Abstract
Long-term ground-based measurements of aerosol optical properties in Athens, Greece, for the period 2008–2018 performed by the National Observatory of Athens are used in order to investigate the aerosol climatology of the area. In this study, we utilize quality-assured measurements of the aerosol optical depth (AOD), Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) and Ångström exponent obtained by CIMEL photometers in the framework of the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) to extract the seasonality and the trends of aerosols in the region. Higher aerosol loads are found during spring and summer months. A 1.1% per year decrease for AOD at 440 nm and 0.4% decrease per year for SSA during the studied period are recorded. Collocated and synchronous PM10 values, for a five-year period, are used in order to study ground-level conditions. Also, the Planetary Boundary Layer Height from ERA-5 is used to investigate the stratification of the particles. The classification of aerosols using AERONET data is performed to separate dust, biomass burning, polluted urban, marine and continental dominant aerosol mixtures. Also, the characterization of AOD provided by Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) is investigated. Finally, seasonal AOD trends recorded from AERONET from satellite sensors (MODIS-Aqua/MODIS-Terra) and estimated by CAMS are examined, and significant differences have been found.
1. Introduction
Aerosols play an important role in Earth’s climate system, as has been reported by the Intergovermental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) [1], and also affect human health in urban and agricultural areas [2,3,4]. Aerosols absorb and scatter solar radiation; however, these mechanisms still remain a major source of uncertainty in climate modelling [5]. Additionally, aerosol estimation is important for diverse applications such as in the correction of the surface’s satellite retrievals [6,7,8] and in forecasting solar energy [9,10].
Over the last two decades, significant improvements have been performed for surface networks and the satellite retrievals of aerosols, contributing to major improvements in the monitoring and understanding of the related procedures. The major surface aerosol networks include AERONET, which operates hundreds of stations around the globe [11]; SKYNET, which operates more than 60 stations globally with main focus on Asia [12]; and the Global Atmospheric Watch/Precision Filter Radiometer (GAW/PFR), which operates approximately 20 stations with long-term measurements [13,14]. Various homogenization activities for these different networks have been reported [15,16]. Data from these networks have been used frequently for climatological studies. Satellite aerosol retrievals are available from several instruments [17], such as Microwave Integrated Retrieval System (MISR) [18], Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) [19], Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) [20]. Satellite-based products of aerosol properties, although geographically denser, are however more uncertain than ground-based measurements.
Aerosol trends in urban environments have attracted specific interest over recent years as anthropogenic emissions (traffic, industry) undergo significant interannual changes. In addition, satellite retrievals above densely populated areas are subject to significant errors [17], leading to different indications of trends in a number of areas when satellite-derived time series are used [21]. Model sulfate concentrations show a slower rate of decline than sulfur emissions across Western Europe and the USA, mainly as a result of the increased availability of H2O2 in clouds, which alters the oxidization rate of SO2 [22]. In Europe, an average aerosol decrease of 2.3% year for the period 1995–2017 has been reported by the Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gases Research Infrastructure (ACTRIS) [23].
The current study focuses on the city of Athens, Greece, which is located near the coastline in the eastern Mediterranean. The Athens greater area constitutes a complex aerosol environment with a multitude of natural and anthropogenic sources. A common natural procedure in the area is the emission of marine aerosols by the sea surface, which are advected by the wind speed/sea waves and then chemically processed by interactions with gases and water vapor [24]. The long-distance transport of Saharan desert dust aerosols is occasionally observed, especially in spring/summer months, with high aerosol loads in the free troposphere in most cases [25,26,27]. Marinou et al. [28] and Koukouli et al. [29] found a very small negative trend in the dust optical depth in the eastern Mediterranean for the period 2007–2015 using satellite data. Wildfires also contribute to the aerosol mixture in the area occasionally, either by nearby events [30,31] or by long-range transport [32,33]. Athanasopoulou et al. [31] showed that wildfires in Greek forests could lead to up to three times higher aerosol optical depth (AOD) values in the area during summer. The Mediterranean basin is moderately to highly polluted over summer and significantly lower during winter months because of air masses originating from Turkish cities and European industrial areas [34]. A major local aerosol source in the greater area of the Athens basin is biomass burning [35,36,37,38,39], which has significantly increased in winter months since 2010 due to the economic crisis and the associated wood burning for residential heating. In addition, secondary aerosol formation makes a significant contribution in the area [40,41,42,43,44]. Especially during summer months, when the long sunshine duration enhances photochemical activity, secondary aerosols are dominant in the area, particularly when air masses arrive from the northern parts of the Balkan peninsula [45]. Emissions of aerosols linked to vehicle traffic have decreased, but the trend has changed since 2014, which is associated with the lifting pf the ban of diesel vehicles in the metropolitan area [44]. An estimate of the contribution of the different sources to the average AOD loadings over Athens is provided by Gerasopoulos et al. [25], who reported that the annually averaged AOD is 40% due to regional and local sources, 23% due to dust from the Saharan desert and 22% due to European continental sources.
In the present study, we have exploited a 10-year-long data set recorded by the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) in the city of Athens. The seasonality of the aerosol optical properties is investigated and discussed. A hybrid database that combines columnar variables from AERONET and in-situ PM10 measurements has been used as a proxy for the layering of aerosols as well as in respect to the Planetary Boundary Layer Height (PBLH). The classification of aerosols using well-established approaches and modeled data is presented and discussed. Finally, trends in optical parameters, both using AERONET data and modelled data, are compared.
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Background
Aerosol optical depth is the quantity that describes the attenuation of radiation when propagating in an aerosol layer and indirectly quantifies the presence of aerosols in an atmospheric column. It is defined as follows:
where λ is the wavelength, TOA is the top of the atmosphere and baer is the extinction over a vertical optical path. Additionally, Ångström [46] proposed the following formula, which includes the spectral dependence of the extinction:
where α is the Ångström exponent, which parameterizes the spectral dependence of the extinction, and β is a variable indicative of the number of particles found in the solar beam path. Using solar direct irradiance measurements from the ground, AOD is calculated through the Beer–Lambert law, which, when solved for atmospheric boundary conditions, is expressed as follows:
where Ιλ is the irradiance measured at ground level at wavelength λ, Io,λ is the extraterrestrial irradiance at wavelength λ, m is the optical air mass along the line of sight connecting the observations point and the sun, τ is the total optical depth and the term R is the Sun–Earth distance in astronomical units, normalized to the variations around the mean distance. Then, the AOD is extracted from τ by eliminating any other extinctors including trace gases and physical processes such as Rayleigh scattering.
AODλ = β λ−α
Iλ = Io,λ exp(−mτ) R−2
The Ångström exponent α is usually calculated as the ratio of AOD between two wavelengths λ1 and λ2:
The Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) is a variable that is defined as the ratio of scattering to total extinction. The SSA a wavelength λ is defined as the relative contribution of the aerosol scattering extinction (bsca) to total extinction (bsca + babs), thus indirectly also describing the absorption contribution (babs):
SSA(λ) = (bsca (λ))/(bsca (λ)+babs (λ))
The values of SSA could theoretically range from 0 to 1, but for aerosol layers in the Earth’s atmosphere, they are very close to 1, as aerosols mainly scatter the solar light, and are rarely found to be lower than 0.65 [47], when very absorbing aerosols dominate the layer.
The planetary boundary layer is the lowest part of the troposphere, is directly affected by the surface conditions and responds to surface forcing in very short time scale [48]. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) is the height that distinguishes the atmospheric boundary layer from the free troposphere, and the highest values on cloudless days are detected around local noon. On cloudy days, the PBLH has a more complex behavior, resulting in a complicated stratification. In most cases, local emissions of aerosols and trace gases are trapped in this layer; thus, it severely affects the dispersion of pollutants. Stratification in the lower troposphere is the main factor leading to the fact that the columnar properties of aerosols are often different from those measured at the surface. Hence, PBLH could be used to interpret patterns caused by the stratification.
When addressing air quality and public health issues, instead of the columnar AOD, the concentration of different fractions of particulate matter (PM) at ground level is used, with PM10 being the most traditional and most commonly used fraction in terms of legislation obligations. PM10 is defined as the concentration of all solid or liquid-suspended particles that have diameters less than 10 μm. PM10 can be monitored by using different methods such as sampling techniques on filters (reference method)—e.g., cascade impactors which use size selective inlets that favor either a certain particle size range or a particular upper cut-off point—or (almost) real-time techniques such as tapered element oscillating microbalance (TEOM) and light scattering systems—e.g., optical particle counters—while currently the most common method is beta gauge monitors (using the attenuation of beta radiation through a filter of specific particle loading).
2.2. Site
Athens is a city of 3.7 million habitants with an estimated 2.5 million automobiles and heavy traffic, which represents the single greatest source of local emissions. The area has been heavily deindustrialized over recent decades, but there are still emissions linked to factories and fossil fuel. Athens is located in a basin in which three mountains with a height of around 1 km trap most of the urban emissions in the greater area, causing poor ventilation. The dispersion of the pollutants is mainly caused by is the sea breeze along the NE–SW axis [49]. Additionally, there are common cases of the long-distance transport of air masses from arid areas of Northern Africa, frequently associated with dust events that affect the area [50,51]. Athens has a temperate climate with warm and dry summers and wet and mild winters, which is typical for the Eastern Mediterranean. The measurements used in this study were conducted at the urban background site of the National Observatory of Athens (NOA) at Thissio (37.97° N, 23.72° E), which is located at an elevation of 130 m a.s.l. and 8 km from the coastline, in a moderately populated area, where the influence of direct local emissions is limited. A detailed description of the measuring site can be found in Paraskevopoulou [35].
2.3. Measurements
Data from the AERONET station ATHENS-NOA have been used for the period May 2008–September 2018. The instrument is located at the site described in the previous paragraph, and the horizon view is clear at a 360° viewing angle.
The CIMEL Sun-photometer is a filter radiometer developed by Cimel Electronics (Paris, France), which performs direct Sun and sky radiance measurements. Measurements are performed at nine bandpass filters between 340 and 1640 nm (eight of them are dedicated to AOD retrieval, and one us used for integrated water vapor (IWV)). During this time period at the station CIMEL CE318, photometer #440 operated as the main instrument, with some months of operations of CIMEL CE318 photometers #110, #240 and #395 as replacement instruments. Instruments #110 and #240 recorded only four channels (440, 675, 870 and 1020 nm), which shortened the time series of the other wavelengths by a total of 350 days (combined for these instruments). Additionally, gaps in the time series are expected due to the frequent calibrations (annually) demanded by the network protocol. All calibrations were performed at Laboratoire d’Optique Appliquée (LOA) at Université de Lille, France.
Direct measurements are performed usually every 10–15 min. These measurements are processed centrally and are widely available from the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) [11]. Aerosol optical depth data are computed for three data quality levels: Level 1.0 (unscreened), Level 1.5 (cloud screened), and Level 2.0 (cloud-screened and quality-assured). Thus, gaps in time series are caused by cloudy skies and multi-day gaps by instrument malfunction. Additionally, there is an around 2-month-long gap in the time series for every calibration of the instrument.
In this study, AERONET version 3 retrievals have been used [52,53] at level 2.0 for direct Sun and inversion products to guarantee the highest quality. The unique exception is Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) inversion retrievals, for which level 1.5 was used. This practice is relatively common in climatology studies, because AERONET level 2.0 criteria for this product are very strict (Solar Zenith Angle (SZA) > 50° AOD > 0.4) and for many areas, including Athens, such cases are rare. For the presented dataset, level 2.0 filtered out all but 186 SSA level points in 10 years, while at level 1.5, there are 8933 measurements available. A conditional sampling has been applied to level 1.5 data in order to ensure that the quality assurance filtered out only based on AOD values. The sampling criterion applied in the current dataset has been described by Kazadzis et al. [54]. The usage of level 1.5 should be performed while always taking in account the higher uncertainty of this product, which could be up to 0.04 higher than level 2.0 depending on the AOD and SZA.
The monitoring of in situ PM10 takes place continuously at Thissio from NOA as part of the routine station measurements, and data are available from 1 January 2014. The PM10 concentrations near the surface were measured by means of a beta-attenuation monitor (Eberline, FH 62 I-R), which pulls ambient air through the sampling line, and a size-selective inlet for PM10, which deposits particles on a clean section of a filter tape (single filter spot principle) and utilizes the radiometric attenuation (Kr-85 noble gas, with a maximum energy 0.67 MeV) by a two-beam compensation method [55]. Measurements are stored at an initial, 1 min temporal resolution; in this study, we have used the hourly averages. The instrument is located 50 m away from the AERONET site.
The Copernicus Program and its Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) combines state-of-the-art atmospheric modelling of aerosols with Earth observation data to provide information services covering European air quality, global atmospheric composition, climate, and UV and solar energy [56]. CAMS is part of European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) numerical weather prediction and combines the assimilation of satellite data on aerosols and trace gases with chemical modelling and ground-based measurements [57,58]. CAMS is one of the main tools used in Europe for forecasting air quality at regional scales. Emissions sources are also included in the modelling procedure, as well as sedimentation and wet and dry deposition processes [59]. In the current study, we have used 3 h time step outputs from CAMS for pixels corresponding to instrument locations, for the variables AOD at 550 and 1020 nm and for dust, black carbon, organic matter, sea salt and sulfate AOD for the period 2008–2018. Sulfate is assumed to be non-absorbing, and all the assumptions used could be found in the work by Benedetti [59]. The spatial resolution of CAMS data is about 80 km, which could be a source of inconsistencies when compared with a point Sun-photometric measurement, especially in a complex environment such as Athens. The CAMS dataset has potential use for climatological studies in areas without ground-based measurements. Thus, we performed an analysis of this data, despite the expected differences from AERONET, in order to assess the provided climatology and especially the classification of optical depths for different aerosol types.
Spaceborne observations of aerosol optical depth at 550 nm (AOD550), acquired from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), have been utilized in order to investigate their consistency against ground-based data obtained by the AERONET ATHENS-NOA station. MODIS, mounted on NASA’s twin polar-orbit satellites Terra and Aqua, provides pre-noon (Terra) and post-noon (Aqua) columnar aerosol observations, almost on a daily basis, thanks to its wide swath (~2330 km). The MODIS AOD product analyzed here resulted from the merging [60] of the corresponding retrievals obtained from three independent algorithms applied over dark continental [61,62] and maritime [62,63] surfaces (Dark Target) as well as over land areas via the Deep Blue approach [64]. In the current study, the Level 2 (L2) MODIS AOD values (10 km x 10 km spatial resolution at nadir view), provided by the latest version of the applied retrieval algorithms (Collection 6.1, C061), are used. The aforementioned data are organized in bands (segments of 5 min intervals) and have been downloaded from the Level 1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (LAADS) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC) [65]. In order to ensure the best quality of AOD retrievals, only those associated with a Quality Assurance flag equal to 3 have been processed [66]. MODIS AODs satisfying the quality control criterion are spatially averaged in a circle centered on the Athens AERONET station with a radius of 20 km. All the regional AOD averages are calculated for every day with available satellite data during the period 2008–2018.
3. Results
3.1. Seasonality
Since the aim of this work is to define the climatology of aerosols in Athens area, the monthly means of AOD at all seven recorded wavelengths are presented in Figure 1. Monthly mean values are counter-proportional to wavelength, as 870, 1020 and 1640 nm show very low mean values (almost always < 0.1), while UV wavelengths record the highest values. Retrievals at 1640, 1020, 870 and 675 nm have peak monthly AOD values in April–May, while 440 nm and UV AODs demonstrate the highest values in July–August. AOD values at 675, 870, 1020 and 1640 nm show a secondary peak during summer months. At all wavelengths, the lowest monthly values are recorded in January and December. Additionally, it should be noted that there is a local maximum at all wavelengths for November mean values. This behavior is mainly explained by the maximum values recorded during November 2010 and 2011. It should be noted that during November 2011, there was a severe drought in Eastern Europe, which resulted in wildfires in Ukraine, Moldova and Slovakia. It has been reported in earlier studies that, depending on synoptic conditions, plumes from these areas reach Greece [67].
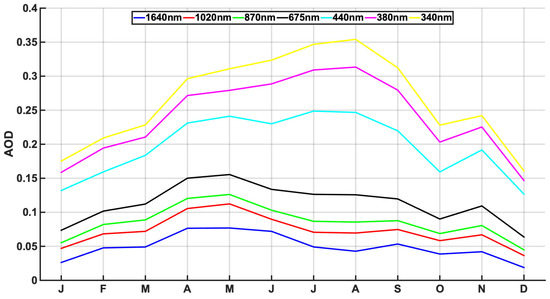
Figure 1.
Monthly mean of aerosol optical depth (AOD) at all seven Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) wavelengths, calculated for months with at least 15 days of data.
Monthly values of the Ångström exponent of 440–870 nm (Figure 2) show that the AOD peak in July–August is related to higher α values, which imply more fine aerosols in the mixture. Meanwhile, in April–May, the Ångström exponent has the lowest values, which indicates a dominance of coarse mode particles. This attribute explains the different spectral behavior of monthly mean values in Figure 1, where higher values are found at shorter wavelengths with different seasonality. Additionally, it should be highlighted that for January and December, when AOD is generally very low, the Ångström exponent has different behavior. The mean December Ångström exponent is high (1.52), but for January, the mean value is 1.02, which implies almost equal fine and coarse fractions. Figure 2 also reports the number of data points per month in the whole measuring period. Since measurements depend on direct solar irradiance, the amount of data is related to the sunshine duration. January and December have the least data, with 2127 and 2100 points, respectively, and August is the month with the largest dataset, with 13,182 data points.
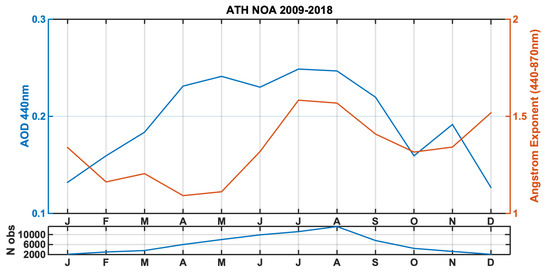
Figure 2.
Monthly mean of AOD 440 nm and Ångström exponent 440–870 nm. The lower plot shows the amount of data per month.
Figure 3 shows the mean size distribution per month, providing more evidence for the arguments presented in the previous paragraph. The coarse mode has its maxima in May, June and April, which is the period with the highest occurrence of Saharan dust events in the area due to enhanced cyclonic activity [50]. Meanwhile, the fine mode shows maximum values during August, September and July. December is the period in which fine mode dominates, while the coarse mode has very low values. In January, the two fractions are almost equal. February also shows a coarse mode double the fine mode. Regarding the coarse mode, June, August and September have their peaks in a higher radius than the other months, suggesting the presence of even bigger particles in the mixture. It should be highlighted that direct sun and inversion retrievals are extracted from different measurements in the data set (direct sun and almucantar), but in the current dataset, the fine/coarse behavior converges.
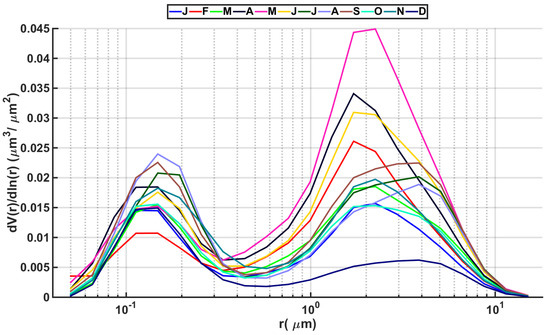
Figure 3.
Mean size distribution per month with AERONET level 2.0.
Mean monthly SSA values at four wavelengths are presented at Figure 4. The lowest values are retrieved during January, July and December; thus, more absorbing particles are presented in these periods. SSA values at 440 nm show very little seasonal variation, ranging between 0.91 and 0.93. This spectral seasonal pattern results in four months (April, May, June and November) with a lower SSA of 440 nm. For the rest of the year, SSA at 440 nm is higher, showing a decrease to longer wavelengths. Thus, the spectral behavior of SSA indicates that, in these periods, the particles also have a varying spectral absorption. Brown carbon is known to highly absorb in UV region, while it is almost non-absorbing above 700 nm [68], which was found in an earlier study to have the highest concentrations in Athens during the same four months [54]. Also, dust aerosols―especially those containing hematite―are known to absorb more at lower wavelengths [69], which also contributes to this behavior for the April–June period.
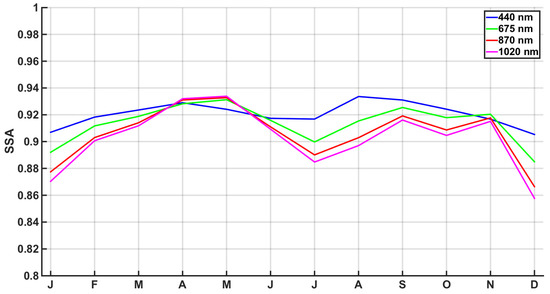
Figure 4.
Mean Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) values at 440, 675, 870 and 1020 nm per month with AERONET level 1.5.
Figure 5 shows all SSA values at 440 nm against an Ångström exponent of 440–870 nm and respective AOD loads according to colors. SSA retrieval has the highest uncertainty when AOD < 0.2; thus, these data points should be treated with caution, especially when very low SSA values are retrieved. Very high AOD (>0.7) cases could by separated into two different groups: one with high SSA, where scattering particles dominate, and one with lower SSA values and an Ångström exponent < 0.6—a condition which best describes the Saharan dust events in the area. The class of 0.4 < AOD < 0.7 AOD shows a high concentration around the mean SSA values for the period which is equally spread in high and low Ångström exponents. Only 9% of cases in this class have an SSA lower than 0.9. The class of 0.2–0.4 AOD also has a considerable SSA uncertainty, containing a large number of measurements which were rejected at AERONET level 2.0. Thus, there is a number of cases with an uncommonly low SSA (13% lower than 0.85), which should be attributed to the uncertainty.
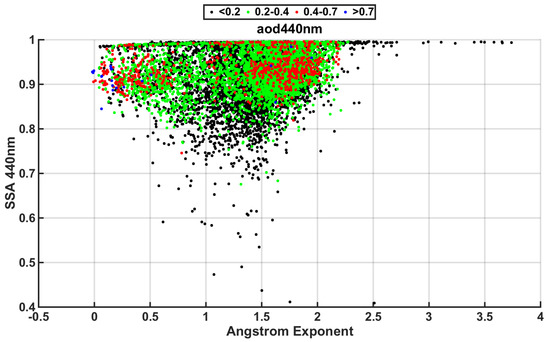
Figure 5.
SSA 440 nm in respect to the Ångström exponent 440–870nm, categorized according to the AOD for the whole period.
3.2. Connection of AOD with PM10
For the comparison of in-situ data with AERONET measurements, a new dataset has been created by the linear interpolation of PM10 hourly averaged values to the CIMEL recording moments. The comparison between these datasets is considered synchronous; otherwise, daily average values have been compared. In Figure 6 and Figure 7, blues lines represent the mean AOD at 440 nm and mean PM10, respectively, for that period. At Table 1, the relative frequencies of the four quadrants created by the mean values (blues lines) are presented in order to clarify the seasonal variations of the conditions.
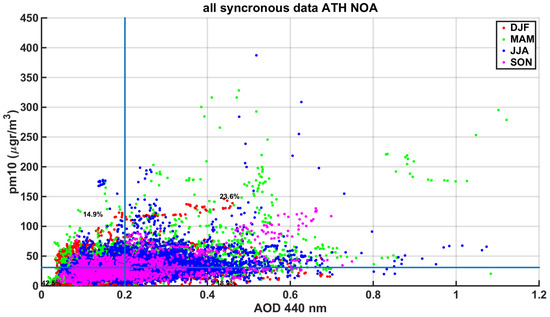
Figure 6.
AOD at 440 nm plotted against synchronous particulate matter (PM)10, separated by season (color), with blue lines for the mean AOD and mean PM10.
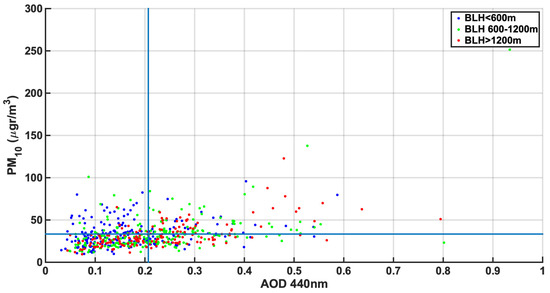
Figure 7.
Daily averages of AOD440 nm against PM10, separated by boundary layer height (color); blue lines show the mean AOD and mean PM10 for this dataset.

Table 1.
Occurrence of cases in each quadrant per season (December-February, March-May, June-August, September-November) for all synchronous values. Quadrants are separated by the mean AOD 440 nm and PM10 values for the whole dataset.
It appears that in winter months, AOD is usually low, but PM10 fluctuates, with both low and high values (compared to the annual mean), which indicates a strong stratification, trapping most of the emissions in lower troposphere. This condition is associated with urban emissions (traffic) and especially with heating. The condition of low AOD and high PM10 is significantly less frequent in other seasons. Only in summer months is there a high occurrence of the condition of low PM10 and high AOD (23.8% of the cases), which indicates high aerosol loads outside the surface layer. One of the factors contributing to this is the presence of dust layers from the Sahara only at higher levels, which occurs mainly during that season, while in the rest of the year, dust appears to be more distributed in height, drastically affecting the layers near the surface [70]. In general, during winter months, 76.1% of the cases have an AOD lower than the annual mean value. Also, summer is the season in which PM10 is lower than the annual mean in 66.1% of the cases. Thus, there is a seasonal anti-correlation of low values of AOD and PM10. Extremely high values of PM10 (>150 μgr/m3) are only recorded during the March–August period and are synchronous at 90.3% with AOD values higher than the annual mean and at 74.5% with AOD values higher than 0.4. Finally, cases with extremely high AOD (>0.8) are separated into two classes: one with high PM10 (>150 μgr/m3), consisting of 48.2% of cases, and one with average PM10 (23–62 μgr/m3), with 51.8% of cases. All the extremely high AOD cases occur in the March–August period. Thus, extremely high AOD values are always associated with long-range transport and high aerosol concentration at higher layers, mainly dust from Sahara, and in almost half the cases co-occur with high PM10, which could be explained either by strong deposition or the presence of an independent layer near the surface. PM10 values during winter show maxima in Athens during night-time, when there are no AERONET measurements, but these data are not used in the above-described comparison.
In Figure 7, daily mean values of AOD at 440 nm and PM10 have been plotted with respect to PBLH at 12:00 UTC for all available days. PBLH is extracted from the ERA5 database, generated using the Copernicus Climate Change Service Information [71], which uses assimilated values from ECMWF outputs. Cases with low PM10 and low AOD values are more frequently (52.1% οf cases) linked with days with low PBL, indicating that the majority of aerosols are found in the lower layer and hardly any particles above that. Cases with low AOD but high PM10 concentration are usually (88.9% of cases) associated with low BL heights. In theory, for these cases, it is expected that most aerosols are concentrated in a relatively short surface layer and originate from local pollution sources. Cases of low PM10 and high AOD are usually measured when PBLH is more than 600 m (84.2% cases). This condition is expected to occur when most particles are found in layers above the PBL. Specific interest should be attracted to cases of high PM10 loads and high AOD values for which the PBL height is lower than 600 m, which gives evidence of the existence of two different aerosol layers at different heights. Taking into account the layering of aerosols in urban areas such as Athens is extremely important for several applications, including in health-related areas.
Figure 8 shows the mean SSA 440 nm values and mean Ångström exponents according to PM10 concentration classes. A high PM10 (>50 μg/m3) is linked with columnar mixtures with coarse mode aerosol dominance. The lowest mean SSA values are found when PM10 concentrations are recorded in the range of 50–60 μgr/m3, which indicates the presence of dust cases in this class and probably some brown carbon during winter. Lower α values are found mainly with high PM10. It is interesting that 87.55% of the data with AOD values > 0.6 also have PM10 values > 60 μgr/m3, α < 1 and SSA > 0.9, which means these are cases of high coarse aerosol loads of a scattering nature spread across the column. PM10 classes lower than 40 μg/m3 are associated with higher Ångström exponents; hence, lower concentrations of surface particles have statistically higher fine mode fractions. SSA error bars represent 1σ, which for all PM10 classes covers the largest part of the expected SSA range in the atmosphere. Beyond that fact, the classes of 40–60 μgr/m3 have a systematically more absorbing columnar behavior.
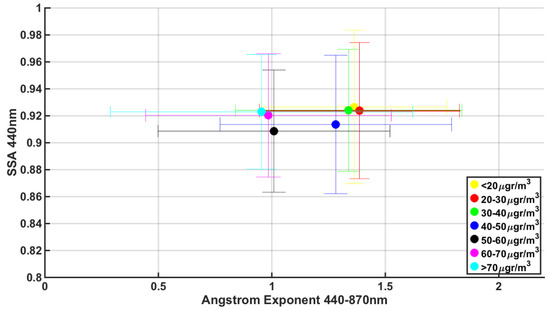
Figure 8.
Mean SSA against the Ångström exponent for different PM10 clusters (colors); error bars represent 1σ.
3.3. Particles Classification
In Figure 9, the commonly used AERONET aerosol classification described by Dubovik et al. [72] is visualized. This approach utilizes the inversion products of AERONET and, by using some data from stations where the dominant aerosol type is well known, it defines threshold values for each class. The disadvantage of this approach is the precision of the threshold values in cases of complicated aerosol mixtures. It should be highlighted that columnar atmospheric mixtures in urban areas such as Athens can almost never have a single type of aerosols. Thus, the classification should be treated as the characterization of the prevailing type(s) to which the recorded optical properties are closest. Using this classification, it appears that polluted-type aerosol mixtures are more commonly detected (27% and 23% of cases for polluted and mixed, respectively), while the fewest occurrences are for biomass burning aerosols (5%). Also, it is clear that the majority of AOD cases higher than 0.7 are characterized either as dust or biomass burning. Marine and continental aerosols dominate the low AOD cases.
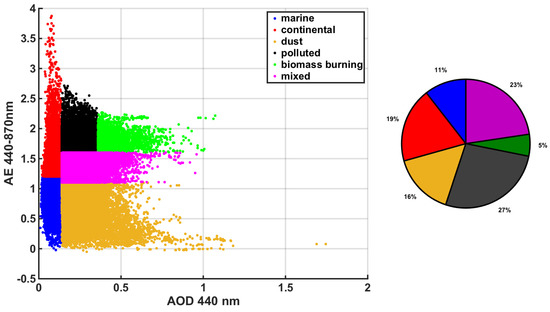
Figure 9.
AOD at 440 nm against the Ångström exponent, classified according to Dubovik et al. [72] for the whole dataset (left). Pie chart of the Dubovik et al. [72]. classification for the whole dataset (right).
When this characterization is applied to the synchronous PM10 data, it appears that marine and continental aerosol cases are usually associated with lower PM10 values, while biomass burning and dust particles are more frequently recorded with higher PM10 values. In Figure 10, the normalized distribution of the classification of the cases in respect to PM10 is presented. It is clear that, above 40 μgr/m3, the recorded columnar condition is at 82% related to dust or biomass burning. Since these conditions are usually attributed to the long-range transport of aerosols, it is interesting that it also leads to higher concentrations on the ground, indicating that there is at least a partial deposition effect.
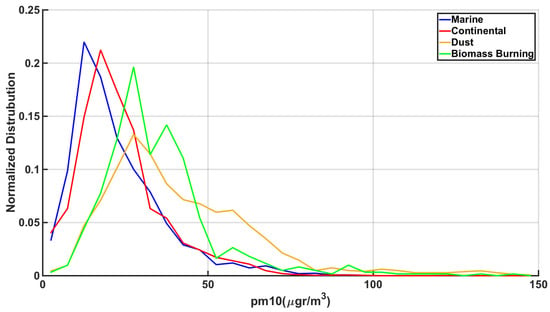
Figure 10.
Normalized distribution of cases in each class in respect to PM10 synchronous recordings according to Dubovik et al. [72].
CAMS data are used in order to benefit from the classification made by the model, always keeping in mind the considerable differences from measurements. CAMS characterizes the aerosol types by using the emission inventories in combination with meteorological and chemical modelling. Even with extrapolated data at the AERONET wavelength (440 nm), there are considerable differences (R2 = 0.74) between the AOD values in the datasets. The seasonality of AOD at 550 nm from the CAMS database appears to have the same pattern as AERONET at 440 nm, as shown in Figure 11. It appears in this dataset that there is a steady sulfate aerosol background, fluctuating at around 0.1 AOD units year-round. Dust aerosols show a peak in the period March–June. It is interesting that the dust AOD seasonal pattern is exactly in phase with AOD at 1240 nm and highly correlated to the AOD 550 nm seasonal pattern. It appears that, in the CAMS dataset, the seasonality of AOD should be mainly attributed to dust events. Organic matter aerosols appear to have a peak during July–August, which is probably linked with wild forest fires. Sea salt AOD has lower values during the summer months and is higher from December to March, which is linked to the higher winds during this period. This characterization of AOD is not directly comparable with the earlier classification which labelled the columnar mixture according to optical properties, while here it is based on emissions and modelling. The separation of AOD made by CAMS converges with AERONET retrievals in the detection of frequent dust presence for spring months and the dominance of fine particles during summer.
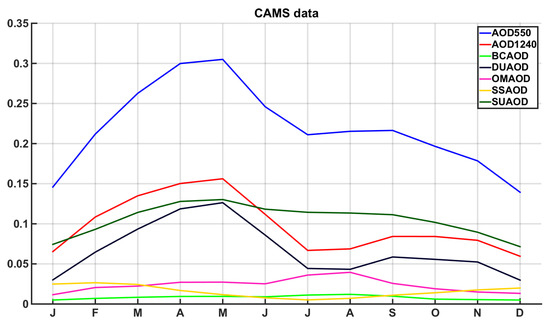
Figure 11.
Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) mean monthly values for AOD at 550 and 1240 nm and AOD for aerosol types (black carbon―BCAOD, dust―DUAOD, organic matter―OMAOD, sea salt―SSAOD, sulfate―SUAOD).
The Gobbi plot [73] is an approach to gain information regarding the spectral variation of aerosol optical properties (Figure 12). To achieve this classification, the Ångström exponent difference, defined as δα = α(440, 675) − α(675, 870) is used. A visual estimation of the contribution of fine aerosol to the AOD (through the fine mode fraction) and the size of the fine aerosol using this approach is presented in Figure 12. It should be mentioned that low aerosol loads (AOD < 0.1) propogate high uncertainty to α and δα, at up to 50% [50]; thus, the yellow points in this plot should be considered as highly uncertain. The average fine mode Rf is found at 0.13 μm, and the same average is found for the most usual AOD class (0.1–0.4) and for the cases of more than 70% fine mode contribution. Higher AODs appear to cluster in two regions of the plot, thus having two different typical behaviors: one is associated with an average fine mode Rf of 0.20 μm and a contribution of the fine mode at less than 30%, meaning that these cases are dominated by the coarse mode, which is most likely to be linked with dust events; the other one is associated with an average fine mode Rf of 0.11 μm and a contribution of fine mode at more than 70%, meaning that these cases are dominated by the finest particles and are most likely to be linked with anthropogenic emissions.
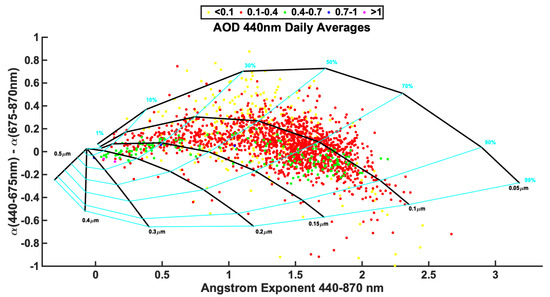
Figure 12.
Gobbi plot for daily-averaged AERONET data [72]. Black lines represent the size of the fine mode Rf, and cyan lines represent the fixed fraction contribution of the fine mode to total AOD. Colors of dots represent ranges of AOD at 440 nm.
3.4. Long-Term Trends
Figure 13 reports the trends of AOD during the measured 10-year period (2008–2018). Deseasonalization is calculated by eliminating the mean monthly value of the corresponding month. Afterwards, the trend calculations are performed by estimating a linear fit in the deseasonalized timeseries. AOD at 440 nm decreases during the measurement period, at a rate of 1.1% per year. The Greek Ministry of Environment and Energy, in its annual report, has reported a 1.6% decrease of mean PM10 daily values, for the same period, for the station Aristotelous, which is located 1 km from NOA’s measuring site [74]. Thus, the negative trend is mainly due to the decrease of urban emissions in the basin during this period. The antipollution measures combined with decreased industrial/transportation activity during the financial crisis are the main factors that are driving a decrease in local urban aerosol emissions. This trend is within the range reported for Europe in the last decade [23].
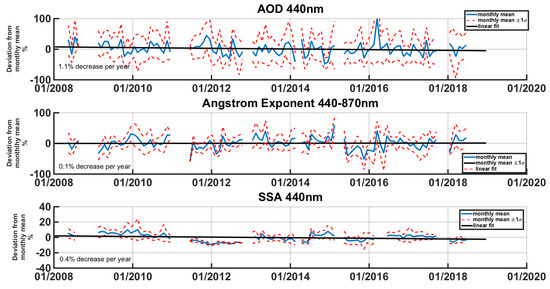
Figure 13.
Anomalies of AOD, Ångström exponent and SSA and deseasonalized trends using AERONET retrievals.
Meanwhile, the Ångström exponent at 440–870 nm practically shows no trend. SSA at 440 nm decreases at 0.4% per year, which is important compared to the actual range of SSA in the atmosphere. This could be interpreted as a 4% decrease in the examined decade, signifying an increase of absorbing aerosol types. This behavior, combined with the findings of the previous sections of this study, gives some evidence for an increase of absorbing particles, without changing the fine/coarse fraction. This could be explained by a substitution of fine particles with more absorbance at 440 nm, such as brown carbon [75].
Table 2 presents the deseasonalized total and seasonal trends for the period, as calculated by AERONET, CAMS and MODIS-Terra and MODIS-Aqua. All months with at least 15 days of data were used to calculate the monthly deseasonalized trends from AERONET data. July is the only month that fulfilled this criterion in all years, while other months have gaps in the range of 1–3 years. MODIS-Terra, MODIS-Aqua and CAMS datasets have full datasets. November has a huge decrease since November 2011, when the AOD mean value is 0.28 (AERONET), which is probably attributed to eastern European wildfires. The peak is also detected by all datasets. All datasets used report a decrease of AOD in the period. Differences could be partially explained by different wavelengths and the gaps in the AERONET database. When collocated data are used (with only the months available for AERONET, used in all datasets), the MODIS-Aqua trend is −1.4%, while the trend for MODIS-Terra is −1.5% and for CAMS is −2.0%. All annual trends are statistically significant at a confidence interval of 95%.

Table 2.
Deseasonalized trends annually and per season for AOD 440 nm. AERONET LV2 and CAMS 500 nm, MODIS-TERRA and MODIS AQUA 550 nm.
Seasonal trends calculated from CAMS are significantly different from the other datasets—in particular for winter period (DJF), when the highest decrease is recorded. Satellite and AERONET trends show the highest decreases during summer, when CAMS estimates the most moderate trend. Ground-based and satellite trends for winter have no statistically significant trend.
4. Conclusions
A decade of AERONET measurements have been studied for the city of Athens, Greece, for the 2008–2018 period. Version 3 Level 2.0 data have been used. Maximum AOD monthly values for 340–440 nm were recorded during August and for 675–1640 nm during May. CAMS data also show a maximum at both 550 and 1240 nm during May and a similar seasonal pattern to AERONET retrievals. The mean monthly Ångström exponent at 440–870 nm had maximum values in July and lowest values in April, which was attributed to anthropogenic sources (including biomass burning) and Sahara dust intrusion, respectively. The mean monthly size distribution reveals a maximum of coarse mode in May and a maximum of fine mode in August. SSA also has lowest values in December–January. All the findings lead to the conclusion that the main seasonal pattern in the area is a maximum AOD during summer with a dominance of fine-mode aerosols and frequent dust events in spring time. Additionally, the more absorbent types of aerosols are found during winter.
PM10 exhibits higher concentrations during winter months and lower concentrations during summer. AOD and PM10 are more frequently correlated when PBLH is higher than 1200 m. Higher PM10 concentrations are related with coarse aerosols in the columnar mixture, while more absorbing aerosol types are linked with PM10 concentrations in the range of 40–60 μgr/m3.
Polluted and anthropogenic–mixed are the aerosol classes which are most frequently dominant in the area, comprising 50% of the cases. Dust and biomass burning aerosols constitute 21% of the cases when higher AOD values are attributed to these types. Additionally, dust and biomass burning aerosol dominance is more frequently related to PM10 concentrations higher than 50 μgr/m3.
CAMS aerosol types AOD show a constant sulfate aerosol background, with higher dust aerosols in spring time and maximum organic matter in August. ThedDust AOD seasonal pattern in CAMS data drives the seasonal pattern of AOD at 1240 nm.
AOD data retrieved from AERONET show a decreasing trend of 1.1% per year for the area, which could be attributed to antipollution measures and the financial crisis. Satellite and CAMS datasets also show a decrease for the period. The Ångström exponent shows practically no trend. SSA exhibits a 0.4% decrease per year, which signifies the increase of absorbing aerosol types in the mixture. Satellite and AERONET datasets show the highest decrease during summer months. CAMS seasonal trends have a different pattern than the other datasets.
The climatological results presented in this study are only an early step towards understanding the behavior of aerosols in the complex environment of a European city; longer records are needed to confirm the recorded trends and fully characterize the seasonal patterns. Further analysis combining more sources of data could more clearly provide the signatures of aerosol types and their stratification. Additionally, similar studies should be performed in other areas in the Eastern Mediterranean area to generalize the findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.-P.R. and S.K.; methodology, I.-P.R. and S.K.; data process, statistical analysis and visualization, I.-P.R.; data acquisition I.-P.R., V.A., N.M., E.G., A.G.; writing, I.-P.R. and A.G.; reviewing and editing by S.K., V.A., E.G., N.M. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge support and funding of this work by the project “Panhellenic Infrastructure for Atmospheric Composition and Climate change” (MIS 5021516) which is implemented under the action “Reinforcement of the Research and Innovation Infrastructure”, funded by the Operational Program “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation” (NSRF 2014–2020) and co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Regional Development Fund).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the European Research Infrastructure for the observation of Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gases (ACTRIS) for maintaining the ATHENS-NOA AERONET station and for calibrating the instruments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Selzle, K.; Pöschl, U. Hazardous components and health effects of atmospheric aerosol particles: Reactive oxygen species, soot, polycyclic aromatic compounds and allergenic proteins. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Ueda, K.; Pozzer, A.; Lammel, G.; Kampf, C.J.; Fushimi, A.; Enami, S.; Arangio, A.M.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Fujitani, Y.; et al. Aerosol health effects from molecular to global scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13545–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; Chapter 7; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Sendra, C. Algorithm for automatic atmospheric corrections to visible and near-IR satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1357–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D. Strategy for direct and indirect methods for correcting the aerosol effect on remote sensing: From AVHRR to EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Herman, J.R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Seftor, C.J.; Arola, A.; Kaurola, J.; Koskinen, L.; Kalliskota, S.; Taalas, P.; Geogdzhaev, I.V. Version 2 TOMS UV algorithm: Problems and enhancements. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2002, 4482, 82–94. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, M.; Troccoli, A. Impact of a fire burn on solar irradiance and PV power. Sol. Energy 2015, 114, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.; Kazadzis, S.; El-Askary, H.; Taylor, M.; Gkikas, A.; Proestakis, E.; Kontoes, C.; El-Khayat, M. Earth-Observation-Based Estimation and Forecasting of Particulate Matter Impact on Solar Energy in Egypt. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Set- zer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Yoon, S.C.; Ramanathan, V.; Shi, G.Y.; Takemura, T.; Higurashi, A.; Takamura, T.; Aoki, K.; Sohn, B.J.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Overview of the Atmospheric Brown Cloud East Asian Regional Experiment 2005 and a study of the aerosol direct radiative forcing in east. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO/GAW. Experts Workshop on a Global Surface-based Network for Long Term Observations of the Column Aerosol Optical Properties; GAW 162; World Meteorological Organization: Davos, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kazadzis, S.; Kouremeti, N.; Nyeki, S.; Gröbner, J.; Wehrli, C. The World Optical Depth Research and Calibration Center (WORCC) quality assurance and quality control of GAW-PFR AOD measurements. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2018, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazadzis, S.; Kouremeti, N.; Diémoz, H.; Gröbner, J.; Forgan, B.W.; Campanelli, M.; Estellés, V.; Lantz, K.; Michalsky, J.; Carlund, T.; et al. Results from the Fourth WMO Filter Radiometer Comparison for aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3185–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, E.; Romero-Campos, P.M.; Kouremeti, N.; Kazadzis, S.; Räisänen, P.; García, R.D.; Barreto, A.; Guirado-Fuentes, C.; Ramos, R.; Toledano, C.; et al. Aerosol optical depth comparison between GAW-PFR and AERONET-Cimel radiometers from long-term (2005–2015) 1 min synchronous measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4309–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Diner, D.J. Retrieval of Aerosol Properties over Land Using MISR Observations; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 67–293. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Kuehn, R.E.; Winker, D.M. The Retrieval of Profiles of Particulate Extinction from Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Data: Uncertainty and Error Sensitivity Analyses. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2013, 30, 395–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, W.M.; North, P.R. Aerosol Optical Depth ftom Dual-View (A)ATSR Satellite Observations; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Alpert, P.; Shvainshtein, O.; Kishcha, P. AOD trends over megacities based on space monitoring using MODIS and MISR. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2012, 1, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manktelow, P.T.; Mann, G.W.; Carslaw, K.S.; Spracklen, D.V.; Chipperfield, M.P. Regional and global trends in sulfate aerosol since the 1980s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, A.; Schulz, M.; Gliss, J. Biennalupdate of ACTRSI-2 Trends Report on Trend Assessment. 2018. Available online: https://www.actris.eu/Portals/46/Documentation/actris2/Deliverables/public/WP13_D13.6_M36(1).pdf?ver=2019-01-09-090544-173 (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Eleftheriadis, K.; Colbeck, I.; Housiadas, C.; Lazaridis, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Mitsakou, C.; Smolik, J.; Ždímal, V. Size distribution, composition and origin of the submicron aerosol in the marine boundary layer during the eastern Mediterranean “SUB-AERO” experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6245–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Kokkalis, P.; Eleftheratos, K.; Andreae, M.O.; Andreae, T.W. Three-year ground based measurements of aerosol optical depth over the Eastern Mediterranean: The urban environment of Athens. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekeri, A.; Amiridis, V.; Kokkalis, P.; Basart, S.; Chaikovsky, A.; Dubovik, O.; Mamouri, R.E.; Papayannis, A.; Baldasano, J.M. Application of a synergetic lidar and sunphotometer algorithm for the characterization of a dust event over Athens, Greece. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2013, 18, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Protonotariou, A.; Papangelis, G.; Tombrou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Long-range transport of Saharan dust and chemical transformations over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, A.; Tsikerdekis, S.; Solomos, E.; Proestakis, D.; Konsta, N.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Tsekeri, G.; Vlastou, P.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouli, M.E.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Ichoku, C.; Balis, D.S.; Bais, A.F. Signs of a negative trend in the MODIS aerosol optical depth over the Southern Balkans. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Zerefos, C.; Kazadzis, S.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Eleftheratos, K.; Vrekoussis, M.; Stohl, A.; Mamouri, R.E.; Kokkalis, P.; Papayannis, A.; et al. Impact of the 2009 Attica wild fires on the air quality in urban Athens. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.D.; Rieger, C.; Walter, H.; Vogel, A.; Karali, M.; Hatzaki, E.; Gerasopoulos, B.; Vogel, C.; Giannakopoulos, M.; Roussos, A. Fire risk, atmospheric chemistry and radiative forcing assessment of wildfires in eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Balis, D.; Giannakaki, E.; Kazadzis, S.; Arola, A.; Gerasopoulos, E. Characterization of the aerosol type using simultaneous measurements of the lidar ratio and estimations of the single scattering albedo. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Argyrouli, A.; Kokkalis, P.; Tsaknakis, G.; Binietoglou, I.; Solomos, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Samaras, S.; Böckmann, C.; Raptis, P.; et al. Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties During a Rare Case of Long-range Transport of Mixed Biomass Burning-polluted Dust Aerosols from the Russian Federation-kazakhstan to Athens, Greece. EPJ Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2016, 119, 18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Smolik, J.; Zdimal, V.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Colbeck, I. Optical properties of aerosols over the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6229–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources of atmospheric aerosol from long-term measurements (5 years) of chemical composition in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fοurtziou L., E.; Liakakou, I.; Stavroulas, C.; Theodosi, P.; Zarmpas, B.; Psiloglou, J.; Sciare, T.; Maggos, K.; Bairachtari, A.; Bougiatioti, E.; et al. Multi-tracer approach to characterize domestic wood burning in Athens (Greece) during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Brunner, D.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Changes in domestic heating fuel use in Greece: Effects on atmospheric chemistry and radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10597–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratsea, M.; Liakakou, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Adamopoulos, A.; Tsilibari, E.; Gerasopoulos, E. The combined effect of reduced fossil fuel consumption and increasing biomass combustion on Athens’ air quality, as inferred from long term CO measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogridis, A.-C.; Vratolis, S.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Eleftheriadis, K. Assessment of wood burning versus fossil fuel contribution to wintertime black carbon and carbon monoxide concentrations in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10219–10236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Theodosi, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Long-term characterization of organic and elemental carbon in the PM2.5 fraction: The case of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13313–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosi, C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Lianou, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Multi-year chemical composition of the fine-aerosol fraction in Athens, Greece, with emphasis on the contribution of residential heating in wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14371–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Tsagkaraki, P.; Zarmpas, P.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources and processes that control the submicron organic aerosol composition in an urban Mediterranean environment (Athens): A high temporal-resolution chemical composition measurement study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaee, S.; Sowlat, M.H.; Diapouli, E.; Ioannis, M.; Vasilatou, V.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Sioutas, C. Science of the Total Environment Source apportionment of the oxidative potential of fi ne ambient. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, K. Long term variability of the air pollution sources reflected on the state of mixing of the urban aerosol. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 8, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiflikiotou, M.A.; Kostenidou, E.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Patoulias, D.; Zarmpas, P.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Diapouli, E.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Florou, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; et al. Summertime particulate matter and its composition in Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the atmospheric transmission of sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geografiska Ann. 1929, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Corr, C.A.; Krotkov, N.; Madronich, S.; Slusser, J.R.; Holben, B.; Gao, W.; Flynn, J.; Lefer, B.; Kreidenweis, S.M. x Retrieval of aerosol single scattering albedo at ultraviolet wavelengths at the T1 site during MILAGRO. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5813–5827. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; p. 666. [Google Scholar]
- Kalabokas, P.D.; Viras, L.G.; Repapis, C.C. Analysis of the 11-year record (1987–1997) of air pollution measurements in Athens, Greece, Part I: Primary air pollutants. Glob. Nest Int. J. 1999, 1, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Gkikas, A.; Basart, S.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Jorba, O.; Gassó, S.; et al. Mediterranean intense desert dust outbreaks and their vertical structure based on remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8609–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Torres, O. Characterization of aerosol episodes in the greater Mediterranean Sea area from satellite observations (2000–2007). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; Eck, T.; Smirnov, A.; Sinyuk, A.; Schafer, J.; Sorokin, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Kraft, J.; et al. AERONET Version 3 Release: Providing Significant Improvements for Multi-Decadal Global Aerosol Database and Near Real-Time Validation, Nasa Technical Reports. 2016. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20160013870 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database – automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazadzis, S.; Raptis, P.; Kouremeti, N.; Amiridis, V.; Arola, A.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Schuster, G.L. Aerosol absorption retrieval at ultraviolet wavelengths in a complex environment. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, K.; Karlsson, V. Comparability of low-volume PM10 sampler with β-attenuation monitor in background air. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 37, 3707–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroedter-Homscheidt, M.; Arola, A.; Killius, N.; Lefèvre, M.; Saboret, L.; Wandji, W.; Wald, L.; Wey, E. The Copernicus atmosphere monitoring service (CAMS) radiation service in a nutshell. In Proceedings of the 22nd So-larPACES Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, J.; Huijnen, V.; Remy, S.; Kipling, Z. Chemistry and aerosol model development for the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service at ECWMF. EGU Gen. Assem. Conf. Abstr. 2017, 19, 16776. [Google Scholar]
- Peuch, V.H.; Engelen, R.; Ades, M.; Barré, J.; Inness, A.; Flemming, J.; Kipling, Z.; Agusti-Panareda, A.; Parrington, M.; Ribas, R.; et al. The Use of Satellite Data in the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (Cams). In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 27 July 2018; pp. 1594–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, A.; Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Dethof, A.; Engelen, R.J.; Fisher, M.; Flentje, H.; Huneeus, N.; Jones, L.; Kaiser, J.W.; et al. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the European centre for medium-range weather forecasts integrated forecast system: 2. Data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.-J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.C.; Li, R.R.; Flynn, L. The MODIS 2.1-/spl mu/m channel-correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Herman, M.; Mattoo, S. Remote sensing of aerosol properties over oceans using the MODIS/EOS spectral radiances. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16971–16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAADS DAAC. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- MODIS Atmosphere QA Plan for Collection 61m Version 9. Available online: https://modis-images.gsfc.nasa.gov/_docs/QA_Plan_C61_Master_2017_03_15.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Amiridis, V.; Balis, D.S.; Giannakaki, E.; Stohl, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Koukouli, M.E.; Zanis, P. Optical characteristics of biomass burning aerosols over Southeastern Europe determined from UV-Raman lidar measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Arola, A. Remote sensing of soot carbon–Part 1: Distinguishing different absorbing aerosol species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1565–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivitis, N.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Vrekoussis, M.; Kouvarakis, G.; Kubilay, N.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Vardavas, I.; Mihalopoulos, N. Dust transport over the eastern Mediterranean derived from Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer, Aerosol Robotic Network, and surface measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) (2017): ERA5: Fifth Generation of ECMWF Atmospheric Reanalyses of the Global Climate. Copernicus Climate Change Service Climate Data Store (CDS). 20 July 2019. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/home (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.P.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Eck, T.F. Classification of aerosol properties derived from AERONET direct sun data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greek Ministry of Environment and Energy. Annual Air Quality Report 2018. Available online: http://www.ypeka.gr/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=FJbhHPSTih4%3d&tabid=490&language=el-GR (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).