Abstract
This paper describes the use of citizen science-derived data for the creation of a land-use regression (LUR) model for particulate matter (PM2.5 and PMcoarse) for a vulnerable community in Imperial County, California (CA), near the United States (US)/Mexico border. Data from the Imperial County Community Air Monitoring Network community monitors were calibrated and added to a LUR, along with meteorology and land use. PM2.5 and PMcoarse were predicted across the county at the monthly timescale. Model types were compared by cross-validated (CV) R2 and root-mean-square error (RMSE). The Bayesian additive regression trees model (BART) performed the best for both PM2.5 (CV R2 = 0.47, RMSE = 1.5 µg/m3) and PMcoarse (CV R2 = 0.65, RMSE = 8.07 µg/m3). Model predictions were also compared to measurements from the regulatory monitors. RMSE for the monthly models was 3.6 µg/m3 for PM2.5 and 17.7 µg/m3 for PMcoarse. Variable importance measures pointed to seasonality and length of roads as drivers of PM2.5, and seasonality, type of farmland, and length of roads as drivers of PMcoarse. Predicted PM2.5 was elevated near the US/Mexico border and predicted PMcoarse was elevated in the center of Imperial Valley. Both sizes of PM were high near the western edge of the Salton Sea. This analysis provides some of the initial evidence for the utility of citizen science-derived pollution measurements to develop spatial and temporal models which can make estimates of pollution levels throughout vulnerable communities.
1. Introduction
Both PM2.5 (particulate matter less than 2.5 μm in diameter) and PM10 (particulate matter less than 10 μm in diameter) are linked to adverse health outcomes such as respiratory and cardiac disease, asthma, and increased mortality [1,2,3,4]. PMcoarse is the difference between PM10 and PM2.5 and, as such, represents a different size fraction than PM2.5, whereas PM10 overlaps with PM2.5. The United States (US) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) refers to particles between 2.5 and 10 μm in diameter as “PMcoarse” [5]. Studying PMcoarse rather than PM10 is, therefore, useful for understanding sources specifically associated with larger particle sizes.
PM differs spatially based on proximity to sources and air pollution transport. However, the ability to collect highly spatially resolved PM measurements is often limited by the number of monitors. This led to the use of modeling to estimate PM concentrations at locations and, for temporally varying data, at times when measurements are not available. One technique used to estimate PM exposure for a population is called land-use regression (LUR). LUR involves modeling PM using a combination of land-use variables such as traffic, area of land types, and distance to known sources. LUR models produce a continuous surface across the study area and can provide accurate PM exposure estimates [6,7]. Eeftens et al. used LUR modeling to predict PM2.5 and PMcoarse across 20 European cities, using the resulting predicted pollution surfaces to estimate PM exposure for a cohort involved in the European Study of Cohorts of Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE) study [6]. Hoek et al. [7] reviewed 25 studies that used LUR models to predict air pollution levels including PM. Most studies employed a series of two-week sampling periods and estimated annual averages. The authors suggest that continuous sampling could help inform shorter-timescale models.
In this paper, a land-use regression model was developed for Imperial County, California (CA), a rural agricultural community in southeast California with a population of around 180,000 [8]. Imperial County has the second highest rate of childhood asthma emergency room visits in the state [9]. It is the home of a primarily Latino population (84%) and has some of the highest rates of unemployment (47%) and poverty (24%) in the nation [8]. The primary sources of air pollution are wind-borne dust, agricultural burning, mobile emissions from cars, trucks, and heavy-duty vehicles, and air pollution transport from Mexicali, Mexico, a city adjacent to the US/Mexico border [10,11,12]. The land-use regression model uses data from the Imperial County Community Air Monitoring Network (“the network”). The network was created through a collaboration between a local community group, Comite Civico del Valle (CCV), the Tracking California Program of the Public Health Institute, and academics at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the University of Washington [13]. The network consists of 40 custom air quality monitors with Dylos particle counters (Dylos Corporation, Riverside, CA), which measure both PM2.5 and PM10, and a relative humidity and temperature sensor. The network is one of the largest community-based air monitoring networks in the US and is considered the first community-designed network of its size in the world [14]. Carvlin et al. showed an R2 between the community monitor and regulatory monitors of 0.79 (hourly) and 0.84 (daily) for PM2.5 and 0.78 (hourly) and 0.81 (daily) for PM10 [15].
The LUR model described herein uses a combination of land-use variables and meteorology. Leave-one-out cross-validated root-mean-square error (RMSE) was used to compare between four different model types. After the model was selected, variable importance statistics were calculated. The goal of this LUR model was to create a two-dimensional (2D) air pollution map at the monthly scale for both PM2.5 and PMcoarse. The predictions were compared to PM measurements made by regulatory monitors as an independent test of the LUR model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Building
The particle counter used in the community monitors was a modified Dylos 1700. The firmware was changed to increase the number of particle size bins from two to four (>0.5 μm, >1.0 μm, >2.5 μm, and >10 μm). A custom circuit board was designed to interface the Dylos with an Arduino Yun to add networking capabilities. The circuit board also integrated a Honeywell HIH 6300 temperature and relative humidity sensor (Honeywell, Charlotte, NC, USA). Each Arduino Yun was then connected to either Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or a T-Mobile cellular modem.
In previous work, we collocated a monitor at the California Air Resources Board (CARB) Calexico-Ethel site, located at the Calexico High School on East Belcher Street, which collects reference measurements of PM from both Federal Equivalent Method (FEM) beta-attenuation monitors (BAMs) and Federal Reference Method (FRM) filter-based gravimetric samplers. By comparing FEM and FRM data with data from the community air monitors, an equation for estimating mass concentrations from the Dylos particle count concentrations was developed. The calibration equation was validated by comparing calibrated monitor results with PM2.5 measured by collocated reference instruments at six other sites. The process was previously described in detail [15].
Community monitoring PM2.5, PM10, relative humidity, and temperature data from 35 sites for a 12-month period, 1 October 2016 to 1 October 2017, were used in the following analyses. Relative humidity is known to change particle size due to the addition or subtraction of water from particles [16]. Since temperature and relative humidity were moderately correlated, only relative humidity was included in the conversion equation. The PM data were converted from particle counts to particle mass as detailed in Carvlin et al. [15]. However, the conversion equation was updated using data from the Calexico-Ethel site for the 12-month study period. The previous PM10 conversion equation used data from 15 January 2016 to 12 July 2016. The conversion equation differed from the previous equation as we used new conversion constants based on the new time period: for PM10, c1 = 9.35, c2 = 0.216, c3 = −0.344; for PM2.5, c1 = 5.41, c2 = 0.00831, c3 = −0.224. PMcoarse was calculated as PM10 − PM2.5. The respective conversion equations used for PM2.5 and PM10 were as follows:
where β0 is the intercept, RH is the relative humidity as measured by the RH sensor on our custom circuit board, and e is the residual error. The factors c1, c2, and c3 were used in the inversion of the model to estimate BAM equivalent PM concentrations from Dylos measurements, as described in Carvlin et al. [15].
Dylosbin1 = β0 + β1BAMPM2.5 + β2RH + e(),
Dylosbin3 = β0 + β1BAMPM10 + β2RH + e(),
As a part of the conversion process, data were run through an automated quality control (QC) process; hours with less than 75% of data and data with particle counts less than 30 in Dylos bin 1 were discarded. After the automatic QC, a manual QC process was performed to identify time periods when the monitor response was slowly attenuated due to incremental dust build-up on the photodiode and when the monitor readings were oscillating rapidly between high and low, which resulted in a further 1.2% of data being dropped. The conversion equation can produce negative numbers, which were used as is in the following analyses unless otherwise noted. Hourly PM2.5 and PMcoarse data were averaged to monthly data using a 50% data completeness cutoff. This left a total of 207 monthly data points across 33 monitors. Each monitor had six months of data on average; however, some monitors had only a few months. The monitors that had the least amount of data were those near the Salton Sea. These monitors have poor cell reception and are subject to harsher environmental conditions, which leads to lower data completeness.
Regulatory data were downloaded from the California Air Resources Board (CARB) website. The regulatory network consists of five sites located near population centers in Imperial Valley that have Met One 1020 PM10 beta attenuation monitors (BAMs) (Met One, Grants Pass, OR, USA) [17]. Two of these sites also have Met One 1020 PM2.5 BAMs. There are also five sites located around the Salton Sea that are operated by the Imperial Irrigation District that have PM2.5 and PM10 Thermo Fischer Scientific Series 1405-D tapered element oscillating microbalances (TEOMs) (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) [18]. These sites were set up to monitor emissions from the Salton Sea as it recedes due to changes in water rights that reduced the agricultural runoff that kept the sea from evaporating. Only QC screened data were used. Values greater than 985 μg/m3 for BAMs were excluded since this is above the range of the instrument [19]. No upper cutoff was used for TEOM measurements since all values were within the instrument range [20]. All negative values from regulatory instruments were kept as is and were included in the analysis.
Land-use variables and community monitor locations were loaded into ArcGIS (ESRI, v. 10.3.1, Redlands, CA, USA). Then, 250 m, 500 m, and 1000 m buffers were created around each monitor. Land-use parameters were sampled within each of these buffers. Geographic information system (GIS) and meteorological variables are listed in Table 1 along with their source, date, buffers, and averaging period. All data manipulation and analyses were performed using R statistical software (v. 3.3.3, https://www.r-project.org/).

Table 1.
Model variables. RH—relative humidity; PM2.5—particulate matter less than 2.5 μm in diameter; US—United states; CARB—California Air Resources Board.
Agricultural burning records were received from the Imperial Air Pollution Control District. Acres burned was recorded on the daily level. This information was added to the model as acres burned within 5 km of a monitoring site within the last day. When multiple burns were recorded within 5 km of a site, they were summed.
Other GIS variables were considered but rejected since all monitors had the same value or nearly the same value for that variable. Dropped variables included indicators of industrial PM emissions since none of our monitors were located near industrial sites that had permits to release PM. Satellite PM2.5 was included, but was not predictive, perhaps because the data were 15 years old and satellite measurements are known to not perform well in desert areas.
Meteorological data completeness was less than ideal, especially for planetary boundary layer height. Because the models require a complete dataset, hours that did not have meteorological data were dropped. This resulted in a limited number of complete hours for October and November 2017 and, therefore, they are not included in the monthly and yearly PM maps.
Some monitors have buffers that cross the US/Mexico border. However, we had no land-use data for Mexico. If only the US side of the land use was used, then the true value of that land use would be underestimated. To adjust for this, the percentage area of the buffer within Mexico was recorded for each site. Then, the variables were multiplied by 100/(100 − % area), which gave the land use for the whole buffer assuming the same distribution in Mexico as in the US. A satellite image of the area showed that, in most cases, land within the buffer on both sides of the border was primarily urban land.
Land-use variables were converted from continuous to categorical or binary. This was done because the monitors do not cover the range of land use seen throughout the valley, particularly the range of land use sampled by the grid of points used for prediction (the fishnet). Therefore, if linear extrapolation was used then the fishnet predictions failed, becoming extremely small or large. Histograms of each variable were analyzed to determine whether the variable should be converted to binary or categorical. The cut point for the binary variables was the first quartile. Most of these variables had nearly all of the measurements around zero and just a few at much higher values. All categorical variables were given three categories. The cut points for the categorical variables were the first quartile, the median, and the third quartile. If the continuous value was less than or equal to the first 25% of all values, it was given the categorical value “low”; if it was between 25% and 75%, it was categorized as “medium”, and if it was greater than 75% it was categorized as “high”. After conversion from continuous to categorical and binary, the fishnet predictions were much closer to the range of the monitoring measurements. However, the choice of cut points is dependent on the data and, therefore, limits the more general application of the models developed in this paper.
Three alternative models were considered. Categorical variables were converted to binary variables for use in models which cannot process categories. The models were a Bayesian additive regression trees (BART) model, a lasso model, and a partial least squares (PLS) model. PLS is a modeling technique that re-projects the data in order to find the dimension in the input variable space that explains the most variance in the outcome. PLS is used in PM modeling, in particular when there are a large number of variables [21]. Lasso is a penalized least squares method that reduces the number of variables in the model based on an alpha parameter. This parameter is chosen based on cross-validated testing. Mercer et al. [22] and Knibbs et al. [23] used lasso to help reduce the number of variables in PM LUR models. BART is a model that sums individual regression trees using a Bayesian approach [24]. It was used to predict torrential rain and avalanches, and to relate vehicle trip duration to household characteristics [25,26,27]. It should be noted that BART has a random component such that, each time it is re-run, it will produce slightly different results. This is why, for model creation and variable selection, it was important to have a large sample size of runs to get a sense of the average response for the model.
Models were compared by leaving out one site at a time and calculating the RMSE at that site using the rest of the sites. For each model, the RMSE was averaged across all sites. BART was found to be the best performing model for PM2.5 and PMcoarse. A variable selection test for these models was performed to identify which variables had the most impact on the model. The variable selection for the BART models was done by dropping one variable at a time from the model and calculating the test R2. Each BART model was run many times and the results were averaged to reduce bias from the random component. The variables that led to the largest decrease in R2 were those that had the most impact on the model. The 10 most important variables for the PM2.5 and PMcoarse models were compared. In order to compare variable selection stability across models, the top 10 BART and lasso variables were compared. Lasso variables were selected based on their standardized coefficient values, corrected by their standard deviations.
2.2. Prediction
The same steps described in Section 2.1 were followed for a grid of points, the fishnet, equally spaced one mile (1.6 km) apart across all of Imperial County (i.e., sampling GIS parameters within buffers at each grid point, finding the nearest meteorological data, etc.).
The BART models were used to predict monthly PM2.5 and PMcoarse concentrations on the fishnet points. The residuals of the PM2.5 and PMcoarse BART models were kriged and added to the model predictions before mapping. This helped the model account for purely spatial variability. These combined PM levels, at both the monthly and study-average timescale, were kriged and a 2D surface was created and compared to kriged PM measurements.
The fishnet predictions were then compared to regulatory PM concentrations. The fishnet point closest to the regulatory site was chosen for comparison. The longest distance between a fishnet point and a regulatory site was <1 km. Model predictions and regulatory measurements were compared using R2 and RMSE on the monthly and yearly timescales.
3. Results
Table 2 presents summary statistics for the community monitors averaged over the 40 sites in the network compared to the regulatory monitors. Regulatory sites are located to provide coverage of populated areas in the Imperial Valley, as well as to monitor the air quality around the Salton Sea, and they consist of a mix of BAM and TEOM instruments [14]. High hourly PM2.5 and very high hourly PM10 and PMcoarse values were seen by both the community monitors and the regulatory monitors. The community monitors produced a similar county average to the regulatory monitors for PM2.5. However, the community monitors measured slightly lower PM10 and PMcoarse.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for hourly PM2.5, PM10, and PMcoarse (difference between PM10 and PM2.5).
Table 3 shows the result of the modeling process for monthly PM2.5. RMSE and R2 were averaged across all of the leave-one-site-out variants. The lasso model chose 47 variables and the PLS model chose 24 variables. In terms of RMSE, lasso and PLS performed similarly and BART performed the best. The average RMSE between model predictions and the test set ranged from 1.50 to 1.79 µg/m3. Model R2 values did not follow the same order as model RMSE. PLS had the highest R2 (0.54), followed by PLS and BART (0.54 and 0.47, respectively). RMSE was used to select the top performing model since a lower prediction error was deemed more important than linearity. Also, there were a variable number of months of data for each site, and low sample size can dramatically change R2, especially when the range of the data is small. For example, some sites only had two months of data and others only had a 2-µg/m3 variation in monthly average PM2.5 over the course of a year. BART was chosen as the top performing model based on RMSE.

Table 3.
Model selection monthly PM2.5. PLS—partial least squares; BART—Bayesian additive regression trees; RMSE—root-mean-square error.
The results of the modeling process for monthly PMcoarse are presented in Table 4. Lasso chose 40 variables and PLS chose seven variables. Lasso and PLS performed similarly and BART performed the best. The average RMSE for PMcoarse models ranged from 9.14 to 12.30 µg/m3. Model R2 values followed the order of model RMSE for PMcoarse. The R2 value for the PMcoarse BART model was 0.65.

Table 4.
Model selection monthly PMcoarse.
The difference in performance between models was found to be unstable while testing differing predictor variables, i.e., the top model would switch between PLS, lasso, and BART depending on which variables were included. This would suggest, with this dataset, that these model types are more or less comparable in terms of performance.
Table 5 shows the results from the variable importance test for the PM2.5 and PMcoarse models. The top variable for the PM2.5 model was relative humidity, and the top variable for the PMcoarse model was temperature. These variables varied monthly and likely accounted for seasonal patterns. It should be noted the relative humidity may have a confounding effect since it was used to correct the Dylos measurements and was used in the model. However, the relative humidity data used in the model were a monthly average. The PM2.5 model places more emphasis on meteorological variables, such as wind direction, wind speed, and planetary boundary layer height, and location, while the PMcoarse model places more emphasis on land-use variables for farmland, native vegetation, and roads. The California Department of Water Resources defines native vegetation as all desert land and non-riparian land near bodies of water.

Table 5.
Variable importance.
For PM2.5, the lasso model chose land-use variables that represented nearly all categories of land use, as well as a variable representing railroad length, whereas the BART model put more emphasis on meteorological variables. For PMcoarse, the lasso model and BART models chose similar variables with more emphasis on land use in the lasso model and more emphasis on transportation in the BART model. The PMcoarse lasso model also did not have any meteorological variables.
Figure 1a,b show the kriged study-average residuals from the PM2.5 and PMcoarse models. The PM2.5 model underpredicted PM (−2.0 to −1.4 µg/m3) in the area west of the Salton Sea and overpredicted PM (0.3 to 1.3 µg/m3) in the area east of the Salton Sea. The PMcoarse model underpredicted PM (−19.4 to −12.6 µg/m3) in the area west of the Salton Sea. The PMcoarse model overpredicted PM (1.2 to 4.0 µg/m3) in the area east of the Salton Sea and in the south of Imperial Valley. The underprediction to the west of the Salton Sea was likely due to that area having high PM and similar land-use features to other sites. Moran’s I (a measure of spatial autocorrelation) was used to see if there was spatial correlation in the residuals by month. PM2.5 had two months where p < 0.05, May and August 2017, and PMcoarse had three months with p < 0.05, January, July, and August 2017.
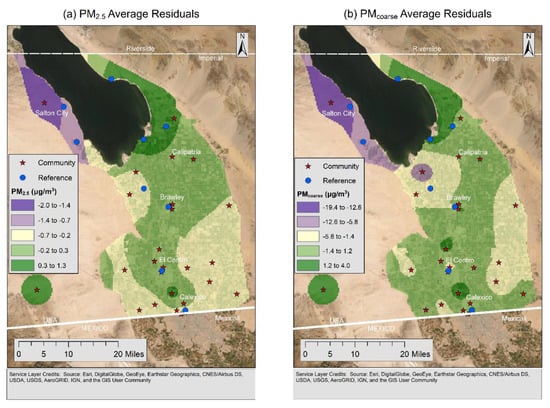
Figure 1.
(a) PM2.5 (particulate matter less than 2.5 μm in diameter) residuals; (b) PMcoarse (difference between PM10 and PM2.5) residuals.
The average measured PM2.5 over the study period is shown in Figure 2a and the average predicted PM2.5 is shown in Figure 2b. The predicted PM2.5 map is a combination of the PM2.5 model and the kriged PM2.5 residuals. The spatial structure of the predicted PM2.5 map matches that of the measured PM2.5 map. The highest average PM2.5 levels were near the US/Mexico border and to the west of the Salton Sea near Salton City. Low-PM2.5 regions appeared primarily to the east of the Salton Sea. The predicted PM2.5 map is biased low compared to the measured PM2.5 map.
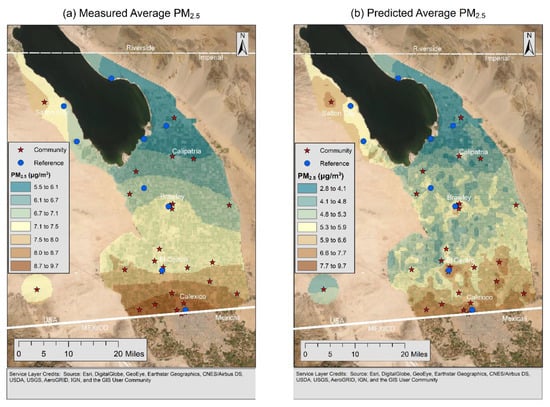
Figure 2.
(a) Measured average PM2.5; (b) predicted average PM2.5.
Figure 3a shows the average measured PMcoarse and Figure 3b shows the average predicted PMcoarse over the study period. The predicted PMcoarse map is a combination of the PMcoarse model and the kriged PMcoarse residuals. The spatial structure of the PMcoarse map differs slightly from the measure PMcoarse map in that the predictions are lower to the southeast of the Salton Sea and higher in the southeast portion of the Imperial Valley. The highest PMcoarse to the west of the Salton Sea and the area east of the Salton Sea had low PMcoarse concentrations. The predicted PMcoarse map is biased low compared to the measured PMcoarse map.
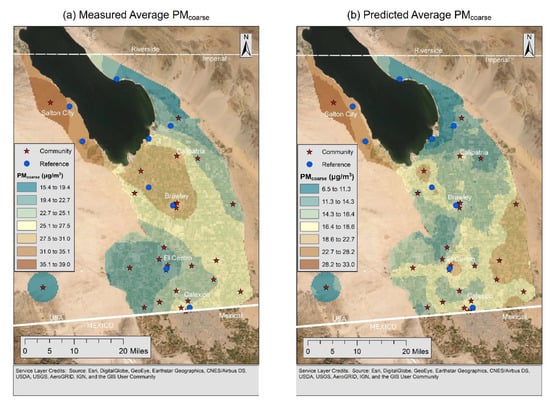
Figure 3.
(a) Measured average PMcoarse; (b) predicted average PMcoarse.
Maps of measured and predicted monthly PM2.5 are displayed in Figure 4a,b. Only monitors that had data for that month were used in each monthly map. There were not enough data to create maps for October and November 2016. The predicted PM2.5 map is a sum of the PM2.5 model and the kriged PM2.5 residuals. The monthly PM2.5 predictions are spatially similar to the monthly PM2.5 measurements; however, the predictions are biased low. The highest PM2.5 concentrations were seen in December 2016 and April through July 2017. PM2.5 was high near the US/Mexico border throughout the year. PM2.5 was high in the center of Imperial Valley near the city of Brawley in May 2017.
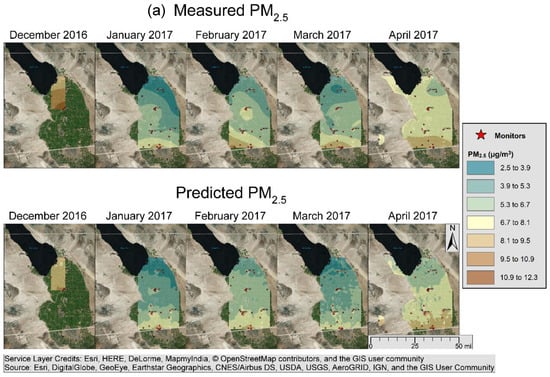
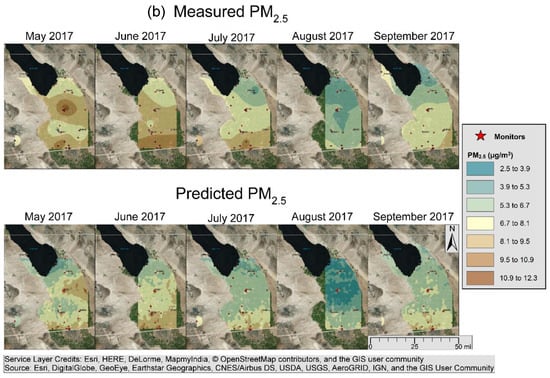
Figure 4.
(a) Monthly measured and predicted PM2.5 (December–April 2017); (b) monthly measured and predicted PM2.5 (May–September 2017).
Figure 5a,b show maps of monthly measured and predicted PMcoarse. The predicted PMcoarse map is a sum of the PMcoarse model and the kriged PMcoarse residuals. There was good spatial agreement between the PMcoarse measurements and predictions; however, the predictions were biased low. The highest PMcoarse was seen around Brawley in May 2017 and in the southeastern part of Imperial Valley in September 2017.
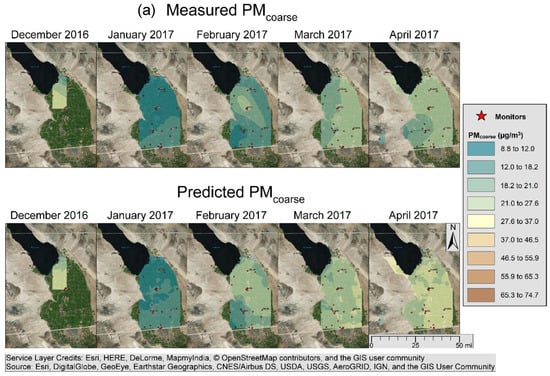
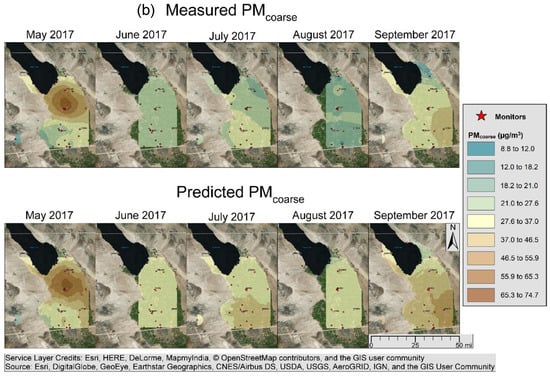
Figure 5.
(a) Monthly measured and predicted PMcoarse (December–April 2017); (b) monthly measured and predicted PMcoarse (May–September 2017).
Table 6 shows summary statistics comparing the fishnet predictions and data from the regulatory monitoring network for monthly and yearly averages. The yearly RMSE was 3.2 µg/m3 for PM2.5 and 17.7 µg/m3 for PMcoarse. The difference between the model prediction and regulatory monitor values is likely driven by spatiotemporal factors not accounted for in the model and measurement error introduced by the monitors and predictor variables. In particular, PMcoarse measurements were biased low compared to regulatory measurements as noted above.

Table 6.
Comparison of predictions with regulatory monitors, by monitor.
4. Discussion
PM LUR models showed variable performance depending on model location and variable selection. The PM2.5 LUR models developed in Eeftens et al. had validation R2 values, comparing the model to validation data, of 0.21 to 0.78 with a mean of 0.59 [6]. Hoek et al. compared PM2.5 LUR models from eight different studies and found model R2 values, comparison of model performance without external validation data, of 0.17 to 0.73 with a mean of 0.52, and RMSE values of 1.1 to 2.3 µg/m3 with a mean of 1.5 µg/m3 [7]. All of these models produced annual averages of PM2.5 and, therefore, are not directly comparable to the monthly models described in this paper. That said, the R2 and RMSE values for the PM2.5 models presented in this paper are within the range of the annual models found in the literature.
Eeftens et al. [6] created PMcoarse LUR models for 20 European cities as a part of the ESCAPE project. The range of validation R2 seen across the 20 models was 0.03 to 0.73, with a median R2 of 0.57. Wolf et al. [28] used the ESCAPE data to create finer-spatial-resolution PMcoarse LUR models for Germany, which had a validation R2 of 0.49. Eeftens et al. [29] modeled PMcoarse using an LUR model for eight areas in Switzerland. The average validation R2 was 0.38. These studies were also annual averages. In general, PMcoarse LUR models seem to have similar or slightly lower performance compared to PM2.5 LUR models. The PMcoarse models presented in this paper have R2 values in the range of the annual models found in the literature.
Ahangar et al. [30] used 2017 data from the community network to obtain a finely resolved concentration map of PM using a dispersion model. The residuals between model estimates at the monitor locations and the measured concentrations were then interpolated to the grid points using kriging. They compared predicted monthly averaged PM with data from a regulatory monitor at one location and found that most of the modeled values fell within a factor of two of the regulatory values; their resulting concentration maps were consistent with this study in showing the highest values of PM at the international border, yet concentrations were higher directly south of the Salton Sea in their study as opposed to the west of the Salton Sea in the present study. These differences may be due to time period differences of the two studies and the different modeling approaches.
This paper helps to elucidate the effect of meteorological and land-use parameters on particulate matter in Imperial County. The variable selection process pointed to seasonality, as measured by relative humidity, meteorological parameters, and length of roads as prime drivers in monthly PM. Important variables for monthly PMcoarse were seasonality, based on temperature, land-use variables for farmland, and length of roads. The predicted PMcoarse map showed areas of high PMcoarse around Brawley and to the west of the Salton Sea. The predicted PM map showed high levels in a large area near the US/Mexico border and to the west of the Salton Sea. This may point to agriculture as a potential source of PMcoarse, cross-border transport as a potential source of PM, and windblown dust as a source of both sizes of PM.
The PM and PMcoarse model variable selection and predicted PM maps seem to agree with the emissions inventories in the 2018 PM2.5 and 2018 PM10 state implementation plans (SIPs) created by the Imperial County Air Pollution Control District (ICAPCD) [9,10]. The 2018 PM2.5 SIP found that the main drivers of PM within Imperial County were unpaved road dust (39%), fugitive windblown dust (30%), off-road vehicles (8%), and agriculture (7%). This was seen in the models as a focus on seasonality and meteorology. The SIP argues that Imperial County would be in compliance with the National Ambient Air Quality Standards but for the transport of pollution from Mexico. As points of evidence, they cite emissions inventories for Calexico and Mexicali, Mexico that suggest that 60% of PM2.5 in Calexico comes from Mexicali. Two other sites in the center of Imperial County, El Centro and Brawley, had an annual PM concentration of 7–8 µg/m3 in 2016, whereas Calexico had an annual PM2.5 concentration of 12.5 µg/m3. This can be seen in the elevated measured and predicted PM2.5 values at the US/Mexico border in Figure 2.
The 2018 PM10 SIP found that the main drivers of PM10 were fugitive windblown dust (75%), unpaved road dust (18%), and agriculture (3%). The PMcoarse models, which can roughly be compared to the SIP’s PM10 emissions inventory, may have picked this up as seasonality and land use, specifically native vegetation, which was defined as primarily desert area. According to the SIP, wind patterns in Imperial County include high speed wind from the west, particularly during April and May, which may account for the high PMcoarse levels seen during May 2017 in Figure 5.
In both Figure 2 and Figure 3, high PM values can be seen west of the Salton Sea. The CARB review of the ICAPCD 2018 PM SIP remarks on this, saying that these high PM concentrations are due to dust from disturbed soils being swept into the air during high-wind events [31].
While there are challenges regarding calibration and accuracy of low-cost sensors, their low cost means they can be assembled into high-density networks that enable detailed modeling such as the LUR presented in this paper. Furthermore, the sensor and model data can be used help double-check and augment existing air monitoring and modeling efforts such as the emissions inventories in the Imperial County SIPs. If the necessary steps are taken to ensure data accuracy and proper display and explanation of sensor data, the authors see citizen science-derived data from low-cost air sensors as a valuable tool for communities, academic researchers, and government air-quality stakeholders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.N.C., A.N., M.J., and P.B.E.; data curation, H.L., E.B., D.M., and M.W.; formal analysis, G.C.; funding acquisition, P.B.E.; investigation, G.N.C., H.L., E.B., A.W., D.M., M.W., G.K., A.N., P.B.E., and J.S.; methodology, G.N.C., M.J., M.Y., T.L., and E.S.; project administration, A.W.; resources, E.B., and J.S.; supervision, M.Y., T.L., and E.S.; writing—original draft, G.N.C.; writing—review and editing, M.J., E.S., and P.B.E.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, under the NIH R01ES022722 grant. Jeff Shirai was partially supported by Award Number 5P30 ES007033-23 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the work of the Community Steering Committee (CSC) and other study participants in assisting with site identification and selection, the air monitor hosts for permitting installation of the community air monitors on their properties, and the CSC in reviewing the IVAN website. We are also very appreciative of the help offered by the Technical Advisory Group (TAG)—a collection of government air-quality stakeholders and academics—who lent their expertise to the project. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) was instrumental to this work by offering their time, equipment, and vast knowledge of air pollution monitoring. We also thank Elena Austin, Kai Zhang, and Allan Hubbard for their suggestions for data analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Newby, D.E.; Rajagopalan, S. The Global Threat of Outdoor Ambient Air Pollution to Cardiovascular Health: Time for Intervention. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Kelly, C.; Tate, J.; Parslow, R.; Lucas, K.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Exposure to Traffic-related Air Pollution and Risk of Development of Childhood Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2017, 100, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Butland, B.K.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Heal, M.R.; Stedman, J.R.; Carslaw, N.; Jarvis, D.; Heaviside, C.; Vardoulakis, S.; Walton, H.; et al. Long-term Exposure to Ambient Ozone and Mortality: A Quantitative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Evidence from Cohort Studies. BMJ Open. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA. What Is PM? Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/region1/airquality/pm-what-is.html (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; Hoogh, K.D.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dėdelė, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression Models for PM2.5, PM2.5 Absorbance, PM10 and PMcoarse in 20 European Study Areas; Results of the ESCAPE Project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; Hoogh, K.D.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D.J. A Review of Land-use Regression Models to Assess Spatial Variation of Outdoor Air Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Census Bureau. State and County QuickFacts, Imperial County, California; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA; U.S. Census Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/06/06025.html (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- California Department of Public Health. Asthma ED Visits, Children. 2014. Available online: http://www.californiabreathing.org/asthma-data/county-comparisons/edvisits-children (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Imperial County Air Pollution Control District. Imperial County 2018 Redesignation Request and Maintenance Plan for Particulate Matter Less Than 10 Microns in Diameter. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/planning/sip/planarea/imperial/sip.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Imperial County Air Pollution Control District. Imperial County 2018 Annual Particulate Matter Less Than 2.5 Microns in Diameter State Implementation Plan. Available online: https://www.co.imperial.ca.us/AirPollution/PublicNotices/PDFs/PublicHearings/20180424PM25AnnualSIP/DraftVersion/2018ICPM25SIPDRAFTv3.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- California Air Resources Board. Chronology of State PM10 Designations. Available online: http://www.arb.ca.gov/desig/changes/pm10.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- English, P.; Olmedo, L.; Bejarano, E.; Lugo, H.; Murillo, E.; Seto, E.; Wong, M.; King, G.; Wilkie, A.; Meltzer, D.; et al. The Imperial County Community Air Monitoring Network: A Model for Community-based Environmental Monitoring for Public Health Action. Environ. Health. Perspect. 2017, 125, 074501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperial IVAN Air Monitoring. Available online: https://ivan-imperial.org/air (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Carvlin, G.; Lugo, H.; Olmedo, L.; Bejarano, E.; Wilkie, A.; Meltzer, D.; Wong, M.; King, G.; Northcross, A.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Development and Field Evaluation of a Community-Engaged Particulate Matter Air Quality Monitoring Network in Imperial, California, USA. J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, P. The growth of atmospheric aerosol particles as a function of the relative humidity-II. An improved concept of mixed nuclei. J. Aerosol. Sci. 1973, 4, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Air Resources Board. Annual Network Plan. 2017. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/aqd/amnr/amnr2017.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Imperial County Air Pollution Control District. Quality Assurance Quality Control Plan for the Salton Sea Air Monitoring Network. Available online: http://www.water.ca.gov/saltonsea/docs/Appendix_10_FINAL_QA-QC_PLAN.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2017).
- Met One. BAM 1020 Particulate Monitor Operation Manual Rev G. pp 7 and 41. 2008. Available online: https://arb.ca.gov/airwebmanual/instrument_manuals/Documents/BAM-1020-9800%20Manual%20Rev%20G.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- ThermoFisher Scientific. TEOM 1405 Ambient Particulare Monitor Revision A. 2008. Available online: https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/manuals/EPM-TEOM1405-Manual.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Sampson, P.D.; Richards, M.; Szpiro, A.A.; Bergen, S.; Sheppard, L.; Larson, T.V.; Kaufman, J.D. A Regionalized National Universal Kriging Model using Partial Least Squares Regression for Estimating Annual PM2.5 Concentrations in Epidemiology. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, L.D.; Szpiro, A.A.; Sheppard, L.; Lindström, J.; Adar, S.D.; Allen, R.W.; Avol, E.L.; Oron, A.P.; Larson, T.F.; Liu, L.-J.S.; et al. Comparing Universal Kriging and Land-use Regression for Predicting Concentrations of Gaseous Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) for the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution (MESA Air). Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4412–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Hewson, M.G.; Bechle, M.J.; Marshall, J.D.; Barnett, A.G. A National Satellite-based Land-use Regression Model for Air Pollution Exposure Assessment in Australia. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipman, H.A.; George, E.I.; McCulloch, R.E. BART: Bayesian Additive Regression Trees. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2010, 4, 266–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, L.; Pan, X. A Novel Bayesian Additive Regression Trees Ensemble Model Based on Linear Regression and Nonlinear Regression for Torrential Rain Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Third International Joint Conference on Computational Science and Optimization (CSO), Huangshan, China, 28–31 May 2010; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattenberger, G.; Fowles, R. Avalanche Forecasting: Using Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART). In Demand for Communications Services—Insights and Perspectives. The Economics of Information, Communication, and Entertainment; Alleman, J., Ní-Shúilleabháin, Á., Rappoport, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Chipman, H.A.; George, E.I.; Lemp, J.; McCulloch, R.E. Bayesian Flexible Modeling of Trip Durations. Transp. Res. B Meth. 2010, 44, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Cyrys, J.; Harciníková, T.; Gu, J.; Kusch, T.; Hampel, R.; Schneider, A.; Peters, A.M. Land Use Regression Modeling of Ultrafine Particles, Ozone, Nitrogen Oxides and Markers of Particulate Matter Pollution in Augsburg, Germany. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 579, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeftens, M.; Meier, R.; Schindler, C.; Aguilera, I.; Phuleria, H.; Ineichen, A.; Davey, M.; Ducret-Stich, R.; Keidel, D.; Probst-Hensch, N. Development of Land Use Regression Models for Nitrogen Dioxide, Ultrafine Particles, Lung Deposited Surface Area, and Four Other Markers of Particulate Matter Pollution in the Swiss SAPALDIA Regions. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangar, F.E.; Freedman, F.R.; Venkatram, A. Using Low-Cost Air Quality Sensor Networks to Improve the Spatial and Temporal Resolution of Concentration Maps. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- California Air Resources Board. Staff Report: 2018 State Implementation Plan for the Imperial County 12 µg/m3 PM2.5 Annual Standard. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/planning/sip/planarea/imperial/staffreport.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).