Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Flux over Fragmented Sea Ice: Floe Size Distribution Effects and the Associated Convection Structure within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Configuration of the WRF Model
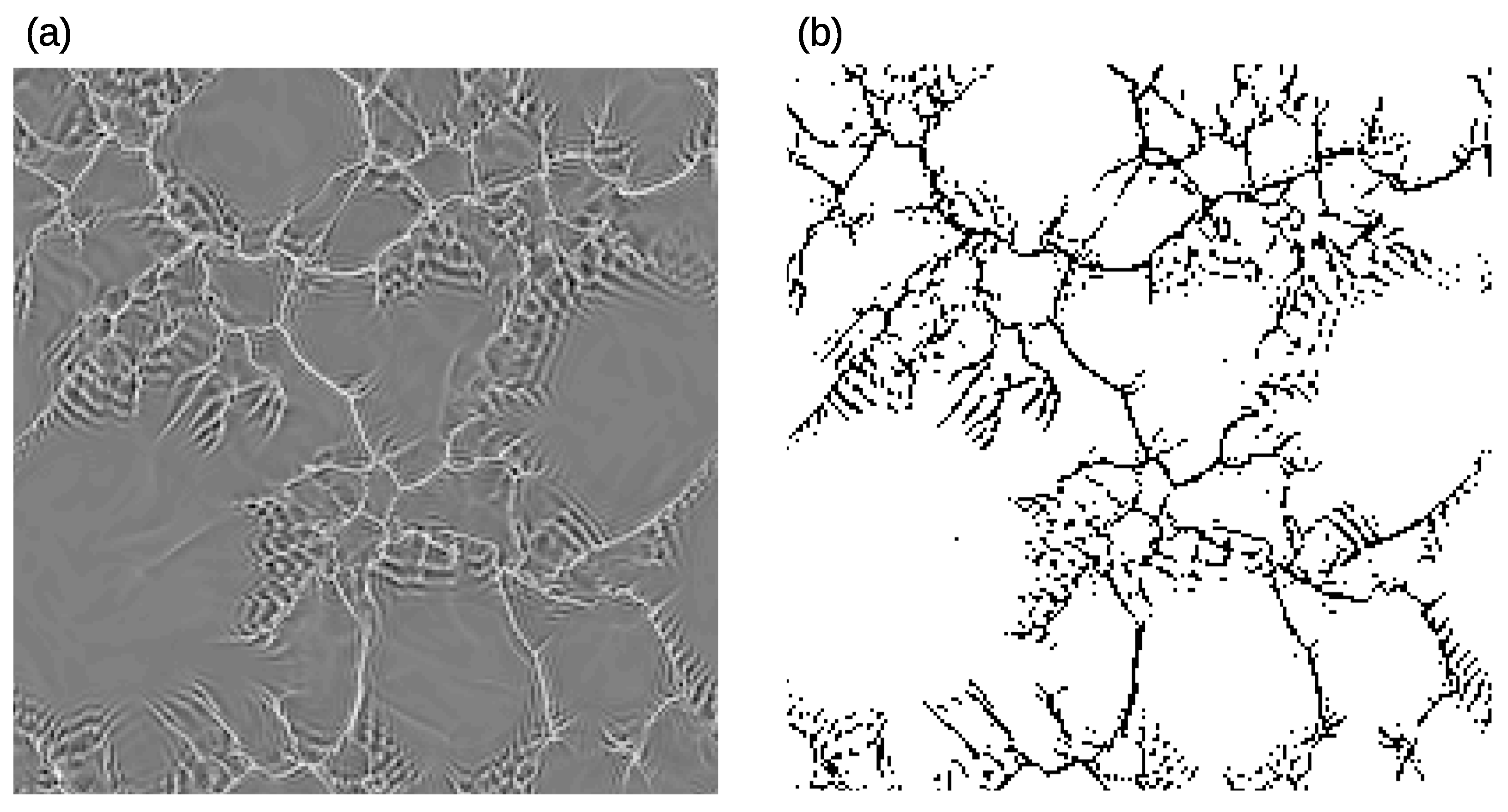
2.2. Calculation of Spatial Coverage of Convective Structures
2.3. Computation of Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Heat Flux
3. Results
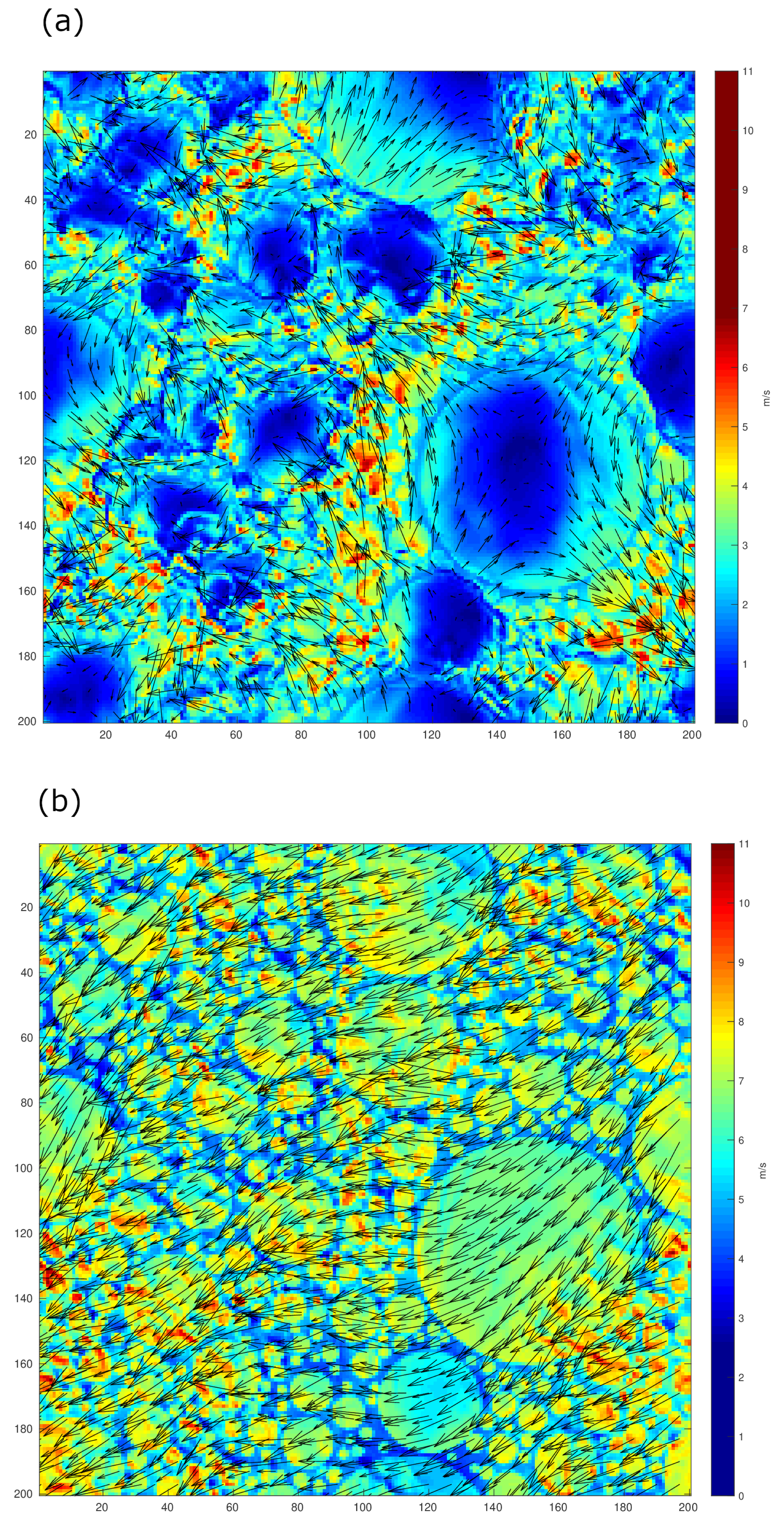
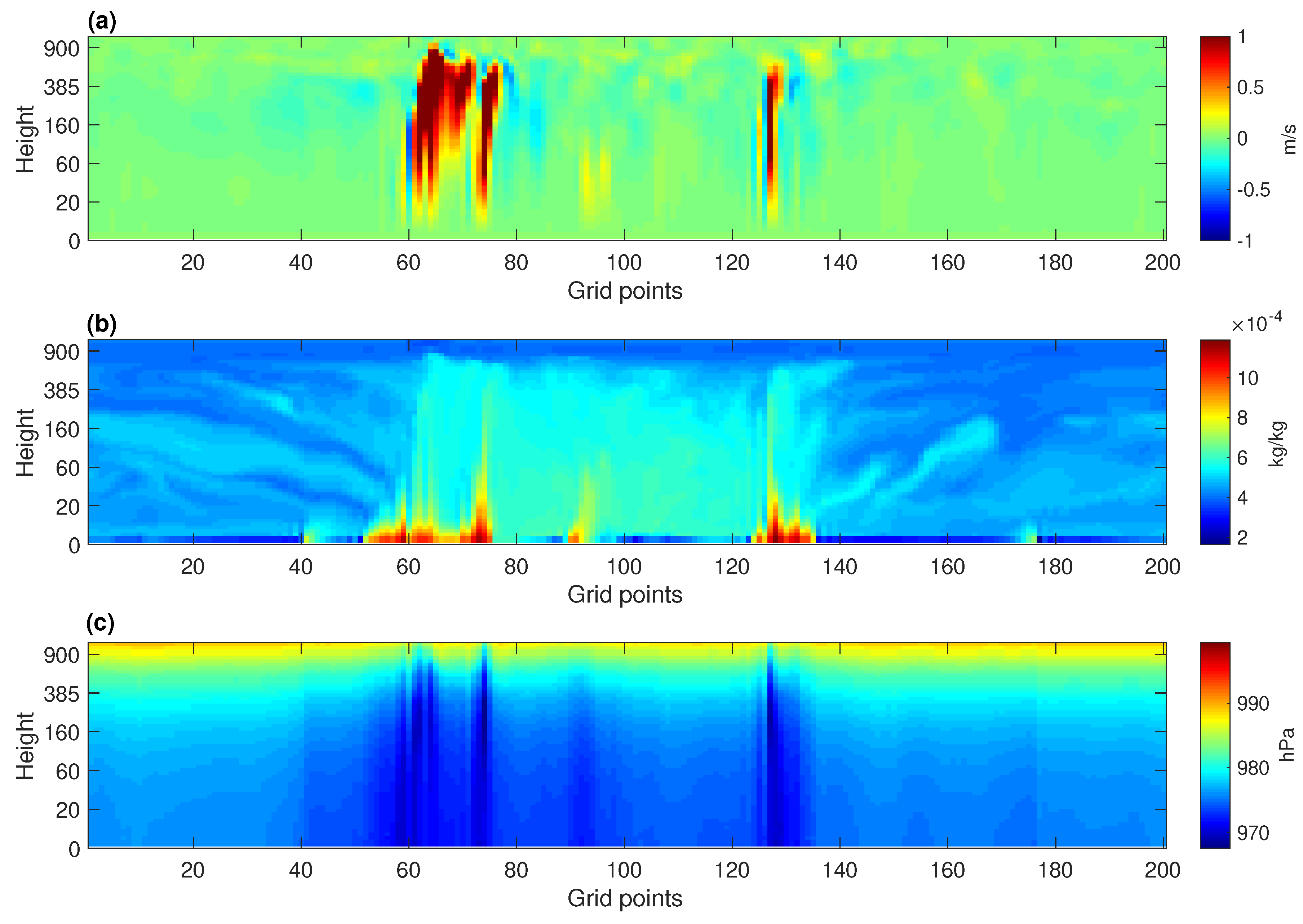
3.1. Horizontal and Vertical Structure of Convection
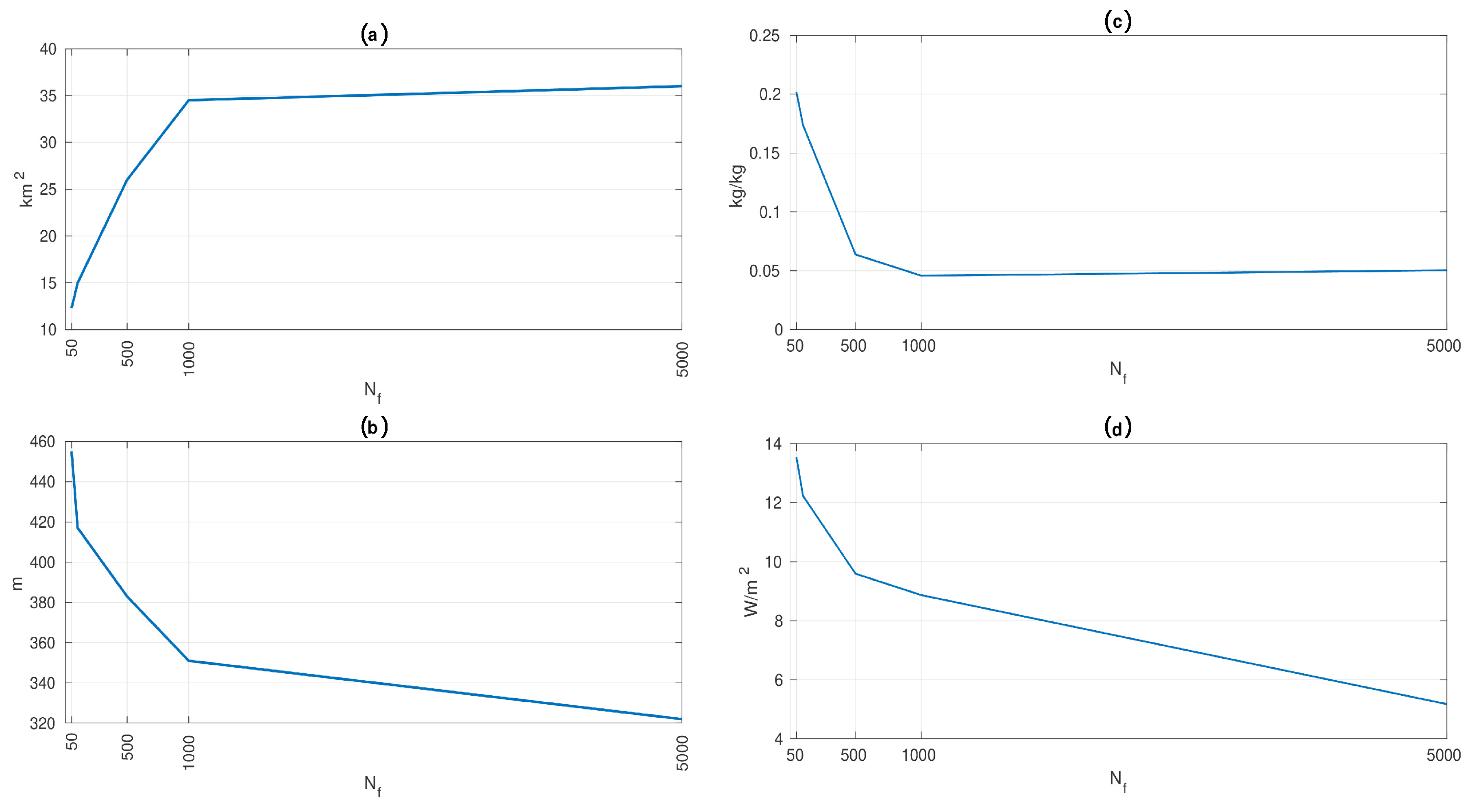
3.2. Correction Coefficient for Surface Moisture Flux
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model Domain | Rectangular, periodic boundaries in both horizontal directions |
| Horizontal resolution | 100 m |
| Number of grid points | 200 × 200 |
| Model top height | 2000 m |
| Air column | 61 -levels with exponential thickness distribution |
| Physics Parametrizations | |
| Microphysics | WRF Single-Moment 5-class scheme |
| Longwave radiation | RRTMG Scheme |
| Surface layer | Eta Similarity Scheme |
| Land Layer | Noah Land Surface Model |
| Large-eddy simulation | 1.5-order TKE scheme |
| Sea Ice Options | |
| Sea ice in a grid cell | Treats sea ice as fractional field. |
| Maximum allowed snow accumulation on sea ice | 10 m |
| Minimum allowed accumulation of snow on sea ice | 0.001 m |
| Default sea ice thickness | 1.5 m |
References
- Vihma, T.; Screen, J.; Tjernström, M.; Newton, B.; Zhang, X.; Popova, V.; Deser, C.; Holland, M.; Prowse, T. The atmospheric role in the Arctic water cycle: A review on processes, past and future changes, and their impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 586–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshutinsky, A.; Steele, M.; Timmermans, M. Forum for Arctic Modeling and Observational Synthesis (FAMOS): Past, current, and future activities. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 3803–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendening, J.; Burk, S. Turbulent transport from an arctic lead: A large-eddy simulation. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1992, 59, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritsen, T.; Svensson, G.; Grisogono, B. Wave flow simulations over Arctic leads. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2005, 117, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüpkes, C.; Gryanik, V.; Witha, B.; Gryschka, M.; Raasch, S.; Gollnik, T. Modeling convection over arctic leads with LES and a non-eddy-resolving microscale model. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulauf, M.; Krueger, S. Two-dimensional numerical simulations of Arctic leads: Plume penetration height. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Isaac, G.; Williams, A.; Marcotte, D.; Strawbridge, K. Turbulent heat fluxes over leads and polynyas, and their effects on arctic clouds during FIRE.ACE: Aircraft observations for April 1998. Atmos.-Ocean 2003, 41, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, A.; Lüpkes, C.; Hartmann, J. Aircraft-based observations of atmospheric boundary-layer modification over Arctic leads. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2839–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.; Miles, W.; Barry, R.; Schnell, R. Lidar-derived particle concentrations in plumes from Arctic leads. Ann. Glaciol. 1990, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffieux, D.; Persson, O.; Fairall, C.; Wolfe, D. Ice pack and lead surface energy budgets during LEADEX 1992. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 1995, 100, 4593–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Curry, J. Lead-induced atmospheric circulations. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, S.; Fett, R.; Englebretson, R. Numerical simulation of cloud plumes emanating from Arctic leads. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16529–16544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, S.; Weiss, J. Influence of leads widths distribution on turbulent heat transfer. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüpkes, C.; Vihma, T.; Birnbaum, G.; Dierer, S.; Garbrecht, T.; Gryanik, V.; Gryschka, M.; Hartmann, J.; Heinemann, G.; Kaleschke, L.; et al. Mesoscale modelling of the Arctic atmospheric boundary layer and its interaction with sea ice. In The ACSYS Decade and Beyond; Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library 43; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 279–324. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, M.; Pang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Fan, P. Estimation of turbulent heat flux over leads using satellite thermal images. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1565–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, R.; Atkinson, W. Atmospheric Response To Spatial Variations In Concentration And Size Of Polynyas In The Southern Ocean Sea-Ice Zone. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenta, M.; Herman, A. The influence of the spatial distribution of leads and ice floes on the atmospheric boundary layer over fragmented sea ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2018, 59, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrak, J.; Müller, M. Atmospheric Response to Kilometer-Scale Changes in Sea Ice Concentration Within the Marginal Ice Zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6702–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P. Sea smoke and steam fog. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1964, 90, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, B.; Overland, J. Observations of Longitudinal Rolls in a Near Neutral Atmosphere. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fett, R.; Burk, S.; Thompson, W.; Kozo, T. Environmental Phenomena of the Beaufort Sea Observed during the Leads Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 2131–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, I. Amplification of turbulent exchange over wide Arctic leads:Large-eddy simulation study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockel, B.; Will, A.; Hense, A. The regional climate model COSMO-CLM (CCLM). Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihma, T. Subgrid parameterization of surface heat and momentum fluxes over polar oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1995, 100, 22625–22646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, A. Parameterization of Turbulent and Mesoscale Fluxes for Heterogeneous Surfaces. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, G.; Kerschgens, M. Comparison of methods for area-averaging surface energy fluxes over heterogeneous land surfaces using high-resolution non-hydrostatic simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avissar, R.; Pielke, R. A Parameterization of Heterogeneous Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Numerical Models and Its Impact on Regional Meteorology. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 2113–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, M. Area-averaging of surface fluxes in a neutrally stratified, horizontally inhomogeneous atmospheric boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 4, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vrese, P.; Schulz, J.; Hagemann, S. On the Representation of Heterogeneity in Land-Surface–Atmosphere Coupling. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2016, 160, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, M.; Jochum, A. The Evaluation of Flux Aggregation Methods using Aircraft Measurements in the Surface Layer. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 98–99, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: Losses and coupled variability (1958–2018). Environ. Res. Lett 2018, 13, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampal, P.; Weiss, J.; Marsan, D. Positive trend in the mean speed and deformation rate of Arctic sea ice, 1979–2007. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, D.; Thorndike, A. Measuring the sea ice floe size distribution. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1984, 89, 6477–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M. Sea ice melting and floe geometry in a simple ice-ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1992, 97, 17729–17738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Schweiger, A.; Steele, M.; Stern, H. Sea ice floe size distribution in the marginal ice zone: Theory and numerical experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 3484–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, C.; Tziperman, E.; Campin, J. Interaction of sea ice floe size, ocean eddies, and sea ice melting. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 8083–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, C.; Tziperman, E. A prognostic model of the sea-ice floe size and thickness distribution. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, L.; Horvat, C.; Dean, S.; Bitz, C. An Emergent Sea Ice Floe Size Distribution in a Global Coupled Ocean-Sea Ice Model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 4322–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A. Discrete-Element bonded-particle Sea Ice model DESIgn, version 1.3a—Model description and implementation. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2016, 9, 1219–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttal, T.; Curry, J.; Mcphee, M.; Perovich, D.; Moritz, R.; Maslanik, J.; Guest, P.; Stern, H.; Moore, J.; Turenne, R.; et al. Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z. Nonsingular Implementation of the Mellor-Yamada Level 2.5 Scheme in the NCEP Mesoscale Model; Office Note #437; National Centers for Environmental Prediction Office: College Park, MD, USA, 2001.
- Janić, Z. The Step-Mountain Eta Coordinate Model: Further Developments of the Convection, Viscous Sublayer, and Turbulence Closure Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.; Obukhov, A. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Contrib. Geophys. Inst. Acad. Sci. USRR 1954, 151, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Young, G.; Kristovich, D.; Hjelmfelt, M.; Foster, R. Rolls, Streets, Waves, and More. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, E.; Irwin, J. Chapter 17: Evaluation Of Air Pollution Models. In Air Quality Modeling—Theories, Methodologies, Computational Techniques, and Available Data Bases and Software, V.II – Advanced Topics; The EnvironComp Institute and Air and Waste Management Association: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 503–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zulauf, M.; Krueger, S. Two-dimensional cloud-resolving modeling of the atmospheric effects of Arctic leads based upon midwinter conditions at the Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean ice camp. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, I.; Sorokina, S. Climatology of Arctic Planetary Boundary Layer. In Atmospheric Turbulence, Meteorological Modeling and Aerodynamics; Langand, P.R., Lombarg, F.S., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–58. [Google Scholar]
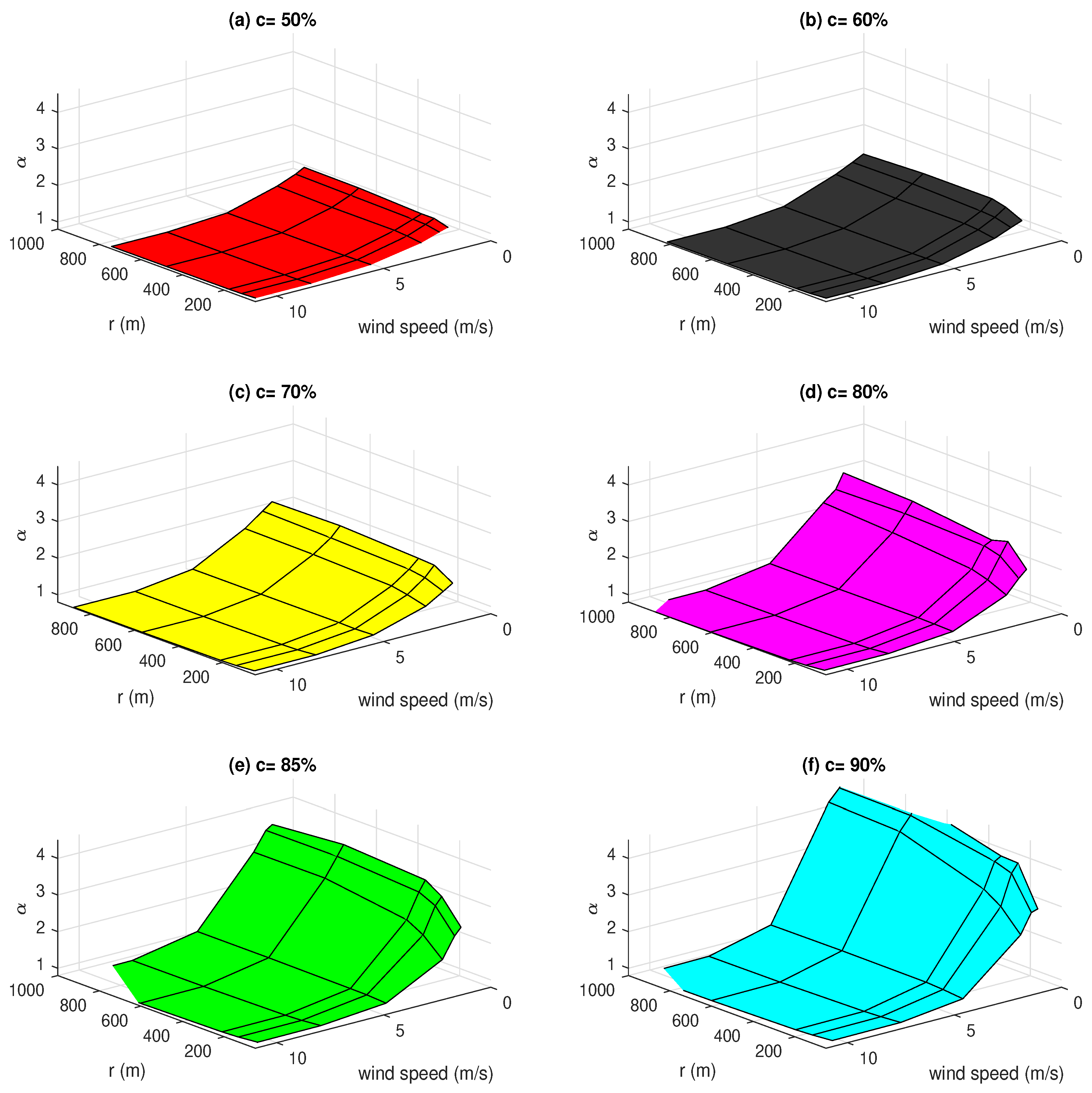
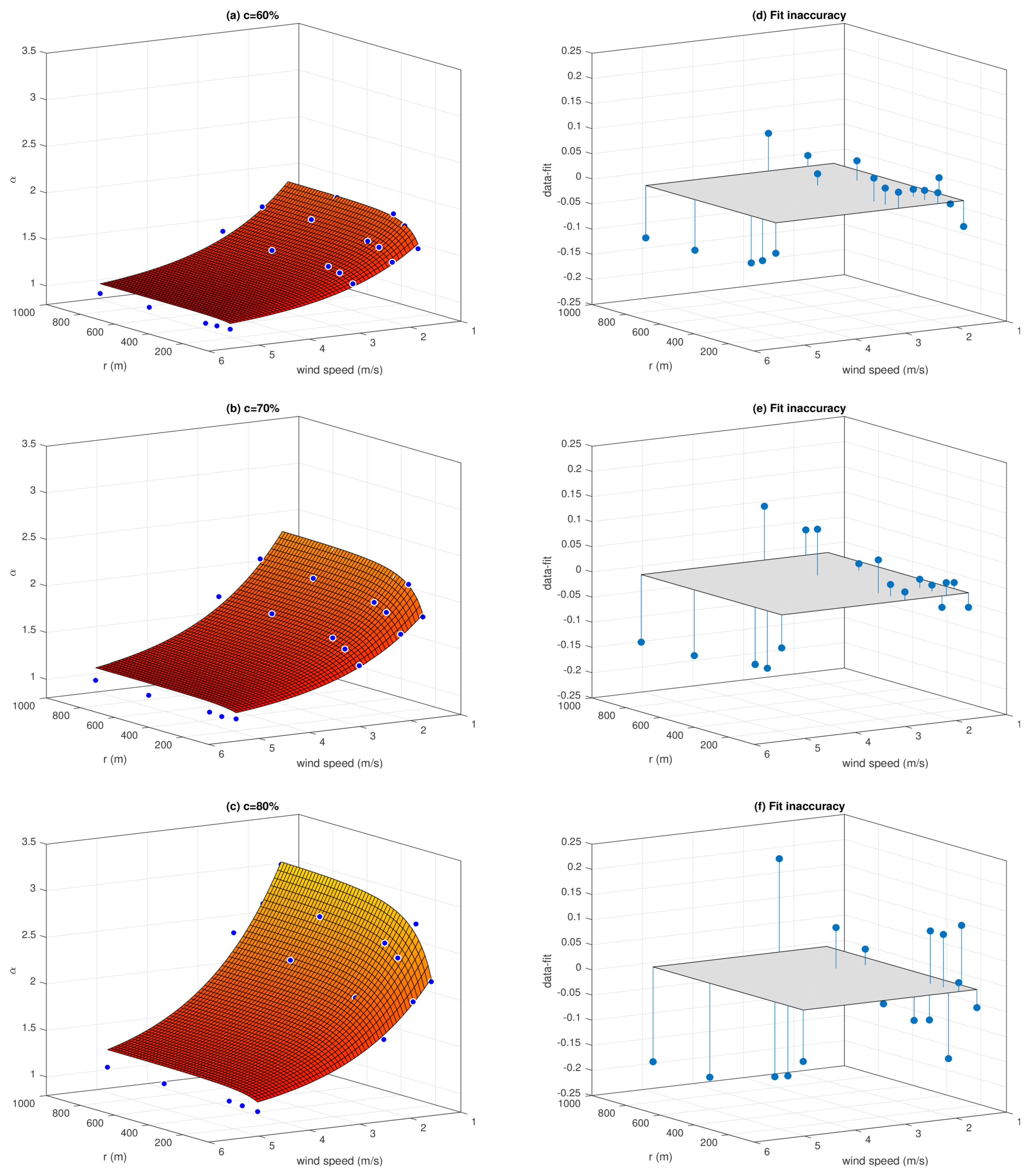
| c | RMSE | CC |
|---|---|---|
| 50% | 0.29 | 0.98 |
| 60% | 0.05 | 0.99 |
| 70% | 0.11 | 0.99 |
| 80% | 0.07 | 0.99 |
| 85% | 0.17 | 0.99 |
| 90% | 0.18 | 0.99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wenta, M.; Herman, A. Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Flux over Fragmented Sea Ice: Floe Size Distribution Effects and the Associated Convection Structure within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110654
Wenta M, Herman A. Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Flux over Fragmented Sea Ice: Floe Size Distribution Effects and the Associated Convection Structure within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(11):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110654
Chicago/Turabian StyleWenta, Marta, and Agnieszka Herman. 2019. "Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Flux over Fragmented Sea Ice: Floe Size Distribution Effects and the Associated Convection Structure within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer" Atmosphere 10, no. 11: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110654
APA StyleWenta, M., & Herman, A. (2019). Area-Averaged Surface Moisture Flux over Fragmented Sea Ice: Floe Size Distribution Effects and the Associated Convection Structure within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere, 10(11), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110654






