Abstract
This study investigated precipitation distribution patterns in association with atmospheric rivers (ARs). The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model was employed to simulate two strong atmospheric river events. The precipitation forecasts were highly sensitive to cloud microphysics parameterization schemes. Thus, radar observed and simulated and were evaluated to provide information about the drop-size distribution (DSD). Four microphysics schemes (WSM-5, WSM-6, Thompson, and WDM-6) with nested simulations (3 km, 1 km, and 1/3 km) were conducted. One of the events mostly contained bright-band (BB) rainfall and lasted less than 24 h, while the other contained both BB and non-bright-band (NBB) rainfall, and lasted about 27 h. For each event, there was no clear improvement in the 1/3 km model, over the 1 km model. Overall, the WDM-6 microphysics scheme best represented the rainfall and the DSD. It appears that this scheme performed well, due to its relative simplicity in ice and mixed-phase microphysics, while providing double-moment predictions of warm rain microphysics (i.e., cloud and rain mixing ratio and number concentration). The other schemes tested either provided single-moment predictions of all classes or double-moment predictions of ice and rain (Thompson). Considering the shallow nature of precipitation in atmospheric rivers and the high-frequency of the orographic effect enhancing the warm rain process, these assumptions appear to be applicable over the southern San Francisco Bay Area.
1. Introduction
Rainfall along the California coast is known to be highly variable, due to its complex topography [1]. Annually, about 25%–50% of the precipitation along the west coast comes in the form of long, narrow corridors of moisture called atmospheric rivers [1,2,3]. These features are typically thousands of kilometers long and less than 500 km in width with anomalously high precipitable water usually exceeding 2 cm [4]. About 80% of water vapor transport in atmospheric rivers exists below 700 hPa (~3 km) [2]. Atmospheric rivers are historically responsible for many floods and extreme precipitation events in the western US [4]. Studies by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Hydrometeorological Testbed (HMT) in 2005 and 2006 found that 18 out of 20 of the most extreme precipitation events in the National Weather Service western region were due to atmospheric rivers [2]. While synoptic-scale dynamics might play a significant role, the dominant force during extreme events is orographic lift [2]. Large mountain ranges are not the only places where precipitation enhancement due to orographic enhancement occurs. Previous research has shown that smaller terrain barriers, such as the Santa Cruz Mountains, ranging from sea-level to 1154 m (3786 ft), can also significantly enhance precipitation [5,6].
Water agencies, such as the Santa Clara Valley Water District (SCVWD) in San José, CA, produce hydrologic models based on quantitative precipitation forecasts (QPF), but their accuracy relies on the quality of initial inputs from mesoscale weather models, which can have large amounts of uncertainty in mountainous regions in association with the rain shadow effect. The Center for Applied Atmospheric Research and Education (CAARE) at San José State University currently run an operational single-domain Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model for the SCVWD at a 1 km horizontal resolution. Since this domain and the water district jurisdiction span multiple areas of differing precipitation properties (i.e., different degrees of orographic enhancement and being in or out of the rain shadow), it is possible that rainfall characteristics, such as drop size, number concentration, and liquid water content might vary significantly throughout the domain. Previous research has found this to be the case at the NOAA Atmospheric River Observatory (ARO), which consists of instrumentation at Bodega Bay and Cazadero, CA. Martner et al. [7] found that for non-bright band (NBB) rainfall, the liquid water content and median drop size were similar at the two sites, but the number of drops was greater at Cazadero than at Bodega Bay. NBB rainfall occurs when condensation and coalescence are the primary processes for creating drops, and most of the precipitating layer exists below the melting layer. While Bodega Bay is situated on the coast, Cazadero is 9 km inland at the nearest coastal point, and as much as 30 km inland, depending on the direction of flow during a rainfall event. Bright-band (BB) rainfall occurs when the depth of the precipitation extends well beyond the melting layer. As precipitating particles fall to the surface, they begin as aggregated snowflakes before reaching the melting layer and becoming large raindrops. When snowflakes reach the melting layer, the outer edge starts to melt first. The fall velocity is still slow at this point, and the phase change from solid to liquid causes an increase in the dielectric constant. Being a factor of drop size and number concentration, radar reflectivity () can be increased by as much as 9 dBZ, since at this point, there are a large number of large drops with a liquid outer coating. Below this point, the large drops typically become aerodynamically unstable, and droplet breakup occurs. Hydrometeor fall velocity also increases, so there are fewer drops per unit area being sampled by the radar beam.
In this study, two strong atmospheric river (AR) events from the 2017–18 winter season were investigated. Using surface and radar observations, we intend to further explore how differing WRF microphysics schemes and horizontal resolutions might perform at accurately modeling the spatial variability of rainfall and precipitation parameters in the Santa Clara Valley. The current CAARE WRF model uses the WRF Single-Moment 3-class scheme [8], due to its simplicity and computational efficiency. However, studies have shown that the improvement from a single-moment to a double-moment scheme, regarding the representation of the real atmosphere, may be well worth the extra computational expense [9]. Igel et al. noted that single-moment schemes might be more beneficial if the purpose is research-specific, or if the user is performing long-term (climate scale) simulations [9]. Since the purpose of the CAARE model is to produce an accurate short-to-medium range forecast, the gamut of this research is the evaluation of model microphysics over areas of the water district jurisdiction where dominant rainfall processes might differ.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Model Setup
Hourly forecasts were generated for three domains at horizontal resolutions of 3 km, 1 km, and 1/3 km (Figure 1). North American Mesoscale Model analysis grids (NAM 218) with a horizontal resolution of 12 km were used as the initial forcing and boundary conditions, supplied to the model every six hours. NAM is one of the major weather models run by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) for producing weather forecasts. The microphysics parameterizations that were evaluated were the WRF Single-Moment 5-class (WSM-5) [8], WRF Single-Moment 6-class (WSM-6) [10], Thompson [11], and WRF Double-Moment 6-class (WDM-6) [12]. The predicted classes of each scheme are found in Table 1. Given the high resolution of the domains, all four were simulated with the cumulus physics turned off, to allow the model to resolve convection explicitly. The longwave and shortwave radiation were parameterized by the RRTM and Dudhia schemes, respectively [13,14]. Noah-MP [15] was used as the land surface model, while the Revised MM5 scheme was used for the surface layer [16]. The boundary layer physics were parameterized using the Yonsei University (YSU) scheme [17]. Although out of the scope of this paper, previous research has shown some non-negligible error in light-to-moderate precipitation rates when using the YSU scheme, as opposed to others [18]. Since the YSU scheme is used in the existing CAARE WRF model, it was retained for this study. Future research to explore boundary layer parameterization sensitivities in this region might be needed. Feedback was disabled to allow each domain to remain free of influence from the higher resolution inner domains. Due to compressional heating in the lee of the Santa Cruz Mountains, it was assumed that evaporation is a key process in hindering the growth and fallout of precipitation [19]. Generally, as model resolution is increased, the total evaporation is also increased [20]. In previous studies, storm structure was generally well represented by single- and double-moment schemes. The main differences in surface QPF were found to be due to differences in evaporation [21]. This led us to believe that a higher resolution model would better represent the overall variability of surface QPF in the domain. Since the CAARE WRF currently runs at a 1 km resolution, only the 1 km and 1/3 km domains were used for this study. The 3 km domain was used to allow an intermediate step between the resolution of the boundary conditions (12 km) and the first nested domain (1 km).
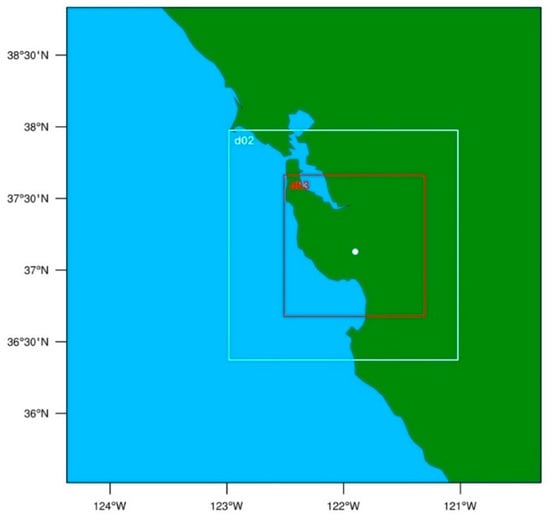
Figure 1.
Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model domain setup. d02 = 1 km, d03 = 1/3 km. The white dot in the center of d03 depicts the location of the San Francisco Bay Area WSR-88D (KMUX).

Table 1.
WRF Microphysics Scheme Predicted Classes.
The simulations were run for 36 h, starting roughly 6 h before the onset of the heaviest precipitation. With a relatively small domain and high-resolution, it was assumed that 6 h would be sufficient for the model to spin-up and to avoid cold-start biases that may occur during the first few hours of model integration. A radar forward operator was used to calculate differential reflectivity () for all schemes and rain number concentration for the single-moment schemes [22]. The operator used the T-matrix scattering table [23], and the index of refraction of liquid water at 10 °C to estimate the electromagnetic scattering properties of drops at S-band radar wavelength (λ = 10 cm). This approach allowed us to directly compare the model output with the radar observations of rain microphysical properties. Currently, the operator used is only valid for liquid drops. This was acknowledged in the research as the data used in these comparisons was carefully quality controlled and limited to below the melting layer.
2.2. Radar Observations
Level 2 data from the San Francisco Bay Area WSR-88D (KMUX) were used to diagnose rainfall microphysics and validate model performance. This radar was suitable for this research because it is not affected by beam blockage over the domain. With the radar situated at the mountaintop height (1057 m), there can be some issues with the radar not observing liquid precipitation, since the melting layer can be below the lowest scan angle. However, in the cases used in this research, the melting layer was high enough that the radar was able to adequately sample liquid precipitation. In order to compare the WRF model output with the radar measurements, the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Radx software was used to interpolate reflectivity (), differential reflectivity (), total differential phase (), and correlation coefficient () onto a Cartesian grid with a horizontal resolution of 1/3 km and a vertical resolution of 1/4 km. Before interpolation, the data were quality controlled by removing any pixels where was less than 0.98 or greater than 1 to limit the data to meteorological targets. External calibration was performed to calculate the bias, following light rain scanning method developed by Rhyzkov et al. [24,25]. As shown in Table 2, the estimated bias using this method was close to the original, as calculated by the internal calibration method. This being the case, the internal calibration method was considered to be accurate and was retained for the radar data.

Table 2.
WSR-88D Internal vs. External Bias Correction.
Observed and model-derived radar data were also used to estimate the drop size distribution (DSD) below the melting layer. Since and are both sensitive to drop size, some assumptions suggested by Brandes et al. could be made to accurately estimate the governing parameters of the DSD using only these two variables [26]. These assumptions were used to estimate the median drop size (), drop number concentration (), and water content (), based on the method [27].
2.3. Surface Observations
Surface precipitation was measured by 46 tipping bucket rain gauges maintained by the SCVWD (Figure 2). Each gauge had a minimum resolution of 1 mm, and data were stored to the nearest second for each measurement. The data were resampled into hourly observations by summing observations occurring within each hour. These gauges are well-maintained by the SCVWD staff (through personal communication with Jack Xu of SCVWD). Quality control (QC) was conducted where the water district gauges were compared with the gauge corrected Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) 1-h quantitative precipitation estimate (QPE) grids. These MRMS QPE grids were created by radar QPE and quality controlled by various rain gauges throughout the continental United States. Within the domain of study, there were 10 Remote Automated Weather Stations (RAWS), which were used in quality control of the MRMS grids (Figure 2a) [28]. The hourly SCVWD observations were evaluated using a process similar to that of an existing and robust real-time gauge quality control algorithm [29]. The MRMS 1-h QPE grids and the SCVWD hourly observations were sequentially summed to create an hourly accumulation grid for the precipitation period. Gauges that recorded no precipitation for more than two hours, while the MRMS QPE was > 0 or gauges that recorded accumulations outside the bounding equations of Qi et al. [29] (Figure 3), were removed from the analysis. Each event was considered separately. In general, the SCVWD gauges correlated very well with the MRMS grid. Figure 3 shows the SCVWD vs. MRMS relationship, before and after, the QC process, as discussed earlier. Due to the good correlation of the quality controlled SCVWD gauges, with the corrected MRMS product, the SCVWD gauges were used to validate the models due to their higher spatial resolution compared to the RAWS stations.
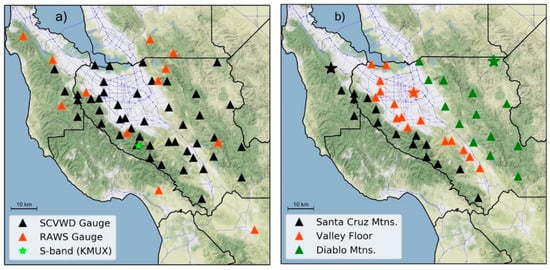
Figure 2.
Station locations within the model domain: (a) Remote Automated Weather Stations (RAWS) gauges are used to perform quality control on Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) grids. Santa Clara Valley Water District (SCVWD) gauges are used for model analysis. Location of KMUX central to the domain provides the entire domain with high quality radar measurements; (b) SCVWD stations as categorized by zone. Stars represent locations used for radar time-height cross-sections. Black star = Huddart Park, red star = San Jose, green star = Biel Ranch.
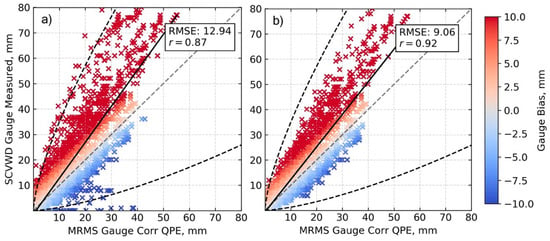
Figure 3.
MRMS vs. SCVWD hourly accumulated precipitation for both events (a) before QC; (b) after QC. Dark dashed lines are bounding equations from Qi et al. [29].
In order to evaluate the wide range of precipitation totals in the domain, the gauges have been grouped into three zones (Santa Cruz Mountains, Valley Floor, and Diablo Mountains) depending on their location, elevation, and total precipitation recorded (Figure 2b). Unless otherwise noted, a reference to any zone means an average of that zone.
2.4. Description of Events
The strengths of the ARs used in this study were diagnosed via integrated vapor transport (IVT), which is representative of the total column integrated water vapor and wind speed and direction [30]. Based on a scale created by Ralph et al. [31], strong ARs have an IVT ranging from 750–1000 kg·m−1·s−1. Each of the events produced widespread precipitation, throughout the entire Bay Area. Rainfall totals from the two events were highly variable (σ2 = 270.06) and ranged from 15–83 mm, with the highest totals occurring in the Santa Cruz Mountains (Diablo Mountains) in the west (east) of San José. Rainfall rates during the November 2017 event were significantly higher () than those during the April 2018 event.
The stronger of the two events occurred on 16 November 2017 (AR1), where as much as 85 mm of rain was recorded in the domain. The Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) polar-orbiting satellite shows the narrow plume of water vapor directed at the California coast with precipitable water (PW) values exceeding 3.5 cm near the coast (Figure 4). The nearest upper-air observing site (Oakland) recorded a PW of 3.54 cm and a freezing level of 3,266 m at 12:00 UTC on 16 November 2017. At this time, an upper-level (500 hPa) trough was located over the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of British Columbia, with weak ridging downstream over the central United States and into Saskatchewan. Strong quasi-geostrophic (QG) ascent existed over the domain with a 115-knot jet streak (300 hPa) stretching from the Bay Area into Western Montana. According to the 12:00 UTC Oakland sounding, the atmosphere was conditionally unstable up to about 500 hPa, beyond which the environmental lapse rate was approximately moist adiabatic. The combination of conditional instability and strong synoptic forcing allowed moist parcels to be lifted well above the feezing level. This is evident when looking at a time–height cross-section of the radar data (Figure 5). One station in each zone with the best possible vertical radar coverage was selected (Figure 2b), and each used the gridded data output from the previously discussed Radx software. All three stations showed radar echoes extending well beyond the freezing level and represented a BB rainfall signature to some degree, which was evident in and . The rainfall came to an abrupt end with the cold frontal passage between 00:00–03:00 UTC on 17 November 2017.
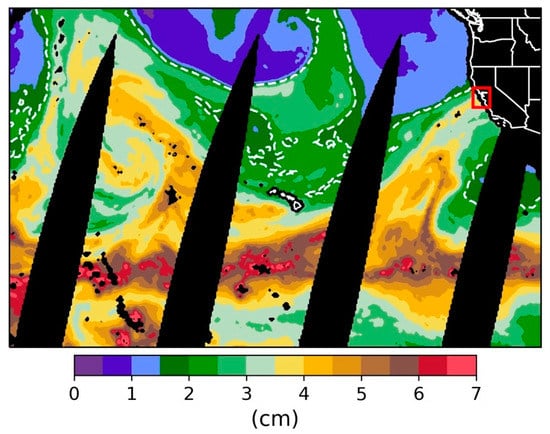
Figure 4.
Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) satellite image of daily average column integrated water vapor for 16 November, 2017. Red box is the approximate model domain. Dashed white line = 2 cm.
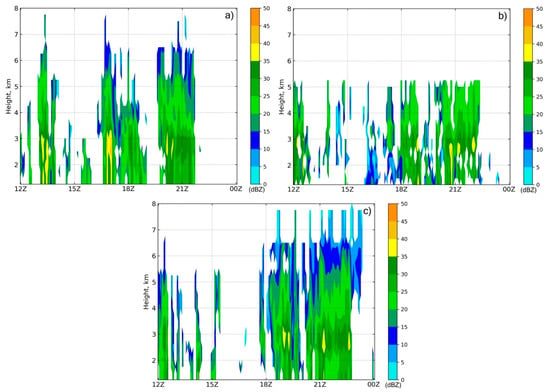
Figure 5.
Time-height cross section of observed for (a) Huddart Park, (b) San Jose, and (c) Biel Ranch starting 16 November 2017 at 12:00 UTC.
The 6 April 2018 event (AR2) was weaker than the November event, with regards to the overall rainfall rate and total accumulation, where the maximum rainfall was only 61 mm over a more extended period (about 27 h, as opposed to about 12 h for the November event). The April event was the wetter of the two, with SSM/I imagery showing PW values between 4.5–5 cm off the coast (Figure 6). The 00:00 UTC (7 April 2018) Oakland sounding measured PW at 4.32 cm and a freezing level of 4267 m. At 12:00 UTC on 6 April 2018, an upper-level (500 hPa) trough was located over the Pacific Ocean, further west than in the November event, with a 150 knot jet streak (300 hPa) offshore with a diffuse exit region over Washington, Oregon, and Northern California. At this time, the atmosphere was absolutely stable up to about 500 hPa where the environmental lapse rate became approximately moist adiabatic. The onset of the precipitation was due to a diffuse warm frontal passage at about 06:00 UTC on 6 April 2018. In the absence of a large-scale QG ascent, the warm front was the primary forcing mechanism during this period, bringing modest rainfall rates of typically less than 2 mm/hour to most of the domain. The passage of the warm front was followed by approximately 17 h in the warm sector where the rainfall persisted, but rates were much lower, and radar echo tops were limited to beneath the freezing level (Figure 7). Observed time–height radar cross-sections confirmed that the rainfall during the warm frontal passage exhibited a BB signature, while all of the rain that occurred in the warm sector was NBB (warm rain process). With the approach of the cold front, rainfall rates increased, and radar observations showed a BB signature, once again, before the rainfall ended with the cold frontal passage at around 14:00–15:00 UTC.
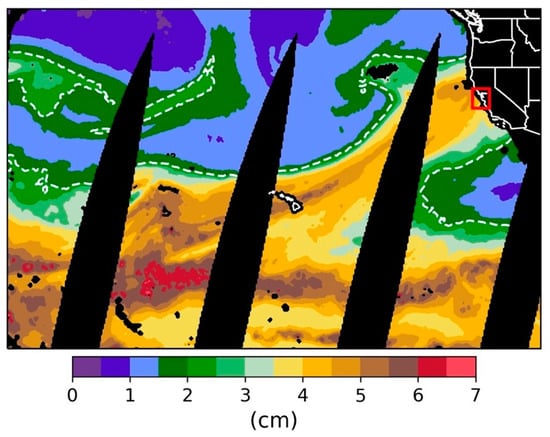
Figure 6.
SSM/I satellite image of daily average column integrated water vapor for 6 April 2018. Red box is the approximate model domain. Dashed white line = 2 cm.
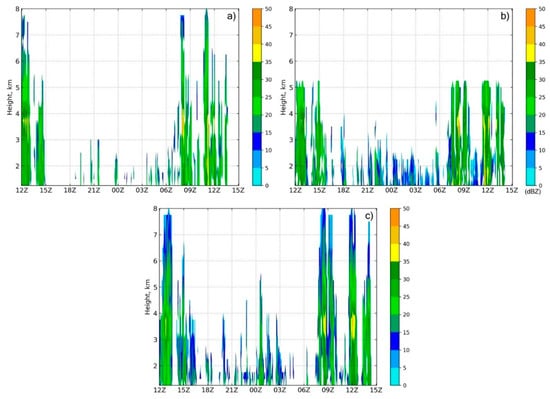
Figure 7.
Time–height cross-section of observed for (a) Huddart Park, (b) San Jose, and (c) Biel Ranch starting 6 April 2018 at 12:00 UTC.
3. Results
3.1. Simulated Precipitation
The timing of the frontal passages was predicted reasonably well by the models, in both events. All of the models were about three hours too slow with the warm frontal passage in AR2. However, all of them reasonably predicted the strength of the forcing near the warm front. Albeit late, the rainfall that fell during the warm front was eventually accounted for by the models. Neiman et al. [32] used the 850–1150 m mean wind speed and PW to derive upslope water vapor flux. The same methodology was applied here to diagnose the degree of orographic forcing present in the ARs (Figure 8). With no profiling sites available, a point was arbitrarily chosen on the windward slope of the Santa Cruz Mountains, near the Big Basin Redwoods State Park (upwind of San José). NAM analysis grids (same as that used for model initialization) were used in place of direct observations. Aside from the onset and ending of rainfall with the frontal passage, integrated water vapor (IWV) did not fluctuate very much throughout the event, so wind speed fluctuations were the main contributors to large changes in upslope water vapor flux during the ARs. Observed rainfall rates generally correlated well with upslope water vapor flux in all zones (Figure 9). With this, we can conclude that orographic forcing played a role in modulating the rainfall rates during both events. During the NBB portion of AR2 (from 6 April 15:00 UTC to 7 April 08:00 UTC), upslope water vapor flux remained high, yet rainfall rates were markedly lower (Figure 9b,d,f). In the absence of strong synoptic or mesoscale forcing, it was evident that orographic forcing was the primary driver of precipitation during this time; thus, the warm rain process dominated. For AR1, it seemed that the strength of the synoptic forcing was overdone by the model in the Valley Floor and the Diablo Mountain zones. The rainfall rates were significantly higher, with not much change in the upslope water vapor flux. After this initial overestimation, all models simulated rainfall rates relatively well.
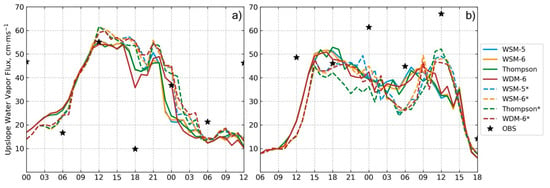
Figure 8.
Upslope water vapor flux at Big Basin Redwoods State Park on (a) 16 November 2017 starting at 00:00 UTC and (b) 6 April 2018 starting at 06:00 UTC. * denotes 1/3 km resolution.
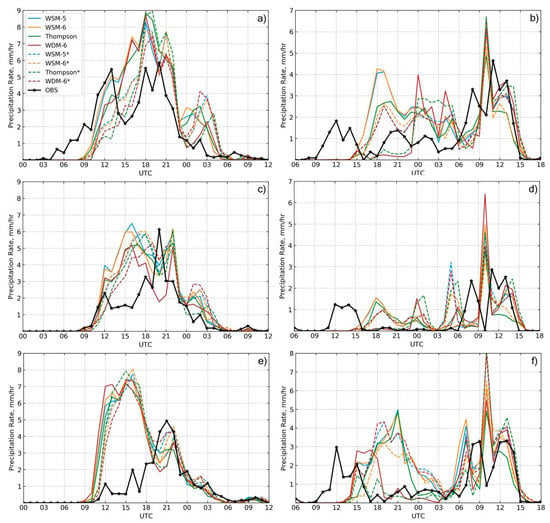
Figure 9.
Zone average simulated and observed hourly precipitation rate for (a,b) Santa Cruz Mountains, (c,d) Valley Floor, and (e,f) Diablo Mountains; (a,c,e) atmospheric rivers (AR1), and (b,d,f) AR2. * denotes 1/3 km resolution.
The models generally predicted rainfall rates with the lowest root-mean-square error in the Valley Floor zone (Figure 10). This agrees with previous research stating that the predictability of precipitation was lower near the threshold between regimes (e.g., in or out of a rain shadow) [6]. Since most of the rain gauges in the Santa Cruz Mountains zone are on the leeward side of the mountain range, these might be considered to be near this threshold. As expected, rainfall rates during AR1 were better represented by the double-moment microphysics (MP) schemes, especially in the Valley Floor zone. This was likely because the cold cloud process dominates much of the precipitation fallout over this area, since the Valley Floor is in a rain shadow and the degree to which orographic forcing enhances precipitation was smaller. In contrast, the single-moment MP schemes predicted rainfall rates with nearly the same amount of accuracy as the double-moment schemes for this event. For AR2, there was no clear winner regarding simulated rainfall rate. An exception was in the Diablo Mountains zone where the high-resolution (1/3 km) WSM-5 scheme, low-resolution (1 km) WDM-6 scheme, and both resolutions of the Thompson scheme predicted rainfall rates with significantly higher accuracy. The low-resolution, single-moment schemes also experienced significant amounts of error when compared to the high-resolution simulations in the Santa Cruz Mountains zone. This could be due to the better representation of the terrain features. The high-resolution, double-moment schemes performed well in this case, possibly due to the relatively simple physics involved in the NBB rainfall process, which dominated AR2. Accumulated rainfall for AR2 was predicted with higher accuracy than for AR1, possibly owing to the long period of precipitation lacking in complex mixed-phase microphysics (NBB rainfall). For the low-resolution simulations, the double-moment MP schemes predicted accumulation with a higher accuracy than the single-moment MP schemes in most cases, except the Valley Floor in AR2, where all schemes performed well.
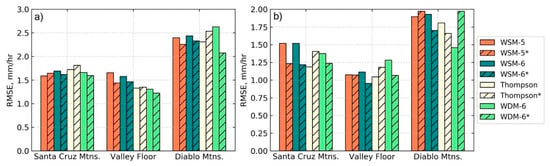
Figure 10.
Hourly precipitation rate root-mean-squared-error for (a) AR1 and (b) AR2. * denotes 1/3 km resolution.
3.2. Simulated Radar and DSD
Model-derived and were compared with observations to study the model representation of the DSD. Note, while the was derived directly using the WRF microphysics, was calculated using the radar forward operator described in Section 2.2 and was limited to below the freezing level. The strength of the bright-band was evaluated by finding the maximum at the bright-band level. For AR1, the single-moment MP schemes overestimated, while the Thompson scheme underestimated the strength of the bright-band, at both resolutions. The WDM-6 scheme provided the best representation without any significant difference between resolutions. For AR2, the single-moment MP schemes more accurately reproduced the bright-band, while the double-moment schemes were too strong. Similar to AR1, there were no significant differences between the two resolutions.
Precipitation parameters calculated via radar variables from the simulations and observations showed little spatial variability, when averaged for each zone (Figure 11). An exception was an increase in the observed inland, which was expected due to the orographic enhancement and was consistent with findings of previous research [7]. Due to the lack of spatial variability in this study, the DSD was evaluated without regard to zone for simplicity. Normalized joint probability density functions (PDF) of vs. were created to study the model representation of raindrop size statistics (Figure 12). The PDFs for the 1/3 km domain were nearly identical to those from the 1 km domain over the same area for both ARs; thus, only the 1 km PDFs are shown. The PDFs for the single-moment schemes were also nearly identical to each other, so the WSM-5 PDF was not shown. The peak frequencies in the observed PDFs were 24 dBZ and 0.11 dB for AR1, and 18 dBZ and −0.1 dB for AR2. 50% of the distribution extended from 15 to 30 dBZ () and −0.4 to +0.5 dB () for AR1, providing evidence of the relatively stable DSD. The PDF of AR2 showed more variability where 50% of the distribution existed in the range of 9 to 30 dBZ () and −0.5 to +0.5 dB (). Both single-moment schemes had abnormally high frequencies of large drops, when compared to the observations for both ARs. The Thompson scheme overestimated the frequency of large drops in AR1 and small drops in AR2. The WDM-6 scheme best represented the maximum frequency in both ARs, but contained too many small drops at a lower . As stated by Brown et al. [22] and seen here, these low reflectivities in the WDM-6 scheme might not have been observed due to a lack of sensitivity in the radar at long ranges. In addition to overestimating the drop sizes, the Thompson scheme overestimated the frequency of high for . The WDM-6 scheme produced an unrealistic DSD with an abnormally high frequency of large across the entire range of for AR2. While the Thompson scheme (both ARs) and the WDM-6 scheme (AR1) produced a similar distribution, they were at a much lower frequency.
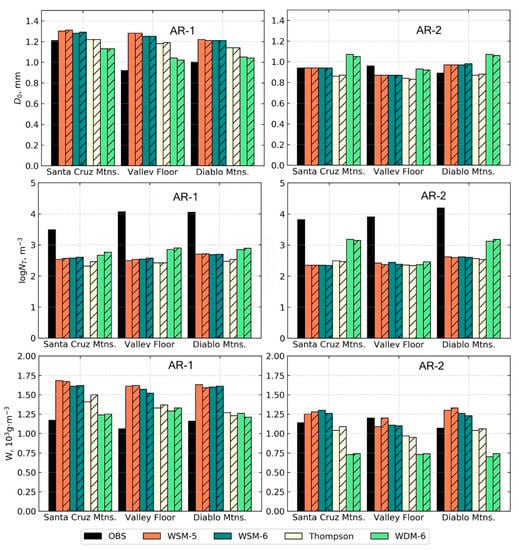
Figure 11.
Radar-derived median drop size (), number concentration (), and water content (). Hatched bars are the 1/3 km model.
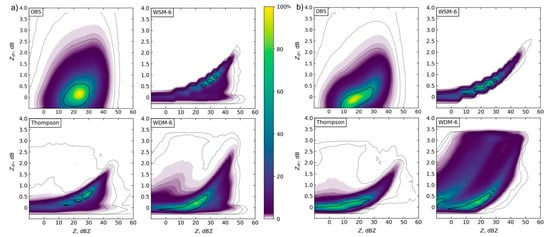
Figure 12.
Normalized joint frequency distributions of and (1 km model) for (a) AR1 and (b) AR2. Solid black contour represents 50%. Grey dotted lines represent 2.5, 1, 0.1, and 0.01%.
4. Conclusions and Remarks
In this study, two strong atmospheric river events that impacted the central California coast were simulated. Four different microphysics parameterizations (WSM-5, WSM-6, Thompson, and WDM-6) at two horizontal resolutions (1 km and 1/3 km) were used to study the model representation of rainfall and the DSD in the southern San Francisco Bay Area (Santa Clara Valley). With highly variable terrain in this area, there was motivation to study whether or not considerable variability exists in the DSD, in which certain MP schemes or resolutions would better represent than others. Using the methods discussed in Section 2.2, the radar-derived precipitation parameters were calculated and showed results similar to previous research where the water content was found to be consistent, but the drop number concentration increased as rainfall was orographically enhanced [7]. This was mainly noticeable in the Diablo Mountains zone, during AR2, where NBB rainfall persisted for most of the forecast period. This phenomenon was less noticeable during AR1, where the BB rainfall process dominated the entire forecast period. This was due to the rainfall production process being the same, no matter the zone, as opposed to the NBB rainfall process being highly variable since it was primarily caused by orographic forcing. Due to these similarities in the precipitation parameters, it was assumed that the DSD was relatively uniform throughout the domain, especially during conditions where heavier rainfall was produced (BB). Future research is planned to quantify this variability, or lack thereof, using OTT Parsivel2 disdrometers and a gap-filling X-band radar, situated within the valley, to better sample the atmosphere closer to the surface. The SCVWD currently uses this radar for quantitative precipitation estimation [33].
Overall, the double-moment MP schemes produced more accurate rainfall rates in the Valley Floor and Diablo Mountains during AR1, but contained similar errors to the single-moment MP schemes during AR2. This was likely due to the simpler precipitation production process (NBB) during much of AR2, in which the simplicity of the single-moment MP schemes might be sufficient to provide an accurate simulation. There seemed to be no clear result regarding the accuracy of the models and horizontal resolution. Due to this reason, and since this model is operational and needs to be as computationally efficient as possible, a resolution of 1 km will be retained. When considering the 1 km resolution model over both events, the WDM-6 scheme provided the lowest error in accumulated rainfall (Figure 13). The performance of this scheme was especially noticeable for AR2, where both rainfall types (BB and NBB) were present for extended periods. Future research will be needed to verify this, but it was hypothesized that this was due to the double-moment warm rain microphysics (mixing ratio and number concentration of cloud and rain), where the Thompson scheme provided double-moment predictions of ice and rain. The warm rain microphysics might be the more important foci for this locale, since mixed-phase and frozen precipitation at the surface are extremely rare, and nearly all precipitating clouds are affected by orographic forcing, to some degree. Previous research in the southeastern United States found that 15%–20% of the total accumulated precipitation can be contributed to NBB rainfall [34]. This is relatively close to what was observed during AR2 (~21%). As expected, the highest NBB accumulations occurred in the Santa Cruz and Diablo Mountains zones, where the orographic forcing was stronger. Further research is needed to determine the contribution of the NBB rainfall on the seasonal scale, but based on the contribution found here in AR2, it is assumed that NBB rainfall accumulations cannot be ignored when evaluating model performance. This is especially true for urban areas and catchments that might flow into urban areas. A multi-year rainfall climatology is needed to further assess the overall contribution of NBB rainfall in this region. Additionally, although the two ARs chosen for this study contained large differences in their durations of BB and NBB rainfall, more events will ultimately need to be studied to fully assess MP scheme accuracy for this region.
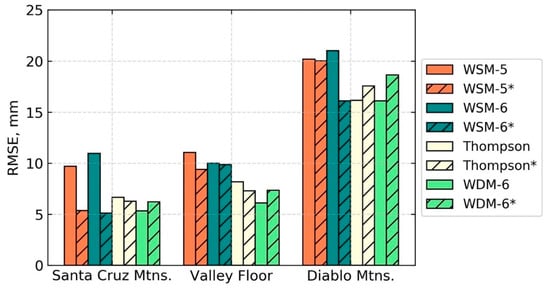
Figure 13.
Accumulated precipitation root-mean-squared-error for both AR events. * denotes 1/3 km resolution.
Considering the simulated results from the two ARs, it is recommended that over the Bay Area the WDM-6 MP is the most suitable scheme for its ability to model mixed-phase processes aloft, while providing double-moment predictions of warm-rain, below the melting layer. This scheme best represented the distribution of vs. frequencies > 50% (Figure 12) and the total accumulated rainfall (Figure 13). It is also recommended that a horizontal resolution of 1 km be retained to keep the model as efficient as possible.
Author Contributions
Writing—Original Draft Preparation, D.B.; writing—Review and Editing, D.B. and S.C.; Supervision, S.C.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge discussions with Jack Xu, Nahm Lee, Liang Xu, and Emily Zedler at the Santa Clara Valley Water District. We would also like to acknowledge high-performance computing support from Cheyenne (doi:10.5065/D6RX99HX) provided by NCAR’s Computational and Information Systems Laboratory, sponsored by the National Science Foundation. Comments and suggestions by two anonymous reviewers were much appreciated. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation Grant OAC-1626645, and NASA MUREP-NNX15AQ02A.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dettinger, M.D.; Ralph, F.M.; Das, T.; Neiman, P.J.; Cayan, D.R. Atmospheric Rivers, Floods and the Water Resources of California. Water 2011, 3, 445–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Dettinger, M.D. Historical and National Perspectives on Extreme West Coast Precipitation Associated with Atmospheric Rivers During December 2010. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Molotch, N.P.; Waliser, D.E.; Fetzer, E.J.; Neiman, P.J. Extreme snowfall events linked to atmospheric rivers and surface air temperature via satellite measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Dettinger, M.D. Storms, Floods, and the Science of Atmospheric Rivers. EOS Trans. AGU 2011, 92, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Coleman, T.; Neiman, P.J.; Zamora, R.J.; Dettinger, M.D. Observed Impacts of Duration and Seasonality of Atmospheric-River Landfalls on Soil Moisture and Runoff in Coastal Northern California. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Persson, P.O.G.; White, A.B.; Strem, E.T.; Andrews, E.D.; Antweiler, R.C. The Impact of a Prominent Rain Shadow on Flooding in California’s Santa Cruz Mountains: A CALJET Case Study and Sensitivity to the ENSO Cycle. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1243–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martner, B.E.; Yuter, S.E.; White, A.B.; Matrosov, S.Y.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Ralph, F.M. Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics in California Coastal Rainfall for Periods with and without a Radar Bright Band. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of Clouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igel, A.L.; Igel, M.R.; van den Heever, S.C. Make It a Double? Sobering Results from Simulations Using Single-Moment Microphysics Schemes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-O.J. The WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM-6). J. Korean Metorol. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit Forecasts of Winter Precipitation Using an Improved Bulk Microphysics Scheme. Part II: Implementation of a New Snow Parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.-S.S.; Hong, S. Development of an Effective Double-Moment Cloud Microphysics Scheme with Prognostic Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) for Weather and Climate Models. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 1587–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Mitchell, K.E.; Chen, F.; Ek, M.B.; Barlage, M.; Kumar, A.; Manning, K.; Niyogi, D.; Rosero, E.; et al. The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J.; González-Rouco, J.F.; Navarro, J.; Montávez, J.P.; García-Bustamante, E. A Revised Scheme for the WRF Surface Layer Formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, G.A.; Zoumakis, N.M.; Melas, D.; Lolis, C.J.; Kassomenos, P. Sensitivity of WRF to boundary layer parameterizations in simulating a heavy rainfall event using different microphysical schemes. Effect on large-scale processes. Atmos. Res. 2013, 132–133, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A. Orographic Effects on Precipitating Clouds. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.H.; Morrison, H. Sensitivity of a Simulated Squall Line to Horizontal Resolution and Parameterization of Microphysics. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, N.; Ćurić, M. Precipitation sensitivity to the mean radius of drop spectra: Comparison of single and double-moment bulk microphysical schemes. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.R.; Bell, M.M.; Frambach, A.J. Validation of simulated hurricane drop size distributions using polarimetric radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, J. High-level interface to T-matrix scattering calculations: Architecture, capabilities and limitations. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.G.; Zittel, W.D.; Lee, R.R.; Ice, R.L.; Hoban, N.P. Methods for Identifying Systematic Differential Reflectivity (Zdr) Biases on the Operational WSR-88D Network. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 16–20 September 2013; Volume 9, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Giangrande, S.E.; Melnikov, V.M.; Schuur, T.J. Calibration issues of dual-polarization radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. An Evaluation of a Drop Distribution–Based Polarimetric Radar Rainfall Estimator. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Drop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Radar: Model and Application. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cockcks, S.; Martinaitis, S.; et al. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) quantitative precipitation estimation: Initial operating capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Martinaitis, S.; Zhang, J.; Cocks, S. A Real-Time Automated Quality Control of Hourly Rain Gauge Data Based on Multiple Sensors in MRMS System. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1675–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Wick, G.A.; Lundquist, J.D.; Dettinger, M.D. Meteorological Characteristics and Overland Precipitation Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Based on Eight Years of SSM/I Satellite Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Dettinger, M.; Cordeira, J.M.; Rutz, J.J.; Schick, L.; Anderson, M.; Smallcomb, C.; Reynolds, D. A Scale to Characterize the Strength and Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Gottas, D.J.; Gutman, S.I. A water vapour flux tool for precipitation forecasting. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2009, 162, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Chen, H.; Johnson, L.E. High Resolution Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the San Francisco Bay Area: Rainfall Monitoring for the Urban Environment. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 96, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Cifelli, R.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Radar rain-rate estimators and their variability due to rainfall type: An assessment based on hydrometeorology testbed data from the southeastern United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2016, 55, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).