Impact of Effective Roughness Length on Mesoscale Meteorological Simulations over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Descriptions of the Land Surface Datasets
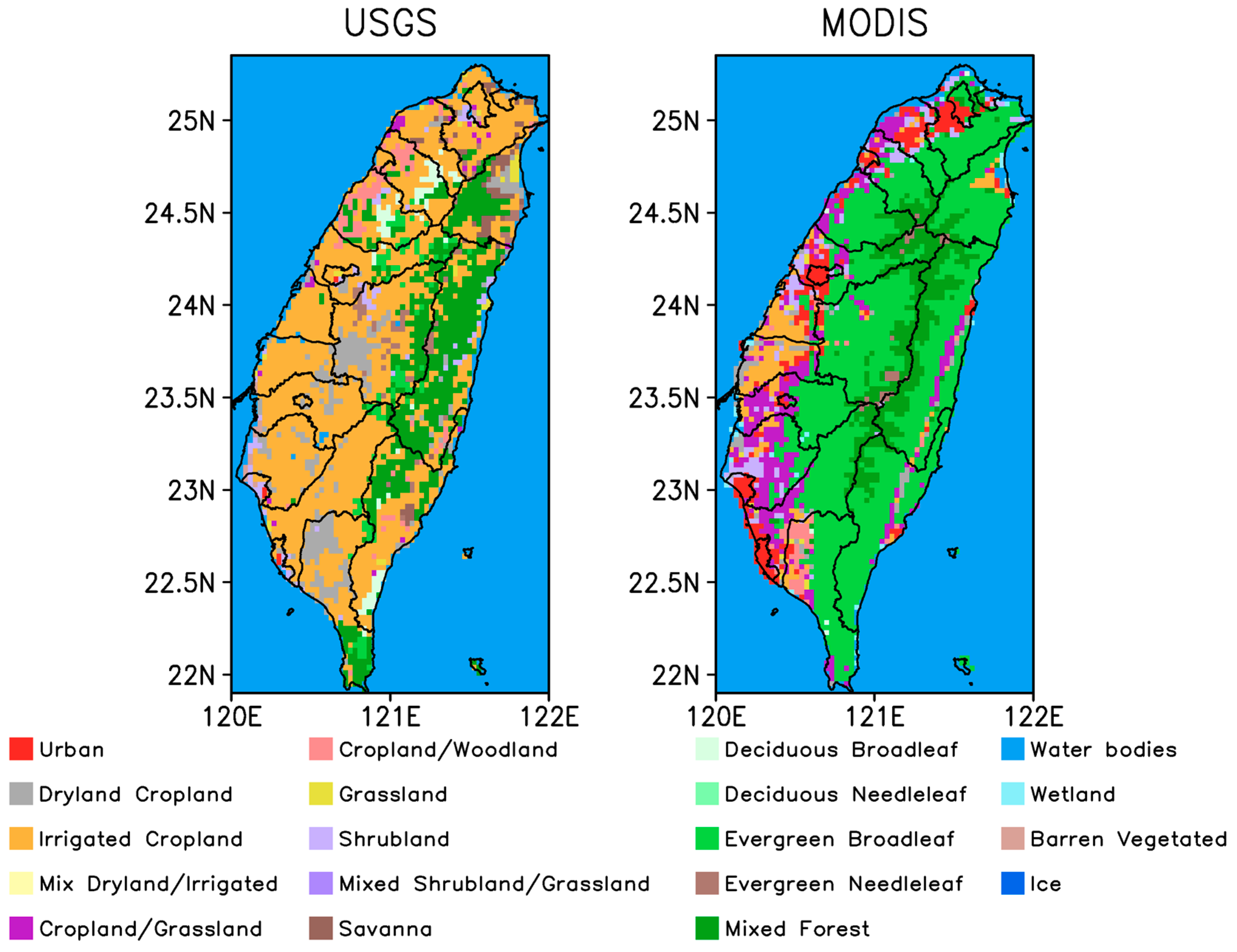
2.1. LU Data
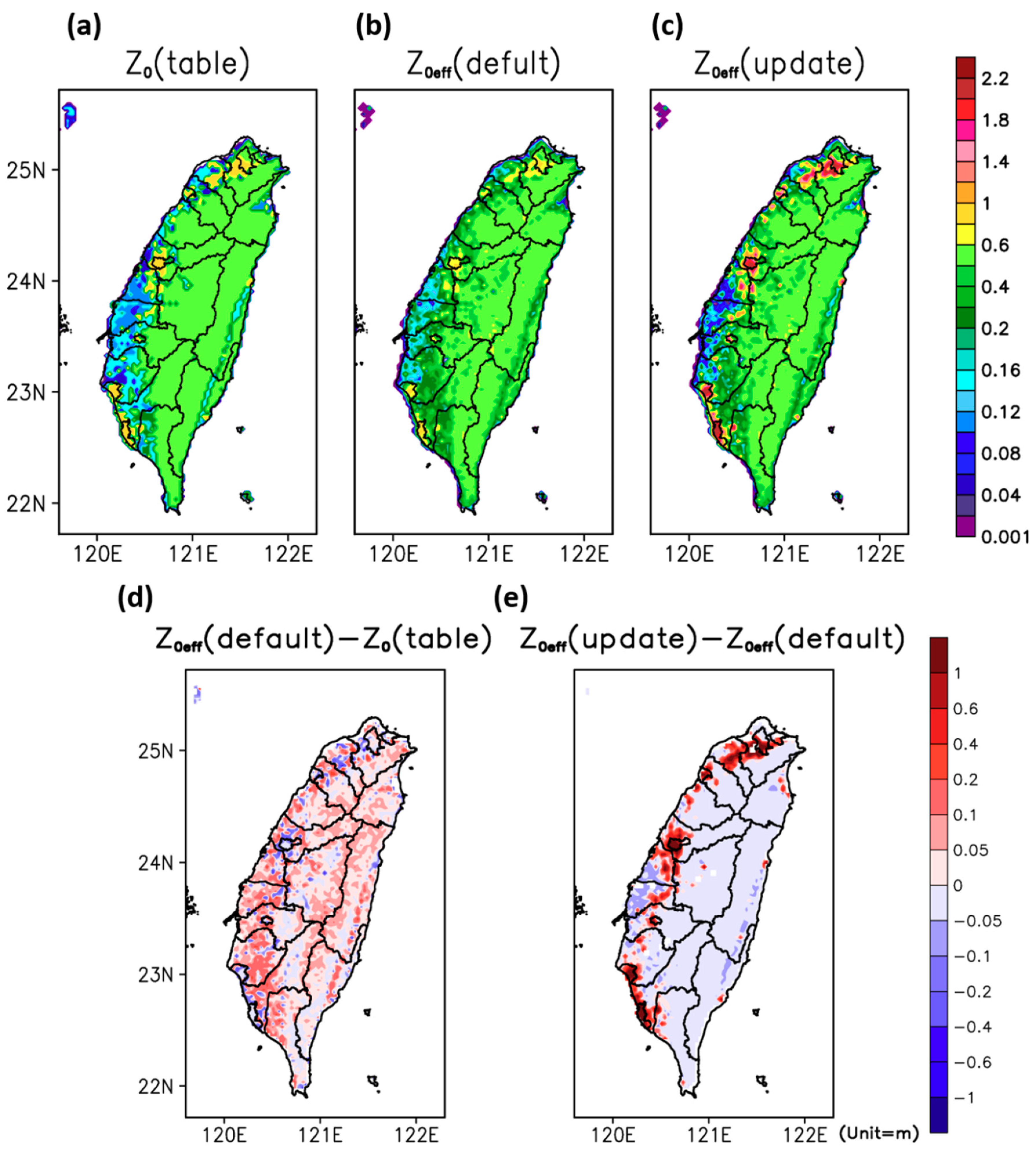
2.2. Aerodynamic Roughness Length
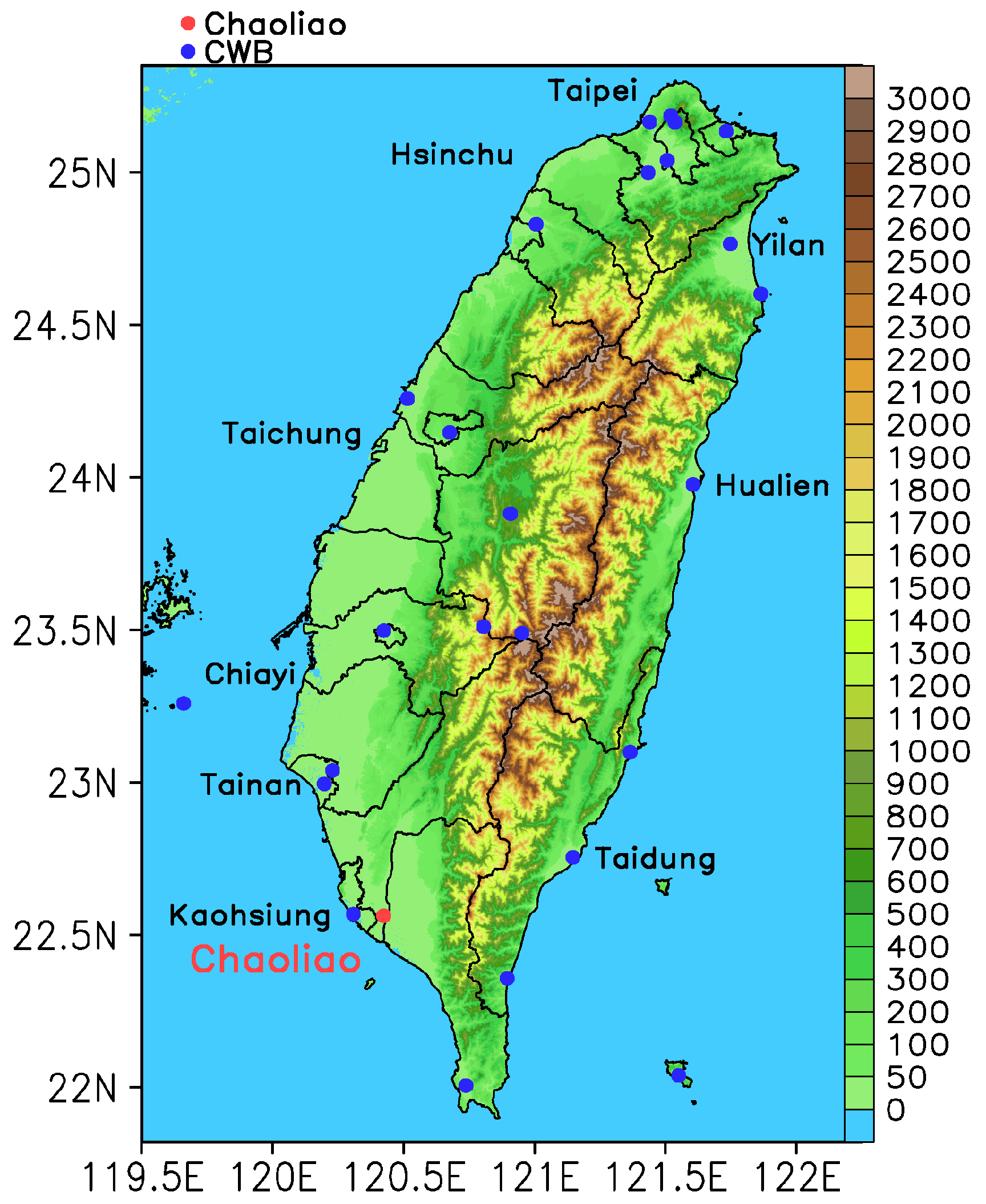
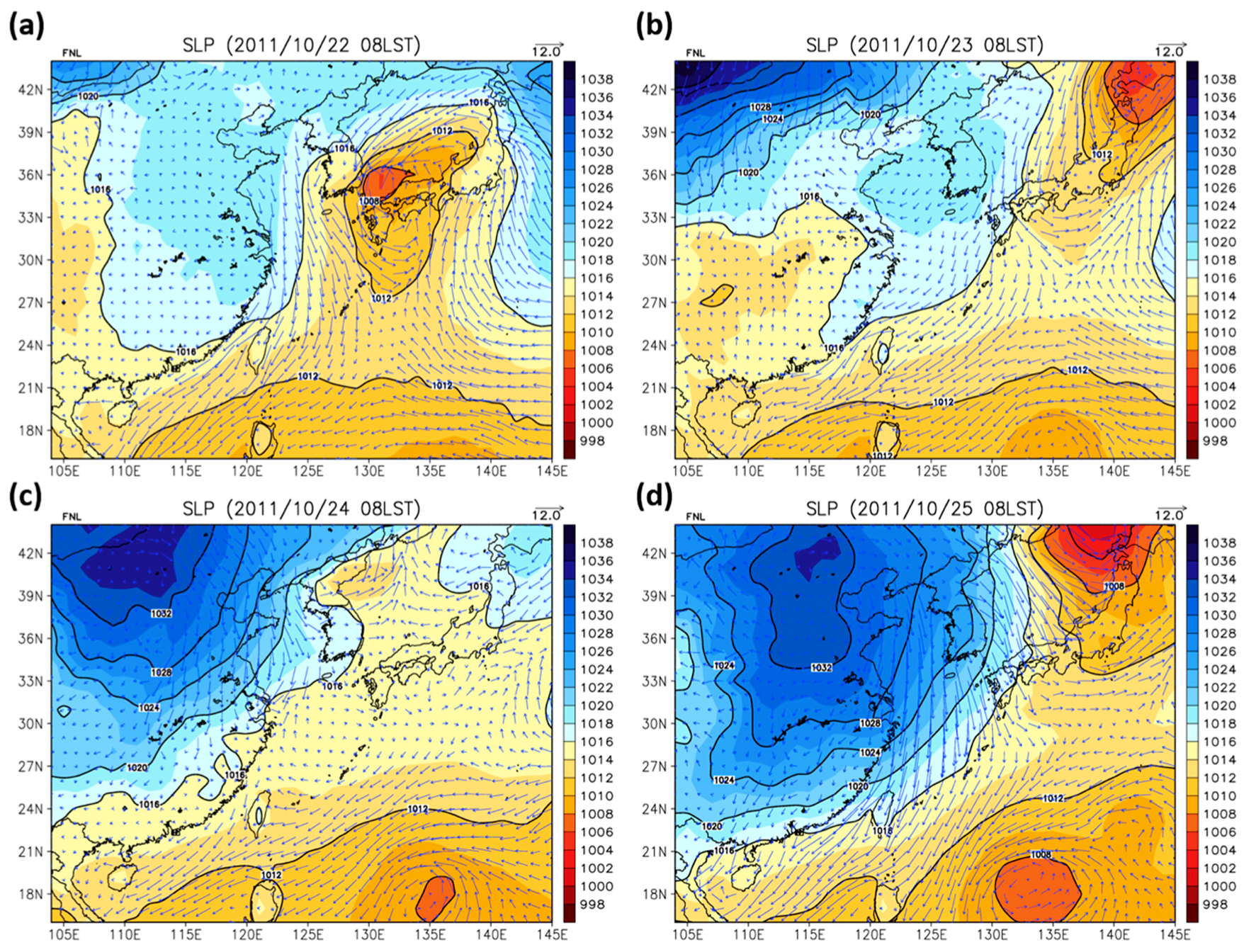
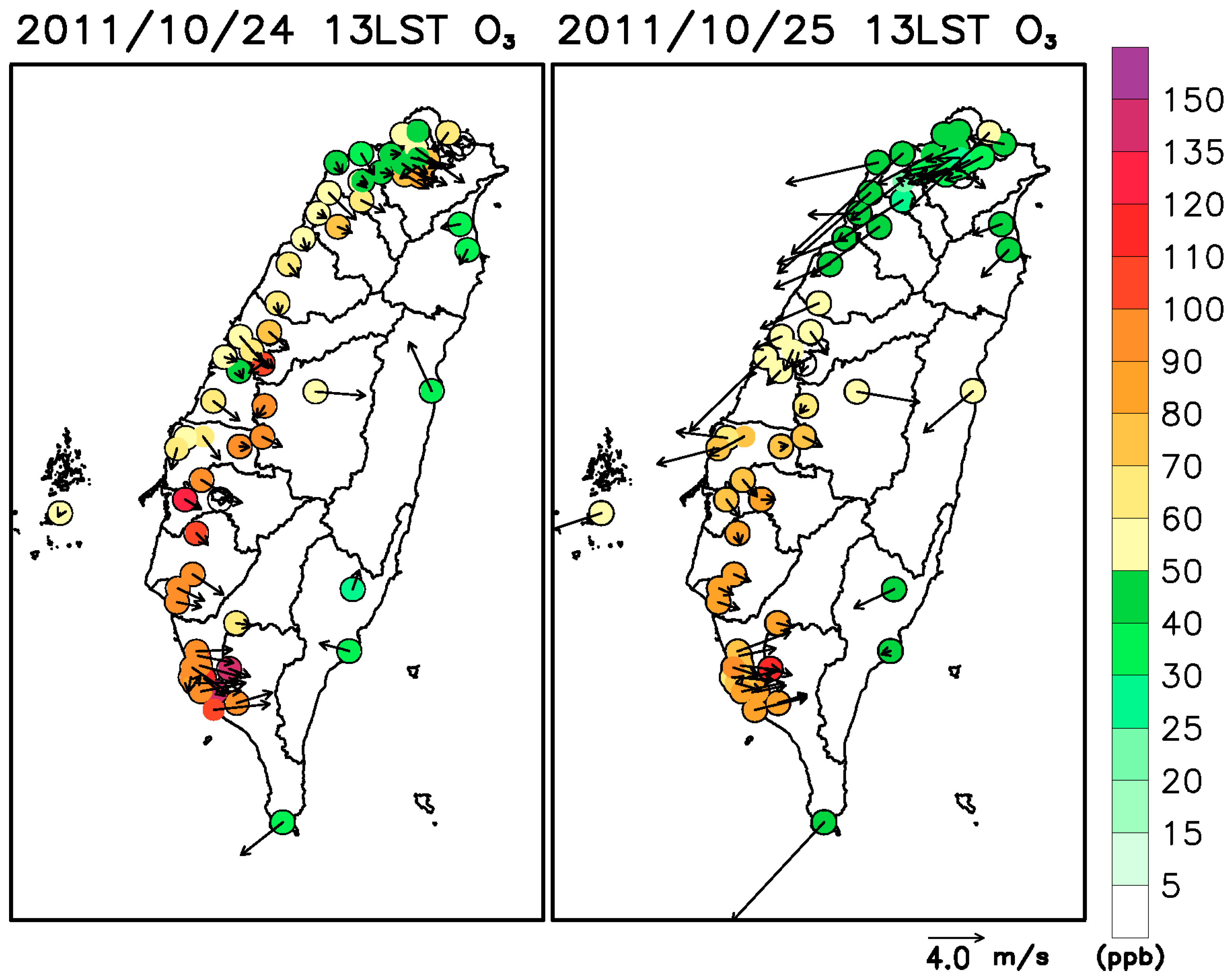
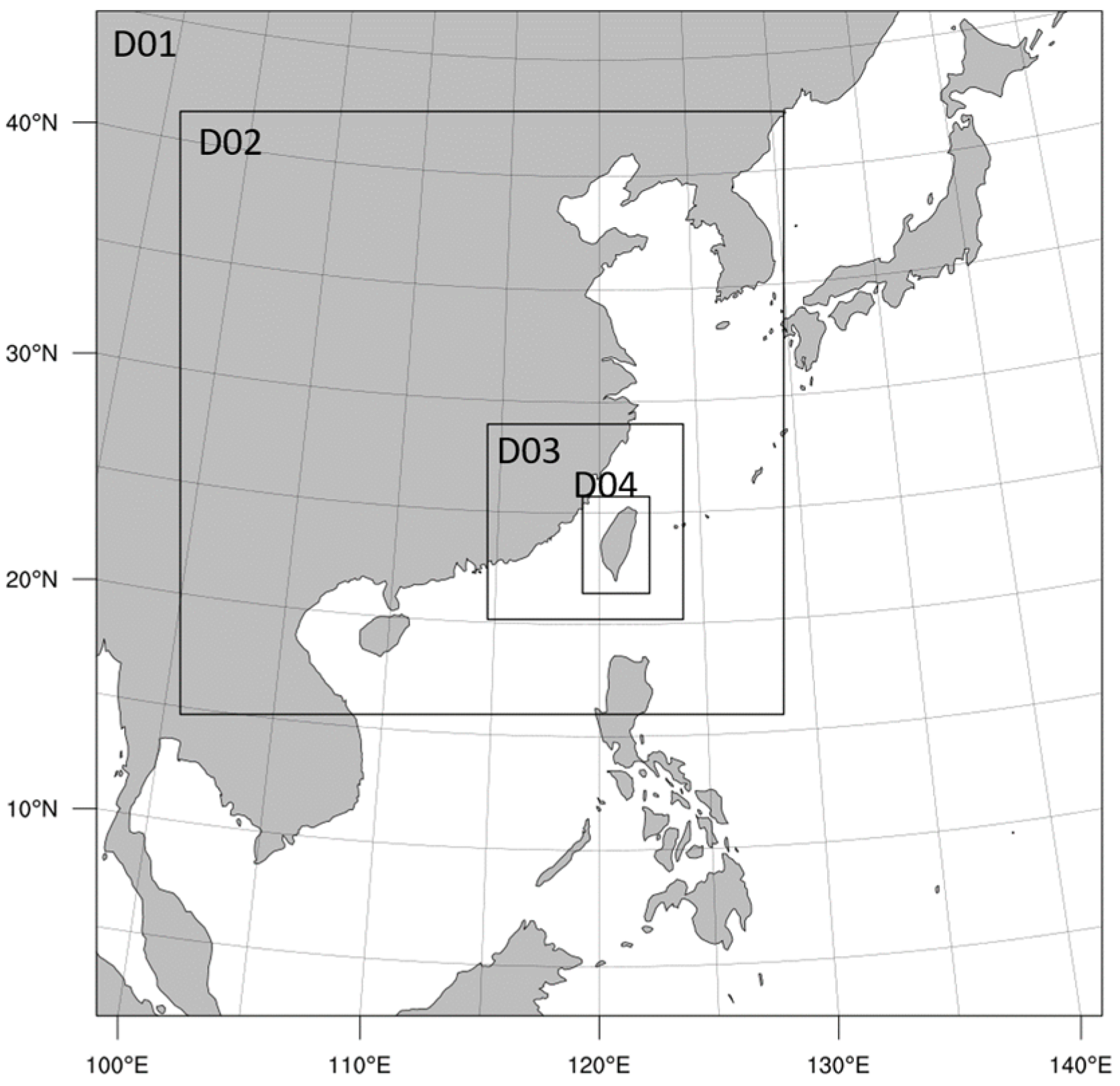
3. Descriptions of the Simulation Episode, Observations and Model Configuration
4. Simulation Results
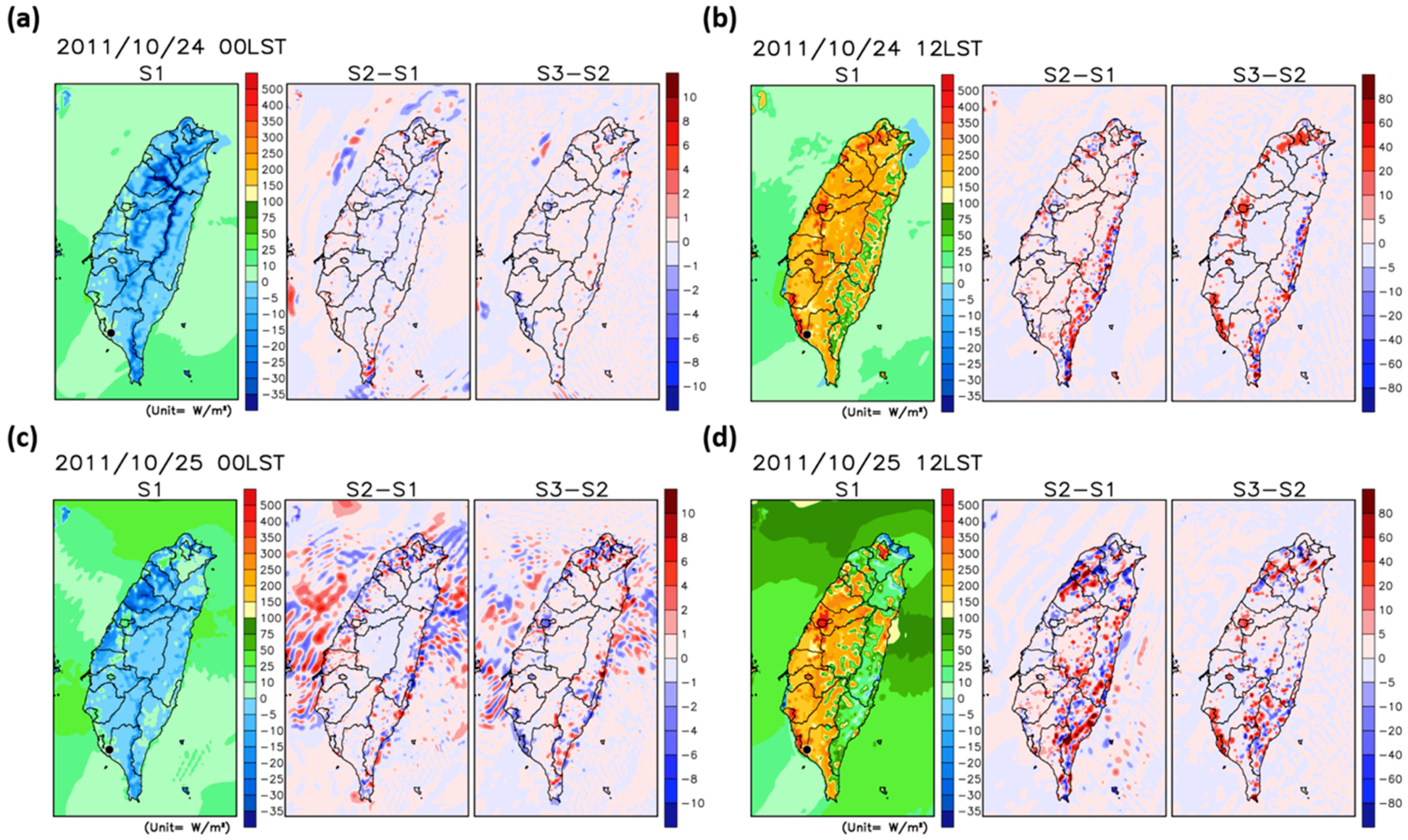
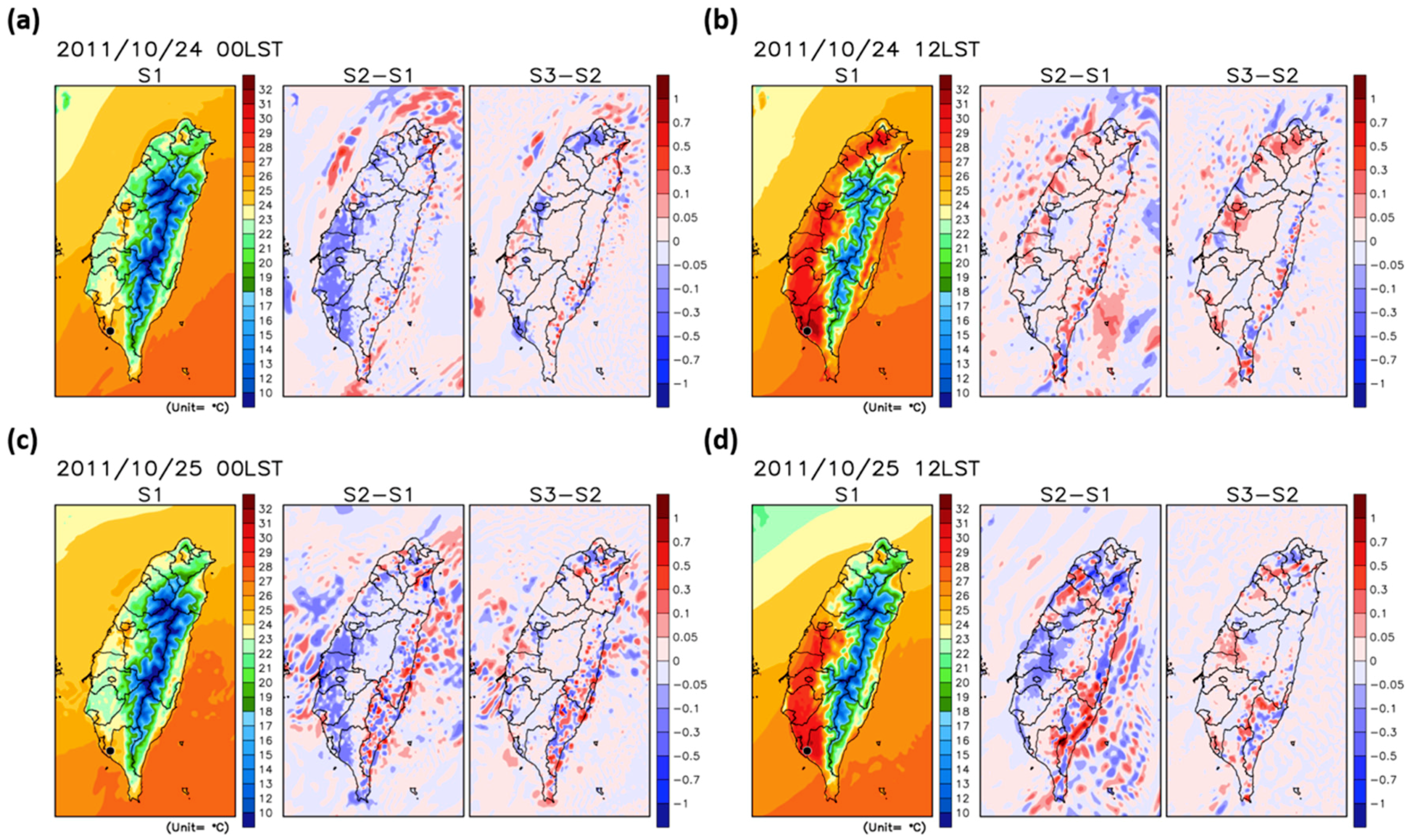
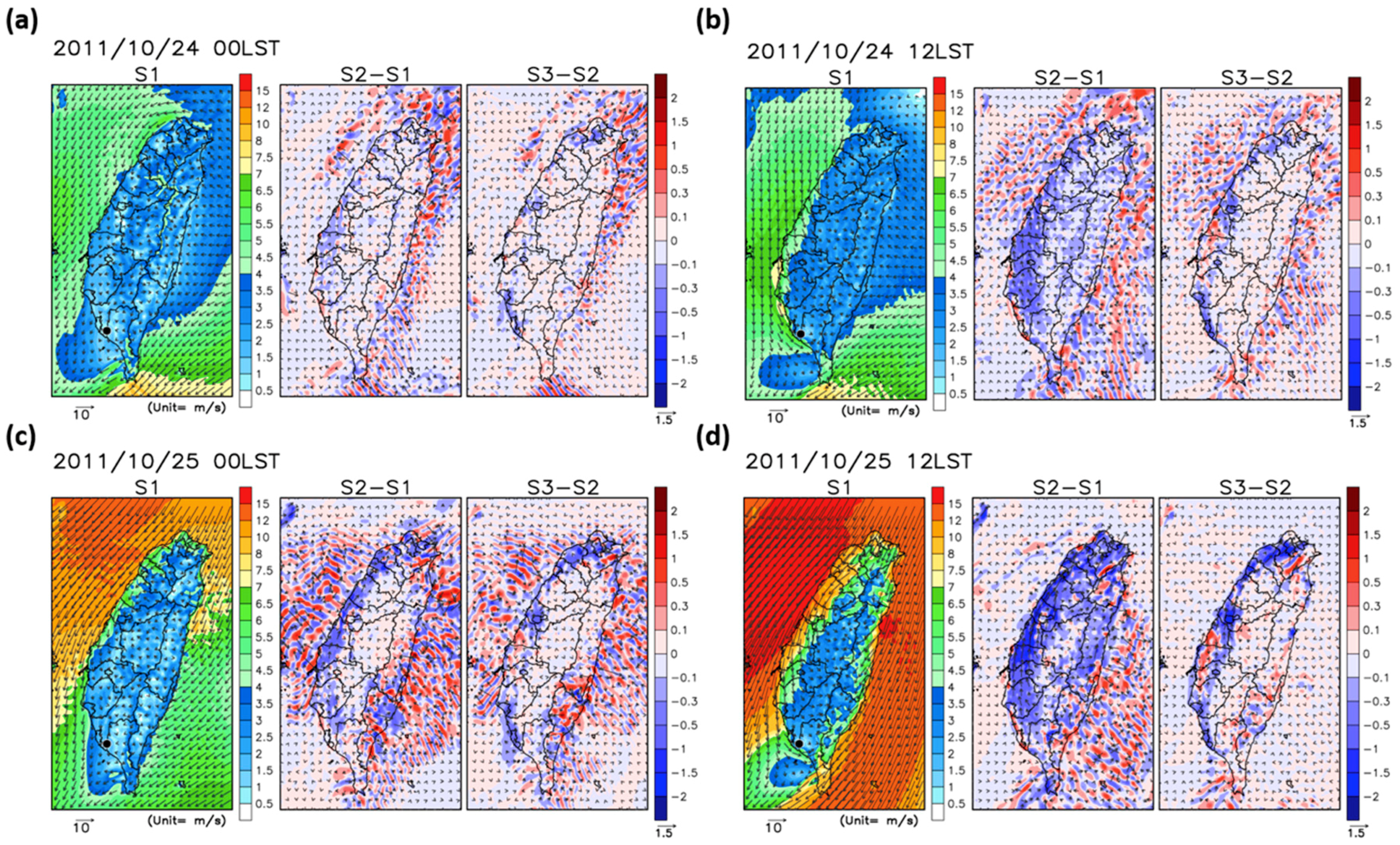
4.1. Spatial Distributions of the SHF, Temperature, and Wind Fields
4.2. Time Series Comparison
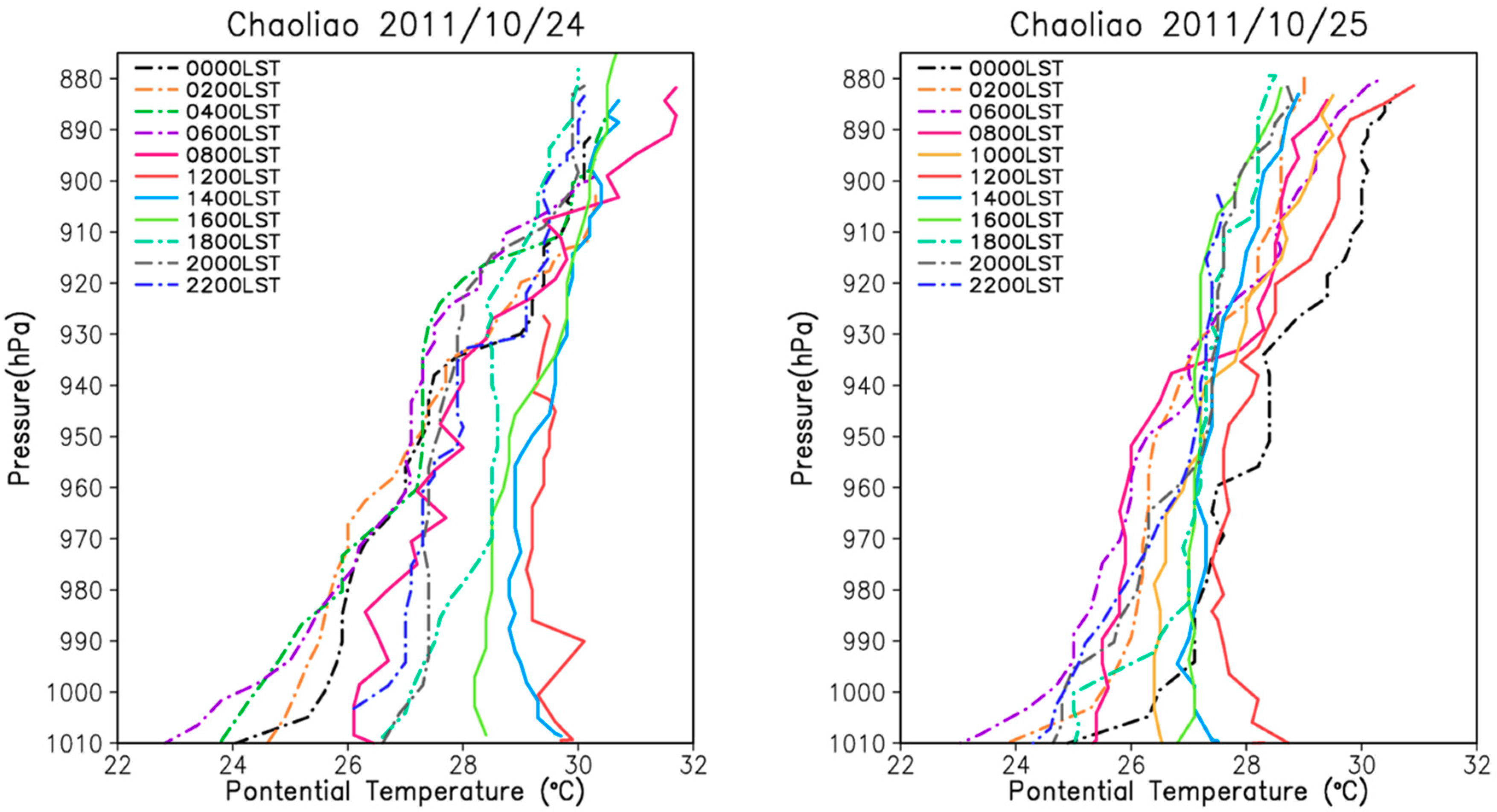
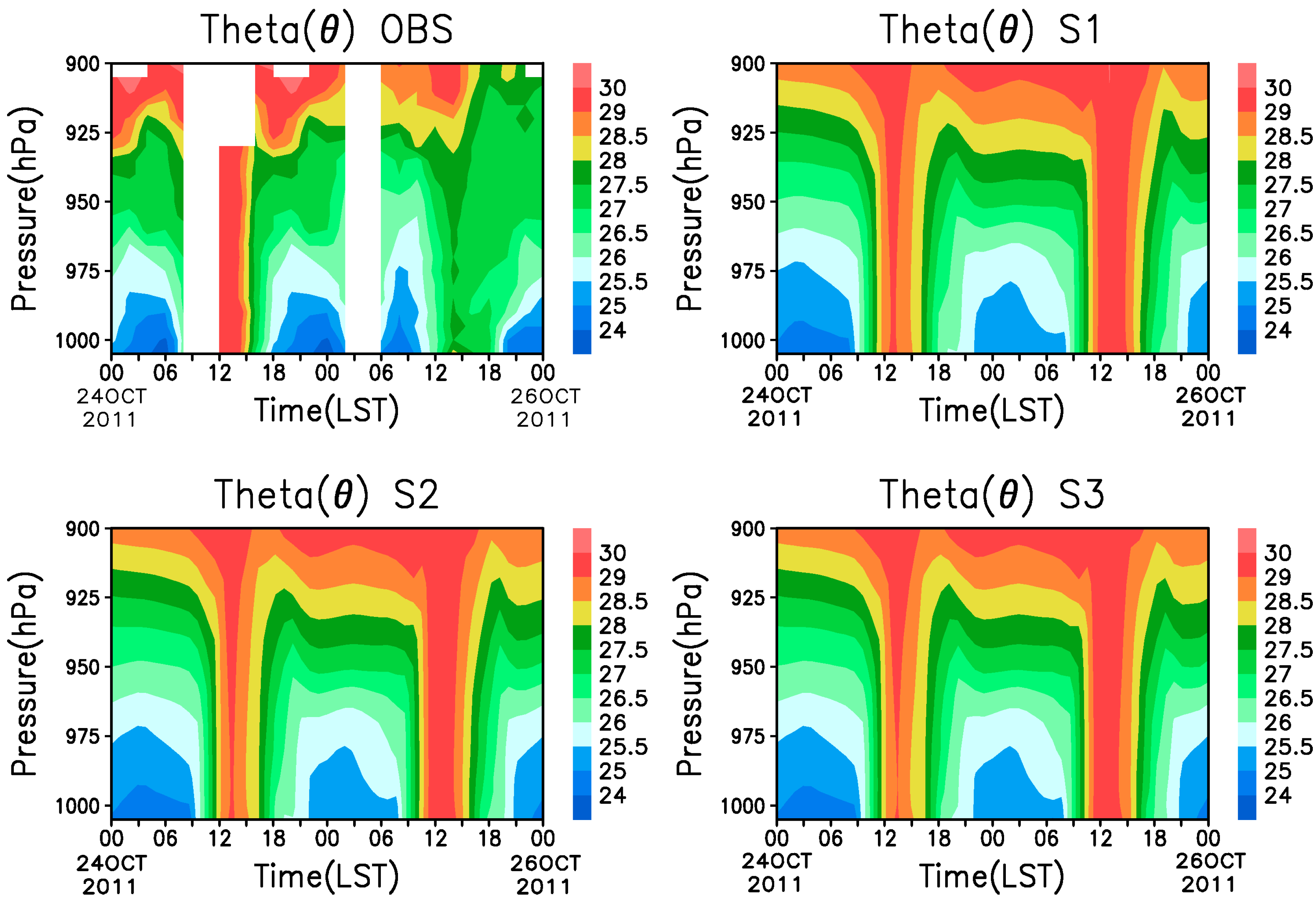
4.3. Comparison with the Tethersonde System
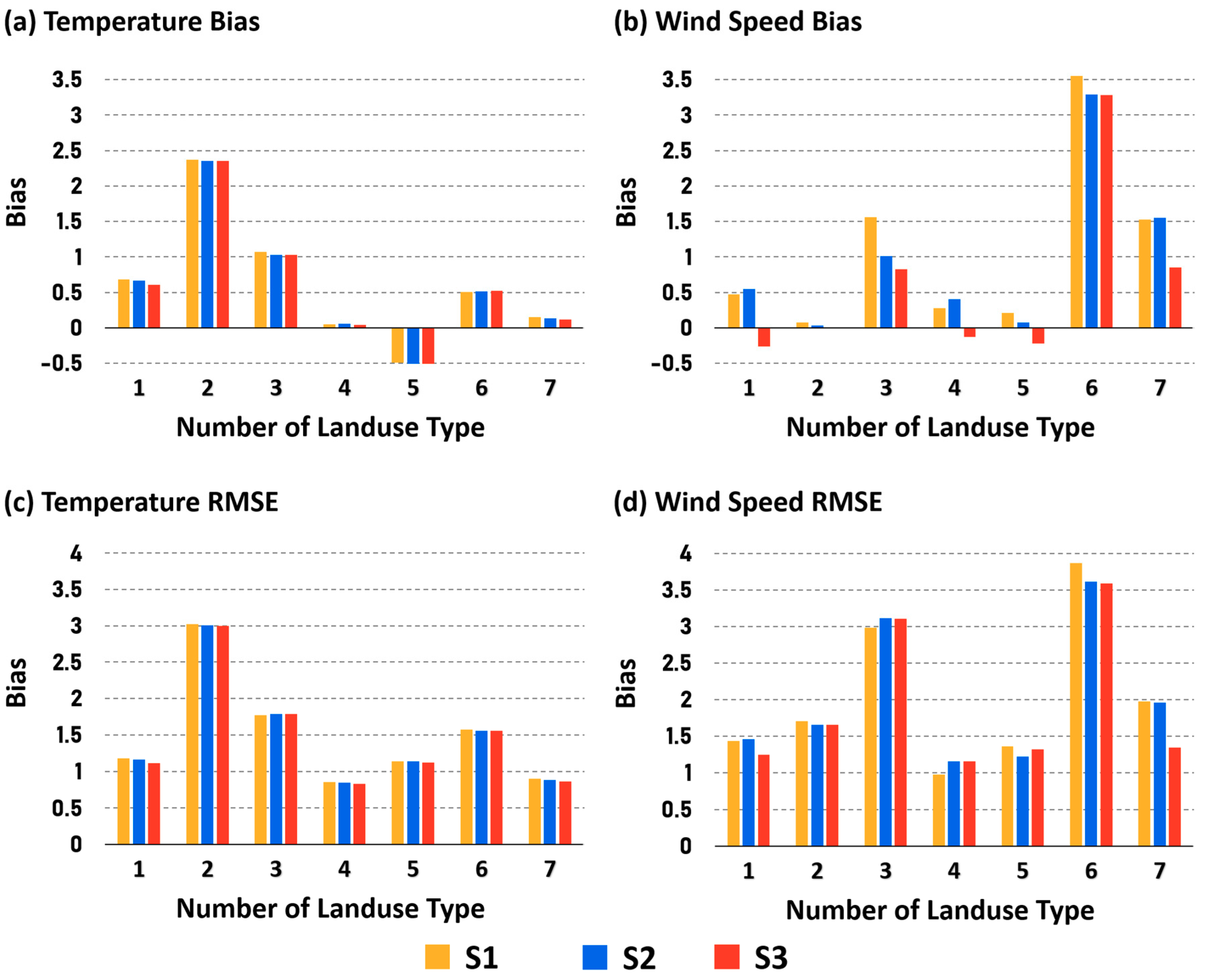
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an advanced land surface–hydrology model with the penn state–NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Lau, A.K.H.; Fung, J.C.H. Application of refined land-use categories for high resolution mesoscale atmospheric modelling. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Byun, D.W. Application of high resolution land use and land cover data for atmospheric modeling in the Houston–Galveston metropolitan area, part I: Meteorological simulation results. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7795–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Yang, K.; Cai, X.; Jia, L.; Wang, J. The characteristics and parameterization of aerodynamic roughness length over heterogeneous surfaces. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, A.; Pleim, J.E. Development of a land surface model. Part I: application in a mesoscale meteorological model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avissar, R.; Pielke, R.A. A parameterization of heterogeneous land surfaces for atmospheric numerical models and its impact on regional meteorology. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 2113–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Manning, K.W.; LeMone, M.A.; Trier, S.B.; Alfieri, J.G.; Roberts, R.; Tewari, M.; Niyogi, D.; Horst, T.W.; Oncley, S.P.; et al. Description and evaluation of the characteristics of the NCAR high-resolution land data assimilation system. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clima. 2007, 46, 694–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Angevine, W.M.; Bianco, L.; McKeen, S.A.; Senff, C.J.; Trainer, M.; Tucker, S.C.; Zamora, R.J. Evaluation of urban surface parameterizations in the WRF model using measurements during the texas air quality study 2006 field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2127–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Barlage, M.; Chen, F.; Smith, J.A. Development and evaluation of a mosaic approach in the WRF-Noah framework. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11918–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, J. Roughness dependent geographic interpolation of surface wind speed average. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 867–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Lin, P.L.; Lin, T.H. Investigation of the effects of different land use and land cover patterns on mesoscale meteorological simulations in the Taiwan area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clima. 2012, 52, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.L.; Tsuang, B.J. Aerodynamic roughness over an urban area and over two farmlands in a populated area as determined by wind profiles and surface energy flux measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 132, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.L.; Tsuang, B.J.; Lu, P.S.; Chang, K.H.; Yao, M.H.; Shen, Y. Measurements of aerodynamic roughness, bowen ratio, and atmospheric surface layer height by eddy covariance and tethersonde systems simultaneously over a heterogeneous rice paddy. J. Hydrom. 2010, 11, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, K.; Belcher, S.E. On the parameterisation of the effective roughness length for momentum transfer over heterogeneous terrain. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1999, 93, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, K. Modelling Surface-Layer Flow over Heterogeneous Terrain. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Reading, England, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Mitchell, K.E.; Chen, F.; Ek, M.B.; Barlage, M.; Kumar, A.; Manning, K.; Niyogi, D.; Rosero, E.; et al. The community noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.J. The formation of areally-averaged roughness lengths. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1988, 114, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lu, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y. A new scheme for effective roughness length and effective zero-plane displacement in land surface models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuang, B.J.; Tsai, J.L.; Lin, M.D.; Chen, C.L. Determining aerodynamic roughness using tethersonde and heat flux measurements in an urban area over a complex terrain. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businger, J.A.; Wyngaard, J.C.; Izumi, Y.; Bradley, E.F. Flux-profile relationships in the atmospheric surface layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Brutsaert, W.H. Momentum roughness and view-angle dependent heat roughness at a southern great plains test-site. J. Hydrol. 1998, 211, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Toya, T.; Yasuda, N. An analytical method for the determination of the roughness parameters over complex regions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 79, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, M.B.; Brutsaert, W. Are radiosonde time scales appropriate to characterize boundary layer wind profiles. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1990, 29, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.; Manning, K.; Wang, W.; Bruyere, C. PSU/NCAR Mesoscale Modeling System Tutorial Class Notes and User’s Guide: MM5 Modeling System Version 3; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Martano, P. Estimation of surface roughness length and displacement height from single-level sonic anemometer data. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Long-term variations in PM 2.5 concentrations under changing meteorological conditions in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The kain–fritsch convective parameterization: An update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Fritsch, J.M. A one-dimensional entraining/detraining plume model and its application in convective parameterization. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 2784–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Cheng, F.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Tsai, J.L. Update of the land surface parameters for Taiwan’s meteorological simulation. Short abstract. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual WRF User’s Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA, 25–29 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Cheng, F.Y. Synoptic weather patterns and associated air pollution in Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lin, N.H. Implementation of a dynamical NH3 emissions parameterization in CMAQ for improving PM2.5 simulation in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.F.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chang, K.H. Performance evaluation of atmospheric particulate matter modeling for East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| LU Type | Default | Updated |
|---|---|---|
| Urban | 0.8 | 2.1 |
| Dry cropland and pasture | 0.15 | 0.07 |
| Irrigated cropland and pasture | 0.10 | 0.03 |
| Cropland/grassland mosaic | 0.14 | 0.095 |
| Cropland/woodland mosaic | 0.2 | |
| Grassland | 0.12 | |
| Shrubland | 0.05 | |
| Mixed shrubland/grassland | 0.06 | |
| Savanna | 0.15 | |
| Deciduous broadleaf forest | 0.5 | |
| Deciduous needleleaf forest | 0.5 | |
| Evergreen broadleaf | 0.5 | |
| Evergreen needleleaf | 0.5 | |
| Mixed forest | 0.5 | |
| Water bodies | 0.0001 | |
| Herbaceous wetland | 0.2 | |
| Barren or sparsely vegetated | 0.01 | |
| Snow or ice | 0.001 |
| Average | R | MB | NME | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°C) | |||||
| OBS | 22.32 | - | - | - | - |
| S1 | 23.07 | 0.823 | 0.749 | 0.961 | 1.09 |
| S2 | 23.05 | 0.822 | 0.735 | 0.961 | 1.088 |
| S3 | 23.03 | 0.824 | 0.71 | 0.95 | 1.077 |
| WS (m/s) | |||||
| OBS | 3.465 | - | - | - | - |
| S1 | 4.63 | 0.580 | 1.167 | 1.573 | 1.707 |
| S2 | 4.5 | 0.579 | 1.039 | 1.499 | 1.641 |
| S3 | 4.19 | 0.579 | 0.724 | 1.364 | 1.507 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, F.-Y.; Lin, C.-F.; Wang, Y.-T.; Tsai, J.-L.; Tsuang, B.-J.; Lin, C.-H. Impact of Effective Roughness Length on Mesoscale Meteorological Simulations over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces in Taiwan. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120805
Cheng F-Y, Lin C-F, Wang Y-T, Tsai J-L, Tsuang B-J, Lin C-H. Impact of Effective Roughness Length on Mesoscale Meteorological Simulations over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces in Taiwan. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120805
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Fang-Yi, Chin-Fang Lin, Yu-Tzu Wang, Jeng-Lin Tsai, Ben-Jei Tsuang, and Ching-Ho Lin. 2019. "Impact of Effective Roughness Length on Mesoscale Meteorological Simulations over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces in Taiwan" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120805
APA StyleCheng, F.-Y., Lin, C.-F., Wang, Y.-T., Tsai, J.-L., Tsuang, B.-J., & Lin, C.-H. (2019). Impact of Effective Roughness Length on Mesoscale Meteorological Simulations over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces in Taiwan. Atmosphere, 10(12), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120805




