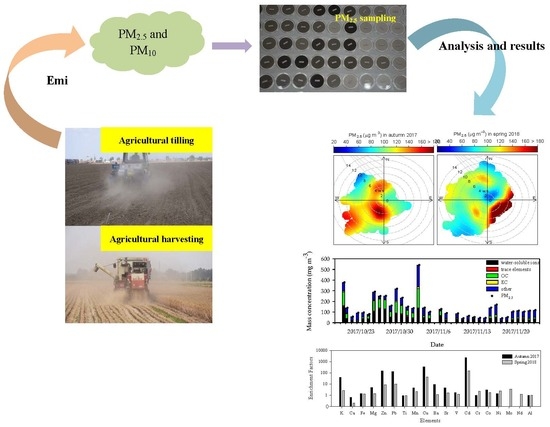
Temporal Variation and Chemical Components of Rural Ambient PM2.5 during Main Agricultural Activity Periods in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
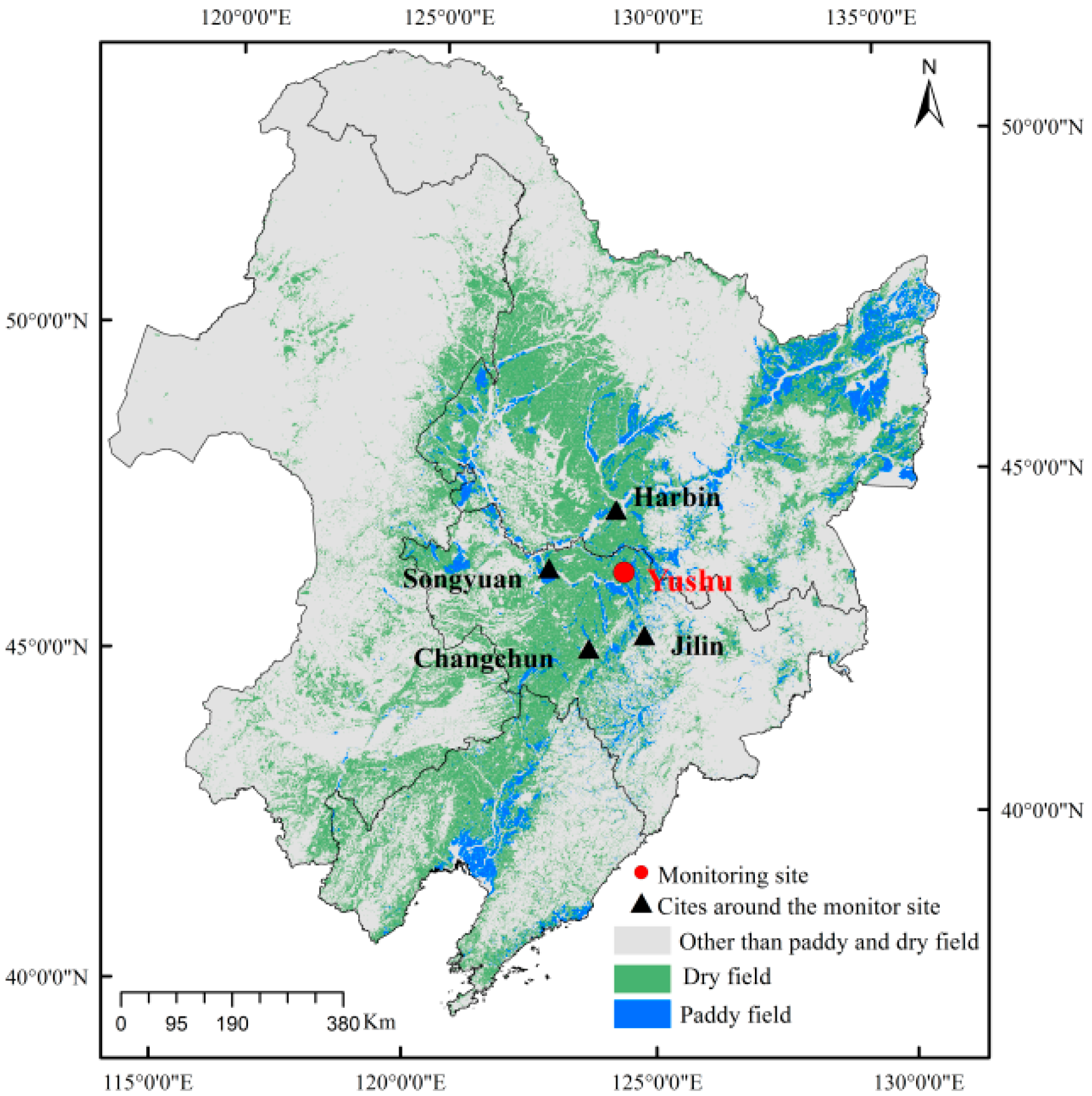
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. PM2.5 Sampling
2.3. Real-Time Measuremnets of PM2.5 and Meteorological Data
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM2.5 Concentrations
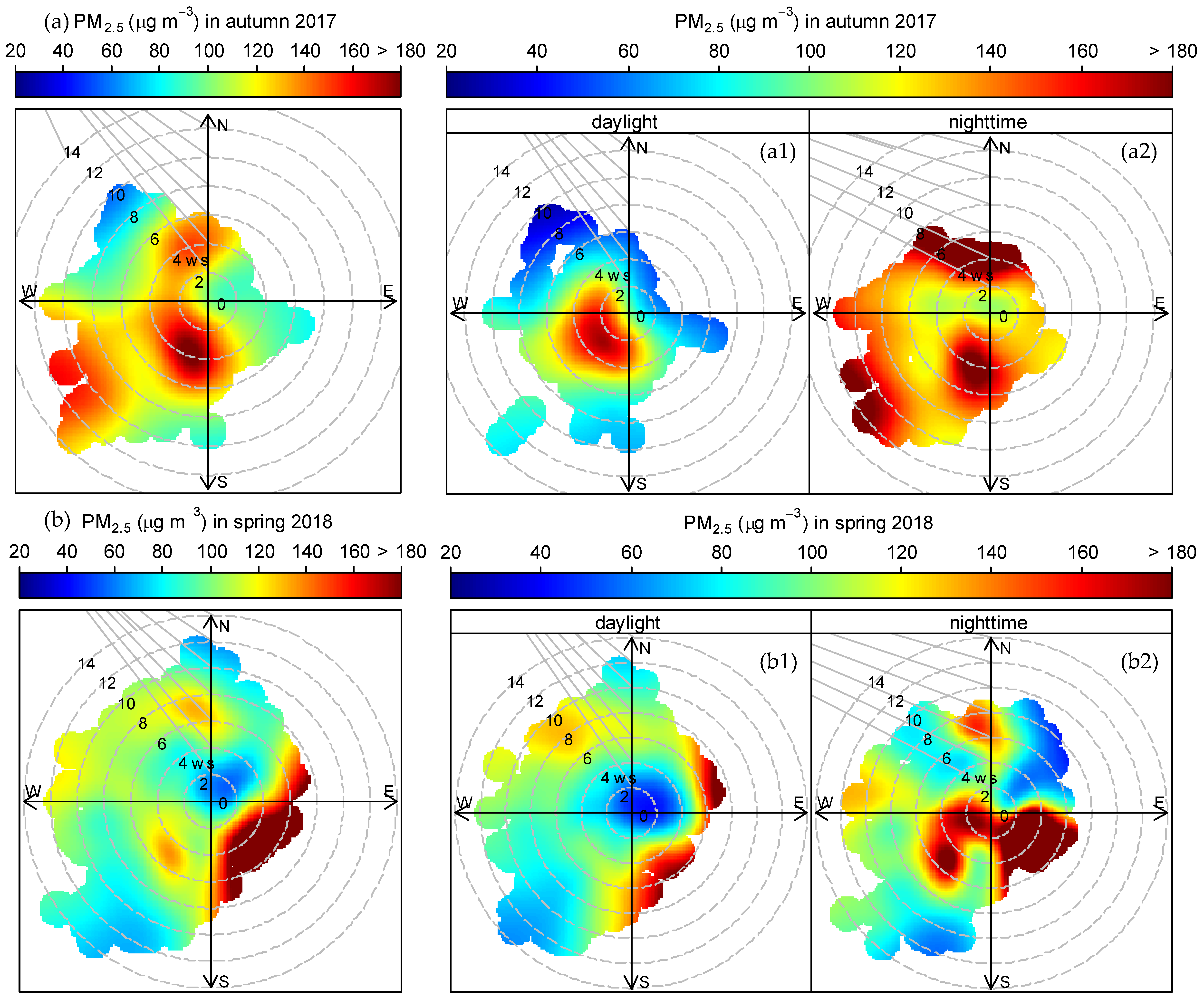
3.2. Relationship of PM2.5 with Wind Speed and Wind Direction
3.3. Chemical Composition of PM2.5
3.3.1. Water-Soluble Ions Analysis
Anion–Cation Balance
3.3.2. Trace Elements Analysis
3.3.3. OC/EC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turnock, S.T.; Butt, E.W.; Richardson, T.B.; Mann, G.W.; Reddington, C.L.; Forster, P.M.; Haywood, J.; Crippa, M.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Johnson, C.E. The impact of European legislative and technology measures to reduce air pollutants on air quality, human health and climate. J. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Pozzer, A.; Cao, C.X.; Lelieveld, J. Long-term (2001–2012) fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and the impact on human health in Beijing, China. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5715–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, B.Q. Temporal and spatial distribution of PM2.5 and PM10 pollution status and the correlation of particulate matters and meteorological factors during Winter and Spring in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 418–427. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Han, B.; Wu, J.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhou, L.D.; Zhang, P.; Feng, Y.C. Using an improved source directional apportionment method to quantify the PM2.5 source contributions from various directions in a megacity in China. J. Chemosph. 2015, 119, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ao, X.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Liu, M.Y.; Ma, F.S. Climatic characteristics of haze days in Northeast of China over the past 50 years. J. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.W.; Zhang, S.C.; Tong, Q.S.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhao, H.M.; Ma, S.Q.; Xiu, A.J.; He, Y.X. Regional characteristics and causes of haze events in Northeast China. J. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Q.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, S.C.; Tong, Q.S.; Bao, Q.Y.; Gao, Z.T. Characteristics and cause analysis of heavy haze in Changchun City in Northeast China. J. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 6, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.L. Analysis of Temporal-Spatial Characteristics of Haze in China Based on Satellite Remote Sending Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.W.; Tong, D.Q.; Dan, M.; Zhang, S.C.; Zhang, X.L.; Pan, Y.P. Typical atmospheric haze during crop harvest season in northeastern China: A case in the Changchun region. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.S.; Zhang, Z.D.; Jin, M.Y.; Zou, P.C.; Wang, J. Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 aerosol during haze periods in Changchun, China. J. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Available online: http://www.ndrc.gov.cn/zcfb/zcfbtz/201603/W020160311487622568348.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- Zhang, R.J.; Fu, C.B.; Han, Z.W.; Zhu, C.S. Characteristics of elemental composition of PM2.5 in the spring period at Tongyu in the semi-arid region of Northeast China. J. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baker, J.B.; Southard, R.J.; Mitchell, J.P. Agricultural dust production in standard and conservation tillage systems in the San Joaquin Valley. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattey, E.; Qiu, G. Trends in primary particulate matter emissions from Canadian agriculture. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmén, B.; Miller, D.; Hiscox, A.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Sammis, T.; Bottoms, R. Near-source particulate emissions and plume dynamics from agricultural field operations. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 59, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wu, F.; Han, Y.M.; Jin, Z.D.; Shen, Z.X.; An, Z.S. Size-differentiated source profiles for fugitive dust in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.Y.; Du, W.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Gao, Q.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, M.X. Aerosol optical properties affected by a strong dust storm in Central and Northern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogman, P.; Cornelis, W.; Rollé, H.; Gabriels, D. Prediction of TSP and PM10 Emissions from Agricultural Operations in Flanders, Belgium. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium, Transport and Air Pollution, Graz, Austria, 1–3 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pattey, E.; Qiu, G.; Fiset, S.; Ho, E.; MacDonald, D.; Liang, C. Primary particulate matter emissions and trends from Canadian agriculture. J. Wit Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 198, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Gao, H.W.; Zhou, J.Z. Experimental study on soil erosion by wind under conservation tillage. J. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2003, 19, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, K.; Chang, S.C.; Yu, S.C.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, P.F.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.P.; Rosenfeld, D.; Seinfeld, J.H. Spatial and temporal distributions of air pollutant emissions from open crop straw and biomass burnings in China from 2002 to 2016. J. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Tang, Q.; Peng, J.F.; Wang, E.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Chai, F.H. Study on characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter in China. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 36, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2012; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Lian, Y.; Gao, Z.T.; Ren, H.L.; Sun, L.; An, G.; Shen, B.Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, W.Z. Desertification development and regional climatic change in northeast china in the 1990s. J. Acta Meteorol. Sinica 2001, 59, 730–736. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, M.E.; Cary, R.A. Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. J. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzalunga, A.; Bernardoni, V.; Fermo, P.; Vecchi, R. Optimisation of analytical procedures for the quantification of ionic and carbonaceous fractions in the atmospheric aerosol and applications to ambient samples. J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.J.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Liu, S.X.; Ding, H.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Qiang, J.; et al. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in Xi’an, China: Seasonal variations and sources. J. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.S.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, J.S.; Zheng, C.J. Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China. Environ. Sci. 1991, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Vassura, I.; Venturini, E.; Marchetti, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Bernardi, E.; Fermo, P.; Passarini, F. Markers and influence of open biomass burning on atmospheric particulate size and composition during a major bonfire event. J. Atmosph. Environ. 2014, 82, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzalunga, A.; Anzano, M.; Collina, E.; Lasagni, M.; Lollobrigida, F.; Pannocchia, A.; Fermo, P.; Pitea, D. Contribution of wood combustion to PAH and PCDD/F concentrations in two urban sites in Northern Italy. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 56, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D.S.; Wang, Y.S. Long-range transport and regional sources of PM2.5 in Beijing based on long-term observations from 2005 to 2010. J. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, S.L.; Chai, F.H. PM2.5 Pollution in Xingtai, China: Chemical characteristics, source apportionment, and emission control measures. J. Atmos. 2019, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.W.; Xu, L.L.; Chen, J.S.; Yu, Y.K.; Niu, Z.C.; Yin, L.Q. Chemical compositions and extinction coefficients of PM2.5 in peri-urban of Xiamen, China, during June 2009–May 2010. J. Atmos. Res. 2012, 106, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, K.; Xu, C.; Tang, A.H.; Chen, J.M.; An, Z.S. The ion chemistry, seasonal cycle, and sources of PM2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai. J. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Guo, Z.G.; Zhang, T.R.; Yao, X.H.; Chan, C.K.; Fang, M. Source and formation of secondary particulate matter in PM2.5 in Asian continental outflow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D03302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Tang, A.H.; Yuan, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, A.H. The ion chemistry and the source of PM2.5 aerosol in Beijing. J. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillapapiromsuk, S.; Chantara, S.; Tengjaroenkul, U.; Prasitwattanaseree, S.; Prapamontol, T. Determination of PM10 and its ion composition emitted from biomass burning in the chamber for estimation of open burning emissions. J. Chemosph. 2013, 93, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogula-Kozlowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Ośródka, L.; Krajny, E.; Błaszczak, B.; Mathews, B. Spatial and seasonal variability of the mass concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Poland. J. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.K.; Liu, X.D.; Yu, T.; Cachie, H. Identification and estimate of biomass burning contribution to the urban aerosol organic carbon concentrations in Beijing. J. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J. Measurement methods to determine compliance with ambient air quality standards for suspended particles. J. Air Repair 1995, 45, 666–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Zhao, W.; Guan, J.J.; Wu, M.H.; Fu, J.M. Composition and sources of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 from the e-waste dismantling area of Taizhou. J. Environ. Chem. 2011, 30, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Duce, R.A.; Arimoto, R.; Ray, B.J.; Unni, C.K.; Harder, P.J. Atmospheric trace elements at Enewetak Atoll: 1. Concentrations, sources, and temporal variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1983, 88, 5321–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.X.; Arimoto, R.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, R.J.; Li, X.X.; Du, N.; Okuda, T.; Nakao, S.; Tanaka, S. Seasonal variations and evidence for the effectiveness of pollution controls on water-soluble inorganic species in total suspended particulates and fine particulate matter from Xi’an, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Arimoto, R.A.; Lee, D.S.; Zhou, M.Y. Input of atmospheric trace elements and mineral matter to the Yellow Sea during the spring of a low-dust year. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 3767–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.K.; Wang, K.; Yuan, C.S.; Wang, G.Z. Study on the seasonal variation and source apportionment of PM10 in Harbin, China. J. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 98, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayor, S.R.; Mclennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.C.; Tan, J.H.; Wang, S.L.; Hao, J.M.; Chai, F.H. Size distributions and sources of elements in particulate matter at curbside, urban and rural sites in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.D.; Luo, B. Composition and pollution characteristics of fine particles in Chengdu from 2012 to 2013. J. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Sternbeck, J.; Sjödin, Å.; Andréasson, K. Metal emissions from road traffic and the influence of resuspension-results from two tunnel studies. J. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmili, W.; Allen, A.G.; Bary, F.; Harrison, M. Trace metal concentrations and water solubility in size-fractionated atmospheric particles and influence of road traffic. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Noone, K. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 2. C1 through C30 organic compounds from medium duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhi, G.R.; Feng, Y.L.; Fu, J.M.; Feng, J.L.; Sheng, G.Y.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurements of emission factors for primary carbonaceous particles from residential raw-coal combustion in China. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L20815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Factor/Unit | Autumn 2017 (N = 34) | Spring 2018 (N = 29) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Average ± SD | Range | Average ± SD | |
| PM2.5/μg m−3 | 39.16–539.03 | 142.82 ± 108.83 | 97.25–976.16 | 241.0 ± 188.6 |
| OC/μg m−3 | 4.70–181.12 | 37.03 ± 42.10 | 5.34–210.77 | 26.73 ± 43.75 |
| EC/μg m−3 | 0.78–16.06 | 3.76 ± 3.47 | 1.33–30.69 | 6.99 ± 7.49 |
| F−/μg m−3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD–0.21 | 0.05 ± 0.06 |
| Cl−/μg m−3 | <LOD–56.78 | 13.22 ± 12.79 | 0.32–5.47 | 1.30 ± 1.25 |
| NO3−/μg m−3 | <LOD–56.23 | 11.36 ± 13.34 | 2.17–20.04 | 7.02 ± 4.65 |
| SO42−/μg m−3 | <LOD–27.75 | 7.74 ± 5.97 | 1.81–17.90 | 6.26 ± 4.49 |
| Na+/μg m−3 | <LOD–2.35 | 0.15 ± 0.41 | 0.12–1.93 | 0.58 ± 0.39 |
| NH4+/μg m−3 | 0.75–31.80 | 8.86 ± 7.66 | 0.77–17.50 | 4.01 ± 3.81 |
| K+/μg m−3 | 0.70–14.34 | 4.14 ± 3.37 | 0.46 - 7.44 | 1.63 ± 1.74 |
| Mg2+/μg m−3 | <LOD–1.16 | 0.22 ± 0.25 | 0.06–1.23 | 0.32 ± 0.29 |
| Ca2+/μg m−3 | 0.01–2.80 | 0.74 ± 0.77 | 0.11–5.37 | 1.59 ± 1.36 |
| K/ng m−3 | 960.67–10091.79 | 3710.83 ± 2430.20 | 660.40–10971.45 | 2891.02 ± 2407.57 |
| Ca/ng m−3 | <LOD–3132.38 | 568.35 ± 639.99 | 232.55–8991.14 | 2094.26 ± 1876.18 |
| Fe/ng m−3 | <LOD–960.18 | 202.23 ± 210.32 | 330.62–13936.93 | 2175.25 ± 2630.90 |
| Al/ng m−3 | <LOD–1542.91 | 340.45 ± 377.65 | 112.44–30947.42 | 3930.28 ± 5884.46 |
| Mg/ng m-3 | <LOD–1505.99 | 201.47 ± 304.03 | <LOD–4157.46 | 626.21 ± 835.26 |
| Zn/ng m−3 | 10.03–147.50 | 54.33 ± 32.56 | 5.50–101.75 | 36.52 ± 27.94 |
| Pb/ng m−3 | <LOD–61.66 | 16.74 ± 13.59 | <LOD–35.82 | 14.56 ± 9.22 |
| Ti/ng m−3 | <LOD–79.98 | 18.26 ± 19.53 | 20.30–1476.56 | 210.5 ± 278.85 |
| Mn/ng m−3 | 2.44–78.82 | 13.6 ± 14.69 | 15.97–392.11 | 72.57 ± 72.58 |
| Cu/ng m−3 | 7.32–302.74 | 40.42 ± 51.45 | 6.15–213.67 | 57.41 ± 46.66 |
| Ba/ng m−3 | <LOD–259.67 | 21.62 ± 50.29 | <LOD–252.02 | 31.94 ± 49.33 |
| Sr/ng m−3 | <LOD–25.94 | 3.88 ± 4.89 | 2.25–95.08 | 16.31 ± 18.32 |
| V/ng m−3 | 0.10–2.60 | 0.74 ± 0.66 | 0.42–2.33 | 5.87 ± 7.08 |
| Cd/ng m−3 | 0.34–2.82 | 1.11 ± 0.71 | <LOD–2.47 | 0.87 ± 0.66 |
| Cr/ng m−3 | <LOD–2.65 | 0.31 ± 0.72 | 3.95–30.82 | 8.24 ± 5.34 |
| Co/ng m−3 | <LOD–0.91 | 0.20 ± 0.30 | <LOD–7.99 | 1.26 ± 1.55 |
| Ni/ng m−3 | <LOD–4.14 | 0.19 ± 0.76 | <LOD–20.60 | 3.80 ± 4.09 |
| Mo/ng m−3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD–6.71 | 0.4 ± 1.39 |
| Nd/ng m−3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD–13.72 | 1.88 ± 2.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Temporal Variation and Chemical Components of Rural Ambient PM2.5 during Main Agricultural Activity Periods in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090510
Wu X, Chen W, Zhang S, Li R, Zhang M, Liu J, Jiang Y, Liu Y. Temporal Variation and Chemical Components of Rural Ambient PM2.5 during Main Agricultural Activity Periods in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090510
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuewei, Weiwei Chen, Shichun Zhang, Ruimin Li, Mengduo Zhang, Juan Liu, Yibing Jiang, and Yang Liu. 2019. "Temporal Variation and Chemical Components of Rural Ambient PM2.5 during Main Agricultural Activity Periods in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090510
APA StyleWu, X., Chen, W., Zhang, S., Li, R., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Jiang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2019). Temporal Variation and Chemical Components of Rural Ambient PM2.5 during Main Agricultural Activity Periods in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Atmosphere, 10(9), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090510