Mesosphere Ozone and the Lower Ionosphere under Plasma Disturbance by Powerful High-Frequency Radio Emission
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Instrumentations
2.1. Method of the Ground-Based Microwave Radiometry
2.2. The Method of the Resonance Scattering of Radio Waves on Artificial Periodic Irregularities of the Ionospheric Plasma
3. Experiments and Results
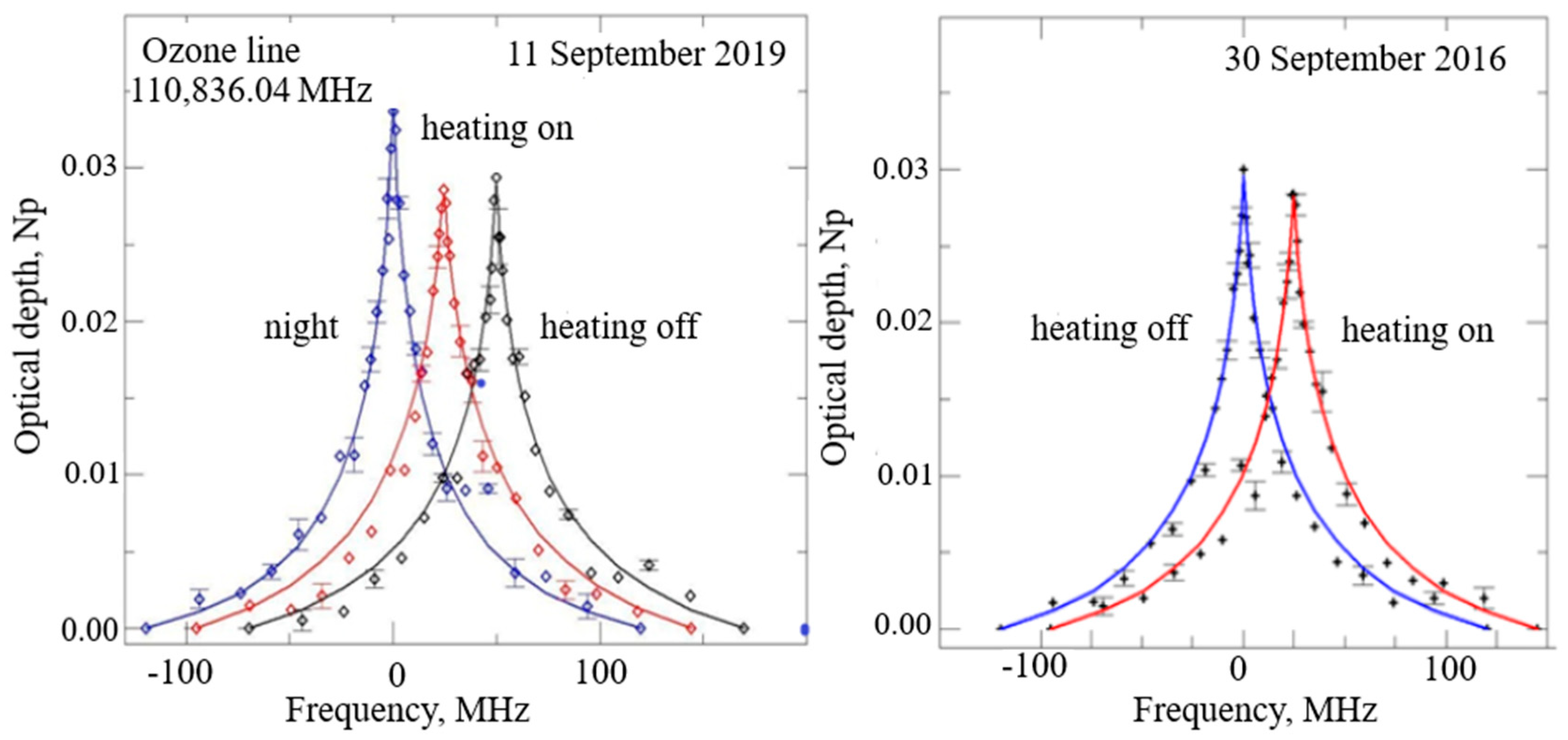
3.1. Microwave Measurements of the Ozone Spectrum
- (1)
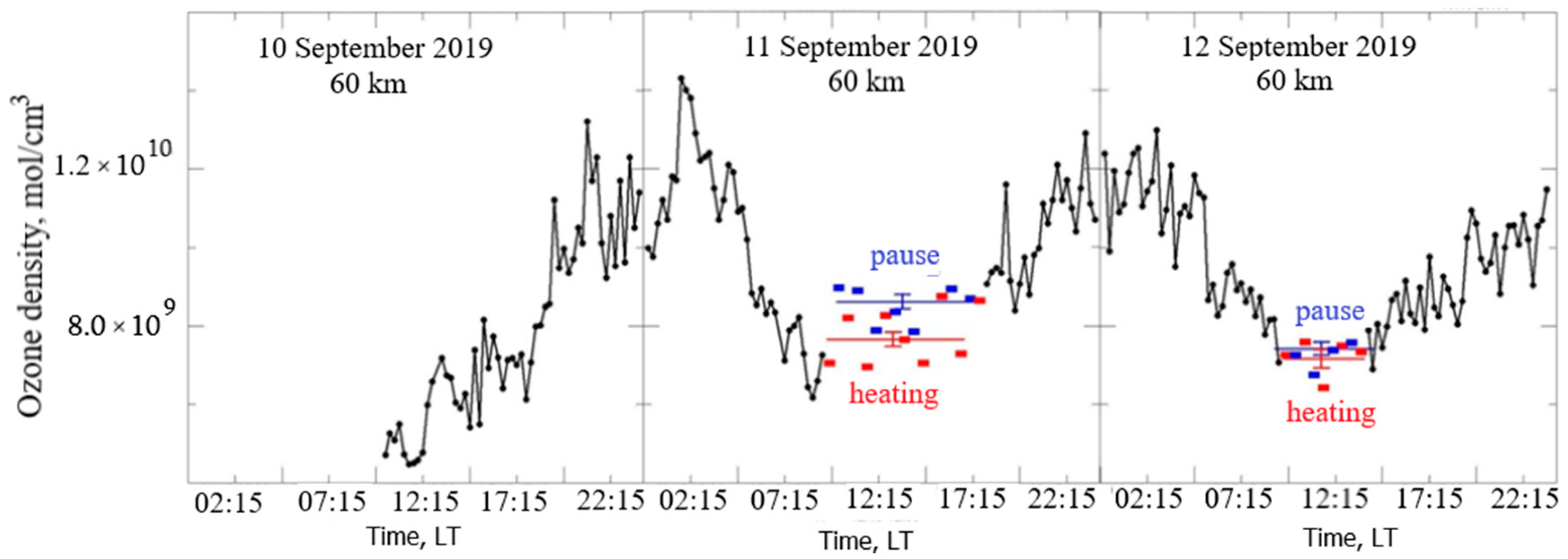
- A significant difference in the results on the change in the ozone density during the heating time for September 11 and 12, both in the average values for the whole day and for individual sessions. In September 12, changes in the ozone density during heating turned on to be on average very small and amounted to no more than 3%. On September 11, they were equal to 12% on average, and in some sessions they increased up to 20%.
- (2)
- Relatively fast and deep variations in the ozone density are clearly visible, ranging from 30 to 50%. They are not related to the heating of the ionosphere, and are probably largely due to the dynamics of this region of the mesosphere, including winds with variations of the direction and magnitude of the velocity, developed atmospheric turbulence, a propagation of atmospheric waves, changes in the composition of the mesosphere at these altitudes over time, and other factors.
- (3)
- One can see wavelike variations in the ozone density with a quasi-period from 45 min to 3 h or more.
- (4)
- Daily variations in the ozone density are visible, with noticeable differences occurring at night and during the day, which corresponds to the usually observed daily variation of ozone density with an excess of nighttime concentration values over daytime; the average amplitude of the daily change in the density of atmospheric ozone was about 40%.
- (5)
- The change in the amplitude of the diurnal variation on different days of observations is clearly noticeable, which can be explained by the influence of natural dynamic processes on the ozone in the mesosphere.
3.2. Diagnostics of the Lower Ionosphere Using the Method of Artificial Periodic Irregularities
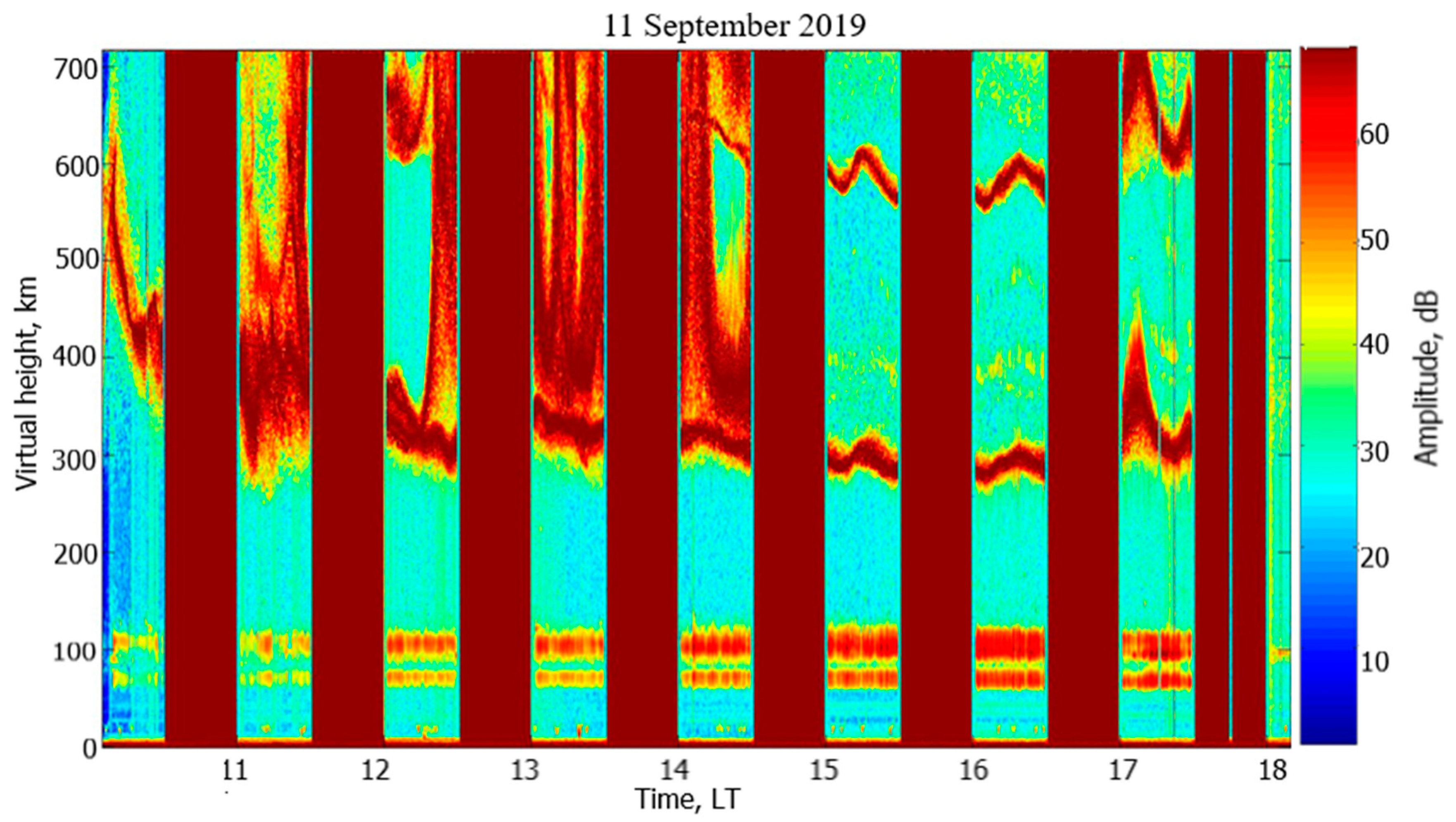
3.2.1. Scattered Signal Characteristics and the Ionosphere Condition
3.2.2. API Scattered Signal Amplitude and Relaxation Time
4. Characteristics of the Ionosphere and Neutral Atmosphere
5. Discussion
5.1. Internal Gravity Waves
5.2. Modification of the D-Region Parameters under Artificial Disturbance of the Ionosphere
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, I.M. MF and HF radar techniques for investigating the dynamics and structure of the 50 to 110 km height region: A review. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Solomon, S. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; p. 651. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.R.; Solomon, S. The effect of breaking gravity waves on the dynamics and chemical composition of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1985, 90, 3850–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, A.L.; Ribeiro, P.; Blanco, J.J.; Barlyaeva, T.V. Temperature and pressure variability in mid-latitude low atmosphere and stratosphere-ionosphere coupling. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2184–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolet, M.; Aikin, A.C. The formation of the D region of the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1960, 65, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.C. Ion chemistry in the D-region. Adv. At. Mol. Phys. 1976, 12, 375–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.V. Photochemistry of Ions at D-region Altitudes of the Ionosphere: A Review. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 259–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryunelli, B.E.; Namgaladze, A.A. Physics of the Ionosphere [in Russian]; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1988; p. 527. [Google Scholar]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Benediktov, E.A.; Tolmacheva, A.V.; Bakhmet’eva, N.V. Ionospheric Research by Means of Artificial Periodic Irregularities; Copernicus GmbH: Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany, 2002; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, T.; Nakajima, H.; Yokota, T.; Kanzawa, H.; Gernandt, H.; Herber, A.; Von Der Gathen, P.; König-Langlo, G.; Sato, K.; Dorokhov, V.; et al. Ozone profiles in the high-latitude stratosphere and lower mesosphere measured by the Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer (ILAS)-II: Comparison with other satellite sensors and ozonesondes. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.K.; Harvey, V.L.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Funke, B.; García-Comas, M.; Hervig, M.; Kaufmann, M.; Kyrölä, E.; López-Puertas, M.; McDade, I.; et al. Satellite observations of ozone in the upper mesosphere. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5803–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsh, D.R.; Skinner, W.R.; Marshall, A.R.; Hays, P.B.; Ortland, D.A.; Yee, J.-H. High Resolution Doppler Imager observations of ozone in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, N.; Selsis, F.; Urban, J.; Lezeaux, O.; Noë, J.D.L.; Ricaud, P. Seasonal and Diurnal Ozone Variations: Observations and Modeling. J. Atmos. Chem. 2005, 50, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, K.; Lainer, M.L.M.; Bernet, L.A.L.; Kämpfer, N. Mesospheric Inversion Layers at Mid-Latitudes and Coincident Changes of Ozone, Water Vapour and Horizontal Wind in the Middle Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutiev, I.; Tsagouri, I.; Perrone, L.; Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Mikhailov, A.; Lastovicka, J.; Jakowski, N.; Buresova, D.; Blanch, E.; et al. Solar activity impact on the Earth’s upper atmosphere. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2013, 3, A06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lean, J.L. Observation of the diurnal variation of atmospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 1982, 87, 4973–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenstein, D.A.; Gattinger, R.L.; Lloyd, N.D.; Bourassa, A.E.; Wiensz, J.T.; Llewellyn, E.J. Observations of an Extended Mesospheric Tertiary Ozone Peak. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, J.M.; Marsh, D.R.; Liu, H.-L.; Solomon, S.C.; Conley, A.J.; Drob, D.P. Simulation of the 21 August 2017 solar eclipse using the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model-eXtended. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3793–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Krasil’nikov, A.A.; Demkin, V.M.; Ryskin, V.G. Variations in the concentration of mesospheric ozone during the total solar eclipse of March 29, 2006, from microwave radiometric data. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2008, 44, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, A.S.; Ratovsky, K.G.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Klimenko, M.V.; Klimenko, V.V.; Bessarab, F.S.; Korenkov, Y.N.; Marichev, V.N.; Kolesnik, S.A. Changes in the stratosphere and ionosphere parameters during the 2013 major stratospheric warming. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd URSI Atlantic Radio Science Meeting (AT-RASC), Meloneras, Spain, 28 May–1 June 2018; Volume 2, p. 8471322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovsky, D.A.; Marichev, V.N.; Virolainen, Y.A.; Poberovsky, V.A.; Timofeyev, Y.M.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Ryskin, V.G. Ground based microwave monitoring of middle atmosphere ozone above Peterhof and Tomsk during stratospheric warming in the winter of 2013–2014. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2016, 59, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalapathi, G.V.; Eswaraiah, S.; Prasanth, P.V.; Lee, J.; Kumar, K.N.; Kim, Y.H. Unusual Changes in Stratospheric Ozone and Water Vapor Over Antarctica and its Relation to Mesosphere Dynamics during a Minor Sudden Stratosphere Warming. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscari, G.; Pezzopane, M.; Romaniello, V.; De Safra, R.L.; Bianci, C.; Fiocco, G. On the potencial impact of large electron concentration on mesospheric ozone. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. 2005, 76, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Pakhomov, S.V.; Knyazev, A.K. Ozone in the mesosphere and electron density in the midlatitude D-region. Geomagn. Aeron. 1988, 28, 976–979. [Google Scholar]
- Langematz, U. Stratospheric ozone: Down and up through the Anthropocene. ChemTexts 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, A.V. Nonlinear Phenomena in the Ionosphere. Physics and Chemistry in Space; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978; p. 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V. Nonlinear effects in the ionosphere. Phys. Uspekhi. 2007, 50, 1091–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.L.; Bakhmet’eva, N.V.; Belikovich, V.V.; Vertogradov, G.G.; Vertogradov, V.G.; Komrakov, G.P.; Kotik, D.S.; Mityakov, N.A.; Polyakov, S.V.; Rapoport, V.O.; et al. Modification of the Earth’s ionosphere by high-power high-frequency radio waves. Phys. Uspekhi. 2007, 50, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Frolov, V.L.; Grigor’ev, G.I.; Demkin, V.M.; Komrakov, G.P.; Krasilnokov, A.A.; Ryskin, V.G. Response of mesospheric ozone to the heating of the lower ionosphere by high-power HF radio emission. Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.) 2013, 53, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Krasilnikov, A.A.; Grigoriev, G.I.; Frolov, V.L. Variations in the microwave radiation of the mesosphere during heating of the ionosphere with high-power radio waves. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2012, 55, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Frolov, V.L. Influence of the artificially disturbed ionosphere on the mesospheric ozone. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 7, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Krasilnikov, A.A.; Shchitov, A.M. New Mobile Ground-Based Microwave Instrument to Research of Stratospheric Ozone (Some Results of Observations). In Proceedings of the 2007 International Kharkov Symposium Physics and Engineering of Microwaves, Millimeter, and Submillimeter Waves (MSMW), Kharkov, Ukraine, 25–30 June 2007; pp. 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, G.M.; Pitts, M.C.; Young, D.F. Ozone reference models for the middle atmosphere. Adv. Space Res. 1990, 10, 317–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.J.; Corney, M. A middle atmosphere temperature reference model from satellite measurements. Adv. Space Res. 1985, 5, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasil’nikov, A.A.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Mazur, A.B.; Ryskin, V.G.; Serov, N.V.; Fedoseev, L.I.; Shvetsov, A.A. Detection of “ozone” clouds in the upper stratosphere of the Earth by means of microwave radiometry technique. Geomag. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.) 1997, 37, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianov, A.F.; Bakhmet’eva, N.V.; Vyakhirev, V.D.; Kalinina, E.E.; Krasilnikov, A.A.; Kulikov, Y.Y. A Study of the Density Variations of Mesospheric Ozone in the Case of Ionospheric Perturbation by the “Sura” Facility Radiation with Simultaneous Diagnostics of Ionospheric Plasma. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2019, 62, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://forecast.izmiran.ru/indexb.php (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Connor, B.J.; Siskind, D.E.; Tsou, J.J.; Parrish, A.; Remsberg, E.E. Ground-based microwave observations of ozone in the upper stratosphere and mesosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 16757–16770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Noe, J.; Baudry, A.; Perault, M.; Dierich, P.; Monnanteuil, N.; Colmont, J.M. Measurements of the vertical distribution of ozone by ground-based microwave techniques at the Bordeaux Observatory during the June 1981 intercomparison campaign. Planet. Space Sci. 1983, 31, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Noe, J.; Turati, C.; Baudry, A.; Monnanteuil, N.; Colmont, J.M.; Dierich, P. Ground-Based Microwave Observations of Mesospheric Ozone at the Bordeaux Observatory. Atmospheric Ozone. In Atmospheric Ozone: Proceedings of the Quadrennial Ozone Symposium Held in Halkidiki, Greece, 3–7 September 1984; Zerefos, C.S., Ghazi, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru, M.C.; Hocke, K.; Kämpfer, N.; Calisesi, Y. Comparison and validation studies related to ground-based microwave observations of ozone in the stratosphere and mesosphere. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2005, 68, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryskin, V.G.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Krasilnikov, A.A.; Kukin, L.M.; Savchenko, V.R. Microwave diagnostics of chemical ozone destruction in the arctic stratosphere. Radiophys. Quantum Elelectron. 2007, 50, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, Y.Y.; Poberovskii, A.V.; Ryskin, V.G.; Yushkov, V.A. Detection of Large Fluctuations in Ozone Content in the Middle Atmosphere during Sudden Stratospheric Warmings and Subpolar Latitudes of the Arctic. Geomagn. Aeron. 2020, 60, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, S.B.; Zavgorodniy, A.S.; Ignatyev, A.N. Microwave measurements of variations in night mesospheric ozone over Moscow. In Proceedings Volume 11152, Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XXIV, SPIE Remote Sensing, Strasbourg, France, 9–12 September 2019; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Benediktov, E.A.; Getmantsev, G.G.; Ignat’ev, Y.A.; Komrakov, G.P. Scattering of radio waves from the artificial perturbed F region of the ionosphere (Engl. Translation). JETP Lett. 1975, 22, 243–244. [Google Scholar]
- Fejer, I.A.; Djuth, F.T.; Gonzales, C.A. Bragg backscatter from plasma inhomogeneities due to a powerful ionospherically reflected radio waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 9145–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuth, F.T.; Groves, K.M.; Elder, J.H.; Shinn, E.R.; Quinn, J.M.; Villasenor, J.; Wong, A.Y. Measurements of artificial periodic inhomogeneities at HIPAS observatory. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 24023–24035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rietveld, M.T.; Turunen, E.; Matveinen, H.; Goncharov, N.P.; Pollari, P. Artificial periodic irregularities in the auroral ionosphere. Ann. Geophys. 1996, 14, 1437–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rietveld, M.T.; Goncharov, N.P. Artificial Periodic Irregularities from the Tromsø Heating facility. Adv. Space Res. 1998, 21, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierinen, J.; Kero, A.; Rietveld, M.T. High latitude artificial periodic irregularity observations with the upgraded EISCAT heating facility. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 105–106, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyssel, D.L.; McCarrick, M.J.; Fallen, C.T.; Vierinen, J. First artificial periodic inhomogeneity experiments at HAARP. GRL 2015, 42, 1033–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Grach, S.M.; Sergeev, E.N.; Shindin, A.V.; Milikh, G.M.; Siefring, C.L.; Bernhardt, P.A.; McCarrick, M. Artificial periodic irregularities in the high-latitude ionosphere excited by the HAARP facility. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Grigor’ev, G.I.; Tolmacheva, A.V. Artificial periodic irregularities, hydrodynamic instabilities, and dynamic processes in the mesosphere-lower thermosphere. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2011, 53, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Benediktov, E.A.; Trunov, D.V. Height profiles of the amplitude and relaxation time of artificial periodic irregularities in the D-region. Geomagn. Aeron. 2000, 40, 733–738. [Google Scholar]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Benediktov, E.A. Study of the Twilight D-Region of the Ionosphere using Artificial Periodic Inhomogeneities. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2002, 45, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Razin, S.V. Formation of artificial periodic irregularities in the D region of the ionosphere, taking attachment and recombination processes into account. Radiofizika 1986, 29, 251–257. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Belikovich, V.V.; Benediktov, E.A. Investigation of the lower D-region of the ionosphere using artificial periodic irregularities. Radiofizika 1986, 29, 1283–1296. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Vyakhirev, V.D.; Kalinina, E.E.; Komrakov, G.P. Earth’s lower ionosphere during partial solar eclipses according to observations near Nizhny Novgorod. Geomagn. Aeron. 2017, 57, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Belikovich, V.V. Results of studying the sporadic E layer by the method of resonant scattering of radio waves by artificial periodic inhomogeneities of the ionospheric plasma. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2008, 51, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.V.; Belikovich, V.V.; Kalinina, E.E. Atmospheric parameters measured using artificial periodic irregularities with different spatial dimensions. Geomagn. Aeron. 2009, 49, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet’eva, N.V.; Belikovich, V.V.; Egerev, M.N.; Tolmacheva, A.V. Artificial periodic irregularities, wave phenomena in the lower ionosphere and the sporadic E-layer. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2010, 53, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.V.; Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Grigoriev, G.I.; Egerev, M.N. Turbopause range measured by the method of the artificial periodic irregularities. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.V.; Belikovich, V.V. Measurements of the temperature and density of the upper atmosphere using artificial periodic irregularities during the summer seasons of 1999–2002. Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron. 2004, 5, 1–8, GI1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, L.M.; Bakhmet’eva, N.V.; Belikovich, V.V.; Tolmacheva, A.V. Structure and dynamics of sporadic layers of ionization in the ionospheric E region. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 1106–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Grigoriev, G.I.; Tolmacheva, A.V.; Zhemyakov, I.N. Investigations of Atmospheric Waves in the Earth Lower Ionosphere by Means of the Method of the Creation of the Artificial Periodic Irregularities of the Ionospheric Plasma. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernogor, L.F.; Frolov, V.L. Traveling ionospheric disturbances generated due to periodic plasma heating by high-power high-frequency radiation. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2012, 55, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernogor, L.F.; Panasenko, S.V.; Frolov, V.L.; Domnin, I.F. Observations of the ionospheric wave disturbances using the Kharkov incoherent scatter radar upon RF heating of the near-earth plasma. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2015, 52, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, S.Z.; Kozlov, S.I.; Tasenko, S.V. Estimation of the ozone decrease possibility in the lower part of the D-region under the action of a powerful radiowave. Geomagn. Aeron. 2016, 56, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, J.; Hocke, K.; Stober, G.; Pfreundschuh, S.; Murk, A.; Kämpfer, N. First measurements of tides in the stratosphere and lower mesosphere by ground-based Doppler microwave wind radiometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2367–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritts, D.C.; Alexander, M.J. Gravity waves dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1003–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginzburg, V.L. The Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves in Plasmas, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1970; p. 615. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Shvartsburg, A.B. Nelineinaya Teoriya Rasprostraneniya Radiovoln v Ionosfere; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1973; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Holway, L.H.; Meltz, G. Heating of the Lower Ionosphere by Powerful Radio Waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltz, G.; Holway, L.H., Jr.; Tomljanovich, N.M. Ionospheric heating by powerful radio waves. Radio Sci. 1974, 9, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomko, A.A.; Ferraro, A.J.; Lee, H.S.; Mitra, A.P. A theoretical model of D-region ion chemistry modifications during high power radio wave heating. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1980, 42, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kero, A.; Vierinen, J.; Enell, C.-F.; Virtanen, I.; Turunen, E. New incoherent scatter diagnostic methods for the heated D-region ionosphere. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovács, T.; Plane, J.M.C.; Feng, W.; Nagy, T.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Verronen, P.T.; Andersson, M.E.; Newnham, D.A.; Clilverd, M.A.; Marsh, D.R. D-region ion–neutral coupled chemistry (Sodankylä Ion Chemistry, SIC) within the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM 4)–WACCM-SIC and WACCM-rSIC. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Vyakhirev, V.D.; Kalinina, E.E. (the article is being prepared for publication).
- Mc Ewan, M.J.; Phillips, L.F.; Dalgarno, A. Chemistry of the Atmosphere. In Atmosphere and Oceanographic Sciences Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 32, p. 644. [Google Scholar]
- Verronen, P.T.; Ulich, T.; Turunen, E.; Rodger, C.J. Sunset transition of negative charge in the D-region ionosphere during high-ionization conditions. Ann. Geophys. 2006, 24, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enell, C.-F.; Kero, A.; Turunen, E.; Ulich, T.; Verronen, P.T.; Seppälä, A.; Marple, S.; Honary, F.; Senior, A. Effects of D-region RF heating studied with the Sodankylä Ion Chemistry mode. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turunen, E.; Matveinen, H.; Tolvanen, J.; Ranta, H. D-region ion chemistry Model. In Handbook of Ionospheric Models; Schunk, R.W., Ed.; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 1996; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakhmetieva, N.V.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Zhemyakov, I.N. Mesosphere Ozone and the Lower Ionosphere under Plasma Disturbance by Powerful High-Frequency Radio Emission. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111154
Bakhmetieva NV, Kulikov YY, Zhemyakov IN. Mesosphere Ozone and the Lower Ionosphere under Plasma Disturbance by Powerful High-Frequency Radio Emission. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111154
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakhmetieva, Nataliya V., Yuri Yu. Kulikov, and Ilia N. Zhemyakov. 2020. "Mesosphere Ozone and the Lower Ionosphere under Plasma Disturbance by Powerful High-Frequency Radio Emission" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111154
APA StyleBakhmetieva, N. V., Kulikov, Y. Y., & Zhemyakov, I. N. (2020). Mesosphere Ozone and the Lower Ionosphere under Plasma Disturbance by Powerful High-Frequency Radio Emission. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111154




