Abstract
Surface ozone (O3) is a harmful pollutant and effective strategies must be developed for its reduction. In this study, the impact of meteorological factors on the annual O3 variability for South Korea were analyzed. In addition, the regional differences of meteorological factors in six air quality regions in South Korea (Seoul Metropolitan Area, SMA; Central region, CN; Honam, HN; Yeongnam, YN; Gangwon, GW; Jeju, JJ) were compared. The analysis of ground observation data from 2001 to 2017 revealed that the long-term variability of O3 concentration in South Korea continuously increased since 2001, and the upward trend in 2010 to 2017 (Period 2, PRD2) was 29.8% higher than that in 2001 to 2009 (Period 1, PRD1). This was because the meteorological conditions during PRD2 became relatively favorable for high O3 concentrations compared to conditions during PRD1. In particular, the increase in the solar radiation (SR) and maximum temperature (TMAX) and the decrease in the precipitation (PRCP) and wind speed (WS) of South Korea in PRD2 were identified as the main causes for the rise in O3 concentrations. When meteorological factors and O3 variability were compared among the six air quality regions in South Korea during PRD1 and PRD2, significant differences were observed. This indicated that different meteorological changes occurred in South Korea after 2010 due to the different topographical characteristics of each region; thus, O3 variability also changed differently in each region. Interestingly, for the regions with almost similar meteorological changes after 2010, the O3 concentration changed differently depending on the difference in the distribution of emissions. These results indicate that the O3–meteorology relationship shows spatiotemporal differences depending on the topographical and emission distribution characteristics of each area and implies that it is necessary to fully consider such differences for efficient O3 reduction.
1. Introduction
Surface ozone (O3) is one of the harmful air pollutants in the lower atmosphere [1,2]. High levels of surface O3 pose serious risks to human health, especially the skin, eye irritation, and respiratory system [3,4]. It also inhibits photosynthesis rates in plants and leads to reduced yields [5]. High levels of O3 also cause economic losses, such as shortening the lifespan of industrial facilities due to the strong oxidizing power of O3.
O3 is a secondary pollutant produced by photochemical reactions primarily associated with nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) [6,7]. The chemistry for determining the concentration of surface O3 is complicated because of the nonlinear relationships between O3 and its precursors [8,9]. The production and/or loss of O3 is strongly affected by emissions [10,11], as well as by meteorological factors like temperature, solar radiation, wind speed, and humidity [12,13,14,15].
The O3 concentration in South Korea (Korea, hereafter) has been steadily increasing despite the efforts of the Korean government to reduce it [16]. The environmental standard for 8 h max O3 in Korea is 0.06 ppm, and it has been exceeded at all valid Korean stations in 2017. In addition, the increase in O3 has become severe since the 2000s compared to other countries [17,18]. The O3 concentration is mainly determined by the absolute amounts of VOCs and NOx, which are major precursors, and the relative ratio between them [10,11]. It is known that the production and disappearance of O3 is balanced through the reaction of O3-NO-NO2 photo stationary state, but the oxidation of VOC causes NO2 production by alkyl-radical (RO2) and hydroxy-radical (HO2) to accumulate O3 [19]. According to previous studies, Korea, with many industrial emission sources, is generally known as a VOC-limited area [20]. Thus, the O3 concentration is mainly determined by the increase in VOC emissions or the decrease in NOx emissions [10,11]. The O3 concentration, however, is not determined by emissions alone [21,22]. For example, in the case of the Seoul Metropolitan Area (SMA), which has the country’s highest population density, NOx (23% reduction in 2013 compared to 2005) and VOC (7% reduction in 2013 compared to 2005) emissions were reduced by initial comprehensive measures for the metropolitan area, but the O3 concentration was not reduced. This suggests that elements other than the emissions (e.g., meteorological factors) must be considered in analyzing the O3 concentration for Korea. Since the mid-2000s, studies on the regional characteristics of meteorological factors, which have major impacts on the O3 concentration, have been conducted in the United States and Europe [21,23,24]. In particular, Camalier et al. [21] and Otero et al. [23] analyzed the regional major meteorological factors for O3 concentration using a statistics regression model. Other studies have also been conducted to examine the effects of certain meteorological factors, such as regional wind pattern [19,20]. In Korea, however, studies on the impacts of meteorological factors on the air quality in different regions are not sufficient and there have only been a few case studies on areas with concentrated emission sources [25,26].
According to a recent study [26], the contribution of meteorological factors on O3 concentrations over the SMA has increased since 2012. The study revealed that the meteorological conditions became stable, which can be favorable for O3 increasing, but the results were for a specific region (SMA), and the effects of other variables were not considered. As reported by Camalier et al. [21], the impact of meteorological conditions on O3 concentration can be different regionally. In particular, meteorological characteristics in Korea are different by region because it is surrounded by seas on three sides, has very complex coastlines, and has mountainous terrains accounting for 70% of its land despite its small area [27,28]. Therefore, for an in-depth understanding of the impact of meteorological conditions on regional O3 concentrations in Korea, it is necessary to examine how the impact of meteorological conditions differs by area and to understand major factors that determine the O3 concentration in each area.
In this study, the regional differences in meteorological impacts on O3 in Korea were investigated. The annual variations in O3 concentrations, emissions, and meteorological factors, from 2001 to 2017, were compared and the relationships were analyzed. This research focused on identifying the predominant drivers determining O3 variability in different regions of Korea. The primary goal of this study is to highlight the spatiotemporal differences of the impacts of meteorological variables on O3 concentrations in Korea.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Domain
Korea is located in the northeast part of Asia with continental climate features and has a complex coastline and mountainous terrain, as shown in Figure 1a. Therefore, the influence of monsoons is complicated by topographical differences, which presents a lot of precipitation in mountainous terrain regions and high temperatures in the south regions. For more efficient air quality control, the Korean Ministry of Environment divided the whole country into six air quality regions: SMA, Central region (CN), Honam (HN), Yeongnam (YN), Gangwon (GW), and Jeju (JJ). The Korean capital, SMA, is located in the northwest part of Korea (37.5° N, 126.9° E) and has significantly high emissions. CN is the western central part of Korea, facing SMA to the north. HN is the southwest part of Korea, a leading agricultural area, with relatively low industrial development. YN is the southeastern part of Korea with high emissions due to heavy traffic and industrial facilities. GW is a mountainous rural region located in the northeast part of Korea and its air quality is frequently affected by pollutants transported from upwind source regions (SMA and CN). JJ is an island region located in the southwestern part of Korea and has the lowest emissions. Since these six air quality regions in Korea have different geographic and topographical features, this study focuses on analyzing and comparing the O3 characteristics in each region.
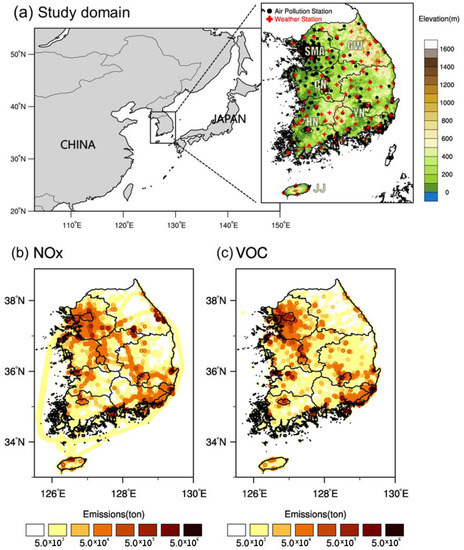
Figure 1.
(a) Locations of the weather observation stations (red cross) and surface ozone (O3) observation stations (black circle), and distributions of O3 precursor emissions for (b) nitrogen oxides (NOx) and (c) volatile organic compounds (VOC) in the most recent year (2015).
2.2. Surface Measurements and Validation Data
In this study, surface observational data from the Air Quality Monitoring Station (AQMS) [29] network operated by the National Institute of Environmental Research of Korea was used. Observed O3 data in 2001–2017 were gathered from AQMS, and meteorological data were obtained from the Automated Surface Observing System (ASOS) operated by the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). The data from 340 AQMS (black circle) and 92 ASOS (red cross) sites were used and the locations of the respective sites are shown in Figure 1a. To analyze the long-term trends of O3 in Korea and compare the regional differences, 8 h max O3 concentrations were calculated at each AQMS site. Invalid data (i.e., fraction of missing values > 25%) were excluded for a more objective analysis.
The factors affecting O3 concentration [21,30] were also calculated: average (92 ASOS sites) daily maximum temperature (TMAX, units: °C), solar radiation duration (SR, units: hour), relative humidity (RH, units: %), precipitation (PRCP, units: mm), and wind speed (WS, units: m/s). These factors were then compared with 8 h max O3 data to identify the primary contributors to annual O3 concentrations in Korea in 2001–2017. In addition, the annual emissions data (2001–2015) for NOx and VOC from the national air pollutants emission service were used to compare the relative impacts of meteorological conditions and emissions on inter-annual O3 variability in Korea. To understand the spatial distribution of these emissions, the Clean Air Policy Support System (CAPSS) [31] data in 2015 provided by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER) are presented in Figure 1b,c.
2.3. Long-Term Trend Analysis
The Kolmogorov–Zurbenco filter (KZ filter) [32] was used to investigate the long-term O3 variability in Korea. The KZ filter can analyze the long-term variability of air pollutants by extracting long-term, seasonal, and short-term (white noise) variability components. It is a low-pass filter that eliminates frequent phenomena by applying a moving average over a period, and this method was applied to an O3 concentration time series to examine the component characteristics [33,34,35]. The parameters suggested by Wise and Comrie [13,14] were used for eliminating short-term fluctuation and extracting long-term variability. The averaged (340 AQMS sites) daily 8 h max O3 data from 2001 to 2017 were used as the raw time series data for Korea. The KZ filter was also utilized in this study to compare the long-term variability of meteorological factors (e.g., temperature, wind speed, precipitation, and so on) with O3 concentration. The averaged (92 ASOS sites) daily data of each meteorological factor from 2001 to 2017 were used as raw time series data.
2.4. Anomaly Analysis
Anomaly analysis is commonly used in climate studies for examining the relative values of raw data compared to the average by subtracting the average from raw values. In this study, the average data of 30 years (1981–2010) were defined as the baseline climate, as proposed by KMA, and then the yearly and monthly anomaly values for each meteorological factor were calculated:
In this instance, a comparison between the anomaly values of each meteorological factor is difficult because each meteorological factor has different data ranges. To address this problem, the difference in the range of each meteorological factor was removed by dividing the anomaly of each meteorological factor by the standard deviation of the factor. Based on this, the calculated normalized anomaly:
was used for comparative analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Ozone (O3) Variability in Korea from 2001 to 2017
Figure 2 illustrates the time series of the averaged (340 AQMS sites) surface O3 concentration in Korea during the most recent seventeen-year period (2001–2017). The surface O3 indicated a clear seasonal variation (Figure 2b) and its fluctuation magnitude gradually increased. The long-term O3 variability obtained from the KZ filter analysis indicated a clear upward trend (slope = +1.93 ppb year−1) and the trend became steeper after 2010 (slope = +3.10 ppb year−1). The short-term O3 variability (Figure 2d) did not show a noticeable trend compared to the long-term O3 variability. To further examine the O3 trend in Korea, the frequency of high O3 in Korea in the 2000s was investigated. The number of days was counted when the averaged surface O3 concentration (340 AQMS sites) exceeded the Korean standard regulation level (8 h max O3 > 60 ppb). As seen in Figure 2e, the number of high O3 days dramatically increased after 2010.
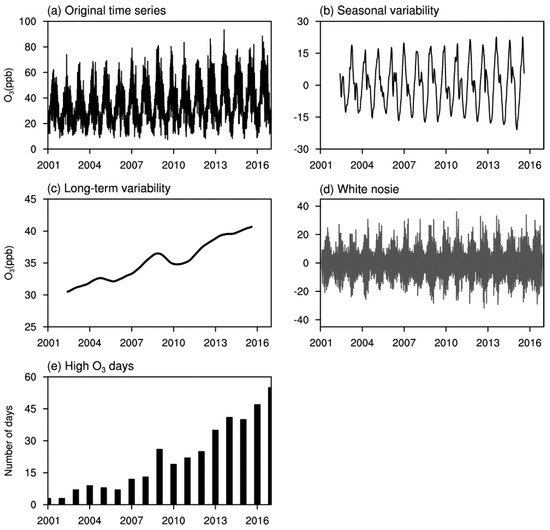
Figure 2.
Kolmogorov–Zurbenco (KZ) filter analysis results: (a) original time series, (b) seasonal variability, (c) long-term variability and (d) white noise, (e) and number of days with high O3 concentration.
These results reveal that the annual O3 variability in the 2010s was different from that in the 2000s. However, the major factors that led to the different O3 variabilities for the two periods remain unclear. Thus, additional analyses were conducted to find the causes for the discrepancy and their relative contributions.
3.2. Contributions of Emissions and Meteorological Factors to Inter-Annual O3 Variability
Korea is generally known as a VOC-limited (sensitive) area [20]. In such an environment, the O3 concentration is generally proportional to VOCs and inversely proportional to NOx. When the annual average O3 concentration and the annual changes in the total emissions of VOCs and NOx in Korea, shown in Figure 3, were examined, the change in the annual average O3 concentration showed a pattern similar to the long-term variability shown in Figure 2c. While the O3 concentration (slope = +0.68 ppb year−1) and VOC emissions (slope = +16.5 kton year−1) steadily increased since 2001, NOx did not show any specific trend (Table 1). NOx decreased from 2004 to 2009 as energy consumption decreased due to the emission reduction policy of the primary metropolitan air quality management [36], but increased again after 2010. In general, the NOx reduction can cause an increase in the O3 concentration in a VOC-limited environment [10,11]. Interestingly, the slope of O3 grew 1.9 times after 2010 compared to the 2000s when the NOx concentration was low. Moreover, the explanatory power (coefficient of determination, R2) of the VOC emissions for O3 variability was as high as 0.80 before 2010, but decreased by 33% to 0.54 after 2010. These results show that the O3 variability of Korea cannot be fully explained by the change in emissions alone after 2010.
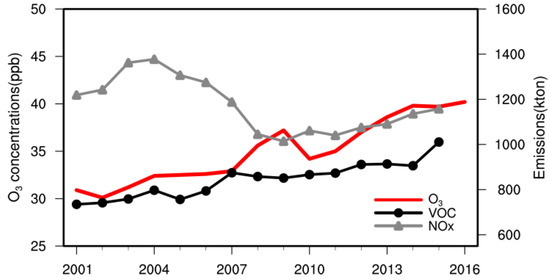
Figure 3.
Annual O3 concentrations (red) and total emissions of VOC (black) and NOx (gray) which are precursors of O3 (units: kton = 1000 ton).

Table 1.
Correlation coefficients, coefficients of determination, and trends of O3 and precursors in different periods.
Meanwhile, meteorological conditions are known to be major influence factors for O3 concentration along with emissions [21,23,37]. In particular, the major meteorological factors include solar radiation (SR), maximum temperature (TMAX), precipitation (PRCP), relative humidity (RH), and wind speed (WS) [35]. O3, a photochemical product, generally shows a positive correlation with SR [38,39]. It also exhibits a positive correlation with TMAX because active chemical reactions occur at high temperatures due to the increased reactivity between precursors [15,21,40,41,42]. PRCP has a negative correlation with O3 because it removes O3 and precursors (e.g., wash-out and wet deposition) [43]. RH has a negative correlation with O3 because its increase causes an increase in the amount of wet deposition/scavenging by the water vapor in the atmosphere [44,45]. Moreover, RH limits the generation of O3 through the reaction of intermediate substances in the photochemical reaction related to O3 generation [46]. In the case of WS, its decrease means a more stable atmospheric condition. As this becomes a favorable condition for O3 generation in terms of photochemical reactions and transport, WS generally has a negative correlation with O3 [47].
The weather in Korea exhibits distinct seasonal variabilities [48] and the correlations between O3 and meteorological factors must be examined from a perspective of long-term variability without the effects of seasonal and daily cycles. To this end, the KZ filter, a method of extracting long-term O3 variability, was applied to the major meteorological factors. As each meteorological factor has a different long-term variability range, the data ranges were normalized as follows:
The normalized long-term variables were compared with the long-term variability of O3 as shown in Figure 4, and the long-term variability trends of O3 and meteorological factors are shown in Table 2.
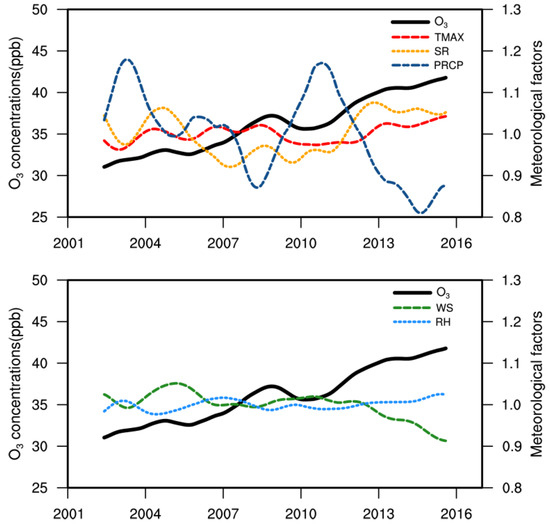
Figure 4.
Long-term variability of O3 (black) and meteorological factors, which maximum temperature (TMAX) (red), solar radiation (SR) (yellow), precipitation (PRCP) (blue), wind speed (WS) (green) and relative humidity (RH) (sky blue) using KZ filters. The meteorological factors are normalized for comparison.

Table 2.
Long-term variability trends of O3 and meteorological factors in different periods.
PRCP with a negative correlation with O3 exhibited a clear downward trend after 2010 (slope = −35.89 × 10−2 mm year−1) while SR with a positive correlation with O3 showed an upward trend after 2010 (slope = +11.41 × 10−2 h year−1). Since 2001, TMAX increased by +0.038 °C year−1 due to global warming but rose steeply by +0.25 °C year−1 after 2010. WS clearly decreased after 2010. RH, with a relatively small variability, slightly increased after 2010. Such trends in the meteorological factors after 2010, especially the increasing trends of TMAX and SR and the decreasing trends of PRCP and WS, may have directly affected the generation and extinction of O3. Thus, it can be estimated that the influence of meteorological factors on the O3 concentration in Korea has increased after 2010. Therefore, in the next section, changes in the correlations between meteorological factors and O3 before and after 2010 are compared and analyzed in a quantitative manner.
3.3. Impact of Varying Meteorological Conditions on Annual O3 Changes in Korea
As shown in Section 3.2, the counts of high-O3 days increased (58.8%) sharply after 2010, revealing the possibility of an amplified impact of meteorological factors on O3 concentrations in Korea. In addition, the standard normal homogeneity test (SNHT), which is the method of change point detection of annual O3 time series, from 2001 to 2017, confirmed statistically significant shifts around 2010 at the 95% confidence level (Supplementary Figure S1). Therefore, to further analyze the annually different meteorological impacts, we compared the impacts of the meteorological variables on the O3 concentrations in Korea during the two separated periods, which is period 1 (2001–2009, PRD1) and period 2 (2010–2017, PRD2).
3.3.1. Annual Changes in the Meteorological Conditions Affecting O3
To analyze changes in the correlations between O3 and meteorological factors before and after 2010, Pearson’s correlation coefficients (R) between the annual average O3 concentration and TMAX, SR, RH, PRCP, and WS during PRD1 and PRD2 were calculated. Figure 5 shows the differences in the R values (PRD2–PRD1) of the two periods. While the correlations between O3 and each meteorological factor were not statistically significant during PRD1, TMAX, SR, PRCP, WS, and RH showed statistically significant correlations with O3 during PRD2. Moreover, the correlations with all the meteorological factors were higher during PRD2 than during PRD1. This result indicates that the impacts of meteorological factors on the O3 concentration increased after 2010. SR, in particular, exhibited opposite trends in its correlation with O3 during PRD1 and PRD2 and showed the highest difference in the R value (PRD2–PRD1) between the two periods (+1.30). As shown in Figure 4, SR showed a decreasing trend and thus a negative correlation with O3 during PRD1 (R = −0.41), but it exhibited an increasing trend and thus a positive correlation with O3 during PRD2 (R = 0.89). These results imply that SR had the largest contribution to the differences in the impacts of meteorological conditions on O3 concentration between the two periods. In addition, the increase in the long-term variability of TMAX after 2010 has been remarkable due to the increase in SR along with global warming (Table 2). For this reason, the estimated R value of TMAX during PRD2 exhibited a significant positive correlation with O3.
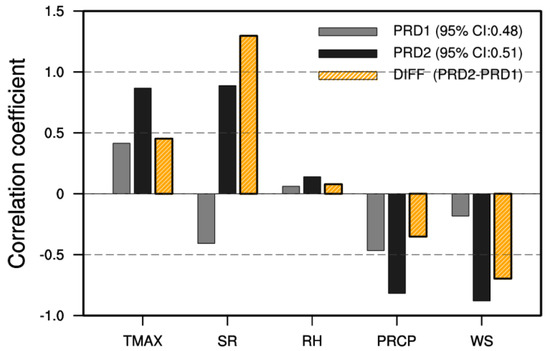
Figure 5.
Correlation coefficients between annual O3 and meteorological factors during the period 1 (2001–2009, PRD1) (gray) and period 2 (2010–2017, PRD2) (black) and their differences (yellow).
In contrast to the results of SR, the negative correlation of WS most significantly increased during PRD2 compared to during PRD1 (−0.70). It appears that the decrease in R value during PRD2 was due to the increase in the O3 concentration caused by the clear wind speed decrease after 2010 (Figure 4). This result agrees with the results of previous studies that explained the stagnant atmosphere and the increase in the concentrations of air pollutants due to the recent decrease in the wind speed around Korea [25,49]. As for PRCP, the decreasing trend in long-term variability has been reinforced after 2010 and thus its negative correlation with O3 increased during PRD2. Meanwhile, RH had no clear long-term variability characteristics and exhibited a relatively low correlation with O3 and showed statistically insignificant results during the entire period. The correlations between all the meteorological factors, except RH, and O3 clearly increased during PRD2 compared to PRD1, and the explanatory power expressed by the coefficient of determination also increased by 67–96% for all the factors, except RH (Table 3). These results confirm that the increase of O3 in Korea has been closely related to changes in the variability of each meteorological factor after 2010. To support the correlation analysis results, we conducted a multiple linear regression analysis. For the analysis, O3 was set as a dependent variable and the meteorological factors (TMAX, SR, RH, PRCP, WS) were set as independent variables. The results from the regression analysis also implied that the explanatory power and significance level increased notably after 2010 (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). Especially, SR and WS, which showed the largest correlation difference between PRD1 and PRD2, were selected as significant predictors from the regression, supporting the correlation analysis results in this study.

Table 3.
Coefficients of determination of O3 and meteorological factors in different periods (the rate of change is presented only when the correlation coefficient in Figure 5 is statistically significant in the 95% confidence interval of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
3.3.2. Causes of the Increase in the O3–Meteorology Relationship after 2010
The analysis results in Section 3.3.1 established that the correlations between O3 and meteorological factors (TMAX, SR, PRCP, and WS) have increased after 2010. To identify the causes of this increase in correlations, the differences in the anomaly (normalized) value of each meteorological factor between the two periods (PRD1 and PRD2) were calculated for every month and compared. As shown in Figure 6, the anomalous differences (PRD2–PRD1) of WS exhibited negative values throughout the year. In addition, TMAX and SR (PRCP) exhibited positive (negative) values throughout May to September. Positive values of RH were exhibited in summer and autumn, but the fluctuations in the absolute value of RH before normalization were insignificant (Figure 2). Interestingly, the major meteorological factors, except RH, maintained the signal with a positive correlation for O3 production from May to September. This period is identical to the O3 season monitored by the Ministry of Environment due to the occurrence of high O3 concentrations [15,50]. The increase in TMAX and SR and the decrease in PRCP during PRD2 were mostly concentrated during the period when high O3 concentrations occurred and can well explain the increase in the impact of meteorological conditions on the O3 concentration in Korea after 2010. This, however, provides a limited explanation on the cause of the increase in the O3–meteorology relationship after 2010 and cannot provide a fundamental explanation on the cause of the differences in the variability of each meteorological factor between PRD1 and PRD2. Thus, further analysis is required.
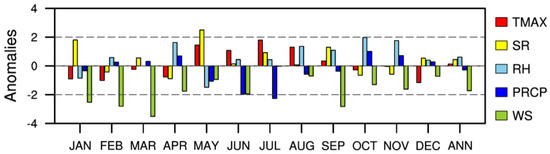
Figure 6.
Normalized monthly anomalies (PRD2–PRD1) of meteorological factors, with TMAX (red), SR (yellow), RH (sky blue), PRCP (blue) and WS (green) (January, JAN; February, FEB; March, MAR; April, APR; May, MAY; Jun, JUN; July, JUL; August, AUG; September, SEP; October, OCT; November, NOV; December, DEC; Annual, ANN).
Wei and Moon [42] suggested that the development of the Western North Pacific Subtropical High (WNPSH) in summer may increase surface O3 concentration by reducing precipitation in Korea. During the high O3 seasons of the PRD2 period, the average of the positive anomalies of WNPSH was 2.5 times higher compared to PRD1 (Supplementary Table S3). This suggests that the decrease in precipitation in Korea after 2010 is significantly related to the development of WNPSH. As precipitation has significant negative correlations with SR and TMAX in atmospheric dynamics, the variability of these factors can also be explained by the impact of WNPSH. Moreover, the development of WNPSH is highly related to the significant decrease in the east–west wind field of Korea [51]. Thus, it is likely to have contributed to the decreasing WS in Korea after 2010. It is also likely that the variability of each meteorological factor during PRD2 compared to PRD1 was directly or indirectly affected by large scale circulation. This, however, needs to be analyzed further because there are various factors that affect the variability of meteorological conditions.
3.3.3. Regional Differences on the Impact of Meteorological Conditions on O3 Variability
The differences among meteorological factors between PRD1 and PRD2 examined above represented the average results across Korea. Thus, the regional differences and regional characteristics could not be analyzed. There are significant regional differences in terms of meteorological conditions due to the topographic effect because Korea has very complex coastlines and most of its land is composed of mountainous terrains. Therefore, it was expected that there would also be regional differences in terms of the impact of meteorological conditions on the O3 concentration. Therefore, O3 variability before and after 2010 as well as the impact of meteorological conditions on O3 variability were closely examined for each of the six air quality regions of Korea.
Table 4 shows the correlation coefficients between the O3 concentration and each meteorological factor by region for each period (PRD1 and PRD2). Figure 7 shows the color-coded differences in the correlation coefficients between PRD1 and PRD2 (PRD2–PRD1) by region. “National” in Table 4 and Figure 7 mean the same value as “DIFF” in Figure 5. Table 4 shows that all the meteorological factors except RH exhibited higher correlation coefficients during PRD2 compared to PRD1 and they showed statistically significant results in most of the regions except JJ. The correlation coefficients between the O3 concentration and SR/TMAX exhibited a clear increase in positive correlation during PRD2 compared to PRD1 in all regions except JJ, while PRCP showed a clear increase in negative correlation in all regions except JJ.

Table 4.
Annual correlation coefficients between O3 and meteorological factors in different air quality regions (Seoul Metropolitan Area, SMA; Central region, CN; Honam, HN; Yeongnam, YN; Gangwon, GW; Jeju, JJ) and different periods (statistically significant R values in the 95% confidence interval of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient are marked with *).
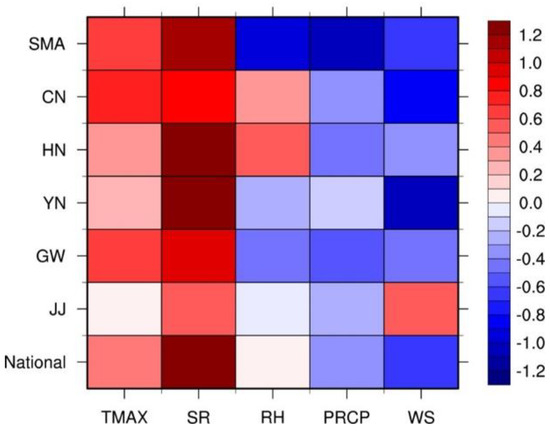
Figure 7.
Correlation coefficient differences between PRD1 and PRD2 (PRD2–PRD1) in air quality regions for the O3–meteorological factors relationship.
The differences in the correlations between O3 and SR/TMAX/PRCP between the periods (PRD2–PRD1) were similar in all regions except JJ. Also, RH exhibited different results by region. There are large regional differences in RH because it is affected by a combination of meteorological conditions, such as atmospheric stability, cloud, and precipitation, as well as the amount of water vapor and temperature. Therefore, although it did not show a significant correlation with O3 on average, statistically significant correlation changes could be confirmed in some regions. When the O3–RH correlation change of SMA was examined (Table 4), the negative correlation was reinforced during PRD2. This appears to be because RH was reduced in SMA during PRD2 and thus, the O3 concentration increased due to the decrease in wet deposition. JJ, an island region located in the south-west of Korea, was the only region that exhibited a clear negative correlation with O3 during the entire period due to its high annual RH. Moreover, JJ showed a statistically significant negative correlation during PRD2 as the correlation was slightly reinforced. As for the O3–WS correlation, the negative correlation was reinforced during PRD2 compared to PRD1 in all regions except SMA and JJ. In SMA, a positive correlation between O3 and WS was observed during PRD1 (0.60), but no significant correlation was observed during PRD2. This result is analyzed in detail in the next section.
3.3.4. Major Drivers for the Strengthened Impact of Meteorological Conditions on O3 after 2010
As examined above, SR, TMAX, and PRCP exhibited increased correlations with O3 in all regions except JJ after 2010 (PRD2), but RH and WS showed significant regional differences. Thus, for the analysis of such regional differences, the changes in meteorological factors (PRD2–PRD1) were examined by region quantitatively and the regional differences in the major meteorological factors that affected O3 after 2010 were identified.
The differences in each meteorological factor were calculated by region using anomaly analysis. The normalized anomalies for the high O3 season (i.e., May to September) are shown in Figure 8. Moreover, O3 trends by region/period are additionally presented in Figure 9 to show the differences for each meteorological factor (PRD2–PRD1) by region as well as the impacts of the differences in the variability of each meteorological factor by region on the O3 trend of each region. Figure 8g shows the averaged results of the differences in the anomalies of each meteorological factor between PRD1 and PRD2 during the high O3 season. The results are the same as the averaged values from May to September in Figure 6. It should be noted that as the results of Figure 8 are the normalized results obtained from the division of each meteorological factor by the standard deviation, regional comparisons for the same factors are possible but it is not possible to compare the absolute impacts of each factor. The results of Figure 8g show that TMAX and SR increased while PRCP and WS decreased during PRD2 compared to PRD1. This accounts for the strengthened O3 upward trend in Korea after 2010 (Figure 9).
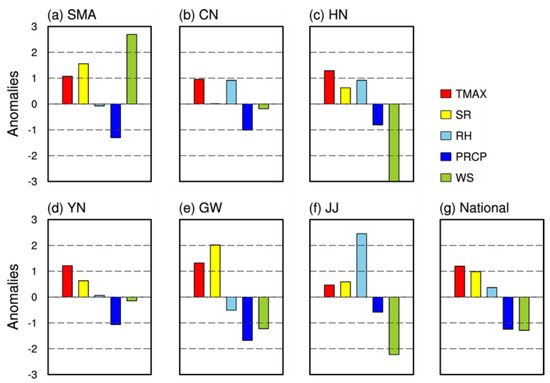
Figure 8.
Normalized anomalies (PRD2–PRD1) of meteorological factors, with TMAX (red), SR (yellow), RH (sky blue), PRCP (blue), and WS (green) in the air quality regions (Seoul Metropolitan Area, SMA; Central region, CN; Honam, HN; Yeongnam, YN; Gangwon, GW; Jeju, JJ) during the O3 season.
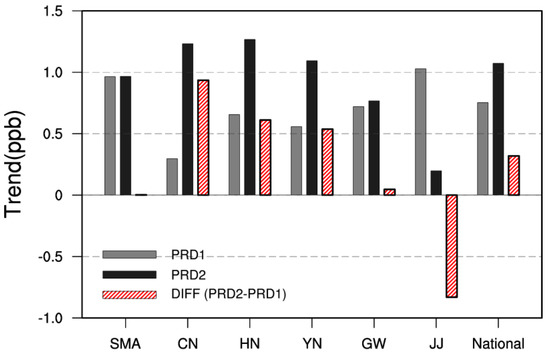
Figure 9.
Annual O3 trends during PRD1 (grey) and PRD2 (black) in different air quality regions and their differences (red).
Changes in anomalies by meteorological factor, however, are different by region. For example, SMA exhibited a clear increase in WS during PRD2 compared to PRD1 in contrast to the other regions (Figure 8a). This appears to have caused the O3–WS correlation during PRD2 to be significantly lower compared to the other regions, except JJ, as shown in Table 4. WS in Korea was reduced during PRD2 on average, but WS increased in SMA. This WS increase in SMA offset the O3 concentration increase caused by the increase in TMAX and SR and the decrease in PRCP. This explains why there was no significant change in the O3 trend in SMA after 2010 (Figure 9). In GW, on the other hand, O3 increased very slightly after 2010 even though meteorological changes favorable to the increase in O3 concentration (the increase in TMAX and SR and the decrease in RH, PRCP, and WS) occurred during PRD2. Since GW is located in the downwind area of SMA, the O3 concentration was significantly affected by O3 transport from SMA [52]. As no significant O3 change occurred in SMA after 2010, GW, a receptor area, also did not show a significant O3 change. Moreover, as GW is a region with low pollutant emissions, the O3 increase was limited despite the meteorological conditions favorable to O3 generation during PRD2. For these reasons, no clear change in the O3 trend occurred in SMA and GW during PRD1 and PRD2.
Meanwhile, the rise in O3 concentration in JJ decreased during PRD2, unlike in other regions (Figure 9). Although the meteorological conditions in JJ became favorable to O3 generation after 2010 due to the increase in TMAX and SR and the decrease in PRCP and WS, a very clear increase in RH occurred, causing a decrease in O3 on average. To further examine the impact of RH on the O3 concentration in JJ, the water vapor pressure (hPa) measurement data (ASOS) was analyzed. The increase in the annual water vapor pressure in JJ after 2010 (PRD2) (+0.16 hPa year−1) was 3.9 times higher compared to the average of the other regions, and the average water vapor pressure was also 25% higher. It is known that the increase in the water vapor quantity generally contributes to the generation of clouds and decreases the O3 concentration through wet deposition [44,53]. Therefore, it can be presumed that the O3 reduction in JJ after 2010 was dominated by the effect of increased water vapor.
Unlike SMA and JJ, the increase in O3 during PRD2 was significant in the CN, HN, and YN regions. When the meteorological conditions of CN and HN were compared (Figure 8), HN was found to provide more favorable conditions for O3 generation but the upward trend in O3 was higher in CN (Figure 1), with more pollutant emissions. In the same manner, although the meteorological conditions in GW were more favorable to O3 increasing than YN, the O3 increasing was higher in YN with more emissions. These results confirm that the impacts of meteorological conditions can be different depending on the distribution of pollutant emissions, especially NOx and VOC, which are the major precursors of O3.
These results strongly suggest that the major meteorological factors that caused the increase in O3 in Korea after 2010 exhibited clear differences by region and that even the same meteorological changes can have different impacts on the O3 concentration depending on the difference in emissions. Moreover, these results show that the impact of meteorological conditions on the O3 concentration is not always constant and may vary depending on the time and space. In particular, they show that the impact of meteorological conditions on O3 variability can be clearly different by region depending on their distinct topographical characteristics and the differences in the distribution of emissions, even in small countries such as Korea (109th largest in the world).
4. Summary and Discussion
In this study, changes in the O3 concentration in South Korea and the impact of meteorological conditions on such changes were examined from 2001 to 2017. For the analysis, the O3 concentration (sourced from AQMS), TMAX, SR, RH, PRCP, and WS (sourced from ASOS) measurement data for South Korea’s six air quality regions were used. The long-term variability of O3 was analyzed by removing the seasonal and short-term variabilities of O3 using the KZ filter. It was confirmed that the long-term variability of the O3 concentration (29.8%) and the occurrence of high-concentration days (58.8%) rapidly increased in South Korea after 2010. During the same period, the emissions of the major precursors of O3 did not show rapid changes favorable to O3 generation, but the long-term variability of the meteorological factors TMAX, SR, PRCP, and WS, exhibited clear changes in trends toward conditions favorable to O3 generation.
To examine the increase in the impact of meteorological conditions on the O3 concentration in South Korea after 2010 in detail, the period from 2001 to 2009 was defined as PRD1 and the period from 2010 to 2017 as PRD2, and the analysis results for each period were compared. The classification of this period was reflected by significant SNHT results at the 95% confidence level. When the correlation coefficients between the O3 concentrations and each meteorological factor were analyzed by period, it was found that the correlations between O3 and all meteorological factors, except RH, increased and were statistically significant during PRD2, thereby confirming that the meteorological factors were related to the increasing trend of O3 after 2010. SR and TMAX exhibited positive correlations with O3, while WS and PRCP exhibited negative correlations with O3. These results agree with the impacts of each meteorological factor on O3 reported by previous studies. Especially, SR exhibited the largest increase in correlation with O3 concentration after 2010, followed by WS, TMAX, and PRCP. However, it should be noted that generalizing those findings could be risky because they are based only on a simple statistical analysis. Additional comparative studies using different methods need to be followed to verify the findings in this study.
When the monthly average anomalies of meteorological factors were analyzed, it was found that the differences in the anomalies of TMAX, SR, and PRCP between PRD1 and PRD2 were concentrated in the high-O3 season (May to September). This shows that the change in the O3 trend after 2010 could be caused by the meteorological changes in the O3 season, and such changes could also be explained by the impact of the variability of the Western North Pacific Subtropical High.
When changes in the correlations between O3 and meteorological factors after 2010 were analyzed by region, it was found that TMAX, SR, and PRCP, which are meteorological factors related to large-scale circulation, were strengthened toward conditions favorable to O3 generation in all regions. In contrast, WS and RH showed different changes in their correlations with O3 by region. WS exhibited decreasing trends in most of the regions, but increased in SMA; therefore, the O3 trend of SMA contrasted with the other regions. The O3 trend of GW located downwind of SMA exhibited similar characteristics to SMA. In JJ, an island located in the south-west of South Korea with different climatological characteristics, the O3 upward trend was found to decrease during PRD2 due to the dominant increase in RH after 2010. Meanwhile, in the regions of YN and GW as well as CN and HN, changes in meteorological factors were similar during PRD2 as compared to PRD1, but their impacts on the change in O3 concentration were different. These results revealed that the impact of meteorological changes on the O3 concentration could be large in regions with high emissions and suggested that the impact of meteorological conditions on O3 concentration varied depending on the time and geography.
In this study, the national background O3 observation data were excluded to analyze the spatiotemporal characteristics of long-term variability of photochemically produced O3 and its association with meteorological factors in Korea. However, a comprehensive understanding of the variability of surface O3 on the national scale should be accompanied by a discussion of long-term pollution transportation and the potential for background O3 inflow from the free and upper troposphere. Gaudel et al. [54] found that the eastern Mediterranean surface O3 in the mid-latitude region was predominantly influenced by O3 subsidence from the troposphere due to synoptic meteorological characteristics, which was consistent with previous studies [55,56]. However, tropospheric ozone in Korea and Japan, located in the mid-latitude of East Asia, showed a decreasing trend so, it was inferred that the impact on surface O3 would be relatively insignificant [57,58]. Nevertheless, the background O3 concentration in eastern China was high in the free troposphere during spring and summer, suggesting the possibility of transportation [53]. To address these issues, a more comprehensive study that considers not only surface O3 variability but also tropospheric background O3 variability and long-range transport of atmospheric boundary pollutants from East Asia should be conducted, and it would be our following research.
In recent studies on future scenarios, TMAX and SR are predicted to increase due to the warming of East Asia and the variability of PRCP and WS in mid-latitudes is predicted to be very large. The variability of meteorological factors vary by region and their impacts on O3 may also vary by region. Therefore, the results of this study can be used to establish more realistic reduction policies.
Supplementary Materials
The Supplementary Materials are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/1/74/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.J. and W.J.; methodology, Y.J.; formal analysis, Y.J.; resources, Y.J.; visualization, Y.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, W.J.; supervision, H.W.L. and W.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2019R1C1C1003428).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Booker, F.; Muntifering, R.; Mcgrath, M.; Burkey, K.; Decoteau, D.; Fiscus, E.; Manning, W.; Krupa, S.; Chappelka, A.; Grantz, D. The ozone component of global change: Potential effects on agricultural and horticultural plant yield, product quality and interactions with invasive species. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2009, 51, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Naik, V.; Horowitz, L.W.; Mauzerall, D.L. Air pollution and associated human mortality: The role of air pollutant emissions, climate change and methane concentration increases from the preindustrial period to present. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1377–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Retama, A. Ozone’s threat hits back Mexico city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, T.I. Effects of exposure to ozone on the ocular surface in an experimental model of allergic conjunctivitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169209. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M.D.; Isebrands, J.G.; Dickson, R.E.; Karnosky, D.F. Photosynthetic productivity of aspen clones varying in sensitivity to tropospheric ozone. Tree Physiol. 1995, 15, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, T.B.; Trainer, M.; Holloway, J.S.; Parrish, D.D.; Huey, L.G.; Sueper, D.T.; Frost, G.J.; Donnelly, S.G.; Schauffler, S.; Atlas, E.L.; et al. Observations of ozone formation in power plant plumes and implications for ozone control strategies. Science 2001, 292, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, I.H.Y.; Clemitshaw, K.C.; Mendoza, A. Observed trends in ground-level O3 in Monterrey, Mexico, during 1993-2014: Comparison with Mexico City and Guadalajara. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9163–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohan, D.S.; Hakami, A.; Hu, Y.; Russell, A.G. Nonlinear response of ozone to emissions: Source apportionment and sensitivity analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6739–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Cohan, D.S.; Byun, D.W.; Ngan, F. Highly nonlinear ozone formation in the Houston region and implications for emission controls. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tonnesen, G.S.; Wang, Z. One-hour and eight-hour average ozone in the California South Coast air quality management district: Trends in peak values and sensitivity to precursors. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Deng, X.J.; Zhu, D.; Gong, D.C.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Tan, H.B.; Deng, T.; Mai, B.R.; Liu, X.T.; et al. Characteristics of 1 year of observational data of VOCs, NOx and O3 at a suburban site in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6625–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcek, C.J.; Yuan, H.-H. Calculated Influence of Temperature-Related Factors on Ozone Formation Rates in the Lower Troposphere. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 34, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, E.K.; Comrie, A.C. Extending the kolmogorov–zurbenko filter: Application to ozone, particulate matter, and meteorological trends. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, E.K.; Comrie, A.C. Meteorologically adjusted urban air quality trends in the Southwestern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, B.J.; Stehr, J.W.; Piety, C.A.; Salawitch, R.J.; Dickerson, R.R. Observed relationships of ozone air pollution with temperature and emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L09803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.P.; Lee, G. Trend of air quality in Seoul: Policy and science. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Han, J.; Lee, M.; Kang, E. The Long-term Variations of Ozone and Nitrogen Oxides in Suwon City during 1991~2012. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 31, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, H.; Mori, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Ohizumi, T.; Itano, Y. Analysis of monitoring data of ground-level ozone in Japan for long-term trend during 1990–2010: Causes of temporal and spatial variation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Air Quality Criteria For Ozone And Related Photochemical Oxidants (Final Report); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Yoo, J.-M.; Jeong, M.-J.; Kim, D.; Stockwell, W.R.; Yang, J.-H.; Shin, H.-W.; Lee, M.-I.; Song, C.-K.; Lee, S.-D. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants (O3, NO2, SO2, CO, PM10, and VOCs) with land-use types. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10857–10885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camalier, L.; Cox, W.; Dolwick, P. The effects of meteorology on ozone in urban areas and their use in assessing ozone trends. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7127–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, A.F.; McKenzie, R.L.; Bernhard, G.; Aucamp, P.J.; Ilyas, M.; Madronich, S.; Tourpali, K. Ozone depletion and climate change: Impacts on UV radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 19–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, N.; Sillmann, J.; Schnell, J.L.; Rust, H.W.; Butler, T. Synoptic and meteorological drivers of extreme ozone concentrations over Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Swall, J.L.; Cox, W.M.; Davis, J.M. Interannual variation in meteorologically adjusted ozone levels in the eastern United States: A comparison of two approaches. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.U.; Jin, C.S.; Hong, S.; Park, R.; Son, S.W.; Bae, C.; Bae, M.A.; Song, C.K.; et al. Recent increase of surface particulate matter concentrations in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, Korea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ghim, Y.S.; Han, J.-S.; Park, S.-M.; Shin, H.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, J.; Lee, G. Long-term Trend Analysis of Korean Air Quality and Its Implication to Current Air Quality Policy on Ozone and PM10. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.-O.; Suh, M.-S.; Rha, D.-K. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Precipitation in South Korea for Recent 30 Years (1976-2005) and Geographic Environments. J. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 2006, 27, 433–449. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.K. Changes in the extreme daily rainfall in South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Air Quality Monitoring Station; AQMS. Available online: http://www.airkorea.or.kr/web/last_amb_hour_data?pMENU_NO=123 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Martins, D.K.; Stauffer, R.M.; Thompson, A.M.; Knepp, T.N.; Pippin, M. Surface ozone at a coastal suburban site in 2009 and 2010: Relationships to chemical and meteorological processes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Clean Air Policy Support System; CAPSS. Available online: http://airemiss.nier.go.kr/module/statistics/materialStatistics.do?siteId=airemiss&id=airemiss_030200000000 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Zurbenko, I.G. Detecting and tracking changes in ozone air quality. Air Waste 1994, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.T.; Zurbenko, I.G.; Neagu, R.; Porter, P.S.; Ku, J.Y.; Henry, R.F. Space and Time Scales in Ambient Ozone Data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovich, F.M. Time scales of surface ozone variations in the regional, non-urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogrefe, C.; Rao, S.T.; Zurbenko, I.G.; Porter, P.S. Interpreting the information in ozone observations and model predictions relevant to regulatory policies in the Eastern United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2083–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, Z.H.; Kim, K.H. Impact of emission control strategy on NO2 in urban areas of Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, Z. Atmospheric Pollution: History, Science, & Regulation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780511802287. [Google Scholar]
- Haigh, J.D. The role of stratospheric ozone in modulating the solar radiative forcing of climate. Nature 1994, 370, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Hogrefe, C.; Foley, K.L.; Napelenok, S.L.; Mathur, R.; Trivikrama Rao, S. Application of the kolmogorov-Zurbenko filter and the decoupled direct 3D method for the dynamic evaluation of a regional air quality model. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, P.M.; Shine, K.P. Radiative forcing and temperature trends from stratospheric ozone changes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 10841–10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Shindell, D.T.; Faluvegi, G.; Wenig, M.; Lam, Y.F.; Ning, Z.; Hao, S.; Lai, C.S. Increase of ozone concentrations, its temperature sensitivity and the precursor factor in South China. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 23455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusede, S.E.; Steiner, A.L.; Cohen, R.C. Temperature and Recent Trends in the Chemistry of Continental Surface Ozone. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3898–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wie, J.; Moon, B.K. Impact of the Western North Pacific Subtropical High on summer surface ozone in the Korean Peninsula. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundel, V.A.; Sterling, M.E.; Biggin, H.J.; Sterling, D.T. Indirect Health Effects of Relative Humidity in Indoor Environments. Environ. Health Perspect. 1986, 65, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.M.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, D.; Jeong, M.J.; Stockwell, W.R.; Kundu, P.K.; Oh, S.M.; Shin, D.B.; Lee, S.J. New indices for wet scavenging of air pollutants (O3, CO, NO2, SO2, and PM10) by summertime rain. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xu, Y. Effects of relative humidity on ozone and secondary organic aerosol formation from the photooxidation of benzene and ethylbenzene. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghim, Y.S.; Oh, H.S.; Chang, Y.S. Meteorological effects on the evolution of high ozone episodes in the greater Seoul area. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Yim, S.; Kwon, M.; Kim, D. Decadal Change in Rainfall During the Changma Period in Early-2000s. Atmosphere 2017, 27, 345–358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Kim, S.J. Significant decrease of PM2.5 in Beijing based on long-term records and kolmogorov–Zurbenko filter approach. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghim, Y.S.; Chang, Y.S. Characteristics of ground-level ozone distributions in Korea fon the period of 1990–1995. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 8877–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, K.Y. Summertime variability of the western North Pacific subtropical high and its synoptic influences on the East Asian weather. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.B.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.; Park, C.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.Y. A study on high ozone formation mechanism associated with change of NOx/VOCs ratio at a rural area in the Korean Peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. National Air Pollutant Emission Trends; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Gaudel, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Ancellet, G.; Barret, B.; Boynard, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F.; Cuesta, J.; Cuevas, E.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone relevant to climate and global atmospheric chemistry model evaluation. Elementa 2018, 6, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanis, P.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Pozzer, A.; Tyrlis, E.; Dafka, S.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Lelieveld, J. Summertime free-tropospheric ozone pool over the eastern Mediterranean/middle east. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabokas, P.; Hjorth, J.; Foret, G.; Dufou, G.; Eremenko, M.; Siour, G.; Cuesta, J.; Beekmann, M. An investigation on the origin of regional springtime ozone episodes in the western Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3905–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Son, S. Evaluation of the Troposphere Ozone in the Reanalysis Datasets: Comparison with Pohang Ozonesonde Observation. Atmosphere 2019, 29, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Oltmans, S.J.; Lefohn, A.S.; Harris, J.M.; Galbally, I.; Scheel, H.E.; Bodeker, G.; Brunke, E.; Claude, H.; Tarasick, D.; Johnson, B.J.; et al. Long-term changes in tropospheric ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3156–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).