Spatio-Temporal Variations of Multiple Primary Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing of China, 2006–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Classification of Air Pollution Sources and Calculation Methods
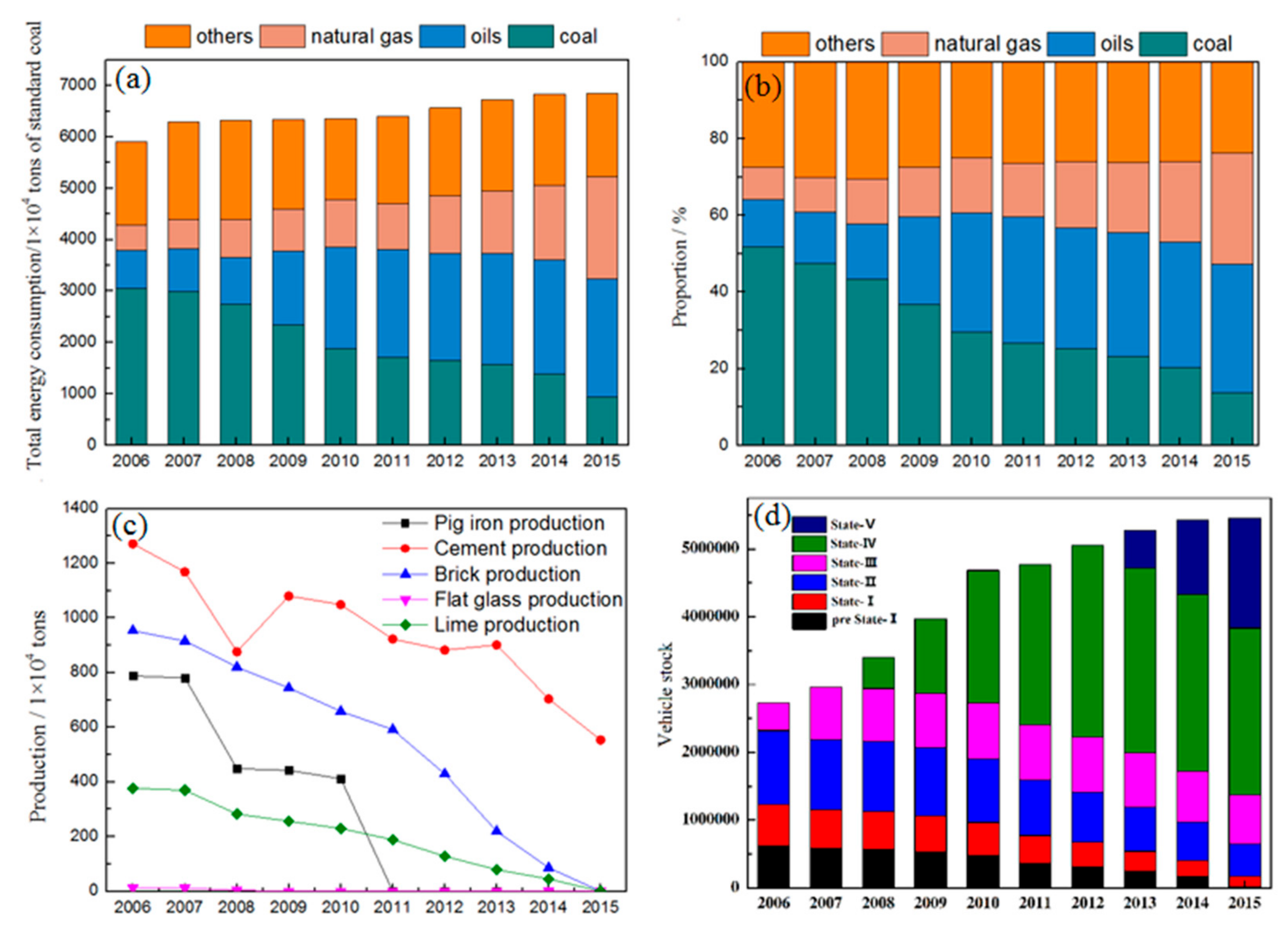
2.2. Activity Levels
2.3. Emission Factors (EFs)
2.4. Spatial Allocation
2.5. Uncertainty Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
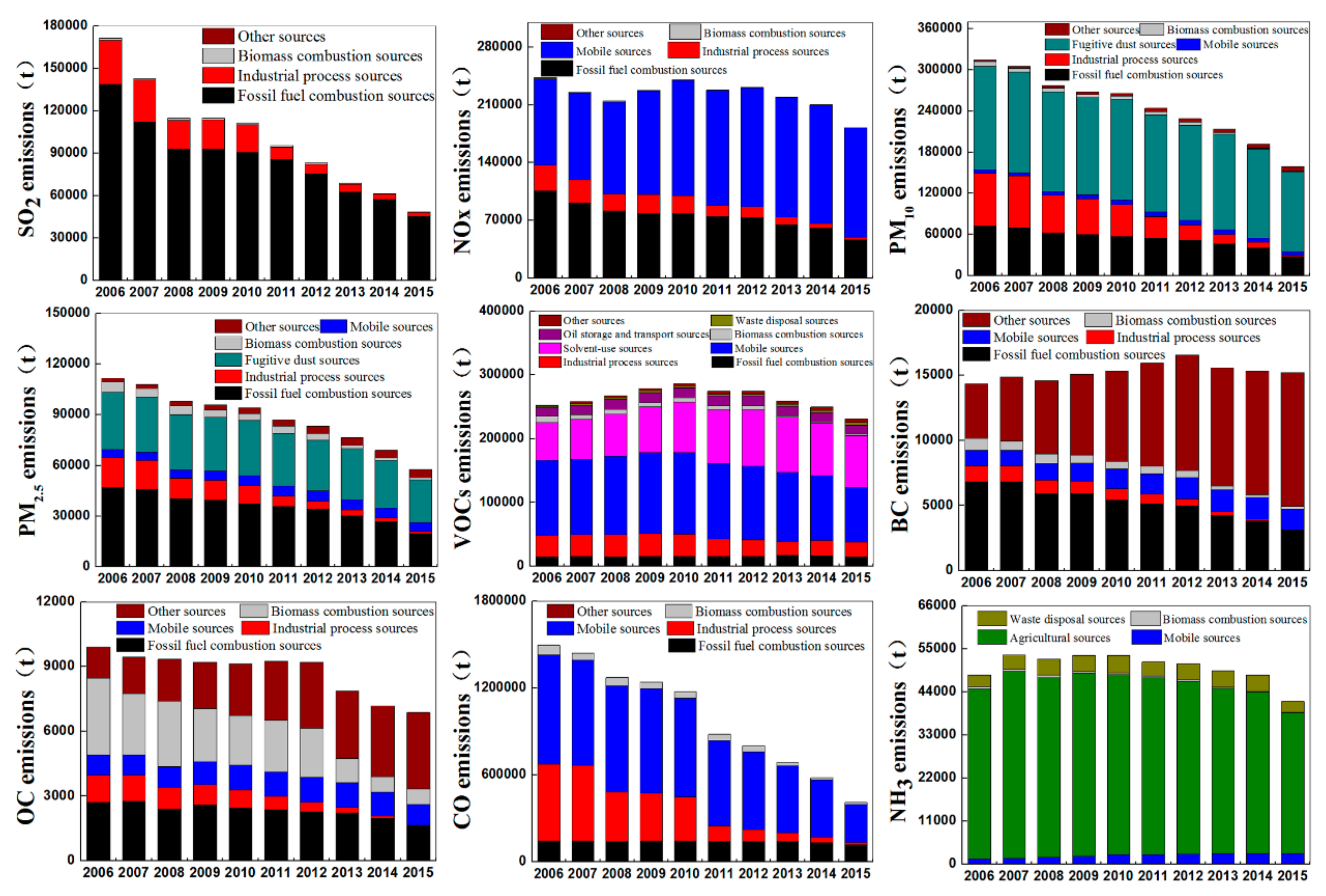
3.1. Temporal Trends of Multiple Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing
3.2. Contribution of Different Pollution Sources
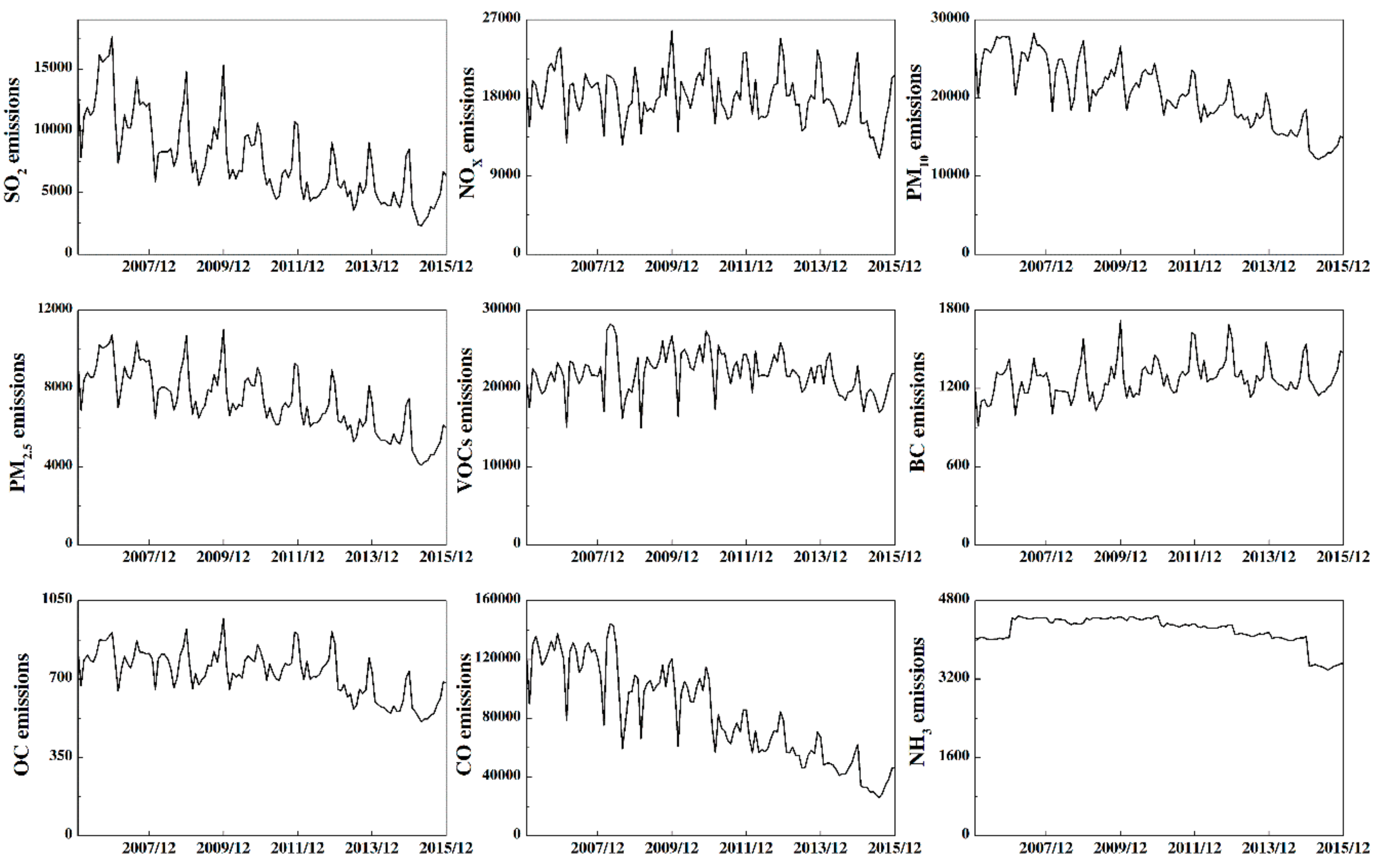
3.3. Monthly Variation Profiles and Characteristics
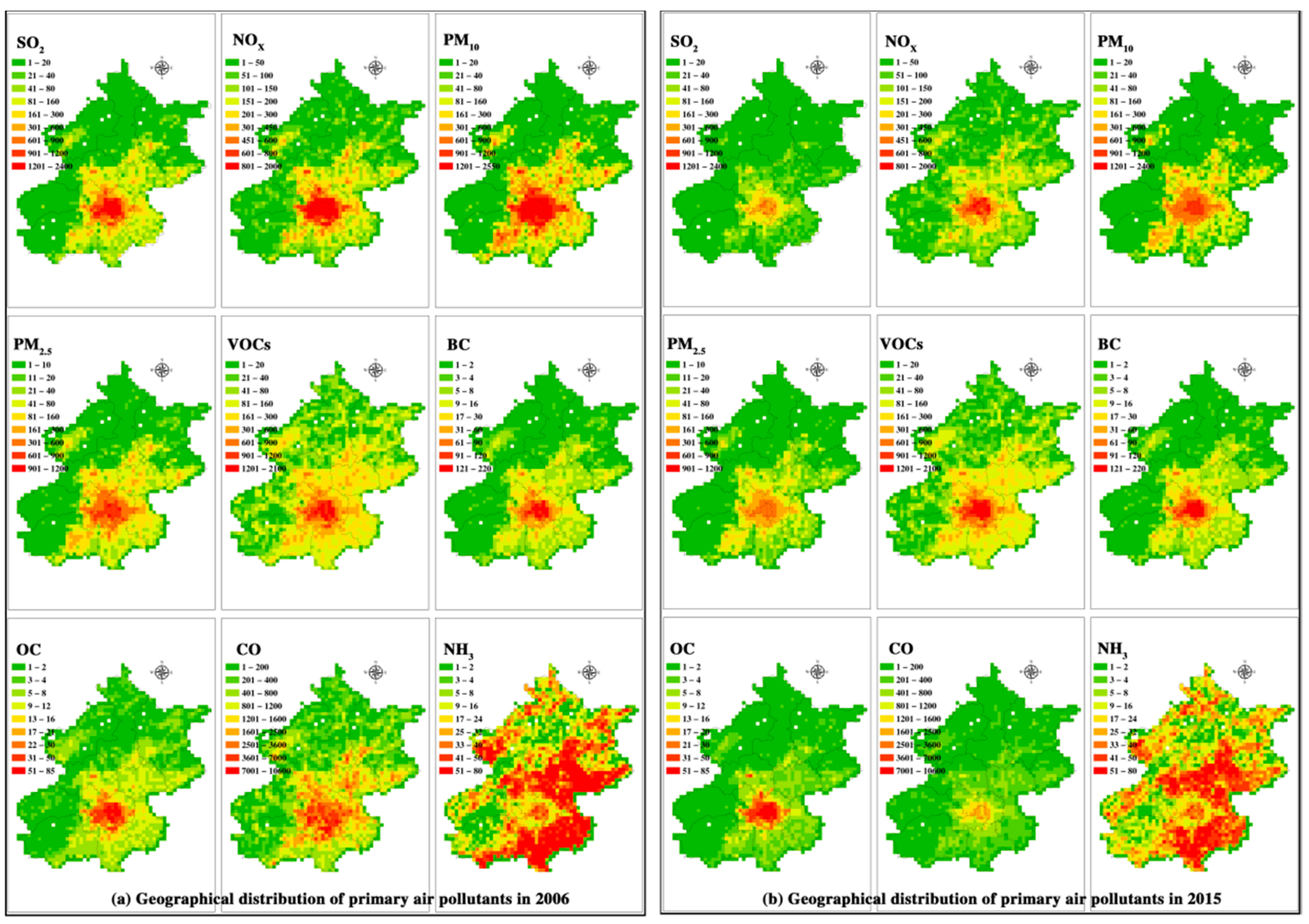
3.4. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
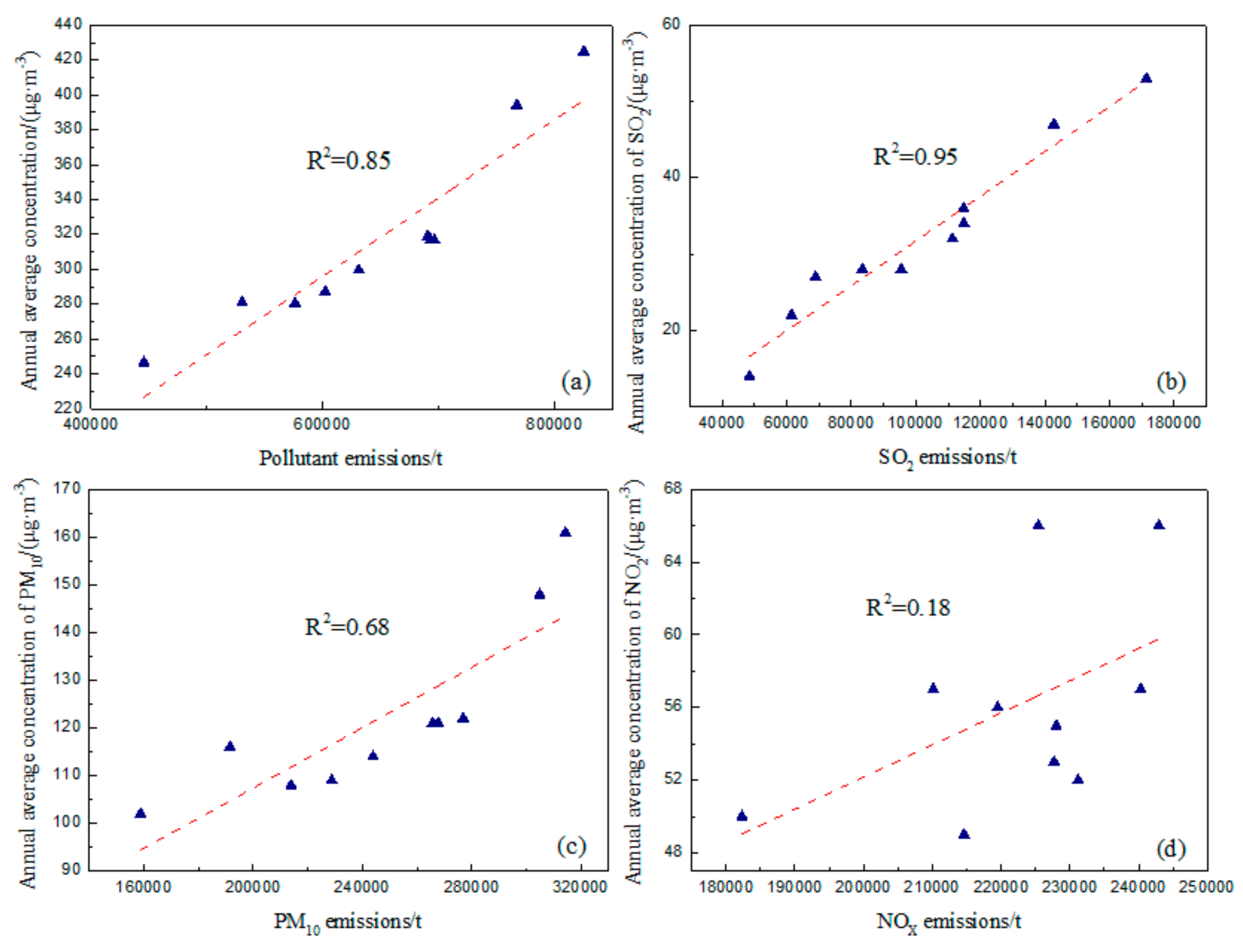
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Pollutant Emissions and Annual Average Pollutant Concentration
3.6. Uncertainty Analysis for Emission Inventory
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matter, J.M.; Stute, M.; Snaebjornsdottir, S.O.; Oelkers, E.H.; Gislason, S.R.; Aradottir, E.S.; Sigfusson, B.; Gunnarsson, I.; Sigurdardottir, H.; Gunnlaugsson, E.; et al. Rapid carbon mineralization for permanent disposal of anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions. Science 2016, 352, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Tian, S.L.; Liu, D.W.; Fang, Y.T.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Michalski, G.; Wang, Y.S. Fossil Fuel Combustion-Related Emissions Dominate Atmospheric Ammonia Sources during Severe Haze Episodes: Evidence from N-15-Stable Isotope in Size-Resolved Aerosol Ammonium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8049–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Chou, C.K. Satellite-Derived Correlation of SO2, NO2, and Aerosol Optical Depth with Meteorological Conditions over East Asia from 2005 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, T.; Wang, K.; Nie, L.; Pan, T.; Wu, X.Q.; Tian, H.Z.; Zhong, L.H.; Li, J.; et al. Trends of multiple air pollutants emissions from residential coal combustion in Beijing and its implication on improving air quality for control measures. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Koo, J.H. Arctic sea ice, Eurasia snow, and extreme winter haze in China. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, C.B.B.; Foltescu, V.; Leeuw, F.D. Air quality status and trends in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklinska, K.; Wolska, L.; Namiesnik, J. Air quality policy in the U.S. and the EU—A review. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Driscoll, C.T.; Beier, C.M.; Burtraw, D.; Fernandez, I.J.; Galloway, G.N.; Gay, D.A.; Goodale, C.L.; Likens, G.E.; Lovett, G.M.; et al. Air pollution success stories in the United States: The value of long-term observations. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 84, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.M.; Xu, X.H.; Ying, Z.K.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, M.H.; Wang, A.X.; Chen, L.C.; Lu, B.; Sun, Q.H. Post-Effect of Air Quality Improvement on Biomarkers for Systemic Inflammation and Microparticles in Asthma Patients After the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games: a Pilot Study. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.T.; Tong, Y.F.; Cui, L.; Kong, X.M.; Sheng, Y.N.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.P. Population-production-pollution nexus based air pollution management model for alleviating the atmospheric crisis in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, S.Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.M.; Wang, X.Q.; Jia, J.; Lang, J.L.; Lv, Z. Characteristics and emission-reduction measures evaluation of PM2.5 during the two major events: APEC and Parade. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xi, F.; Zhu, L.; Bing, L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, B.; Guan, D. The spatiotemporal features of Greenhouse Gases Emissions from Biomass Burning in China from 2000–2012. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, S0959652618302348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Su, J.P.; Cui, T.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Sun, F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, Y.X.; Li, Y.S.; et al. Dominant role of emission reduction in PM2.5 air quality improvement in Beijing during 2013–2017: A model-based decomposition analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6125–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.B. Technical Manual for the Preparation of Urban Air Pollutants Emission Inventory; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, D.; Chen, C.C.; Hong, C.P.; Li, M.; Geng, G.N.; Lei, Y.; Huo, H.; He, K.B. Resolution dependence of uncertainties in gridded emission inventories: A case study in Hebei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Yu, F.; Chen, C.C.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.F.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.B. A high-resolution air pollutants emission inventory in 2013 for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.X.; Zhao, S.D.; He, L.H.; Liu, H.J.; Xu, H. Temporal and spatial trends in air quality in Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 185, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMBS (Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics). Beijing Statistical Yearbook. 2007. Available online: http://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/nj/main/2007/index.htm (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- BMBS (Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics). Beijing Statistical Yearbook. 2016. Available online: http://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/nj/main/2016-tjnj/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Jing, B.Y.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.J.; Gong, S.N.; He, J.J.; Zou, C.; Song, G.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, Z. Development of a vehicle emission inventory with high temporal–spatial resolution based on NRT traffic data and its impact on air pollution in Beijing—Part 1: Development and evaluation of vehicle emission inventory. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, C.Y.; Yuan, W.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.J. High-resolution vehicle emission inventory and emission control policy scenario analysis, a case in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Wu, B.B.; Liu, S.H.; Shao, P.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Xue, Y.F.; Gao, J.J.; et al. A regional high-resolution emission inventory of primary air pollutants in 2012 for Beijing and the surrounding five provinces of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.Y.; Fu, K.; Klimont, Z.; Hao, J.M.; He, K.B.; Cofala, J.; Amann, M. NOx emissions in China: historical trends and future perspectives. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 16047–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.P.; Tian, H.Z.; Zhu, C.Y.; Liu, K.; Gao, J.J.; Zhou, J.R. An elaborate high resolution emission inventory of primary air pollutants for the Central Plain Urban Agglomeration of China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Zhu, C.Y.; Gao, J.J.; Cheng, K.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.R. Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10127–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Tian, H.Z.; Hao, Y.; Gao, J.J.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Hua, S.B.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.J. A high-resolution emission inventory of anthropogenic trace elements in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN (United Nation) Environment. A Review of 20 Years’ Air Pollution Control in Beijing. 2019. Available online: http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/ztzl/bj20ndqwrzllcyzw/index.html (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, L.L.; Petäjä, T.; Zha, Q.Z.; Gong, C.S.; Li, S.X.; Pan, Y.P.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.Y.; et al. Increased inorganic aerosol fraction contributes to air pollution and haze in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5881–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Liu, M.X.; Zhang, M.S.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, T.T.; Wang, T.T.; Yan, C.Q.; Zhou, T.; et al. High efficiency of livestock ammonia emission controls in alleviating particulate nitrate during a severe winter haze episode in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5605–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zheng, H.T.; Wang, S.X.; Smith, K.R.; Lu, X.; Aunan, K.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, D.; Xing, J.; et al. Change in household fuels dominates the decrease in PM2.5 exposure and premature mortality in China in 2005–2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12401–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Emission Source | Uncertainty Range (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | NOX | PM10 | PM2.5 | VOCs | BC | OC | CO | NH3 | |
| FCS | (−21%,30%) | (−45%,46%) | (−31%,41%) | (−34%,46%) | (−61%,64%) | (−22%,29%) | (−21%,28%) | (−32%,40%) | |
| IPS | (−25%,36%) | (−55%,52%) | (−38%,54%) | (−40%,55%) | (−75%,73%) | (−27%,35%) | (−26%,35%) | (−40%,45%) | |
| MS | (−62%,74%) | (−38%,66%) | (−46%,70%) | (−73%,98%) | (−39%,60%) | (−36%,57%) | (−56%,70%) | (−50%,71%) | |
| SUC | (−69%,76%) | ||||||||
| AS | (−58%,83%) | ||||||||
| FDS | (−75%,84%) | (−72%,86%) | |||||||
| BCS | (−55%,79%) | (−64%,69%) | (−43%,64%) | (−48%,69%) | (−84%,94%) | (−35%,50%) | (−33%,48%) | (−51%,62%) | (−61%,77%) |
| OSS | (−62%,71%) | ||||||||
| WDS | (−26%,48%) | (−20%,29%) | |||||||
| OS | (−31%,44%) | (−50%,51%) | (−34%,48%) | (−37%,52%) | (−67%,70%) | (−25%,35%) | (−24%,34%) | (−37%,44%) | (−50%,59%) |
| Total | (−20%,29%) | (−41%,44%) | (−39%,54%) | (−42%,57%) | (−67%,78%) | (−22%,32%) | (−21%,30%) | (−33%,39%) | (−27%,36%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Shi, A.; Xu, K.; Tian, H. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Multiple Primary Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing of China, 2006–2015. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090494
Xue Y, Zhang S, Zhou Z, Wang K, Liu K, Wang X, Shi A, Xu K, Tian H. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Multiple Primary Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing of China, 2006–2015. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090494
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yifeng, Shihao Zhang, Zhen Zhou, Kun Wang, Kaiyun Liu, Xiaoyan Wang, Aijun Shi, Kangli Xu, and Hezhong Tian. 2019. "Spatio-Temporal Variations of Multiple Primary Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing of China, 2006–2015" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090494
APA StyleXue, Y., Zhang, S., Zhou, Z., Wang, K., Liu, K., Wang, X., Shi, A., Xu, K., & Tian, H. (2019). Spatio-Temporal Variations of Multiple Primary Air Pollutants Emissions in Beijing of China, 2006–2015. Atmosphere, 10(9), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090494






