Human Health and Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah: An Expert Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Physical and Societal Context of the Study Region
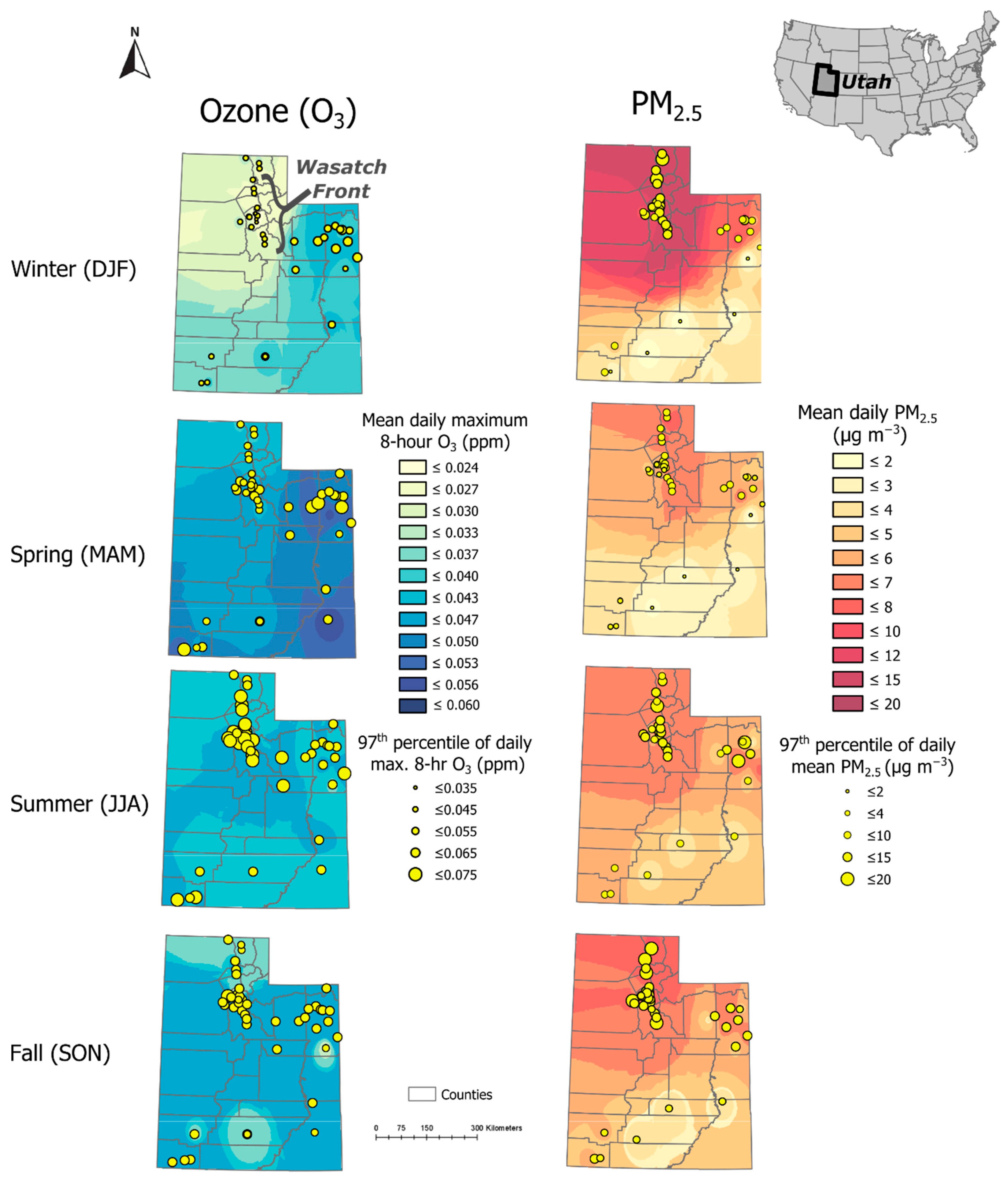
2.2. History of Air Pollution Efforts and Research in Utah
2.3. Expert Assessment Methods
2.4. Questionnaire
2.5. Data Analysis and Calculations
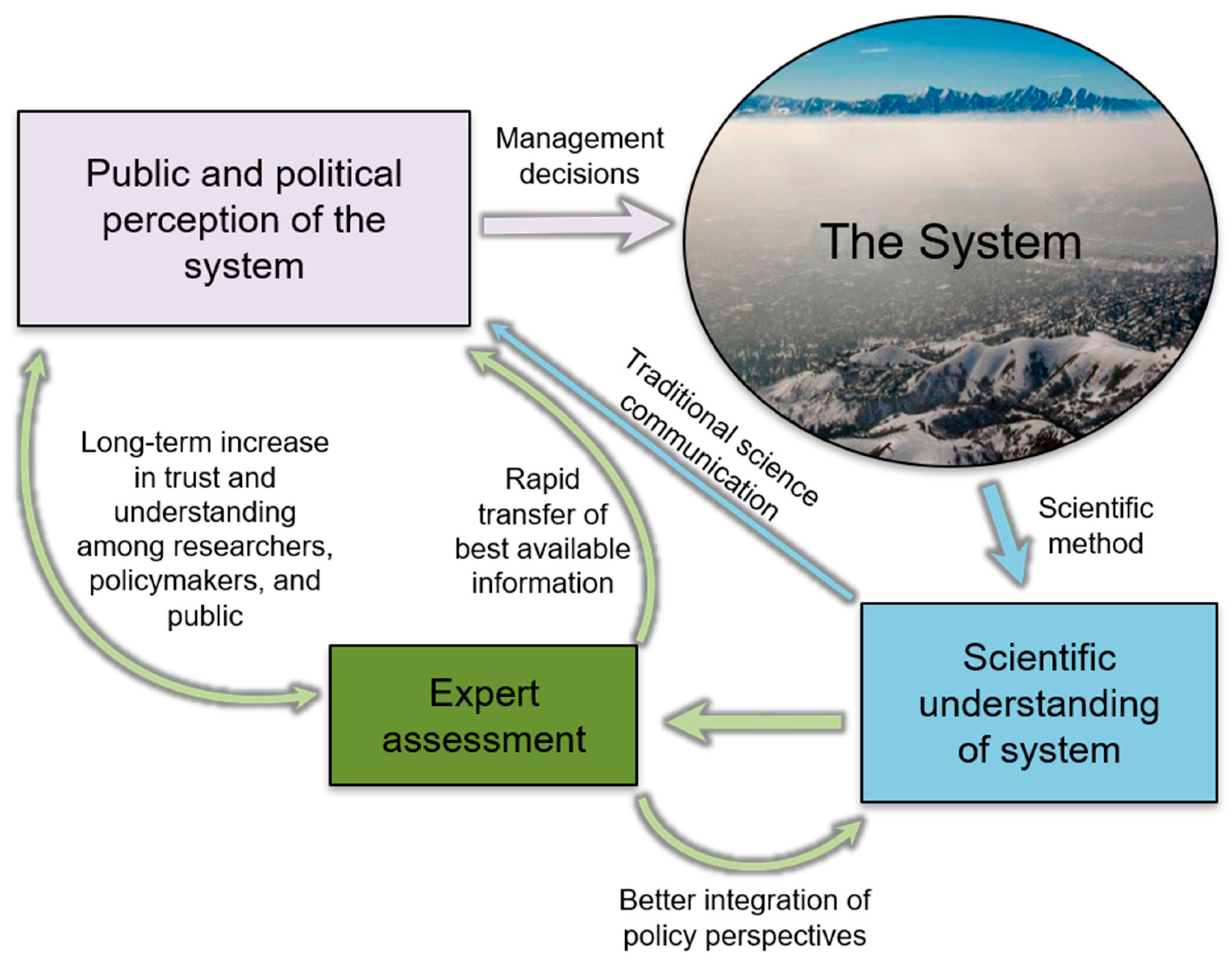
2.6. Initial Report and Public Relations Efforts
3. Results
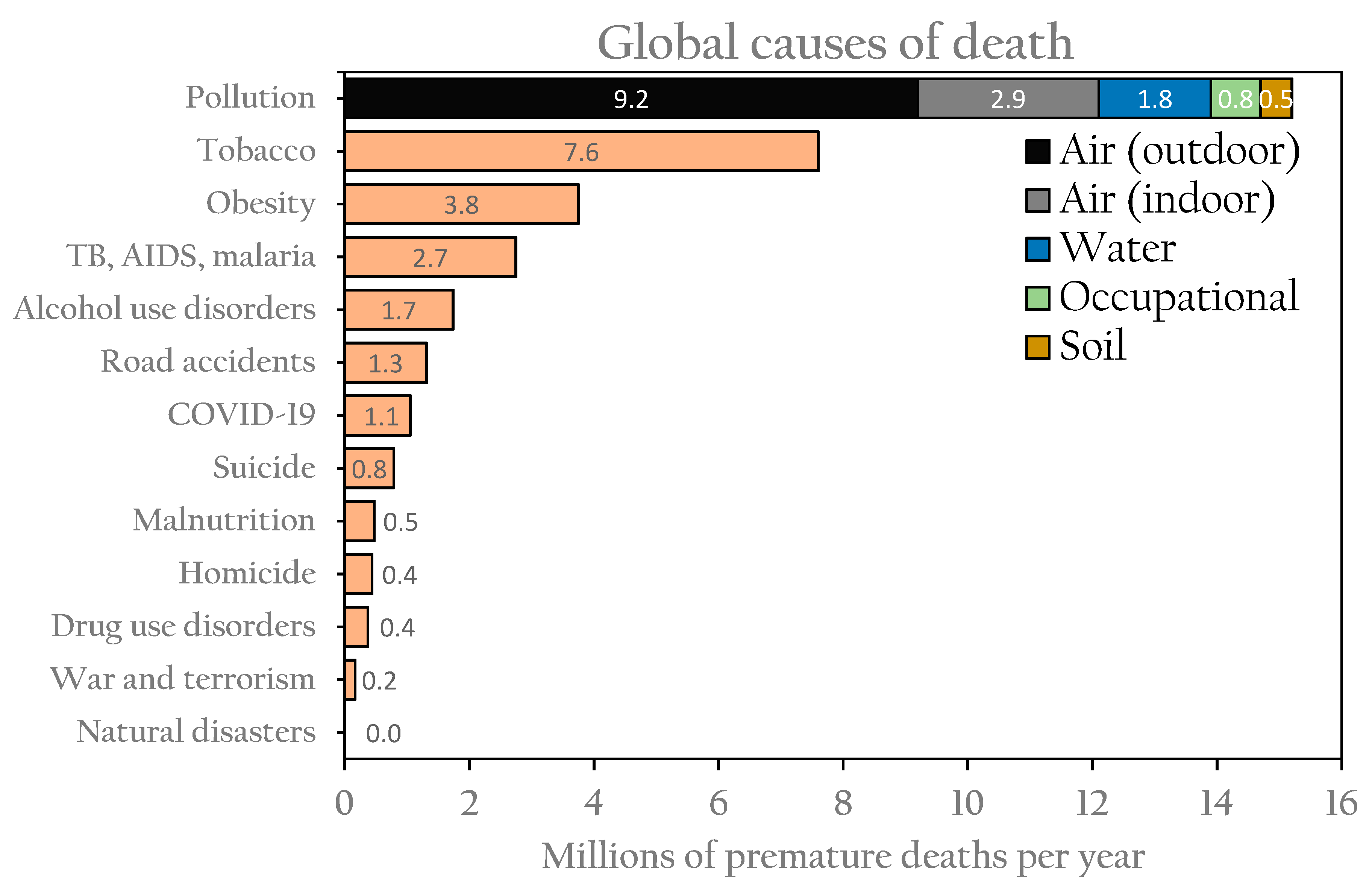
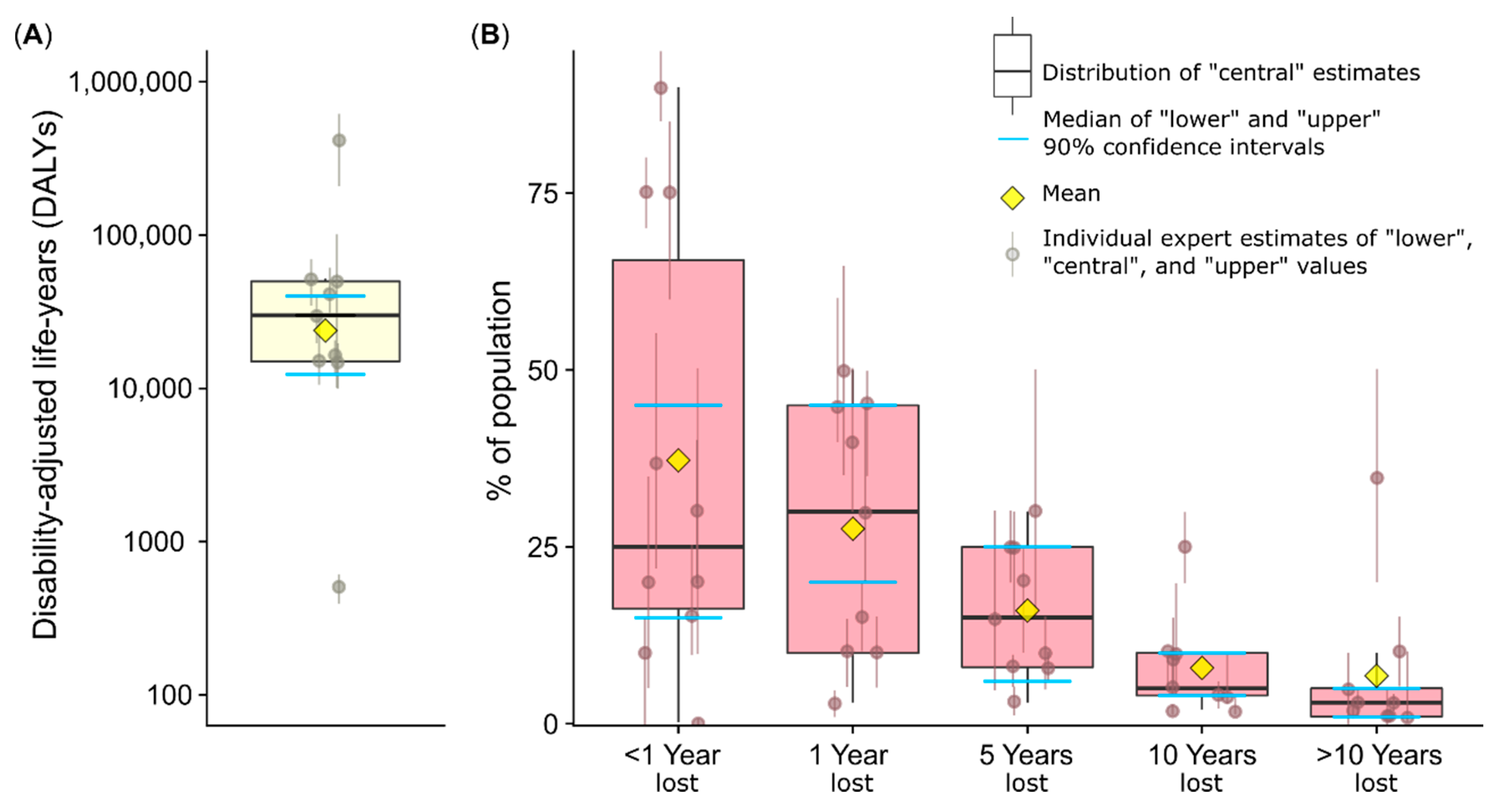
3.1. Human Health Consequences of Air Pollution in Utah
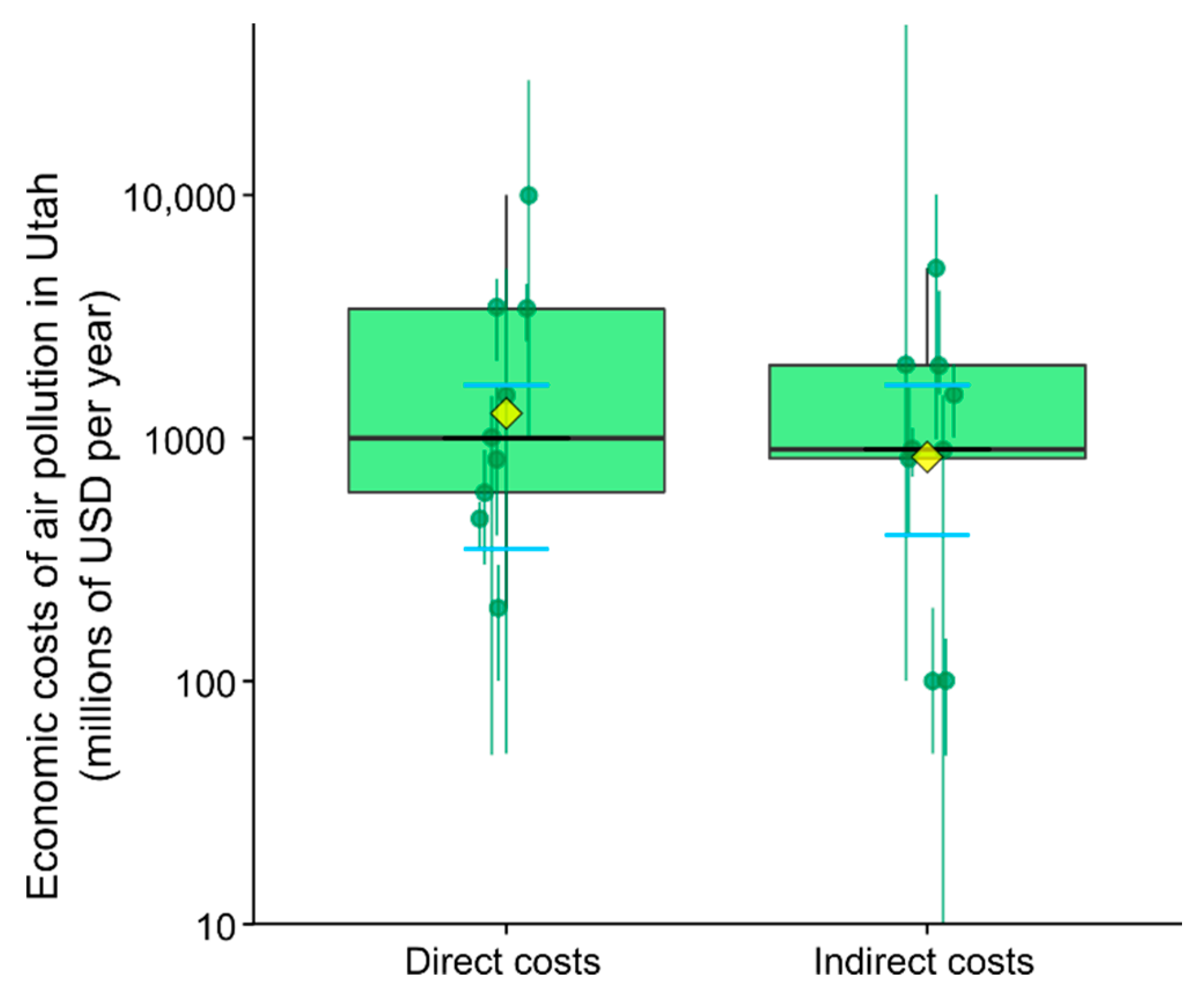
3.2. Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah
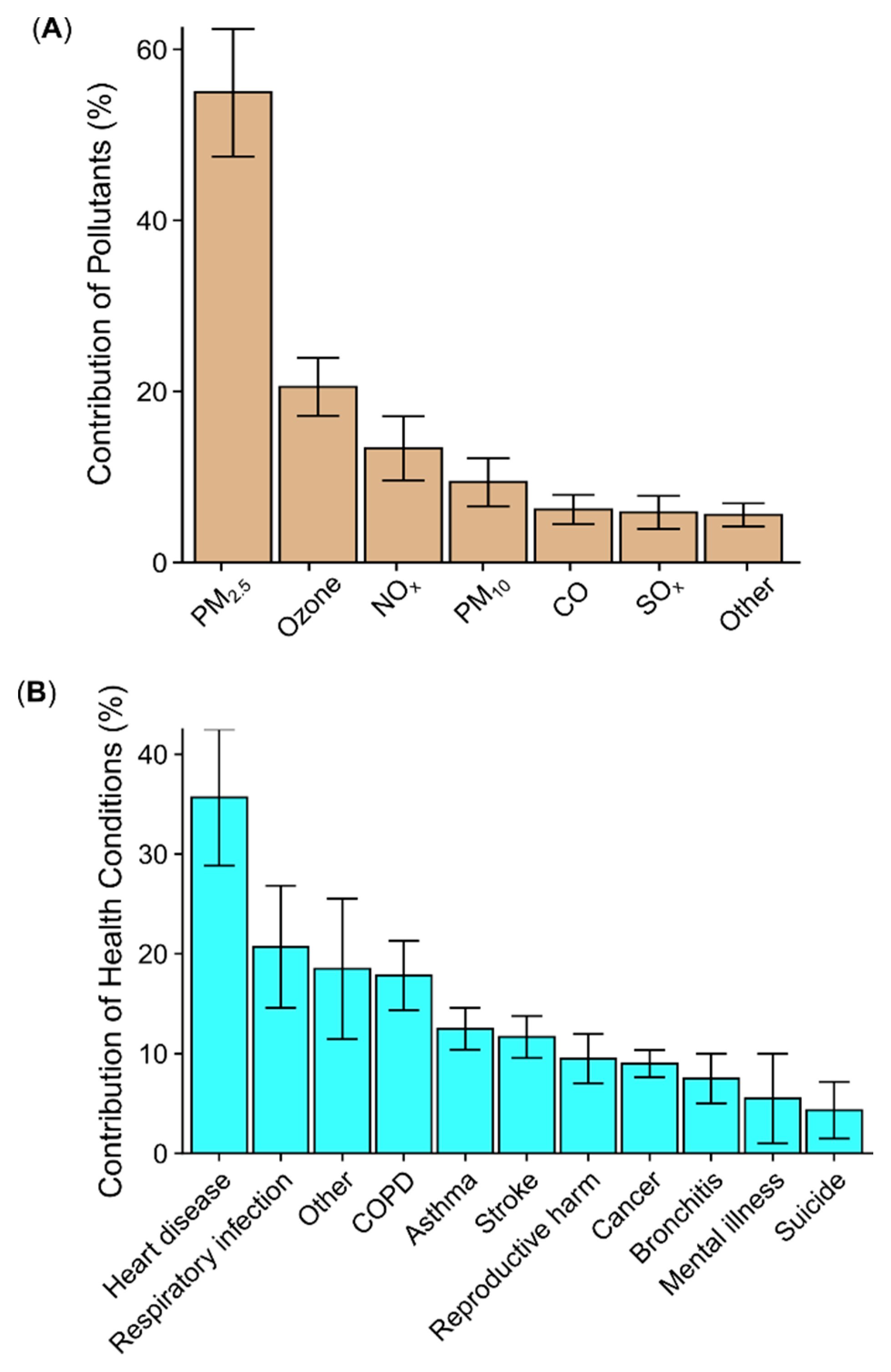
3.3. Attributing Losses to Specific Pollutants and Health Conditions
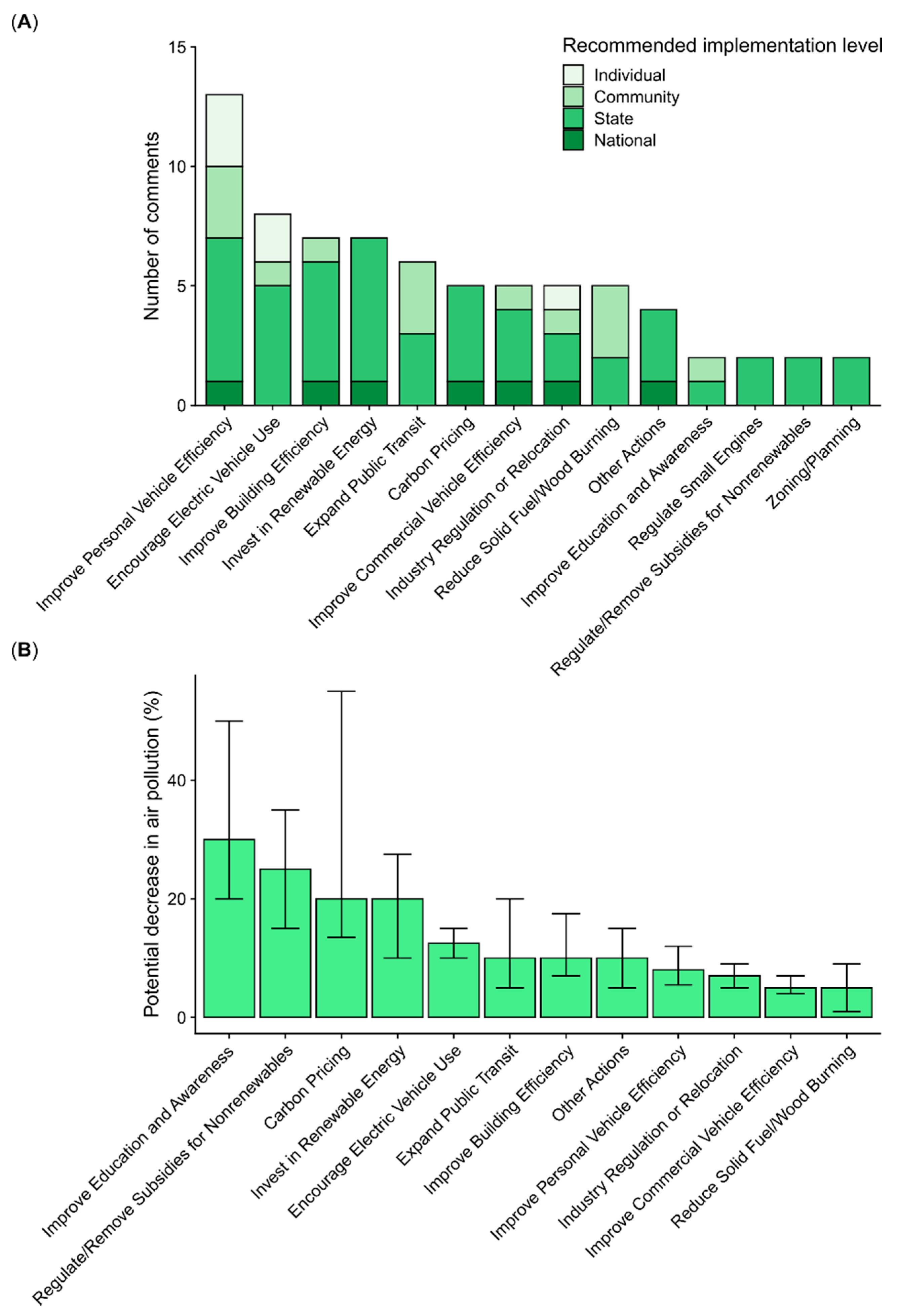
3.4. Recommendations for Improving Air Quality
3.5. Legislative and Public Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Expert Estimates with Downscaled National Data
4.2. Are Local Estimates of Pollution Costs more Pertinent and Persuasive?
4.3. Building Community Networks to Accelerate Progress
4.4. The Moral Imperative to Solve Air Pollution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global estimates of mortality associated with long-term exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; Matteis, S.D.; Jung, S.-H.; Mortimer, K.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.B.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Sood, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases: A Review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, Part 1: The Damaging Effects of Air Pollution. Chest 2019, 155, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates 2016: Death by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2016; Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Statistics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Our World in Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Caiazzo, F.; Ashok, A.; Waitz, I.A.; Yim, S.H.L.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air pollution and early deaths in the United States. Part I: Quantifying the impact of major sectors in 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodkind, A.L.; Tessum, C.W.; Coggins, J.S.; Hill, J.D.; Marshall, J.D. Fine-scale damage estimates of particulate matter air pollution reveal opportunities for location-specific mitigation of emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8775–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Goodkind, A.; Tessum, C.; Thakrar, S.; Tilman, D.; Polasky, S.; Smith, T.; Hunt, N.; Mullins, K.; Clark, M.; et al. Air-quality-related health damages of maize. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Aaron, C.P.; Madrigano, J.; Hoffman, E.A.; Angelini, E.; Yang, J.; Laine, A.; Vetterli, T.M.; Kinney, P.L.; Sampson, P.D.; et al. Association Between Long-term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Change in Quantitatively Assessed Emphysema and Lung Function. JAMA 2019, 322, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bares, R.; Lin, J.C.; Hoch, S.W.; Baasandorj, M.; Mendoza, D.L.; Fasoli, B.; Mitchell, L.; Catharine, D.; Stephens, B.B. The Wintertime Covariation of CO2 and Criteria Pollutants in an Urban Valley of the Western United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2684–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, C.C.; McDuffie, E.E.; Edwards, P.M.; Bares, R.; Gouw, J.A.; Docherty, K.S.; Dubé, W.P.; Fibiger, D.L.; Franchin, A.; Gilman, J.B.; et al. An Odd Oxygen Framework for Wintertime Ammonium Nitrate Aerosol Pollution in Urban Areas: NOx and VOC Control as Mitigation Strategies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerjee, S.; Smith, L.; Long, R.; Lonneman, W.; Kaushik, S.; Colon, M.; Oliver, K.; Whitaker, D. Particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, ozone, and select volatile organic compounds during a winter sampling period in Logan, Utah, USA. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, C.; Sánchez-Benavides, G.; Martínez, D.; Gotsens, X.; Gramunt, N.; Cirach, M.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Sunyer, J.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Crous-Bou, M.; et al. Effect of long-term exposure to air pollution on anxiety and depression in adults: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Ji, M.; Yan, H.; Guan, C. Impact of ambient air pollution on obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gładka, A.; Rymaszewska, J.; Zatoński, T. Impact of air pollution on depression and suicide. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2018, 31, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiser, C.L.; Hanson, H.A.; Sawyer, K.; Steenblik, J.; Al-Dulaimi, R.; Madsen, T.; Gibbins, K.; Hotaling, J.M.; Ibrahim, Y.O.; VanDerslice, J.A.; et al. Acute effects of air pollutants on spontaneous pregnancy loss: A case-crossover study. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 111, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, A.J. Doctors Group Says Studies Show Air Pollution Even More Damaging than We Thought. 2019. Available online: DeseretNews.com (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Roberts, S.; Arseneault, L.; Barratt, B.; Beevers, S.; Danese, A.; Odgers, C.L.; Moffitt, T.E.; Reuben, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Fisher, H.L. Exploration of NO2 and PM2.5 air pollution and mental health problems using high-resolution data in London-based children from a UK longitudinal cohort study. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 272, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; González-Maciel, A.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Pérez-Guillé, B.; Gayosso-Chávez, C.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Cross, J.V.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.V.; et al. Combustion- and friction-derived magnetic air pollution nanoparticles in human hearts. Environ. Res. 2019, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; De Matteis, S.; Hoffman, B.; Kim, W.J.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.; Sood, A.; Vanker, A.; Wuebbles, D.J. Health Benefits of Air Pollution Reduction. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA National Center for Environmental Assessment, R.T.P.N.; Sacks, J. Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Beard, J.D.; Beck, C.; Graham, R.; Packham, S.C.; Traphagan, M.; Giles, R.T.; Morgan, J.G. Winter Temperature Inversions and Emergency Department Visits for Asthma in Salt Lake County, Utah, 2003–2008. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendola, P.; Ha, S.; Pollack, A.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Seeni, I.; Kim, S.S.; Sherman, S.; Liu, D. Chronic and Acute Ozone Exposure in the Week Prior to Delivery Is Associated with the Risk of Stillbirth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivin, J.G.; Neidell, M. Air pollution’s hidden impacts. Science 2018, 359, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. The Cost of Air Pollution: Strengthening the Economic Case for Action; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency the Clean Air Act and the Economy|Overview of the Clean Air Act and Air Pollution|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/clean-air-act-overview/clean-air-act-and-economy#_edn3 (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Muller, N.Z.; Mendelsohn, R.; Nordhaus, W. Environmental Accounting for Pollution in the United States Economy. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 1649–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, E.A.; Heo, J.; Muller, N.Z.; Tessum, C.W.; Hill, J.D.; Marshall, J.D.; Adams, P.J. An inter-comparison of the social costs of air quality from reduced-complexity models. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archsmith, J.; Heyes, A.; Saberian, S. Air Quality and Error Quantity: Pollution and Performance in a High-Skilled, Quality-Focused Occupation. J. Assoc. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2018, 5, 827–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnery, S.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Liu, J.; Horowitz, L.W. Global crop yield reductions due to surface ozone exposure: 2. Year 2030 potential crop production losses and economic damage under two scenarios of O3 pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S.; Murphy, L.B.; Khavjou, O.; Giles, W.H.; Holt, J.B.; Croft, J.B. Total and state-specific medical and absenteeism costs of COPD among adults aged ≥18 years in the United States for 2010 and projections through 2020. Chest 2015, 147, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Economic Consequences of Outdoor Air Pollution; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, A.P.K.; Val Martin, M. Impacts of ozone air pollution and temperature extremes on crop yields: Spatial variability, adaptation and implications for future food security. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Choirat, C.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Zanobetti, A.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Short term exposure to fine particulate matter and hospital admission risks and costs in the Medicare population: Time stratified, case crossover study. BMJ 2019, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, J.; van der Zwaan, B.; Brink, C.; Eerens, H. Local air pollution and global climate change: A combined cost-benefit analysis. Resour. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzi, E.; Dellink, R.; Chateau, J. The sectoral and regional economic consequences of outdoor air pollution to 2060. Energy Econ. 2018, 71, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Klimont, Z.; Smith, S.J.; Van Dingenen, R.; Dentener, F.; Bouwman, L.; Riahi, K.; Amann, M.; Bodirsky, B.L.; van Vuuren, D.P.; et al. Future air pollution in the Shared Socio-economic Pathways. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 42, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.P. The Costs of Environmental Regulation in a Concentrated Industry. Econometrica 2012, 80, 1019–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.E.; Tamura-Wicks, H.; Parks, R.M.; Burnett, R.T.; Iii, C.A.P.; Bechle, M.J.; Marshall, J.D.; Danaei, G.; Ezzati, M. Particulate matter air pollution and national and county life expectancy loss in the USA: A spatiotemporal analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Health impact of China’s Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan: An analysis of national air quality monitoring and mortality data. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, C.D.; Jaffe, D.A. US particulate matter air quality improves except in wildfire-prone areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7901–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; Krotkov, N.A.; Pickering, K.E.; Streets, D.G.; Lu, Z.U.S. NO2 trends (2005–2013): EPA Air Quality System (AQS) data versus improved observations from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 110, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Kwan, M.-P. Individual exposure estimates may be erroneous when spatiotemporal variability of air pollution and human mobility are ignored. Health Place 2017, 43, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Craft, E.; Zhang, K. Characterizing spatial variability of air pollution from vehicle traffic around the Houston Ship Channel area. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, G.W.; Font, A. Keeping air pollution policies on track. Science 2019, 365, 322–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Delaimy, W.K. Health of People, Health of Planet and Our Responsibility; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-31125-4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Rao, C.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. A comparison of individual exposure, perception, and acceptable levels of PM2.5 with air pollution policy objectives in China. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, W.A.; Ahanchian, H.; Asante, K.A.; Carpenter, D.O.; Diaz-Barriga, F.; Ha, E.-H.; Huo, X.; King, M.; Ruchirawat, M.; Da Silva, E.R.; et al. Environmental Pollution: An Under-recognized Threat to Children’s Health, Especially in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, A41–A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.B. Environmental pollution: An enormous and invisible burden on health systems in low- and middle-income counties. World Hosp. Health Serv. Off. J. Int. Hosp. Fed. 2014, 50, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S. EPA Scientists Said U.S. Should Tighten Key Air Pollution Limit. The Agency’s Head Just Said No. E&E News. 14 April 2020. Available online: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/04/epa-scientists-said-us-should-tighten-key-air-pollution-limit-agency-s-head-just-said (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Greenberg, H.; Leeder, S.R.; Raymond, S.U. And Why So Great a “No?”: The Donor and Academic Communities’ Failure to Confront Global Chronic Disease. Glob. Heart 2016, 11, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, R. A Chronology of Global Assistance Funding for NCD. Glob. Heart 2016, 11, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmark, A.J.; Witko, C. Pollution, Politics, and Preferences for Environmental Spending in the States. Rev. Policy Res. 2007, 24, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltra, C.; Sala, R. Perception of risk from air pollution and reported behaviors: A cross-sectional survey study in four cities. J. Risk Res. 2018, 21, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K. Risk perception research: Socio-cultural perspectives on the public experience of air pollution. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaiuto, M.; Breakwell, G.M.; Cano, I. Identity Processes and Environmental Threat: The Effects of Nationalism and Local Identity upon Perception of Beach Pollution. J. Community Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 6, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, I.; Zou, B. Pollution perception: A challenge for intergenerational equity. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2008, 55, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, J.C.; Wilson, D.J.; Parra, J.; Bontempo, B.D.; Hart, M.; Sailor, D.J.; George, L.A. Public perception and behavior change in relationship to hot weather and air pollution. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. Clearing the smog? Public responses to air-quality information. Local Environ. 1999, 4, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, K.; Cashore, B.; Bernstein, S.; Auld, G. Overcoming the tragedy of super wicked problems: Constraining our future selves to ameliorate global climate change. Policy Sci. 2012, 45, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittel, H.W.J.; Webber, M.M. Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sci. 1973, 4, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, G.T.; Dominici, F. Don’t abandon evidence and process on air pollution policy. Science 2019, 363, 1398–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J. Air pollution science under siege at US environment agency. Nature 2019, 568, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Fisher, E.; Pascual, P. Whose science? A new era in regulatory “science wars”. Science 2018, 362, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oreskes, N.; Conway, E.M. Merchants of Doubt: How a Handful of Scientists Obscured the Truth on Issues from Tobacco Smoke to Global Warming; Bloomsbury Publishing: New York City, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-60819-293-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Particulate Air Pollution. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrey, S. Geneva to Counter Study by Pope. Dly. Her: Provo, UT, August 30, 1989, 26, 1. Available online: https://newspapers.lib.utah.edu/details?id=24081733&q=Lamm&rows=200&sort=date_tdt+asc%2Cparent_i+asc%2Cpage_i+asc&year_start=1987&year_end=1990&facet_paper=%22Provo+Daily+Herald%22 (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Reilly, S. Trump’s EPA Scraps Air Pollution Science Review Panels. E&E News. 12 October 2018. Available online: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/10/trump-s-epa-scraps-air-pollution-science-review-panels (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Adler, R.W. Coevolution of Law and Science. Colombia Journal of Environmental Law. 2019, 44, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.C. Short Circuiting Policy: Interest Groups and the Battle Over Clean Energy and Climate Policy in the American States; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-0-19-007427-2. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.W.; Jones, J.B.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Chapin, F.S.C., III; Bowden, W.B.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Epstein, H.E.; Flannigan, M.D.; Harms, T.K.; Hollingsworth, T.N.; et al. Biomass offsets little or none of permafrost carbon release from soils, streams, and wildfire: An expert assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 034014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.G. Use (and abuse) of expert elicitation in support of decision making for public policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7176–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; Abbott, B.W.; Bowden, W.B.; Brovkin, V.; Camill, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Chanton, J.P.; Chapin, F.S.; Christensen, T.R.; Ciais, P.; et al. Expert assessment of vulnerability of permafrost carbon to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2013, 119, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, W.P. Structured elicitation of expert judgment for probabilistic hazard and risk assessment in volcanic eruptions. Stat. Volcanol. 2006, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bordley, R.F. Combining the Opinions of Experts Who Partition Events Differently. Decis. Anal. 2009, 6, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickfeld, K.; Morgan, M.G.; Frame, D.J.; Keith, D.W. Expert judgments about transient climate response to alternative future trajectories of radiative forcing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12451–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, M.; Oreskes, N.; Jamieson, D.; O’Reilly, J.; Brysse, K.; Shindell, M.; Wazeck, M. Discerning Experts: The Practices of Scientific Assessment for Environmental Policy; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-226-60201-1. [Google Scholar]
- Brownell, K.D.; Roberto, C.A. Strategic science with policy impact. Lancet 2015, 385, 2445–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, M.C.; Mooney, C. Framing Science. Science 2007, 316, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, B.A.; Schulz, A.J.; Parker, E.A.; Becker, A.B. Review of Community-Based Research: Assessing Partnership Approaches to Improve Public Health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1998, 19, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, F.; Giger, M.; Harari, N.; Moser, S.; Oberlack, C.; Providoli, I.; Schmid, L.; Tribaldos, T.; Zimmermann, A. Transdisciplinary co-production of knowledge and sustainability transformations: Three generic mechanisms of impact generation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 102, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, N.; Murphy, S.T. How to unring the bell: A meta-analytic approach to correction of misinformation. Commun. Monogr. 2018, 85, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskes, N.; Edenhofer, O. Why Trust Science? Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-691-17900-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sleeth-Keppler, D. Seeing the World in Black and White: The Effects of Perceptually Induced Mind-Sets on Judgment. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01976.x (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Leiserowitz, A. Communicating the risks of global warming: American risk perceptions, affective images, and interpretive communities. In Creating a Climate for Change: Communicating Climate Change and Facilitating Social Change; Dilling, L., Moser, S.C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 44–63. ISBN 978-0-521-04992-4. [Google Scholar]
- Scannell, L.; Gifford, R. Personally Relevant Climate Change: The Role of Place Attachment and Local Versus Global Message Framing in Engagement. Environ. Behav. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.C.; Mukherjee, N.; Simmons, B.I.; Tew, E.R.; Robertson, R.J.; Vadrot, A.B.M.; Doubleday, R.; Sutherland, W.J. Policy windows for the environment: Tips for improving the uptake of scientific knowledge. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for PM; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Utah DAQ. Utah Division of Air Quality 2018 Annual Report; Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018. Available online: https://documents.deq.utah.gov/air-quality/annual-reports/DAQ-2019-000949.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Matichuk, R.; Tonnesen, G.; Luecken, D.; Gilliam, R.; Napelenok, S.L.; Baker, K.R.; Schwede, D.; Murphy, B.; Helmig, D.; Lyman, S.N.; et al. Evaluation of the Community Multiscale Air Quality Model for Simulating Winter Ozone Formation in the Uinta Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 13545–13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.M.; Brown, S.S.; Roberts, J.M.; Ahmadov, R.; Banta, R.M.; deGouw, J.A.; Dubé, W.P.; Field, R.A.; Flynn, J.H.; Gilman, J.B.; et al. High winter ozone pollution from carbonyl photolysis in an oil and gas basin. Nature 2014, 514, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom, M.R.; Pope, C.A. Elementary school absences and PM10 pollution in Utah Valley. Environ. Res. 1992, 58, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, A.; Fibiger, D.L.; Goldberger, L.; McDuffie, E.E.; Moravek, A.; Womack, C.C.; Crosman, E.T.; Docherty, K.S.; Dube, W.P.; Hoch, S.W.; et al. Airborne and ground-based observations of ammonium-nitrate-dominated aerosols in a shallow boundary layer during intense winter pollution episodes in northern Utah. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17259–17276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, C.; Gardner Policy Institute. The Utah Roadmap: Positive Solutions on Climate and Air Quality; Gardner Policy Institute: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, D.L.; Buchert, M.; Lin, J.C. Modeling net effects of transit operations on vehicle miles traveled, fuel consumption, carbon dioxide, and criteria air pollutant emissions in a mid-size U.S. metro area: Findings from Salt Lake City, UT. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Williams, A.P. Impact of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire across western US forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11770–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.W.; Errigo, I.M.; Jarvis, D.K. Commentary: Utah air pollution is literally killing us. The Salt Lake Tribune, 2 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman, G. Study shows rise in ozone-related deaths in Salt Lake City. KSL News, 22 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C. Doctor says Utah’s air pollution leading to premature death of thousands. KUTV, 15 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Penrod, E. Utah’s air quality is sickening, even killing locals year-round, new research suggests. The Salt Lake Tribune, 9 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UPHE. 2019 Report on Air Pollution and Health Research—Utah Physicians for Healthy Environment; Utah Physicians for a Healthy Environment: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Envision Utah Envision Utah—Home. Available online: https://www.envisionutah.org/ (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- US EPA. Outdoor Air Quality Data. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/outdoor-air-quality-data/download-daily-data (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Maffly, B. Salt Lake City’s air quality is nation’s 7th worst among large metro areas. The Salt Lake Tribune, 28 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman, C.D.; Hoch, S.W.; Horel, J.D.; Charland, A. Relationship between particulate air pollution and meteorological variables in Utah’s Salt Lake Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, B.; Follett, A.; Davis, J. The Making of the Clean Air Act; Hastings, L.J., Ed.; San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://repository.uchastings.edu/hastings_law_journal/vol71/iss4/3 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Cromar, K.R.; Gladson, L.A.; Ewart, G. Trends in Excess Morbidity and Mortality Associated with Air Pollution Above American Thoracic Society–Recommended Standards, 2008–2017. Ann. ATS 2019, 16, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Bechle, M.; Hankey, S.; Sheppard, L.; Szpiro, A.A.; Marshall, J.D. Concentrations of criteria pollutants in the contiguous U.S., 1979 – 2015: Role of prediction model parsimony in integrated empirical geographic regression. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Yan, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Burden of Cause-Specific Mortality Associated with PM2.5 Air Pollution in the United States. JAMA Netw Open 2019, 2, e1915834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, L.E. History of Air Quality in Utah 2020. Presented at Air Quality Science for Solutions, 16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hindsley, G.; Johnston, M. Temperature Inversions, Utah, Provo Herald; Provo, UT, USA, 2019. Available online: https://deq.utah.gov/air-quality/inversions (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Kay, J.; Brown, C.J. Mormon beliefs about land and natural resources, 1847–1877. J. Hist. Geogr. 1985, 11, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.G. The Scandinavian Immigrant Experience in Utah, 1850–1920: Using Material Culture to Interpret Cultural Adaptation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deseret Evening News the Nuisance of Smoke. Deseret Evening News, 3 December 1881.
- Salt Lake Tribune the Smoke Nuisance. The Salt Lake Tribune, 22 February 1893.
- Deseret Evening News to Abate the Smoke Nuisance. Deseret Evening News, 21 December 1891.
- Perrott, G.S.J. Smoke Problem at Salt Lake City. Power Plant Eng. 1920, 24, 784–785. [Google Scholar]
- Monnett, O. Smoke Abatement; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1923.
- Henry, R.C.; Hidy, G.M. Multivariate analysis of particulate sulfate and other air quality variables by principal components—II. Salt Lake City, Utah and St. Louis, Missouri. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1982, 16, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III. Respiratory disease associated with community air pollution and a steel mill, Utah Valley. Am. J. Public Health 1989, 79, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Schwartz, J.; Ransom, M.R. Daily mortality and PM10 pollution in Utah Valley. Arch. Environ. Health: Int. J. 1992, 47, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakian, A.V.; Huber, R.S.; Coon, H.; Gray, D.; Wilson, P.; McMahon, W.M.; Renshaw, P.F. Acute air pollution exposure and risk of suicide completion. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, R.A.; Sloan, C.D.; Cooper, V.C.; Robinson, D.R.; Hendrickson, N.R.; McCord, T.A.; Johnston, J.D. Personal exposure to fine particulate air pollution while commuting: An examination of six transport modes on an urban arterial roadway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivey, C.E.; Balachandran, S.; Colgan, S.; Hu, Y.; Holmes, H.A. Investigating fine particulate matter sources in Salt Lake City during persistent cold air pool events. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, C.; Grineski, S.; Collins, T.; Xing, W.; Whitaker, R.; Sayahi, T.; Becnel, T.; Goffin, P.; Gaillardon, P.-E.; Meyer, M.; et al. Patterns of distributive environmental inequity under different PM2.5 air pollution scenarios for Salt Lake County public schools. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utah, G.C.A.C. Governor’s Clean Air Commission: Summary of Recommendations; All Five Work Group Reports; Utah State Publications; Governor’s Clean Air Commission: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1990; p. 543.
- Heaney, R.J.; Winn, G.S.; Thorne, W.; Lloyd, L.H. Air Resources of Utah; Utah Legislative Council; Air Pollution Advisory Committee: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Aspinall, W. A route to more tractable expert advice. Nature 2010, 463, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; Ellison, D. The wisdom of crowds—Ensembles and modules in environmental modelling. Geoderma 2008, 147, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarstad, J. Expert credibility and truth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.M.; Wilson, A.M.; Tuomisto, J.T.; Morales, O.; Tainio, M.; Evans, J.S. A probabilistic characterization of the relationship between fine particulate matter and mortality: Elicitation of European experts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6598–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustovski, F.; Colantonio, L.D.; Galante, J.; Bardach, A.; Caporale, J.E.; Zárate, V.; Chuang, L.H.; Pichon-Riviere, A.; Kind, P. Measuring the Benefits of Healthcare: DALYs and QALYs—Does the Choice of Measure Matter? A Case Study of Two Preventive Interventions. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2017, 7, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Kelly, C.; Tate, J.; Parslow, R.; Lucas, K.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution and risk of development of childhood asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2017, 100, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellano, P.; Quaranta, N.; Reynoso, J.; Balbi, B.; Vasquez, J. Effect of outdoor air pollution on asthma exacerbations in children and adults: Systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease and Risk Factors; Lopez, A.D., Mathers, C.D., Ezzati, M., Jamison, D.T., Murray, C.J.L., Eds.; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-8213-6262-4. [Google Scholar]
- Egunsola, O.; Raubenheimer, J.; Buckley, N. Variability in the burden of disease estimates with or without age weighting and discounting: A methodological study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksalmis, E.; Kabak, Ö. Deriving decision makers’ weights in group decision making: An overview of objective methods. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, W.J.; Burgman, M. Policy advice: Use experts wisely. Nat. News 2015, 526, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, R.M.; ElSaadany, S.; Huang, X. On the performance of social network and likelihood-based expert weighting schemes. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgman, M.A.; McBride, M.; Ashton, R.; Speirs-Bridge, A.; Flander, L.; Wintle, B.; Fidler, F.; Rumpff, L.; Twardy, C. Expert Status and Performance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBIS-Public Health IBIS-PH—Query Result—Years of Potential Life Lost (YPLL—Premature Mortality) Before Age 75 for Utah Counties—Rate of Potential Life Lost per 100,000 Population. Available online: https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/result/ypll/YPLLCntyICD10/CrudeRate.html (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Abbott, B.W. Ben Abbott: Earth Day at 50 has never been so relevant. The Salt Lake Tribune, 21 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Sherman, J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagalan, L.; Bickford, C.; Weikum, W.; Lanphear, B.; Brauer, M.; Lanphear, N.; Hanley, G.E.; Oberlander, T.F.; Winters, M. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Air Pollution with Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Ee, N.; Peters, J.; Booth, A.; Mudway, I.; Anstey, K.J. Air Pollution and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 70, S145–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackmann, D.; Sjöberg, E. Ambient air pollution and pregnancy outcomes—a study of functional form and policy implications. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa Vizcaíno, M.A.; González-Comadran, M.; Jacquemin, B. Outdoor air pollution and human infertility: A systematic review. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 897–904.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zanobetti, A.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Choirat, C.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Air Pollution and Mortality in the Medicare Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, T. Legislature falls far short of governor’s goal of investing $100M to improve air quality. Advocates say it’s a good first step. The Salt Lake Tribune, 14 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sörqvist, P.; Langeborg, L. Why People Harm the Environment Although They Try to Treat It Well: An Evolutionary-Cognitive Perspective on Climate Compensation. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditto, P.H.; Liu, B.S.; Clark, C.J.; Wojcik, S.P.; Chen, E.E.; Grady, R.H.; Celniker, J.B.; Zinger, J.F. At Least Bias Is Bipartisan: A Meta-Analytic Comparison of Partisan Bias in Liberals and Conservatives. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 14, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGillivray, B.H.; Franklin, A. Place as a boundary device for the sustainability sciences: Concepts of place, their value in characterising sustainability problems, and their role in fostering integrative research and action. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsen, A. Nine Years of Smoke-Abatement Work at Salt Lake City; U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Mines: Wasington, DC, USA, 1930.
- U.S. National Air Pollution Control Administration. Report for Consultation on the Wasatch Front Intrastate Air Quality Control Region (Utah); U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Moore, F.C.; Obradovich, N.; Lehner, F.; Baylis, P. Rapidly declining remarkability of temperature anomalies may obscure public perception of climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4905–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muindi, K.; Egondi, T.; Kimani-Murage, E.; Rocklov, J.; Ng, N. “We are used to this”: A qualitative assessment of the perceptions of and attitudes towards air pollution amongst slum residents in Nairobi. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Thompson Klein, J.; Pohl, C. Linking transdisciplinary research projects with science and practice at large: Introducing insights from knowledge utilization. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 102, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musch, A.-K.; von Streit, A. (Un)intended effects of participation in sustainability science: A criteria-guided comparative case study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 104, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, S.; Zwi, A.B. Pathways to “Evidence-Informed” Policy and Practice: A Framework for Action. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, R.E.; Emmons, K.M. How Can We Increase Translation of Research into Practice? Types of Evidence Needed. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2007, 28, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, P.A.; Minkler, M.; Garcia, A.P.; Gordon, M.; Garzón, C.; Palaniappan, M.; Prakash, S.; Beveridge, B. Community-Based Participatory Research and Policy Advocacy to Reduce Diesel Exposure in West Oakland, California. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, S166–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bueren, E.M.; Klijn, E.; Koppenjan, J.F.M. Dealing with Wicked Problems in Networks: Analyzing an Environmental Debate from a Network Perspective. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2003, 13, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.W.; Moatar, F.; Gauthier, O.; Fovet, O.; Antoine, V.; Ragueneau, O. Trends and seasonality of river nutrients in agricultural catchments: 18 years of weekly citizen science in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonney, R.; Phillips, T.B.; Ballard, H.L.; Enck, J.W. Can citizen science enhance public understanding of science? Public Underst. Sci. 2016, 25, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Grainger, S.; Acosta, L.; Alemie, T.C.; Bastiaensen, J.; De Bièvre, B.; Bhusal, J.; Clark, J.; Dewulf, A.; et al. Citizen science in hydrology and water resources: Opportunities for knowledge generation, ecosystem service management, and sustainable development. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannadaki, D.; Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A. Implementing the US air quality standard for PM2.5 worldwide can prevent millions of premature deaths per year. Environ Health 2016, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskes, N.; Conway, E.M. Defeating the merchants of doubt. Nature 2010, 465, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.; Cox, R. The Routledge Handbook of Environment and Communication; Routledge: New York City, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-134-52131-9. [Google Scholar]
- Selin, H.; VanDeveer, S.D. Mapping Institutional Linkages in European Air Pollution Politics. Glob. Environ. Politics 2003, 3, 14–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, B. How Environmental Laws Work: An Analysis of the Utility Sector’s Response to Regulation of Nitrogen Oxides and Sulfur Dioxide under the Clean Air Act. Tul. Envtl. L.J. 2000, 14, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, B.; Steele, M.; Sun, L.G. Just Environmentalism; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, N.; McKay-Nesbitt, J. Pro-environment advertising messages: The role of regulatory focus. Int. J. Advert. 2016, 35, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economists Opinion | Economists’ Statement on Carbon Dividends. Wall Str. J. 16 January 2019. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/economists-statement-on-carbon-dividends-11547682910 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Wei, M.; Patadia, S.; Kammen, D.M. Putting renewables and energy efficiency to work: How many jobs can the clean energy industry generate in the US? Energy Policy 2010, 38, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; A Delucchi, M.; Bazouin, G.; Bauer, Z.A.F.; Heavey, C.C.; Fisher, E.; Morris, S.B.; Piekutowski, D.J.Y.; Vencill, T.A.; Yeskoo, T.W. 100% clean and renewable wind, water, and sunlight (WWS) all-sector energy roadmaps for the 50 United States. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2093–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, U.; Lutz, C.; Edler, D. Green jobs? Economic impacts of renewable energy in Germany. Energy Policy 2012, 47, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, S.; Calisch, S.; Fraser, L. Rewiring America: Online Blog. 2020. Available online: https://www.rewiringamerica.org/ (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessum, C.W.; Apte, J.S.; Goodkind, A.L.; Muller, N.Z.; Mullins, K.A.; Paolella, D.A.; Polasky, S.; Springer, N.P.; Thakrar, S.K.; Marshall, J.D.; et al. Inequity in consumption of goods and services adds to racial–ethnic disparities in air pollution exposure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6001–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, B.-S.; Mohai, P.; Lee, S.; Sametshaw, A.M. Proximity of public schools to major highways and industrial facilities, and students’ school performance and health hazards. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A. We Can Draw School Zones to Make Classrooms Less Segregated. This Is How Well Your District Does. Available online: https://www.vox.com/2018/1/8/16822374/school-segregation-gerrymander-map (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Pastor, M.P.; Morello-Frosch, R.; Sadd, J.L. The Air Is Always Cleaner on the Other Side: Race, Space, and Ambient Air Toxics Exposures in California. J. Urban Aff. 2005, 27, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, R. The Color of Law: A Forgotten History of How Our Government Segregated America; Liveright Publishing: New York City, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-63149-286-0. [Google Scholar]
- Domonoske, C. Interactive Redlining Map Zooms in On America’s History of Discrimination. Available online: https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2016/10/19/498536077/interactive-redlining-map-zooms-in-on-americas-history-of-discrimination (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Gross, T. A “Forgotten History” of How The U.S. Government Segregated America: NPR. Available online: https://www.npr.org/2017/05/03/526655831/a-forgotten-history-of-how-the-u-s-government-segregated-america (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Cole, L.W. Remedies for Environmental Racism: A View from the Field. Mich. Law Rev. 1992, 90, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.P.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. National Patterns in Environmental Injustice and Inequality: Outdoor NO2 Air Pollution in the United States. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C. Canaries on the Rim: Living Downwind in the West; Verso: New York City, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-1-85984-750-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, A. Socioeconomic outcomes of redlining in Salt Lake City, Utah 2019. Presented at American Association of Geographers, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 14 October 2019. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Errigo, I.M.; Abbott, B.W.; Mendoza, D.L.; Mitchell, L.; Sayedi, S.S.; Glenn, J.; Kelly, K.E.; Beard, J.D.; Bratsman, S.; Carter, T.; et al. Human Health and Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah: An Expert Assessment. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111238
Errigo IM, Abbott BW, Mendoza DL, Mitchell L, Sayedi SS, Glenn J, Kelly KE, Beard JD, Bratsman S, Carter T, et al. Human Health and Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah: An Expert Assessment. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111238
Chicago/Turabian StyleErrigo, Isabella M., Benjamin W. Abbott, Daniel L. Mendoza, Logan Mitchell, Sayedeh Sara Sayedi, Jeffrey Glenn, Kerry E. Kelly, John D. Beard, Samuel Bratsman, Thom Carter, and et al. 2020. "Human Health and Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah: An Expert Assessment" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111238
APA StyleErrigo, I. M., Abbott, B. W., Mendoza, D. L., Mitchell, L., Sayedi, S. S., Glenn, J., Kelly, K. E., Beard, J. D., Bratsman, S., Carter, T., Chaney, R. A., Follett, A., Freeman, A., Frei, R. J., Greenhalgh, M., Holmes, H. A., Howe, P. D., Johnston, J. D., Lange, L., ... Wilson, D. (2020). Human Health and Economic Costs of Air Pollution in Utah: An Expert Assessment. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111238








