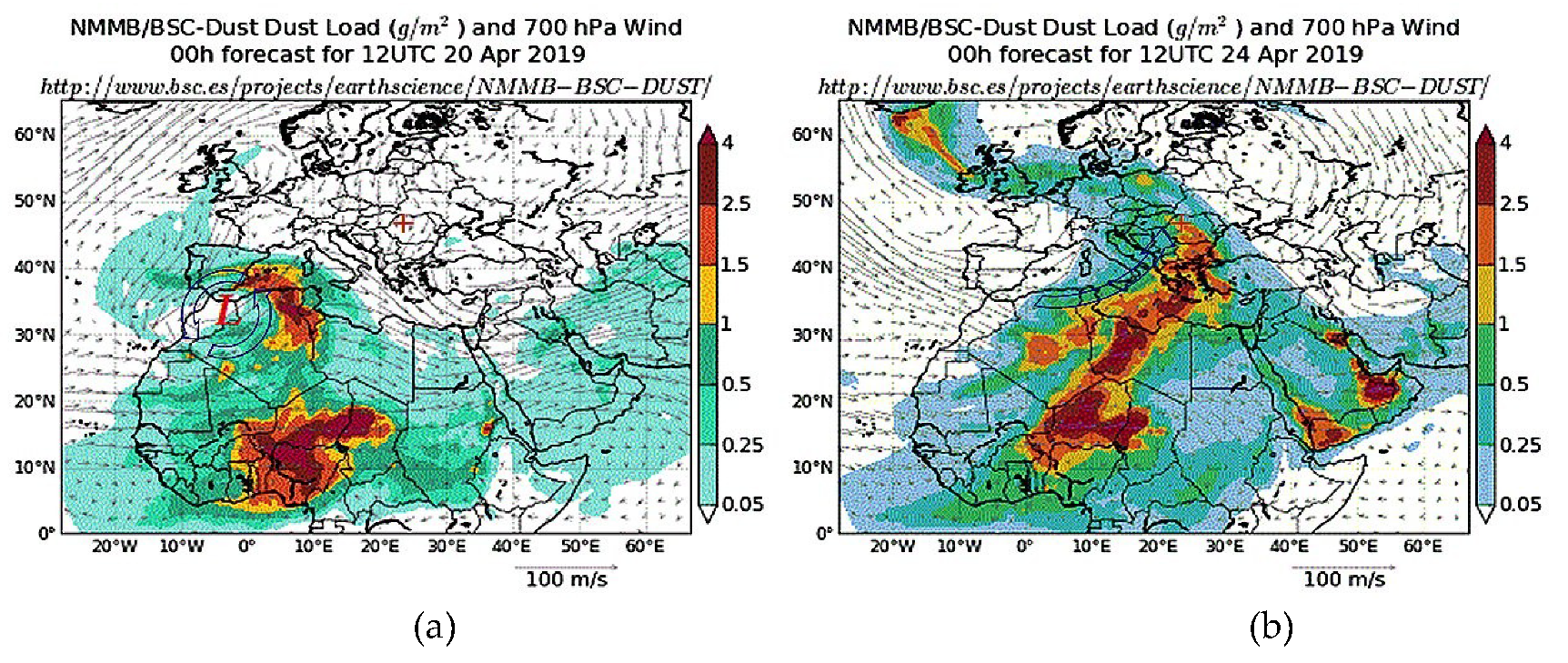
3.4. Modelling Data Analysis
3.5. In-Situ Ground Measurements Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013–The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.; Linares, C.; Carmona, R.; Russo, A.; Ortiz, C.; Salvador, P.; Trigo, R.M. Saharan dust intrusions in Spain: Health impacts and associated synoptic conditions. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafoggia, M.; Zauli-Sajani, S.; Pey, J.; Samoli, E.; Alessandrini, E.; Basagaña, X.; Cernigliaro, A.; Chiusolo, M.; Demaria, M.; Díaz, J.; et al. MED-PARTICLES Study Group. Desert dust outbreaks in Southern Europe: Contribution to daily PM10 concentrations and short-term associations with mortality and hospital admissions. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, N.; Polenske, K.R. Socioeconomic impact analysis of yellow-dust storms: An approach and case study for Beijing. Econ. Syst. Res. 2008, 20, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hemoud, A.; Al-Sudairawi, M.; Neelamanai, S.; Naseeb, A.; Behbehani, W. Socioeconomic effect of dust storms in Kuwait. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M. Climate effects of changing atmospheric aerosol levels. In World Survey of Climatology, Future Climate of the World; Henderson Sellers, A.H., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 16, pp. 341–392. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolae, V.; Talianu, C.; Andrei, S.; Antonescu, B.; Ene, D.; Nicolae, D.; Dandocsi, A.; Toader, V.-E.; Ștefan, S.; Savu, T.; et al. Multiyear Typology of Long-Range Transported Aerosols over Europe. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Amiridis, V.; Mona, L.; Tsaknakis, G.; Balis, D.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovski, A.; De Tomasi, F.; Grigorov, I.; Mattis, I.; et al. Systematic lidar observations of Saharan dust over Europe in the frame of EARLINET (2000–2002). J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Almeida, S.M.; Cardoso, J.; Almeida-Silva, M.; Nunes, T.; Cerqueira, M.; Alves, C.; Reis, M.A.; Chaves, P.C.; Artinano, B.; et al. Composition and origin of PM10 in Cape Verde: Characterization of long-range transport episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; D’Odorico, P.; Breshears, D.D.; Field, J.P.; Goudie, A.S.; Huxman, T.E.; Li, J.; Okin, G.S.; Swap, R.J.; Thomas, A.D.; et al. Aeolian processes and the biosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; Mctainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Pey, J.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Cusack, M.; Pérez, N.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kallos, G.; et al. African dust contributions to mean ambient PM10 mass-levels across the Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallos, G.; Astitha, M.; Katsafados, P.; Spyrou, C. Long-Range Transport of Anthropogenically and Naturally Produced Particulate Matter in the Mediterranean and North Atlantic: Current State of Knowledge. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 1230–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamancusa, C.; Wagstrom, K. Global transport of dust emitted from different regions of the Sahara. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, M.; Barragan, R.; Dulac, F.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Mallet, M. Aerosol optical, microphysical and radiative properties at regional background insular sites in the western Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12177–12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, E.; Gómez-Peláez, A.J.; Rodríguez, S.; Terradellas, E.; Basart, S.; Garcia, R.D.; Garcia, O.E.; Alonso-Perez, S. The pulsating nature of large-scale Saharan dust transport as a result of interplays between mid-latitude Rossby waves and the North African Dipole Intensity. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.; Amodeo, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Pappalardo, G. Saharan dust intrusions in the Mediterranean area: Three years of Raman lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelevich, P.; Ganor, E.; Alpert, P.; Kishcha, P.; Stupp, A. Predominant transport paths of Saharan dust over the Mediterranean Sea to Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, L.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Veselovskii, I.; Baars, H. Temporal variations in optical and microphysical properties of mineral dust and biomass burning aerosol derived from daytime Raman lidar observations over Warsaw, Poland. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.; Malavelle, F.F.; Adam, M.; Buxmann, J.; Sugier, J.; Marenco, F.; Haywood, J. Saharan dust and biomass burning aerosols during ex-hurricane Ophelia: Observations from the new UK lidar and sun-photometer network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3557–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bègue, N.; Tulet, P.; Chaboureau, J.-P.; Roberts, G.; Gomes, L.; Mallet, M. Long-range transport of Saharan dust over northwestern Europe during EUCAARI 2008 campaign: Evolution of dust optical properties by scavenging. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.; Metzger, S.; Mamouri, R.E.; Astitha, M.; Barrie, L.; Levin, Z.; Lelieveld, J. Dust–air pollution dynamics over the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9173–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ștefănie, H.; Ajtai, N.; Botezan, C.; Țoancă, F.; Török, Z.; Ozunu, A. Detection of a desert dust intrusion over ClujNapoca, Romania using an elastic backscatter LIDAR system. Ecoterra-J. Environ. Res. Prot. 2015, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tudose, O.G. Contributions to the Study of Atmospheric Aerosols Optical Properties Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iasi, Iasi, Romania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rogora, M.; Mosello, R.; Marchetto, A. Long-term trends in the chemistry of atmospheric deposition in Northwestern Italy: The role of increasing Saharan dust deposition. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2004, 56, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, N.; D’Amico, G.; Gialitaki, A.; Ajtai, N.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Amiridis, V.; Baars, H.; Balis, D.; Binietoglou, I.; et al. An EARLINET Early Warning System for atmospheric aerosol aviation hazards. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020. in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazacu, M.M.; Tudose, O.G.; Timofte, A.; Rusu, O.; Apostol, L.; Leontie, L.; Gurlui, S. A case study of the behavior of aerosol optical properties under the incidence of a saharan dust intrusion event. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 14, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labzovskii, L.; Toanca, F.; Nicolae, D. Determination of saharan dust properties over bucharest, Romania part 2: Study cases analysis. Rom. J. Phys. 2014, 59, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Gothard, M.; Nemuc, A.; Radu, C.; Dascalu, S. An intensive case of saharan dust intrusion over south east Romania. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2014, 66, 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Rosu, I.A.; Cazacu, M.M.; Prelipceanu, O.S.; Agop, M. A Turbulence-Oriented Approach to Retrieve Various Atmospheric Parameters Using Advanced Lidar Data Processing Techniques. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, N.; Stefanie, H.; Arghius, V.; Meltzer, M.; Costin, D. Characterization of Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties Over North-Western Romania In Correlation with Predominant Atmospheric Circulation Patterns. In Proceedings of the 17th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geoconference (SGEM 2017), Albena, Bulgaria, 29 June–5 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, N.; Ștefănie, H.; Ozunu, A. Description of aerosol properties over Cluj-Napoca derived from AERONET sun photometric data. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2013, 12, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talianu, C.; Nemuc, A.; Nicolae, D.; Cristescu, C.P. Dust Event Detection from Lidar Measurements. Sci. Bull. Politeh. Univ. Buchar. Ser. A Appl. Math. Phys. 2007, 69, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cazacu, M.M.; Tudose, O.; Boscornea, A.; Buzdugan, L.; Timofte, A.; Nicolae, D. Vertical and temporal variation of aerosol mass concentration at Magurele–Romania during EMEP/PEGASOS campaign. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2017, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mărmureanu, L.; Marin, C.A.; Andrei, S.; Antonescu, B.; Ene, D.; Boldeanu, M.; Vasilescu, J.; Vițelaru, C.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E. Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severe Weather Europe. Available online: http://www.severe-weather.eu/mcd/extent-of-airborne-saharan-dust-over-europe-on-wednesday-and-thursday/ (accessed on 3 October 2019).
- Pappalardo, G.; Amodeo, A.; Apituley, A.; Comeron, A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; et al. EARLINET: Towards an advanced sustainable 20 European aerosol lidar network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2389–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET-A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACTRIS. Available online: https://www.actris.eu/ (accessed on 6 September 2019).
- AERONET. Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Dubovik, O.; King, M. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Aerosol Research Lidar Network. Available online: https://www.earlinet.org (accessed on 18 September 2019).
- Freudenthaler, V. About the efects of polarising optics on lidar signals and the D90 calibration. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4181–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belegante, L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Nicolae, D.; Nemuc, A.; Ene, D.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Pappalardo, G.; D’Amico, G.; et al. Experimental techniques for the calibration of lidar depolarization channels in EARLINET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1119–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.-J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and merged data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J. Algorithm for Remote Sensing of Tropospheric Aerosol over Dark Targets from MODIS: Collections 005 and 051: Revision 2; MODIS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. 2009. Available online: https://atmosphere-imager.gsfc.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/ModAtmo/ATBD_MOD04_C005_rev2_0.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2019).
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.-C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model Access via NOAA ARL READY Website. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory. 2015; College Park. Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Pérez, C.; Haustein, K.; Janjic, Z.; Jorba, O.; Huneeus, N.; Baldasano, J.M.; Black, T.; Basart, S.; Nickovic, S.; Miller, R.L.; et al. An online mineral dust aerosol model for meso to global scales: Model description, annual simulations and evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13001–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.; King, M.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A.A. Using single-scattering albedo spectral curvature to characterize East Asian aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2037–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Gasteiger, J.; Freudenthaler, V.; Wiegner, M.; Geiß, A.; Schladitz, A.; Toledano, C.; Kandler, K.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; et al. Characterization of the planetary boundary layer during SAMUM-2 by means of lidar measurements. Tellus B 2011, 63, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Gross, S.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M. Profiling of Saharan dust and biomass-burning smoke with multiwavelength polarization Raman lidar at Cape Verde. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 649–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sokolik, I. Analysis of Dust Aerosol Retrievals Using Satellite Data in Central Asia. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, O.V.; Kahn, R.A. Mineral dust plume evolution over the Atlantic from MISR and MODIS aerosol retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupiona, O.; Samaras, S.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Böckmann, C.; Papayannis, A.; Moreira, G.A.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bedoya-Velasquez, A.E.; Olmo, F.J.; et al. Retrieval of optical and microphysical properties of transported Saharan dust over Athens and Granada based on multi-wavelength Raman lidar measurements: Study of the mixing processes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calitate Aer. Available online: www.calitateaer.ro (accessed on 25 September 2019).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajtai, N.; Ștefănie, H.; Mereuță, A.; Radovici, A.; Botezan, C. Multi-Sensor Observation of a Saharan Dust Outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040364
Ajtai N, Ștefănie H, Mereuță A, Radovici A, Botezan C. Multi-Sensor Observation of a Saharan Dust Outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(4):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjtai, Nicolae, Horațiu Ștefănie, Alexandru Mereuță, Andrei Radovici, and Camelia Botezan. 2020. "Multi-Sensor Observation of a Saharan Dust Outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019" Atmosphere 11, no. 4: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040364
APA StyleAjtai, N., Ștefănie, H., Mereuță, A., Radovici, A., & Botezan, C. (2020). Multi-Sensor Observation of a Saharan Dust Outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019. Atmosphere, 11(4), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040364





