Abstract
The Marano and Grado Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea) has been affected by mercury (Hg) contamination coming from two sources, mining activity and discharges from a chlor-alkali plant (CAP). Sediments and water contamination have been previously well characterised, but little is known about the atmospheric compartment, where Hg is easily emitted and can persist for a long time as gaseous elemental mercury (GEM). In this work, atmospheric GEM levels and its spatial distribution over the lagoon were monitored at several sites by means of both continuous discrete instrumental measurements over several months and the determination of Hg bioaccumulated in lichens (Xanthoria parietina L.). Average GEM levels varied from 1.80 ± 0.74 to 3.04 ± 0.66 ng m−3, whereas Hg in lichens ranged between 0.06 to 0.40 mg kg−1. In both cases, the highest values were found downwind of the CAP, but excluding this point, spatial patterns of Hg in the atmosphere and lichens reflected the concentration of this metal in the sediments of the lagoon, showing a decrease moving westward. These results could indicate that the lagoon acts as a secondary source of Hg into the atmosphere: future work is needed to characterise the quantity of releases and depositions at different environments inside the lagoon.
1. Introduction
Mercury (Hg) is a persistent pollutant of global concern due to its significant negative impact on both human and environmental health [1,2]. Once released into the environment Hg is subject to a complex biogeochemical cycle [3] in which the atmosphere plays a key role, favouring the transport and dispersion of this contaminant at local and global scales [4,5,6]. Atmospheric Hg mainly consists of its elemental form, often denoted as Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM), which thanks to its high volatility and chemical inertness can persist in the atmosphere for 0.8 to 1.3 years [7] and can be subjected to long-range transport before being removed via depositions [8]. In this way, Hg can have an impact on remote ecosystems far from the point of emission [9,10,11]. It is estimated that more than 90% of Hg occurring in surface waters is derived from the atmosphere [12]. Once deposited, inorganic Hg can be converted to its organic form methylmercury [9], a potent neurotoxin which can easily be biomagnified through the food chain and harm wildlife and humans [13,14]. Moreover, deposited Hg can be re-emitted back to the atmosphere as GEM from soil, vegetation, and water surfaces, further extending the global redistribution of this element [15]. GEM generally represents more than 98% of the total atmospheric pool of this element [16], thus its levels can be considered indicative of the total amount of gaseous mercury in the atmosphere [17]. Atmospheric Hg can also occur under oxidised forms (Reactive Gaseous Mercury (RGM)) or bound to particulate material (Particulate Bound Mercury (PBM)). These last two species are characterised by a shorter atmospheric lifetime than GEM (from days to weeks) and thanks to their lower vapor pressure, are easily scavenged by wet and dry depositions [18,19], limiting their impact around the point of emission [6]. Oxidation of GEM to RGM in the presence of oxidants (e.g., alogens) and the subsequent deposition to ecosystems is considered an important removal process for atmospheric Hg [20].
Human activities have profoundly influenced the natural atmospheric cycle of Hg. This element is emitted in the atmosphere from both natural and anthropic sources for an estimated overall amount of 6500 ÷ 8300 Mg yr−1, but only a small fraction of these releases (~4–5%) is associated with primary geogenic sources, such as volcanoes, geothermal activities, and the weathering of naturally enriched rocks and soils [21,22]. Primary anthropogenic releases instead contribute to approximately 1/3 of the overall Hg emissions into the atmosphere (estimated 2220 Mg in 2015, [23]), whereas the remaining fraction (4600–5300 Mg yr−1) is attributed to re-emission from water and soil surfaces of previously deposited Hg, usually of anthropic origin [21]. Among activities which cause the release of Hg into the atmosphere (i.e., small-scale gold mining, coal combustion, cement production, waste incineration, the chlor-alkali industry, [23]), Hg mining itself represents only a minor source [24]. As a result, it is estimated that the current atmospheric Hg budget is enriched by an order of magnitude relative to pre-anthropogenic levels [25,26] and also atmospheric deposition to ecosystems have increased 3- to 5-fold compared to the pre-industrial period [27].
Currently, the GEM background level is estimated to be 1.5–1.7 ng m−3 in the northern hemisphere [28] and 1.1–1.3 ng m−3 in the southern hemisphere [29], slightly lower due to the lesser abundance of emission sources [30]. Recent observations show that GEM levels are declining over Europe and North America, likely due to regulatory interventions regarding emissions [31].
Atmospheric GEM concentrations show notable spatio-temporal variations among different environments in response to factors such as proximity to sources, availability of atmospheric oxidants, aerosol characteristics, micrometeorology, and surface conditions ([32] and references therein, [33]). Consequently, different diurnal and seasonal patterns of GEM have been observed between marine, coastal, rural, urban, and elevated locations, as summarised in a recent review by Mao et al. [34]. In contaminated sites, GEM can reach high levels [35,36,37,38], thus monitoring these sites provides useful information regarding their role in the context of the global Hg cycle, frequently omitted in global inventories [31], and provide a useful study area to better understand the behaviour and relative contribution of release, transport and deposition of GEM.
The Marano and Grado Lagoon, along the Northern Adriatic coast (Italy), has suffered significant Hg contamination from two distinct sources. The most notable of these sources is related to the inputs originating from the historic Hg mining activity at Idrija (Slovenia), which over the course of 500 years caused the release of considerable amounts of this metal into the environment [39,40]. Several studies have proved that Hg is then delivered as particulate matter by the Isonzo/Soča River downstream to the Gulf of Trieste [41,42,43,44] and then, under peak river discharge and favourable wind conditions, can be transported westerly, entering the nearby Marano and Grado Lagoon [45]. The second source is attributable to the activity of a chlor-alkali plant (CAP) located further inland, which until the installation of a wastewater treatment system in 1984, deliberately discharged Hg into the Aussa River, a freshwater tributary of the lagoon [46,47]. The impact of this second source is more restricted over time and space, as evidenced by the Hg concentrations in the sediments. In the eastern part of the lagoon, more subject to inputs coming from the Isonzo River, Hg is high (up to 14 μg g−1) and progressively decreases westward [48]. Here, Hg concentrations in sediments are higher than the natural background estimated for this area (0.02–0.13 μg g−1, [49]), and also waters show Hg concentrations higher than other parts of the Mediterranean area [50].
A complete investigation of GEM levels, dispersion, and associated bioaccumulation in selected organisms in the Marano and Grado Lagoon is still lacking. In this work, we present data regarding atmospheric GEM levels in different sites distributed over the entire lagoon and selected sites in its surroundings, in order to investigate whether the extended substrate contamination has repercussions for the air quality. Furthermore, a determination of total Hg concentration in selected lichen (Xanthoria parietina (L) Th. Fr.) collected at the same sites was carried out in order to ascertain the spatial dispersion pattern of the contaminant in the air [51]. Lichens have been extensively employed as biomonitors in several areas worldwide and X. parientina is a good indicator to detect long-term GEM dispersion ([52] and references) and largely employed in the biomonitoring of native lichens in Italy [53]. The results of this study will be an added value to the knowledge of GEM distribution in the entire area of the Gulf of Trieste [54].
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Marano and Grado Lagoon is located along the northern Adriatic coast and covers an area of about 160 km2 between the Tagliamento and Isonzo river deltas, extending for approximately 32 km in length and up to 5 km in width and connected with the sea through six tidal inlets [55]. Tidal inlets are the main source of sediment for the lagoon, mainly from the Isonzo and Tagliamento river deltas [56]. The lagoon is divided into two sectors separated by an 8 m deep canal for commercial shipping [57]. The western sector (Marano Lagoon) is affected by freshwater inputs from the small spring rivers of the Friulian plain and has few areas above sea-level, whereas the eastern part (Grado Lagoon) is shallower (<1 m on average) and characterised by a complex network of tidal channels, tidal flats and saltmarshes [58]. This lagoon is one of the best conserved transitional environments in the Mediterranean area, hosting several protected species and habitats, thus it has been classified as a Special Protection Area (Bird Directive 2009/147/CE) and a Site of Community Importance (SCI-IT3320037–Habitats Directive 92/43/CEE). However, the lagoon also hosts several economic and touristic activities such as fish-farming, clam harvesting, fishing, etc. [59].
The lagoon is characterised by a sub-Mediterranean climate with warm air temperatures for most of the year (11.9 °C on average from 1999 to 2017, [60]) and sporadic episodes of summer drought. Water temperature varies seasonally from a minimum of 5 °C (or less) in January to a maximum of over 30 °C in July [55]. The lagoon is subject to a regular sea-breeze regime, with light winds (2–3 m s−1) from the NE during the night and morning and slightly more intense winds (3–4 m s−1) from the sea in the afternoon. The climate of the lagoon is also influenced by the eruptions of strong Bora winds, which during winter can cause the freezing of shallow water areas [60]. Details of wind and temperature during the sampling periods are reported in Supplementary Materials Table S1.
2.2. Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) Measurements
Atmospheric GEM concentrations were measured in ten selected sites around the Grado and Marano lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea; Figure 1) distributed over its coastal margin and some islands in different environmental contexts, including more pristine areas and others with high anthropogenic impact.
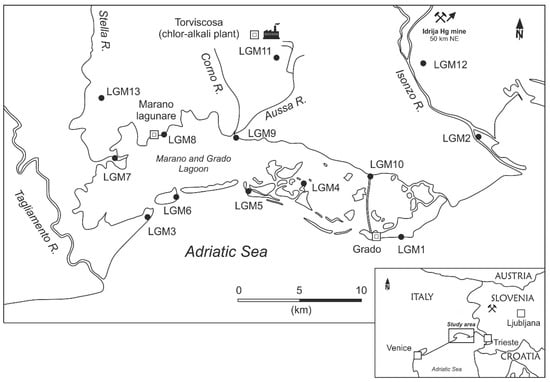
Figure 1.
Study area of the Marano and Grado Lagoon, and selected sampling sites. The location of the Idrija Hg mine and the decommissioned chlor-alkali plant in Torviscosa are also indicated.
Measurements were conducted by means of a Lumex RA-915M Portable Mercury Analyzer. The Lumex RA-915M relies on atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). The instrument has a multipath analytical cell and the Zeeman background correction providing both high sensitivity and minimal interference: the accuracy of the method is 20% [61]. The dynamic range covers four orders of magnitude (2–25,000 ng m–3), and the detection limit is governed by shot noise and equals 2.0 ng m–3 (average measuring time 5 s) and 0.3 ng m–3 (average measuring time 30 s). A complete calibration is done by a Lumex technician each year, while a calibration check of the instrument is performed prior to taking measurements by means of an internal accessory cell containing a known amount of Hg. During field work, real-time measurements were visualised on a digital display and stored in an internal data logger. Subsequently, the data were recovered by RAPID 1.00.442 software.
The data were acquired over a fixed time range of 15′ over January, February, April and May 2013 with a sampling rate set at 10 s. Values below the limit of detection (LOD) of the instrument (2 ng m–3) were treated with the medium bound approach, thus set to ½ of the LOD (1 ng m–3) [62].
2.3. Lichen Survey
In order to check the GEM dispersion, a lichen survey was conducted in the study area (n = 13 sites, 10 collecting sites corresponding to GEM sampling sites). These organisms are very suitable for Hg biomonitoring purposes [63]. In this study we used Xanthoria parietina (L) Th. Fr, a lichen which is ubiquitous in the whole area. As reported in Vannini et al. [64], this species is able to maintain a constant kinetic of Hg absorption in a wide range of temperatures (T = 10–30 °C). Lichen samples were collected from the trunks of at least three different trees [65] 1.5–2 m above the ground using stainless steel tweezers. Samples were stored in proper plastic bags prior to laboratory analysis: after drying at room temperature, the most peripheral part of thalli (1.5–2 mm, roughly corresponding to the last year lichen’s growth and therefore bioaccumulation) were selected, extraneous matter was cleaned off, mashed, and homogenised. Total mercury analysis was performed using a Direct Mercury Analyzer (DMA-80) in accordance with the US EPA 7473 method. The range of instrumental measurements is from 0.001 to 50 mg kg−1.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. GEM Level and Distribution
The final dataset consists of 2682 GEM measurements. The basic descriptive univariate statistic of the surveyed areas is reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic univariate statistics of the gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) dataset and Hg content in lichens grouped by sampling sites. n.d. = not determined. LGM is the abbreviation of Grado and Marano Lagoon.
The results show that GEM levels are quite low (on average <3.00 ng m−3, except at LMG11-Torviscosa) if compared to the threshold values and safety regulation reported in Oyarzun et al. [66] (World Health Organization guideline fixed at 1000 ng m−3; The United States Environmental Protection Agency reference concentration for inhalation 300 ng m−3) and in Vaselli et al. [67] (values recommended by the issuing Tuscany Regional authorities, <300 ng m−3, referred to contaminated soils), thus resulting in a null risk of exposure through inhalation pathway for the local inhabitants. In general, the average GEM concentrations observed in this study are slightly higher than the natural background estimated for the northern hemisphere (1.5–1.7 ng m−3, [28]) and for the Mediterranean area (1.75–1.80 ng m−3, [68]), except for the values obtained in the western part of the lagoon (LGM8 = 1.80 ± 0.74 ng m−3; LGM3 = 1.86 ± 0.71 ng m−3) which are in line with the above cited background levels. Moreover, average GEM concentrations over the lagoon are in the same order of magnitude as those found for the coastal area of the nearby Gulf of Trieste [54] and for the marine boundary layer of the Northern Adriatic Sea [69]. A significant difference was found between sample medians by applying the Kruskal–Wallis test [70] (p = same = 2.81 × 10−136), a nonparametric method for testing whether there are statistically significant differences between two or more groups of an independent variable. The box and whisker plot representation (Figure 2) shows the marked dispersion of data at sites LGM4, LGM9 and together with the presence of several outliers which could be due to the micrometeorological variability of the sites during sampling [54]. The maximum value of GEM found in this study near Torviscosa (LGM11 = 3.04 ± 0.66 ng m−3 on average) is related to the presence of the decommissioned CAP, where some areas such as the ex-cell house and distiller displayed GEM levels up to 5000 ng m−3 [36]. Here, GEM is emitted from the contaminated materials of old buildings due to high temperatures and the intensity of solar radiation [36] and is dispersed by the prevalent northern winds (see Figure 3c).
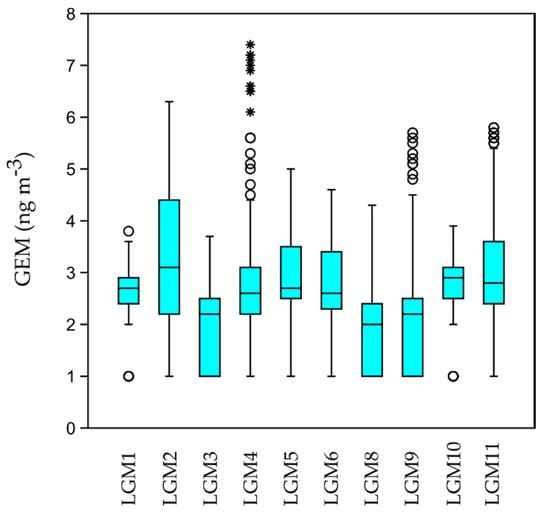
Figure 2.
Boxplots of GEM measured in the investigated sites.
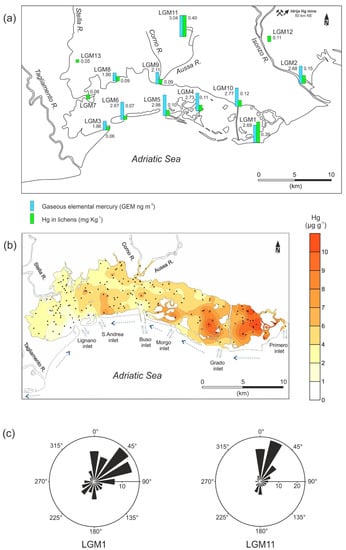
Figure 3.
(a) GEM concentrations (light blue) and Hg contents in lichens (green). (b) Distribution of Hg concentrations in the sediments of the Marano and Grado Lagoon (modified from [48]); dotted arrows represent longshore currents and related sediment transport, simple arrows indicate tidal fluxes through the lagoon inlets. (c) Wind rose for LGM1 (Grado) and LGM11 (Torviscosa, CAP) calculated from 2013 wind data in selected sites. The radius length indicates the frequency of wind directions.
The GEM levels reported in this study are similar to or slightly lower than those found in other coastal areas highly impacted by Hg from industrial sources. In the Mediterranean area, GEM levels between 1.5 ± 0.4 and 2.1 ± 0.98 ng m−3 were reported by Bagnato et al. [71] in the Augusta Bay (Sicily, Italy), whereas average values from 2.8 to 8.7 ng m−3 were found by Gibicar et al. [72] near Rosignano Solvay (Tuscany, Italy). Both sampling areas are located in the proximity of large industrial complexes where several activities such as CAPs can be responsible for the release of Hg. Moreover, over the well-known Minamata Bay (Japan), in a recent study Marumoto et al. [73] found an average atmospheric GEM concentration equal to 1.90 ± 0.40 ng m−3, which is also similar to those reported in our study.
In Table 2, a comparison between atmospheric GEM levels found in this study and values measured in different coastal environments around the world is reported. It should be noted that the reported results were obtained by means of different GEM measurement techniques. However, Esbrí et al. [37] stated that the results of an intercalibration/intercomparison exercise between the Lumex RA-915+ and the Tekran 2537B were good, when a compatibility index (see ref. ISO/IEC 1997 [74]) of less than 1 was found during all experiments [75].

Table 2.
GEM concentrations measured in the atmosphere in the Marano and Grado Lagoon compared to data found in the literature from other coastal environments. For a more detailed description on methods and averages refer to the original articles.
As expected, GEM levels over the Marano and Grado Lagoon are higher than those of most coastal sites not subject to Hg contamination (e.g., Mace Head, Ireland [76]; San Lucido, Italy [68]; Cape Point, South Africa; Cape Grimm, Australia; Galapagos Island, Pacific Ocean [77]; Calhau, Cabo Verde [30], see Table 2). On the other hand, GEM levels over the lagoon are of the same order of magnitude or slightly lower than those of other urban and/or industrialised areas (e.g., Xiamen, China [78]; Pearl River Delta, China [79]; Beilun, China [80]; Toronto, Canada [81]; see Table 2), where several industrial activities such as coal power plants, oil refineries, CAPs, etc., are responsible for the release of GEM into the atmosphere (e.g., [35,79,80]).
In addition, it should be stressed that atmospheric GEM concentrations are usually heavily influenced by local wind conditions, which can represent a supply of GEM for areas not characterised by Hg contamination or alternatively favour the dilution of the local emissions of this contaminant depending on the origin of air masses [33,92]. The transport of GEM from inland can represent the most important source of atmospheric Hg for coastal areas not subject to a relevant contamination of this metal. In these areas, particularly if located downwind of relevant industrial sources, GEM concentrations can reach values comparable with those observed in our study despite a lower degree of Hg contamination in the substrate. An example of this is the case of Thau Lagoon (north-western Mediterranean Sea), where Hg concentrations in the substrate are lower than those of the Marano and Grado Lagoon [93] but GEM values up to 3.30 ng m−3 were detected ([68], Table 2), which are similar to those found in our study. In this case, high GEM concentrations are related to the occurrence of air masses coming from an inland industrial area where several sources of atmospheric Hg are present (coal power plants, waste incinerators) [68]. A similar situation can frequently be found in East Asian rural locations (e.g., Chengshantou, China [92]; An-Myun, South Korea [91]; see Table 2), impacted by air masses coming from inland where significant Hg emissions occur [23]. Conversely, several coastal urban and densely populated areas listed in Table 2, where one can expect an important emission of GEM from anthropic activities, show GEM values which are on average lower than those observed in our study. (e.g., Houston, USA [33]; Dartmouth, Canada [85]; San Diego-San Francisco, USA [84]; New York, USA [86]; Grand Bay, USA [87]; Tokyo, Japan [83]; Nieuw Nickerie, Suriname [88], see Table 2). In these cases, a possible explanation is that these areas are usually reached by clean marine air masses, which dilute the Hg emitted in the atmosphere [94] and, due to their content in oxidants (e.g., bromine), promote the oxidation of GEM and its subsequent deposition, favouring the removal of Hg from the atmosphere [95]. In the Marano and Grado Lagoon, the atmospheric dilution effect is likely less effective because before reaching the lagoon, air masses coming from the sea pass over the Gulf of Trieste, which is impacted by Hg, and likely represent an additional source in the atmosphere [54,68,96]. Air masses coming from inland likely contain GEM emitted by anthropic activities [69] or contaminated soils [97].
The spatial distribution of the average GEM concentrations, except for site LGM11, over the Marano and Grado Lagoon shows a gradual increase moving eastward, starting from minimum average values of 1.80 ng m−3 (LGM8) in the western sector up to 2.77 ng m−3 (LGM10) in the eastern sector of the lagoon (Figure 3a). Sites located in the eastern part of the lagoon (LGM1, LGM4, LGM10) and near the tidal inlets of Porto Buso (LGM5) and S. Andrea (LGM6) are characterised by higher concentrations of GEM. Thus, the atmospheric GEM distribution is quite consistent with the dispersal pattern of Hg in sediments of the Marano and Grado Lagoon (Figure 3b) as reported by Acquavita et al. [48].
A possible explanation for the observed distribution pattern could be that due to diffuse Hg contamination, the lagoon acts as a secondary source of GEM for the atmosphere. The Mediterranean area is largely considered a hotspot of Hg emission due to the intense insolation and to contributions of this metal from land and cinnabar deposits [98], and the extended contamination of the lagoon could further increase this phenomenon. As stated above, the main source of Hg contamination for the lagoon is represented by the suspended material enriched in this metal as a result of historical mining activity in Idrija (Slovenia) and transported by the Isonzo River. This material enters the lagoon mainly through the eastern tidal inlets, and its dispersion and deposition in the lagoon is controlled by tidal fluxes [45,48,56]. However, under favourable conditions, deposed Hg can be released from the sediments to the water column through different processes such as sediment resuspension [99], diffusion from porewaters, dissolution of a fraction of surface sediments, and methylation [100]. Once present in the water column, Hg can potentially be subject to photo-reduction or biotic reduction to its volatile elemental form [101], thus available for release into the atmosphere. This process could be even more favoured thanks to the shallow water column (1 m depth on average), which allows the incident radiation to penetrate the entire water column, as observed in other estuarine environments (e.g., [102]). Finally, partially emerged (e.g., saltmarshes) or regularly flooded (tidal flats) portions of the lagoon are in turn characterised by high Hg contamination [103] and under appropriate conditions of insolation and temperature could constitute a source of GEM for the atmosphere [104].
In this work, as stated above, most of the sites which show high GEM concentrations (LGM1, LGM4, LGM10) are located in the eastern part of the lagoon, characterised by the highest Hg content in sediments (Figure 3). Site LGM6, located near a part of the western sector of the lagoon is characterised by a higher Hg content in submerged [48] and saltmarsh sediments [105] compared to the surrounding zones; this could justify the relatively high GEM concentrations detected at this site, which are similar to those found in the eastern part of the lagoon and higher than those recorded at the other sites located in the western sector (LGM3, LGM8). Moreover, the intense water circulation at the tidal inlets [55] can further enhance sediment resuspension and the availability of Hg in the water column for reduction and volatilisation, potentially explaining the high GEM values detected at sites LGM5 and LGM6.
3.2. Total Hg in Lichens
In this study X. parietina showed THg levels ranging from 0.05 to 0.39 mg kg−1 (mean ± s.d. = 0.14 ± 0.12 mg kg−1). A comparison of our results with similar monitoring conducted with the same species is reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Total Hg levels observed in monitoring conducted in different sites with the species X. parietina.
Overall, our results are significantly lower than those found in sites impacted by CAP activities [52,111,116], past mining [108,109,110] and natural Hg emissions [108,113]. Following the percentile-based, 7 class, naturality/alteration scales for bioaccumulation proposed by Nimis and Bargagli [65], the worst cases in our study can be classified as middle/alteration, whereas most of the samples show results consistent with high naturality.
In the scatterplot reported in Figure 4, which compares GEM measurements and Hg concentrations in the lichens of Table 1, three groups of data can be identified. Groups 1 and 2 show differences in GEM concentrations, which can be ascribed to Hg distribution in the sediments of the lagoon as stated above, but they do not show substantial differences with regard to Hg content in lichens.
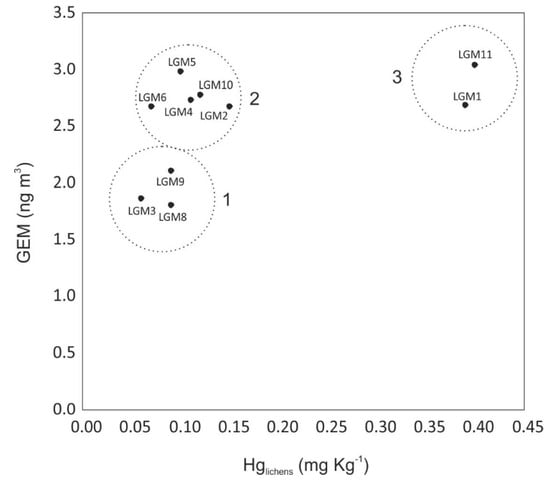
Figure 4.
Scatterplot between GEM values and Hg content in lichens in the same sampling sites.
On the other hand, Group 3 sites (LGM1, LGM11) show GEM concentrations comparable with those of Group 2, but with higher Hg bioaccumulation. This is likely related to isolated events of high atmospheric GEM concentrations, undetected in these surveys. These events could occur in these locations due to the atmospheric transport of GEM driven by prevalent winds (Figure 3c) from upwind sources: the Torviscosa CAP and the Isonzo River plain, respectively, where high-amplitude anomalous peaks of atmospheric GEM have been previously documented [36,54]. Based on the results of this study, LGM11 can be classified as a site heavily impacted by the CAP, which still acts as the secondary source of Hg in the area, even though the plant has been decommissioned [36]. However, the reason for the anomaly at site LGM1 is not clear; although there are high Hg concentrations in sediments in that part of the lagoon, we hypothesise that also some infrequent anthropogenic activities such as vehicular and maritime traffic can mobilise Hg more effectively from sediments and water enhancing phase transfer processes [99]. For the sites from Groups 1 and 2, which show lower Hg bioaccumulation in lichens, it could be hypothesised that they are less exposed to these anomalous events during the year. A continuous instrumental monitoring of atmospheric GEM concentrations for a long period in these sites would be useful to verify this hypothesis.
We emphasise the fact that the 15′ of continuous GEM measurements recorded in this study in four different months could reflect the spatial distribution of Hg-bearing sediments in such a complex and wide study area regardless of any daily micrometeorological-induced GEM variations in the atmosphere. These considerations are supported by the relationship between air GEM and THg concentrations in lichens despite the different monitoring approach: the first one is ascribable as punctual, the second one as continuous for about a year.
4. Conclusions
In this study, gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) atmospheric levels and spatial distribution over the Marano and Grado Lagoon were monitored through direct instrumental measurements and lichen surveys, completing the recently published assessment of the occurrence of this contaminant in the area of the Gulf of Trieste [54]. This lagoon has a high natural and economic value, but it is also historically Hg-contaminated due to the contributions of this metal associated with the dispersion of Hg-rich suspended material from the Isonzo River, resulting from mercury mining at Idrija, and with the discharges of a nearby CAP at Torviscosa. GEM concentrations reported in this study were lower than 10 ng m−3, thus they do not reach levels of concern for human health for exposure through inhalation.
The highest GEM levels in the atmosphere and Hg concentrations in lichens were recorded at the site located downwind of the CAP, confirming that contaminated factory buildings still represent a source of atmospheric Hg. Excluding this point, both atmospheric GEM levels and Hg concentrations in lichens decrease moving westward, showing an interesting spatial distribution which roughly corresponds to the Hg concentrations in the sediments of the lagoon. The highest Hg levels were recorded in the eastern part of the lagoon, more subject to mining-derived contamination. Based on these data, it is possible to hypothesise that the lagoon acts as an active secondary source of Hg for the atmosphere. However, further research is needed to confirm this hypothesis, focusing on the processes at the water-air and sediment-air interfaces, and considering the flooding routine. Furthermore, future works are required to study the role of saltmarsh vegetation in the biogeochemical cycle of Hg in these environments, as it could represent a possible sink of atmospheric Hg through depositions and foliar uptake [118], but could also release significant amounts of GEM to the atmosphere, especially in contaminated saltmarsh environments, even if this is still a matter of debate [119]. Finally, based on the results obtained in this study, continuous monitoring of Hg species concentrations in the atmosphere in selected points of the lagoon, e.g., downwind from the CAP, could be useful to evaluate the temporal dynamics of this element in this environment and to assess possible contributions of the atmospheric dry and wet deposition to the global Hg contamination of the lagoon.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/12/1280/s1, Table S1: Basic univariate statistic of gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) dataset and wind and air temperature data during sampling periods. Meteorological data are given as hourly averages. Siap/MICROS: OSMER-ARPA FVG meteorological network, CAE: Protezione Civile FVG monitoring network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, field work, data curation A.A., N.S. Data curation F.F., N.B. Processing of data F.F., N.B., P.H. Writing-original draft and writing review A.A., N.S., F.F., N.B., S.C. Final editing F.F., A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Antonio Tortora of ARPA FVG who supported the sampling operations and to the staff of ARPA FVG Laboratory for analysis. OSMER-ARPA FVG and Protezione Civile FVG are acknowledged for providing meteorological data. The useful suggestions of two anonymous reviewers were greatly appreciated. Karry Close is warmly acknowledged for proofreading the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wright, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Aherne, J.; Wentworth, G.R. Impacts and Effects Indicators of Atmospheric Deposition of Major Pollutants to Various Ecosystems—A Review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1953–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, R.A. Mercury Toxicity and Treatment: A Review of the Literature. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, N.E. Global Biogeochemical Cycling of Mercury: A Review. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travnikov, O. Atmospheric Transport of Mercury. In Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology of Mercury; Liu, G., Cai, Y., O’Driscoll, N., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 329–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinchuk, V.V.; Lopatnikov, E.A.; Astakhov, A.S.; Ivanov, M.V.; Hu, L. Distribution of Atmospheric Gaseous Elemental Mercury (Hg(0)) from the Sea of Japan to the Arctic, and Hg(0) Evasion Fluxes in the Eastern Arctic Seas: Results from a Joint Russian-Chinese Cruise in Fall 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 753, 142003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.H.; Munthe, J. Atmospheric Mercury-An Overview. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Lopez, A.; Sitkiewicz, S.P.; Roca-Sanjuán, D.; Oliva-Enrich, J.M.; Dávalos, J.Z.; Notario, R.; Jiskra, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Thackray, C.P.; et al. Photoreduction of Gaseous Oxidized Mercury Changes Global Atmospheric Mercury Speciation, Transport and Deposition. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travnikov, O. Contribution of the Intercontinental Atmospheric Transport to Mercury Pollution in the Northern Hemisphere. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7541–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, W.F.; Engstrom, D.R.; Mason, R.P.; Nater, E.A. The Case for Atmospheric Mercury Contamination in Remote Areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Lepak, R.F.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Hurley, J.P. Sedimentary Records of Mercury Stable Isotopes in Lake MichiganMercury Isotopic Records in Sediment Cores of Lake Michigan. Elementa 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, A.Y.; Blum, J.D.; Washburn, S.J.; Baskaran, M. Changes in the Mercury Isotopic Composition of Sediments from a Remote Alpine Lake in Wyoming, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, K.; Foulkes, M.; Worsfold, P. Methods for the Determination and Speciation of Mercury in Natural Waters—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celo, V.; Lean, D.R.S.; Scott, S.L. Abiotic Methylation of Mercury in the Aquatic Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, W.F.; Clarkson, T.W. Mercury and Monomethylmercury: Present and Future Concerns. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 96, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, F.; Rinklebe, J. Cycling of Mercury in the Environment: Sources, Fate, and Human Health Implications: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 693–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Beauvais, C.; Constant, P.; Zhang, H.H. A Year of Continuous Measurements of Three Atmospheric Mercury Species (GEM, RGM and Hgp) in Southern Québec, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Talbot, R.W.; Sigler, J.M.; Sive, B.C.; Hegarty, J.D. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations of Hg° over New England. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1403–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Holmes, C.D.; Fisher, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Yantosca, R.M.; Corbitt, E.S.; Galarneau, E.; Rutter, A.P.; Gustin, M.S.; et al. Gas-Particle Partitioning of Atmospheric Hg (II) and Its Effect on Global Mercury Deposition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Cao, S.; Zhao, Y. Atmospheric Mercury Deposition over the Land Surfaces and the Associated Uncertainties in Observations and Simulations: A Critical Review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15587–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, H.; Ambrose, J.L.; Jaffe, D.A. Oxidation of Elemental Hg in Anthropogenic and Marine Airmasses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P. Mercury Emissions from Natural Processes and Their Importance in the Global Mercury Cycle. In Mercury Fate and Transport in the Global Atmosphere: Emissions, Measurements and Models; Pirrone, N., Mason, R.P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment. Global Mercury Assessment 2018; United Nations Environment Programme, Chemicals and Health Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Sundseth, K.; Munthe, J.; Kindbom, K.; Wilson, S.; Steenhuisen, F.; Maxson, P. Global Emission of Mercury to the Atmosphere from Anthropogenic Sources in 2005 and Projections to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Streets, D.G.; Sunderland, E.M. Legacy Impacts of All-Time Anthropogenic Emissions on the Global Mercury Cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrico, M.; Le Roux, G.; Heimbürger, L.E.; Van Beek, P.; Souhaut, M.; Chmeleff, J.; Sonke, J.E. Holocene Atmospheric Mercury Levels Reconstructed from Peat Bog Mercury Stable Isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5899–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Sheu, G.R. Role of the Ocean in the Global Mercury Cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Ebinghaus, R.; Kock, H.; Dommergue, A. A Review of Worldwide Atmospheric Mercury Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8245–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slemr, F.; Brunke, E.G.; Ebinghaus, R.; Kuss, J. Worldwide Trend of Atmospheric Mercury since 1995. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4779–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Bencardino, M.; D’Amore, F.; Carbone, F.; Cinnirella, S.; Mannarino, V.; Landis, M.; Ebinghaus, R.; Weigelt, A.; et al. Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations Observed at Ground-Based Monitoring Sites Globally Distributed in the Framework of the GMOS Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11915–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N.E. A Review of Global Environmental Mercury Processes in Response to Human and Natural Perturbations: Changes of Emissions, Climate, and Land Use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.N.; Cheng, I.; Gratz, L.E.; Weiss-penzias, P.; Zhang, L. An Updated Review of Atmospheric Mercury. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Talbot, R.; Laine, P.; Lefer, B.; Flynn, J.; Torres, A. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations of Total Gaseous Mercury in Urban Houston, TX, USA. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Cheng, I.; Zhang, L. Current Understanding of the Driving Mechanisms for Spatiotemporal Variations of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury: A Review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12897–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, P.; Oyarzun, R.; Kotnik, J.; Esbrí, J.M.; Martínez-Coronado, A.; Horvat, M.; López-Berdonces, M.A.; Llanos, W.; Vaselli, O.; Nisi, B.; et al. A Compilation of Field Surveys on Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) from Contrasting Environmental Settings in Europe, South America, South Africa and China: Separating Fads from Facts. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 713–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquavita, A.; Biasiol, S.; Lizzi, D.; Mattassi, G.; Pasquon, M.; Skert, N.; Marchiol, L. Gaseous Elemental Mercury Level and Distribution in a Heavily Contaminated Site: The Ex-Chlor Alkali Plant in Torviscosa (Northern Italy). Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2017, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbrí, J.M.; Martínez-Coronado, A.; Higueras, P.L. Temporal Variations in Gaseous Elemental Mercury Concentrations at a Contaminated Site: Main Factors Affecting Nocturnal Maxima in Daily Cycles. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaselli, O.; Nisi, B.; Rappuoli, D.; Cabassi, J.; Tassi, F. Gaseous Elemental Mercury and Total and Leached Mercury in Building Materials from the Former Hg-Mining Area of Abbadia San Salvatore (Central Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, J.; Horvat, M.; Dizdarevič, T. Current and Past Mercury Distribution in Air over the Idrija Hg Mine Region, Slovenia. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7570–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, M.; Žibret, G. Mercury Contents in the Vertical Profiles through Alluvial Sediments as a Reflection of Mining in Idrija (Slovenia). J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, M.; Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Logar, M.; Mandić, V.; Rajar, R.; Širca, A.; Žagar, D. Mercury in Contaminated Coastal Environments; a Case Study: The Gulf of Trieste. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 237–238, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Brambati, A. Mercury Contamination of Coastal Sediments as the Result of Long-Term Cinnabar Mining Activity (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Fontolan, G.; Faganeli, J.; Ogrinc, N. Anthropogenic Markers in the Holocene Stratigraphic Sequence of the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Geol. 2006, 230, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, D.; Ogrinc, N.; Hintelmann, H. Tracing Mercury Contamination from the Idrija Mining Region (Slovenia) to the Gulf of Trieste Using Hg Isotope Ratio Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covelli, S.; Piani, R.; Acquavita, A.; Predonzani, S.; Faganeli, J. Transport and Dispersion of Particulate Hg Associated with a River Plume in Coastal Northern Adriatic Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piani, R.; Covelli, S.; Biester, H. Mercury Contamination in Marano Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy): Source Identification by Analyses of Hg Phases. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Acquavita, A.; Piani, R.; Predonzani, S.; De Vittor, C. Recent Contamination of Mercury in an Estuarine Environment (Marano Lagoon, Northern Adriatic, Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquavita, A.; Covelli, S.; Emili, A.; Berto, D.; Faganeli, J.; Giani, M.; Horvat, M.; Koron, N.Ž.; Rampazzo, F. Mercury in the Sediments of the Marano and Grado Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea): Sources, Distribution and Speciation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Petranich, E.; Langone, L.; Emili, A.; Acquavita, A. Historical Sedimentary Trends of Mercury and Other Trace Elements from Two Saltmarshes of the Marano and Grado Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1972–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turritto, A.; Acquavita, A.; Bezzi, A.; Covelli, S.; Fontolan, G.; Petranich, E.; Piani, R.; Pillon, S. Suspended Particulate Mercury Associated with Tidal Fluxes in a Lagoon Environment Impacted by Cinnabar Mining Activity (Northern Adriatic Sea). J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R. Moss and Lichen Biomonitoring of Atmospheric Mercury: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbrí, J.M.; López-Berdonces, M.A.; Fernández-Calderón, S.; Higueras, P.; Díez, S. Atmospheric Mercury Pollution around a Chlor-Alkali Plant in Flix (NE Spain): An Integrated Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4842–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunialti, G.; Frati, L. Bioaccumulation with Lichens: The Italian Experience. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 71, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barago, N.; Floreani, F.; Acquavita, A.; Esbrí, J.M.; Covelli, S.; Higueras, P. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Gaseous Elemental Mercury over a Highly Impacted Coastal Environment (Northern Adriatic, Italy). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Bajo, M.; Bellafiore, D.; De Pascalis, F.; Ghezzo, M.; Mattassi, G.; Scroccaro, I. Hydraulic Zonation of the Lagoons of Marano and Grado, Italy. A Modelling Approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambati, A. Provenienza, Trasporto e Accumulo Dei Sedimenti Recenti Nelle Lagune Di Marano e Grado e Nei Litorali Tra i Fiumi Isonzo e Tagliamento. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1970, 9, 281–329. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Covelli, S.; Langone, L.; Acquavita, A.; Piani, R.; Emili, A. Historical Flux of Mercury Associated with Mining and Industrial Sources in the Marano and Grado Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquavita, A.; Aleffi, I.F.; Benci, C.; Bettoso, N.; Crevatin, E.; Milani, L.; Tamberlich, F.; Toniatti, L.; Barbieri, P.; Licen, S.; et al. Annual Characterization of the Nutrients and Trophic State in a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon: The Marano and Grado Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranich, E.; Covelli, S.; Acquavita, A.; Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Contin, M. Evaluation of Mercury Biogeochemical Cycling at the Sediment–Water Interface in Anthropogenically Modified Lagoon Environments. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARPAFVG-OSMER. Schede Climatiche Del Friuli Venezia Giulia. 2015. Available online: http://www.clima.fvg.it (accessed on 13 October 2020). (In Italian).
- Sholupov, S.E.; Ganeyev, A.A. Zeeman Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Using High Frequency Modulated Light Polarization. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1995, 50, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Environmental Information. Guidance for Data Quality Assessment: Practical Methods for Data Analysis EPA QA/G-9 QA00 UPDATE; EPA/600/R-96/084; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000.
- López Berdonces, M.A.; Higueras, P.L.; Fernández-Pascual, M.; Borreguero, A.M.; Carmona, M. The Role of Native Lichens in the Biomonitoring of Gaseous Mercury at Contaminated Sites. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Nicolardi, V.; Bargagli, R.; Loppi, S. Estimating Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations with Lichens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8754–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.L.; Bargagli, R. Linne Guida per l’utilizzo Di Licheni Epifiti Come Bioaccumulatori Di Metalli in Traccia. In Biomonitoraggio Della Qualità Dell’aria sul Territorio Nazionale; ANPA Serie Atti: Rome, Italy, 1999. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Oyarzun, R.; Higueras, P.; Esbrí, J.M.; Pizarro, J. Mercury in Air and Plant Specimens in Herbaria: A Pilot Study at the MAF Herbarium in Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 387, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaselli, O.; Higueras, P.; Nisi, B.; María Esbrí, J.; Cabassi, J.; Martínez-Coronado, A.; Tassi, F.; Rappuoli, D. Distribution of Gaseous Hg in the Mercury Mining District of Mt. Amiata (Central Italy): A Geochemical Survey Prior the Reclamation Project. Environ. Res. 2013, 125, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wängberg, I.; Munthe, J.; Amouroux, D.; Andersson, M.E.; Fajon, V.; Ferrara, R.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Horvat, M.; Mamane, Y.; Melamed, E.; et al. Atmospheric Mercury at Mediterranean Coastal Stations. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Atmospheric Mercury Species over the Adriatic Sea. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnato, E.; Sproveri, M.; Barra, M.; Bitetto, M.; Bonsignore, M.; Calabrese, S.; Di Stefano, V.; Oliveri, E.; Parello, F.; Mazzola, S. The Sea-Air Exchange of Mercury (Hg) in the Marine Boundary Layer of the Augusta Basin (Southern Italy): Concentrations and Evasion Flux. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibičar, D.; Horvat, M.; Logar, M.; Fajon, V.; Falnoga, I.; Ferrara, R.; Lanzillotta, E.; Ceccarini, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Denby, B.; et al. Human Exposure to Mercury in the Vicinity of Chlor-Alkali Plant. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marumoto, K.; Hayashi, M.; Takami, A. Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations at Two Sites in the Kyushu Islands, Japan, and Evidence of Long-Range Transport from East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC. Proficiency Testing by Interlaboratory Comparisons Part 1: Development and Operation of Laboratory Proficiency Testing. 1997. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_catalogue/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=27216 (accessed on 18 March 2015).
- Fernández-Patier, R.; Ramos-Díaz, M.C. Informe Del Ejercicio de Lntercomparacion de Mercurio Gaseoso Total En Aire Ambiente BIN SITU^ (Año 2011); Ined. Repport: Paris, France, 2011. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, D.; Ebinghaus, R.; Gerard Spain, T.; Bieser, J. Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Mercury in the Remote Marine Atmosphere: Mace Head GAW Station, Irish Western Coast. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7929–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slemr, F.; Angot, H.; Dommergue, A.; Magand, O.; Barret, M.; Weigelt, A.; Ebinghaus, R.; Brunke, E.G.; Pfaffhuber, K.A.; Edwards, G.; et al. Comparison of Mercury Concentrations Measured at Several Sites in the Southern Hemisphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3125–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Niu, Z.; Tong, L.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y. Characteristics and Sources of Atmospheric Mercury Speciation in a Coastal City, Xiamen, China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Xie, Z. Total Gaseous Mercury in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2008 Winter Period. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Tong, L.; Lin, J.M.; Cai, Q.L.; Wang, K.Q.; Dai, X.R.; Li, J.R.; Chen, J.S.; Xiao, H. Temporal Variation and Long–Range Transport of Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) over a Coastal Site of East China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 233, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Cheng, I.; Lu, J. Annual Atmospheric Mercury Species in Downtown Toronto, Canada. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floreani, F.; Acquavita, A.; Petranich, E.; Covelli, S. Diurnal Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury from the Water-Air Interface in Coastal Environments of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukawa, M.; Sakata, M.; Marumoto, K.; Asakura, K. Air-Sea Exchange of Mercury in Tokyo Bay. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 62, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Penzias, P.S.; Williams, E.J.; Lerner, B.M.; Bates, T.S.; Gaston, C.; Prather, K.; Vlasenko, A.; Li, S.M. Shipboard Measurements of Gaseous Elemental Mercury along the Coast of Central and Southern California. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Blanchard, P.; Tordon, R.; Dalziel, J. Seasonal and Diurnal Patterns of Speciated Atmospheric Mercury at a Coastal-Rural and a Coastal-Urban Site. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLagan, D.S.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Steffen, A.; Hung, H.; Shin, C.; Stupple, G.W.; Olson, M.L.; Luke, W.T.; Kelley, P.; Howard, D.; et al. Global Evaluation and Calibration of a Passive Air Sampler for Gaseous Mercury. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5905–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Luke, W.T.; Kelley, P.; Cohen, M.D.; Olson, M.L.; Walker, J.; Cole, R.; Archer, M.; Artz, R.; Stein, A.A. Long-Term Observations of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury at a Coastal Site in the Northern Gulf of Mexico during 2007–2018. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Wip, D.; Warneke, T.; Holmes, C.D.; Dastoor, A.; Notholt, J. Sources of Atmospheric Mercury in the Tropics: Continuous Observations at a Coastal Site in Suriname. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7391–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, H.H.; Bieber, E.; Ebinghaus, R.; Spain, T.G.; Thees, B. Comparison of Long-Term Trends and Seasonal Variations of Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations at the Two European Coastal Monitoring Stations Mace Head, Ireland, and Zingst, Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7549–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolke, S.R.; Schroeder, W.H.; Kock, H.H.; Schneeberger, D.; Munthe, J.; Ebinghaus, R. Simultaneous Measurements of Total Gaseous Mercury at Four Sites on a 800 Km Transect: Spatial Distribution and Short-Time Variability of Total Gaseous Mercury over Central Europe. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Hong, S.; Youn, Y.H.; Shon, Z.H.; Lee, J.S. Monitoring of Atmospheric Mercury at a Global Atmospheric Watch (GAW) Site on An-Myun Island, Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 185, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Z. Atmospheric Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) over a Coastal/Rural Site Downwind of East China: Temporal Variation and Long-Range Transport. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faganeli, J.; Hines, M.E.; Covelli, S.; Emili, A.; Giani, M. Mercury in Lagoons: An Overview of the Importance of the Link between Geochemistry and Biology. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, T.; Liu, L.; Talbot, R.W.; Torres, A.; Lan, X. Comparison of Atmospheric Mercury Speciation at a Coastal and an Urban Site in Southeastern Texas, USA. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, E.G.; Keeler, G.J.; Landis, M.S. The Effects of the Coastal Environment on the Atmospheric Mercury Cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Covelli, S.; Fajon, V.; Logar, M.; Lipej, L.; Cermelj, B. Mercury and Methylmercury in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquavita, A.; Brandolin, D.; Felluga, A.; Maddaleni, P.; Meloni, C.; Poli, L.; Skert, N.; Zanello, A. Mercury Distribution and Speciation in Soils Contaminated by Historically Mining Activity: The Isonzo River Plain. In Proceedings of the Congresso SIMP-SGI-SOGEI 2019, Parma, Italy, 16–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, R.; Ceccarini, C.; Lanzillotta, E.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Sommar, J.; Horvat, M.; Logar, M.; Fajon, V.; Kotnik, J. Profiles of Dissolved Gaseous Mercury Concentration in the Mediterranean Seawater. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquavita, A.; Emili, A.; Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Predonzani, S.; Koron, N.; Carrasco, L. The Effects of Resuspension on the Fate of Hg in Contaminated Sediments (Marano and Grado Lagoon, Italy): Short-Term Simulation Experiments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emili, A.; Koron, N.; Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Acquavita, A.; Predonzani, S.; Vittor, C.D. Does Anoxia Affect Mercury Cycling at the Sediment-Water Interface in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea)? Incubation Experiments Using Benthic Flux Chambers. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; De Vittor, C.; Predonzani, S.; Acquavita, A.; Horvat, M. Benthic Fluxes of Mercury Species in a Lagoon Environment (Grado Lagoon, Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, S.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Dabrin, A.; Lanceleur, L.; Masson, M. Gaseous Mercury at the Air-Water Interface of a Highly Turbid Estuary (Gironde Estuary, France). Mar. Chem. 2009, 117, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranich, E.; Terribili, L.; Acquavita, A.; Pavoni, E.; Langone, L.; Covelli, S. The Role of a Tidal Flat–Saltmarsh System as a Source–Sink of Mercury in a Contaminated Coastal Lagoon Environment (Northern Adriatic Sea). Aquat. Geochem. 2020, 26, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmur, T.; McArthur, G.; Risk, D.; Tordon, R.; O’Driscoll, N.J. Gaseous Mercury Flux from Salt Marshes Is Mediated by Solar Radiation and Temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, E.; Petranich, E.; Acquavita, A.; Canário, J.; Emili, A.; Covelli, S. Mercury Uptake by Halophytes in Response to a Long-Term Contamination in Coastal Wetland Salt Marshes (Northern Adriatic Sea). Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretiach, M.; Pittao, E. Biomonitoraggio di Metalli Mediante Licheni in Cinque Aree Campione Della Provincia di Pordenone: Stato Attuale e Confronto Con i Dati del 1999; Provincia di Pordenone: Pordenone, Italy, 2008. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Fortuna, L.; Carniel, F.C.; Capozzi, F. Congruence Evaluation of Mercury Pollution Patterns Around a Waste Incinerator over a 16-Year-Long Period Using Different Biomonitors. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Barghigiani, C. Lichen Biomonitoring of Mercury Emission and Deposition in Mining, Geothermal and Volcanic Areas of Italy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1991, 16, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loppi, S.; Paoli, L.; Gaggi, C. Diversity of Epiphytic Lichens and Hg Contents of Xanthoria parietina Thalli as Monitors of Geothermal Air Pollution in the Mt. Amiata Area (Central Italy). J. Atmos. Chem. 2006, 53, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimondi, V.; Benesperi, R.; Beutel, M.W.; Chiarantini, L.; Costagliola, P.; Lattanzi, P.; Medas, D.; Morelli, G. Monitoring of Airborne Mercury: Comparison of Different Techniques in the Monte Amiata District, Southern Tuscany, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Iosco, F.P.; Leonzio, C. Monitoraggio Di Elementi in Tracce Mediante Licheni Epifiti. Inquinamento 1985, 2, 33–37. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Scerbo, R.; Ristori, T.; Possenti, L.; Lampugnani, L.; Barale, R. Lichen (Xanthoria Parietina) Biomonitoring of Trace Element Contamination and Air Quality Assessment in Pisa Province (Tuscany, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 286, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghigiani, C.; Bargagli, R.; Siegel, B.; Siegel, S. Source and Selectivity in the Accumulation of Mercury and Other Metals by the Plants of Mt. Etna. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1988, 39, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Grangeon, S.; Guédron, S.; Asta, J.; Sarret, G.; Charlet, L. Lichen and Soil as Indicators of an Atmospheric Mercury Contamination in the Vicinity of a Chlor-Alkali Plant (Grenoble, France). Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, D.; Davranche, L.; Thomas, P.; Kempa, M.; van Haluwyn, C. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Trace Element Contents in Xanthoria parietina Thalli Collected in a Highly Industrialized Area in Northern France as an Element for a Future Epidemiological Study. J. Atmos. Chem. 2004, 49, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, M.; Jeran, Z.; Spiric, Z.; Jacimovic, R.; Miklavcic, V. Mercury and Other Elements in Lichens near the INA Naftaplin Gas Treatment Plant, Molve, Croatia. J. Environ. Monit. 2000, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenisoy-Karakaş, S.; Tuncel, S.G. Geographic Patterns of Elemental Deposition in the Aegean Region of Turkey Indicated by the Lichen, Xanthoria parietina (L.) Th. Fr. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 329, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharro, R.; Esbrí, J.M.; Amorós, J.A.; Higueras, P.L. Experimental Assessment of the Daily Exchange of Atmospheric Mercury in Epipremnum Aureum. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3185–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canário, J.; Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Caetano, M.; Hintelmann, H.; O’Driscoll, N.J. Salt-Marsh Plants as Potential Sources of Hg0 into the Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).