Characteristics of PM2.5 at a High-Altitude Remote Site in the Southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in Premonsoon Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aerosol Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
2.3. PM2.5 Source Apportionment
2.4. Concentration-Weighted Trajectory (CWT) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
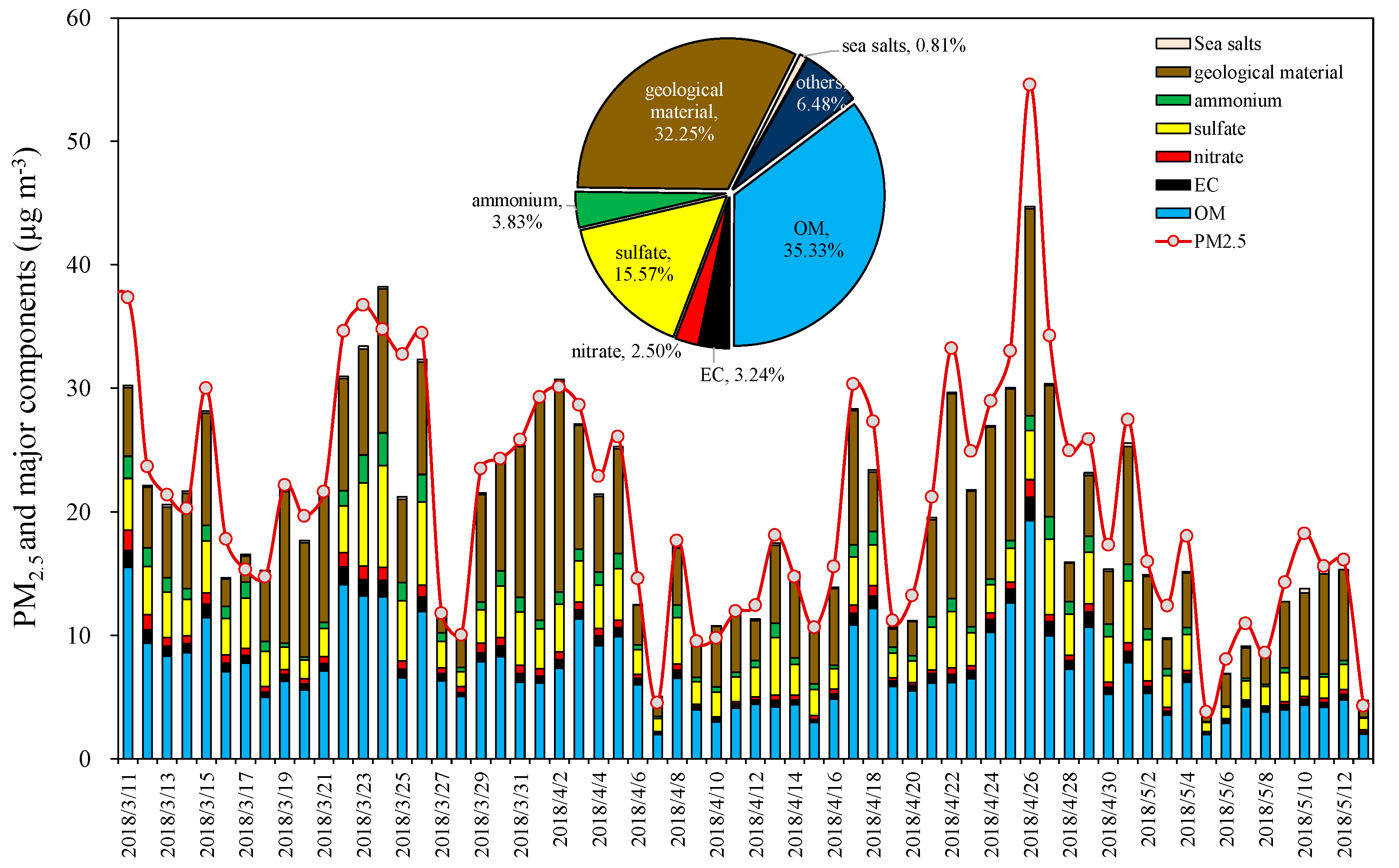
3.1. General Characteristics of PM2.5 and Chemical Compositions
3.1.1. Carbonaceous Aerosol
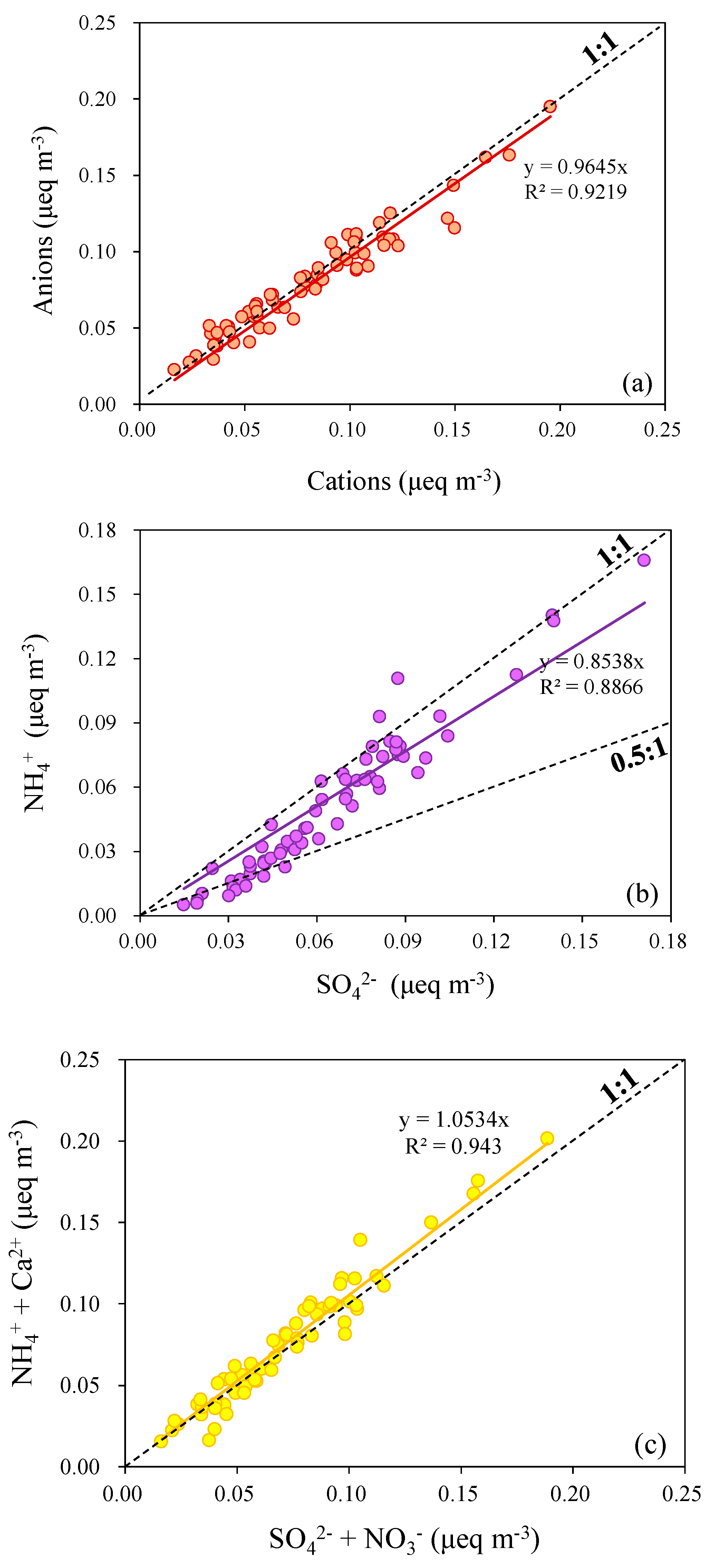
3.1.2. Water-Soluble Ions
3.1.3. Minerals and Trace Elements
3.1.4. Material Balance
3.2. Source Apportionment
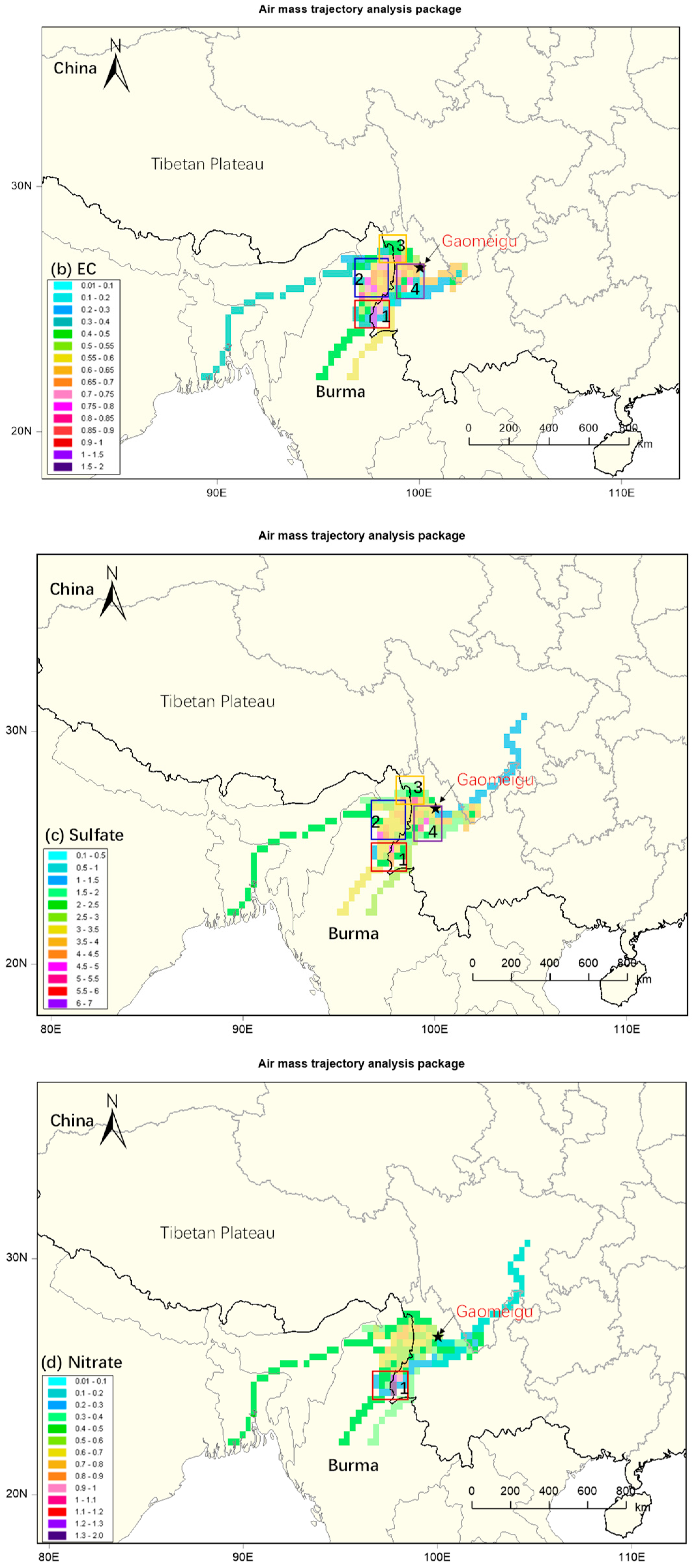
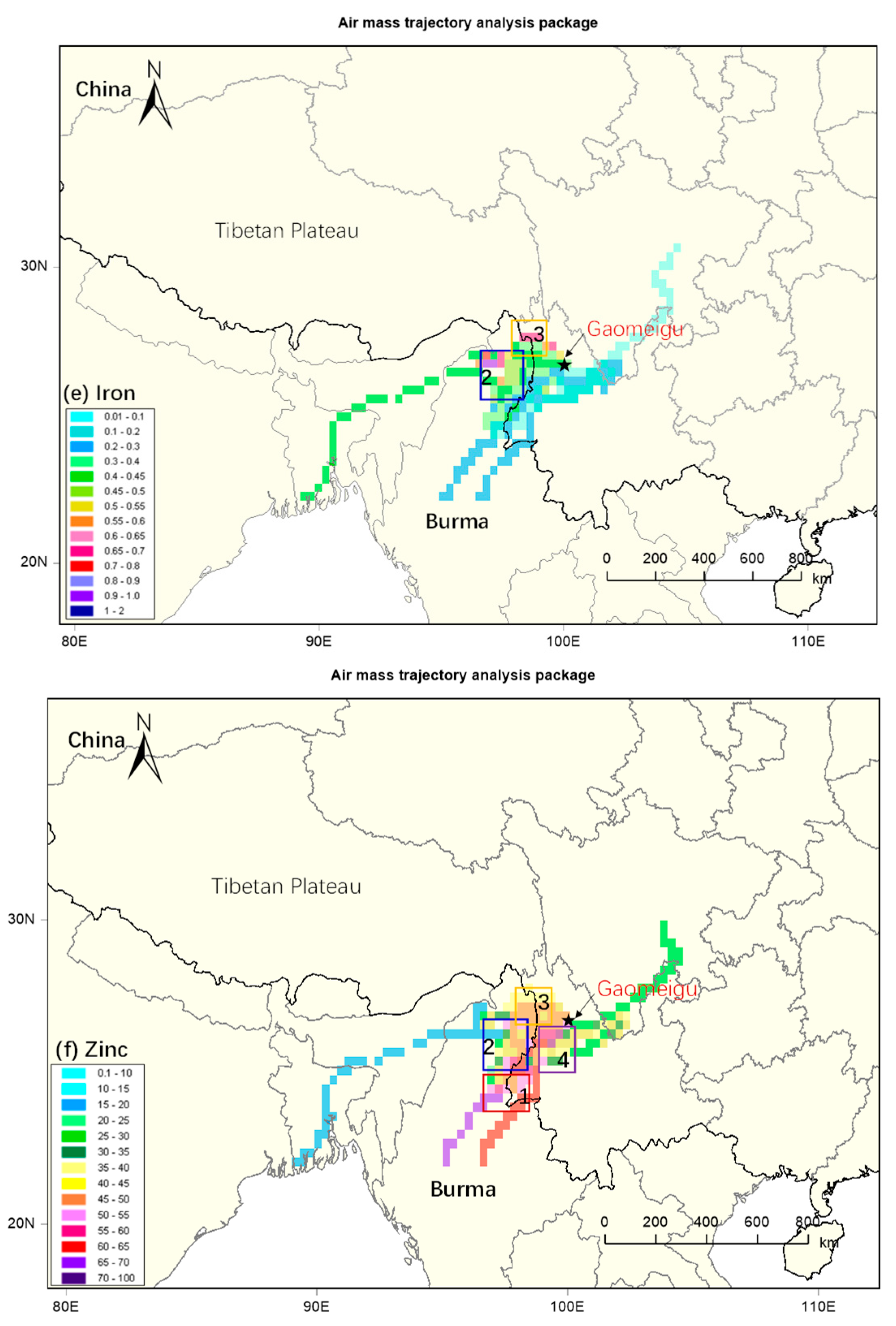
3.3. Identification of Source Regions
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, B.; Cao, J.; Hansen, J.; Yao, T.; Joswia, D.R.; Wang, N.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.B.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; et al. Black soot and the survival of tibetan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22114–22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.K.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, W.-S. Enhanced surface warming and accelerated snow melt in the himalayas and tibetan plateau induced by absorbing aerosols. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.M. Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: The role of the tibetan plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 26, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Xu, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, L.W.A.; Su, X.; Liu, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, G. Aerosol particles at a high-altitude site on the southeast tibetan plateau, china: Implications for pollution transport from south asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11360–11375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bosch, C.; Kang, S.; Andersson, A.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, Z.; Chen, B.; Qin, D.; Gustafsson, O. Sources of black carbon to the himalayan-tibetan plateau glaciers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.-S.; Cao, J.-J.; Hu, T.-F.; Shen, Z.-X.; Tie, X.-X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Močnik, G.; et al. Spectral dependence of aerosol light absorption at an urban and a remote site over the tibetan plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, Z.L.; Bojan, S.; Kim, S.W.; Lauer, A.; Mues, A.; Rupakheti, M.; Kang, S. Atmospheric brown clouds reach the tibetan plateau by crossing the himalayas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 4, 28105–28146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoni, P.; Laj, P.; Angelini, F.; Arduini, J.; Bonafè, U.; Calzolari, F.; Cristofanelli, P.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Fuzzi, S.; et al. The abc-pyramid atmospheric research observatory in himalaya for aerosol, ozone and halocarbon measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 391, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoni, P.; Laj, P.; Marinoni, A.; Sprenger, M.; Angelini, F.; Arduini, J.; Bonafè, U.; Calzolari, F.; Colombo, T.; Decesari, S.; et al. Atmospheric brown clouds in the himalayas: First two years of continuous observations at the nepal climate observatory-pyramid (5079 m). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7515–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Carbone, C.; Giulianelli, L.; Rinaldi, M.; Finessi, E.; Fuzzi, S.; Marinoni, A.; Cristofanelli, P.; Duchi, R.; et al. Chemical composition of pm10 and pm1 at the high-altitude himalayan station nepal climate observatory-pyramid (nco-p) (5079 ma.S.L.). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4583–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, B.; Shen, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhu, C.; Su, X.; Zhao, S.; Long, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Black carbon aerosol and its radiative impact at a high-altitude remote site on the southeastern tibet plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5515–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Kawamura, K.; Liu, B.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Fu, P. Carbonaceous aerosols on the south edge of the tibetan plateau: Concentrations, seasonality and sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Chung, C.; Kim, D.; Bettge, T.; Buja, L.; Kiehl, J.; Washington, W.; Fu, Q.; Sikka, D.; Wild, M. Atmospheric brown clouds: Impacts on south asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, A.; Cristofanelli, P.; Laj, P.; Duchi, R.; Calzolari, F.; Decesari, S.; Sellegri, K.; Vuillermoz, E.; Verza, G.P.; Villani, P.; et al. Aerosol mass and black carbon concentrations, a two year record at nco-p (5079 m, southern himalayas). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8551–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engling, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, C.; Sang, X.F.; Lin, M.; Ho, K.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Lee, J.J. Characterization and sources of aerosol particles over the southeastern tibetan plateau during the southeast asia biomass-burning season. Tellus B 2011, 63, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielpo, P.; Fermo, P.; Comite, V.; Mastroianni, D.; Viviano, G.; Salerno, F.; Tartari, G. Chemical characterization of biomass fuel particulate deposits and ashes in households of mt. Everest region (nepal). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ram, K.; Fu, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Stone, E.A.; Pradhan, B.B.; Dangol, P.M.; Panday, A.K.; et al. Water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric aerosols from godavari (nepal), a regional representative of south Asia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Barros, A.P.; Khlystov, A. Chemical composition and aerosol size distribution of the middle mountain range in the nepal himalayas during the 2009 pre-monsoon season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11605–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellegri, K.; Laj, P.; Venzac, H.; Boulon, J.; Picard, D.; Villani, P.; Bonasoni, P.; Marinoni, A.; Cristofanelli, P.; Vuillermoz, E. Seasonal variations of aerosol size distributions based on long-term measurements at the high altitude himalayan site of nepal climate observatory-pyramid (5079 m), nepal. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 6537–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, S.; Laj, P.; Roger, J.C.; Villani, P.; Sellegri, K.; Bonasoni, P.; Marinoni, A.; Cristofanelli, P.; Verza, G.P.; Bergin, M. Aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing in the high himalaya based on measurements at the nepal climate observatory-pyramid site (5079ma.S.L.). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5859–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yan, F.; Kang, S.; Chen, P.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Qu, B.; Sillanpää, M. Light absorption characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in two remote stations of the southern fringe of the tibetan plateau, china. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Xiao, C.; Sun, J.; Kang, S.; Bonasoni, P. Carbonaceous particles in the atmosphere and precipitation of the nam co region, central tibet. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Luo, C.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Gao, S.; Li, X. Trace elements and lead isotopic composition of pm10 in lhasa, tibet. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6210–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Hu, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, S. Chemical composition of pm2.5 at a high-altitude regional background site over northeast of tibet plateau. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Cheng, C.; Cao, J. Atmospheric oxalic acid and related secondary organic aerosols in qinghai lake, a continental background site in tibet plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Xu, B.Q.; He, J.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Zhu, C.S. Concentrations, seasonal variations, and transport of carbonaceous aerosols at a remote mountainous region in western china. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4444–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Tie, X.X.; Xu, B.Q.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Zhu, C.S.; Li, G.H.; Liu, S.X. Measuring and modeling black carbon (bc) contamination in the se tibetan plateau. J. Atmos. Chem. 2010, 67, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Vecchi, R.; Valli, G.; Ceriani, M. A tga/ft-ir study for measuring oc and ec in aerosol samples. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccia, E.; Massabò, D.; Ariola, V.; Bove, M.C.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Prati, P. Size-resolved comprehensive characterization of airborne particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J.P. Toward a standardised thermal-optical protocol for measuring atmospheric organic and elemental carbon: The eusaar protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.T.; Pabroa, P.C.B.; Santos, F.L.; Quirit, L.L.; Asis, J.L.B.; Dy, M.A.K.; Martinez, J.P.G. Intercomparison between NIOSH, IMPROVE_a, and EUSAAR_2 protocols: Finding an optimal thermal—Optical protocol for philippines oc/ec samples. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Ng, W.; Griffith, S.; Yu, J. Inter-comparison of niosh and improve protocols for oc and ec determination: Implications for inter-protocol data conversion. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2016, 9, 4547–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Crow, D.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Merrifield, T. Comparison of improve and niosh carbon measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Chen, L.W.A.; Arnott, W.P.; Moosmüller, H.; Fung, K. Equivalence of elemental carbon by thermal/optical reflectance and transmittance with different temperature protocols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cao, J.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; An, Z.; Jin, Z.; Fung, K.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for discrimination between char- and soot-ec. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Robles, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Trimble, D.L.; Kohl, S.D.; Tropp, R.J.; Fung, K.K. Quality assurance and quality control for thermal/optical analysis of aerosol samples for organic and elemental carbon. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.; Tie, X.; Shen, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Ho, K.; Qiang, J. Water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols measured in xi’an, china: Seasonal variations and sources. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cao, J.; Chow, J.C.; Huang, R.J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, L.W.A.; Ho, K.F.; Watson, J.G. Inter-annual variability of wintertime pm2.5 chemical composition in xi’an, china: Evidences of changing source emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Cao, J.J.; Ho, K.F.; Ding, H.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Khol, S.D. Lead concentrations in fine particulate matter after the phasing out of leaded gasoline in xi’an, china. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Chen, A.L.W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Tian, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, C.; et al. Multi-wavelength light absorption of black and brown carbon at a high-altitude site on the southeastern margin of the tibetan plateau, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.A.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Watson, J.G.; Koracin, D.; Kumar, N.; Knipping, E.M.; Wheeler, N.; Craig, K.; Reid, S. Toward effective source apportionment using positive matrix factorization: Experiments with simulated pm2.5 data. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belis, C.A.; Pikridas, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Petralia, E.; Cavalli, F.; Calzolai, G.; Berico, M.; Sciare, J. Source apportionment of fine pm by combining high time resolution organic and inorganic chemical composition datasets. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 3, 116816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.; Eberly, S.; Paatero, P.; Norris, G.A. Methods for estimating uncertainty in pmf solutions: Examples with ambient air and water quality data and guidance on reporting pmf results. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Hopke, P.K.; Song, X.-H.; Ramadan, Z. Understanding and controlling rotations in factor analytic models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 60, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. Trajstat: Gis-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, R.; Draxler, G.D.H. An overview of the HYSPIT_4 modelling system for trajectories, dispersion and deposition. Aust. Met. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhu, C.; Ni, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Z.; Han, Y.; Cao, J. Seasonal transport and dry deposition of black carbon aerosol in the southeastern tibetan plateau. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Pongpiachan, S.; Zhang, N.; Han, Y.; Tian, J.; Wu, C.; Long, X.; et al. High contribution of secondary brown carbon to aerosol light absorption in the southeastern margin of tibetan plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 4962–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Eddleman, H.; Novakov, T. Towards the development of a global inventory for black carbon emissions. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 1277–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassura, I.; Venturini, E.; Marchetti, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Bernardi, E.; Fermo, P.; Passarini, F. Markers and influence of open biomass burning on atmospheric particulate size and composition during a major bonfire event. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during scaqs. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Cao, J.-J.; Tsai, C.-J.; Chou, C.C.K.; Liu, S.-C.; Roam, G.-D. Characterization of carbon fractions for atmospheric fine particles and nanoparticles in a highway tunnel. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Lee, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Ho, K.F.; An, Z.S. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of char-ec and soot-ec in the atmosphere over china. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6066–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Soot carbon and excess fine potassium: Long-range transport of combustion-derived aerosols. Science 1983, 220, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kaspari, S. Major ionic composition of precipitation in the nam co region, central tibetan plateau. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, K.; Sarin, M.M. Day-night variability of ec, oc, wsoc and inorganic ions in urban environment of indo-gangetic plain: Implications to secondary aerosol formation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Arimoto, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Du, N.; Okuda, T.; Nakao, S.; Tanaka, S. Seasonal variations and evidence for the effectiveness of pollution controls on water-soluble inorganic species in total suspended particulates and fine particulate matter from xi’an, china. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre, C.N.E.M. Environmental Background Values of Soil in China; China Environmental Science Press: Hangzhou, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M. Pm2.5, ec and oc in atmospheric outflow from the indo-gangetic plain: Temporal variability and aerosol organic carbon-to-organic mass conversion factor. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciare, J.; Oikonomou, K.; Cachier, H.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Andreae, M.O.; Maenhaut, W.; Sarda-Estève, R. Aerosol mass closure and reconstruction of the light scattering coefficient over the eastern mediterranean sea during the minos campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Li, J.S.; Yan, J.G. Integrated information ore-finding model and direction in the south-central segment of the “sanjiang metallogenic belt”, southwestern China. Geol. China 2008, 35, 101–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Green, M.C.; Chen, L.W.A.; DuBois, D.W.; Molenar, J.V. Fine particulate matter and visibility in the lake tahoe basin: Chemical characterization, trends, and source apportionment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, L.Q.; Tang, J.X.; Danzhen, W.X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Geological characteristics of lead-zinc ore deposits in qinghai-tibet plateau. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 83–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Study on the Characteristics and Metallogenic Conditions of Copper-Polymetallic Deposits in Middle-Northern Lanpin Basin, Western Yunnan. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Win, S.; Myint, M.M. Mineral potential of myanmar. Resour. Geol. 1998, 48, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Cao, J.; Ho, K.; He, Y. Chemical characterization of aerosol collected at mt. Yulong in wintertime on the southeastern tibetan plateau. Atmos. Res. 2012, 107, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, J.M.; Pacyna, E.G. An assessment of global and regional emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources worldwide. Environ. Rev. 2011, 9, 269–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Sources of fine organic aerosol. 3. Road dust, tire debris, and organometallic brake lining dust: Roads as sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Components | AVE | STD | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | PM2.5 | 20.99 | 9.80 | 3.79 | 54.57 |
| Carbonaceous species | OC | 3.92 | 1.94 | 1.09 | 10.55 |
| EC | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 1.91 | |
| POC | 2.97 | 1.56 | 0.43 | 8.36 | |
| SOC | 0.97 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 2.91 | |
| char-EC | 0.56 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 1.46 | |
| soot-EC | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.45 | |
| Water-soluble inorganic ions | F− | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Cl− | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.22 | |
| NO2− | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.15 | |
| NO3− | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 1.64 | |
| SO42− | 3.10 | 1.49 | 0.71 | 8.21 | |
| Na+ | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.16 | |
| NH4+ | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 2.65 | |
| K+ | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.001 | 0.37 | |
| Mg2+ | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.21 | |
| Ca2+ | 0.53 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 1.30 | |
| Elements | Ca | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 1.83 |
| Fe | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.94 | |
| Ti (ng m−3) | 35.85 | 23.49 | 1.17 | 102.91 | |
| Mn (ng m−3) | 9.21 | 4.92 | 1.93 | 21.52 | |
| Ni (ng m−3) | 2.29 | 1.60 | 0.38 | 5.07 | |
| Cu (ng m−3) | 28.14 | 13.70 | 6.88 | 73.24 | |
| As (ng m−3) | 3.85 | 3.09 | 0.38 | 15.66 | |
| Ba (ng m−3) | 14.37 | 7.30 | 0.78 | 26.57 | |
| Pb (ng m−3) | 5.78 | 2.48 | 1.34 | 12.63 | |
| Zn (ng m−3) | 46.76 | 22.21 | 0.78 | 88.25 | |
| Br (ng m−3) | 4.81 | 2.23 | 0.77 | 11.86 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Han, Y.; Ye, Z.; Pongpiachan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Tian, R.; Cao, J. Characteristics of PM2.5 at a High-Altitude Remote Site in the Southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in Premonsoon Season. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110645
Zhao Z, Wang Q, Li L, Han Y, Ye Z, Pongpiachan S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Tian R, Cao J. Characteristics of PM2.5 at a High-Altitude Remote Site in the Southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in Premonsoon Season. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(11):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110645
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhuzi, Qiyuan Wang, Li Li, Yongming Han, Zhaolian Ye, Siwatt Pongpiachan, Yong Zhang, Suixin Liu, Ruixia Tian, and Junji Cao. 2019. "Characteristics of PM2.5 at a High-Altitude Remote Site in the Southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in Premonsoon Season" Atmosphere 10, no. 11: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110645
APA StyleZhao, Z., Wang, Q., Li, L., Han, Y., Ye, Z., Pongpiachan, S., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Tian, R., & Cao, J. (2019). Characteristics of PM2.5 at a High-Altitude Remote Site in the Southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in Premonsoon Season. Atmosphere, 10(11), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110645








