Uncertainties in Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Associated with Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Datasets Using the CICE5 Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
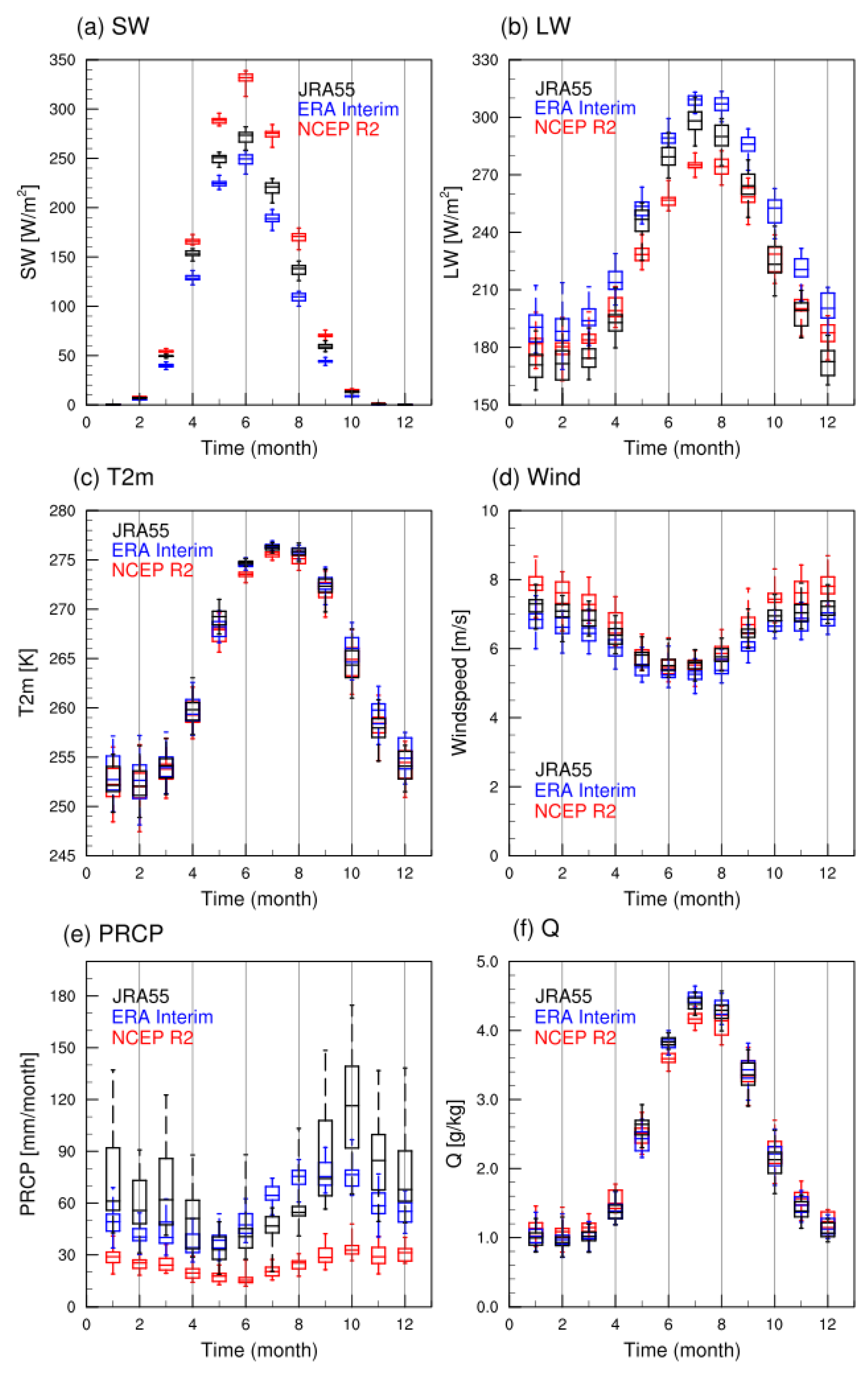
2. Methods
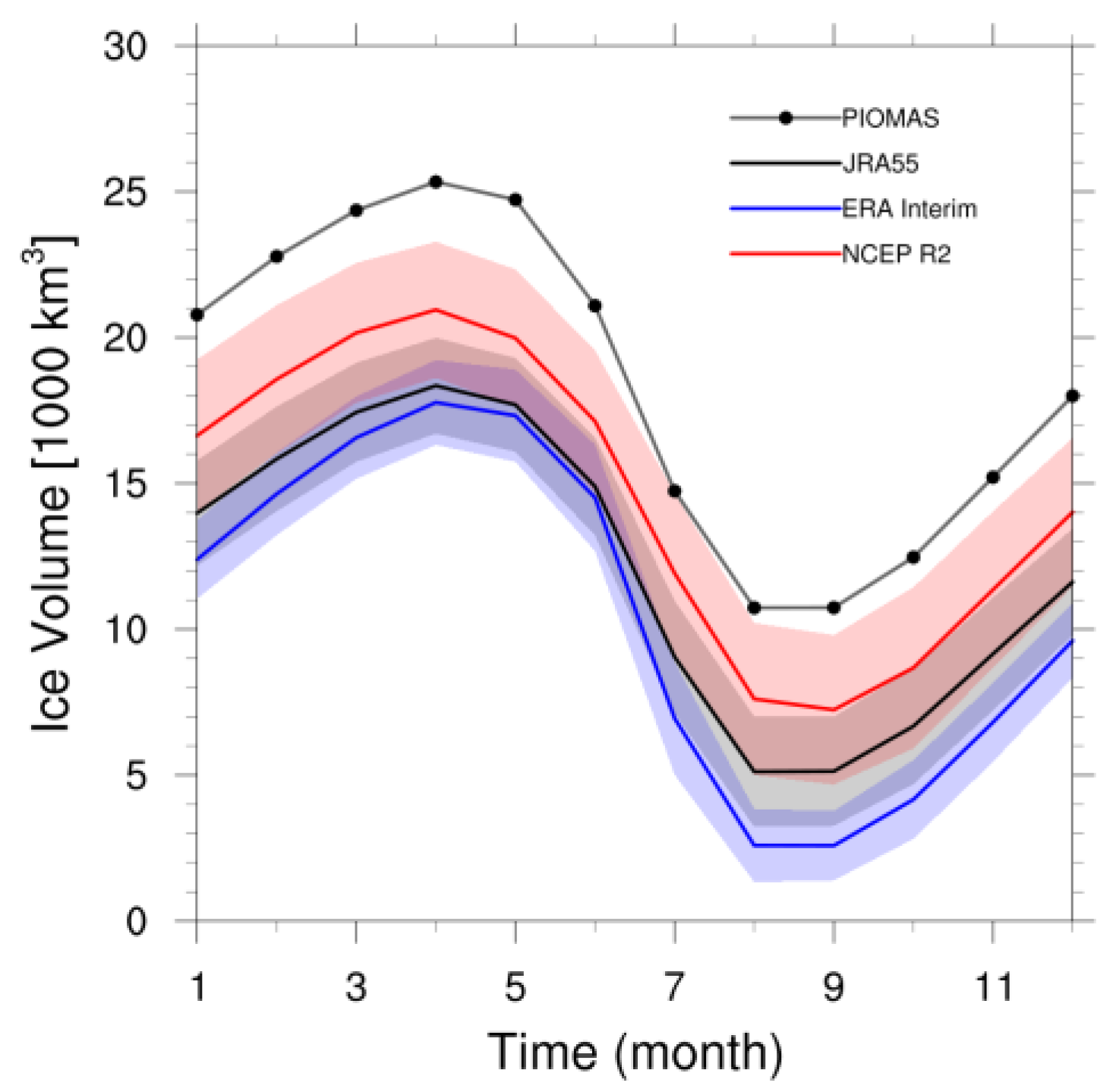
3. Impact of Atmospheric Forcings on the Sea Ice Model
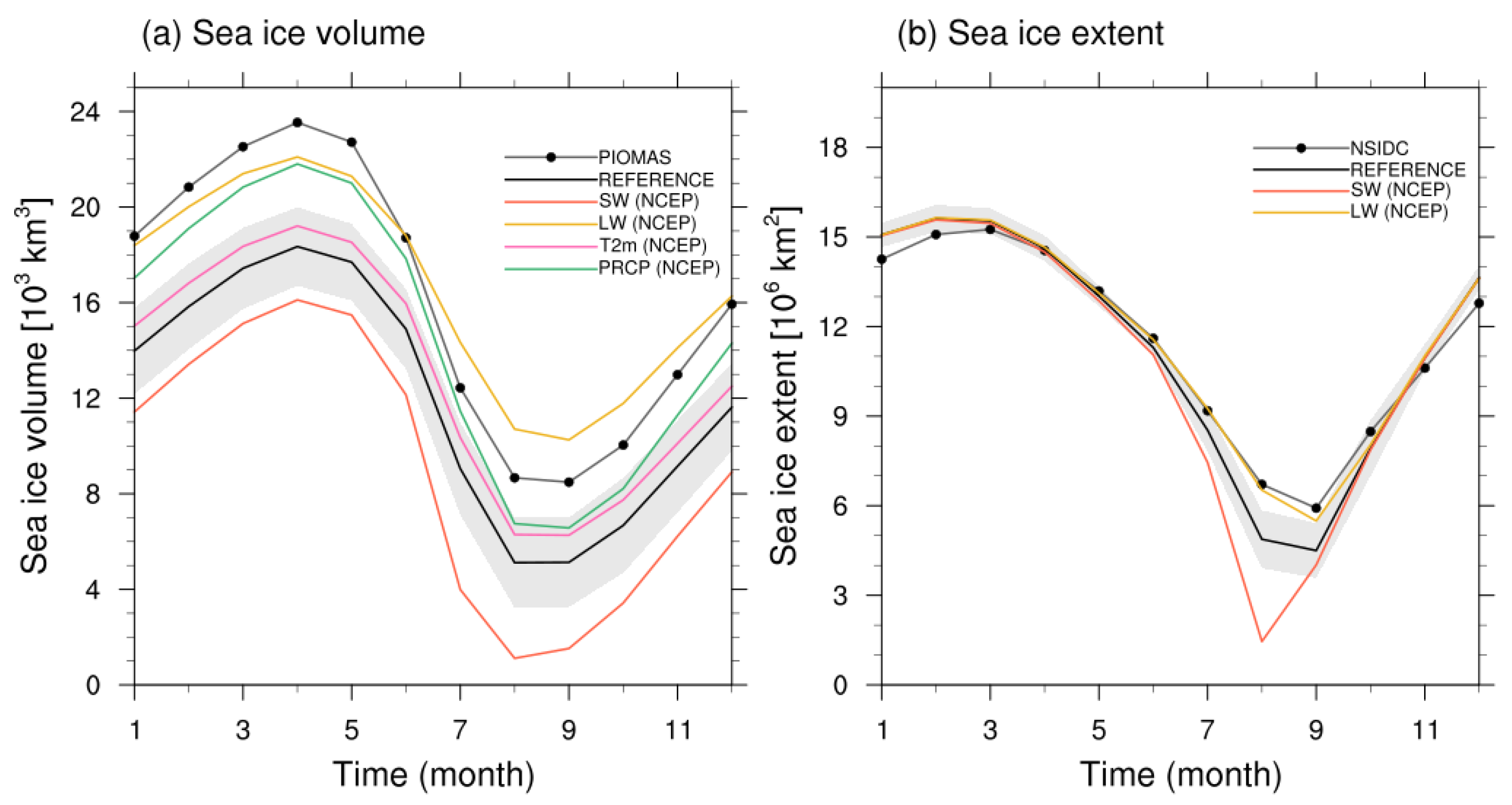
4. Responses of Sea Ice Properties to Atmospheric Forcings
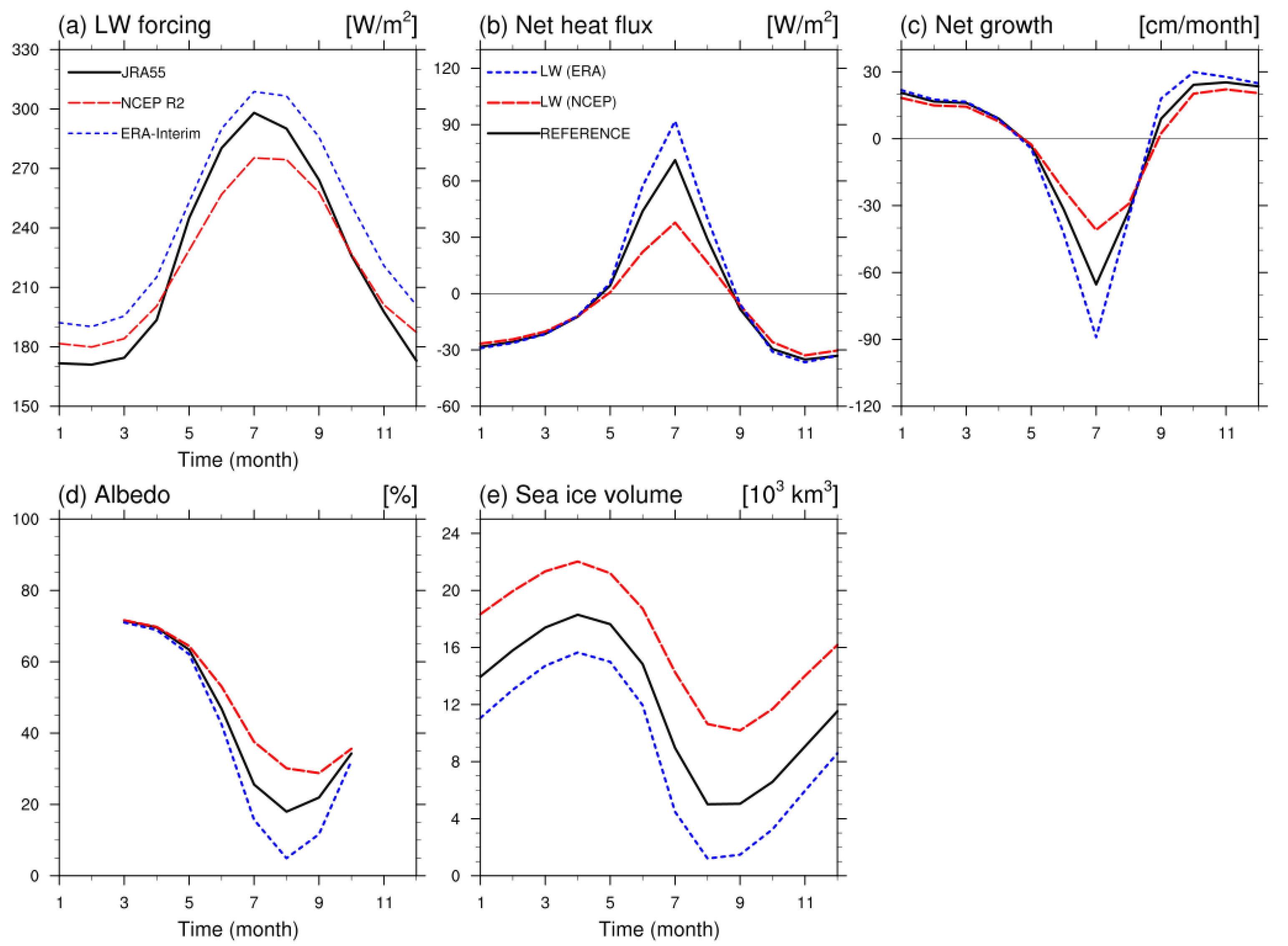
4.1. Sea Ice Response to Radiative Forcing
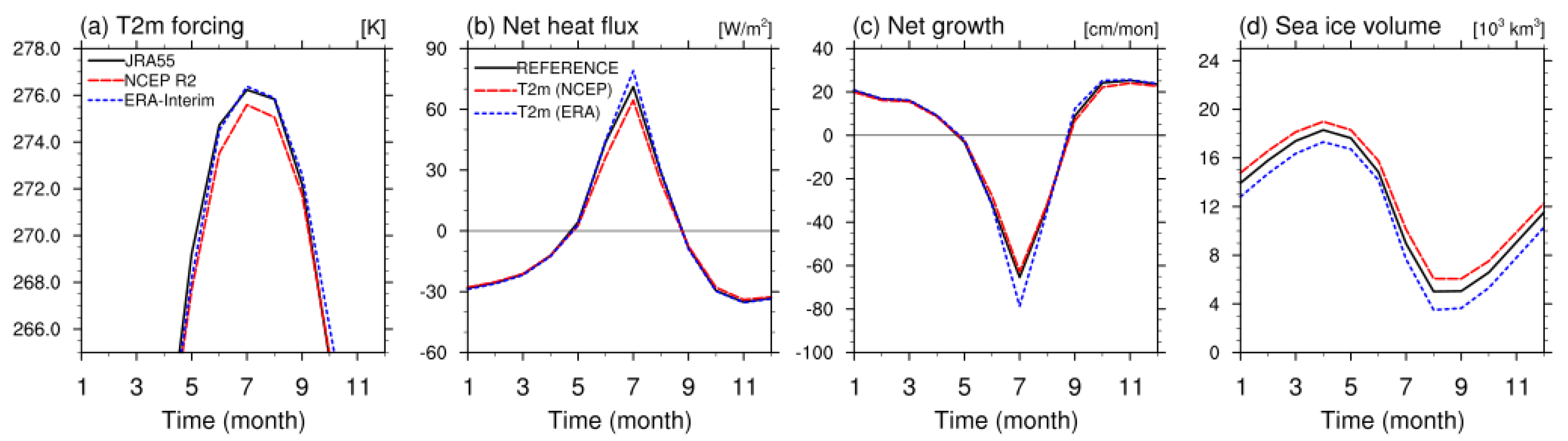
4.2. Sea Ice Response to Temperature Forcing
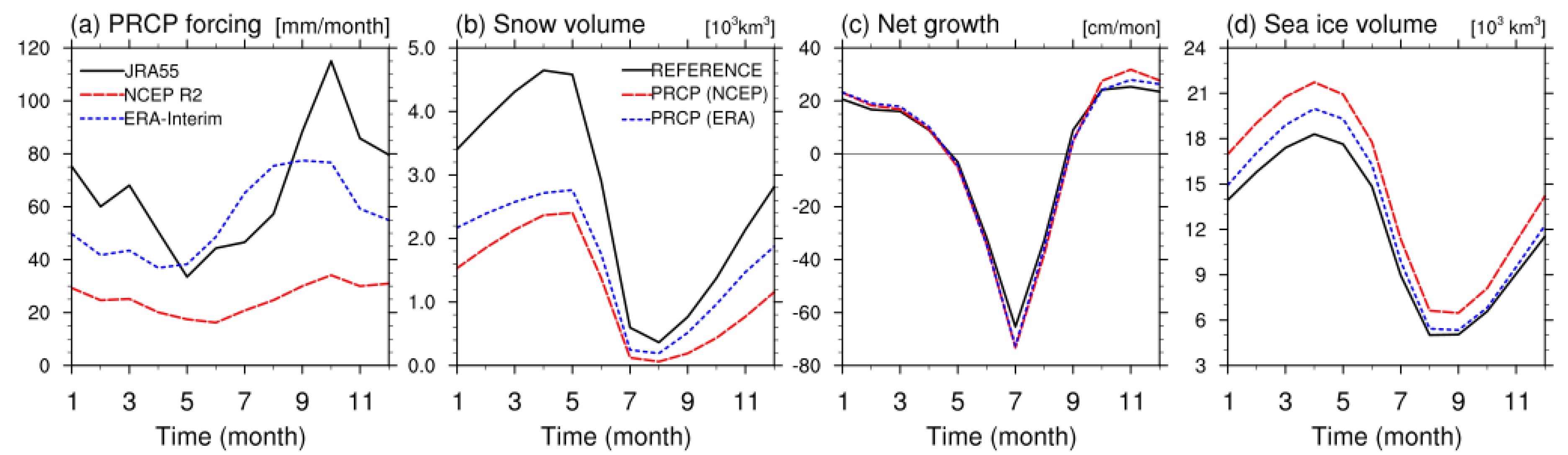
4.3. Sea Ice Response to Hydrological Forcings
5. Discussion and Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Comiso, J.C. Large Decadal Decline of the Arctic Multiyear Ice Cover. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L.; DiGirolamo, N.E. New visualizations highlight new information on the contrasting Arctic and Antarctic sea-ice trends since the late 1970s. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onarheim, I.H.; Eldevik, T.; Smedsrud, L.H.; Stroeve, J.C. Seasonal and regional manifestation of Arctic sea ice loss. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4917–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Kay, J.E.; Malanik, J.; Barrett, A.P. The Arctic’s rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: a research synthesis. Clim. Change 2012, 110, 1005–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Cunningham, G.F. Variability of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume from CryoSat-2. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2015, 373, 20140157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Comiso, J.C. On the 2012 record low Arctic sea ice cover: Combined impact of preconditioning and an August storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, D.; Feltham, D.L.; Flocco, D.; Tsamados, M. September Arctic sea-ice minimum predicted by spring melt-pond fraction. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C.; Bitz, C.M. Age characteristics in multidecadal Arctic sea ice simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C08013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A.; Simmonds, I. Erroneous Arctic temperature trends in the ERA-40 reanalysis: A closer look. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.H.; Ponte, R.M.; Nguyen, A.T. A comparison of atmospheric reanalysis products for the Arctic Ocean and implications for uncertainties in air–sea fluxes. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5411–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Yamazaki, A.; Ono, J.; Dethloff, K.; Maturilli, M.; Neuber, R.; Edwards, P.; Yamaguchi, H. Additional Arctic observations improve weather and sea-ice forecasts for the Northern Sea Route. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Inoue, J.; Yamazaki, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Maturilli, M.; Dethloff, K.; Hudson, S.R.; Granskog, M.A. Improved forecasts of winter weather extremes over midlatitudes with extra Arctic observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, L.N.; Webster, M.A.; Petty, A.A.; Markus, T.; Bromwich, D.H.; Cullarther, R.I. Intercomparison of precipitation estimates over the Arctic Ocean and its peripheral seas from reanalyses. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8441–8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, D.; Haumann, F.A.; Haak, H.; Jungclaus, J.H.; Marotzke, J. Arctic sea-ice evolution as modeled by Max Planck Institute for meteorology’s Earth system model. J. Adv. Model. Earth, Syst. 2013, 5, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Wensnahan, M.; Schweiger, A.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Seven Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Products in the Arctic. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2588–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.E.; Chapman, W.L. Arctic cloud-radiation-temperature associations in observational data and atmospheric reanalyses. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 3030–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makshtas, A.; Atkinson, D.; Kulakov, M.; Shutilin, S.; Krishfield, R.; Proshutinsky, A. Atmospheric forcing validation for modeling the central Arctic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüpkes, C.; Vihma, T.; Jakobson, E.; König-Langlo, G.; Tetzlaff, A. Meteorological observations from ship cruises during summer to the central Arctic: A comparison with reanalysis data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C.; Holland, M.M. Global atmospheric forcing data for Arctic ice-ocean modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C04S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, J.A.; Flato, G.M.; Weaver, A.J. The impact of varying atmospheric forcing on the thickness of arctic multi-year sea ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Woodgate, R.; Moritz, R. Sea ice response to atmospheric and oceanic forcing in the Bering Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1729–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Perovich, D.K.; Holmgren, J. Thermal conductivity and heat transfer through the snow on the ice of the Beaufort Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107(C21), 8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C.; Lipscomb, W.H.; Turner, A.K.; Jeffery, N.; Elliott, S. CICE: The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model Documentation and Software User’s Manual Version 5.1 LA-CC-06-012; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2015; Volume 115.
- Wilchinsky, A.V.; Feltham, D. Modelling the rheology of sea ice as a collection of diamond-shaped floes. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 2006, 138, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.K.; Hunke, E.C.; Bitz, C.M. Two modes of sea-ice gravity drainage: A parameterization for large-scale modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woollen, J.; Yang, S.-K.; Hnilo, J.J.; Fiorino, M.; Potter, G.L. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 83, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebita, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Moriya, M.; Kumabe, R.; Onogi, K.; Harada, Y.; Yasui, S.; Miyaoka, K.; Takahashi, K.; et al. The Japanese 55-year Reanalysis “JRA-55”: An interim report. SOLA 2011, 7, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, W.G.; Yeager, S.G. The global climatology of an interannually varying air-sea flux data set. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rothrock, D.A. Modelling global sea ice with a thickness and enthalpy distribution model in generalized curvilinear conditions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterer, F.; Knowles, K.; Meier, W.; Savoie, M. Sea Ice Index, Digital Media; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger, A.; Lindsay, R.; Zhang, J.; Steele, M.; Stern, H.; Kwok, R. Uncertainty in modeled Arctic sea ice volume. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C00D06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Haas, C.; Hendricks, S.; Hunkeler, P.; Kurtz, N.; Paden, J.; Panzer, B.; Sonntag, J.G.; Yungel, J.; Zhang, J. Seasonal forecasts of Arctic sea ice initialized with observations of ice thickness. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L21502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxon, S.W.; Giles, K.A.; Ridout, A.L.; Wingham, D.J.; Willatt, R.; Cullen, R.; Kwok, R.; Schweiger, A.; Zhang, J.; Haas, C.; et al. CryoSat-2 estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Barrett, A.; Serreze, M.; Schweiger, A. Using records from submarine, aircraft and satellites to evaluate climate model simulations of Arctic sea ice thickness. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, S.; Danabasoglu, G. The origins of late 20th century variations in the large-scale North Atlantic circulation. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 3222–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobson, E.; Vihma, T.; Palo, T.; Jakobson, L.; Keernik, H.; Jaagus, J. Validation of atmospheric reanalyses over the central Arctic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsch, M.-L.; Graversen, R.G.; Tjernstorom, M.; Bintanja, R. The effect of downwelling longwave and shortwave radiation on Arctic summer sea ice. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Schroder, D.; Tsamados, M.; Feltham, D. Warm winter, thin ice? Cryosphere 2018, 12, 1791–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, W.G.; Yeager, S.G. Diurnal to decadal global forcing for ocean and sea-ice models: The data sets and climatologies. NCAR Technical Report TN-460+STR 2004, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, G.; Stranne, C.; Borenäs, K. The sensitivity of the Arctic Ocean sea-ice thickness and its dependence on the surface albedo parameterization. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C. Sea ice volume and age: Sensitivity to physical parameterizations and resolution in the CICE sea ice model. Ocean Model. 2014, 82, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C. Weighing the importance of surface forcing on sea ice—A September 2007 modeling study. Q. J. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 142, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovich, D.; Polashenski, C.; Arntsenk, A.; Stwertka, C. Anatomy of a late spring snowfall on sea ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | CICE5 Stand Alone |
|---|---|
| Initial condition | No ice |
| Atmospheric forcings | Monthly: downward longwave radiation (W m−2), downward shortwave radiation (W m−2), total precipitation rate (kg m−2 s−1) 6 hourly: 2 m air temperature (K), 10 m wind speed (zonal and meridional, m s−1), 2 m specific humidity (kg kg−1), air density (kg m−3) |
| Oceanic forcings | Monthly HadISST, constant sea surface salinity (34 psu) |
| Dynamics | Elastic-Anisotropic-Plastic (EAP) |
| Thermodynamics | Mushy |
| Integration period | 1982–2014 |
| EXP Name | Description |
|---|---|
| REFERENCE | All variables from JRA-55 |
| SW (NCEP or ERA) | Same as REFERENCE except downward shortwave radiation from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| LW (NCEP or ERA) | Same as REFERENCE except downward longwave radiation from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| T2m (NCEP or ERA) | same as REFERENCE except temperature from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| WIND (NCEP or ERA) | same as REFERENCE except U and V wind from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| PRCP (NCEP or ERA) | same as REFERENCE except precipitation from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| Q (NCEP or ERA) | same as REFERENCE except surface specific humidity from NCEP R2 or ERA-Interim |
| Sea Ice Volume | Summer (JJAS) | Winter (ONDJFMAM) | Sea Ice Extent | Summer (JJAS) | Winter (ONDJFMAM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Norm. Std. | Mean | Norm. Std. | Mean | Norm. Std. | Mean | Norm. Std. | ||
| PIOMAS | 12.07 | 1.00 | 18.42 | 1.00 | NSIDC | 8.35 | 1.00 | 13.03 | 1.00 |
| REFERENCE | 8.55 | 0.57 | 13.84 | 0.61 | REFERENCE | 7.30 | 0.91 | 13.30 | 0.93 |
| NCEP | *10.97 | 0.81 | *16.29 | 0.90 | NCEP | 7.73 | 0.97 | 13.47 | 0.93 |
| ERA | 6.66 | 0.47 | 12.41 | 0.48 | ERA | 6.92 | 1.05 | 13.04 | 0.86 |
| SW (NCEP) | *4.69 | 0.30 | *11.27 | 0.33 | SW (NCEP) | *5.99 | 0.92 | 13.23 | 0.94 |
| SW (ERA) | *11.66 | 0.58 | *16.54 | 0.70 | SW (ERA) | 7.80 | 0.77 | 13.37 | 0.92 |
| LW (NCEP) | *13.53 | 0.72 | *18.17 | 0.86 | LW (NCEP) | *8.21 | 0.79 | 13.34 | 0.93 |
| LW (ERA) | *4.82 | 0.35 | *10.95 | 0.39 | LW (ERA) | *6.15 | 1.00 | 13.12 | 0.96 |
| T2m (NCEP) | 9.72 | 0.82 | 14.78 | 0.93 | T2m (NCEP) | 7.52 | 1.03 | 13.41 | 0.94 |
| T2m (ERA) | 7.39 | 0.55 | 12.82 | 0.60 | T2m (ERA) | 6.99 | 1.02 | 13.32 | 0.90 |
| WIND (NCEP) | 8.72 | 0.59 | 14.08 | 0.62 | WIND(NCEP) | 7.33 | 0.91 | 13.47 | 0.92 |
| WIND(ERA) | 8.65 | 0.53 | 13.78 | 0.55 | WIND(ERA) | 7.48 | 0.91 | 13.17 | 0.90 |
| PRCP (NCEP) | *10.65 | 0.64 | *16.70 | 0.68 | PRCP (NCEP) | 7.55 | 0.84 | 13.22 | 0.90 |
| PRCP (ERA) | 9.33 | 0.59 | 14.91 | 0.58 | PRCP (ERA) | 7.43 | 0.87 | 13.24 | 0.90 |
| Q (NCEP) | 9.29 | 0.64 | 14.43 | 0.72 | Q (NCEP) | 7.45 | 0.92 | 13.27 | 0.94 |
| Q (ERA) | 7.82 | 0.57 | 13.32 | 0.61 | Q (ERA) | 7.14 | 0.99 | 13.33 | 0.92 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-B.; Kim, B.-M.; Ukita, J.; Ahn, J.-B. Uncertainties in Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Associated with Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Datasets Using the CICE5 Model. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070361
Lee S-B, Kim B-M, Ukita J, Ahn J-B. Uncertainties in Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Associated with Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Datasets Using the CICE5 Model. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(7):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su-Bong, Baek-Min Kim, Jinro Ukita, and Joong-Bae Ahn. 2019. "Uncertainties in Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Associated with Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Datasets Using the CICE5 Model" Atmosphere 10, no. 7: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070361
APA StyleLee, S.-B., Kim, B.-M., Ukita, J., & Ahn, J.-B. (2019). Uncertainties in Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Associated with Different Atmospheric Reanalysis Datasets Using the CICE5 Model. Atmosphere, 10(7), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070361





