Determination of Semivolatile Organic Nitrates in Ambient Atmosphere by Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization–Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Instrumentation
2.4.1. Chromatography Condition
2.4.2. MS Condition
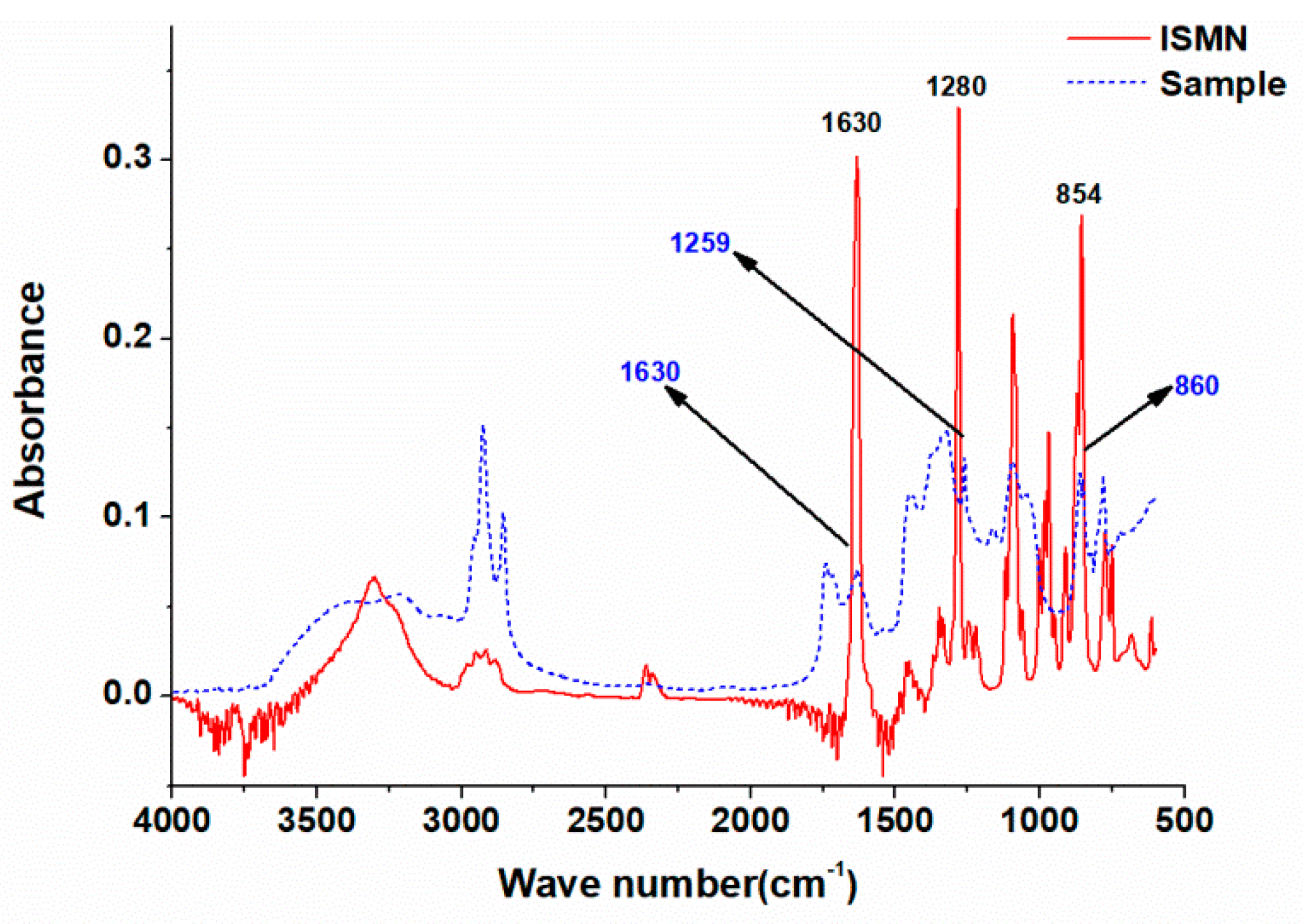
2.4.3. FTIR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
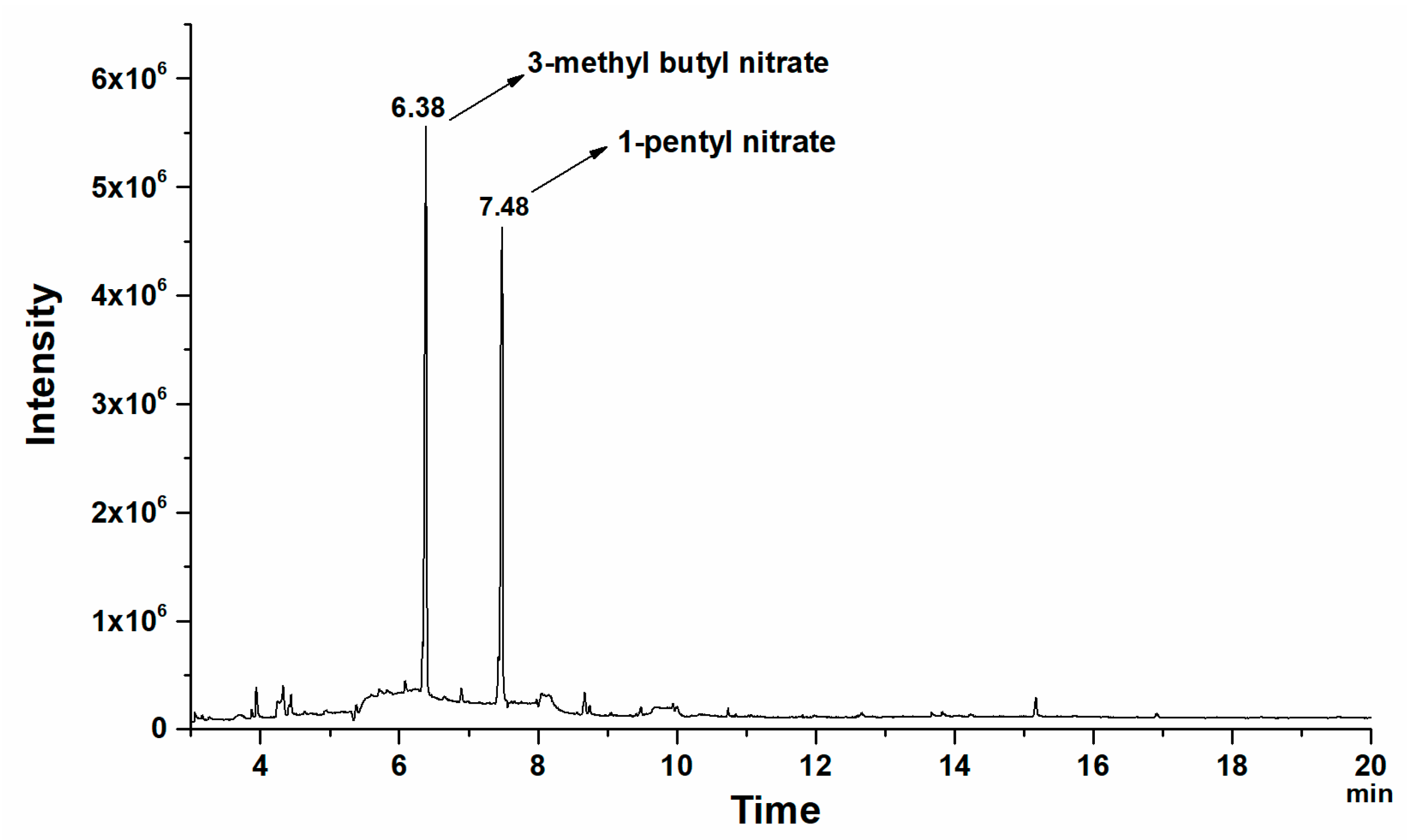
3.1. Optimization of the GC-MS Method
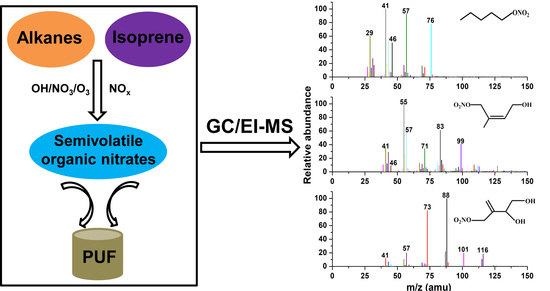
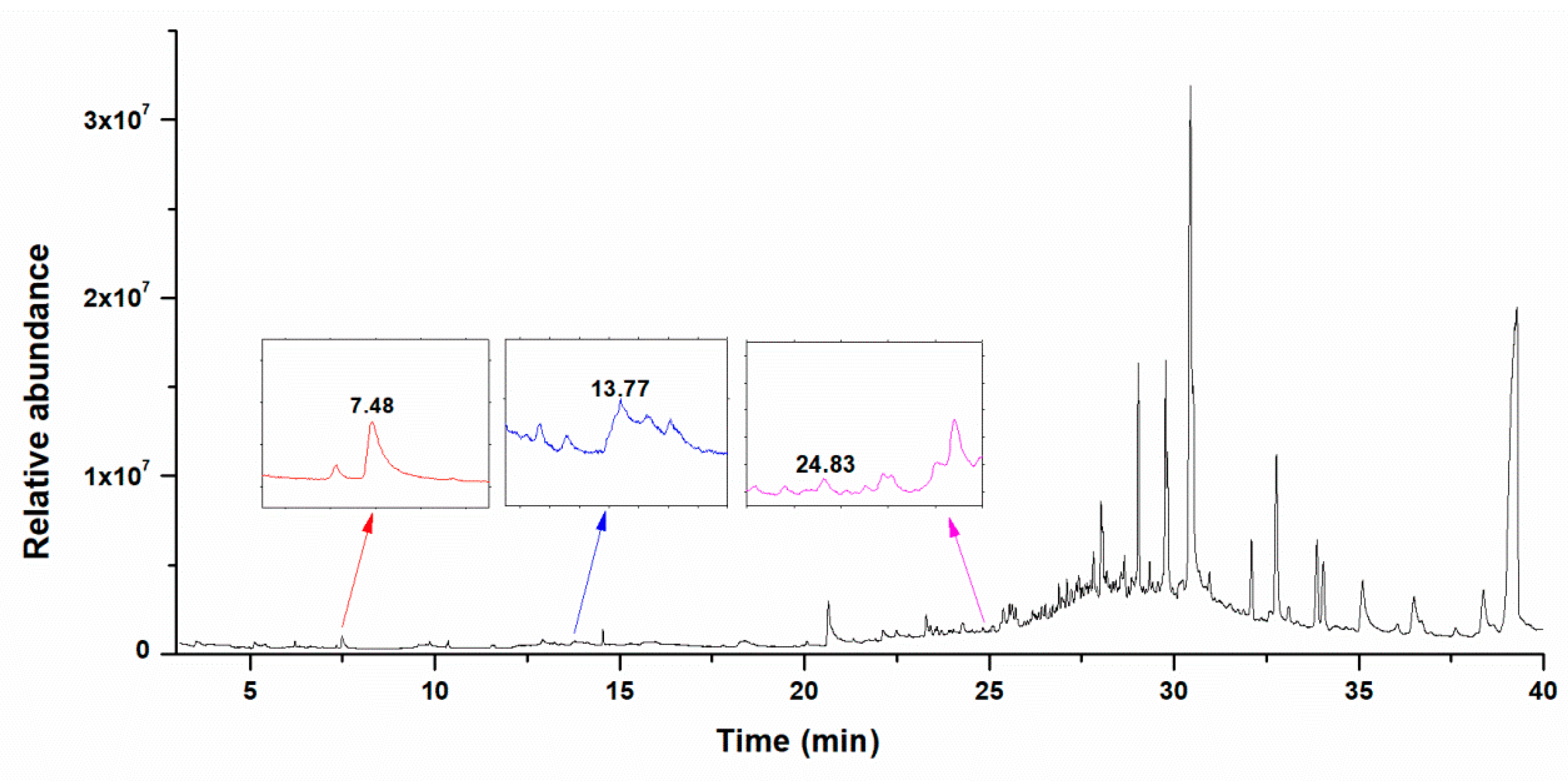
3.2. Identification of the SVONs
3.2.1. 1-Pentyl Nitrate
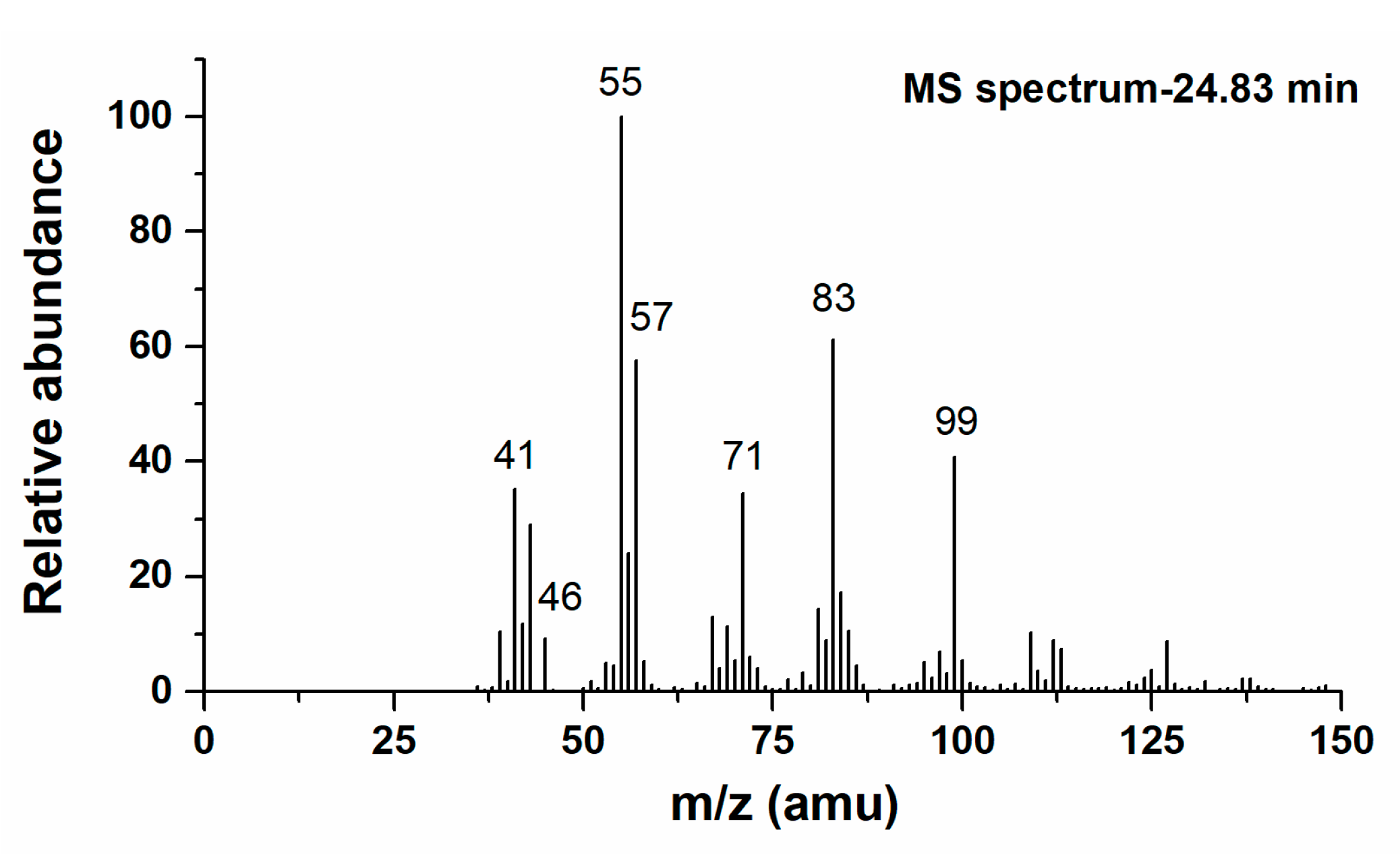
3.2.2. 4-Hydroxy-Isoprene Nitrate
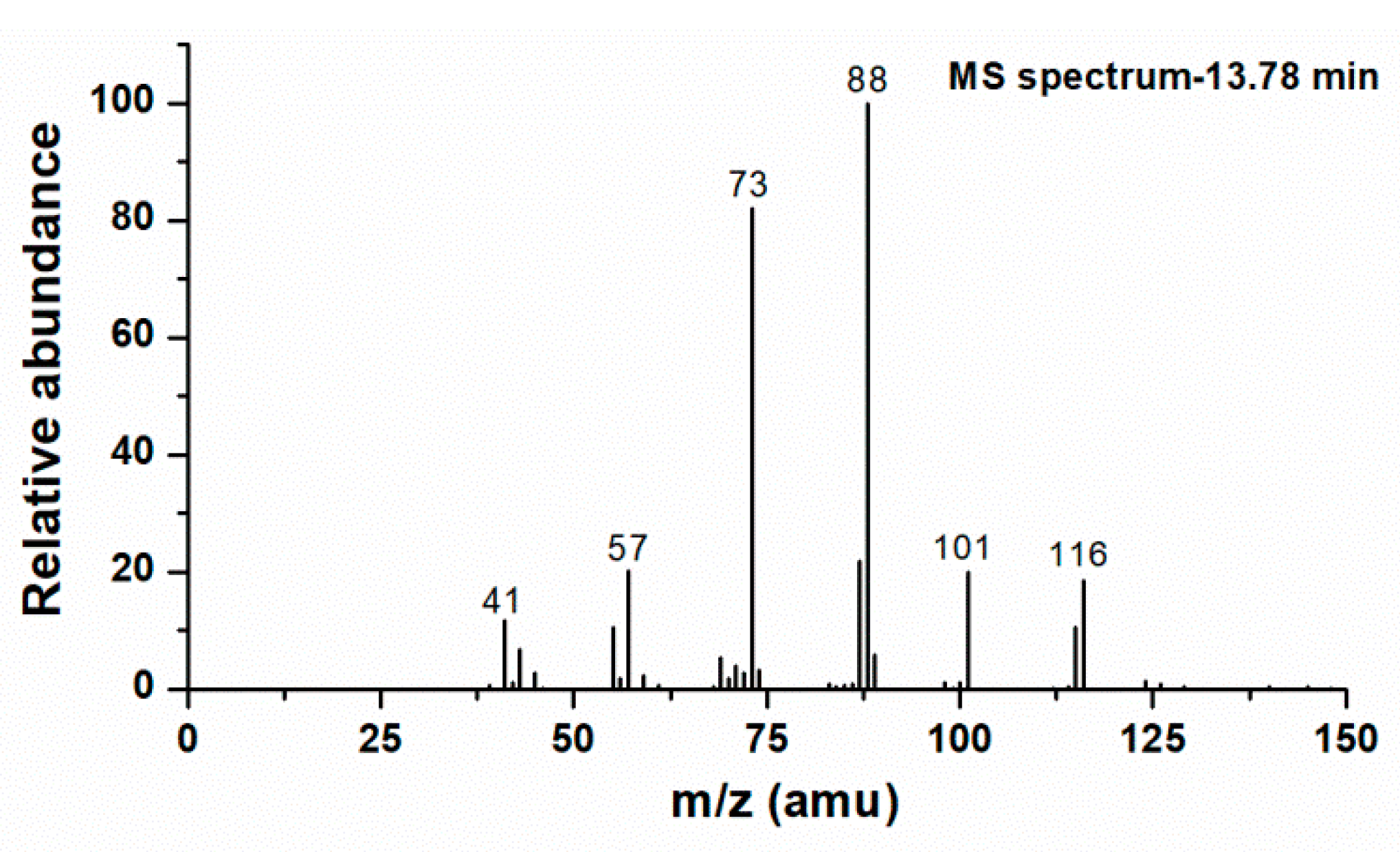
3.2.3. (3,4)-Di-Hydroxy-Isoprene Nitrate
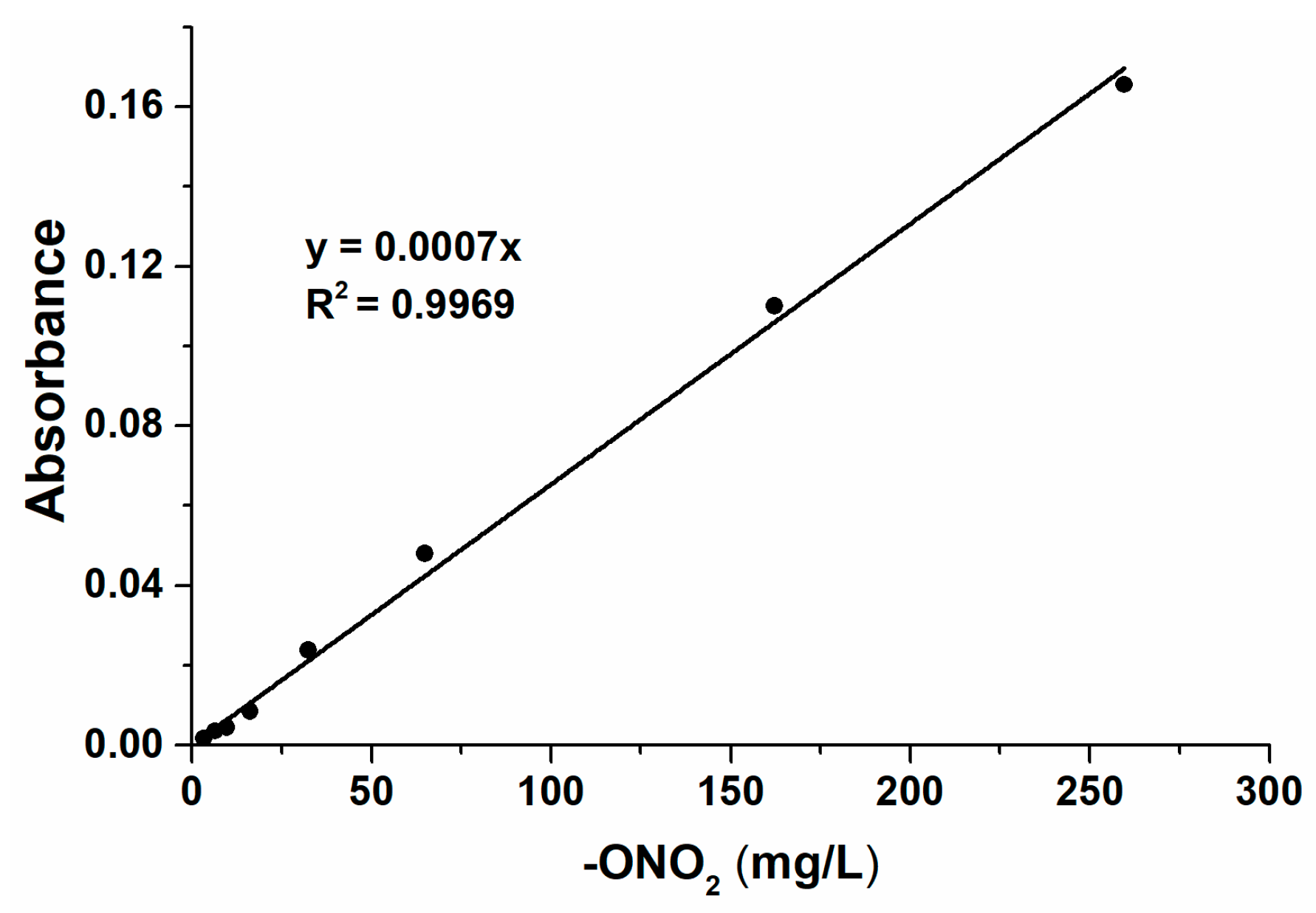
3.3. Quantification of SVONs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blake, N.J.; Blake, D.R.; Swanson, A.L.; Atlas, E.; Flocke, F.; Rowland, F.S. Latitudinal, vertical, and seasonal variations of C1-C4 alkyl nitrates in the troposphere over the Pacific Ocean during PEM-Tropics A and B: Oceanic and continental sources. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.J.; Wang, T.; Guo, H.; Kwok, Y.; Flocke, F.; Atlas, E.; Meinardi, S.; Rowland, F.S.; Blake, D.R. Long-term atmospheric measurements of C1–C5 alkyl nitrates in the Pearl River Delta region of southeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renbaum, L.H.; Smith, G.D. Organic nitrate formation in the radical-initiated oxidation of model aerosol particles in the presence of NOx. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treves, K.; Shragina, L.; Rudich, Y. Henry’s law constants of some β-, γ-, and δ-hydroxy alkyl nitrates of atmospheric interest. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; McAvey, K.M.; Pratt, K.A.; Groff, C.J.; Hostetler, M.A.; Lipton, M.A.; Starn, T.K.; Seeley, J.V.; Bertman, S.B.; Teng, A.; et al. Observation of isoprene hydroxynitrates in the southeastern United States and implications for the fate of NOx. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11257–11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, B.R.; Allen, H.M.; Draper, D.C.; Brown, S.C.; Wild, R.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Day, D.A.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Hu, W.; de Gouw, J.; et al. Organic nitrate aerosol formation via NO3 + biogenic volatile organic compounds in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13377–13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauderly, J.L.; Chow, J.C. Health effects of organic aerosols. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.L.; Brown, S.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Atlas, E.; Cohen, R.C.; Crowley, J.N.; Day, D.A.; Donahue, N.M.; Fry, J.L.; Fuchs, H.; et al. Nitrate radicals and biogenic volatile organic compounds: Oxidation, mechanisms, and organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2103–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, D.K.; Matsunaga, A.; Docherty, K.S.; Surratt, J.D.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Ziemann, P.J.; Jimenez, J.L. Response of an aerosol mass spectrometer to organonitrates and organosulfates and implications for atmospheric chemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6670–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, A.L. Direct evidence for a marine source of C1 and C2 alkyl nitrates. Science (80-) 2002, 297, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arey, J.L.; Aschmann, S.M.; Kwok, E.S.C.; Atkinson, R. Alkyl nitrate, hydroxyalkyl nitrate, and hydroxycarbonyl formation from the NOx−air photooxidations of C5−C8 n-alkanes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, D.A.; Liu, S.; Russell, L.M.; Ziemann, P.J. Organonitrate group concentrations in submicron particles with high nitrate and organic fractions in coastal southern California. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, J.L.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; Rollins, A.W.; Brauers, T.; Brown, S.S.; Dorn, H.-P.; Dubé, W.P.; Fuchs, H.; Mensah, A.; Rohrer, F.; et al. SOA from limonene: Role of NO3 in its generation and degradation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3879–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.J.; Chan, A.W.H.; Ng, N.L.; Kjaergaard, H.G.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Wennberg, P.O. Peroxy radical chemistry and OH radical production during the NO3-initiated oxidation of isoprene. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2259–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalter, R.; Neeb, P.; Grossmann, D.; Kolloff, A.; Horie, O.; Moortgat, G. Products and mechanism of the gas phase reaction of ozone with β-pinene. J. Atmos. Chem. 2000, 35, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, J.L.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; Rollins, A.W.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Brown, S.S.; Fuchs, H.; Dubé, W.; Mensah, A.; Maso, M.D.; Tillmann, R.; et al. Organic nitrate and secondary organic aerosol yield from NO3 oxidation of β-pinene evaluated using a gas-phase kinetics/aerosol partitioning model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1431–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.S.; Wood, E.C.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Thornton, J.A.; Day, D.A.; Küster, W.; Williams, E.J.; Jobson, B.T.; Cohen, R.C. Observations of total alkyl nitrates during Texas Air Quality Study 2000: Implications for O3 and alkyl nitrate photochemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 7050–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surratt, J.; Murphy, S.M.; Kroll, J.H.; Ng, N.L.; Hildebrandt, L.; Sorooshian, A.; Szmigielski, R.; Vermeylen, R.; Maenhaut, W.; Claeys, M.; et al. Chemical composition of secondary organic aerosol formed from the photooxidation of isoprene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 9665–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.S.; Ziemann, P.J. Reaction of oleic acid particles with NO3 radicals: Products, mechanism, and implications for radical-initiated organic aerosol oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 3567–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, W.A.; Herner, J.D.; Green, P.G.; Kleeman, M.J. Size distribution of health-relevant trace elements in airborne particulate matter during a severe winter stagnation event: Implications for epidemiology and inhalation exposure studies. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepson, P.B.; Muthuramu, K.; Roussel, P.B.; O’Brien, J.M.; Hao, C.; Niki, H.; Hastie, D.R.; Taylor, R. Measurements of alkyl and multifunctional organic nitrates at a rural site in Ontario. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 22795. [Google Scholar]
- Thieser, J.; Schuster, G.; Schuladen, J.; Phillips, G.J.; Reiffs, A.; Parchatka, U.; Pöhler, D.; Lelieveld, J.; Crowley, J.N.; Phillips, G.; et al. A two-channel thermal dissociation cavity ring-down spectrometer for the detection of ambient NO2, RO2NO2 and RONO2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 553–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Suresh, S.; Guo, H.; Weber, R.J.; Ng, N.L. Aerosol characterization over the southeastern United States using high-resolution aerosol mass spectrometry: Spatial and seasonal variation of aerosol composition and sources with a focus on organic nitrates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7307–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.; Egeløv, A.H.; Granby, K.; Skov, H. Observations on particulate organic nitrates and unidentified components of NOy. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, P.J.; Perring, A.E.; Bertram, T.H.; Flocke, F.M.; Roberts, J.M.; Singh, H.B.; Huey, L.G.; Thornton, J.A.; Wolfe, G.M.; Murphy, J.G.; et al. Total Peroxy Nitrates (ΣPNs) in the atmosphere: The Thermal Dissociation-Laser Induced Fluorescence (TD-LIF) technique and comparisons to speciated PAN measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, W.; Wen, L.; Li, D.; Chen, T. Understanding unusually high levels of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in winter in Urban Jinan, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Nie, W.; Simpson, I.J.; Gao, R.; Blake, D.R.; et al. Summertime C1-C5 alkyl nitrates over Beijing, northern China: Spatial distribution, regional transport, and formation mechanisms. Atmos. Res. 2018, 204, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Xu, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, B. Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and peroxypropionyl nitrate (PPN) in urban and suburban atmospheres of Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8173–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Gu, R.; Lu, C.; Zhu, F.; Xue, L.; Xie, H.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Identification and semi-quantification of biogenic organic nitrates in ambient particulate matters by UHPLC/ESI-MS. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 176, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutzel, A.; Rodigast, M.; Iinuma, Y.; Böge, O.; Herrmann, H. An improved method for the quantification of SOA bound peroxides. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jing, X.; Fleischmann, S.; Wilke, B.-M. Comparative study of extraction methods for the determination of PAHs from contaminated soils and sediments. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljevic, B.; Hedayat, F.; Stevanovic, S.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Bottle, S.E.; Ristovski, Z.D. To sonicate or not to sonicate PM filters: Reactive oxygen species generation upon ultrasonic irradiation. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesz, P.; Berdahl, D.; Christman, C.L. Free radical generation by ultrasound in aqueous and nonaqueous solutions. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 64, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, E.A.; Perraud, V.; Zelenyuk, A.; Ezell, M.J.; Johnson, S.N.; Yu, Y.; Imre, D.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Alexander, M.L. Comparison of FTIR and particle mass spectrometry for the measurement of particulate organic nitrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, G.P.; Hiatt-Gipson, G.D.; Bew, S.P.; Reeves, C.E. Measurement of isoprene nitrates by GCMS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4533–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Ling, Z.; Guo, H.; Saunders, S.; Lam, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, T. Re-examination of C1–C5 alkyl nitrates in Hong Kong using an observation-based model. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.J.; Blake, N.J.; Atlas, E.; Flocke, F.; Crawford, J.; Fuelberg, H.E.; Kiley, C.M.; Meinardi, S.; Rowland, F.S. Photochemical production and evolution of selected C2–C5 alkyl nitrates in tropospheric air influenced by Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, A.L.; Shepson, P.B.; Fiddler, M.N.; Alaghmand, M. Isoprene nitrates: Preparation, separation, identification, yields, and atmospheric chemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10625–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, K.T.; Allen, H.M.; Crounse, J.D.; Praske, E.; Xu, L.; Noelscher, A.C.; Wennberg, P.O. Low-pressure gas chromatography with chemical ionization mass spectrometry for quantification of multifunctional organic compounds in the atmosphere. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6815–6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraud, V.; Bruns, E.A.; Ezell, M.J.; Johnson, S.N.; Greaves, J.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. Identification of organic nitrates in the NO3 radical initiated oxidation of α-pinene by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5887–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattigan, O.V.; Law, K.S.; Clemitshaw, K.C.; Williams, J.; Shallcross, D.E.; Cox, R.A. Gas-phase ultraviolet absorption cross-sections and atmospheric lifetimes of several C2-C5 alkyl nitrates. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 1997, 102, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.-F.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.-M.; Yu, J.-Z.; Fu, X.-X.; Liu, T.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, J.; Chen, D.-H.; Zhong, L.-J.; et al. Organosulfates from pinene and isoprene over the Pearl River Delta, South China: Seasonal variation and implication in formation mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9236–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Su, H.; Guo, D. Technologies of Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]

| Organic Nitrates | Retention Time (min) | Molecular Formula | Structure Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-pentyl nitrate | 7.48 | C5H11NO3 |  |
| 4-hydroxy-isoprene nitrate | 24.83 | C5H9NO4 | 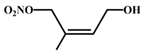 |
| (3,4)-di-hydroxy-isoprene nitrate | 13.78 | C5H9NO5 | 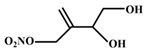 |
| SVONs | Concentration (ng m−3) | Concentration (N ng m−3) | ON/TSVONFTIR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-pentyl nitrate | 20.2 ± 7.2 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 5.6 ± 0.6 |
| 4-hydroxy-isoprene nitrate | 13.2 ± 7.2 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 2.3 |
| (3, 4)-di-hydroxy-isoprene nitrate | 36.5 ± 8.4 | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 2.8 |
| Sum | 69.9 ± 15.7 | 6.5 ± 1.5 | 20.2 ± 5.5 |
| TSVONs | 380.0 ± 190.8 | 63.4 ± 70.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Du, L.; Xue, L.; Bi, X.; Tang, M.; Wang, W. Determination of Semivolatile Organic Nitrates in Ambient Atmosphere by Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization–Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020088
Li R, Jiang X, Wang X, Chen T, Du L, Xue L, Bi X, Tang M, Wang W. Determination of Semivolatile Organic Nitrates in Ambient Atmosphere by Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization–Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rui, Xiaotong Jiang, Xinfeng Wang, Tianshu Chen, Lin Du, Likun Xue, Xinhui Bi, Mingjin Tang, and Wenxing Wang. 2019. "Determination of Semivolatile Organic Nitrates in Ambient Atmosphere by Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization–Mass Spectrometry" Atmosphere 10, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020088
APA StyleLi, R., Jiang, X., Wang, X., Chen, T., Du, L., Xue, L., Bi, X., Tang, M., & Wang, W. (2019). Determination of Semivolatile Organic Nitrates in Ambient Atmosphere by Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization–Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere, 10(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020088