Evaluation of the Performance of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors at a High Mountain Station with Complex Meteorological Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Measurement Techniques
3. Inter-Comparison Results
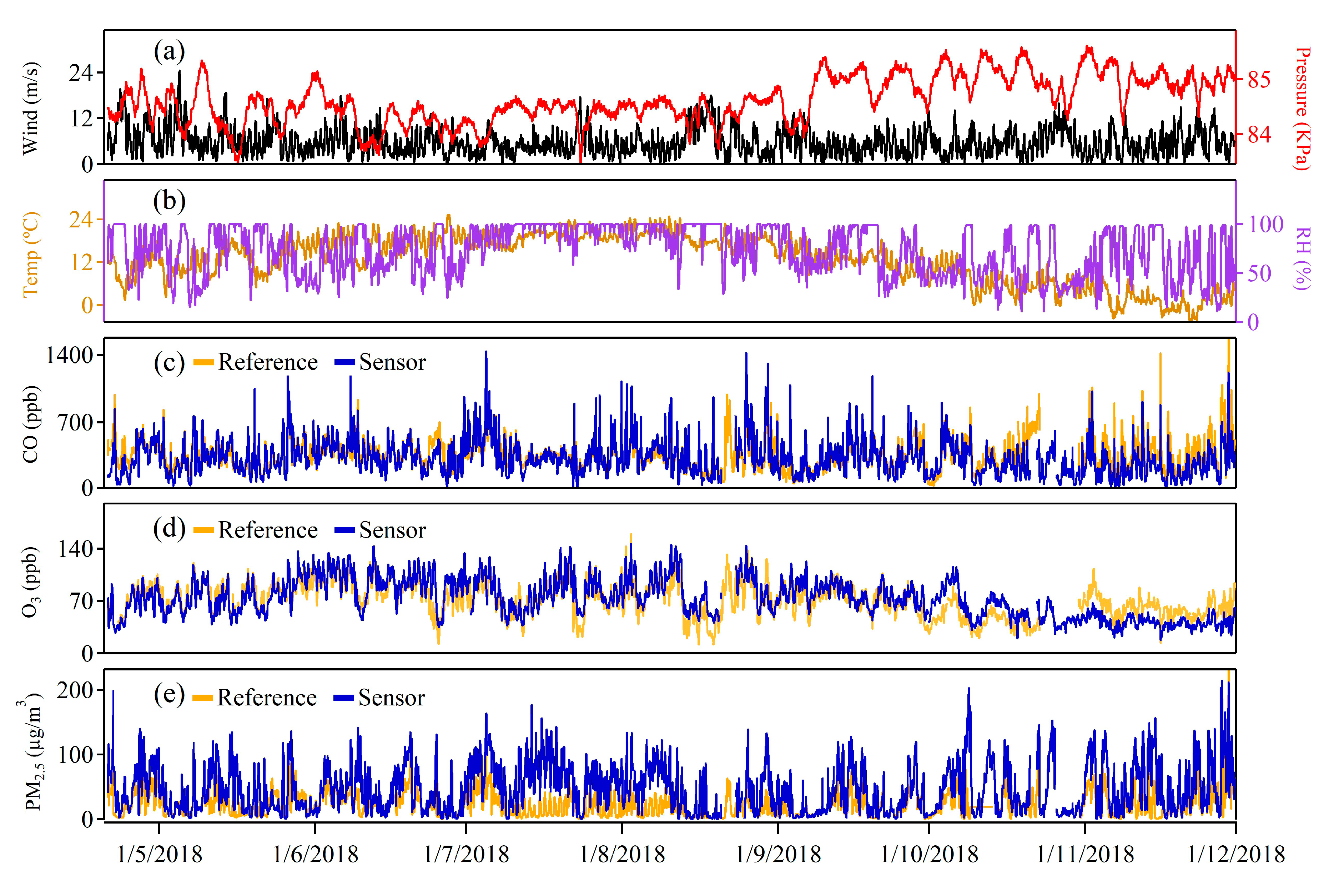
3.1. Overview of the Measured Air Quality and Meteorological Conditions
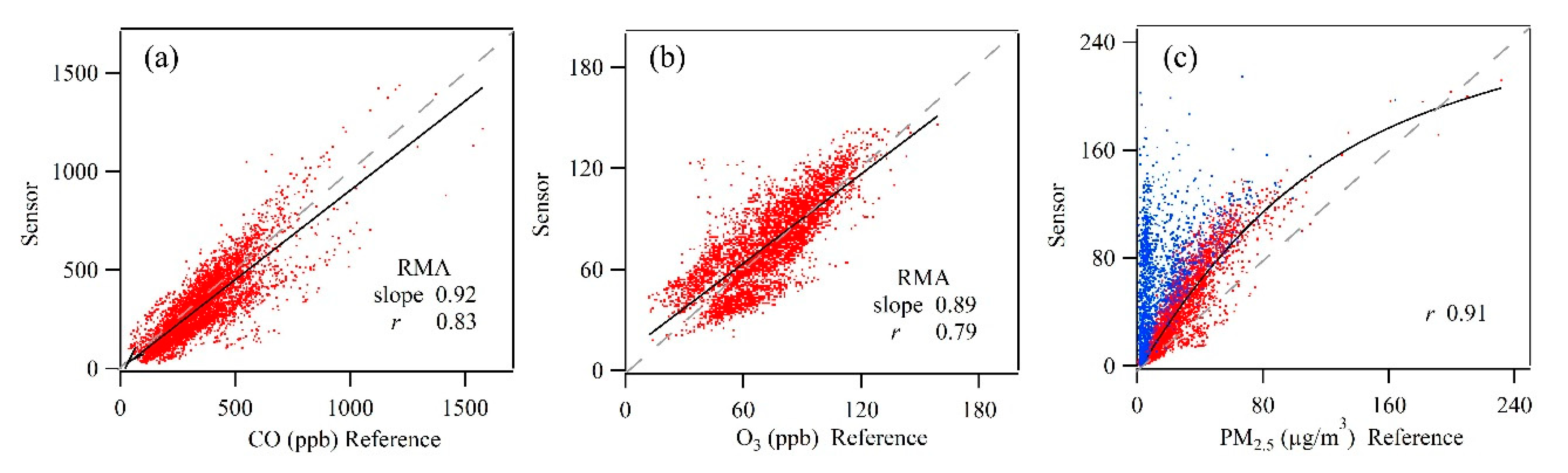
3.2. Inter-Comparison between Sensors and Reference Analyzers
3.3. Effect of Meteorological Factors on the Sensor Measurements
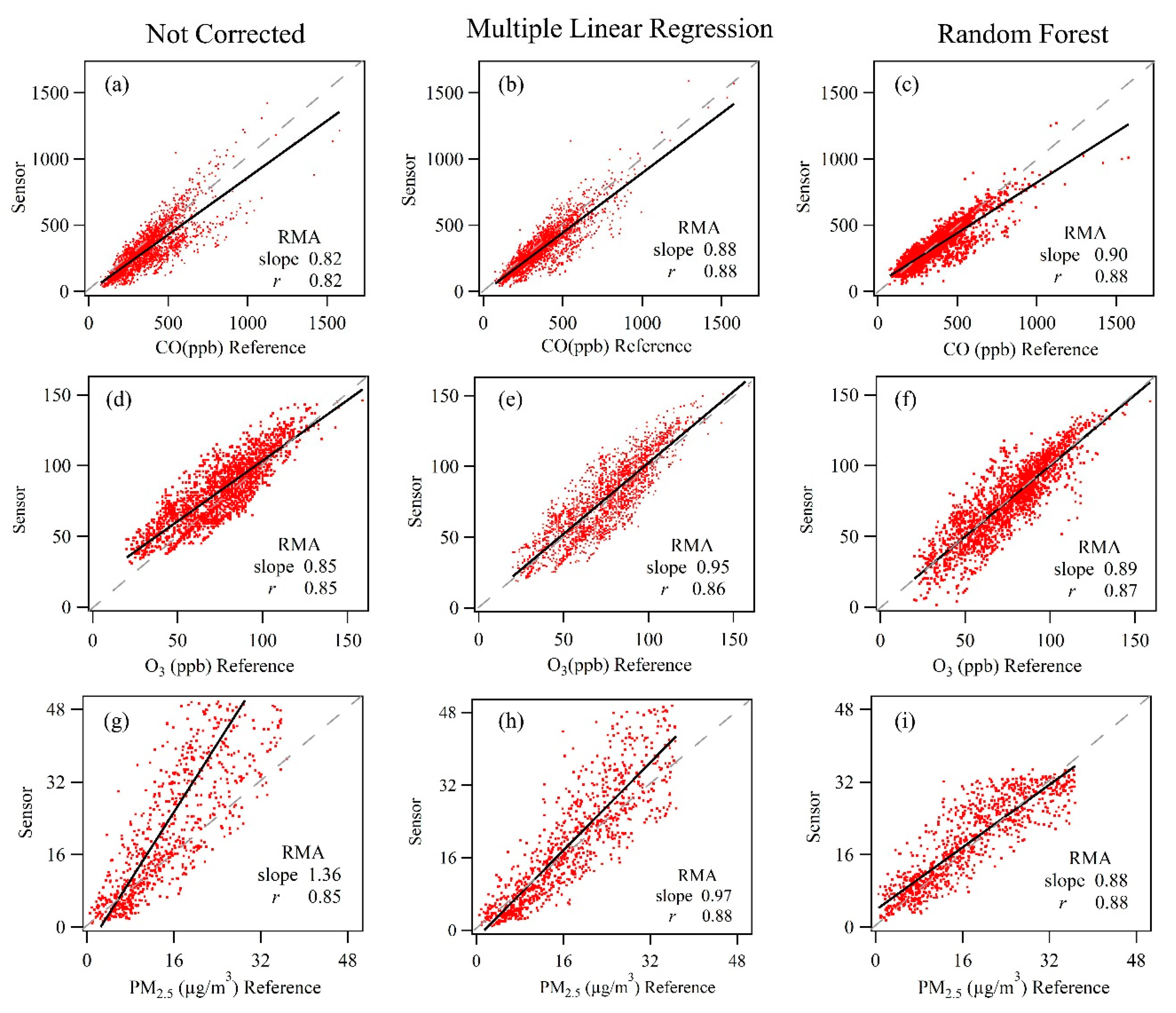
4. Correction of the Sensor Measurement Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chameides, W.L.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.C.; Bergin, M.; Zhou, X.; Mearns, L.; Wang, G.; Kiang, C.S.; Saylor, R.D.; Luo, C. Case Study of the Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols and Regional Haze on Agriculture: An Opportunity to Enhance Crop Yields in China through Emission Controls? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13626–13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chameides, W.L.; Xingsheng, L.; Xiaoyan, T.; Xiuji, Z.; Luo, C.; Kiang, C.S.; St John, J.; Saylor, R.D.; Liu, S.C.; Lam, K.S.; et al. Is ozone pollution affecting crop yields in China? Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Kulka, R.; Dubeau, A.; Martin, C.; Wang, D.; Dales, R. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability and Respiratory Function in Urban Cyclists. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.J.; Sherwood, S.C.; Norris, J.R.; Zender, C.S. Recent Northern Hemisphere tropical expansion primarily driven by black carbon and tropospheric ozone. Nature 2012, 485, U350–U393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, J.E.; Wu, J.; Lombardi, C.; Qiu, J.H.; Meyers, T.J.; Wilhelm, M.; Cockburn, M.; Ritz, B. Childhood Cancer and Traffic-Related Air Pollution Exposure in Pregnancy and Early Life. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Schneider, P.; Haugen, R.; Vogt, M. Performance Assessment of a Low-Cost PM2.5 Sensor for a near Four-Month Period in Oslo, Norway. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstius, D.M.; Pillarisetti, A.; Smith, K.R.; Seto, E. Field calibrations of a low-cost aerosol sensor at a regulatory monitoring site in California. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousan, S.; Koehler, K.; Hallett, L.; Peters, T.M. Evaluation of the Alphasense optical particle counter (OPC-N2) and the Grimm portable aerosol spectrometer (PAS-1.108). Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.S.; Williams, L.R.; Lewis, D.K.; Magoon, G.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Kaminsky, M.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jayne, J.T. Use of electrochemical sensors for measurement of air pollution: Correcting interference response and validating measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenfratz, D.; Saukh, O.; Walser, C.; Hueglin, C.; Fierz, M.; Arn, T.; Beutel, J.; Thiele, L. Deriving high-resolution urban air pollution maps using mobile sensor nodes. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2015, 16, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, I.; Bright, V.B.; McLeod, M.W.; Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Jones, R.L. Source attribution of air pollution by spatial scale separation using high spatial density networks of low cost air quality sensors. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Castell, N.; Vogt, M.; Dauge, F.R.; Lahoz, W.A.; Bartonova, A. Mapping urban air quality in near real-time using observations from low-cost sensors and model information. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.C.; Roberge, B.; Goyer, N. Cross-sensitivities of electrochemical detectors used to monitor worker exposures to airborne contaminants: False positive responses in the absence of target analytes. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 8, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, T.M.; Ott, D.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T. Comparison of the Grimm 1.108 and 1.109 portable aerosol spectrometer to the TSI 3321 aerodynamic particle sizer for dry particles. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2006, 50, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, E.; Novosselov, I.; Seto, E.; Yost, M.G. Laboratory Evaluation of the Shinyei PPD42NS Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.K.; Chen, D.R. Performance calibration of low-cost and portable particular matter (PM) sensors. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2017, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapostolou, V.; Zhang, H.; Feenstra, B.J.; Polidori, A. Development of an environmental chamber for evaluating the performance of low-cost air quality sensors under controlled conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.B.; Shaw, M.D.; Gillot, S.; Lewis, A.C. The impacts of water vapour and co-pollutants on the performance of electrochemical gas sensors used for air quality monitoring. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2018, 266, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Ning, Z.; Ye, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.H.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K. Impact Analysis of Temperature and Humidity Conditions on Electrochemical Sensor Response in Ambient Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Jing, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.K.; Biswas, P. Laboratory Evaluation and Calibration of Three Low- Cost Particle Sensors for Particulate Matter Measurement. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.B.; Shaw, M.D.; Lewis, A.C.; Carpenter, L.J.; Batchellier, T. Electrochemical ozone sensors: A miniaturised alternative for ozone measurements in laboratory experiments and air-quality monitoring. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 240, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, B.; Fine, P.M.; Delfino, R.; Sioutas, C. Performance evaluation of the active-flow personal DataRAM PM2.5 mass monitor (Thermo Anderson pDR-1200) designed for continuous personal exposure measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost commercially available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part B: NO, CO and CO2. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part A: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2015, 215, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gillespie, J.; Schuder, M.D.; Duberstein, W.; Beverland, I.J.; Heal, M.R. Evaluation and calibration of Aeroqual series 500 portable gas sensors for accurate measurement of ambient ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, N.; Piedrahita, R.; Hannigan, M. Quantification Method for Electrolytic Sensors in Long-Term Monitoring of Ambient Air Quality. Sensors 2015, 15, 27283–27302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Mead, M.I.; Jones, R.L. Development of a baseline-temperature correction methodology for electrochemical sensors and its implications for long-term stability. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Hagler, G.; Williams, R.; Sharpe, R.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Judge, R.; Caudill, M.; Rickard, J.; Davis, M.; et al. Community Air Sensor Network (CAIRSENSE) project: Evaluation of low-cost sensor performance in a suburban environment in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogulski, M. Low-cost PM monitors as an opportunity to increase the spatiotemporal resolution of measurements of air quality. In International Scientific Conference-Environmental and Climate Technologies; Valtere, S., Ed.; Elsevier Science Bv: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 128, pp. 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.S.; Bergin, M.H.; Johnson, K.K.; Tripathi, S.N.; Shirodkar, S.; Landis, M.S.; Sutaria, R.; Carlson, D.E. Field evaluation of low-cost particulate matter sensors in high-and low-concentration environments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4823–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The use of electrochemical sensors for monitoring urban air quality in low-cost, high-density networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.; Lee, J.D.; Edwards, P.M.; Shaw, M.D.; Evans, M.J.; Moller, S.J.; Smith, K.R.; Buckley, J.W.; Ellis, M.; Gillot, S.R.; et al. Evaluating the performance of low cost chemical sensors for air pollution research. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagulian, F.; Gerboles, M.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Lagler, F.; Borowiak, A. Review of Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring; Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alejandro, V.; Renato, F.; Filippo, G.; Bartolomeo, M.; Maurizio, R. A Mobile and Low-Cost System for Environmental Monitoring: A Case Study. Sensors 2016, 16, 710. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H. Fine Particle Sensor Based on Multi-Angle Light Scattering and Data Fusion. Sensors 2017, 17, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaliere, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Martelli, F.; Matese, A.; Toscano, P.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A. Development of Low-Cost Air Quality Stations for Next Generation Monitoring Networks: Calibration and Validation of PM2.5 and PM10 Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.W.; Du, Y.J.; Wang, J.N.; Li, T.T. Calibration of a low-cost PM2.5 monitor using a random forest model. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, C.; Ginja, J.; Coutinho, M.; Ribeiro, C.; Karatzas, K.; Sioumis, T.H.; Katsifarakis, N.; Konstantinidis, K.; De Vito, S.; Esposito, E.; et al. Assessment of air quality microsensors versus reference methods: The EuNetAir joint exercise. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 147, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Mueller, M.; Grange, S.K.; Ghermandi, G.; Hueglin, C. Performance of NO, NO2 low cost sensors and three calibration approaches within a real world application. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, J.M.; Borge, R.; Narros, A. Using statistical methods to carry out in field calibrations of low cost air quality sensors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 267, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, X.F.; Xu, C.H.; Chen, T.S.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, W.X. Summertime fine particulate nitrate pollution in the North China Plain: Increasing trends, formation mechanisms and implications for control policy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11261–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.K.; Ding, A.J.; Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, X.Z.; Lei, H.C.; Jin, D.Z.; Qi, Y.B. Aircraft measurements of the vertical distribution of sulfur dioxide and aerosol scattering coefficient in China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kivekas, N.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, X.C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Particle Climatology in Central East China Retrieved from Measurements in Planetary Boundary Layer and in Free Troposphere at a 1500-m-High Mountaintop Site. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, L.L.; Lin, J.T.; Ni, R.J.; Yan, Y.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.Z.; et al. Impacts of meteorology and emissions on summertime surface ozone increases over central eastern China between 2003 and 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Ding, A.J.; Cooper, O.R.; Lin, M.Y.; Xu, P.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.F.; et al. Significant increase of summertime ozone at Mount Tai in Central Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10637–10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, L.K.; Yao, L.; Li, Q.Y.; Wen, L.; Zhu, Y.H.; Chen, T.S.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, T.; et al. Carbonyl compounds at Mount Tai in the North China Plain: Characteristics, sources, and effects on ozone formation. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Ding, A.J.; Liu, C.B. Observational study of ozone and carbon monoxide at the summit of mount Tai (1534 m a.s.l.) in central-eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4779–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.K.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Deliger; Poon, C.N.; Ding, A.J.; Zhou, X.H.; Wu, W.S.; Tang, J.; et al. Source of surface ozone and reactive nitrogen speciation at Mount Waliguan in western China: New insights from the 2006 summer study. J. Geophys. Res.Atmos. 2011, 116, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Chen, T.S.; Zheng, P.G.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.F.; Mellouki, A.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, W.X. Nitrous acid in marine boundary layer over eastern Bohai Sea, China: Characteristics, sources, and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, D.J. A comparative-analysis of the reduced major axis technique of fitting lines to bivariate data. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 17, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Subramanian, R. A machine learning calibration model using random forests to improve sensor performance for lower-cost air quality monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | CO (ppb) | O3 (ppb) | PM2.5 (μg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation Principle | Three-electrode electrochemical | Three-electrode electrochemical | Laser scattering method |
| Nominal Range | 0–200 ppm | 0–5 ppm | 0.0–1999.9 μg/m3 |
| Resolution | <0.1 ppm | <0.02 ppm | <10 μg/m3 |
| Response Time | <40 s | <60 s | 1 s |
| Maximum Zero Shift | 2 ppm | 0.1 ppm | - |
| Relative Humidity Range | 15%–90% | 15%–90% | 0%–99% |
| Temperature Range | −20 °C to 50 °C | −20 °C to 50 °C | 5 °C to 50 °C |
| Pressure Range | Atmospheric ± 10% | Atmospheric ± 10% | 86–110 kPa |
| Expected Operation Life | 3 years in air | 2 years in air | 3 years |
| Species | Median | Average | Standard Deviation | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 5.1 | 5.8 | 3.6 | 24.5 | 0.0 |
| Temperature (°C) | 14.0 | 12.6 | 6.7 | 25.4 | −4.8 |
| Relative Humidity (%) | 77.6 | 73.0 | 24.2 | 100.0 | 10.7 |
| Atmospheric Pressure (kPa) | 84.6 | 84.6 | 0.4 | 85.6 | 83.4 |
| CO (ppbv, sensor) | 299 | 324 | 179 | 1436 | 17 |
| CO (ppbv, reference) | 342 | 360 | 164 | 1578 | 38 |
| O3 (ppbv, sensor) | 72 | 73 | 25 | 146 | 18 |
| O3 (ppbv, reference) | 72 | 72 | 22 | 159 | 12 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3, sensor) | 38.0 | 46.6 | 36.7 | 214.5 | 0.4 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3 reference) | 17.9 | 22.5 | 19.7 | 231.9 | 0.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T.; Jiang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Yin, X.; Wu, D.; et al. Evaluation of the Performance of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors at a High Mountain Station with Complex Meteorological Conditions. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020212
Li H, Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Chen T, Jiang Y, Shan Y, Liu Y, Mu J, Yin X, Wu D, et al. Evaluation of the Performance of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors at a High Mountain Station with Complex Meteorological Conditions. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(2):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongyong, Yujiao Zhu, Yong Zhao, Tianshu Chen, Ying Jiang, Ye Shan, Yuhong Liu, Jiangshan Mu, Xiangkun Yin, Di Wu, and et al. 2020. "Evaluation of the Performance of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors at a High Mountain Station with Complex Meteorological Conditions" Atmosphere 11, no. 2: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020212
APA StyleLi, H., Zhu, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, T., Jiang, Y., Shan, Y., Liu, Y., Mu, J., Yin, X., Wu, D., Zhang, C., Si, S., Wang, X., Wang, W., & Xue, L. (2020). Evaluation of the Performance of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors at a High Mountain Station with Complex Meteorological Conditions. Atmosphere, 11(2), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020212







