1. Introduction
One meteorological variable which has a profound effect on the weather is the vertical velocity of the atmospheric air (hereafter denoted by
in m s
−1) [
1,
2,
3]. Through sustained vertical motions, rising moist air cools adiabatically forming precipitating cloud [
4], sometimes accompanied with more notable phenomena, like lightning and thunder [
1]. Rising motions can lead to a steeper environmental temperature lapse rate [
5] and strengthening of cyclonic systems [
1,
3]. On the contrary, descending air is heated by diabatic compression leading to cloud dissipation, damping of precipitation, clearer skies, and finer weather.
Bearing in mind the importance of vertical motions in the atmosphere, this study presents the methodology and results of an attempt to deduce information about the character of the vertical air motion adopting a methodology that combines measurements from three data sources: a Joss–Waldvogel disdrometer, radiosonde measurements, and fields from an atmospheric reanalysis.
For scales of motion in the Earth’s atmosphere with horizontal dimensions exceeding 100 km, the (horizontal) length scale significantly exceeds the depth (vertical) scale; most importantly and in connection to the focus of this paper, typical magnitudes of the horizontal velocity component exceed those of the vertical velocity component by several orders of magnitude [
1,
2], except in very strong convection currents where horizontal and vertical velocities attain comparable values (see [
2]).
Typical large-scale vertical motions in the atmosphere are of the order of 0.01–0.1 m s
−1. However, for highly unstable environments, the vertical velocity can reach values in excess of 70 m s
−1 [
2]. Such motions are extremely difficult to measure directly with sufficient accuracy. The existing worldwide network of radiosonde stations, which operates under the coordination of the World Meteorological Organization, does not incorporate vertical motions in its routinely observable and reported atmospheric variables, but the horizontal wind velocity is routinely reported; typical observational errors for wind measurements are of the order of 1 m s
−1 [
6]. Since the vertical motions are so important both in atmospheric research and in operational weather forecasting, quantitative estimates of vertical velocity must be inferred from quantities that can be directly measured with sufficient accuracy; the methodology adopted herein is explained below (
Section 2.2 and
Section 2.3).
Of all the instruments that use telemetry signals to collect upper-air data, radiosondes continue to be the basic platform for such observations. Most radiosondes in use today measure basic variables, such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. These measurements are carried out by sensors mounted in a package which also contains a radio-frequency transmitter [
7].
The use of radiosondes as atmospheric probing systems dates before the satellite observing era. Radiosondes comprise an essential component of the global atmospheric observing system since the mid-20th century [
8]. They constitute a systematic global-wise basic system providing meteorological information on the vertical profile of the atmosphere, from the Earth’s surface to several kilometers upwards. They are carried out at predefined times in a coordinated international effort of routinely collecting data which are subsequently used both for operational applications but also for research.
Horizontal wind profiles from radiosondes are derived from tracking the displacement of the balloon carrying the sonde (i.e., the probe that incorporates the sensors used to probe the meteorological variables), as a function of time. Modern balloons routinely used by most meteorological services are made of rubber or synthetic latex which expand as they ascend and lift the radiosonde commonly to heights between 20 and 26 km above the Earth’s surface, before bursting. The weight of the balloon depends largely on the size (volume) of the balloon, which is related to the speed of the flight. The mass of these balloons is usually between 0.2 and 0.5 kg.
The radiosonde can be tracked using a number of tracking techniques (such as a radar, radiotheodolite, and registering the navigational signals transmitted by the radiosonde). With the advent of modern space technologies though, most of these systems have been replaced by more accurate GPS (Global Positioning System) satellite tracking systems. An additional advantage of modern GPS-based technologies is that they allow a temporal resolution of the rate of ascent of the balloons. In the present research the rate of ascent is two seconds.
The estimation of sufficiently accurate vertical velocity fields is a long-standing issue [
4]. Two widely known approaches for inferring the vertical motion field from other atmospheric variables are the kinematic method (based on the equation of continuity) and the adiabatic method (based on the thermodynamic energy equation) [
4]. These two approaches have traditionally been adopted in a wide spectrum of meteorological applications where the vertical velocity is a core parameter. On the one hand, the kinematic method is quite sensitive to small inaccuracies in the horizontal velocity field. On the other hand, a disadvantage of the adiabatic method is that the local rate of change of temperature is required which is generally difficult to determine accurately over a large area; the adiabatic method is also rather inaccurate in situations where strong diabatic heating is present, such as storms in which heavy rainfall occurs over a large area [
3].
Despite their deficiencies, both methods are widely applied adopting an isobaric coordinate system, (i.e., a coordinate system in which the vertical coordinate is atmospheric pressure instead of geometric height) so that ω = dp/dt is inferred rather than = dz/dt (p denotes atmospheric pressure, z the geometric height above the earth’s surface, and t is time). In an isobaric coordinate system where as explained above pressure replaces height as the vertical coordinate, the pressure tendency, namely ω, plays the role of vertical velocity = dz/dt in the Cartesian coordinate system; hence, ω = dp/dt is often referred to as the ω-vertical velocity following the motion.
Most commonly, vertical velocities available in data repositories of atmospheric variables are given in terms of ω. For example, vertical velocities in the ERA-Interim database (employed hereafter) maintained by the European Centre for Medium Range Forecasts (ECMWF) are given as pressure tendencies, ω = dp/dt. Nevertheless, as shown later in this paper, converting from ω-velocity to -velocity is feasible.
An alternative approach for estimating
ω fields in the atmosphere, based on the so-called omega equation [
3], that is free from the difficulties inherent in the above mentioned kinematic and adiabatic methods may be adopted. Nevertheless, this approach is also not free from deficiencies, despite its wide utilization [
9].
The problem of direct observability of vertical velocities in the atmosphere is quite difficult and despite efforts to establish suitable directly observing systems, the problem is far from reaching a globally satisfactory level of coverage. On the one hand, lidar, sodar and wind profiling radar are capable of measuring vertical velocities (e.g., [
10,
11]), but only under conditions of presence of cloud droplets or ice crystals or aerosol particles, whereas under clear air conditions, no vertical velocities can be determined [
12]. Hence, both lidars and cloud radars are practically used to derive information about particle velocities. On the other hand, wind profilers can measure vertical velocities in clear air [
13]. However, although they have been explored for this purpose [
14], their global-scale distribution is still very limited. Instruments like the above that can be used to observe directly vertical velocities of the air, are still under exploration mostly in campaign experiments [
12].
SODAR (SOnic Detection And Ranging) comprise another technique that is used to measure wind speed at various heights above the ground; this wind profiler is based on the scattering of sound waves by atmospheric turbulence. SODAR has also been around for several decades [
15].
The application of proxy techniques in estimating vertical velocities is also under investigation. For example, trace gas observations from satellite remote sensing instruments are compared to modeled trace gas distributions [
16].
In any case, no global observing network for vertical velocities of the atmospheric air is in place and it is not foreseen to be established any time soon. This gap leaves ample room for further research focusing on the vertical velocity issue. The continual scientific interest in the determination of the vertical velocity fields is reflected in recent studies, such the one by Stepanyuk [
17] where the authors present a comparison between
ω derived from the ERA-Interim database (discussed immediately below) and values of ω derived from the generalized omega relationship.
Reanalyses of meteorological fields comprising long-term data sets with high spatiotemporal resolution are suitable for climate studies (e.g., [
18]); the production of homogeneous data sets is at the core of such endeavors. However, comparing five reanalyses, Iwasaki et al. [
19] noted important differences, even in zonally averaged vertical velocities. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that several aspects in the latest generation reanalyses have been enhanced [
20]. Despite the improvements, vertical velocities in reanalyses still suffer from inaccuracies, especially in relation to particular applications [
18].
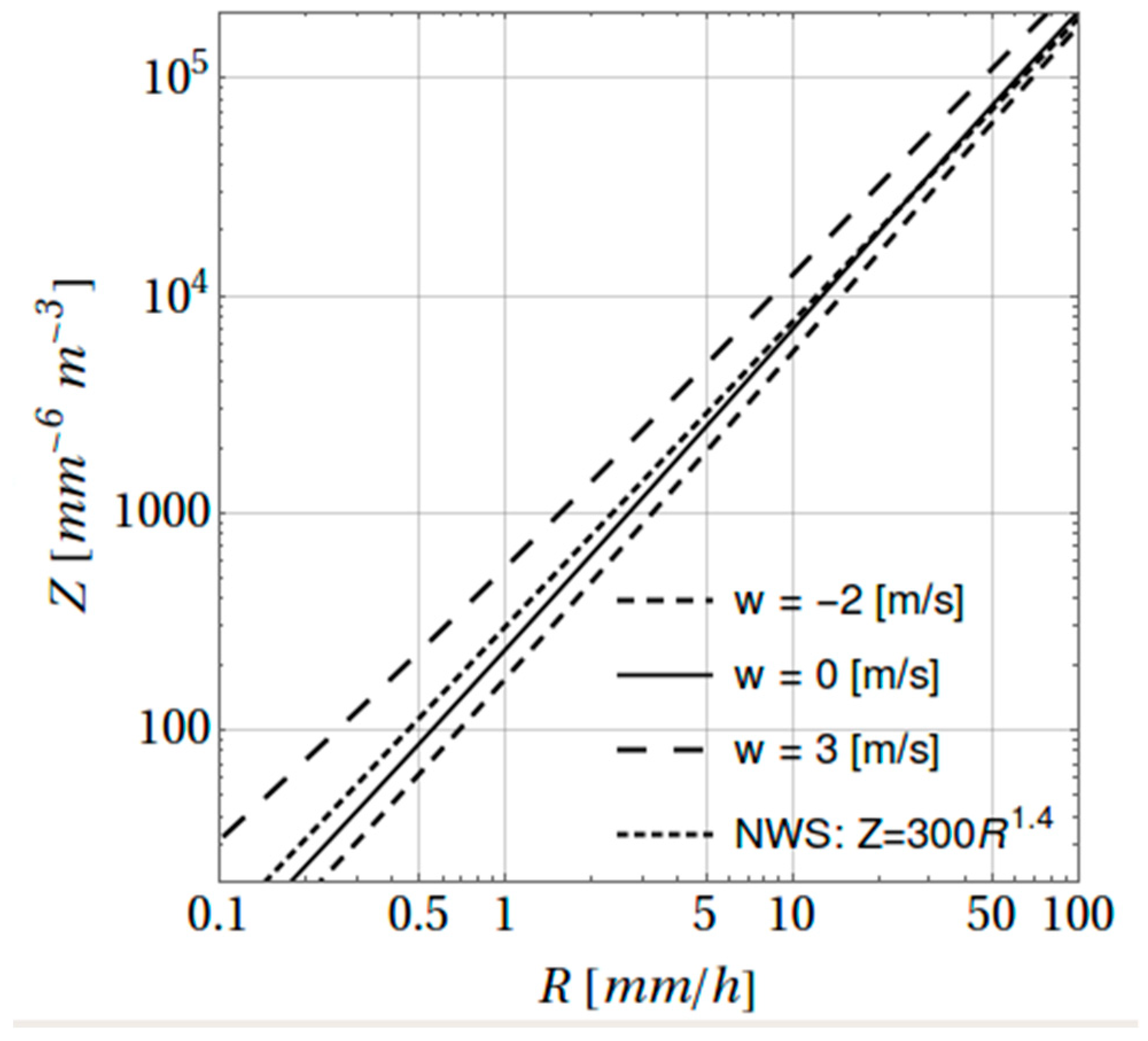
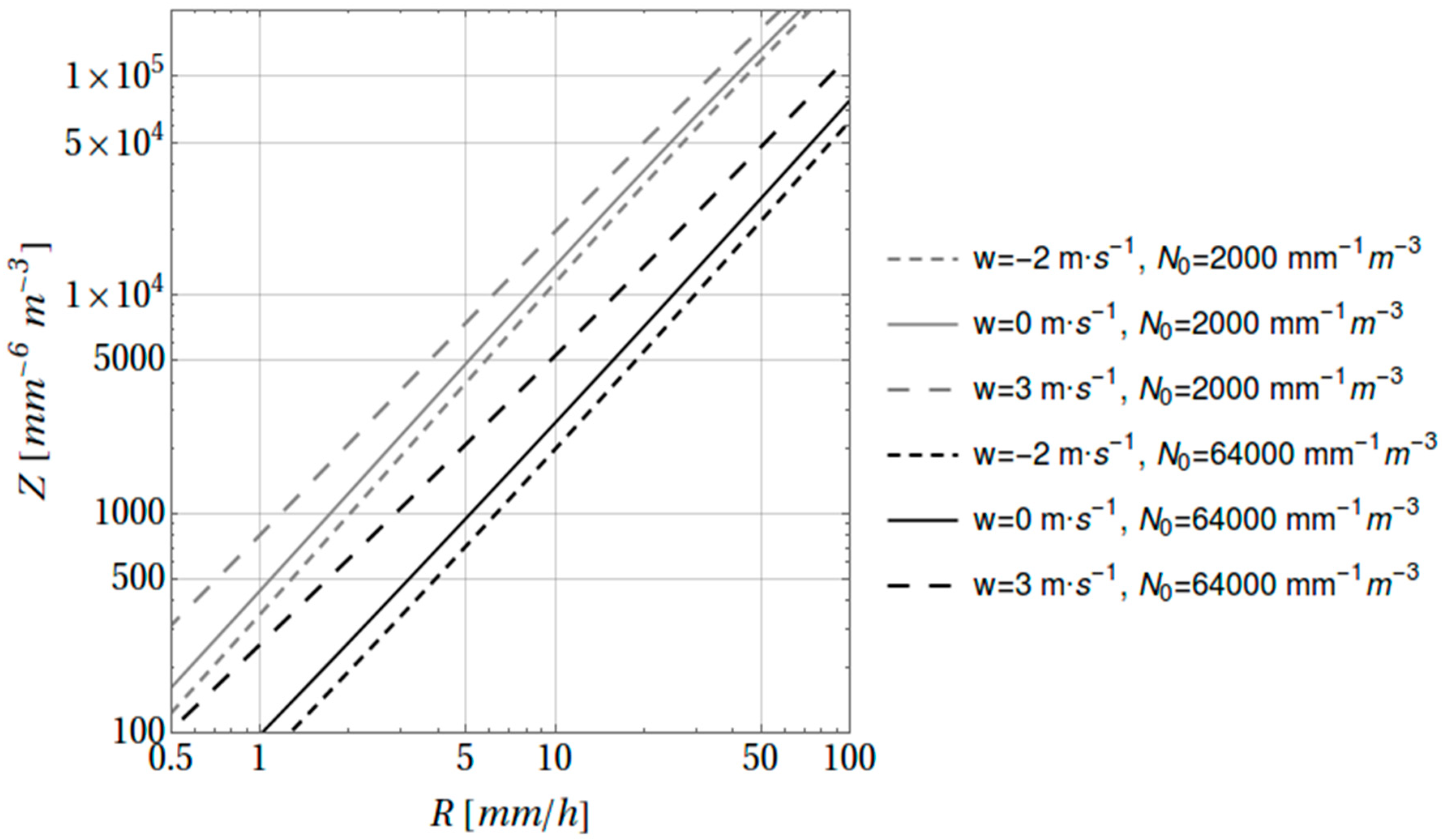
Employing disdrometer DSD data to estimate the vertical air velocity
has been approached in different ways, depending on the nature of the disdrometer. The method discussed in this current work is based on a procedure presented in previous work [
21], using impact disdrometer data. In this case, the disdrometer extracted
A-b coefficients, where
Z =
ARb, seem to be influenced by the magnitude of
and especially the sign. In a more recent work, Kim and Song [
22] have compared
measured by a three-axis ultrasonic anemometer and by a collocated laser disdrometer. The
considered by Kim and Song [
22] is not the same
considered by Lane et al. [
21] and in this current paper. In the present work,
is an average value from the surface to a reference height of
zref = 10 km. In the work by Kim and Song [
22],
is the value measured at the surface. On a flat surface,
should be zero, but because Kim and Song studied areas near mountain slopes, the vertical component of air motion at the surface can be non-zero.
The aim of the present research comprises an attempt to deduce information about the character of the vertical air motion from the disdrometer data. In this respect, the results of combining measurements from a Joss–Waldvogel disdrometer, radiosonde measurements and fields from atmospheric reanalysis are presented and discussed. The present paper aspires to contribute towards the better understanding of the long-standing vertical velocity estimation issue through the combined interplay of these three sources of data.
Section 2 presents the data used in this analysis together with the preprocessing approaches adopted. The methodology adopted is outlined in
Section 3, whereas, the research outcomes are presented in
Section 4 and discussed in
Section 5. The paper concludes with
Section 6. A list with the abbreviations and symbols used in this paper is given in
Appendix A.
2. Data and Their Preprocessing
In this study, three different sources were used: disdrometer data, co-located radiosonde data, and data from the European Centre for Medium Range Forecasts (ECMWF). These data sources are discussed in the following together with the preprocessing procedures adopted in order to formulate them for further use in this research.
This study sets the theoretical foundations in reaching the aim of this research and only a limited number of cases were investigated. Eleven days in the period 2011–2014 were selected to showcase the aim of this research. The dates selected are the same used in a previous study by Lane et al. [
21] and are shown in
Table 1 of the present paper. In searching for candidate dates, the authors have tried to balance the updraft and downdraft cases and a variety of DSD types was also pursued. The relation to stratiform—convective precipitation was described in the paper by Lane et al. [
21] in which all vertical speeds were simulated values and parameter fits. In the current work, matching ERA-Interim reanalysis data was used to get vertical velocity data, together with collocated radiosonde data.
2.1. Disdrometer Data
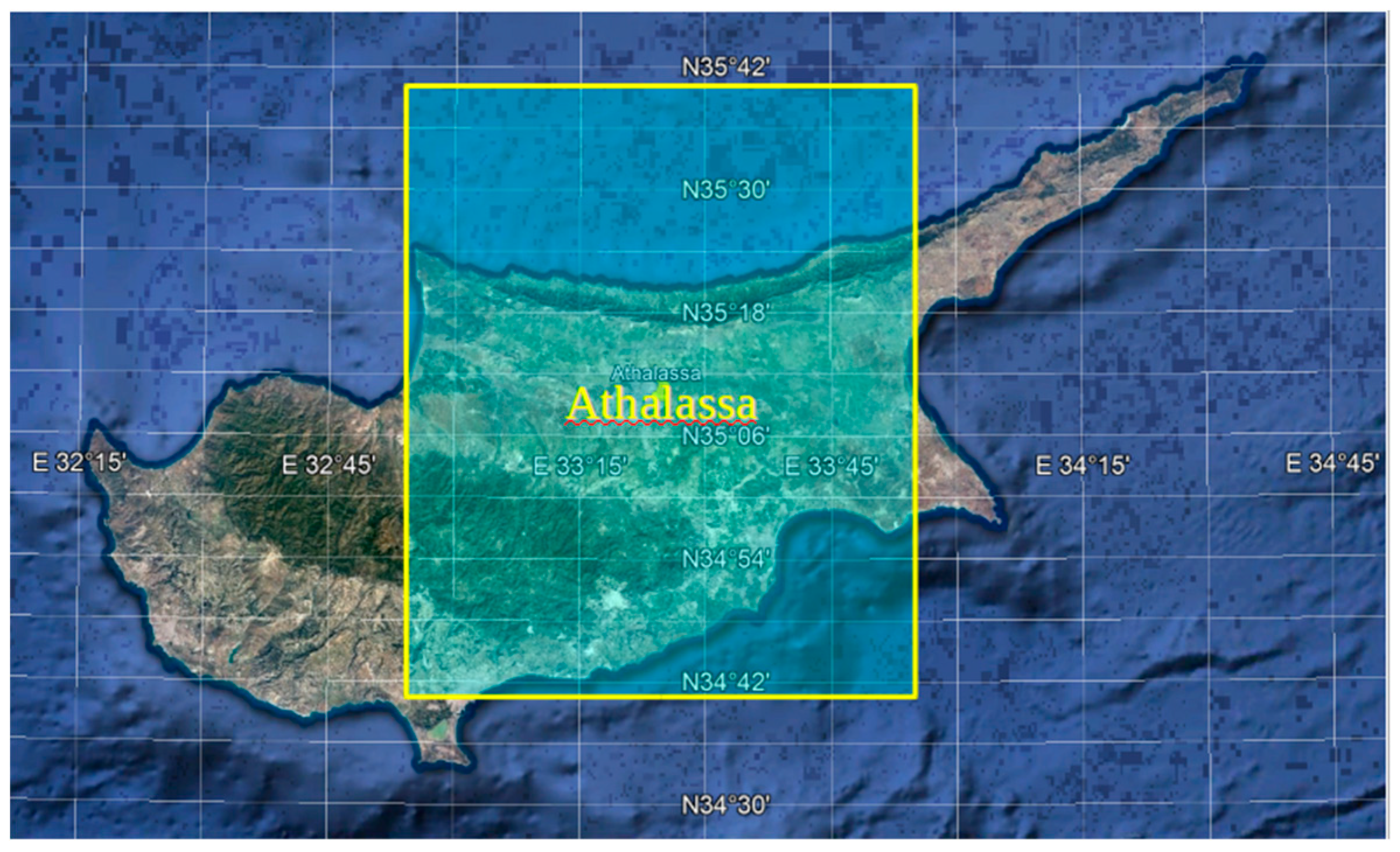
The disdrometer data were recorded by using a Joss–Waldvogel impact disdrometer located on the roof of a building at Athalassa, Cyprus (35.15° N, 33.40°, 161.0 m above Mean Sea Level, MSL). The impact sensor on the instrument produces an electrical impulse of size dependent on the momentum of the drop falling on the sense surface, and it is calibrated by the manufacturer to convert impulse size to drop diameter. The Joss–Waldvogel impact disdrometer is able to record drop diameters from 0.3 mm to 5.5 mm in 10-second intervals, thereby allowing for the establishment of the drop size distribution (DSD) representing this range of drop sizes [
23,
24]. As long as the manufacturer’s calibration certificate has not expired, the data is considered to be reliable.
2.2. Radiosonde Data
The data from the radiosonde station at Athalassa (next to the disdrometer) are collected for each of the days in the study. The equipment used is a Vaisala DigiCora
® Sounding System MW41 which is GPS-based. The data are automatically collected by the ground station and are registered for every two seconds, as the radiosonde ascends freely in the atmosphere. A sample of a file containing radiosonde data is given in
Appendix B. These data consist of the pressure (
p), geopotential height (
, in geopotential meters, gpm), temperature (
T, in °C), relative humidity (RH, in %), Dew-point temperature depression (i.e., the difference between temperature and dew-point temperature, in °C), virtual temperature (in °C), temperature lapse rate (in °C km
−1), and balloon ascent rate (
in m s
−1).
Vertical air motion is deduced from the radiosonde data by comparing its GPS-based ascent velocity to the theoretical ascent velocity of a balloon in still air. Wang et al. [
25] developed a procedure which results in Equation (1), yielding a calculated balloon still air ascent velocity,
is the initial balloon volume at the surface before release,
is the air density at the surface,
is air density as a function of height,
is the mass of the complete radiosonde-balloon system (
= 0.9 kg, for the radiosonde system considered in this work), and
is the global average of the acceleration due to gravity at MSL. The radiosonde reports several variables during its ascent as a function of time, which can easily be transformed into a function of height. Air density is neither measured by the radiosonde sensors nor reported in the radiosonde data file; however, density can be calculated from the variables that are being reported in the radiosonde data file, as explained immediately below.
From the ideal gas law, air density can be expressed as a function of pressure (
p), temperature (
T in K) and the gas constant for moist air (
)
where,
is defined by
with
Rd (287.058 J kg
−1 K
−1) and
Rv (461.5 J kg
−1 K
−1), denoting the gas constants for dry air and water vapor, respectively;
q denotes the specific humidity (in kg kg
−1). In the radiosonde data, however, specific humidity is not reported; instead the relative humidity (i.e., RH) is reported. To convert from relative humidity to specific humidity, we use the following relationship which is based on the Clausius–Clapeyron equation
where,
T0 is a reference temperature (typically taken to be 273.16 K). Hence, specific humidity is
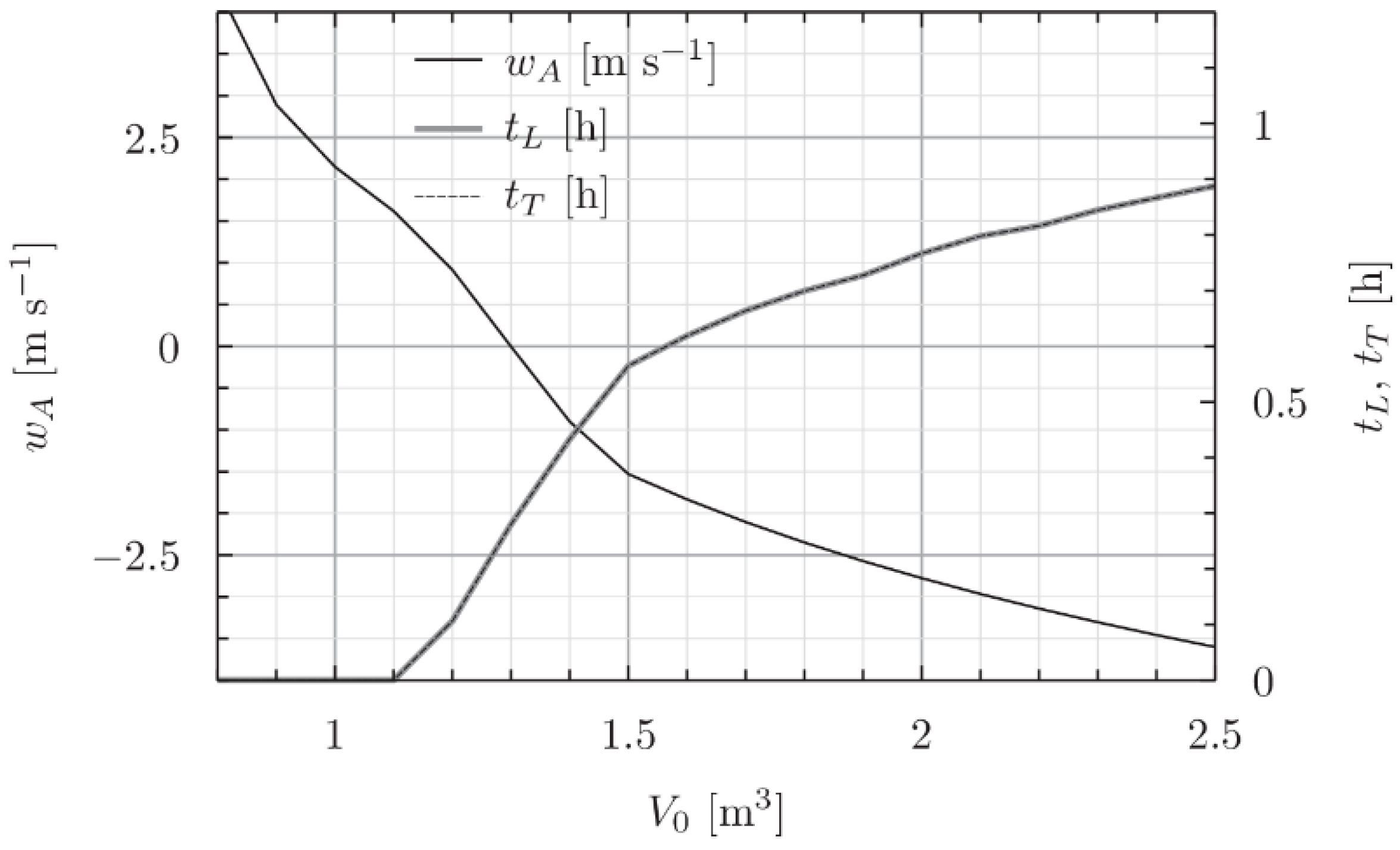
These values provide the preprocessing needed to compute Reynold’s number , coefficient of drag , and calculated still air vertical ascent speed . These three values are coupled and require a numerical algorithm to compute, as discussed below.
Ultimately, Equation (1) is defined for our needs as a function of height z and it should work for any planet with an atmosphere. If there is no atmosphere, Equation (1) fails to predict anything useful, since it is really the solution to a buoyancy problem such that > .
Equation (1) seems straightforward, but there is one problem: the coefficient of drag
is a function of Reynold’s number, which is a function of
. Wang et al. [
25] take an easy way out and define
to be a constant during the entire ascent. The value they use is in the range of 0.4 to 0.5. Sóbester et al. [
26] go one step further and define
to be a simplified function of Reynold’s number
where,
= 0.425,
= 0.225,
= 329600, and
= 365900. This improvement comes at a cost, since
is a function of
and
where,
ρ and
are from Equation (1),
is the balloon diameter (which can be calculated directly from balloon volume
V), and
μ is the dynamic viscosity of the air (in kg m
−1·s
−1) given by the formula
where, the constants are:
= 1.862 × 10
−7 and
β = 0.8062.
Equations (1), (6), and (7) represent a coupled set of equations that must be solved iteratively. A simple recursive solution to the above set of equations is to define an error
which is then used to recursively find a solution to
,
, and
. The iterative algorithm to find a solution starts by calculating
from
, using Equation (6). Next,
is calculated using
and Equation (1). An error is calculated which is then used to update
where,
γ is the recursion gain factor set equal to 0.4 in this work. Equations (9) and (10) are computed
N times with an initial guess for
= 10
5. After
N = 100 iterations, the value of
drops to < 10
−4 percent for all cases tried, resulting in the convergence of vertical speed at radiosonde sample time.
2.3. ECMWF ERA-Interim Reanalysis Data
In this paper, the ERA-Interim reanalysis dataset was utilized. The data is provided by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) via its internet portal and it will be shown below how the meteorological fields retrieved are used in this work to estimate the vertical velocity, denoted by (in m s−1).
ERA-Interim is a global atmospheric reanalysis from 1979, continuously updated in real time. The ERA-Interim atmospheric model and reanalysis system uses cycle 31r2 of ECMWF’s Integrated Forecast System (IFS) [
27]. The ERA-Interim reanalysis is described by Dee et al. (2011).
The ERA-Interim analyses produced and distributed by ECMWF, refer to an atmospheric model based on a hybrid vertical coordinate system [
27,
28]. Such a hybrid system consists of a terrain following coordinate
σ =
p/
ps near the surface (where,
p is pressure and
ps is the surface pressure), but with a gradual transition to a pressure coordinate with height. In addition, archived ERA-Interim products comprise reanalysis fields from the atmospheric model evaluated on standard pressure levels; this latter form of data have been retrieved from ECMWF’s portal and are subsequently utilized in the present work.
The retrieved data refer to the finest grid available for the ERA-Interim, namely 0.125° × 0.125° (which over Cyprus corresponds to a grid with approximate distances along latitude and longitude of 13.9 km and 11.4 km, respectively). The data cover the area from 30 to 40° N and from 30 to 40° E. In the vertical, data for the 23 standard pressure levels in the range from 1000 to 200 hPa.
For the needs of the study here, a 1° × 1° sub-area centered at the disdrometer site at Athalassa has been considered, as shown in
Figure 1. This area is bounded by meridians 33.0° E and 34.0° E and by latitude circles 34.6° N and 35.6° N. Because of the 0.125° × 0.125° ECMWF grid spacing, the sub-area that is extracted from the dataset needs to be no smaller than about 0.2° × 0.2°, otherwise the number of data points becomes too sparse for most calculations. With a 0.2° × 0.2° region, at least one data grid point will exist for every 1000 m increment above the surface.
ECMWF provides daily atmospheric data corresponding to a horizontal latitude-longitude grid and are available for every 6 h. This vast data set provides the spatiotemporal fields of many meteorological variables, including vertical air speed. The following meteorological variables were retrieved from the ERA-Interim database for each grid point and each pressure level: eastward and northward wind components (u, and v, respectively, in m s−1), temperature (T, in K), geopotential (Φ, in m−2s−2), specific humidity (q, in kg kg−1), and vertical velocity (ω = dp/dt, in Pa s−1, where p is pressure and t is time; as explained above, ω is defined as pressure tendency in a system where pressure is considered as the vertical coordinate).
The vertical velocity is calculated from the ERA-Interim data using the following relationship [
3,
29]
where,
ρ is density (in kg m
−3) and
g is the acceleration due to gravity. Substituting
ρ from Equation (2), the equation used for calculating the vertical velocity becomes
where,
is defined by Equation (3).
The acceleration due to gravity is adjusted for latitude,
φ, and height above the MSL,
z, as follows: (
https://www.sensorsone.com/local-gravity-calculator/)
where, IGF is the International Gravity Formula (in m s
−2), given by the relationship [
30,
31]
and FAC is the Free Air Correction (in m s
−2), given by the relationship
From the definition of the geopotential Φ(
z) at height
z as the work required to raise a unit mass to height
z from MSL, and from the conversion of the geopotential into geopotential height
where
is the global average of acceleration due to gravity at MSL,
≡ 9.80665 m s
−2, the geopotential height
is derived. In the troposphere and lower stratosphere, the geopotential height
is numerically almost identical to the geometric height
z, therefore the former can be used in Equation (15) to calculate the free air correction.
Figure 2 shows 3D contour plots of 1° × 1° ECMWF vertical wind data for each of the radiosonde observation times: 06:00 UTC and12:00 UTC 17 April 2013. The legend colors correspond to the range of values of
. One notable characteristic of these plots is the apparent uniformity of air speeds at various height levels. This uniformity removes any significant dependence on region’s window size, as long as a minimum window of 0.2° × 0.2° is used. A maximum window of 1° × 1° is likely to provide minimum variation at the horizontal levels. All of the variation is in the vertical direction. This appears to be true at the 1 deg × 1 deg scale and smaller. Note that because of the spacing of ECMWF grid points, microscale features are not likely to show up.
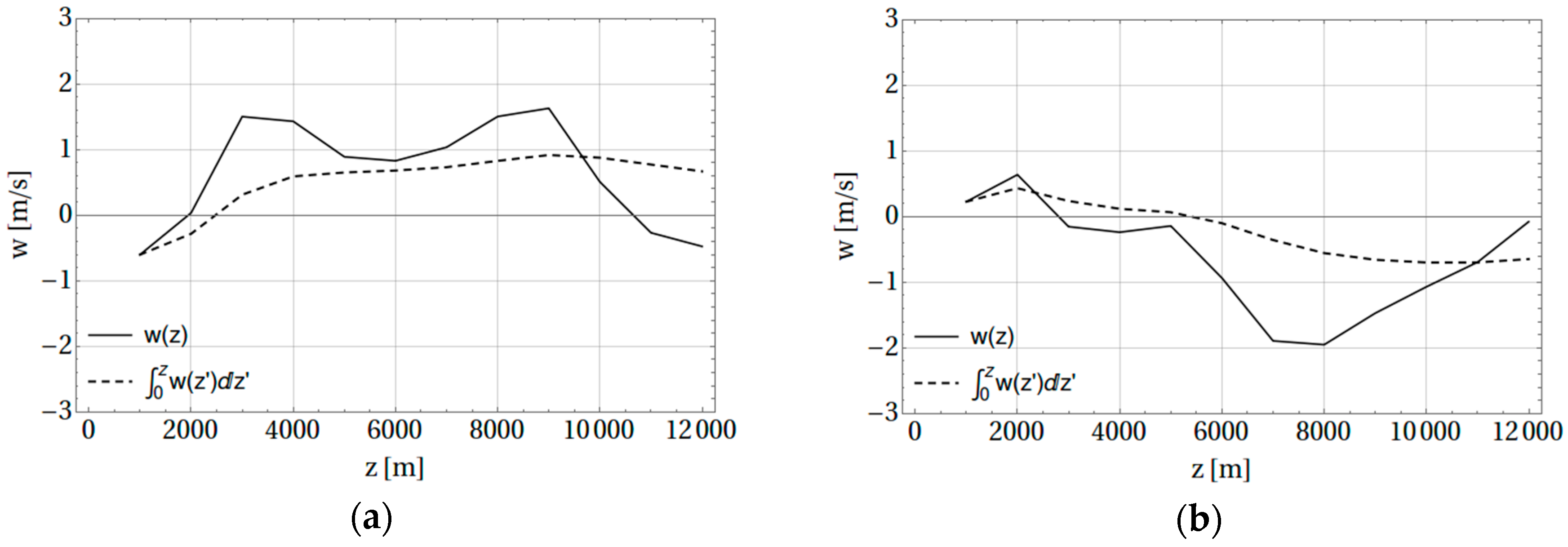
In order to extract a useful and meaningful value of
from the ECMWF data, all data at 1000 m levels are averaged to create wind profiles, as shown in
Figure 3. The wind profile is integrated from the surface to form an accumulated average of the wind data profile. Finally, for comparison to the disdrometer derived
A and
b parameters as discussed below, the accumulated wind profile at a reference level is used. The reference level chosen for this comparison is
zref = 10,000 m. The
zref seems to provide a consistent comparison to the disdrometer
A-b data;
(
zref) is simply the average of the wind profile from
z = 0 to
zref.
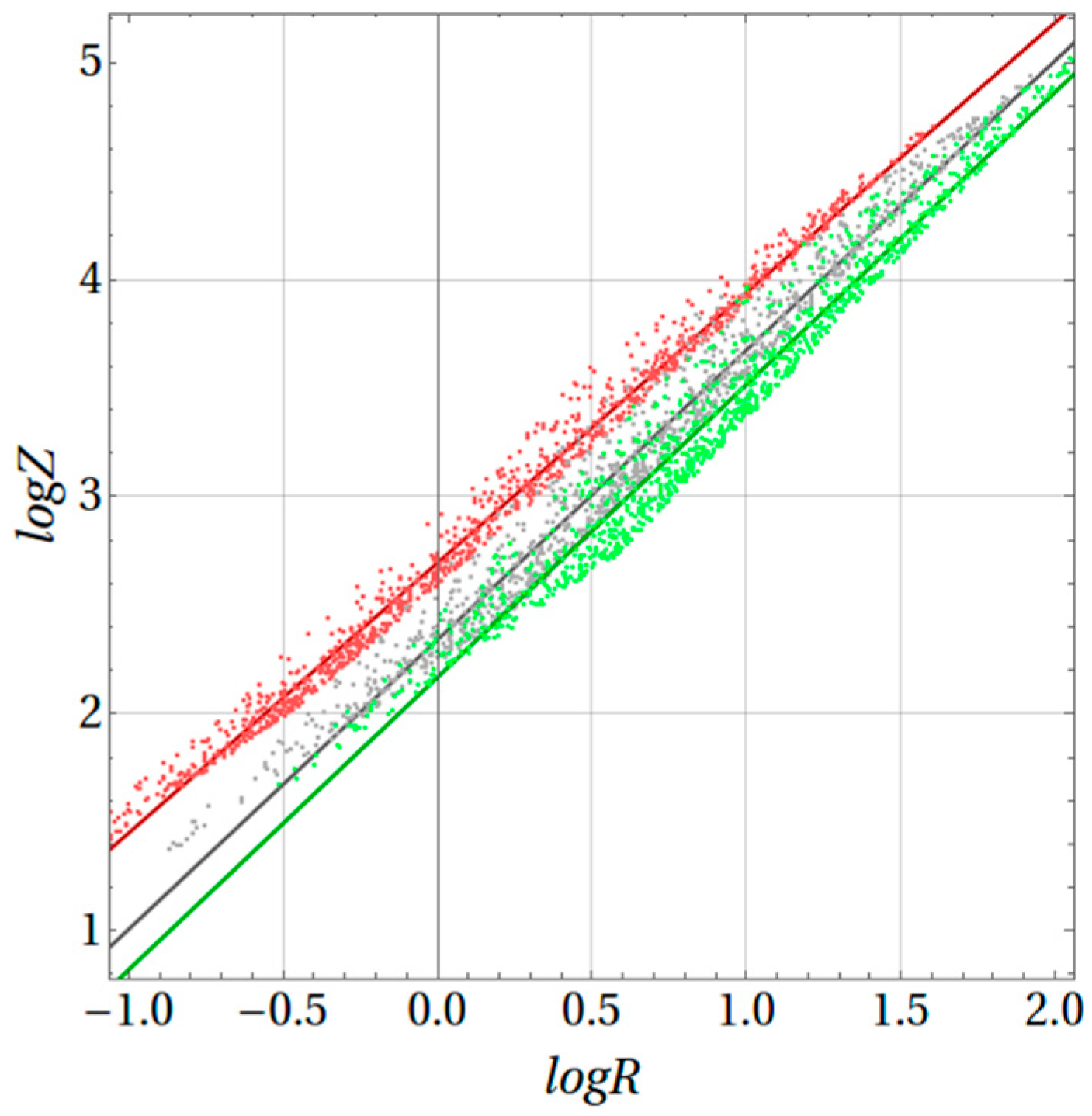
Table 1 summarizes these results for 11 days of disdrometer-ECMWF data.
6. Conclusions
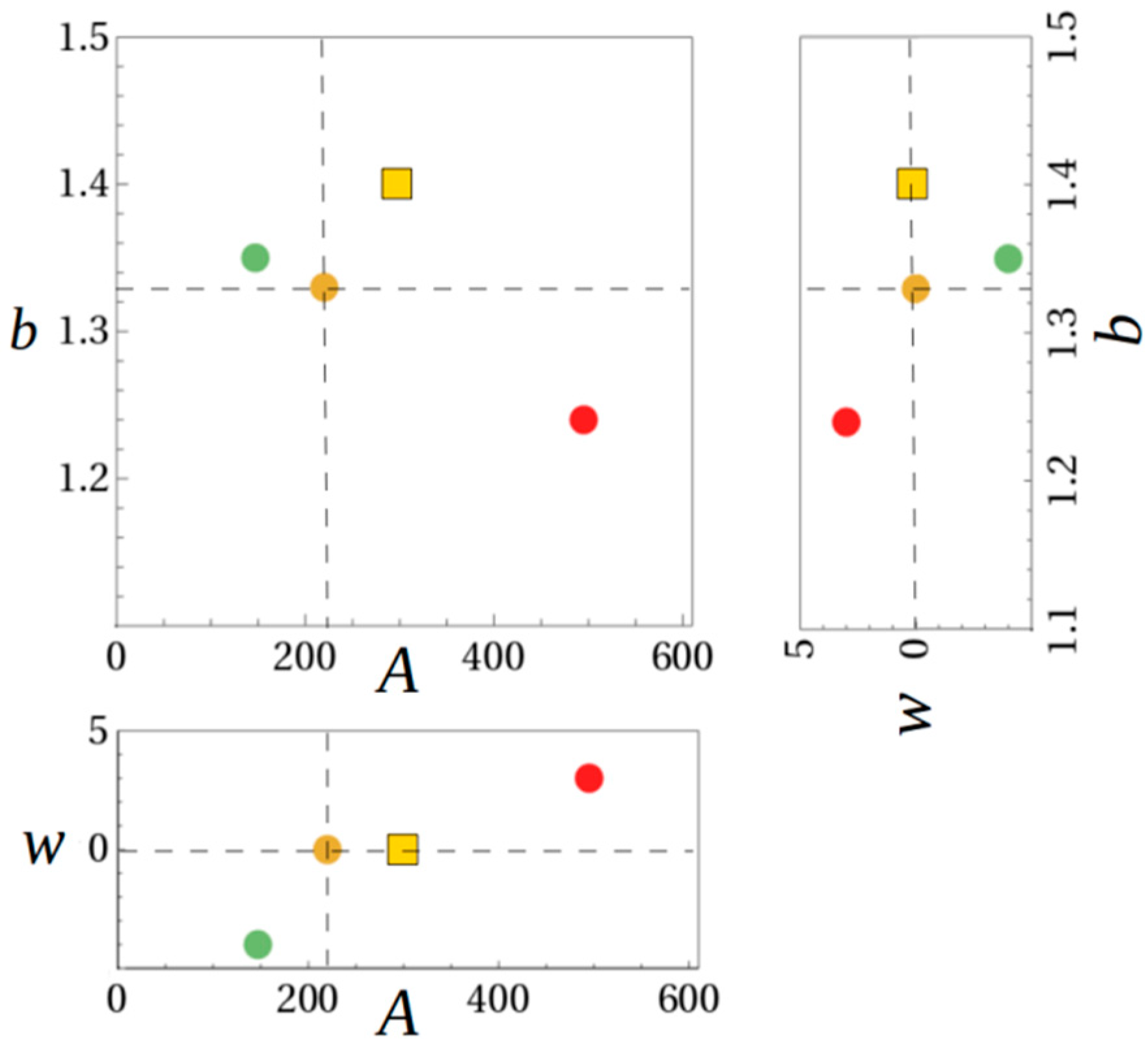
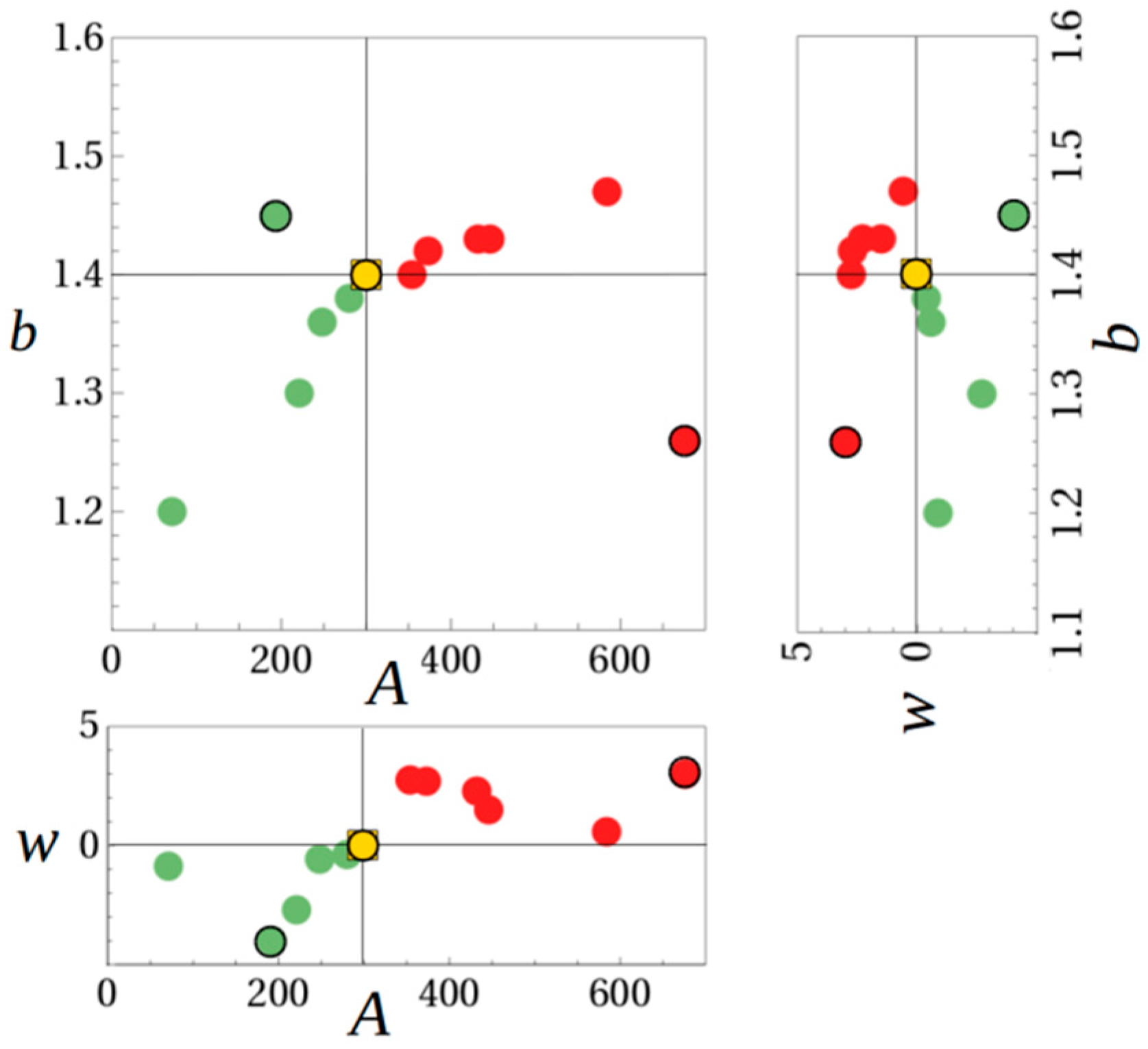
The FCM-DSD is based on the exponential DSD and is modified by the relationship between drop terminal velocity
and vertical air speed
. The FCM-DSD has a similar appearance to the popular gamma DSD for
< 0 (see [
21]). When points {
A,
b,
} are plotted, as shown by
Figure 12, a clear segregation is seen in the
A- plane for both data and model. The points from data are also clearly segregated in the
b- plane, but the model data are on opposite sides of the
= 0 line. Another surprise is that the segregation lines intersecting at
= 0, yield the NWS standard
A-b parameters, 300 and 1.4, respectively.
Generalizing any methodology that makes use of radiosonde data of different time periods or diverse localities should take into account issues related to radiosonde data homogeneity [
37].
Radiosonde data are routinely assimilated in numerical weather prediction (NWP) models which are subsequently used in the atmospheric data reanalyses. However, NWP models are generally non-hydrostatic, considering vertical velocity as a prognostic variable of the model. However, no specific assimilation on this variable is normally performed [
38]. The model derives its own vertical velocity field from the other meteorological fields in its first time-steps of integration. The reason behind is that no observing capability is able to produce some vertical velocity observations which are comparable to the model vertical velocity (at the scale of its mesh). A drastic increase on spatial resolutions of high-resolution NWP models is needed before these models can resolve the clouds and produce some vertical motion which can be compared to, for example, Doppler radar vertical velocity observations [
36,
39].
Radiosonde data constitute a unique source of information about the vertical atmospheric profile, hence they are essential for the assimilation efforts in generating climate databases, such as the ECMWF reanalyses [
28] (and other reanalyses too, e.g., MERRA-2 [
40] and JRA-55 [
41]). However, vertical velocities are not directly measured from radiosonde observations and, in this respect, directly measured vertical velocities from radiosondes are not assimilated in reanalyses but the vertical velocity field is derived from other observable fields (refer, for example, to the kinematic method used in ERA-Interim). It is worth noting here that interrelationships between reanalysis data and radiosonde timeseries may also be used to homogenize the latter [
42]
In this work, it was demonstrated that can be extracted from radiosonde data if initial balloon volume is accurately measured, along with an accurate measurement of . To accomplish this, vertical velocities from radiosonde data were equated to ECMWF vertical velocity fields, thus solving for with set to a constant 0.9 (kg). The resulting values of are shown to be within a reasonable range of values.
Future work will focus on using laser disdrometer and radiosonde data to further investigate the relationship between disdrometer derived A-b coefficients and vertical air speed . The disagreement between model and data of the b parameter location in the -b plane will be investigated in greater detail, but for now it remains inexplicable.