Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution
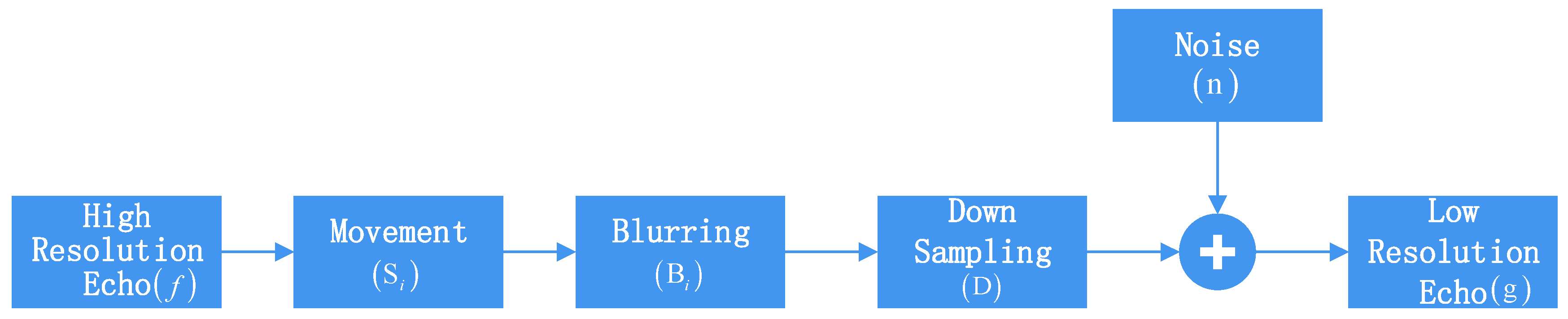
2.1. Super-Resolution Observation Model
2.2. Sparse Representation of Radar Echo
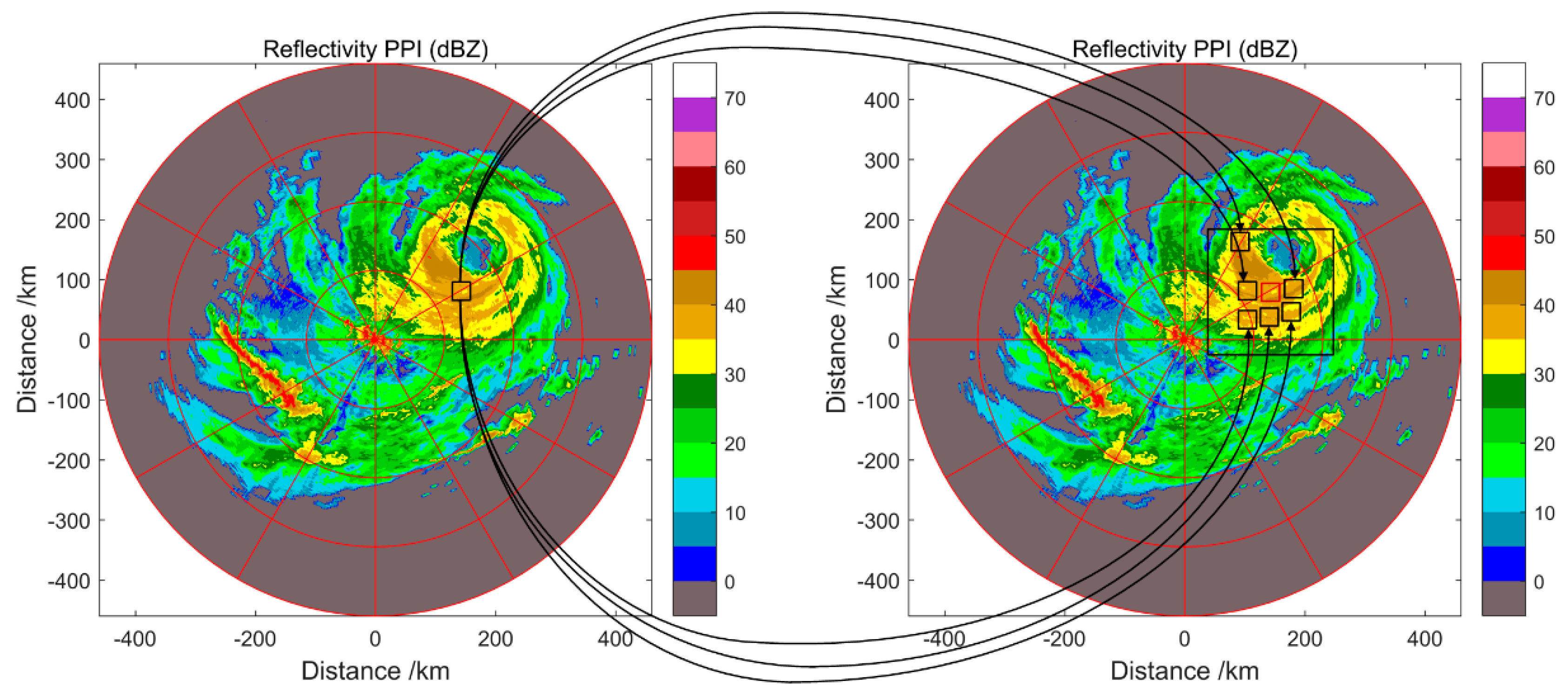
3. Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation (NSSR)
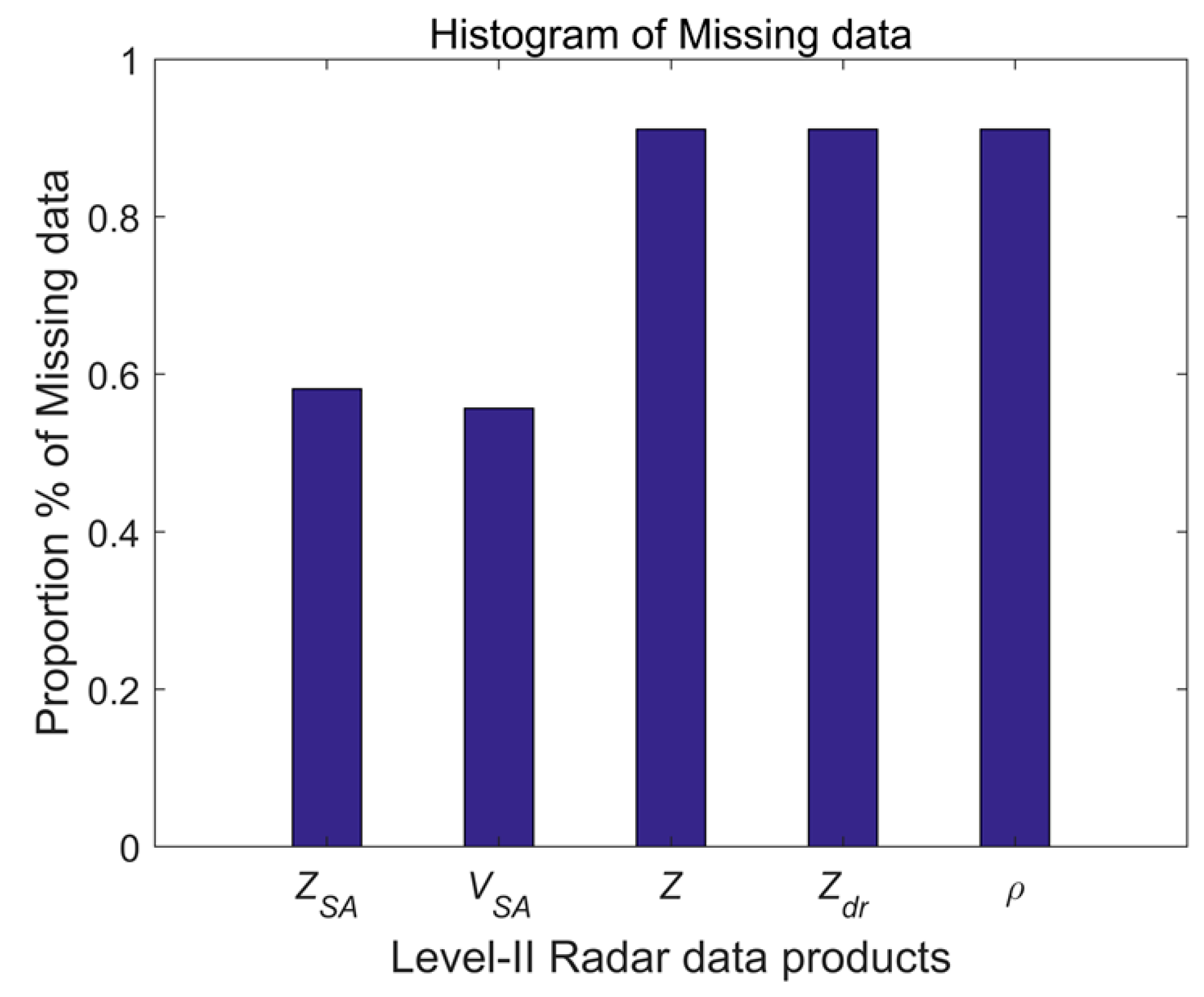
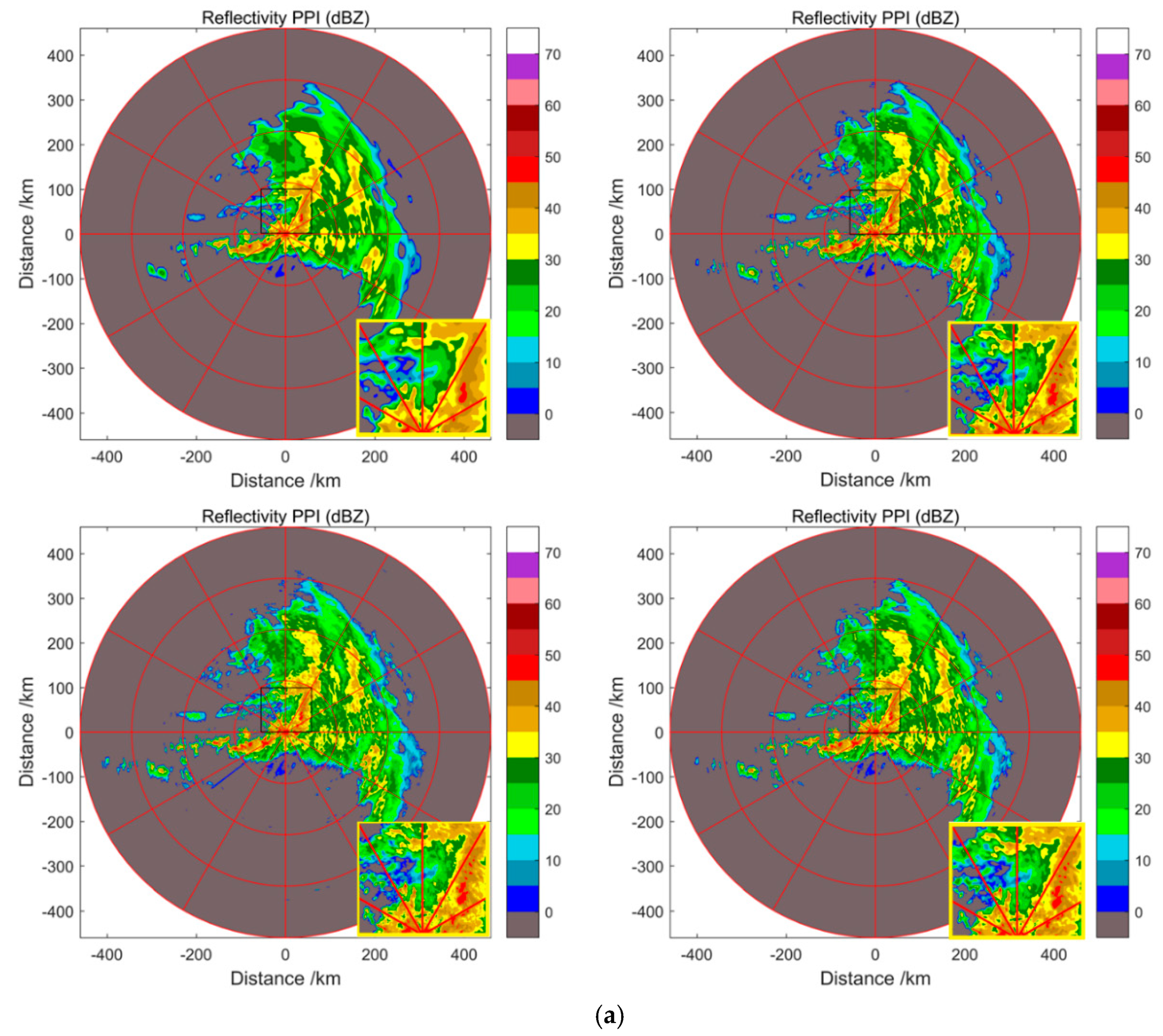
4. Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peleg, N.; Marra, F.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P.; Morin, E.; Sharma, A.; Burlando, P. Intensification of convective rain cells at warmer temperatures observed from high-resolution weather radar data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, E.J.; Roberts, N.M.; Fowler, H.J.; Roberts, M.J.; Chan, S.C.; Senior, C.A. Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Strohmer, T. High-resolution radar via compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Melnikov, V.M.; Schuur, T.J. Rapid-scan super-resolution observations of a cyclic supercell with a dual-polarization WSR-88D. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 3762–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowska, L.; Zhang, G.; Zrnić, D.S. Considerations for oversampling in azimuth on the phased array weather radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.M.; Curtis, C.D.; Technology, O. The Impact of Range-Oversampling Processing on Tornado Velocity Signatures Obtained from WSR-88D Superresolution Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, J.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. Weather radar range and angular super-resolution reconstruction technique on oversampled reflectivity data. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2011, 8, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. An alternating direction method for angular super-resolution in scanning radar. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 1626–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. TSVD with least squares optimization for scanning radar angular super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 1450–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. Penalized Maximum Likelihood Angular Super-Resolution Method for Scanning Radar Forward-Looking Imaging. Sensors 2018, 18, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Realization of airborne forward-looking radar super-resolution algorithm based on GPU frame. In Proceedings of the 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; He, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, X. Weather Radar Data Compression Based on Spatial and Temporal Prediction. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ren, H.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. Super-Resolution reconstruction algorithm of weather radar based on IBP. J. Sichuan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 51, 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Makur, A. Sparse recovery of radar echo signals using Adaptive Backtracking Matching Pursuit. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 27–30 October 2015; pp. 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Tihonov, A.N. Solution of incorrectly formulated problems and the regularization method. Sov. Math 1963, 4, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; Defrise, M.; De Mol, C. An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. J. Issued Courant Inst. Math. Sci. 2004, 57, 1413–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Esedoglu, S.; Park, F.; Yip, A. Recent developments in total variation image restoration. Math. Models Comput. Vis. 2005, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A. Adaptive total variation image deblurring: A majorization–minimization approach. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ren, H.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. Super-resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Based on the Improved Total Variation. Comput. Simul. 2014, 31, 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, E.; Michal, A. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar]
- Mairal, J.; Bach, F.; Ponce, J.; Sapiro, G.; Zisserman, A. Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 2272–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Weisheng, D.; Lei, Z.; Guangming, S.; Xiaolin, W. Image deblurring and super-resolution by adaptive sparse domain selection and adaptive regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1838–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G.; Li, X. Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Gao, W. Group-based sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 3336–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarroll, S.; Yeary, M.; Hougen, D.; Lakshmanan, V.; Smith, S. Approaches for Compression of Super-Resolution WSR-88D Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; He, J. Deployment and performance of an X-band dual-polarization radar during the Southern China Monsoon Rainfall Experiment. Atmosphere 2017, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G.; Zhang, Z. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 3397–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibulevsky, M.; Elad, M. L1-L2 Optimization in Signal and Image Processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquina, A.; Osher, S.J. Image super-resolution by TV-regularization and Bregman iteration. J. Sci. Comput. 2008, 37, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Burger, M.; Bresson, X.; Osher, S. Bregmanized nonlocal regularization for deconvolution and sparse reconstruction. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2010, 3, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner, D.; Bagon, S.; Irani, M. Super-resolution from a single image. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Candes, E.J.; Wakin, M.B.; Boyd, S.P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted ℓ 1 minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2008, 14, 877–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E.; Bishop, C.M. Bayesian image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2003 Advances in neural information processing systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–13 December 2003; pp. 1303–1310. [Google Scholar]

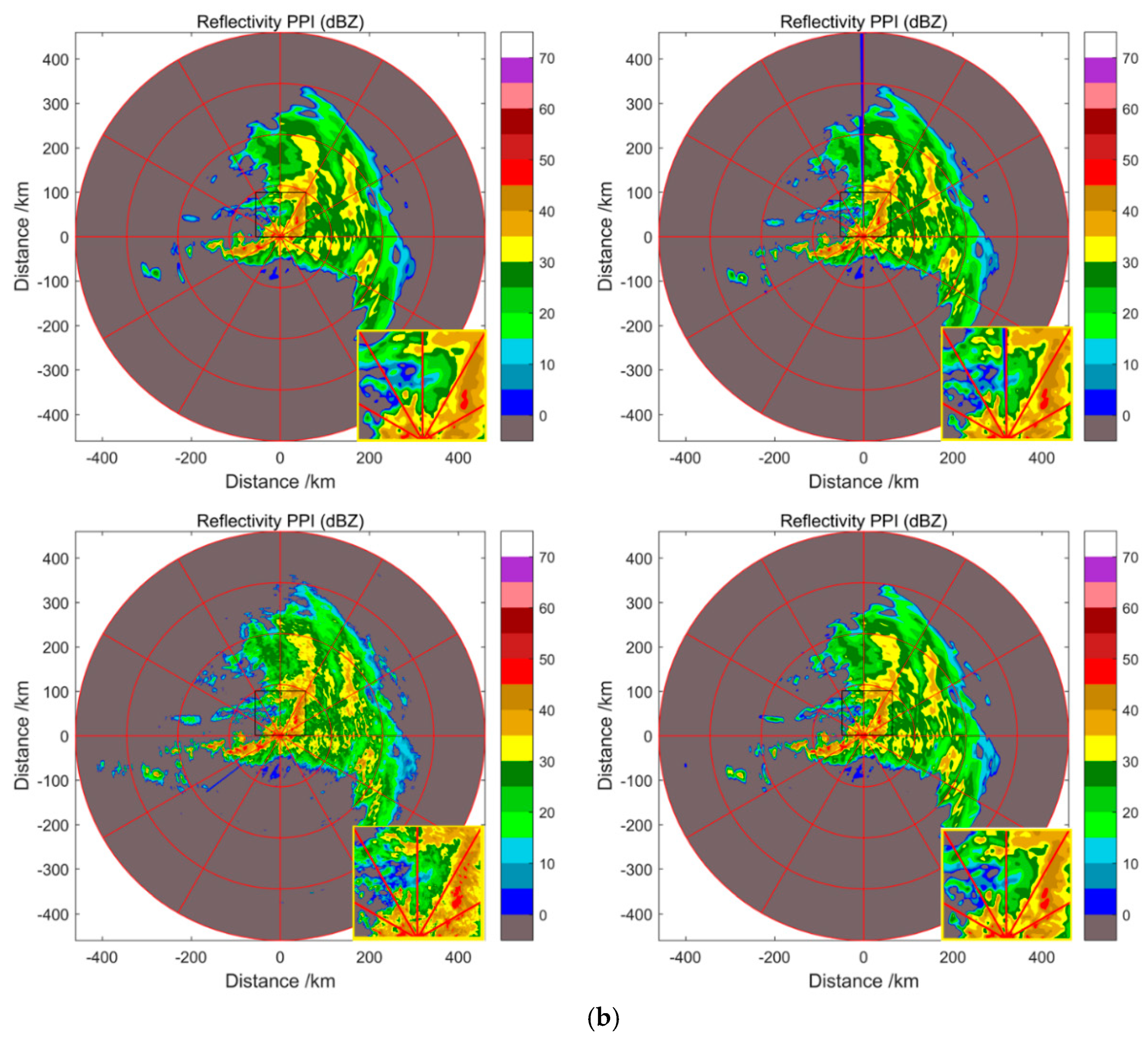
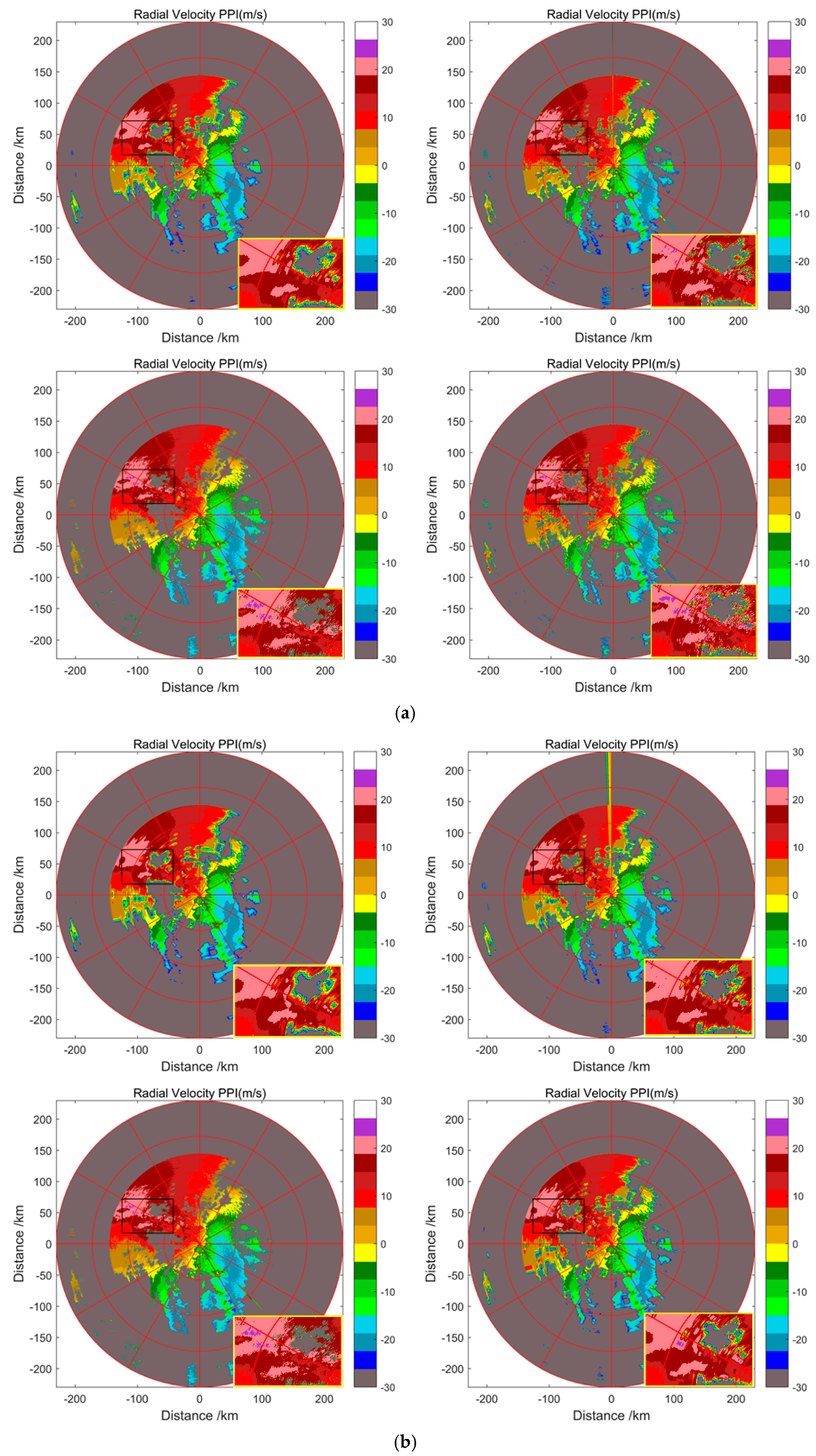

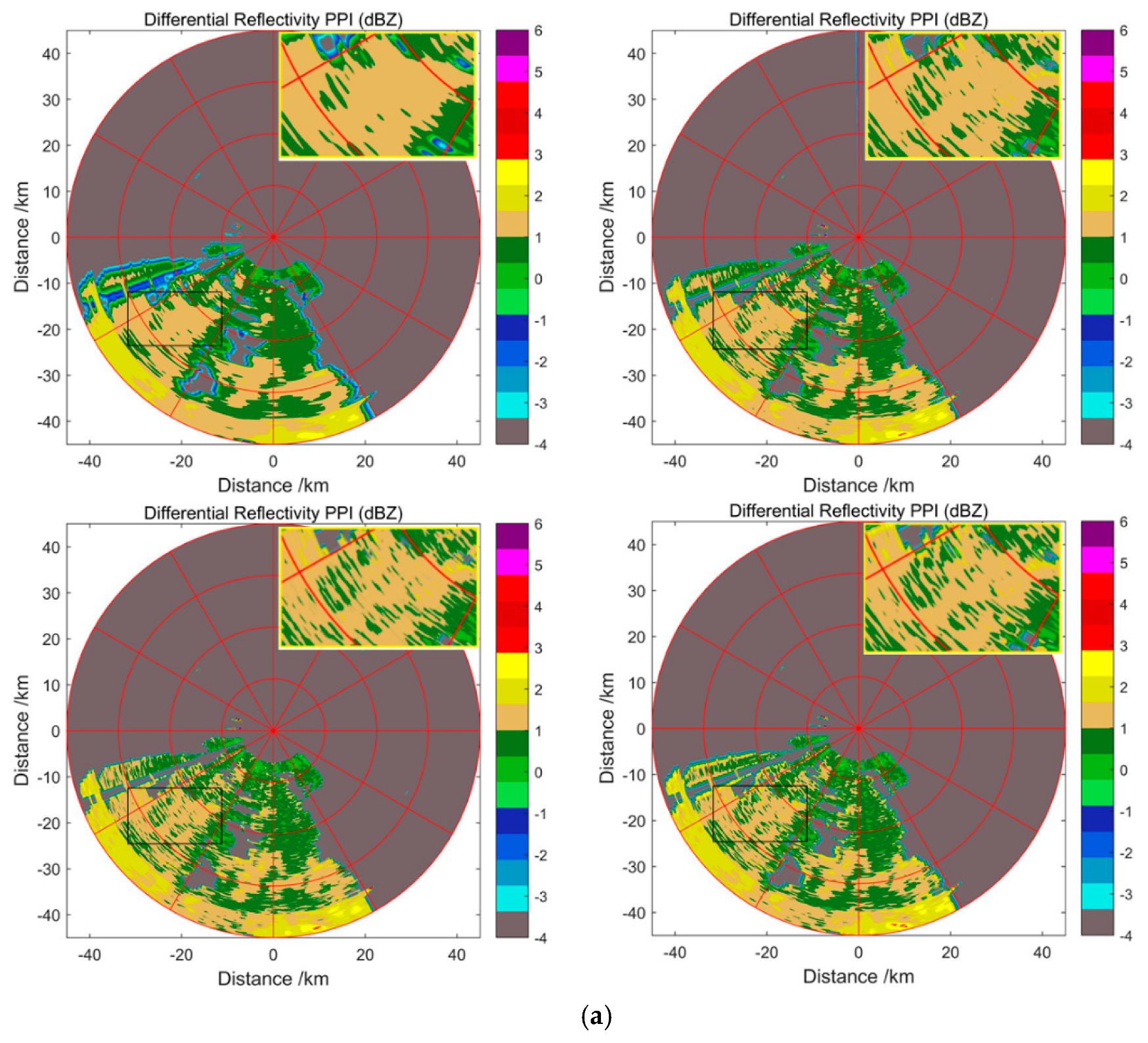

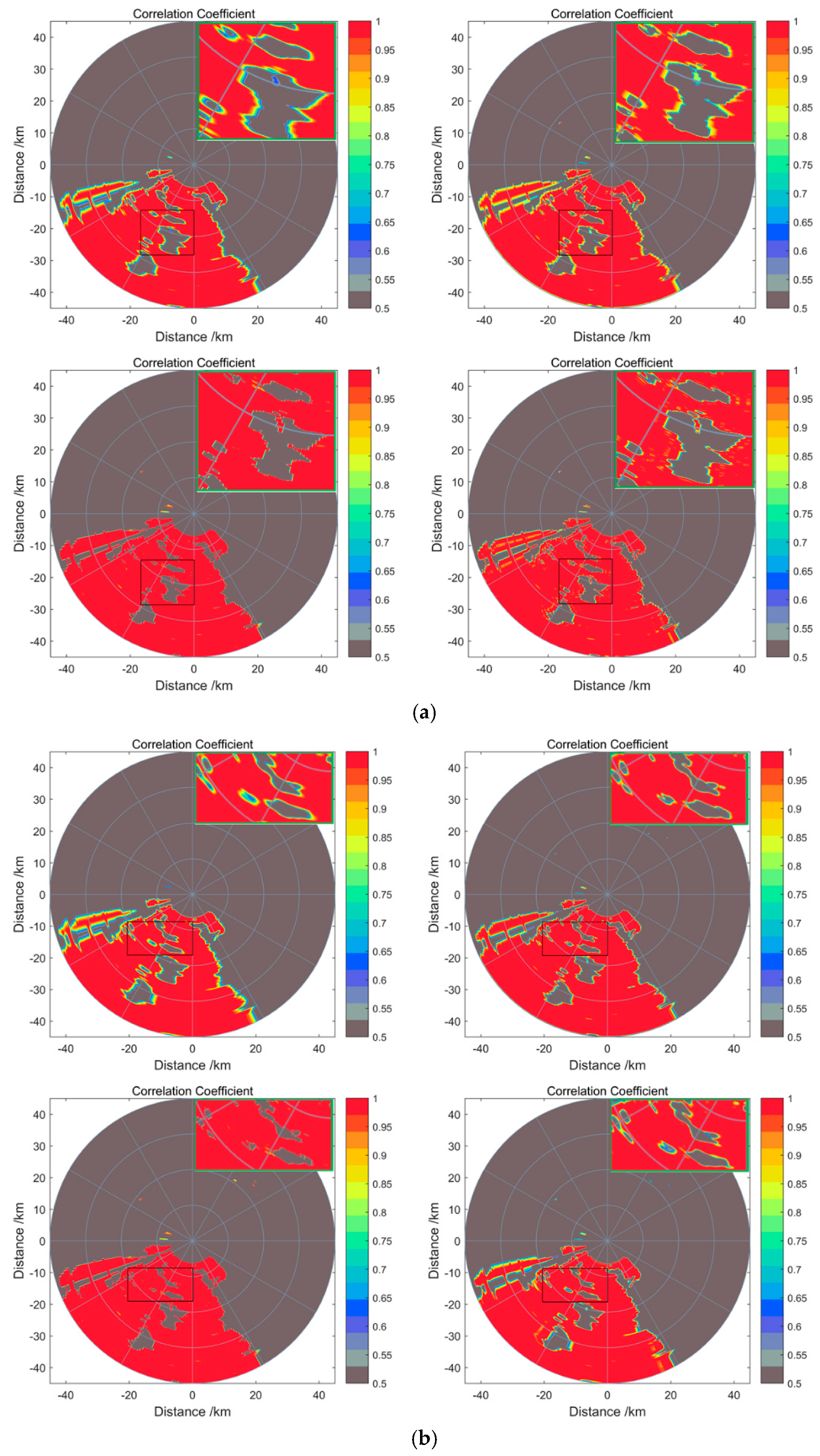
| Proposed Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation (NSSR) Algorithm |
|---|
| 1. Initialization: Set the initial estimation, , and initial regularization parameter, . 2. Outer loop: Dictionary learning and parameter estimation. Iterate on : (a) Update the dictionaries . (b) Inner loop: reconstruct radar echo. Iterate on . (I) Initialize . (II) Compute . (III) Each radar echo patch, , computes the nonlocal estimation, , using Equations (9) and (10). (IV) Repeat the above three steps until its convergence in the iteration. Compute using Equation (8). (V) Radar echo estimate update: using Equation (6). 3. Results: Output the reconstructed HR radar echo, . |
| Level-II Radar Data Products (2×) | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Sun Day | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | |
| Reflectivity | 32.996 | 35.055 | 37.123 | 31.669 | 34.141 | 35.750 | 33.817 | 35.228 | 36.353 |
| 0.8933 | 0.9500 | 0.9598 | 0.8450 | 0.9284 | 0.9441 | 0.9098 | 0.9421 | 0.9552 | |
| Velocity | 27.911 | 29.459 | 30.169 | 26.999 | 28.916 | 30.562 | 29.194 | 30.025 | 32.343 |
| 0.8287 | 0.8937 | 0.9056 | 0.8465 | 0.8948 | 0.9209 | 0.8572 | 0.9179 | 0.9345 | |
| Level-II Radar Data Products (4×) | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Sun Day | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | |
| Reflectivity | 30.588 | 30.694 | 33.411 | 30.244 | 31.213 | 32.486 | 33.817 | 35.228 | 36.353 |
| 0.8412 | 0.8699 | 0.9031 | 0.8241 | 0.8356 | 0.8978 | 0.9098 | 0.9421 | 0.9552 | |
| Velocity | 26.921 | 26.883 | 28.415 | 26.332 | 26.127 | 28.179 | 29.194 | 30.025 | 32.343 |
| 0.7546 | 0.8324 | 0.8501 | 0.7231 | 0.8035 | 0.8471 | 0.8572 | 0.9179 | 0.9345 | |
| Level-II Radar Data Products (2×) | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Sun Day | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | |
| Reflectivity | 35.362 | 38.798 | 40.809 | 35.691 | 38.038 | 40.557 | 37.188 | 38.524 | 41.807 |
| 0.9338 | 0.9823 | 0.9844 | 0.9393 | 0.9789 | 0.9843 | 0.9598 | 0.9843 | 0.9989 | |
| Differential Reflectivity | 51.007 | 52.840 | 55.621 | 46.910 | 48.501 | 50.410 | 46.860 | 48.822 | 50.635 |
| 0.9891 | 0.9935 | 0.9975 | 0.9821 | 0.9835 | 0.9942 | 0.9851 | 0.9853 | 0.9947 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | 67.436 | 70.223 | 72.121 | 67.936 | 70.404 | 72.029 | 70.080 | 72.246 | 74.542 |
| 0.9996 | 0.9998 | 0.9999 | 0.9996 | 0.9997 | 0.9999 | 0.9998 | 0.9998 | 0.9999 | |
| Level-II Radar Data Products (4×) | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Sun Day | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | Bicubic | IBP | NSSR | |
| Reflectivity | 32.294 | 32.458 | 35.525 | 32.883 | 32.454 | 36.140 | 34.531 | 33.325 | 37.698 |
| 0.8834 | 0.9113 | 0.9446 | 0.8966 | 0.9185 | 0.9519 | 0.9348 | 0.9461 | 0.9689 | |
| Differential Reflectivity | 48.479 | 48.562 | 50.156 | 45.055 | 45.128 | 47.124 | 45.627 | 45.500 | 47.130 |
| 0.9816 | 0.9876 | 0.9924 | 0.9654 | 0.9727 | 0.9831 | 0.9741 | 0.9779 | 0.9855 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | 64.571 | 65.487 | 67.102 | 65.799 | 66.175 | 68.058 | 65.794 | 68.315 | 70.231 |
| 0.9988 | 0.9992 | 0.9996 | 0.9986 | 0.9993 | 0.9998 | 0.9990 | 0.9996 | 0.9998 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zeng, Q.; Shi, Z. Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050254
Zhang X, He J, Zeng Q, Shi Z. Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(5):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050254
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xing, Jianxin He, Qiangyu Zeng, and Zhao Shi. 2019. "Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation" Atmosphere 10, no. 5: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050254
APA StyleZhang, X., He, J., Zeng, Q., & Shi, Z. (2019). Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation. Atmosphere, 10(5), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050254






