Abstract
Odour in the atmosphere is usually characterized by an intermittent time series of high peaks and periods of low (or zero) concentrations. The peak-to-mean ratio (PMR) is commonly used to estimate short-term peaks from long-term averages to assess the odour impact. The objective of this study was to quantify the peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity (PMR_OI) in the atmosphere near swine operations. Fifteen human assessors (sniffers) were trained to use an 8 point odour intensity scale to measure odour intensity in the ambient air near two swine operations. In each measurement session, the sniffers were placed 0° (in the direction of wind), 30°, and 45° from the wind directions at 100, 500, and 1000 m from the swine operations to sniff odour in the air every 10 s for 30 min. The results showed that odour in the atmosphere was intermittent. The intermittency (% of time when odour was detected) increased with the averaging time and decreased with the distance from the odour source and the direction from the wind. The measured intermittency ranged from 13% to 85%. The PMR_OI increased with the averaging time, the distance from the source, and the direction from the wind. In the wind direction, the largest difference in PMR_OI between 1 and 30 min averaging times was 68% (2.5 vs. 4.2), which occurred at 1000 m from the odour source under stability class B. The average PMR_OI increased from 1.5 at 100 m to 3.5 at 1000 m. Atmospheric stability had a noticeable effect on PMR_OI. At 1000 m, the 30 min PMR_OI decreased from 4.2 at stability class B (unstable) to 2.4 at E (slightly stable).
1. Introduction
Odour emission from swine operations has been a major cause of confrontation between producers and the neighbouring residents. One of the most critical issues in dealing with odour is to assess or predict odour impact near swine operations, and a commonly used assessment tool is dispersion modelling. When dispersion models are used to assess the downwind odour impact, the predicted downwind concentration represents an average concentration over a period of time (typically one hour as dictated by the meteorological data). However, large fluctuations and short-term peaks of odour in the ambient air have been consistently reported by researchers, and they are considered a characteristic feature of the atmospheric dispersion process [1]. Short-term concentrations of odorous compounds are usually characterised by an intermittent time series of high peaks and periods of low (or zero) concentrations [2]. The instantaneous peaks may be two orders of magnitude higher than the average concentration, and a few seconds of odour exposure at high levels are enough to cause human annoyance [3]. In other words, the peaks that exceed the odour detection threshold can cause odour nuisance, even if the long-term average concentration is well below the odour detection. Therefore, the short-term odour peaks should be taken into consideration in assessing odour impact.
Intermittent bursts of odour in the atmosphere near swine operations are a fundamental characteristic of pollutant dispersion in the atmosphere. Based on the dispersion of a tracer gas, Mylme and Mason [4] showed that the time series of gas concentration in the atmosphere consisted of intermittent occurrences of non-zero concentrations interspersed by periods of essentially zero concentration. The intermittency (factor), defined as the proportion of time of non-zero concentration, is often used to characterize the intermittent occurrence of pollutants in the atmosphere [4].
The peak-to-mean ratio (PMR) has been commonly used to estimate the short-term concentrations of air pollutants from the long-term averages predicted by dispersion models [5,6,7,8]. However, there are no universally accepted values for the odour PMR; different PMR values are used in different jurisdictions for odour regulations [9]. For dispersion of pollutants in the atmosphere, a one-fifth power law with sampling time for sampling periods from 3 min to half an hour was suggested by Stewart et al. [10]. The power law was also reported by Cramer [11] to be applicable for sampling times from 3 s to 10 min. Gifford [1] reported that for a source and receptor located at the same level, the PMR could be expected to be in the range from 1 to about 5. However, when concentrations are observed at levels considerably off the release height, or off the centre line, the PMR could be much higher than those given by the power law. Singer [5] reported that the atmospheric stability and the type of terrain also affected the PMR. Hino [12] examined the relationships between ground-level pollutant concentrations and sampling times and concluded that the concentration was proportional to the sampling time to the −0.5 power for sampling periods between 10 min and 5–6 h. A power function suggested by Smith [6] is commonly used in dispersion modelling to estimate the peak concentration (Cp) during a short time interval (tp) from the mean concentration (Cm) over a long time interval (tm):
where
ψ = peak-to-mean ratio of odour (pollutant) concentration (PMR_OC);
Cp = peak concentration;
Cm = mean concentration;
tp = averaging time for peak concentration (short-term);
tm = averaging time for mean concentration (long-term);
q = exponent (empirical constant).
The exponent q in the above equation takes different values for different stability classes of the atmosphere [13]. Schauberger et al. [14] further incorporated the downwind distance into the PMR calculation using a relationship developed by Mylne and Mason [4] as follows:
where
ψx = peak-to-mean ratio of concentration at distance x from source;
T = travel time to distance x at the mean wind speed;
tl = γ/g;
σ = variance of wind speed averaged over three wind components;
γ = rate of dissipation of turbulent energy.
The PMR for odour from livestock operations is influenced not only by atmosphere dispersion but also source characteristics (e.g., frequent changes in odour emission rate). Best et al. [2] pointed out that industrial and agricultural odour PMRs depended on source characteristics, downwind distance, and atmospheric stability. Based on the review of published literature, Schauberger et al. [8] listed the following variables that influence the peak-to-mean ratio for odour: atmospheric stability; intermittency; travel time or distance from the source; lateral distance from the axis of the wake; and geometry of the source (emission height and source configuration).
Although there is a general agreement that the peak values of odour from livestock operations may be much higher than the average over a certain time period, there is a need for field data to quantify the relationship between the peak and the average odour levels. The current methods of estimating the PMR for odour are mostly based on experiments using tracer gases (e.g., [4]). The tracer methods may provide high accuracy of measurement, but the tracer release may not accurately reflect odour emission from livestock operations (i.e., the emission characteristics of livestock operations may be different from the controlled releases of tracer gases). Furthermore, odour quantification goes beyond measuring the concentration of odorants (or tracers)—it involves human perception and sensitivity.
The objective of this study was to use human sniffers (odour assessors) to determine the peak-to-mean ratios of odour intensity (PMR_OI) in the atmosphere near large-scale commercial swine operations. The effects of such variables as the averaging time, downwind distance, and atmospheric stability were investigated. The intermittency of odour in the field conditions was also assessed.
It should be noted that the PMR_OI determined in this study was based on odour intensity measurement and might not be applicable directly to odour concentrations because the relationship between the odour intensity and odour concentration is not linear. For example, the Stevens power law is commonly used to relate odour intensity to concentration as follows [15]:
where
I = odour intensity;
C = odour concentration;
n = characteristic exponent;
k = proportionality constant.
Using the Stevens power law, the peak-to-mean ratio for odour concentration (PMR_OC) may be estimated from PMR_OI as follows:
where
Ip = peak odour intensity;
Im = mean odour intensity.
Although it is theoretically possible to transform PMR_OI to PMR_OC, the exponent n is not readily available for livestock odour.
2. Experiment
2.1. Description of Study Sites
Field odour measurements were conducted on two commercial swine farms of 3000 sow farrowing operations, located in southern Manitoba, Canada. The two farms were almost identical in layout, and the only difference between the two farms was that one had an extra quarantine room, which was normally empty and did not contribute to odour emission. Each farm had 17 production rooms that were mechanically ventilated with 84 wall-mounted exhaust fans. Manure on both farms was handled as liquid, which was stored in under-floor shallow gutters and then removed to outdoor earthen manure storage once every week from gestation/breeding rooms and once every three weeks from farrowing rooms. The topography around the two farms was flat cropland.
2.2. Odour Measurement Grid
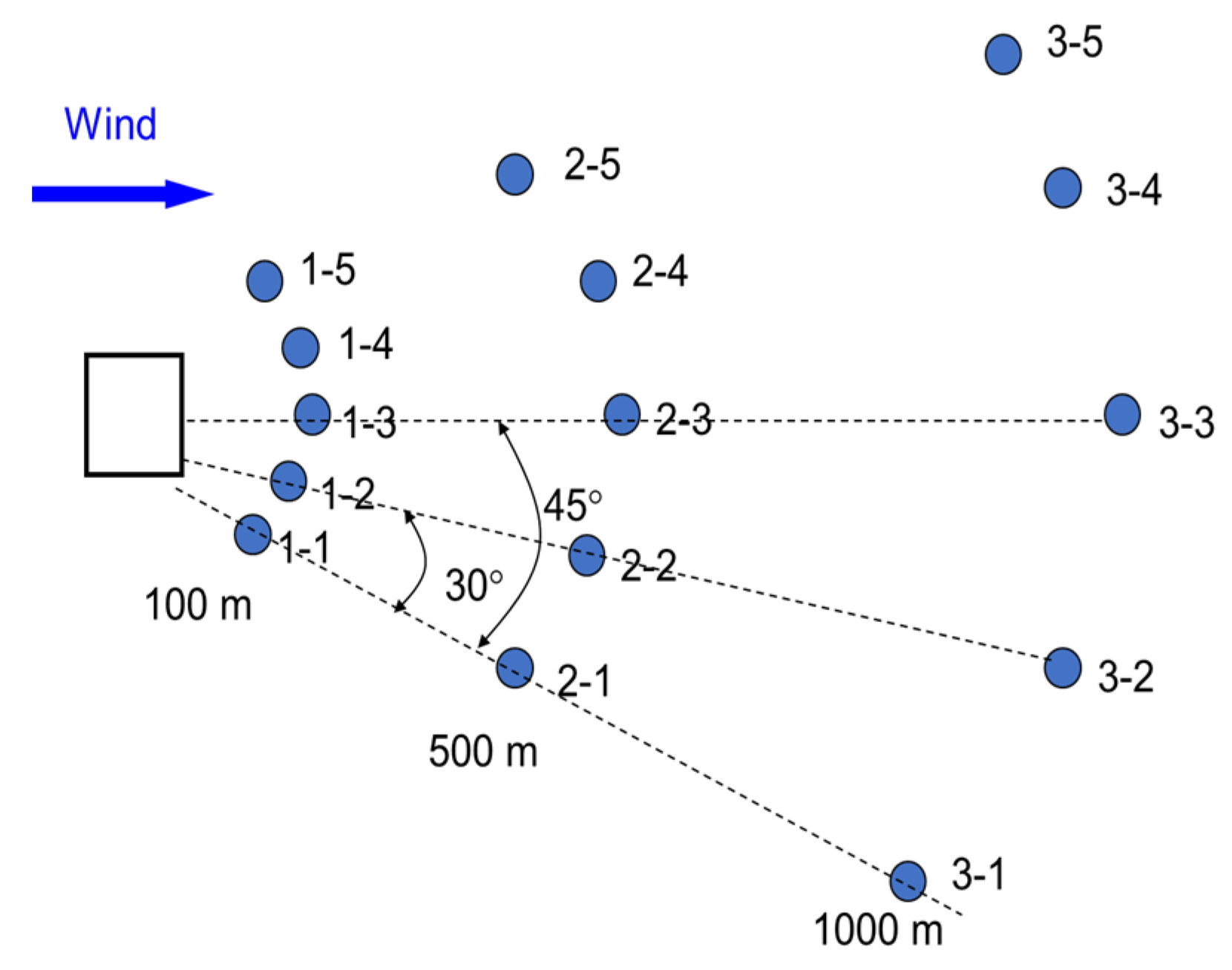
To measure odour intensity in the air downwind from the farms, 15 trained human sniffers were hired in each measurement (sniffing) session and placed in pre-determined positions based on the wind direction at the times (Figure 1). For each sniffing session, a weather station was set up first to determine wind direction. Based on the wind direction, 15 trained sniffers were placed in a three-row grid system downwind of the farm, with the first row (5 assessors) at 100 m from the farm, the second row at 500 m, and the third row at 1000 m (Figure 1). These distances were similar to those used by Mylme and Mason [4] in their study of concentration fluctuations of a tracer gas in the atmosphere. Three sniffers at positions 1–3, 2–3, and 3–3 were directly downwind from the farm (odour source) at 100, 500, and 1000 m, respectively. Each sniffer carried a GPS unit to guide them to the pre-determined grid point and then recorded their exact position based on the longitude and latitude readings from the GPS.
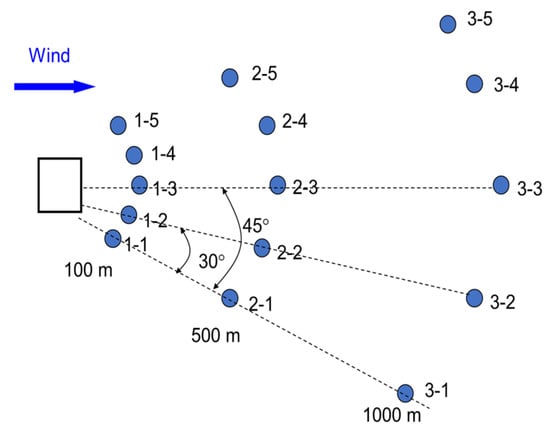
Figure 1.
Grid for odour measurement in the field, with the positions of 15 human assessors denoted as 1–1 to 3–5 at 0°, 30°, and 45° from the wind direction at 100, 500, and 1000 m from the odour source.
2.3. Selection and Training of Field Human Odour Sniffers
Quantifying (measuring) odour in the ambient air is challenging. We followed the principle of the field inspection methods in the European Standard [16,17]—using trained human sniffers (assessors). Over 40 students were recruited from the University of Manitoba as potential human sniffers. The recruits were screened based on their sensitivity and ability to determine odour intensities of n-butanol solutions (in water). The 8 point Odour Intensity Reference Scale in the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standard (Table 1) [18] was adopted to screen and train human sniffers. According to the concentrations in Table 1, eight samples of n-butanol solutions were prepared in 45 mL glass bottles with Teflon-coated lids. In the screening test, each participant was asked to sniff the eight samples in a random order and place them in the order from the weakest to the strongest odour levels. The inversion (error) value was then calculated, and those who scored 0 or 1 were selected for further training. Of the 40 recruits, 22 passed the screening test and were selected for further training.

Table 1.
ASTM standard 8 point n-butanol odour intensity reference scale [18].
A series of training sessions were conducted to train the selected recruits, and each training session consisted of three phases. In phase 1, every sniffer was provided with a set of eight n-butanol samples at the concentrations described in Table 1 and asked to sniff the samples one by one from #1 (0 ppm) to #8 (15,500 ppm) repeatedly until they felt confident that they had “memorized” the concentration scale. To minimize the effect of any odour in the ambient air, the sniffers wore a carbon filtered mask for 10–20 s before each sniffing. In phase 2, each sniffer was given 3 to 6 coded samples of certain concentrations (but unknown to the sniffer) and asked to evaluate these samples one at a time and assign a scale (0 to 8) to each sample. Those who correctly rated all samples were asked to check with the standard solution bottles of n-butanol to reinforce their ratings. Sniffers who incorrectly rated a sample(s) had to sniff both the standard and the coded samples to “feel” the difference until she/he could correctly rate all samples. In phase 3, three samples of swine manure odour simulant [19] were presented to each sniffer for assessment one at a time. Each sniffer assigned a scale (0–8) to each of the three samples of simulated swine manure odour, and the process was repeated until a group consensus was reached for each of the three samples. The results were collected after each training session to evaluate the performance of sniffers over the entire training period. Each sniffer was allowed to be one level off for the wrong identification; otherwise further training had to be conducted (repeated).
2.4. Field Odour Intensity Measurement Procedure
At the beginning of each odour measurement session (before leaving for field), the sniffers “checked” their noses by sniffing the eight standard n-butanol solutions and recorded their ratings on a labelled magnitude scale sheet [20], which was kept to track the history of each sniffer’s performance in each field session. After reaching the field measurement positions as illustrated in Figure 1, the sniffers waited for instructions from a central coordinator through a two-way radio to start a sniffing session. Following a similar procedure to that outlined by Mannebeck et al. [21], the sniffers inhaled the ambient air to assess (sniff) odour every 10 s and repeated sniffing for 10 min. Three 10 min sessions were conducted consecutively with a 10 min break between each session. The timing of each sniffing was synchronized by a central coordinator, i.e., through the two radios, the coordinator broadcast the instruction to the sniffers every 10 s to start and stop sniffing. To prevent the nose from being “saturated” by odour in the air, every sniffer wore a carbon filtered mask and only took off the mask briefly every 10 s to sniff odour. Each sniffer recorded her/his sniffing result (an intensity value of between 0 and 8) every 10 s and a brief description of odour characteristics on a data recording sheet.
In total, 51 odour sniffing sessions were carried out on the two farms between June and October, when swine odour was considered to be a problem for the local residents. Two or three sessions were normally conducted in one day to cover different times of the day, specifically, from early morning to noon or from afternoon to early evening. The selected measurement dates and times covered a range of atmospheric stability conditions (Table 2). However, the stability class was not known until the collected weather data was analysed after each field session. Although some sessions were conducted in the early morning (before sunrise) with the intention of capturing stable atmospheric conditions, no stability class F was measured.

Table 2.
Summary of Pasquill stability classes for 51 field odour assessment sessions.
2.5. Meteorological Condition Monitoring
A portable weather station (WatchDog Model 550, Spectrum Technologies, Inc., Plainfield, IL, USA) was used to record the on-site meteorological conditions, including solar radiation, temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed and direction. The data was recorded every minute. Based on the wind direction at the time, an open area on the farm was selected to place the weather station at a height of 2 m above the ground level.
2.6. Data Analysis
The odour intensity measurement method used in this study was based on magnitude estimation scaling. Therefore, the measured intensity data could be analysed statistically by using parametric methods, such as computation of means, variance analysis (ANOVA), and regression [22]. Furthermore, the mean of intensity values was calculated as the arithmetic mean [23,24,25]. Minitab (Minitab 19, Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA) was used to perform the statistical analyses.
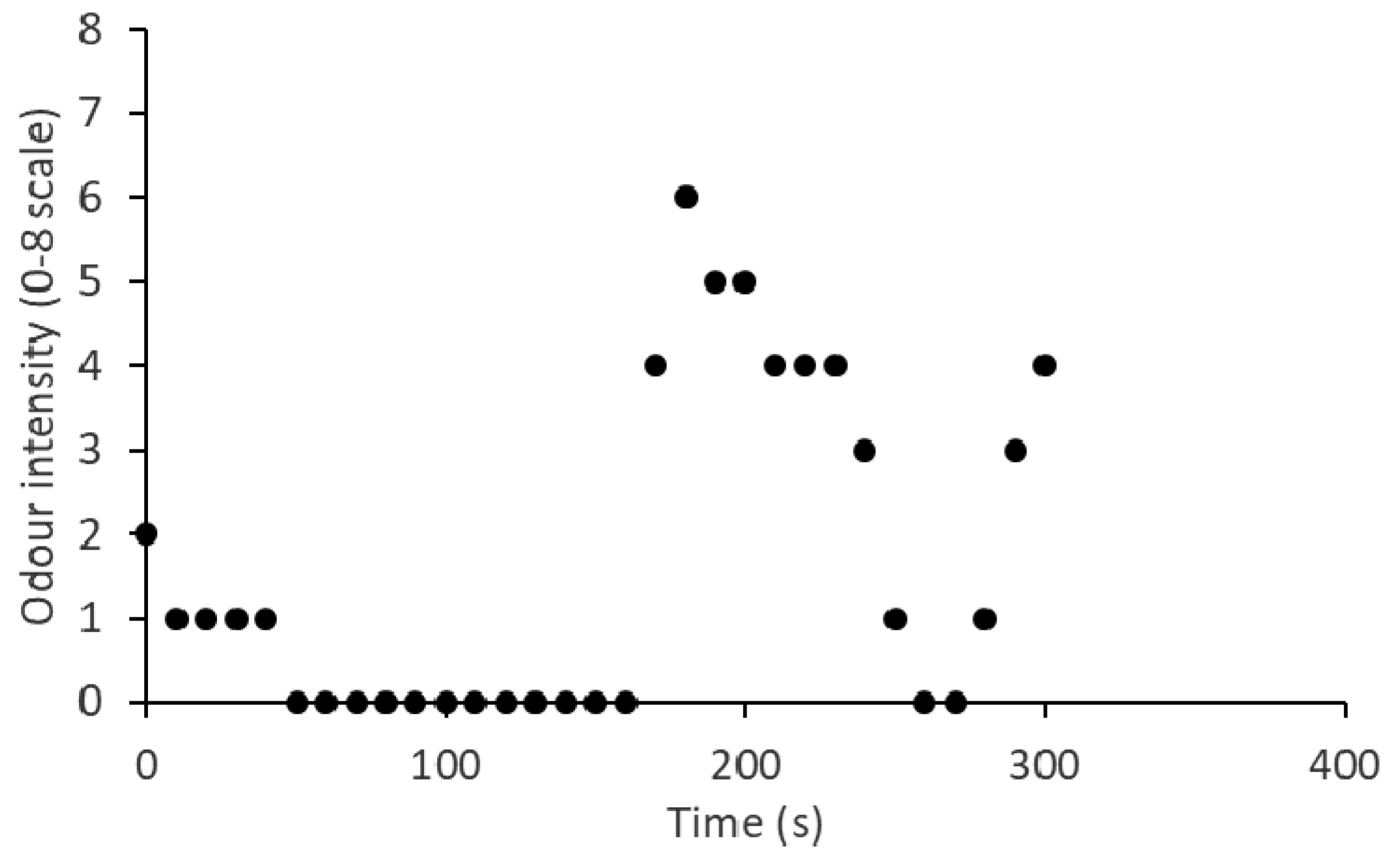
A sample of field measurement data for a 5 min period is presented in Figure 2 to illustrate the calculations of PMR_OI and intermittency (η). This sample data had a total of 31 intensity values recorded by a sniffer, with a maximum of 6.0 and an arithmetic mean of 1.6 (Im). In the context of odour dispersion modelling, the peak value is estimated from a long-term average value by using empirical equations, such as Equation (1). This estimated peak value is commonly used to define the acceptable odour level. However, researchers are still debating the definition of the peak value [8]. In the current study, the peak intensity value (Ip) was defined as the 90th percentile of measured odour intensity values during the time period of interest [8], which was calculated to be Ip = 4.0 in this example. Therefore, the PMR_OI in this example was calculated to be PMR_OI = Ip/Im = 4.0/1.6 = 2.5. In addition, 14 zero values (no odour) were reported, based on which the intermittency was calculated to be η = (1 − 14/31) = 0.548 (or 54.8%). The conditioned mean odour intensity, defined as the mean of the non-zero readings [4], was calculated to be 2.9 and the 90th percentile 5.0. Therefore, the corresponding conditioned peak-to-mean ratio (CPMR_OI) was determined to be 5.0/2.9 = 1.7.
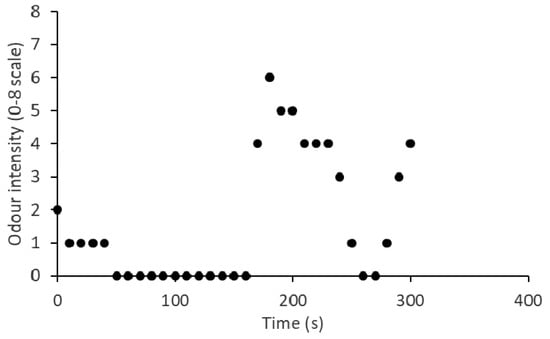
Figure 2.
A sample of odour intensity measurements for a 5 min period, reported by a human sniffer.
To improve the data quality, retrospective screening was performed on the datasets in the following three steps: (1) the mean and standard deviation of the data at each of the 15 measurement positions (1–1 to 3–5) were calculated for the 30 min session; (2) any data points that were outside three standard deviations were removed; (3) the means and standard deviations were calculated again for the screened dataset, and the process was repeated until no change in the mean was observed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Test
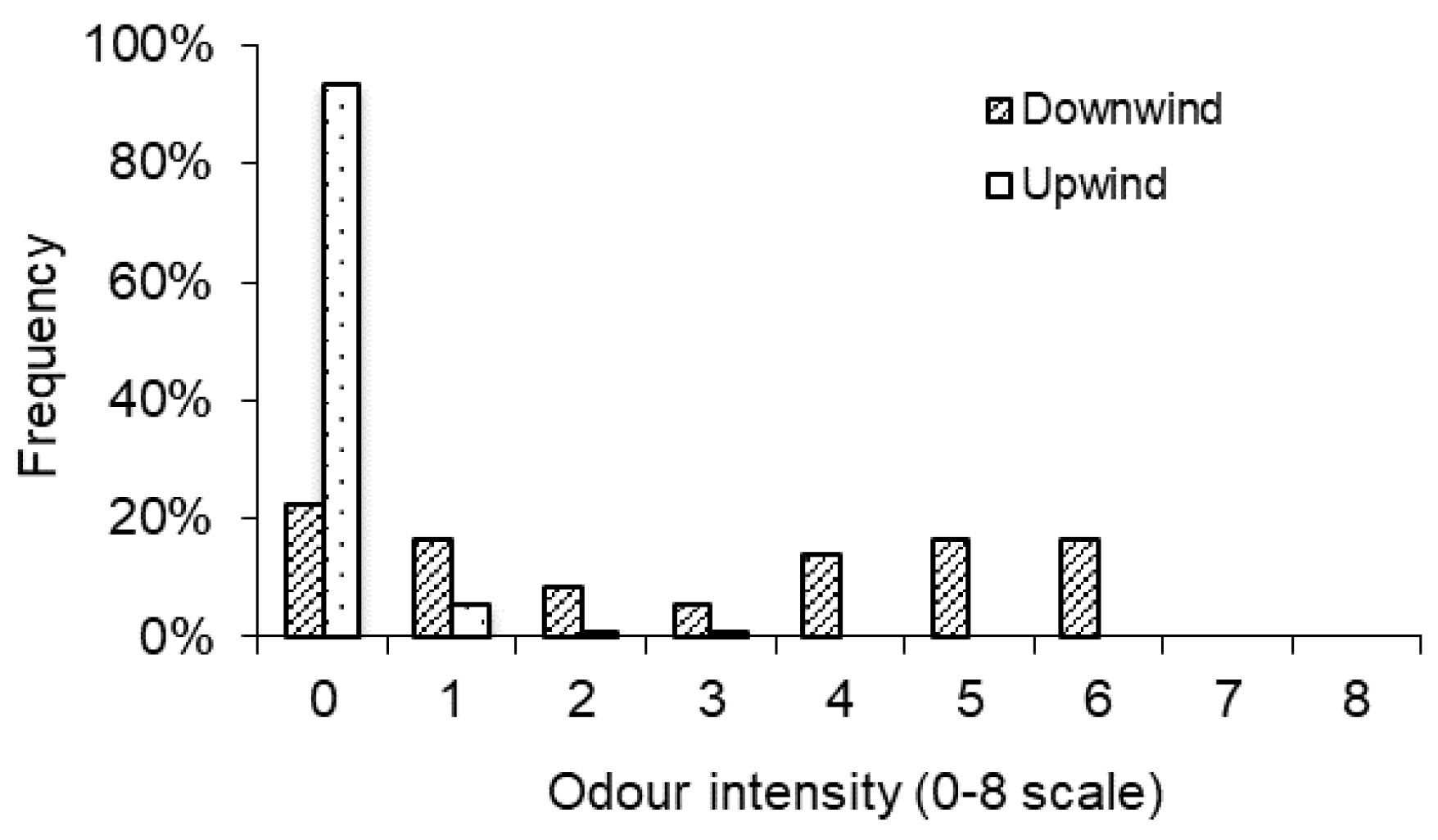
Visual cues could modulate olfactory perceptions [26]. A preliminary test was conducted to check if seeing the odour source (farm) might bias the odour rating by human sniffers. Two odour sniffing sessions were conducted, one upwind and one downwind of a farm. It was expected that the sniffers would report odour only when they were downwind from the farm if they were not biased. Of the 2745 data points reported by 15 sniffers, 93% were at level 0 (no odour), 5% at level 1, and about 1% each at levels 2 and 3, when the sniffers were upwind from the odour source (Figure 3). The sniffers reported much higher odour intensity levels when they were downwind from the farm. Specifically, the frequencies of reporting intensity levels of 4, 5, and 6 were 14%, 17%, and 17%, respectively (Figure 3). The average reported odour intensity was close to zero (0.1) for upwind and 2.9 for downwind. The above two sets of data confirmed that seeing the odour source did not bias the odour assessments by human sniffers.
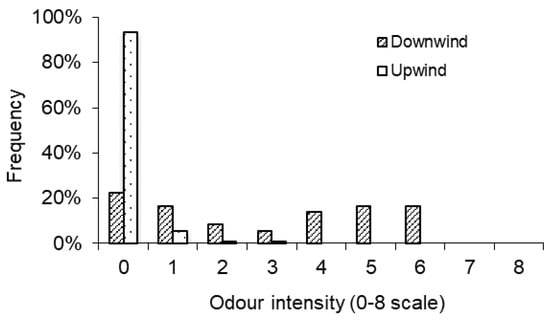
Figure 3.
Odour intensity assessed by human sniffers upwind and downwind of the farm.
3.2. Intermittency
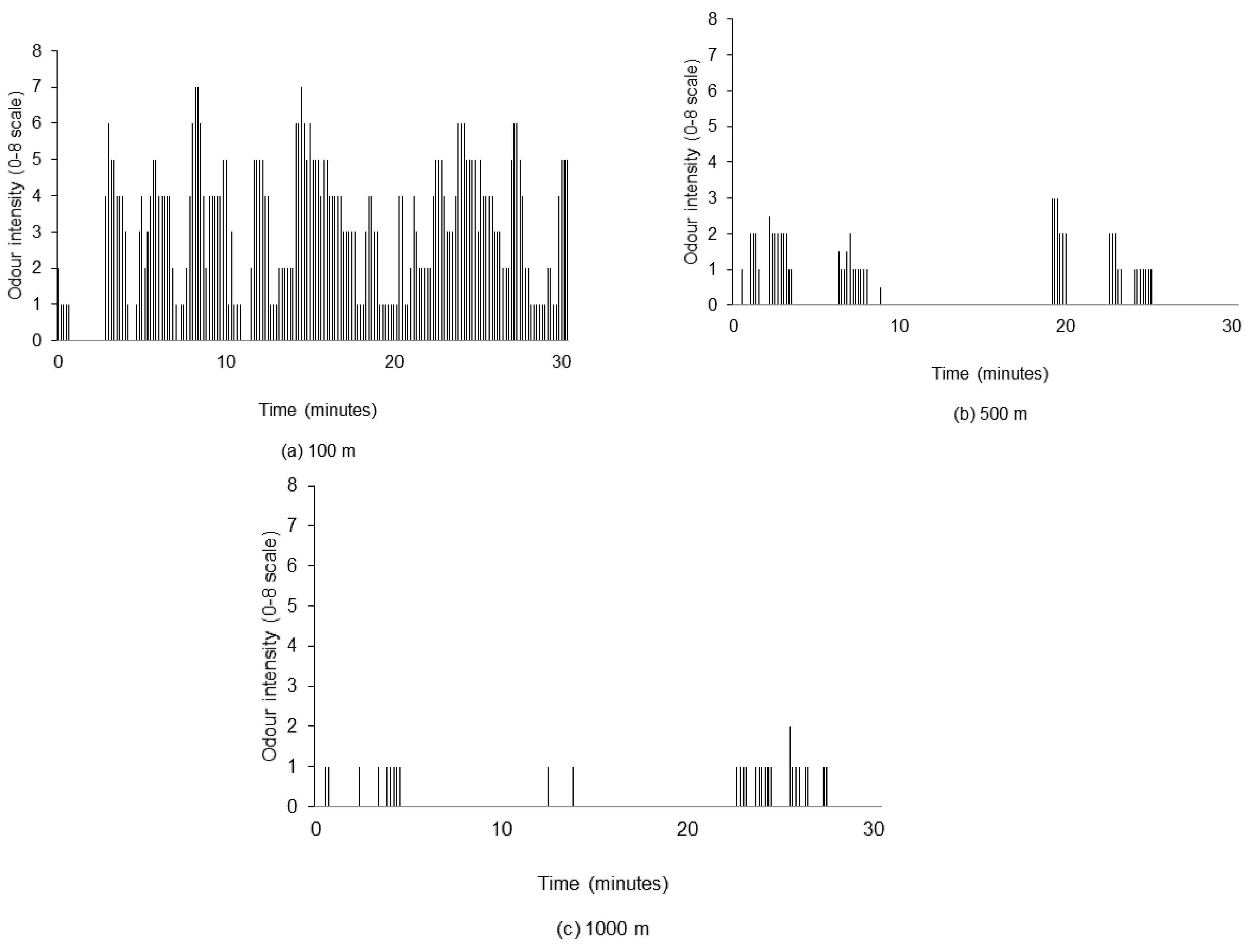
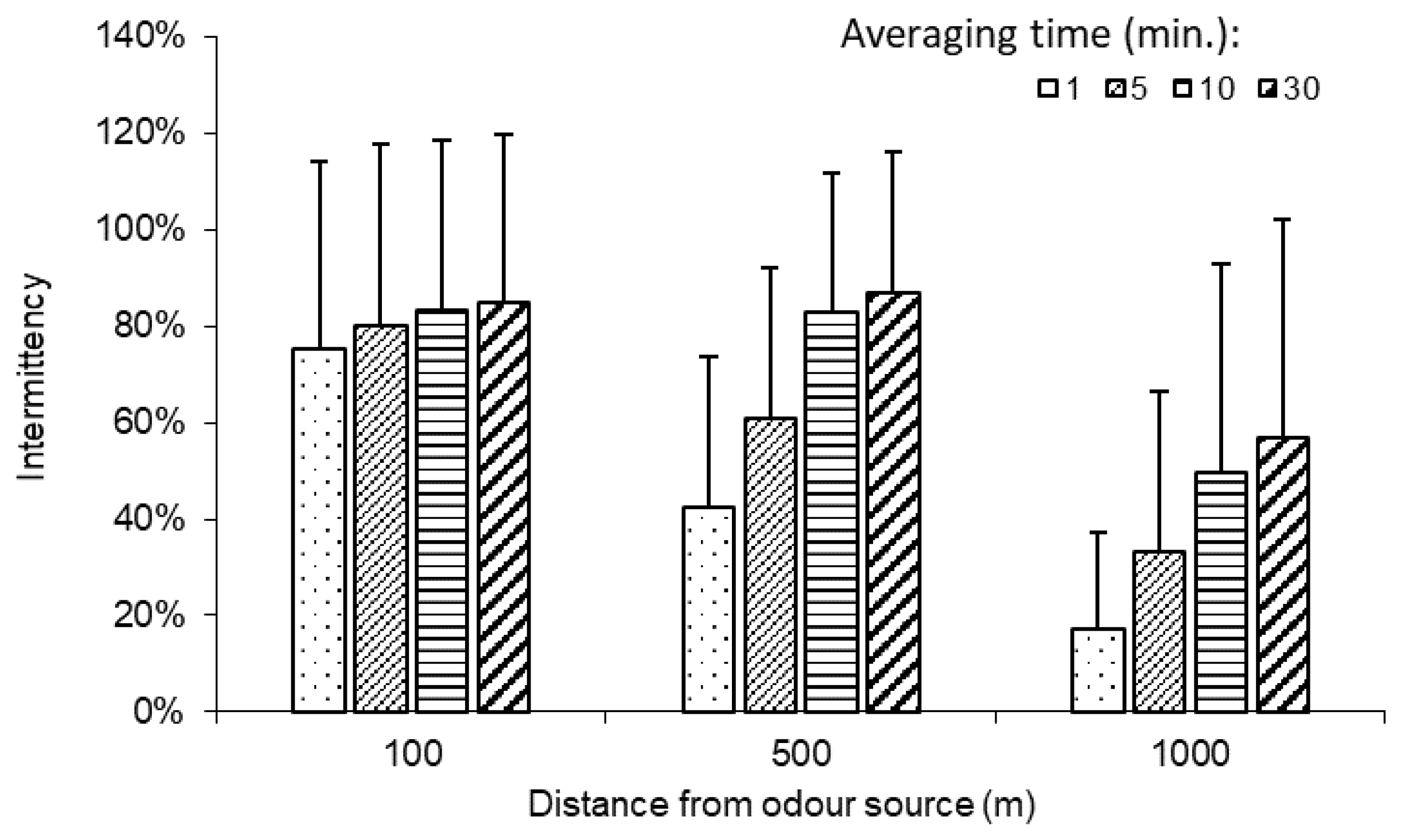
One of the important characteristics of odour dispersion in the atmosphere is “intermittency”, i.e., it occurs in bursts with low or no odour between bursts. It should be noted that the intermittency of odour in the atmosphere around swine operations is dependent on both the atmospheric conditions and the variability of odour emission (e.g., changes in ventilation in swine barns). This intermittent characteristic of odour in the atmosphere was clearly shown by the measured data (Figure 4). It was observed that more zeros (lower intermittency) were reported as the distance from the odour source increased. The calculated intermittency values based on the data from all 51 field measurement sessions are presented in Figure 5 for different distances and average times along the wind direction.
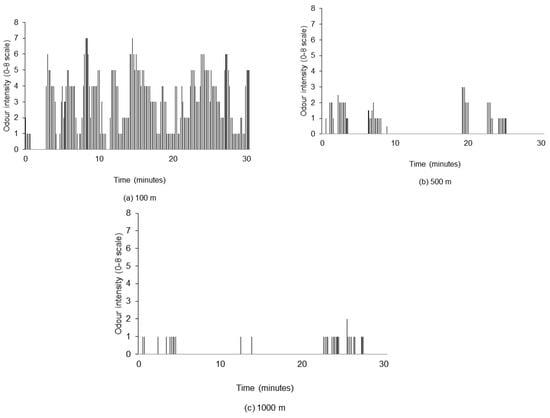
Figure 4.
A sample of field odour intensity measurements reported by human assessors in a 30 min sniffing session at: (a) 100 m, (b) 500 m, and (c) 1000 m from odour source (August 5, Session 2).
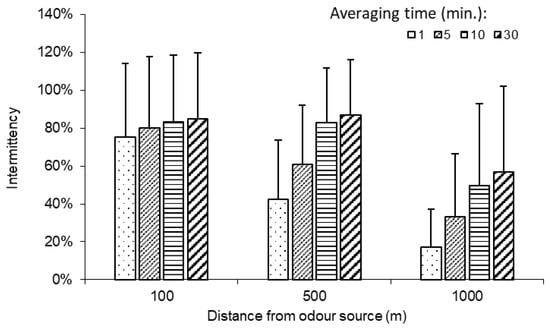
Figure 5.
Intermittency measured along the wind direction at 100, 500, and 1000 m from odour source (bar: standard deviation).
Two-way ANOVA indicated that both the averaging time and the downwind distance had a significant (p < 0.05) effect on the intermittency. The intermittency generally decreased with the distance from the odour source, and the largest decreases were observed for the averaging time of 1 min. Specifically, the intermittency was 75%, 42%, and 17% at 100, 500, and 1000 m, respectively, for a 1 min averaging time. This trend agrees with the observation reported by Mylne and Mason [4]. In comparison, the changes in intermittency with distance were less pronounced for a 30 min averaging time (85%, 87%, and 57% at 100, 500, and 1000 m, respectively).
The intermittency increased with the averaging time, and the increases were more pronounced at longer distances. At 100 m, the average intermittency value increased from 75% to 80%, 83%, and 85% as the averaging time increased from 1 to 5, 10, and 30 min, respectively. In comparison, the increases in intermittency at 1000 m were more pronounced: 17%, 33%, 50%, and 57% for the four averaging times, respectively, or an increase of 3.4 times when the averaging time increased from 1 to 30 min.
The intermittency decreased with the angle from the wind direction, i.e., the highest intermittency occurred along the wind direction (0°, Table 3). The differences in intermittency between the 0° and 45° angles were larger at longer distances from the odour source. The intermittency at 45° was on average 8% lower than that at 0° at 100 m, 17% at 500 m, and 30% at 1000 m. ANOVA indicated that the difference in intermittency between 0° and 45° was significant (p < 0.05) at 500 and 1000 m, but not significant at 100 m. This was because odour was relatively strong and less intermittent at locations close to the source.

Table 3.
Comparison of intermittency between the along-wind (0°) condition and 45° from the wind direction.
3.3. Peak-To-Mean Ratio of Odour Intensity
3.3.1. PMR_OI versus CPMR_OI
Two definitions were used to calculate peak-to-mean ratios of odour intensity: the commonly used “true” PMR_OI that included all data points, and the less commonly used conditioned peak-to-mean ratio (CPMR_OI) based on non-zero odour readings only. While this paper was focused on the PMR_OI, the CPMR_OI was used for comparison to illustrate the effect of intermittency on the calculation of the peak-to-mean ratio.
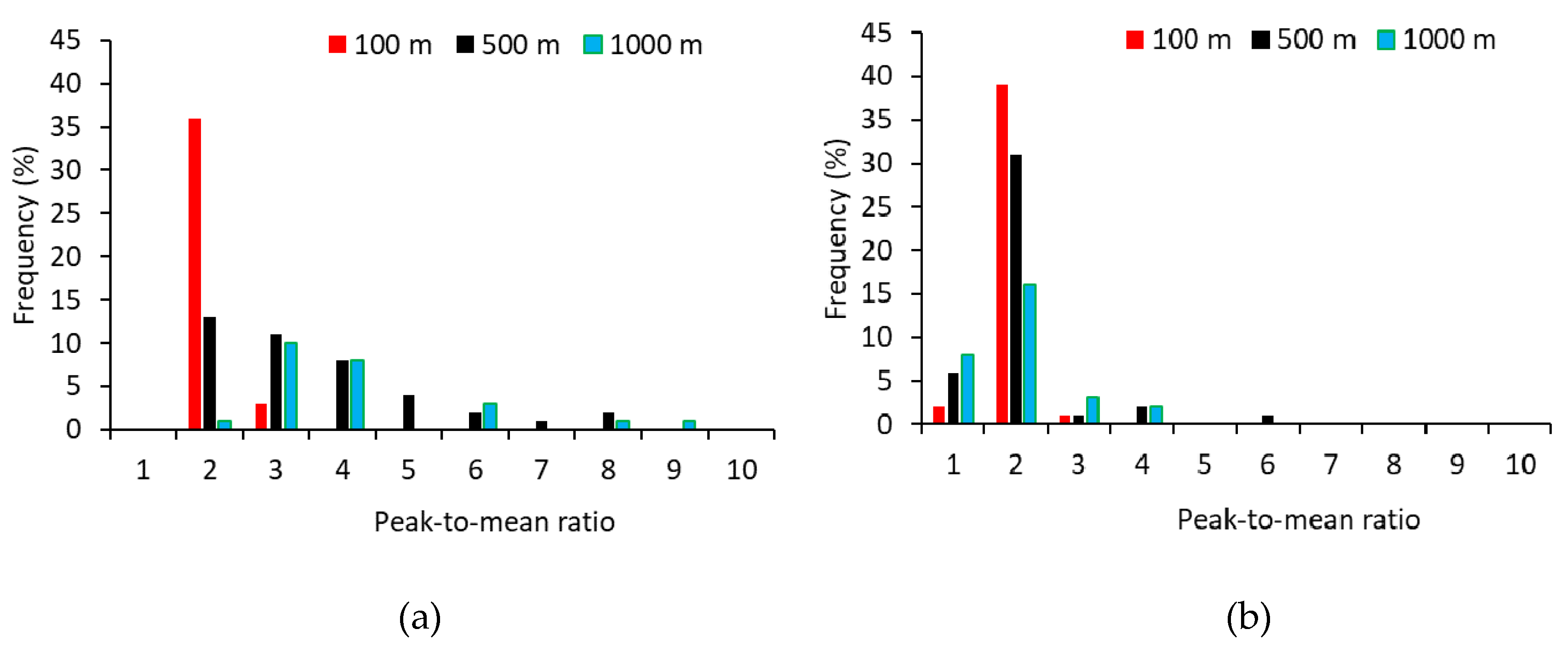
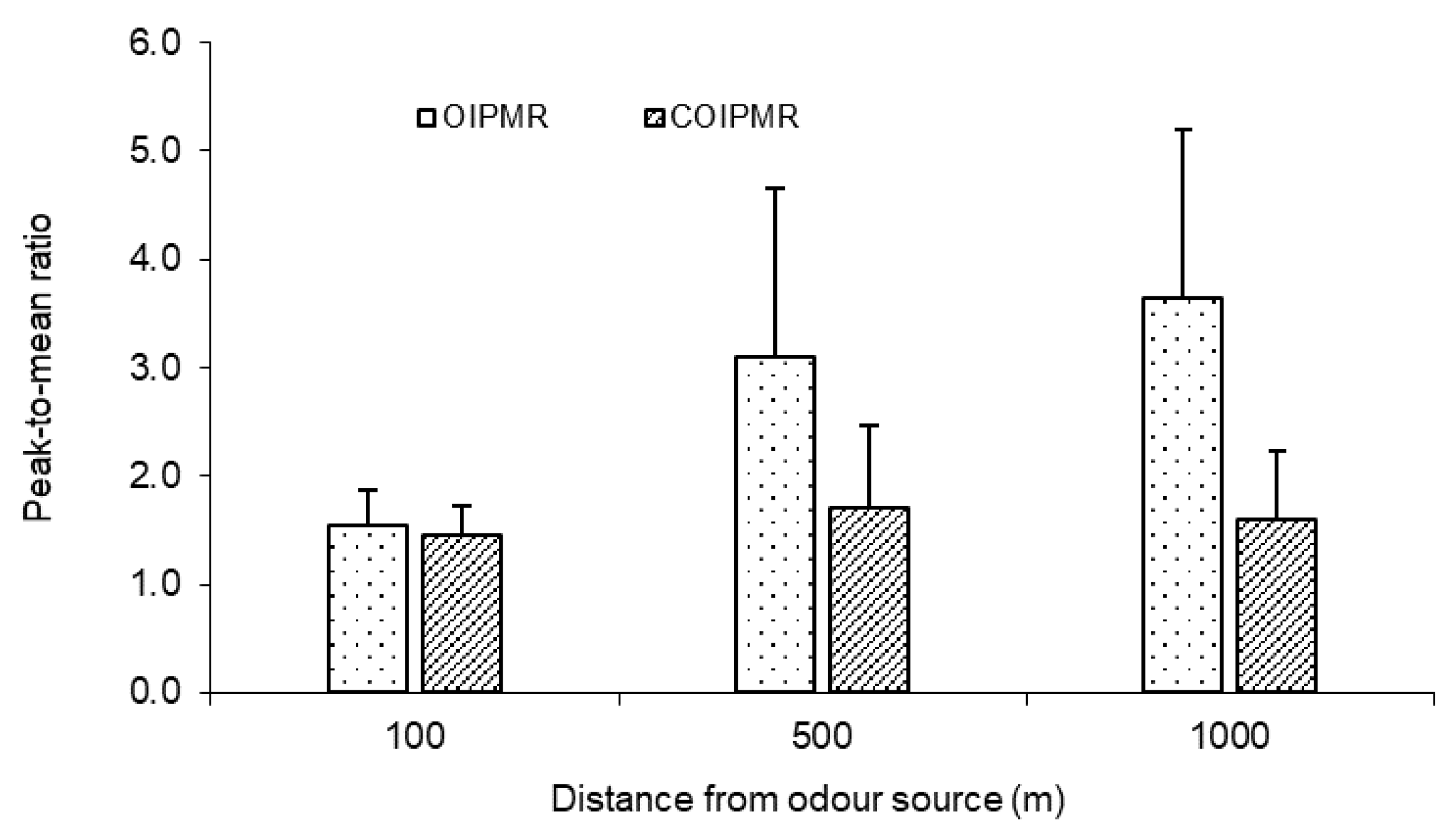
The measured PMR_OI varied markedly within a measurement session (with time and location) and from session to session, with values ranging from 1 to 9 (Figure 6a). A wider spread of PMR_OI was observed at longer distance from the source. For example, the PMR_OI was mostly between 1 and 2 at 100 m from the source, while the PMR_OI ranged from 2 to 9 at 1000 m. In comparison, the highest CPMR_OI was 6, and most CPMR_OI values were between 1 and 2 for all three distances (Figure 6b). This clearly indicated that zero odour readings between bursts (i.e., intermittency) had a drastic effect on the PMR_OI because the zero readings lowered the average odour intensity, thus resulting in a higher PMR_OI. The difference between the PMR_OI and CPMR_OI was statistically significant (p < 0.05) at 500 and 1000 m, but not at 100 m (Figure 7). For the 30 min averaging time, the PMR_OI was 1.8 and 2.3 times higher than the CPMR_OI for 500 and 1000 m, respectively.
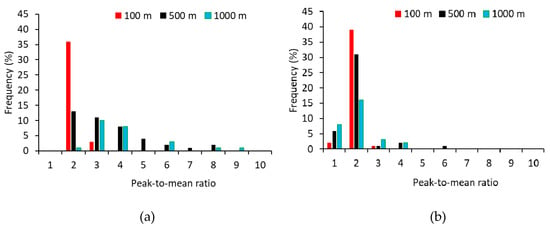
Figure 6.
Frequency distribution of the peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity along the wind direction at 100, 500, and 1000 m from the odour source. (a) PMR_OI (true peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity) and (b) CPMR_OI (conditioned peak-to-mean ratio).
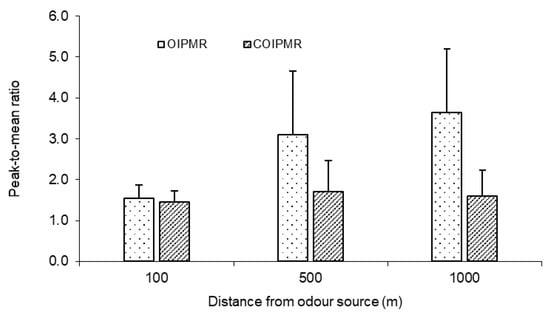
Figure 7.
Comparison of measured PMR_OI (peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity) and CPMR_OI (conditioned peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity) (30 min averaging time) along the wind direction at 100, 500, and 1000 m from odour source (bar: standard deviation).
3.3.2. Variation of PMR_OI with Distance to the Odour Source
It was observed that the PMR_OI increased with the distance from the odour source, while the CPMR_OI changed little with the distance (Figure 7). For example, the PMR_OI for a 30 min averaging time increased from 1.5 to 3.1 and 3.6 as the distance increased from 100 to 500 and 1000 m. ANOVA indicated that the effect of distance from the odour source on PMR_OI was statistically significant (p < 0.05). Comparing Figure 5 and Figure 7 indicated that the intermittency had a dominant effect on the PMR_OI. Specifically, decreasing intermittency at longer distances could result in a lower mean odour intensity and higher PMR_OI. To support this argument, the following set of simplified equations was proposed to estimate the PMR_OI:
where
PMR_OI* = peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity as a function of intermittency;
Ii = a reading of odour intensity at a time point;
N = total number of readings within a time period.
Based on the definition of PMR_OI*, all zero Ii values are included in the calculation. If the zeros are excluded, the conditioned mean Im,c is obtained. Given that the difference between the “true” odour intensity mean Im and the conditioned mean Im,c is due to the intermittency, it is reasonable to assume that the mean was proportional to the intermittency and the conditioned mean, that is, Im = ληIm,c. The PMR_OI* is now calculated as
where
Im,c = conditioned mean intensity (the mean of non-zero readings);
η = intermittency;
λ = a proportional constant.
Given that both Ip and Im,c are independent of intermittency, it was further assumed that they both follow a similar exponential decay pattern in the atmosphere as the distance to the source increases (due to dilution):
where
= peak odour intensity (constant) at x = 0;
= conditioned mean odour intensity (constant) at x = 0;
x = distance from the odour source;
a = constant.
Substituting Equation (7) into (6) yields:
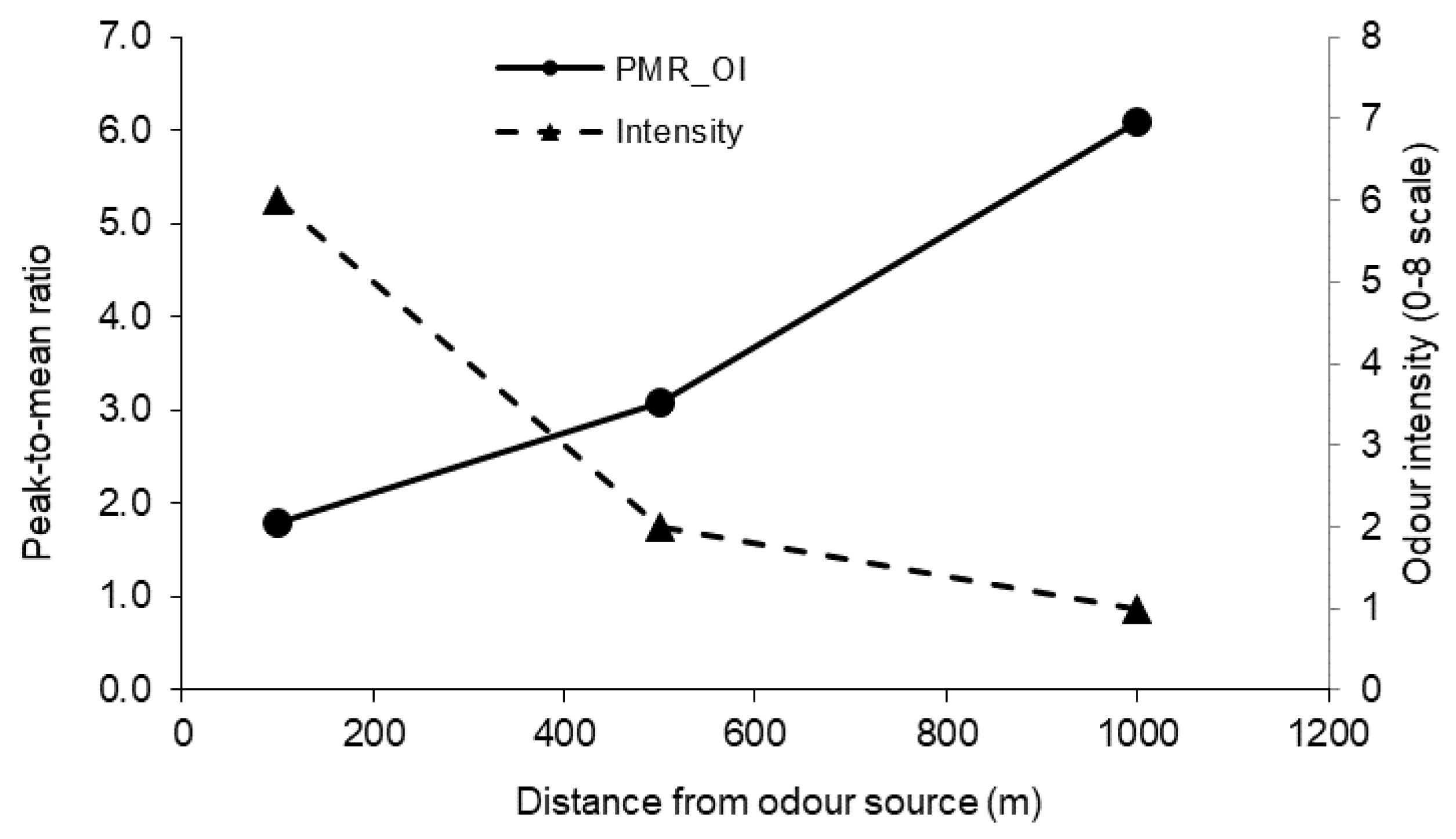
The above equation indicates that PMR_OI* increases as the intermittency decreases. The intermittency η decreases with distance x (Table 3), and therefore, PMR_OI* increases with distance. It should be noted that at longer distances, the actual odour levels were much lower even though the PMR_OI was higher. Taking the measurement session of August 5 as an example (the measurements of other dates had similar patterns), the PMR_OI was 1.8, 3.1, and 6.1 for 100, 500, and 1000 m, respectively, while the measured peak odour intensity was 6.0, 2.0, and 1.0 at the three distances, respectively (Figure 8).
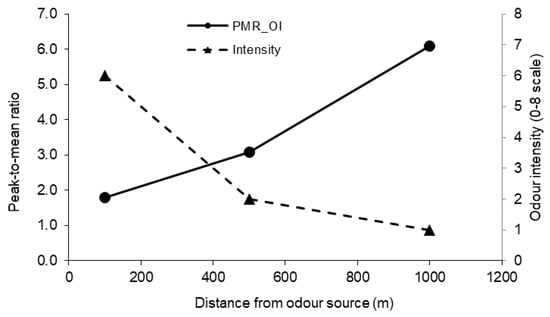
Figure 8.
Variations of the PMR_OI (30 min averaging time) and odour intensity with distance from the odour source.
3.3.3. Effect of Wind Direction on PMR_OI
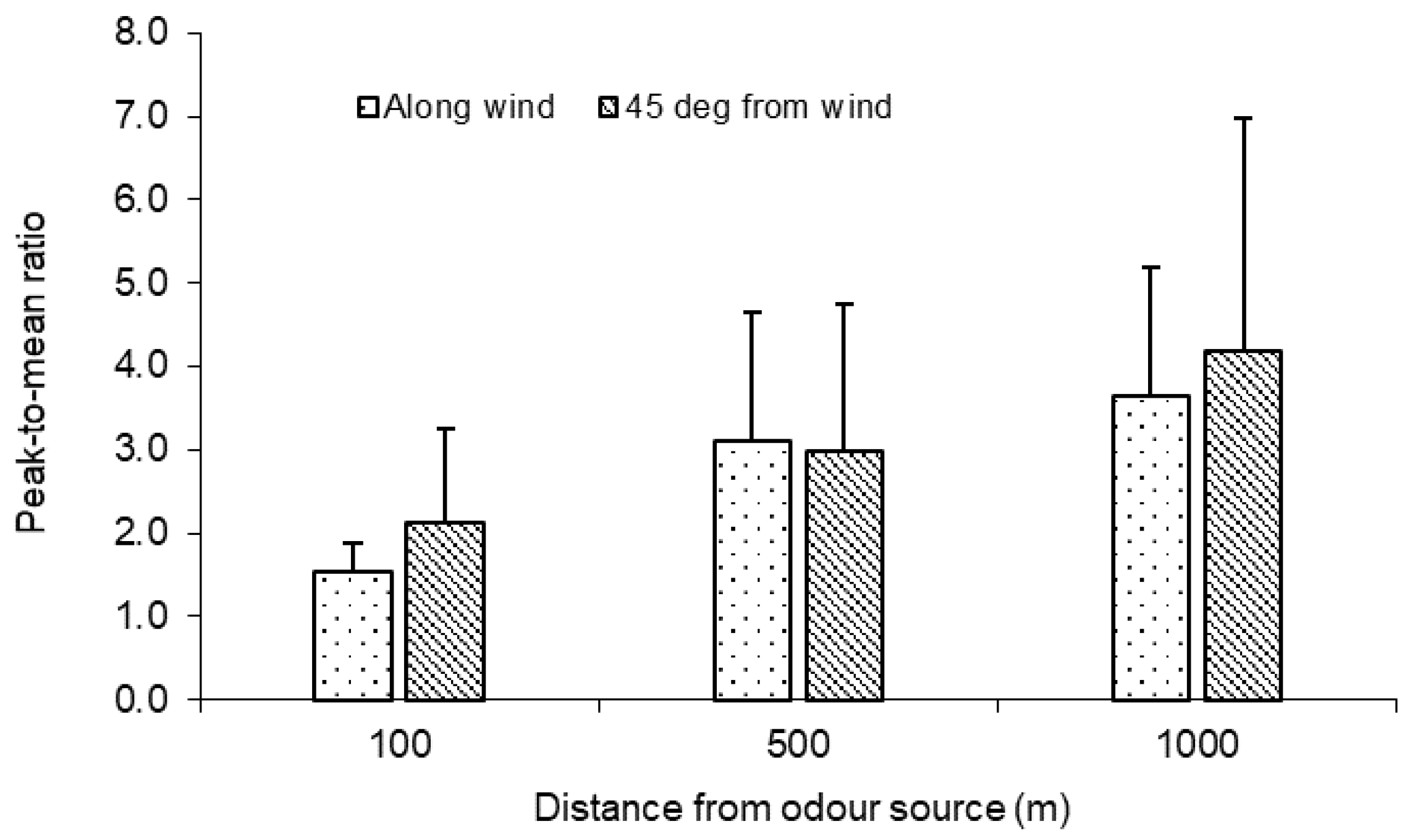
In the off-wind directions, more zero odour readings were generally recorded, and consequently, higher PMR_OIs were observed (Figure 9). Two-way ANOVA, considering the effects of the angle from the wind direction and the distance from the odour source, indicated that the angle effect on the PMR_OI was not significant (p > 0.05) at 500 m but was significant at 100 and 1000 m. The largest difference in PMR_OI between the 0° and 45° angles was about 17% (3.6 vs. 4.2) at 1000 m.
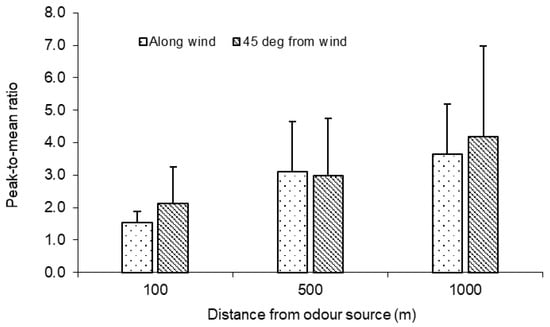
Figure 9.
Comparison of measured PMR_OIs (30 min averaging time) between 0° (along the wind direction) and 45° from wind direction at 100, 500, and 1000 m from the odour source.
3.3.4. Effect of Atmospheric Stability on PMR_OI
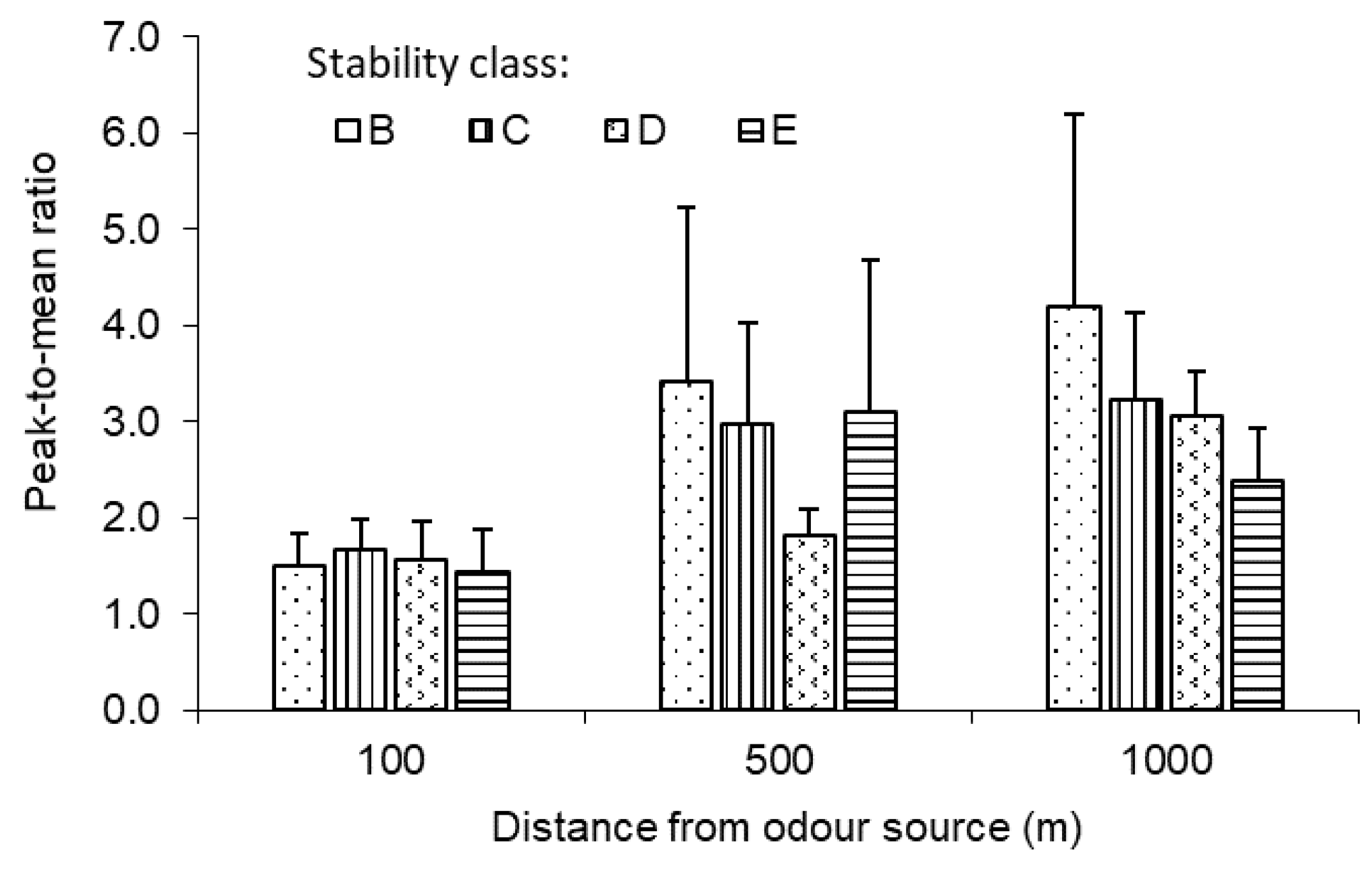
Of the 51 measurement sessions, there were only two sessions at atmospheric stability class A, which did not generate sufficient data to include stability class A in the statistical analysis. Therefore, only the data for atmospheric stability classes B, C, D, and E were analysed. Two-way ANOVA indicated that the effect of atmospheric stability on the PRM_OI was not significant (p > 0.05) at 100 and 500 m and was significant at 1000 m (Figure 10). At 1000 m, the more turbulent (unstable) the atmosphere was, the higher the PMR_OI. Specifically, the PMR_OI decreased from 4.2 to 3.2, 3.1, and 2.4 as the stability changed from B (unstable) to, C, D, and E (slightly stable).
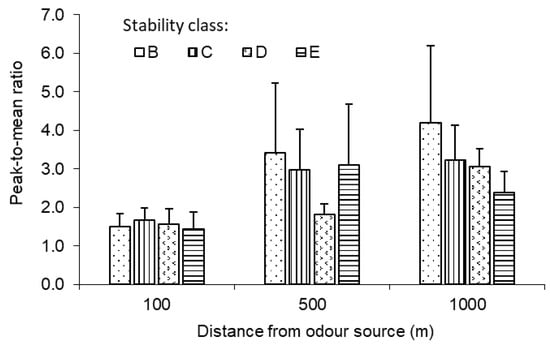
Figure 10.
Measured PMR_OI for 30 min averaging time under different stability classes (B, C, D, and E) at 100, 500, and 1000 m from the odour source.
3.3.5. Effect of Averaging Time on PMR_OI
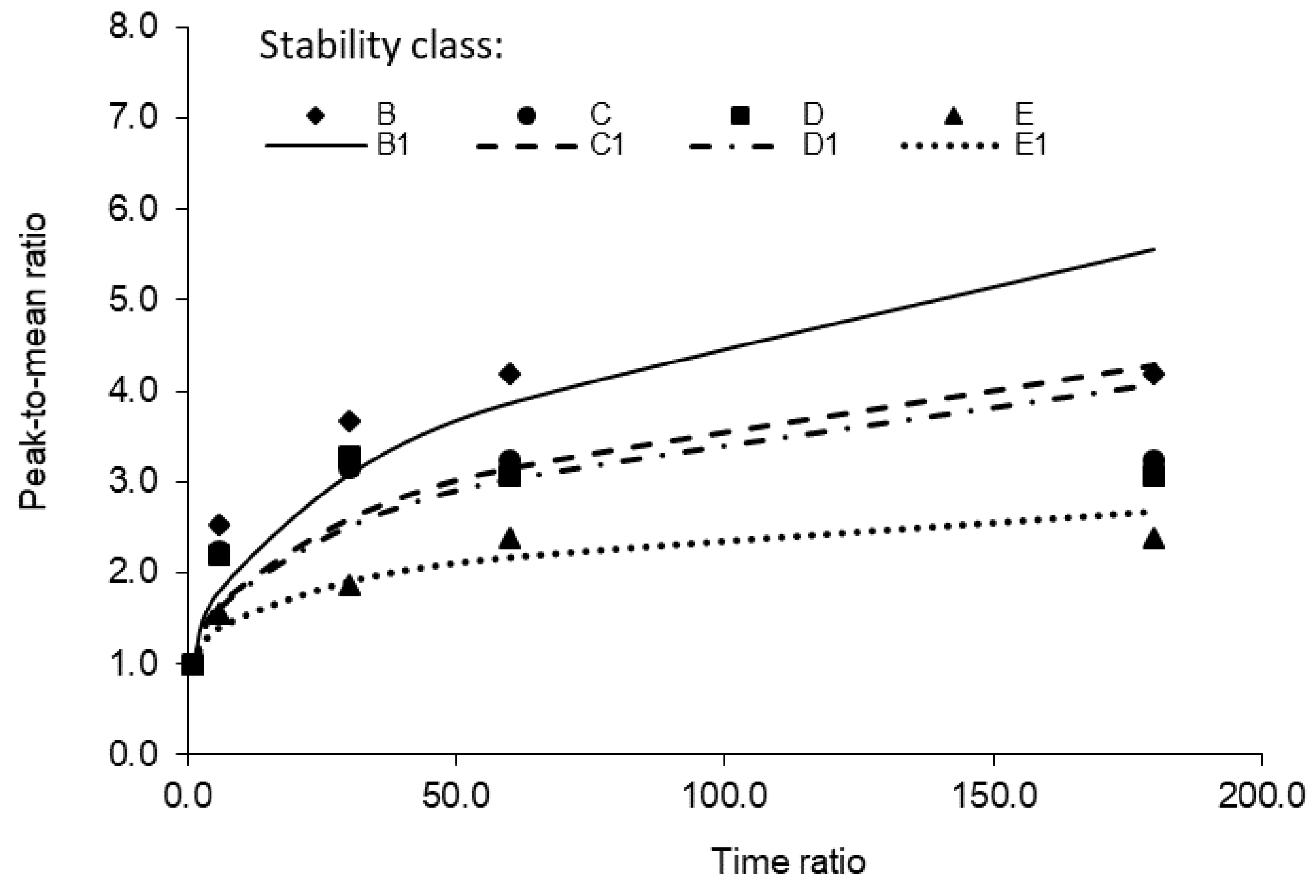
The measured PMR_OI increased with the averaging time, and the largest increase was observed at 1000 m under stability class B: from 2.5 to 4.2 when the averaging time increased from 1 to 30 min. The increase of the PMR_OI with the averaging time followed a non-linear pattern (Figure 11). Therefore, the same power function as defined in Equation (1), i.e., PMR_OI = (tm/tp)q, was used to predict the PMR_OI from the time ratio (tm/tp). To evaluate the exponent q in the equation, the PMR_OI was plotted against (tm/tp) in the log–log scale and the exponent q was determined as the slope of the regression line (Table 4). The exponent q decreased from 0.33 for stability class B (unstable) to 0.19 for E (slightly stable). The measured exponent values were lower than those reported in the literature for unstable atmosphere conditions. Smith [13] gave the following q-values for three stability classes: 0.65 (stability class B), 0.52 (C), and 0.35 (D). Duffee et al. [27] reported values of q being 0.50 for stability class A or B, 0.33 for C, 0.20 for D, and 0.17 for E and F.
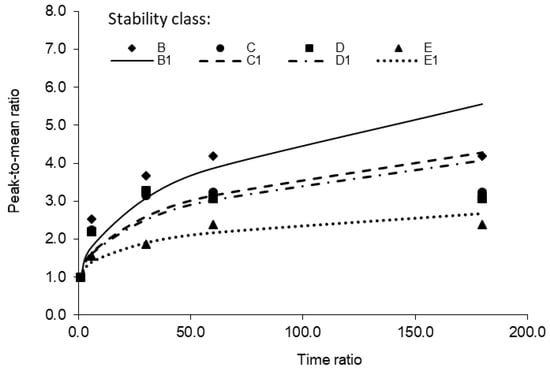
Figure 11.
Variation of the PMR_OI with the time ratio (tm/tp) at 1000 m from the odour source under different atmospheric stability classes (B1, C1, D1, and E1 are curves predicted by the equation PMR_OI = (tm/tp)q for stability classes B, C, D, and E, respectively).

Table 4.
Results of the regression for log(PMR_OI) = q log(tm/tp) for different stability classes.
4. Conclusions
Odour in the atmosphere near (within 1000 m) swine operations was intermittent. The intermittency, defined as the proportion of time when odour was detected, generally decreased with the distance from the odour source, and the decreases were more pronounced for the shorter averaging time of 1 min. The intermittency also increased with the averaging time, in particular at longer distances.
The peak-to-mean ratio of odour intensity (PMR_OI) in the atmosphere increased with the distance from the odour source. Along the wind direction, the 30 min PMR_OI increased from 1.5 at 100 m to 3.6 at 1000 m. The higher PMR_OI at longer distance from the odour source was primarily due to the lower intermittency at longer distances.
The effect of atmospheric stability on PMR_OI was not apparent within 500 m from the odour source. At 1000 m, the PMR_OI decreased as the atmospheric stability changed from unstable (B) to slightly stable (E) conditions.
The PMR_OI increased with the averaging time in a non-linear pattern. The increase of the PMR_OI with the peak-to-mean time ratio could be reasonably predicted by the power law, with the exponent decreased from 0.33 to 0.19 as the atmospheric stability class changed from stability class B to E.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z.; methodology, Q.Z. and X.Z.; software, Q.Z.; validation, Q.Z. and X.Z.; formal analysis, Q.Z. and X.Z.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, Q.Z.; data curation, X.Z. and Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.Z. and X.Z.; visualization, Q.Z. and X.Z.; supervision, Q.Z.; project administration, Q.Z.; funding acquisition, Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Manitoba Livestock Manure Management Initiative, grant number MLMMI 03-HERS-01, and the APC was funded by the University of Manitoba.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gifford, F. Peak to average concentration ratios according to a fluctuating plume dispersion model. Int. J. Air Pollut. 1960, 3, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, P.R.; Lunney, K.E.; Killip, C.A. Statistical elements of predicting the impact of a variety of odour sources. In Proceedings of the 1st IWA International Conference on Odour and VOCs: Measurement, Regulation and Control Techniques, The University of NSW, Sydney, 25–29 March 2001; pp. 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Latos, M.; Karageorgos, P.; Mpasiakos, C.H.; Kalogerakis, N.; Lazaridis, M. Dispersion modeling of odours emitted from pig farms: winter-spring measurements. Global NEST J. 2010, 12, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mylne, K.R.; Mason, P.J. Concentration fluctuation measurements in a dispersing plume at a range of up to 1000 m. Quart. J Royal Meteorol Soc. 1991, 117, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, I.A. The relationship between peak and mean concentrations. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1961, 11, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E. Recommended Guide for the Prediction of the Dispersion of Airborne Effluents; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Nicell, J.A. Assessment and regulation of odour impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauberger, G.; Piringer, M.; Schmitzer, R.; Kamp, M.; Sowa, A.; Koch, R.; Eckhof, W.; Grimm, E.; Kypke, J.; Hartung, E. Concept to assess the human perception of odour by estimating short-time peak concentrations from one-hour mean values. Reply to a comment by Müller, et al. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.; Guarino, M.; Bacenetti, J. Measurements techniques and models to assess odor annoyance: A review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, N.G.; Gale, H.J.; Crooks, R.N. The atmospheric diffusion of gases discharged from the chimney of the Harwell Reactor BEPO. Int. J. Air Pollut. 1958, 1, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, H.E. Measurements of turbulence structure near the ground within the frequency range from 0.5 to 0.01 cycles/sec. In Advances in Geophysics; Landsberg, H.E., Van Mieghem, J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959; Volume 6, pp. 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hino, M. Maximum ground-level concentration and sampling time. Atmos. Environ. 1968, 2, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J. Dispersion of odours from ground level agricultural sources. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1993, 54, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauberger, G.; Piringer, M.; Petz, E. Diurnal and annual variation of the sensation distance of odour emitted by livestock buildings calculated by the Austrian odour dispersion model (AODM). Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4839–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.S. On the psychophysical law. Psychol. Rev. 1957, 64, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambient Air-Determination of Odour in Ambient Air by Using Field Inspection-Part 1: Grid Method; EN 16841-1; European Committee for Standardization CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Ambient Air-Determination of Odour in Ambient Air by Using Field Inspection-Part 2: Plume Method; EN 16841-2:2016; European Committee for Standardization CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- ASTM. E544-10: Standard Practices for Referencing Suprathreshold Odour Intensity; Annual Book of ASTM Standards; American Society of Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- York, R.K.; Zhang, Q.; King, M.W. Evaluation of Uptake of Swine Odour Simulant Components onto Cloth Swatches Using Instrumental (Electronic Nose) and Sensory Panel Assessments; Paper No. ASCE 02-602; Joint conference of the CSAE/SCGR and Agricultural Institute of Canada: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B.G.; Shaffer, G.S.; Gilmore, M.M. Derivation and evaluation of a semantic scale of oral sensation magnitude with apparent ratio properties. Chem. Senses 1993, 18, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannebeck, B.; Mannebeck, C.; Mannebeck, D.; Hauschildt, H.; Van Den Burgd, A. Field inspections according to prEN 16841-1:2015 in a naturally evolved neighborhood of industry and living areas, state-of-the-art-technology of a comprehensive data collection, interaction of different sources and effects on the perceiving citizens. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 54, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, C.; Schulte, D.; Hoff, S.; Jacobson, L.; Parkhurst, A. Comparison of Ambient Odor Assessment Techniques in a Controlled Environment. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.; Guo, H.; Schmidt, D.; Nicolai, R.; Zhu, J.; Janni, K. Development of the OFFSET model for determination of odor-annoyance-free setback distances from animal production sites: Part I. Review and experiment. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Jacobson, L.; Schmidt, R.; Nicolai, R.; Zhu, J.; Janni, K. Development of the OFFSET model for determination of odor-annoyance-free setback distances from animal production sites: Part II. Model development and evaluations. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.; Zhang, T. Smelling directions: Olfaction modulates ambiguous visual motion perception. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffee, R.A.; O’Brien, M.A.; Ostojic, N. Recent developments and current practices in odour regulations, controls and technology. “Odour Modeling—Why and How. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. Trans. 1991, 18, 289–306. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).