Performance Evaluation of an Operational Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean (Greece)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Data
2.1. Study Area, Selected Wildfires and Data
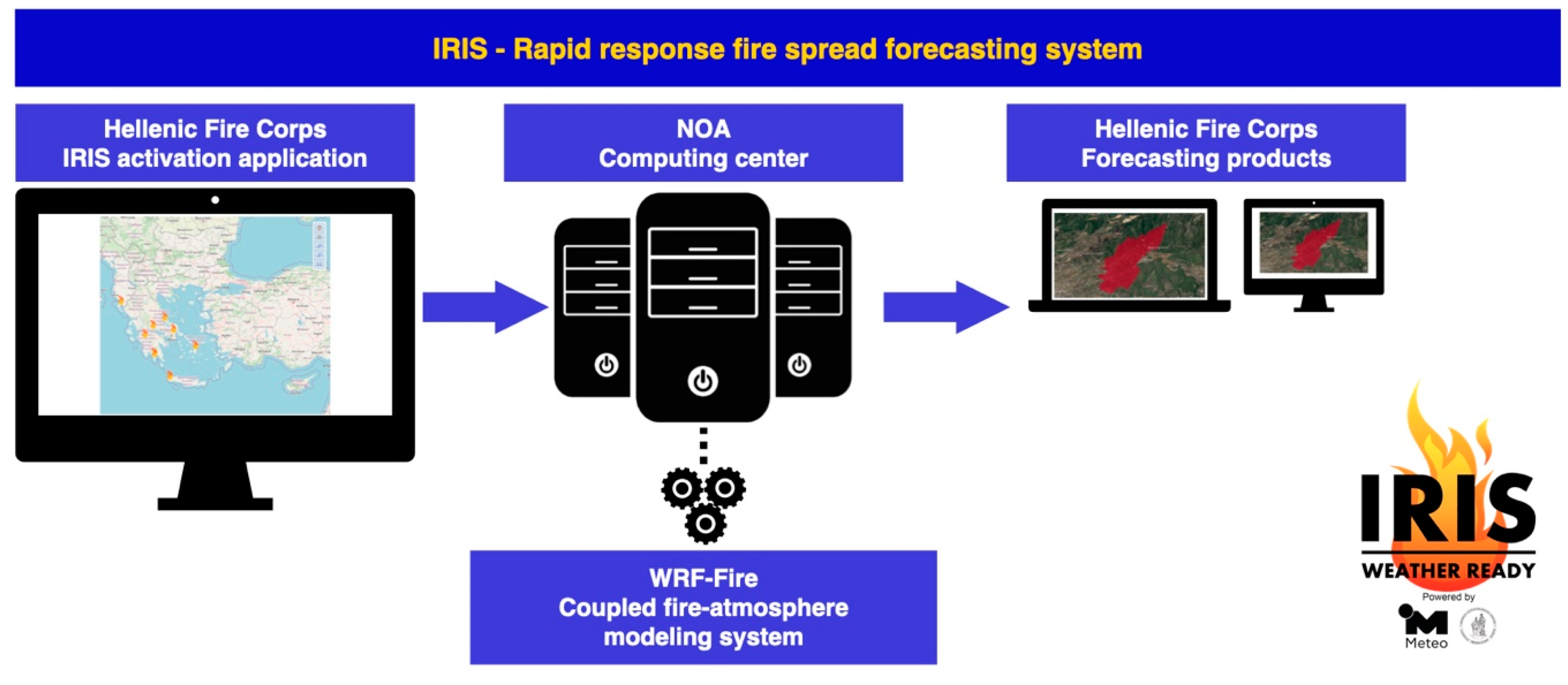
2.2. IRIS—Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System
2.2.1. The WRF-Fire Coupled Fire-Atmosphere Modeling System
2.3. Evaluation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Wind Forecasts
3.2. Wildfire Spread Forecasts
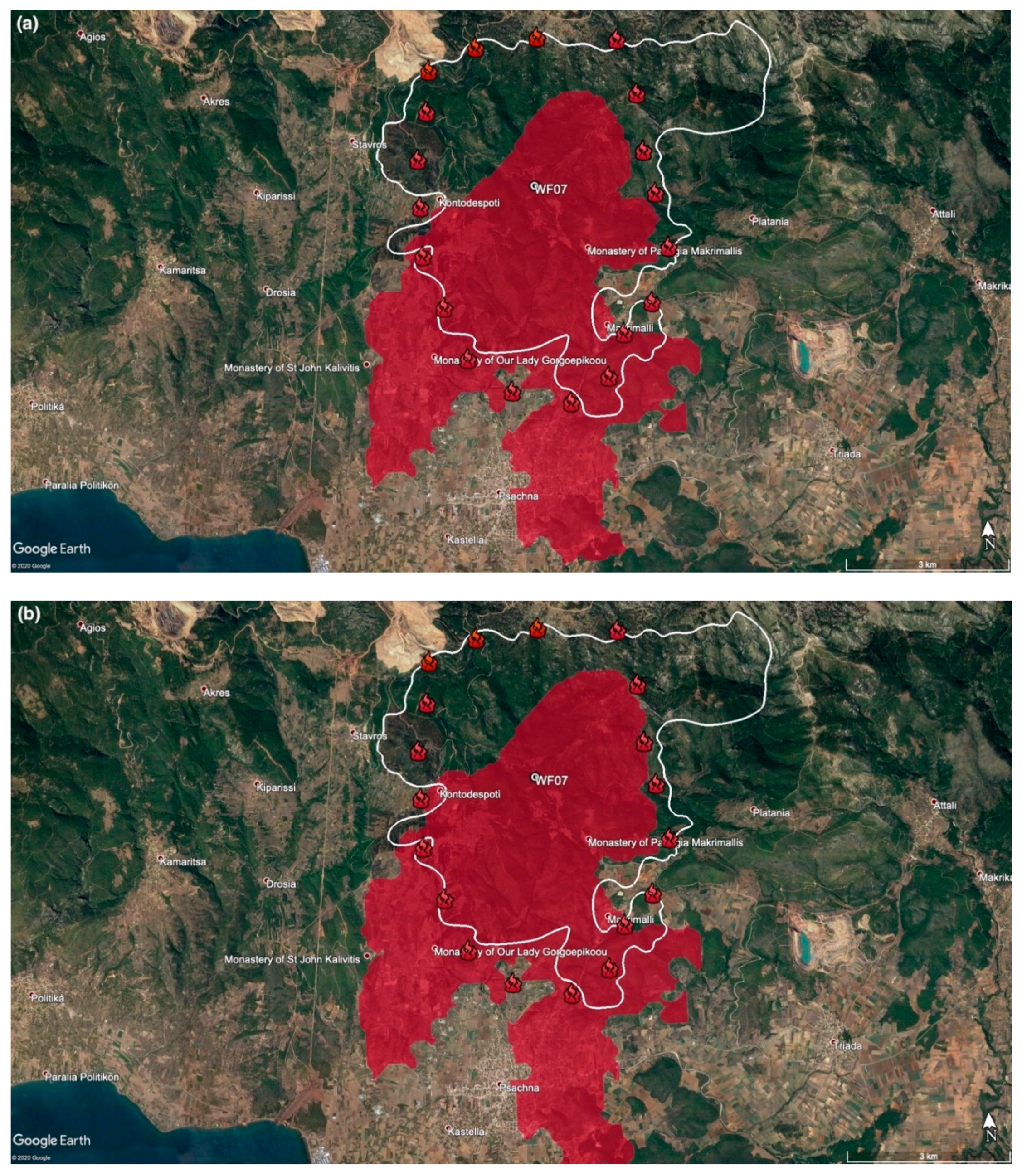
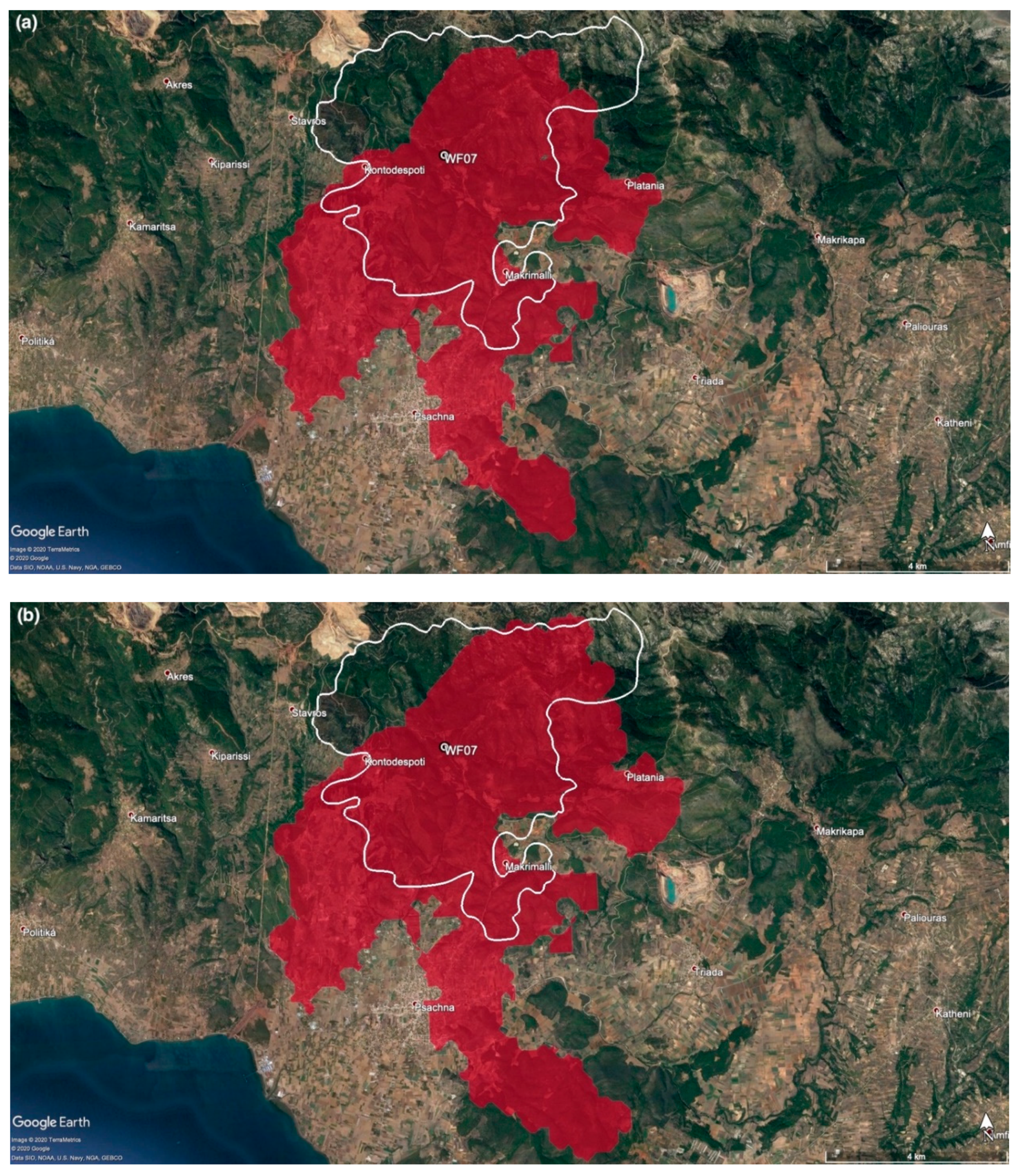
3.3. The Kontodespoti Wildfire (WF07)
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bond, W.J.; Woodward, F.I.; Midgley, G.F. The global distribution of ecosystems in a world without fire. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pausas, J.G.; Vallejo, V.R. The role of fire in European Mediterranean ecosystems. In Remote Sensing of Large Wildfires; Chuvieco, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Durrant, T.; Boca, R.; Liberta, G.; Branco, A.; de Rigo, D.; Ferrari, D.; Maianti, P.; Artes Vivancos, T.; Pfeiffer, H.; et al. Forest Fires in Europe, Middle East and North Africa 2018; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; pp. 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Camia, A. Forest fires. In Mapping the Impacts of Natural Hazards and Technological Accidents in Europe. An Overview of the Last Decade; Wehrli, A., Herkendell, J., Jol, A., Eds.; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Terrén, D.M.; Xanthopoulos, G.; Diakakis, M.; Ribeiro, L.; Caballero, D.; Delogu, G.M.; Viega, D.X.; Silva, C.A.; Cardil, A. Analysis of forest fire fatalities in souther Europe: Spain, Portugal, Greece and Sardinia (Italy). Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakesby, R.A. Post-wildfire soil erosion in the Mediterranean: Review and future research directions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Moreno, J.M.; Camia, A. Analysis of large fires in European Mediterranean landscapes: Lessons learned and perspectives. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2013, 294, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Forest Fires in Europe 2003 Fire Campaign; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Giannaros, T.M.; Dafis, S. Meteorological conditions conducive to the rapid spread of the deadly wildfire in Eastern Attica, Greece. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, M.D.; Krawchuk, M.A.; de Groot, W.J.; Wotton, B.M.; Gowman, L.M. Implications of changing climate for global wildland fire. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganteaume, A.; Camia, A.; Jappiot, M.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Long-Fournel, M.; Lampin, C. A review of the main driving factors of forest fire ignition over Europe. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, P.; Finney, M.; Fischetti, M. Predicting wildfires. Sci. Am. 2007, 297, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, B.; Ghisu, T.; Casula, M.; Salis, M.; Duce, P. A web-based wildfire simulator for operational applications. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, J. Some requirements for simulating wildland fire behavior using insight from coupled weather—Wildland fire models. Fire 2018, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linn, R.; Reisner, J.; Colman, J.J.; Winterkamp, J. Studying wildfire behavior using FIRETEC. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2002, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mell, W.; Jenkins, M.A.; Gould, J.; Cheney, P. A physics-based approach to modeling grassland fires. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2007, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, M.A. FARSITE: Fire Area Simulator—Model Development and Evaluation; US Forest Service: Ogden, UT, USA, 1998.
- Andrews, P.L. BehavePlus fire modeling system: Past, present and future. In Proceedings of the 7th Symposium on Fire and Forest Meteorology, Bar Harbor, ME, USA, 23–25 October 2007. Paper J2.1. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.D.; Pavlidou, F.N. A comparative review of wildfire simulators. Syst. J. IEEE 2011, 5, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, A.L. Wildland surface fire spread modeling, 1990–2007. 1: Physical and quasi-physical models. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, M.G.; Alexander, M.E. Uncertainty associated with model predictions of surface and crown fire rates of spread. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 47, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, J.-B.; Bosseur, F.; Mari, C.; Lac, C. Simulation of a large wildfire in a coupled fire-atmosphere model. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Muñoz-Esparza, G.; Kosović, B. A high resolution coupled fire-atmosphere forecasting system to minimize the impacts of wildland fires: Applications to the Chimney Tops II wildland event. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giannaros, T.M.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K. IRIS—Rapid response fire spread forecasting system: Development, calibration and evaluation. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2019, 279, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, J.L. Simulation of the Big Elk fire using coupled atmosphere-fire modeling. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, J.-B.; Pialat, X.; Clements, C.B. Assessment of Forefire/Meso-NH for wildland fire/atmosphere coupled simulation of the FireFlux experiment. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanski, A.K.; Jenkins, M.A.; Mandel, J.; Beezley, J.D.; Clements, C.B.; Krueger, S. Evaluation of WRF-SFIRE performance with field observations from the Fireflux experiment. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1109–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochanski, A.K.; Jenkins, M.A.; Mandel, J.; Beezley, J.D.; Krueger, S. Real time simulation of 2007 Santa Ana fires. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2013, 294, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peace, M.; Mattner, T.; Mills, G.; Keppert, J.; McCaw, L. Coupled fire-atmosphere simulations of the Rocky River fire using WRF-SFIRE. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1151–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivanen, J.; Engle, C.B.; Reeder, M.J.; Lane, T.P.; Davies, L.; Webster, S.; Wales, S. Coupled atmosphere-fire simulations of the Black Saturday Kilmore East wildfires with the Unified Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallia, D.V.; Kochanski, A.K.; Kelly, K.E.; Whitaker, R.; Xing, W.; Mitchell, L.E.; Jacques, A.; Farguell, A.; Mandel, A.; Gaillardon, P.-E.; et al. Evaluating wildfire smoke transport within a coupled fire-atmosphere model using a high-density observation network for an episodic smoke event along Utah’s Wasatch Front. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2020JD032712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, D.V.; Kochanski, A.K.; Urbanski, S.P.; Mandel, J.; Farguell, A.; Krueger, S.K. Incorporating a canopy parameterization within a coupled fire-atmosphere model to improve smoke simulation for a prescribed burn. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanski, A.K.; Mallia, D.V.; Fearon, M.G.; Mandel, J.; Souri, A.H.; Brown, T. Modeling wildfire smoke feedback mechanisms using a coupled fire-atmosphere model with a radiatively active aerosol scheme. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 9099–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.L.; Jenkins, M.A.; Coen, J.; Packham, D. A coupled atmosphere-fire model: Role of the convective Froude number and dynamic fingering at the fireline. Int. J. Wildland Fire 1996, 6, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, C.C.; Sharples, J.J.; Evans, J.P. Resolving vorticity-driven lateral fire spread using the WRF-Fire coupled atmosphere-fire numerical model. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peace, M.; Mattner, T.; Mills, G.; Keppert, J.; McCaw, L. Fire-modified meteorology in a coupled fire-atmosphere model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, J.-B.; Bosseur, F.; Pialat, X.; Santoni, P.A.; Strada, S.; Mari, C. Simulation of coupled fire/atmosphere interaction with the MesoNH-ForeFire models. J. Combust. 2011, 2011, 540390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finney, M.A.; Grenfell, I.C.; McHugh, C.W.; Seli, R.C.; Trethewey, D.; Stratton, R.D.; Brittain, S. A method for ensemble wildland fire simulation. Environ. Model. Assess. 2011, 16, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabokidis, K.; Athanasis, N.; Gagliardi, F.; Karayiannis, F.; Palaiologou, P.; Parastatidis, S.; Vasilakos, C. Virtual fire: A web-based GIS platform for forest fire control. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 16, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, M.; Arca, B.; Alcasena, F.; Arianoutsou, M.; Bacciu, V.; Duce, P.; Duguy, B.; Koutsias, N.; Mallinis, G.; Mitsopoulos, I.; et al. Predicting wildfire spread and behavior in Mediterranean landscapes. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forthofer, J.M.; Butler, B.W.; Wagenbrener, N.S. A comparison of three approaches for simulating fine-scale surface winds in support of wildland fire management. Part I. Model formulation and comparison against measurements. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forthofer, J.M.; Butler, B.W.; McHugh, C.W.; Finney, M.A.; Bradshaw, L.S.; Stratton, R.D.; Shannon, K.S.; Wagenbrenner, N.S. A comparison of three approaches for simulating fine-scale surface winds in support of wildland fire management. Part II. An exploratory study of the effect of simulated winds on fire growth simulations. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotroni, V.; Cartalis, C.; Michaelides, S.; Stoyanova, J.; Tymvios, F.; Bezes, A.; Christoudias, T.; Dafis, S.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Giannaros, T.M.; et al. DISARM early warning system for wildfires in the eastern Mediterranean. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Esparza, D.; Kosović, B.; Jiménez, P.A.; Coen, J.L. An accurate fire-spread algorithm in the Weather Research and Forecasting model using the level-set method. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 908–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrakopoulos, A.P. Mediterranean fuel models and potential fire behavior in Greece. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2002, 11, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannaki, K.; Giannaros, T.M.; Lykoydis, S.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K. Weather-related thresholds for wildfire danger in a Mediterranean region: The case of Greece. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Fire Corps. Available online: https://www.fireservice.gr/el_GR/synola-dedomenon (accessed on 26 August 2020).
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Schulte, E.; Schmuck, G.; Camia, A.; Srobl, P.; Libertà, G.; Giovando, C.; Boca, R.; Sedano, F.; Kempeneers, P.; et al. Comprehensive monitoring of wildfires in Europe: The European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS). In Approaches to Monitor Disaster—Assessing Hazards, Emergencies and Disaster Impacts; Tiefenbacher, J.P., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Bezes, A.; Koletsis, I.; Kopania, T.; Lykoudis, S.; Mazarakis, N.; Papagiannaki, K.; Vougioukas, S. The automatic weather stations NOANN network of the National Observatory of Athens: Operation and database. Geosci. Data J. 2017, 4, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothermel, R.C. A Mathematical Model for Predicting Fire Spread in Wildland Fuels; USDA Forest Service: Ogden, UT, USA, 1972.
- Coen, J.L.; Cameron, M.; Michalakes, J.; Patton, E.G.; Riggan, P.J.; Yedinak, K.M. WRF-Fire: Coupled weather-wildland fire modeling with the Weather Research and Forecasting model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Model Version 4; National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR): Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono, M.G.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmusse, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J.; Gonzalerz-Rouco, J.F.; Navarro, J.; Montavez, J.P.; Garcia-Bustamante, E. A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.; Cuenca, R.H. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5233–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, T.A. A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content, and its application to analysis of the vegetation of Danish commons. K. Dan. Vidensk. Selsk. 1948, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Coen, J.L.; Riggan, P.J. Simulation and thermal imaging of the 2006 Esperanza wildfire in southern California: Application of a coupled weather-wildland fire model. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, J.L.; Schroeder, W. The high park fire: Coupled weather-wildland fire model simulation of a windstorm-driven wildfire in Colorado’s front range. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, J.L.; Stavros, E.N.; Fites-Kaufmann, J.A. Deconstructing the King megafire. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1565–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
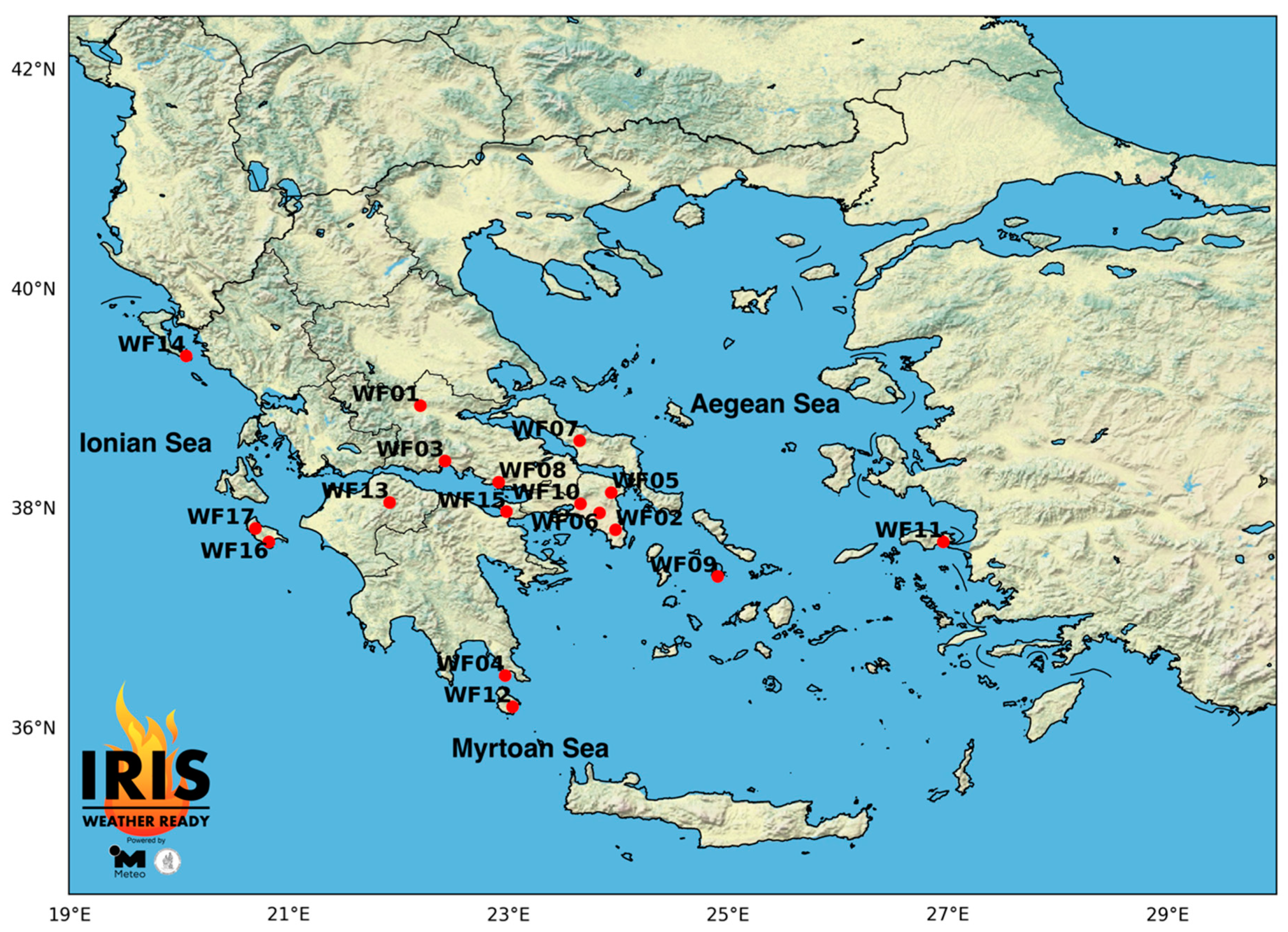
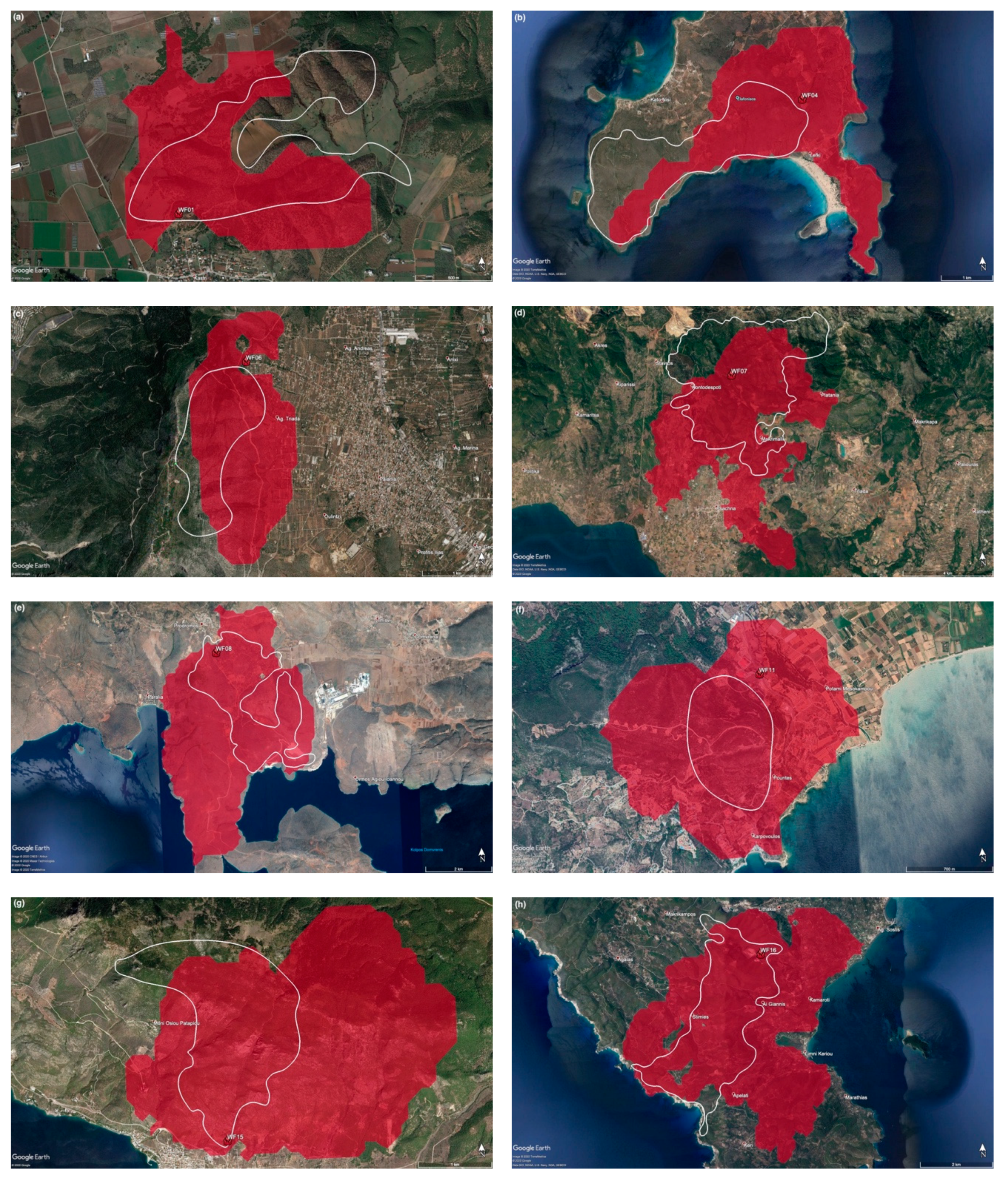

| ID | Region | Date and Time (UTC) | IRIS Activation (UTC) | Location (°N, °E) | Duration (hh: mm) | BA (ha) | Perimeter Acquisition Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF01 | Kastri | 8 July 2019 11:37 | 8 July 2019 12:40 | 38.94925, 22.20243 | 09:23 | 98 | 8 July 2019 |
| WF04 | Elafonissos | 10 August 2019 02:40 | 10 August 2019 06:56 | 36.48591, 22.97353 | 38:20 | 535 | 11 August 2019 |
| WF06 | Hymettus | 12 August 2019 00:19 | 12 August 2019 01:20 | 37.97047, 23.83132 | 06:41 | 180 | 12 August 2019 |
| WF07 | Kontodespoti | 13 August 2019 00:10 | 13 August 2019 01:25 | 38.62776, 23.65245 | 38:50 | 2889 | 15 August 2019 |
| WF08 | Prodromos | 13 August 2019 02:35 | 13 August 2019 03:40 | 38.24905, 22.91353 | 12:25 | 735 | 13 August 2019 |
| WF11 | Mesokampos | 24 August 2019 14:09 | 24 August 2019 14:48 | 37.70667, 26.96484 | 14:51 | 59 | 26 August 2019 |
| WF15 | Loutraki | 14 September 2019 12:36 | 14 September 2019 13:27 | 37.98038, 22.98734 | 20:24 | 352 | 16 September 2019 |
| WF16 | Lithakia | 15 September 2019 08:00 | 15 September 2019 08:32 | 37.70666, 20.82235 | 22:30 | 919 | 16 September 2019 |
| ID | Station | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Verification Period (UTC) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF01 | Makrakomi | 38.9375 | 22.1168 | 8 July 2019 13:00– 8 July 2019 21:00 | 7.5 km WSW of ignition location |
| WF04 | Kavomalias | 36.4758 | 23.1012 | 10 August 2019 07:00– 11 August 2019 06:00 | 11 km ESE of ignition location |
| WF06 | Palini | 37.9978 | 23.8928 | 12 August 2019 02:00– 12 August 2019 07:00 | 6 km NE of ignition location |
| WF07 | Psachna | 38.5694 | 23.6492 | 13 August 2019 02:00– 14 August 2019 03:00 | 6.4 km S of ignition location |
| WF08 | Kapareli | 38.2433 | 23.2117 | 13 August 2019 04:00– 13 August 2019 15:00 | 26.5 km E of ignition location |
| WF11 | Samos | 37.7937 | 26.6820 | 24 August 2019 15:00– 25 August 2019 05:00 | 26 km NW of ignition location |
| WF15 | Loutraki | 37.9696 | 22.9799 | 14 September 2019 14:00– 15 September 2019 09:00 | 1.4 km SSW of ignition location |
| WF16 | Zakynthos | 37.7810 | 20.8450 | 15 September 2019 09:00– 16 September 2019 07:00 | 8.4 km NNE of ignition location |
| Wind Speed (m s−1) | Wind Direction (°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | ME | RMSE | ME | RMSE |
| WF01 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 18.9 |
| WF04 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 29.1 | 36.8 |
| WF06 | 1.7 | 2.3 | −52.9 | 136.6 |
| WF07 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 19.4 | 61.5 |
| WF08 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 41.5 | 52.1 |
| WF11 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| WF15 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 30.2 | 103.7 |
| WF16 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 44.7 | 49.8 |
| ID | KC | SC | OI | BAA (ha) 1 | BAO (ha) 2 | BAU (ha) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF01 | 0.63 * | 0.68 | 0.44 | 75 | 52 | 20 |
| WF04 | 0.45 * | 0.49 | 0.06 | 268 | 298 | 266 |
| WF06 | 0.45 * | 0.48 | 0.45 | 114 | 180 | 68 |
| WF07 | 0.52 * | 0.57 | 0.32 | 1899 | 1908 | 989 |
| WF08 | 0.57 * | 0.60 | 0.93 | 702 | 909 | 35 |
| WF11 | 0.49 * | 0.52 | 0.96 | 57 | 104 | 2 |
| WF15 | 0.42 * | 0.46 | 0.79 | 283 | 604 | 71 |
| WF16 | 0.52 * | 0.55 | 0.84 | 814 | 1217 | 103 |
| ID | KC | SC | OI | BAA (ha) 1 | BAO (ha) 2 | BAU (ha) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Prediction | ||||||
| WF07 | 0.52 * | 0.57 | 0.32 | 1899 | 1908 | 989 |
| Retrospective Prediction | ||||||
| WF07 | 0.52 * | 0.57 | 0.49 | 2101 | 2288 | 787 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannaros, T.M.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V. Performance Evaluation of an Operational Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean (Greece). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111264
Giannaros TM, Lagouvardos K, Kotroni V. Performance Evaluation of an Operational Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean (Greece). Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111264
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannaros, Theodore M., Konstantinos Lagouvardos, and Vassiliki Kotroni. 2020. "Performance Evaluation of an Operational Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean (Greece)" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111264
APA StyleGiannaros, T. M., Lagouvardos, K., & Kotroni, V. (2020). Performance Evaluation of an Operational Rapid Response Fire Spread Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean (Greece). Atmosphere, 11(11), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111264







