Generation of Viable Bacterial and Fungal Aerosols during Biomass Combustion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Laboratory Investigation-Microorganisms’ Survivability during Combustion
2.1.1. Bacterial Strains and Cultivation
2.1.2. Samples Preparation
2.1.3. Laboratory Set-Up
2.1.4. Combustion and Bioaerosol Collection
2.1.5. Ash Aerosolization
2.2. Field Investigation–Generation of Bioaerosols during Biomass Combustion
2.2.1. 5 August 2018, Cainbable, Queensland
2.2.2. 28 June 2019, Dirranbandi, Outback Queensland
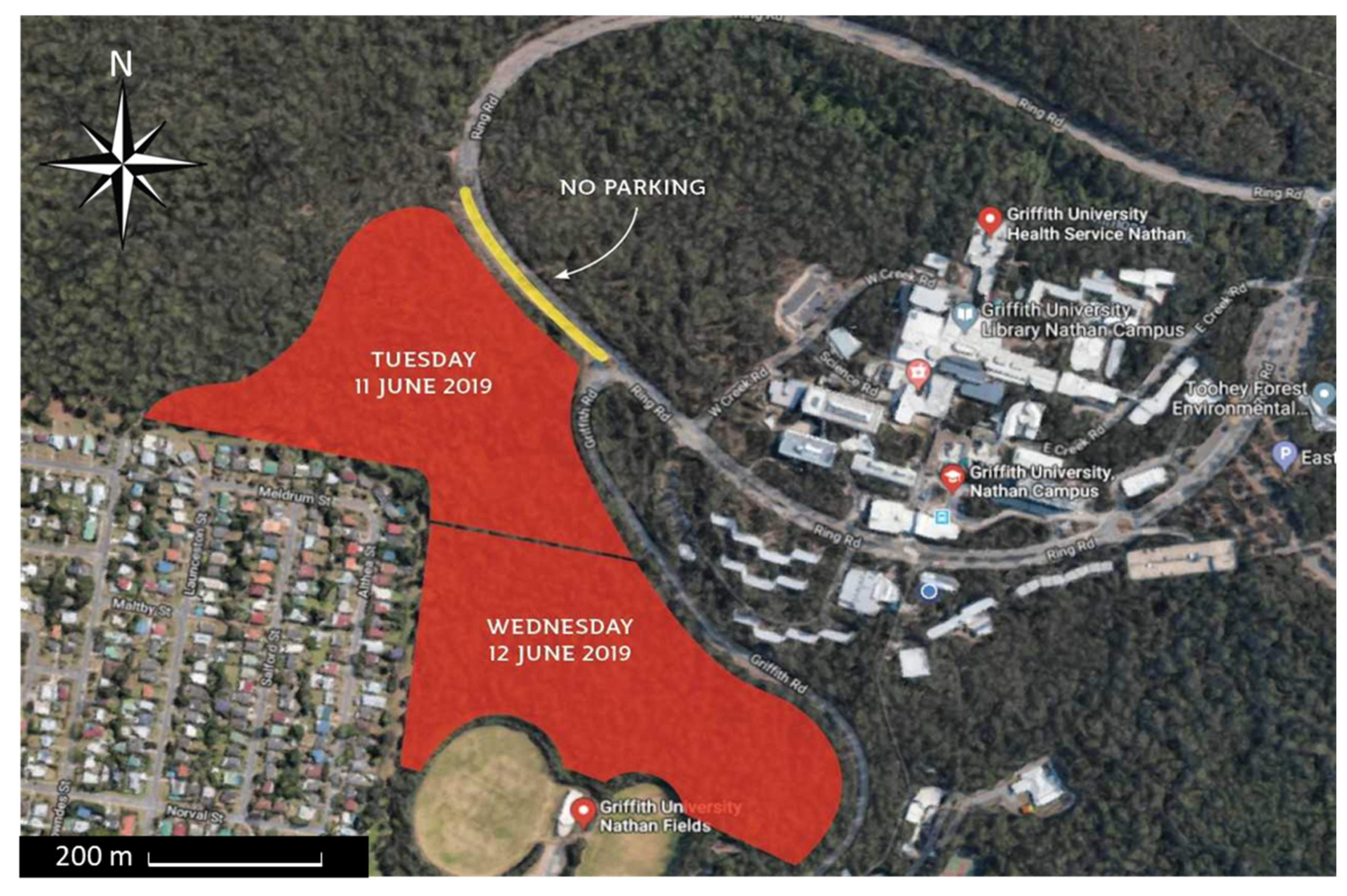
2.2.3. 11 and 12 June 2019, Nathan Campus of Griffith University
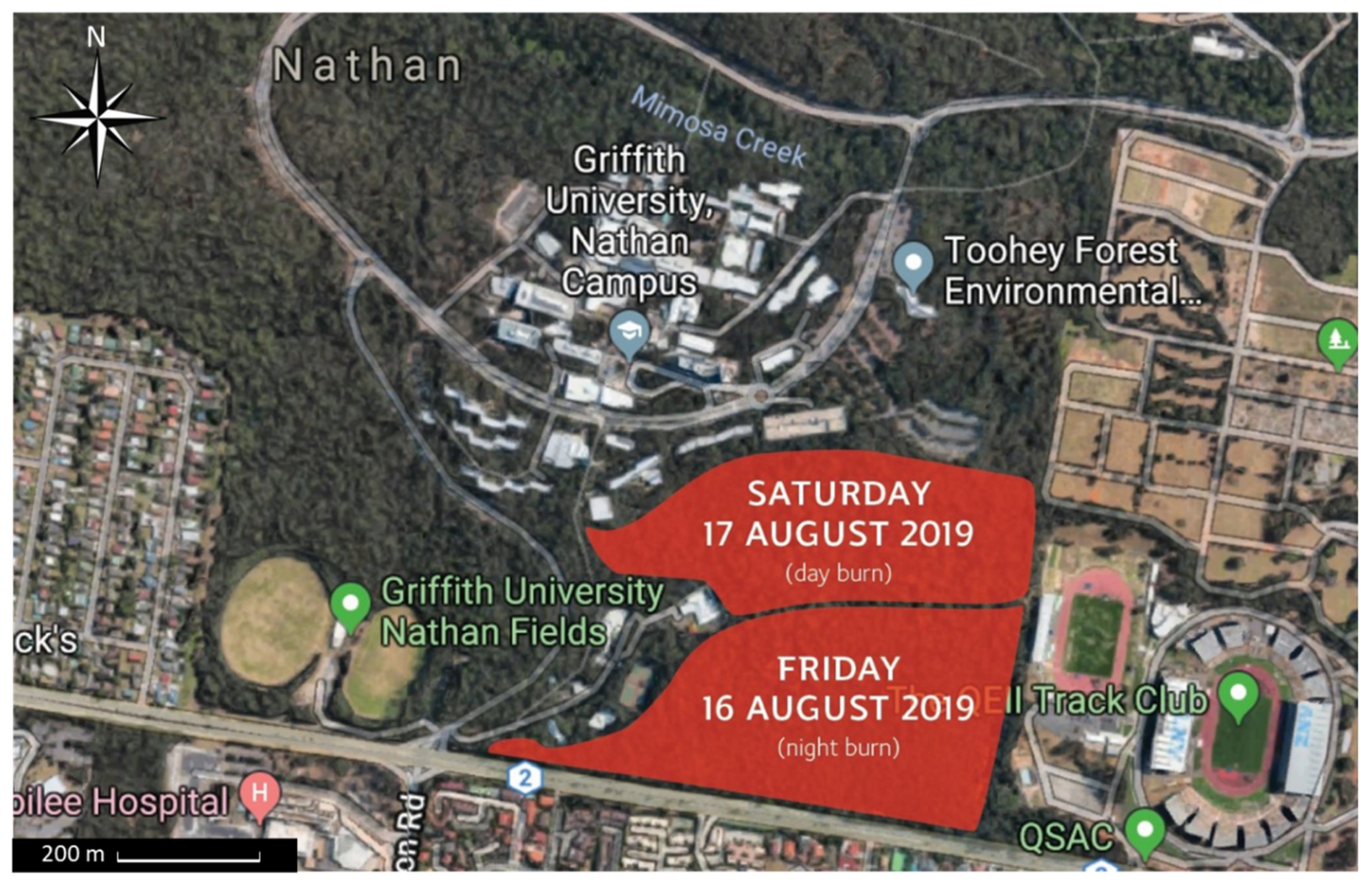
2.2.4. 17 and 18 August 2019, Nathan Campus of Griffith University
3. Results
3.1. Contaminated Material Combustion and Bioaerosol Collection
3.2. Generation of Bioaerosols during Biomass Combustion
3.3. Prescribed Burning Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.S. Thermal effects on bacterial bioaerosols in continuous air flow. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, E.F.; Reponen, T.; Succop, P. Evaluation of bioaerosol components, generation factors, and airborne transport associated with lime treatment of contaminated sediment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirskaya, E.; Agranovski, I.E. Generation of bacterial aerosols by interaction of microbial suspension with hot surfaces. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2017, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.H.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109, D14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, C.A.; Lemieux, C.L.; Long, A.S.; Kystol, J.; Vogel, U.; White, P.A.; Madsen, A.M. Physical-chemical and microbiological characterization, and mutagenic activity of airborne PM sampled in a biomass-fueled electrical production facility. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 2011, 52, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, A.; Campleman, S.; Long, C.; Peterson, M.; Weatherstone, S.; Quick, W.; Lewis, A. Potential occupational exposures and health risks associated with biomass-based power generation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8542–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, S.; Laitinen, J.; Fagernäs, L.; Korpijärvi, K.; Korpinen, L.; Ojanen, K.; Jokiniemi, J. Exposure to biological and chemical agents at biomass power plants. Biomass Bioenerg. 2016, 93, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, S.; Devakumar, D.; Fullerton, D.G.; Thorne, P.S.; Metwali, N.; Costello, A.; Ayres, J.G. Airborne endotoxin concentrations in homes burning biomass fuel. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.; Miller, D.; Ruest, K.; Guay, M.; Judek, S. Airborne endotoxin is associated with respiratory illness in the first 2 years of life. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 114, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, I.; Góis, A.; Camacho, R.; Nóbrega, V.; Fernandez. The impact of urban and forest fires on the airborne fungal spore aerobiology. Aerobiologia 2018, 34, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Lv, G. Characteristics of atmospheric bacterial and fungal communities in PM2. 5 following biomass burning disturbance in a rural area of North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agranovski, I.E.; Agranovski, V.; Reponen, T.; Willeke, K.; Grinshpun, S.A. Development and evaluation of a new personal sampler for culturable airborne microorganisms. ATM Environ. 2002, 36, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agranovski, I.E.; Pyankov, O.V.; Altman, I.S. Bioaerosol contamination of ambient air as the result of opening envelopes containing microbial materials. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 2005, 39, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobziar, L.N.; Pingree, M.R.; Larson, H.; Dreaden, T.J.; Green, S.; Smith, J.A. Pyroaerobiology: The aerosolization and transport of viable microbial life by wildland fire. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Short-term effects of biomass burning on soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J.; Hallgren, S.W.; Wilson, G.W. Frequency of prescribed burning in an upland oak forest determines soil and litter properties and alters the soil microbial community. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 265, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, T.; Whitman, E.; Woolet, J.; Flannigan, M.D.; Thompson, D.K.; Parisien, M.A. Soil bacterial and fungal response to wildfires in the Canadian boreal forest across a burn severity gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Guo, H. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovicheva, O.; Kistler, M.; Kireeva, E.; Persiantseva, N.; Timofeev, M.; Kopeikin, V.; Kasper-Giebl, A. Physicochemical characterization of smoke aerosol during large-scale wildfires: Extreme event of August 2010 in Moscow. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Lucarelli, F.; Amato, F.; Becagli, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Udisti, R. Biomass burning contributions estimated by synergistic coupling of daily and hourly aerosol composition records. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Park, W.M. Concentrations of PM 10 and airborne bacteria in daycare centers in Seoul relative to indoor environmental factors and daycare center characteristics. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Hu, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. The distribution variance of airborne microorganisms in urban and rural environments. Environ. Pollut 2019, 247, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, P.; Anjum, M.H.; Gupta, T. One year record of bioaerosols and particles concentration in Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of biomass burning emissions to high-level of endotoxin exposure. Environ Pollut 2017, 224, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Kawamura, K.; Fu, P.; Bikkina, S.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z. Impact of biomass burning on soil microorganisms and plant metabolites: A view from molecular distributions of atmospheric hydroxy fatty acids over Mount Tai. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2684–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Vicente, E.D.; Evtyugina, M.; Vicente, A.; Pio, C.; Amado, M.F.; Mahía, P.L. Gaseous and speciated particulate emissions from the open burning of wastes from tree pruning. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Tao, J.; Lin, M.; Engling, G.; Zhang, Z.; Su, L. Observation of elevated fungal tracers due to biomass burning in the Sichuan Basin at Chengdu City, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 431, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.A.; Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; Fortier, K.; Chow, J.C.; Alonzo, F.; Cruz, P. Evaluation of epifluorescence methods for quantifying bioaerosols in fine and coarse particulate air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, E.V.; Skowronski, N.; Thomas, J.C.; Clark, K.; Gallagher, M.R.; Hadden, R.; Simeoni, A. Local measurements of wildland fire dynamics in a field-scale experiment. Combust Flame 2018, 194, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Units | Before Combustion | Post Combustion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Filter | Leaf Matter | Paper Filter | Leaf Matter | ||
| Mass | g | 0.65(±0.01) | 1.89(±0.28) | 0.04(±0.00) | 0.71(±0.11) |
| Concentration | CFU/g | 2.51(±0.38) × 106 | 6.33(±0.95) × 103 | 6.90(±1.04) × 105 | 1.13(±0.17) × 103 |
| Mass reduction | % | - | - | 94% | 62% |
| Bacteria recovery | % | - | - | 28% | 18% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirskaya, E.; Agranovski, I.E. Generation of Viable Bacterial and Fungal Aerosols during Biomass Combustion. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030313
Mirskaya E, Agranovski IE. Generation of Viable Bacterial and Fungal Aerosols during Biomass Combustion. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirskaya, Ekaterina, and Igor E. Agranovski. 2020. "Generation of Viable Bacterial and Fungal Aerosols during Biomass Combustion" Atmosphere 11, no. 3: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030313
APA StyleMirskaya, E., & Agranovski, I. E. (2020). Generation of Viable Bacterial and Fungal Aerosols during Biomass Combustion. Atmosphere, 11(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030313





