Suitable Pattern of the Natural Environment of Human Settlements in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River
Abstract
1. Introduction
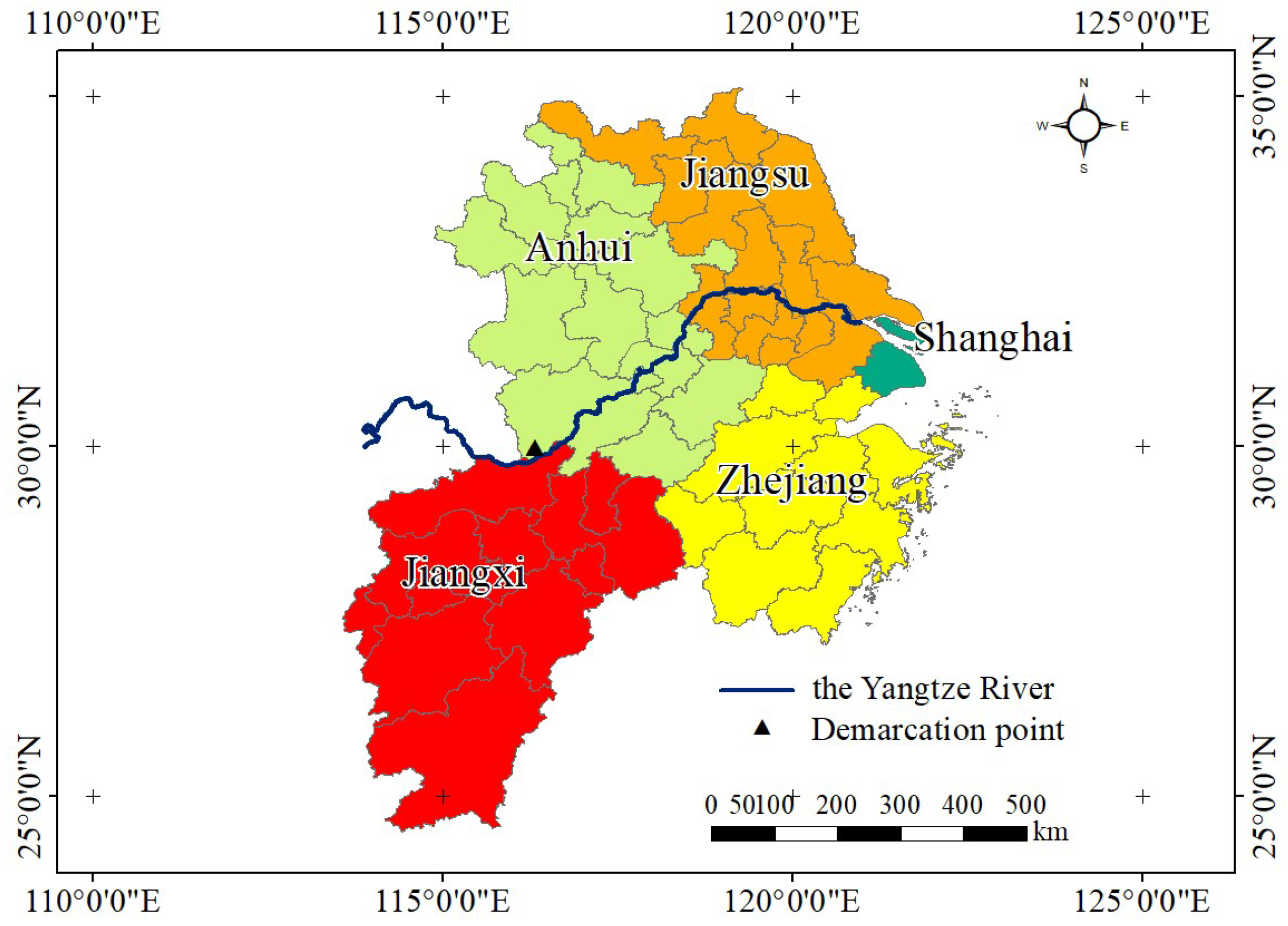
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
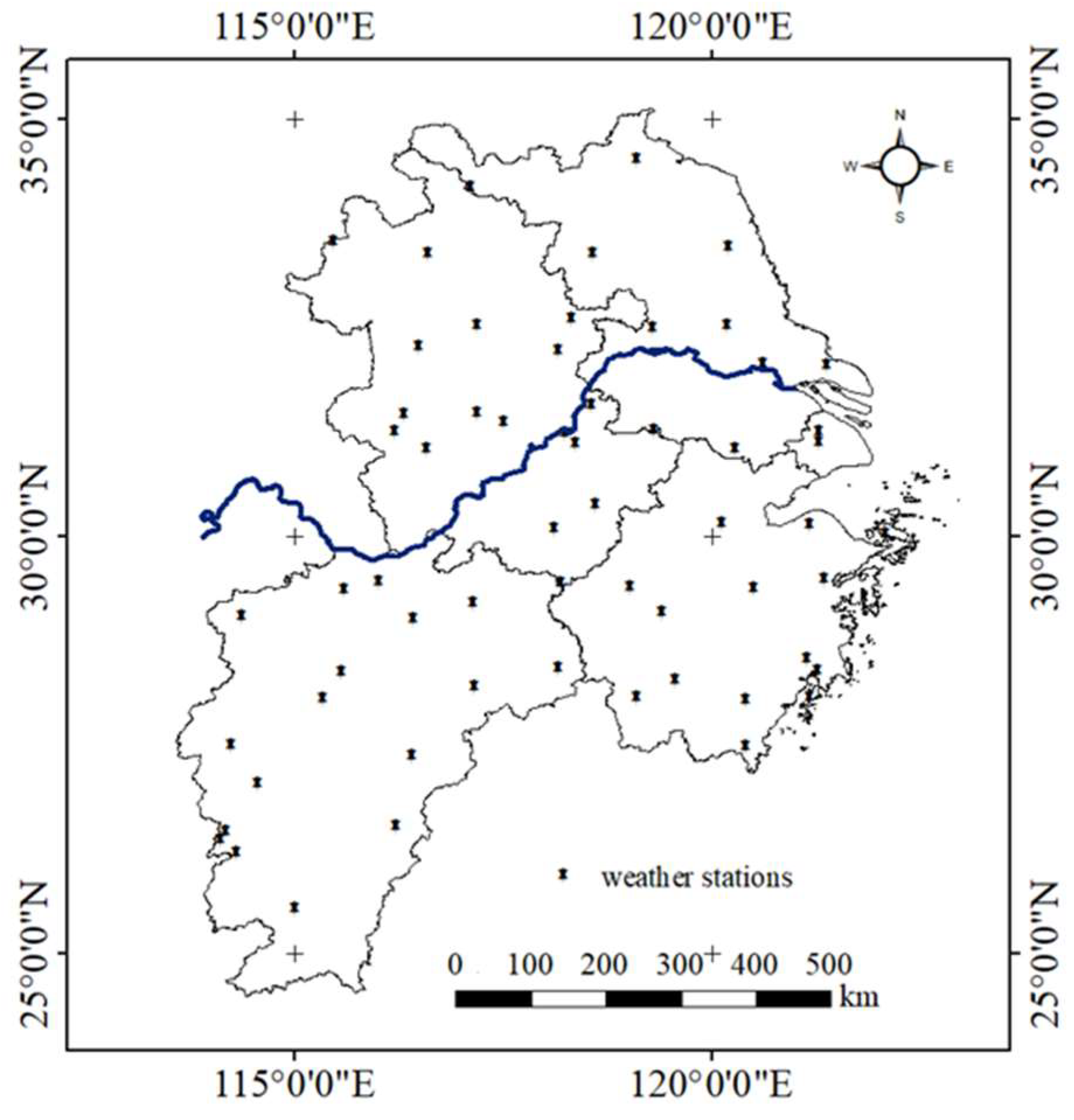
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Methods of Single Factor Model
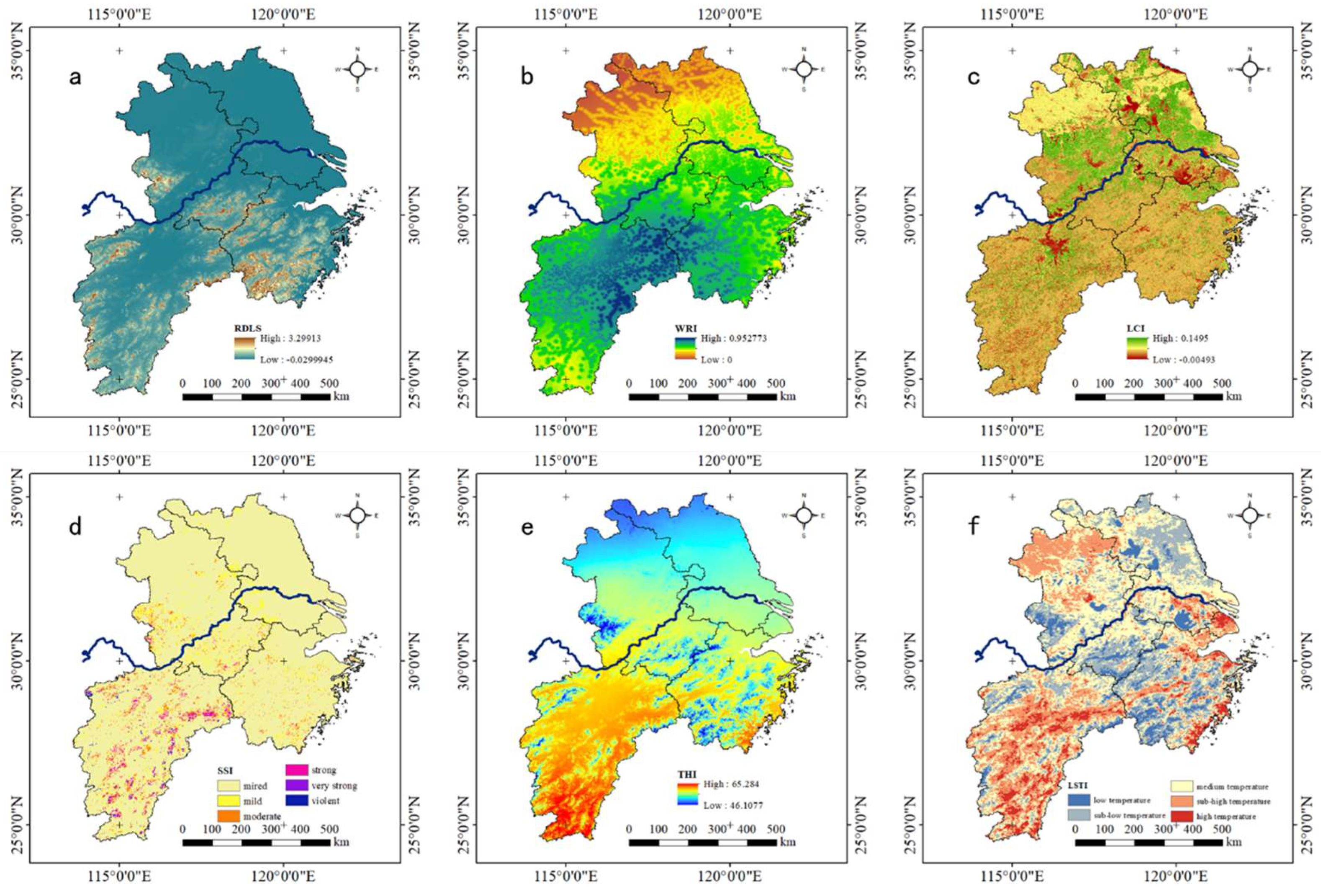
3.2.1. Relief Degree of Land Surface
3.2.2. Water Resource Index
3.2.3. Land Cover Index
3.2.4. Soil Suitability Index
3.2.5. Temperature–Humidity Index
3.2.6. Land Surface Temperature Index
3.3. Methods of Human Settlement Natural Environment Model
3.3.1. Scoring Criteria
3.3.2. Establishment of Human Settlement Natural Environment Index
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results of Single Natural Factor
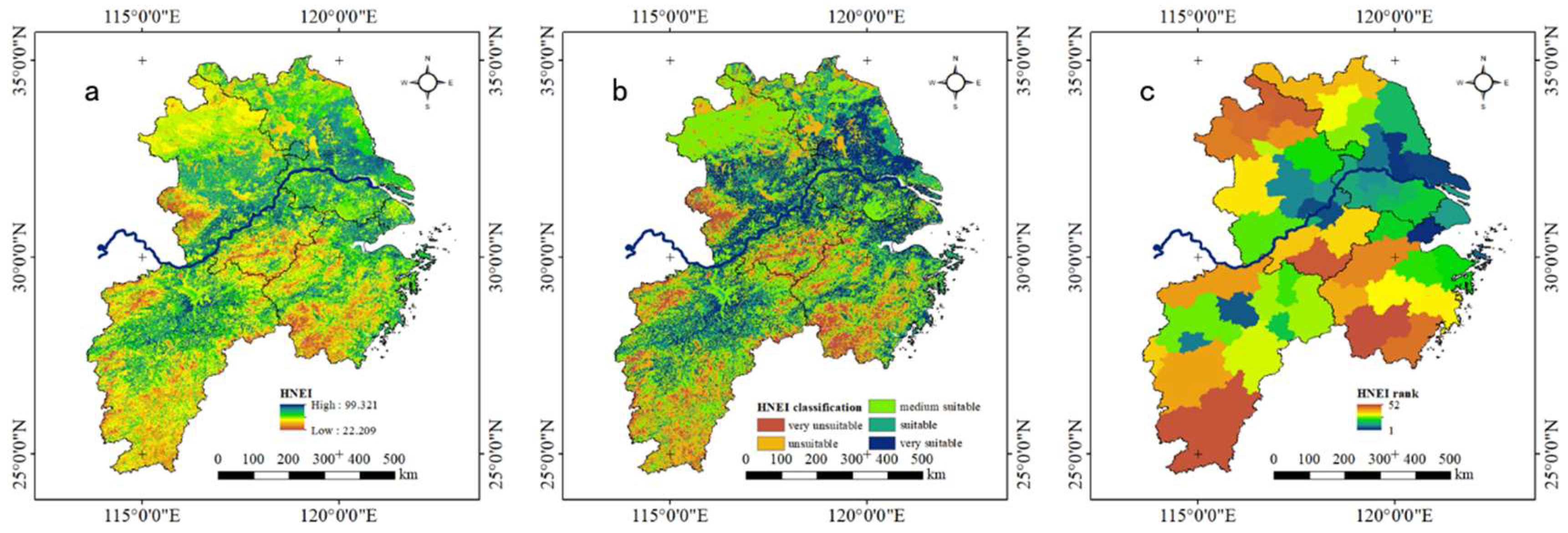
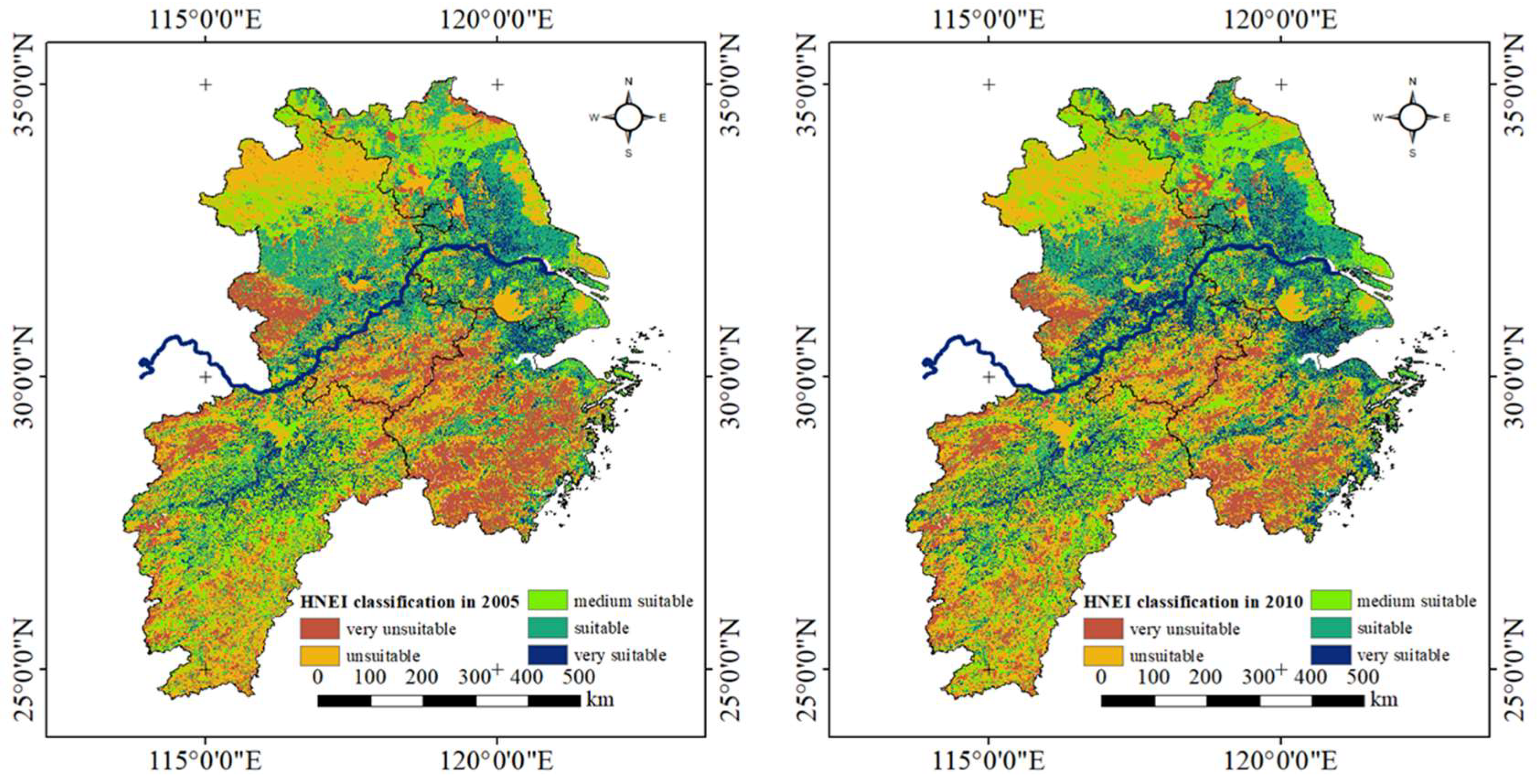
4.2. Results of Human Settlement Natural Environment
4.3. Time Evolution Analysis of HNEI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aynur, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.J.; Yan, F.; Xue, G.L. Evaluations of living environment suitability of Hotan Prefecture in Xinjiang based on GIS. Arid Land Geogr. 2012, 35, 847–855. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Evaluation of Nature Suitability for Human Settlement in Chongqing. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2014, 23, 1351–1359. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, R.; Ruhizal, R.; Mohd, S.; Ahamad, S. Land evaluation suitability for settlement based on soil permeability, topography and geology ten years after tsunami in Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Egypt. J. Remot Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Safa, M.; Majed, B.; Doaa, A.H. GIS approach for assessment of land suitability for different land use alternatives in semi arid environment in Jordan: Case study (Al Gadeer Alabyad-Mafraq). Inf. Proc. Agric. 2019, 6, 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, M.R.; Tshesane, M.; Kangethe, M. The strategically located land index support system for human settlements land reform in South Africa. Cities 2017, 60, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdanavičiūtė, I.; Valiūnas, J. GIS-based land suitability analysis integrating multi-criteria evaluation for the allocation of potential pollution sources. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1797–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y. Search for the Theory of Science of Human Settlement. Planners 2001, 17, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y. Introduction to Sciences of Human Settlements; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Shi, P.J.; Feng, H.C.; Wang, X.F. Study on the Suitability Evaluation of the Human Settlements Environment in Arid Inland River Basin—A Case Study on the Shiyang River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 1940–1950. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, C.; Lu, M.Q.; Lu, Y.Q. Assessing the suitability of regional human settlements environment from a different preferences perspective: A case study of Zhejiang Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.F.; Wang, T.F.; Zhang, W.Z.; Yu, J.H.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.P.; Feng, G.Q. Overview and progress of Chinese geographical human settlement research. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.L.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.R.; Yu, B. Assessment of Human Settlements in Prefecture-level Cities of Sichuan Province. Sichuan Environ. 2009, 28, 42–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Lin, A.W.; Zhu, H.J. Evolvement of Spatial Pattern of Urban Human Settlement Environment Suitability in Yangtze River Delta. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 112–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.X.; Wang, T.; Li, L. Human Settlement Assessment in Yellow River Valley Based on Factor Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 189–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, X.M. Application Research on Quality Evaluation of Urban Human Settlements Based on The BP Neural Network Improved by GA. Econ. Geogr. 2007, 32, 99–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.R.; Fang, C.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Ma, H.T. Urban Construction Land Suitability Evaluation Based on Improved Multi-criteria Evaluation Based on GIS (MCE-GIS): Case of New Hefei City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L. China Annual Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Spatial Distribution Data. Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn/DOI/doi.aspx?DOIid=49 (accessed on 2 November 2018). (In Chinese).
- Xu, X.L. Spatial Distribution Data of Soil Erosion in China. Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn/DOI/doi.aspx?DOIid=47 (accessed on 2 November 2018). (In Chinese).
- Cheng, S.J.; Zhu, Z.L.; Bai, L.B. GIS-based Assessment on Ecological Suitability for Human Settlement—A Case Study in the Central Arid Zone in Ningxia. Arid Zone Res. 2015, 32, 176–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.M.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, D. Relief degree of land surface and its influence on population distribution in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Qi, P.C.; Li, D.; Ma, X.L. Relief and Suitability Evaluation of the Human Settlements in Shaanxi Province. J. Northwest Normal Univ. 2013, 49, 96–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lang, L.L.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhu, Q.J.; Long, E. A Comparative Analysis of the Multi-criteria DEM Extracted Relief–Taking Fujian Low Mountainous Region as an Example. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2007, 1, 135–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.M.; Ren, Z.Y. Evaluation of Nature Suitability for Human Settlement in Shaanxi Province Based on Grid Data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 498–506. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.M.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Y. Natural environment suitability for human settlements in China based on GIS. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.M.; Ren, Z.Y.; Xue, L.; Jiang, Y.F. Quantitative Study on Response of Ecosystem to Land Use/Cover Changes in Yulin Area Based on 3S Technology. Prog. Geogr. 2007, 96, 106–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.Z.; Yu, K.L.; Li, Z.; Wen, Z.M.; Zhang, C. Integrating potential natural vegetation and habitat suitability into revegetation programs for sustainable ecosystems under future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 269, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Environmental Protection Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Technical Criterion for Ecosystem Status Evaluation; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.B.; Zhang, Q.N. GIS-Based Evaluation of Natural Suitability of Human Settlement Environment in Guangdong Province. Acta Scientiarum Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2014, 53, 127–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Liu, C.X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X. Evaluation on the human settlements environment suitability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Chongqing based on RS and GIS. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.J.; Ding, M.J.; Li, L.H.; Chen, Z.P.; Hou, H.Y. Design and Achievement of Soil Erosion Assessment System of Jiangxi Province. Soil Water Conserv. China 2014, 46, 63–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.F.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.Q.; Shi, Z. Modelling and mapping soil erosion potential in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Yang, Z.Q.; Gerard, G. Soil and water conservation measures reduce soil and water losses in China but not down to background levels: Evidence from erosion plot data. Geoderma 2019, 337, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Dai, W.Y. Fujian Province Tour Climate Evaluation. J. Fujian Normal Univ. 2005, 103–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aynur, M.; Wahap, H.; Gulgena, H.; Rebiyam, M. Assessment of residential environment suitability for southern Xinjiang based on GIS. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2012, 26, 11–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Halik, W.; Mamat, A.; Dang, J.H.; Deng, B.S.; Tiyip, T. Suitability analysis of human settlement environment within the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China. Quatern. Int. 2013, 311, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokaie, M.; Zarkesh, M.K.; Arasteh, P.D.; Hosseini, A. Assessment of Urban Heat Island based on the relationship between land surface temperature and Land Use/ Land Cover in Tehran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Sun, Z.Y.; Sun, X.H.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, J. Prediction and analysis of urban thermal environment risk and its spatio-temporal pattern. Acta Econ. Sin. 2019, 39, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.Y.; Li, G.Z.; Liu, C.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Xu, C.H. Evaluation of the natural suitability of human settlements environment in Jilin Province based on RS and GIS. Remot Sens. Land Resour. 2013, 25, 138–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| The Name of the Data | Data Types | Year of Data | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital elevation model data | Raster data, 90 × 90 m | 2015 | The resource and environmental data cloud platform of the Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Land use data | Raster data, 1 × 1 km | 2005,2010,2015 | The resource and environmental data cloud platform of the Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Annual precipitation spatial interpolation data | Raster data, 1 × 1 km | 2004–2006,2009–2011,2014–2016 | The resource and environmental data cloud platform of the Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Normalized difference vegetation index data | Raster data, 1 × 1 km | 2005,2010,2015 | The resource and environmental data cloud platform of the Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Soil erosion spatial distribution data | Raster data, 1 × 1 km | 2015 | The resource and environmental data cloud platform of the Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Annual data for natural indicators of weather stations | Point data | 2004–2006,2009–2011,2014–2016 | Chinese academy of sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| MODIS land surface temperature data | Raster data, 1 × 1 km | 2005,2010,2015 | United States Atmosphere Archive & Distribution System, Distributed Active Archive Center (https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/). |
| Land-Use Type | Weight | Classification | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arable land | 0.25 | Paddy field | 0.65 |
| Dry field | 0.35 | ||
| Woodland | 0.18 | Forest land | 0.34 |
| Shrub land | 0.26 | ||
| Sparse wood | 0.2 | ||
| Other woodland | 0.2 | ||
| Grass land | 0.15 | Grassland with high coverage | 0.4 |
| Grassland with moderate coverage | 0.33 | ||
| Grassland with low coverage | 0.27 | ||
| Water area | 0.17 | Canal | 0.31 |
| Lake | 0.29 | ||
| Reservoir and pit-pond | 0.2 | ||
| Mudflat | 0.1 | ||
| Bottomland | 0.1 | ||
| Construction land | 0.2 | Urban and town land | 0.44 |
| Village land | 0.35 | ||
| Other construction land | 0.21 | ||
| Unused land | 0.05 | Wetland | 0.48 |
| Bare land | 0.28 | ||
| Bare rock | 0.24 |
| RDLS | WRI | LCI | |
| I (90 grades) | [−0.02, 0.15] | (0.67, 0.96] | (0.1209, 0.1495] |
| II (70 grades) | (0.15, 0.44] | (0.54, 0.67] | (0.0807, 0.1209] |
| III (50 grades) | (0.44, 1.03] | (0.41, 0.54] | (0.0562, 0.0807] |
| IV (30 grades) | (1.03, 1.68] | (0.25, 0.41] | (0.0323, 0.0562] |
| V (10 grades) | (1.68, 3.30] | [0, 0.25] | [−0.004, 0.0323] |
| SSI | THI | LSTI | |
| I (90 grades) | mired | (61, 63] | low temperature |
| II (70 grades) | mild | (59, 61], (63, 66] | sub-low temperature |
| III (50 grades) | moderate | (57, 59] | medium temperature |
| IV (30 grades) | strong | (55, 57] | sub-high temperature |
| V (10 grades) | very strong and violent | [46, 55] | high temperature |
| Grades | Classification of GDP (unit: Yuan per km2) |
|---|---|
| 10 | [0, 424] |
| 20 | (425, 558] |
| 30 | (558, 983] |
| 40 | (983, 2337] |
| 50 | (2337, 6654] |
| 60 | (6654, 20,415] |
| 70 | (20,415, 64,282] |
| 80 | (64,282, 204,114] |
| 90 | (204,114, 649,851] |
| 100 | (649,851, 2,070,711] |
| Very Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Medium Suitable | Suitable | Very Suitable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 7.20% | 20.14% | 34.56% | 16.91% | 21.19% |
| 2010 | 14.30% | 30.82% | 22.29% | 18.31% | 14.28% |
| 2005 | 17.80% | 31.93% | 20.04% | 20.59% | 9.64% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, F. Suitable Pattern of the Natural Environment of Human Settlements in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040200
Song F, Yang X, Wu F. Suitable Pattern of the Natural Environment of Human Settlements in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(4):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040200
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Fan, Xiaohua Yang, and Feifei Wu. 2019. "Suitable Pattern of the Natural Environment of Human Settlements in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River" Atmosphere 10, no. 4: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040200
APA StyleSong, F., Yang, X., & Wu, F. (2019). Suitable Pattern of the Natural Environment of Human Settlements in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Atmosphere, 10(4), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040200






