Abstract
Mineral dust composition affects a multitude of processes in the atmosphere and adjacent compartments. Dust dry deposition was collected near source in northwest Africa, in Central Asia, and on Svalbard and at three locations of the African outflow regime. Samples were subjected to automated scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis to obtain size and composition of 216,000 individual particles. Results show low temporal variation in estimated optical properties for each location, but considerable differences between the African, Central Asian, and Arctic regimes. No significant difference was found between the K-feldspar relative abundances, indicating comparable related ice-nucleation abilities. The mixing state between calcium and iron compounds was different for near source and transport regimes, potentially in part due to size sorting effects. As a result, in certain situations (high acid availability, limited time) atmospheric processing of the dust is expected to lead to less increased iron solubility for near-source dusts (in particular for Central Asian ones) than for transported ones (in particular of Sahelian origin).
1. Introduction
Mineral dust is one of the most important and prominent aerosol types and affects many processes in the Earth system [1,2]. In addition to the importance of its microphysical properties [3,4], dust composition plays a crucial role for several processes. With regard to radiative forcing, in the solar radiation spectrum iron oxides are dominating its absorption effects [5,6], whereas in the terrestrial spectrum major mineral groups like calcite, kaolinite, and quartz impact on the optical properties [7,8]. Indirectly, this absorption can change atmospheric stability, which modifies the cloud processes [9]. Moreover, dust composition also directly impacts on cloud microphysics by supplying materials suitable to act as ice-nucleating particles [10,11,12] and giant cloud condensation nuclei [13]. Certain dust compounds also interact with atmospheric gaseous and liquid phases of particles by providing suitable surfaces for heterogeneous reactions [14,15], acting as a catalyzer or promoting photochemical reactions [16,17], or reacting, for example, with atmospheric acids [18,19].
Dust composition also affects the marine and terrestrial biosphere by supplying nutrients, but also supplying substances with adverse health effects [20]. Tropical as well as extra-tropical ecosystems apparently rely in part on atmospheric inputs [21,22]. Ocean surface waters can be depleted in essential nutrients supplied by the dust [23,24], thus composition plays an important role [25,26].
Several of these effects are not only affected by the overall composition, but also by the distribution of the compounds between the particles (i.e., internal or external mixing). For example, optical properties are strongly dependent on the mixing state [27,28]. In addition, chemical processes might be considerably affected by the particle mixing state [29].
Consequently, a more detailed knowledge of dust composition is expected to yield a better understanding and increased model quality. Information on bulk aerosol is available with respect to different properties (e.g., [6,7,30,31]) and finds its way into models [32]. In contrast, detailed properties like the aerosol mixing state are generally not yet regarded, probably due to scarcity of this information.
In the present study, dust from different transport regimes—African near-source and outflow, Central Asian near-source, and a high-latitude source—is analyzed to provide information on its composition and variation. With respect to the importance of the mixing state, a single particle attempt was chosen. A particular focus of this study is the distribution of iron amongst individual particles, and its internal mixture with calcium compounds, as the iron compounds are of high interest for different processes. These processes include radiation absorption, photocatalytic reactions, and ocean fertilization.
2. Experiments
Atmospheric aerosol dry deposition was collected at different places using two types of passive samplers: ‘flat plate’ and ‘Sigma-2′. Both samplers compare well for particle composition measurements in general [33]. For size distribution measurements, differences occur for particles larger than 10 µm in aerodynamic diameter. More details on the sampling techniques can be found elsewhere [33]. Each sample substrate was exposed to the atmospheric flow for 24–72 h, depending on the estimated aerosol concentrations. Particles were collected in the Sahara Desert, the Saharan outflow, in Central Asia, and for comparison near an extra-tropical source on Svalbard, North Atlantic Ocean (see Table 1 and Figure 1 for details).

Table 1.
Measurement locations and time periods, collector type, number of samples, number of particles analyzed, and reference/data reference. ‘Alt’ denotes the altitude above sea level in m.
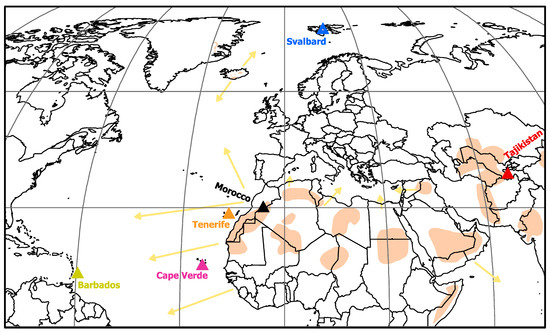
Figure 1.
Map of the measurement locations, dust sources, and major transport pathways. Sources and pathways were drawn according to literature information [30,31,45,46,47,48,49,50].
Particles were collected on carbon adhesive tabs (Plano Spectrotabs, Wetzlar, Gemany). Samples were stored at dry conditions at room temperature. Without further treatment (e.g., coating), samples were subject to automated scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis (SEM-EDX). As a result, for each particle the projected area diameter and the chemical composition as elemental contribution were available. Particles were analyzed in the size range of 0.7–50 µm projected area diameter. Details on the technique can be found elsewhere [42] and references therein. For the present study, only particles with dust compositions (“dust component”) were regarded. This includes mainly silicates like illite, kaolinite, smectites, feldspars, and quartz, carbonates like calcite and dolomite, gypsum, iron(III) oxide(-hydroxide)s like hematite and goethite, and apatite. This excludes mainly sulfate- (apart from gypsum) and sea-salt-like compositions from further data analysis (“non-dust component”). This was required due to the marine influence at some measurement locations.
Based on the single particle composition quantification, an element index for the element X was introduced [36,42] as
where the element symbols represent the relative contribution in atom% measured for each particle. Note C, N, and O are disregarded due to their high uncertainty and substrate contributions, so the element index is—without further calculation—no direct measure for the elemental contribution to the particle mass.
Particles are classified according to their composition into mineral analogy classes using rule sets for elemental ratios. As the basis, ideal compositions of the minerals are used, taking into account natural variability and measurement uncertainty [39]. For the present paper, only three particle groups with major clay mineral compositions are selected by this approach. The according rules are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Conditions for element-based major clay mineral identification. The element symbols represent the concentration in atom%. All conditions must be met. In addition, a low contribution of sea-salt-affine elements is required, defined by the additional condition: (|Na| + |Cl| + 2|S|)/(|Al| + |Si|) < 0.25. As no structural mineral analysis was carried out, the particle classes are termed ‘-like’ to express the similarity in chemical fingerprint.
In another approach, the particles are classified according to their Fe index. For , only the Fe index is used as a classification criterion, whereas for , an additional condition is used for ruling out the classification of particles dominated by non-silicate components (), for which this approach would lead to high uncertainty. In addition, from the iron content of the single particles, the imaginary part of the index of refraction at 470 nm wavelength (k470) is estimated following an empirical approach from Di Biagio et al. [51], who established a relationship between the iron content and the optical properties. To estimate the single particle iron content, the dust compounds Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, K, Ti, and Fe are assumed to exist in their oxidized form. Ca was assumed to be present as CaCO3; the small amounts of S as SO42−. At the end, the sample average refractive index is then calculated with a volume mixing rule [52].
A third approach focuses on the feldspar abundance. Feldspar and K-feldspar indices are defined (Appendix A), showing the similarity of the measured particle composition to a feldspar composition. As it was found that index values >0.8 identify a feldspar particle with high probability [42], this threshold value is used here to assess the contribution of feldspar particles to the total deposition. Note that for example a layer of clay minerals covering a feldspar grain might therefore prohibit the classification as (pure) feldspar.
Finally, the inter-particle mixing state of Ca and Fe compounds is assessed by classifying the particles into a matrix spanned by the Ca and Fe index. Note that this approach might misinterpret Ca-Fe-bearing minerals (e.g., certain groups of amphiboles) as internally mixed particles. However, these are usually trace to minor species [31,53]. As an estimate for Ca atmospheric processing, single particle apparent relative ion balances can be defined [42]. Here, we use the Ca-Mg-S relative ion balance, defined as
This relative ion balance is calculated for each particle. For example, in the case of unprocessed calcite it would become 1, for gypsum 0, and for ammonium sulfate −1.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the fingerprint of the deposition samples in terms of the clay mineral class compositions. Clearly, different geographical regions and atmospheric measurement regimes can be distinguished in the ternary diagram. The Saharan/Sahelian western outflow is dominated by kaolinite-like particles. This is the case for all measurements even though there are different transport patterns for altitudes above and below the trade wind inversion [54,55,56]. The dust observed near the arid source regions in Morocco shows a considerably higher contribution of illite-like particles. This is most probably linked to the composition of the more arid conditions in the Saharan region in comparison to the Sahel [57], which is frequently the source for more southerly transport observed at the other Atlantic Ocean locations [42,58,59,60]. All Saharan/Sahelian dusts show a comparatively low contribution of chlorite-like particles. The dust observed in Tajikistan, in contrast, has higher illite-like and chlorite-like contributions, potentially caused by the similarity to Morocco with respect to arid source regions close by and the geological basement [31]. Interestingly, Svalbard dust has even higher chlorite-like contributions. When looking at the variability of the Western Saharan/Sahelian outflow across the Atlantic Ocean, despite the separation distance of several thousands of kilometers for the measurement locations, it is comparatively low, demonstrating a relatively constant average composition.
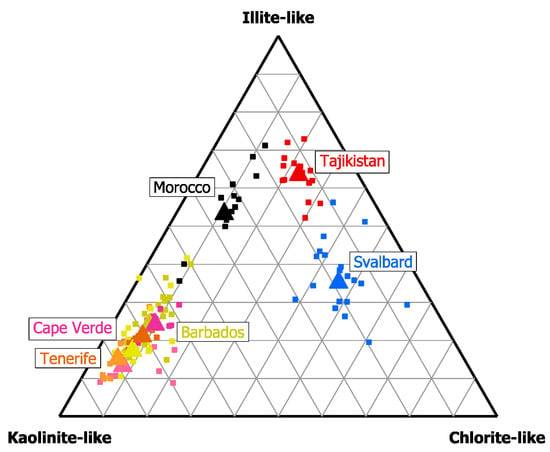
Figure 2.
Ternary diagram of the number abundances of major clay mineral compositions in dust dry deposition. Each data point represents one sample. Averages for the different locations are symbolized by the larger triangle. For Tenerife (orange), Cape Verde (rose), and Barbados (olive), data for two campaigns with according campaign averages are shown.
The iron distribution among the single silicate particles—commonly the dominating compositional type in dust—as a function of particle size is shown in Figure 3 along with the size distribution observed in the deposition. With respect to the latter, clearly the near-source locations (Figure 3a,e,f) can be distinguished by the transport (Figure 3b,c) and the deposition regime (Figure 3d) by the decreasing median particle sizes, as shown previously [61]. Generally, most of the silicate particles have a Fe index between 0.03 and 0.1, indicating that most of the iron is internally mixed with the silicate phases, either built into the crystal lattice, or as small oxide/oxyhydroxide grains [34,62,63,64]. Comparing the different regimes, one observes that the near-source samples from Morocco (Figure 3a) and Tajikistan (Figure 3e) are very similar with a relative high contribution of particles with low Fe index. The samples from the African outflow regime (Figure 3b–d) are nearly indistinguishable from each other, but with a slightly higher contribution of particles with higher Fe indices. This is corresponding to the clay mineral composition and probably related to the more iron-rich soils in the respective source regions [31]. The Arctic sample (Figure 3f) has a much higher iron contribution to the single particles, potentially related to the different weathering regime and geological basement. While the total iron content optical properties cannot be derived directly with high accuracy due to the varying contribution of structural iron [51,65], it was shown that estimates of the imaginary part of the refractive index obtained from composition measurements agree reasonably well with optical measurements [6,51]. For the size range of 4–20 µm (transported cross-section maximum), the total deposited aerosol imaginary part of the refractive index for 470 nm wavelength k470 is 0.4 × 10−3 at Tenerife and (0.6–0.7) × 10−3 at all other locations except for Svalbard, where it is 0.9 × 10−3. For particles between 1 µm and 4 µm diameter, values in Africa range between (0.4–0.8) × 10−3. Tajikistan (1.3 × 10−3) and Svalbard (3.2 × 10−3) show considerably higher values, owing to the different iron distribution. Note that due to the empirical estimate approach based on the iron content, the values for 370 nm and 660 nm can be estimated from the given data by multiplication by 1.345 and 0.476, respectively.
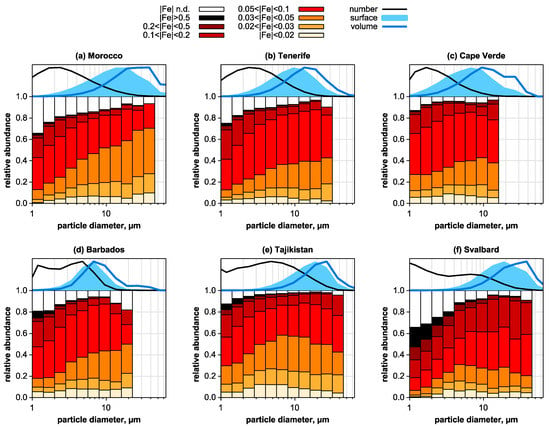
Figure 3.
Size-resolved abundance of silicate particles with different iron indices. (a) Morocco, (b) Tenerife, (c) Cape Verde, (d) Barbados, (e) Tajikistan, and (f) Svalbard. On the top, relative size distributions are given for the deposited silicate particles. Black line: number; shaded area: surface/cross-section; blue line: volume. Particle diameter is given as projected area diameter. ‘n.d.’ means not detected. Note that not all samples for (a) could be analyzed due to overloading of the sampler during dust storms, so the plot does not include dust storm days. Abundance bars are not shown for size intervals with less than 40 particles to avoid the presentation of data with high statistical uncertainty.
The feldspar relative number abundance for the different locations is shown in Figure 4 for total feldspars and for K-rich feldspars. K-rich feldspars were found to be highly efficient in acting as ice nuclei [66,67] and, therefore, are of particular interest for atmospheric processes. For most of the locations, a generally increasing trend of feldspar abundance with increasing particle size can be observed, which is possibly linked to particle mechanical stability and weathering sequence [57]. This trend is much stronger for the Central Asian and Arctic regime than for the African ones. The total feldspar contribution is also higher for these two regimes, indicating a different geological basement. In contrast, the K-feldspar abundance—generally on a low level—shows much less variation between the regimes.
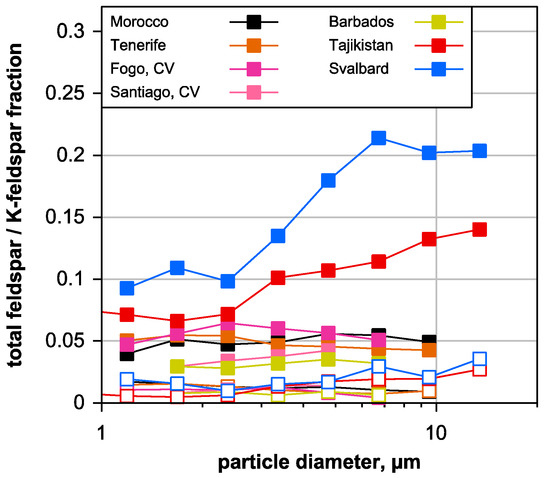
Figure 4.
Feldspar particle number abundance relative to the total deposited silicate particles as a function of aerodynamic particle diameter. Filled symbols show the total feldspar abundance, whereas open symbols depict the K-feldspar one. Only data points with less than 30% relative counting error (central 95% confidence interval, Poisson statistics) are shown.
The chemical processing of aerosol in the atmosphere is dependent on environmental conditions and time. Under suitable conditions, for example, iron can be transferred from a structural state into a more bio-available form like oxide grains [25,68]. In Figure 5, a simplified conceptual model is given for the processing of internally versus externally mixed particles between compounds with high and low reactivity. Calcium was chosen as a high-reactivity component, as it is the major constituent of the most reactive calcite and dolomite minerals. Iron was chosen as a low-reactivity compound due to its importance for atmospheric processes. The model should account for atmospheric processing being in part a non-equilibrium process. The axis indicates the amount of available reactive non-particulate species (e.g., acids) and the processing intensity, which can be a function of time or other environmental conditions, like humidity and temperature. For example, if there is plenty of acid available, but the processing intensity is low (e.g., lack of time due to dilution or rain-out), calcium compounds internally mixed with iron compounds in one particle may protect the iron compound from being processed [29]. If there is only a low amount of acid available, but plenty of time, the calcium compound might completely buffer the acid, so the iron compound would be less processed as well; however, in this case, the mixing state is probably of less importance, as the acid in a gaseous state probably follows the gradient to the strongest sinks (the calcium compound particles in our case). With an acid amount beyond the total calcium buffering capacity and a high processing intensity, the effect of the mixing state probably diminishes.
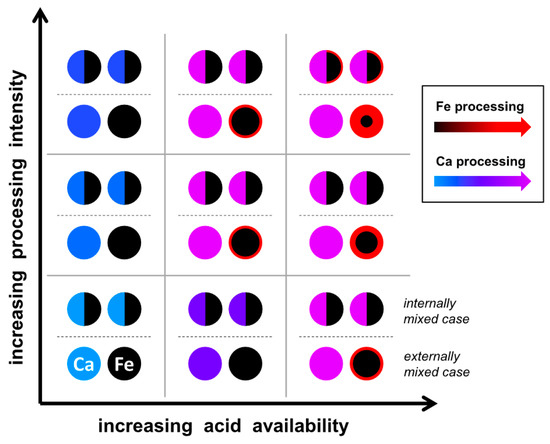
Figure 5.
Conceptual model of atmospheric acid processing for dust particles mixed internally or externally with respect to calcium and iron compounds.
A graphical summary of the internal mixing of calcium and iron based on the element indices is shown in Figure 6. The areas of the circles show the total mass of iron and calcium in each class, integrated over all samples. A 1:1 ratio of calcium to iron would be represented by two identical circles covering each other (i.e., only one circle would be visible). In addition, the calcium–sulfate processing is indicated by the color of the calcium circle. Note that nitric acid processing cannot be assessed reliably using the electron microscopy technique. Generally, for all locations (Figure 6a–f), a fraction of calcium and iron co-exist in the same particle. Most of the mass exists in two populations, which are more distinct in some places (Figure 6c,d) and show a gradual transition in others (Figure 6e,f). One population consists of particles with a Fe index between 0.05 and 0.1 and a low Ca index (<0.02) (i.e., silicates with iron and calcium content). The other consists of particles with a Fe index smaller than 0.05 and a high Ca index (>0.3) (e.g., calcite with iron oxide grains). The abundance, however, is different between the measurement locations.
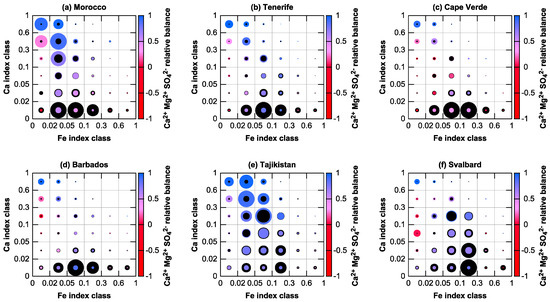
Figure 6.
Mixing state of iron (black circles) and calcium (colored circles) as functions of Ca and Fe indices for near-source (a,e,f) and transported (b–d) dust dry deposition. The circle area is proportional to total iron or calcium mass found in each class, normalized to the highest mass for each sampling location. The blue-red transition shows the average relative ion balance of Ca2+ + Mg2+ versus SO42−, indicating atmospheric processing.
While the African outflow locations are similar in appearance, near-source in Morocco and Tajikistan, many calcium-rich particles mixed with a non-negligible total mass of iron exist. In Tajikistan, even higher abundances of internal mixtures occur, which are present as concretions between silicates containing iron and calcium carbonate (Figure 7). In contrast to the Saharan dust, most of the iron in the Central Asian one is internally mixed with considerable amounts of calcium compounds. For Arctic dust, the situation is intermediate between the other two regimes, while the contribution of high-calcium compounds is low. Interestingly, the abundance of mixed particles is also a function of particles size. Except for Tenerife, it increases from 1 µm to 8 µm in particle diameter by a factor of 3–10 (i.e., for large particles these mixtures are more common). In conjunction with the large particle loss during transport (relative size distributions shown in Figure 3), this might explain partly the differences observed between near-source and transport regimes. Overall, 68–86% of the iron mass in the African samples are not mixed with calcium, and only 2–4% in the outflow and 11% near the source are mixed with considerable amounts (|Ca| > 0.1). In Central Asia, only 51% of the iron mass are not mixed with calcium and 15% are mixed with considerable amounts. Again, Arctic dust is intermediate (62% and 11%, respectively).
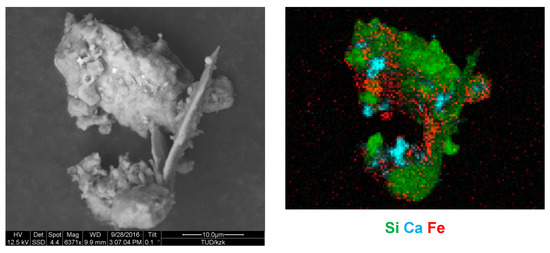
Figure 7.
Concreted particle as frequently found in Dushanbe dust deposition. Left: Secondary electron image. Right: Combined localized chemical information from scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis (SEM-EDX) mapping. The intensity of the element is given as color intensity (arbitrary units). The sample was collected on 2 September 2016, from 04:30 to 12:30 (UTC).
Looking at the sulfate processing state of the calcium component, it can be observed that Tajikistan is least processed, whereas Morocco and the African outflow generally have higher sulfur compound contributions. Dust at Barbados is more processed than the one at Tenerife as to be expected due to the longer transport. Cape Verde cannot directly be compared due to its different transport regime—humid marine boundary layer versus dry Saharan air layer [54,56]—so sulfur compounds are abundant here too [39,69]. The sulfate contribution in Morocco is similarly high, showing its common presence already at source in the arid Saharan regions [70,71]. For Svalbard, the calcium internally mixed with iron shows a low processing grade, whereas calcium without iron is highly processed; the latter might be therefore of marine origin.
4. Conclusions
By the general agreement of the clay mineral fingerprint with literature data [30,31], the capability of the applied technique for distinguishing clay mineral classes based on very small sample amounts is demonstrated. In addition, apparently the clay mineral fingerprint can be used for distinction of different large-scale source regions. In addition, it becomes clear that for the locations under study, the major dust composition is different. Therefore, the use of different optical properties with respect to the real part of the refractive index for African, Central Asian, and Arctic dust should be considered, as for example shown by Stegmann et al. [72]. Similarly, while the variation in the imaginary part is comparatively low for the African transport region, different values should be used for Central Asian and Arctic dust, as well as for near-source situations. In particular when size-resolved optical properties can be regarded, the regions should be treated differently.
While the total feldspar abundance is different between the regimes, the K-feldspars are comparatively constant. If evidence strengthens further the theory that K-feldspar can be dominating the ice-nucleation ability, it might be justifiable using a single size-dependent K-feldspar parameterization for describing the observed dust regimes.
Between African and Central Asian as well as Arctic dust regimes, there exist considerable differences in iron–calcium mixing state. It can be concluded that in near-source situations like in Morocco and Tajikistan, iron processing might be slowed by the calcium available in the same particles, whereas in the African transport regime, this effect is less pronounced. As a result, African outflow dust from the Sahel region when coming into contact with atmospheric acids is expected to show a higher increase in iron bio-availability than, for example, dust from Central Asian outflow would. Overall, most of the iron mass are not mixed internally with calcium. Depending on the processing intensity and state, a buffering effect of calcium carbonate therefore might be smaller than estimated from the overall dust composition (e.g., the bulk carbonate content).
In generalizing the results of this study, however, one has to bear in mind that the measurements were carried out for a couple of weeks during one or two seasons only. For a more robust assessment, therefore, permanent long-term measurements are required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K.; methodology, K.K., K.S., J.H., and S.A.; software, K.K. and K.S.; validation, K.K., K.S., and J.H.; investigation, K.K., A.W., D.A., J.H., J.H., S.F.A., and A.N.M.; resources, K.K., D.A., J.H., S.F.A., and A.N.M.; data curation, K.K., A.W., and S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, A.W., S.A., and D.A.; visualization, K.K.; funding acquisition, K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)–264907654; 264912134; 378741973; 416816480. We acknowledge additional support by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Technische Universität Darmstadt.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the help of Helena Reinardy and Renate Fenzlein for obtaining the samples from Svalbard. The authors also thank the people working at Ragged Point and Izaña Measurement stations for their continuous logistic support. K.K. wishes to thank Zhongbo Shi for the workshop discussions regarding the potential impact of internal particle mixture on iron bio-availability and Dirk Scheuvens for the ones regarding general mineralogy. Measurement data of this work are available from the Pangaea archive [35,37,38,40,41,43] and from elsewhere [42].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Scheme of Calculating the Feldspar Indices as Chemical Fingerprint for Identifying Particles Consisting Probably of Feldspar
The index values show the similarity of a particle composition to pure feldspar. They are composed of three properties, the overall contribution of feldspar-specific elements to the particle composition and the closeness to the feldspar Al/Si ratio as well as to the K/Si or alkali/Si ratio. The formulas below also correct a previous error [42].
The overall contribution of specific elements is calculated as
The closeness with respect to Al/Si is determined as
Vicinity with respect to the K and alkali ratio is calculated as
The similarity of a particle’s composition to pure feldspar in expressed then as
and to pure K-feldspar as
For example, the Pfsp value becomes 1 for pure microcline or plagioclase and 0 for sodium chloride or quartz. Comparing with particle morphology, a threshold value of 0.8 was suitable for distinguishing feldspar from non-feldspar components in naturally weathered sieved sediment derived from granite.
References
- Knippertz, P.; Stuut, J.-B. (Eds.) Mineral Dust: A Key Player in the Earth System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; p. 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, C.; Schulz, M.; Guibert, S.; Kinne, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.; Berntsen, T.; Berglen, T.; Boucher, O.; Chin, M.; et al. Analysis and quantification of the diversities of aerosol life cycles within AeroCom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1777–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Bréon, F.-M.; Collins, W.; Fuglestvedt, J.; Huang, J.; Koch, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lee, D.; Mendoza, B.; et al. Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 659–740. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Incorporation of mineralogical composition into models of the radiative properties of mineral aerosol from UV to IR wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 9423–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Engelbrecht, J.P.; Skiba, M.; Frey, G.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Single scattering albedo of fine mineral dust aerosols controlled by iron concentration. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biagio, C.; Formenti, P.; Balkanski, Y.; Caponi, L.; Cazaunau, M.; Pangui, E.; Journet, E.; Nowak, S.; Caquineau, S.; Andreae, M.O.; et al. Global scale variability of the mineral dust long-Wave refractive index: A new dataset of in situ measurements for climate modeling and remote sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1901–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Modeling the radiative characteristics of airborne mineral aerosols at infrared wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 8813–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, L. The effects of heating by transported dust layers on cloud and precipitation: A numerical study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, F.; Weinbruch, S.; Schütz, L.; Hofmann, H.; Ebert, M.; Kandler, K.; Worringen, A. Ice nucleation properties of the most abundant mineral dust phases. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D23204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakobi-Hancock, J.D.; Ladino, L.A.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Feldspar minerals as efficient deposition ice nuclei. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11175–11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoose, C.; Möhler, O. Heterogeneous ice nucleation on atmospheric aerosols: A review of results from laboratory experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9817–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Levin, Z.; Reisin, T.G.; Tzivion, S. The effects of giant cloud condensation nuclei on the development of precipitation in convective clouds—A numerical study. Atmos. Res. 2000, 53, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, C.R.; Michel, A.E.; Grassian, V.H. Reactions on Mineral Dust. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4883–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullerstam, M.; Vogt, R.; Langer, S.; Ljungström, E. The kinetics and mechanism of SO2 oxidation by O3 on mineral dust. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 4694–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiertny, D.M.; Young, M.A.; Grassian, V.H. Chemistry and Photochemistry of Mineral Dust Aerosol. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndour, M.; Conchon, P.; D′Anna, B.; Ka, O.; George, C. Photochemistry of mineral dust surface as a potential atmospheric renoxification process. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L05816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatz, D.F.; Barnard, W.R.; Stensland, G.J. The role of alkaline materials in precipitation chemistry: A brief review of the issues. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1986, 30, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.; Sarin, M.M. Chemistry of aerosols over a semi-Arid region: Evidence for acid neutralization by mineral dust. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L23815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paytan, A.; Mackey, K.R.M.; Chen, Y.; Lima, I.D.; Doney, S.C.; Mahowald, N.; Labiosa, R.; Post, A.F. Toxicity of atmospheric aerosols on marine phytoplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4601–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swap, R.; Garstang, M.; Greco, S.; Talbot, R.; Kållberg, P. Saharan dust in the Amazon Basin. Tellus 1992, 44B, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, A.; Almond, P.C.; Condron, L.M. Phosphorus fertilization by active dust deposition in a super-Humid, temperate environment—Soil phosphorus fractionation and accession processes. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Jickells, T.D.; Baker, A.R.; Artaxo, P.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Bergametti, G.; Bond, T.C.; Chen, Y.; Cohen, D.D.; Herut, B.; et al. Global distribution of atmospheric phosphorus sources, concentrations and deposition rates, and anthropogenic impacts. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2008, 22, GB4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.S.; Baker, A.R.; Tegen, I.; Mahowald, N.M.; Dentener, F.J.; Duce, R.A.; Galloway, J.N.; Hunter, K.; Kanakidou, M.; Kubilay, N.; et al. Impacts of atmospheric nutrient deposition on marine productivity: Roles of nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2011, 25, GB2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Jickells, T.D.; Bonneville, S.; Carslaw, K.S.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Baker, A.R.; Benning, L.G. Impacts on iron solubility in the mineral dust by processes in the source region and the atmosphere: A review. Aeolian Res. 2012, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journet, E.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Caquineau, S.; Colin, J.-L. Mineralogy as a critical factor of dust iron solubility. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L07805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, H.; Jokinen, O.; Kandler, K.; Scheuvens, D.; Nousiainen, T. Single scattering by realistic, inhomogeneous mineral dust particles with stereogrammetric shapes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousiainen, T.; Kandler, K. Light scattering by atmospheric mineral dust particles. In Light Scattering Reviews 9. Light Scattering and Radiative Transfer; Kokhanovsky, A.A., Ed.; Springer Praxis: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Feng, Y. Role of dust alkalinity in acid mobilization of iron. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9237–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Schütz, L.; Balkanski, Y.; Desboeufs, K.; Ebert, M.; Kandler, K.; Petzold, A.; Scheuvens, D.; Weinbruch, S.; Zhang, D. Recent progress in understanding physical and chemical properties of mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8231–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Schütz, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S. Bulk composition of northern African dust and its source sediments-A compilation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlwitz, J.P.; Pérez García-Pando, C.; Miller, R.L. Predicting the mineral composition of dust aerosols–Part 2: Model evaluation and identification of key processes with observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11629–11652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waza, A.; Schneiders, K.; May, J.; Rodríguez, S.; Epple, B.; Kandler, K. Field comparison of dry deposition samplers for collection of atmospheric mineral dust: Results from single-Particle characterization. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schütz, L.; Deutscher, C.; Hofmann, H.; Jäckel, S.; Knippertz, P.; Lieke, K.; Massling, A.; Schladitz, A.; Weinzierl, B.; et al. Size distribution, mass concentration, chemical and mineralogical composition, and derived optical parameters of the boundary layer aerosol at Tinfou, Morocco, during SAMUM 2006. Tellus 2009, 61B, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Deutscher, C.; Schütz, L.; Schneiders, K.; Heuser, J. Microphysics and Chemical Composition of Particulate Dry Deposition Measured in Tinfou, Morocco. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Benker, N.; Bundke, U.; Cuevas, E.; Ebert, M.; Knippertz, P.; Rodríguez, S.; Schütz, L.; Weinbruch, S. Chemical composition and complex refractive index of Saharan Mineral Dust at Izaña, Tenerife (Spain) derived by electron microscopy. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8058–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schneiders, K.; Heuser, J.; Cuevas, E. Microphysics and chemical composition of particulate dry deposition measured in Izaña, Tenerife, Spain. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waza, A.; Schneiders, K.; Kandler, K. Daily dust deposition fluxes at Izana, Tenerife collected by different techniques: Particle size and composition from single particle electron microscopy. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Benker, N.; Emmel, C.; Küpper, M.; Müller-Ebert, D.; Ebert, M.; Scheuvens, D.; Schladitz, A.; Schütz, L.; et al. Electron microscopy of particles collected at Praia, Cape Verde, during the Saharan Mineral dust experiment: Particle chemistry, shape, mixing state and complex refractive index. Tellus 2011, 63B, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Deutscher, C.; Lieke, K.; Schütz, L. Microphysics and chemical composition of particulate dry deposition measured in Praia, Santiago, Cape Verde. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Schneiders, K.; Heuser, J. Microphysics and chemical composition of particulate dry deposition measured at Fogo, Cape Verde. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schneiders, K.; Ebert, M.; Hartmann, M.; Weinbruch, S.; Prass, M.; Pöhlker, C. Composition and mixing state of atmospheric aerosols determined by electron microscopy: Method development and application to aged Saharan dust deposition in the Caribbean boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13429–13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Althausen, D.; Hofer, J.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N. Microphysics and chemical composition of particulate dry deposition measured at Dushanbe, Tajikistan. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schneiders, K.; Heuser, J. Microphysics and chemical composition of particulate dry deposition measured in Longyearbyen, Svalbard, Norway. PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léon, J.-F.; Legrand, M. Mineral dust sources in the surroundings of the north Indian Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Irannejad, P.; Shao, Y. Climatology of the Middle East dust events. Aeolian Res. 2013, 10, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-Scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridnejad, A.; Karimi, N.; Ariya, P.A. A new inventory for middle east dust source points. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.P.; Derbyshire, E. Airborne Mineral Dust. Elements 2010, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnalds, O.; Dagsson-Waldhauserova, P.; Olafsson, H. The Icelandic volcanic aeolian environment: Processes and impacts—A review. Aeolian Res. 2016, 20, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biagio, C.; Formenti, P.; Balkanski, Y.; Caponi, L.; Cazaunau, M.; Pangui, E.; Journet, E.; Nowak, S.; Andreae, M.O.; Kandler, K.; et al. Complex refractive indices and single scattering albedo of global dust aerosols in the shortwave spectrum and relationship to iron content and size. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S.; Rausch, A.; Gorzawski, G.; Helas, G.; Hoffmann, P.; Wex, H. Complex refractive index of aerosols during LACE 98 as derived from the analysis of individual particles. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.P.; Moosmüller, H.; Pincock, S.; Jayanty, R.K.M.; Lersch, T.; Casuccio, G. Technical note: Mineralogical, chemical, morphological, and optical interrelationships of mineral dust re-Suspensions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10809–10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapello, I.; Bergametti, G.; Gomes, L.; Chatenet, B.; Dulac, F.; Pimenta, J.; Santos Suares, E. An additional low layer transport of Sahelian and Saharan dust over the North-Eastern Tropical Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 3191–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Does, M.; Korte, L.F.; Munday, C.I.; Brummer, G.J.A.; Stuut, J.B.W. Particle size traces modern Saharan dust transport and deposition across the equatorial North Atlantic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13697–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyampudi, V.M.; Palm, S.P.; Reagen, J.A.; Fang, H.; Grant, W.B.; Hoff, R.M.; Moulin, C.; Pierce, H.F.; Torres, O.; Browell, E.; et al. Validation of the Saharan Dust Plume Conceptual Model Using Lidar, Meteosat, and ECMWF Data. Bull. Am. Met. Soc. 1999, 80, 1045–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L.; Tyler, S.A.; Willis, A.L.; Bourbeau, G.A.; Pennington, R.P. Weathering Sequence of Clay-Size Minerals in Soils and Sediments. I. Fundamental Generalizations. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1948, 52, 1237–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinzierl, B.; Ansmann, A.; Prospero, J.M.; Althausen, D.; Benker, N.; Chouza, F.; Dollner, M.; Farrell, D.; Fomba, W.K.; Freudenthaler, V.; et al. The Saharan Aerosol Long-Range Transport and Aerosol–Cloud-Interaction Experiment: Overview and Selected Highlights. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1427–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Saharan dust: Sources and trajectories. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2001, 26, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Lamb, P.J. African Droughts and Dust Transport to the Caribbean: Climate Change Implications. Science 2003, 302, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, L. Long range transport of desert dust with special emphasis on the Sahara. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1980, 338, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Kandler, K.; Küpper, M.; Lieke, K.; Zorn, S.; Ebert, M.; Schütz, L.; Weinbruch, S. Individual-Particle analysis of airborne dust samples collected over Morocco in 2006 during SAMUM 1. Tellus 2011, 63B, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Achterberg, E.P. Chemistry and mineralogy of clay minerals in Asian and Saharan dusts and the implications for iron supply to the oceans. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12415–12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboudt, K.; Gloter, A.; Mussi, A.; Flament, P. Red-ox speciation and mixing state of iron in individual African dust particles. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivlev, L.S.; Popova, S.I. The complex refractive indices of substances in the atmospheric-Aerosol dispersed phase. Izv. Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 1973, 9, 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, J.D.; Murray, B.J.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Whale, T.F.; Baustian, K.J.; Carslaw, K.S.; Dobbie, S.; O’Sullivan, D.; Malkin, T.L. The importance of feldspar for ice nucleation by mineral dust in mixed-Phase clouds. Nature 2013, 498, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.D.; Whale, T.F.; Carpenter, M.A.; Holden, M.A.; Neve, L.; O′Sullivan, D.; Vergara Temprado, J.; Murray, B.J. Not all feldspars are equal: A survey of ice nucleating properties across the feldspar group of minerals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10927–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Bonneville, S.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D.; Benning, L.G. Formation of Iron Nanoparticles and Increase in Iron Reactivity in Mineral Dust during Simulated Cloud Processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6592–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.; Lehmann, S.; van Pinxteren, D.; Gnauk, T.; Niedermeier, N.; Wiedensohler, A.; Herrmann, H. Particle characterization at the Cape Verde atmospheric observatory during the 2007 RHaMBLe intensive. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi-Aissa, B.; Valles, V.; Aventurier, A.; Ribolzi, O. Soils and Brine Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Hyperarid Desert Playa, Ouargla Basin, Algerian Sahara. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2004, 18, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, D.; Cao, J.; Xu, H.; An, Z. Soil-Derived sulfate in atmospheric dust particles at Taklimakan desert. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L24803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, P.G.; Yang, P. A regional, size-Dependent, and causal effective medium model for Asian and Saharan mineral dust refractive index spectra. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 114, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).