Release of Highly Active Ice Nucleating Biological Particles Associated with Rain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Analysis
2.1. Identification of INPs by the IDFM
2.2. Individual Particle Analyses
3. Results and Discussions
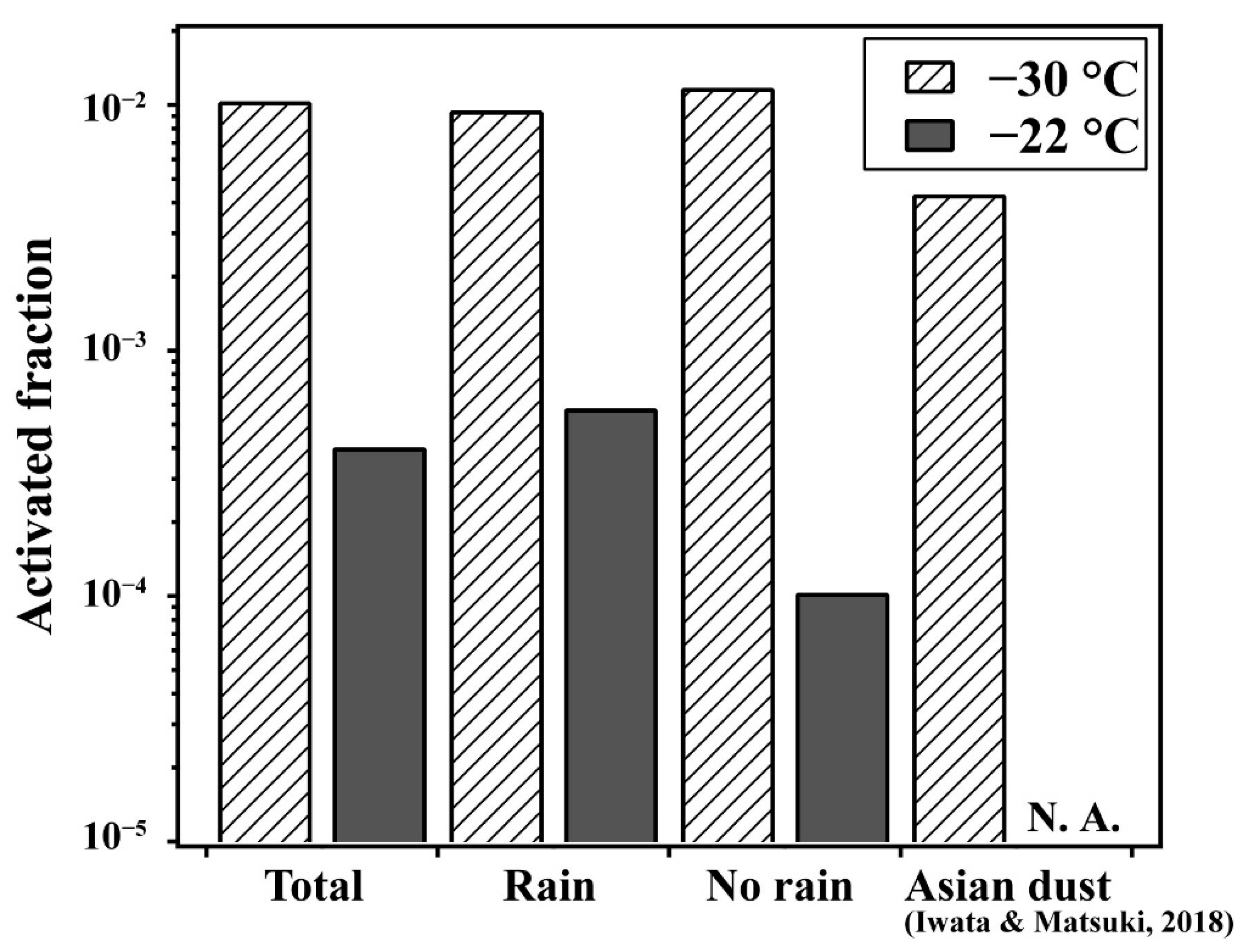
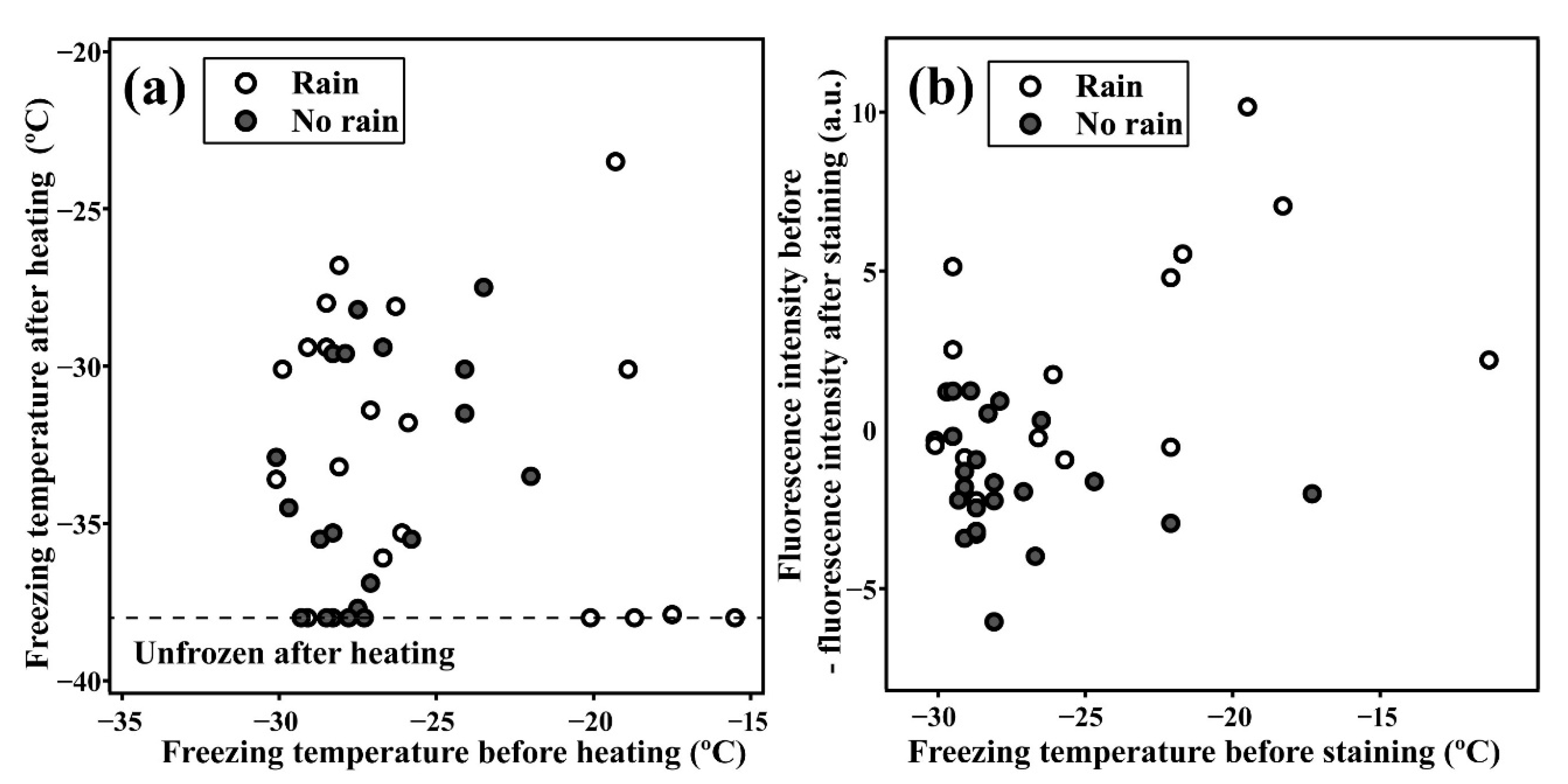
3.1. Relationship between Highly Active INPs and Weather Conditions
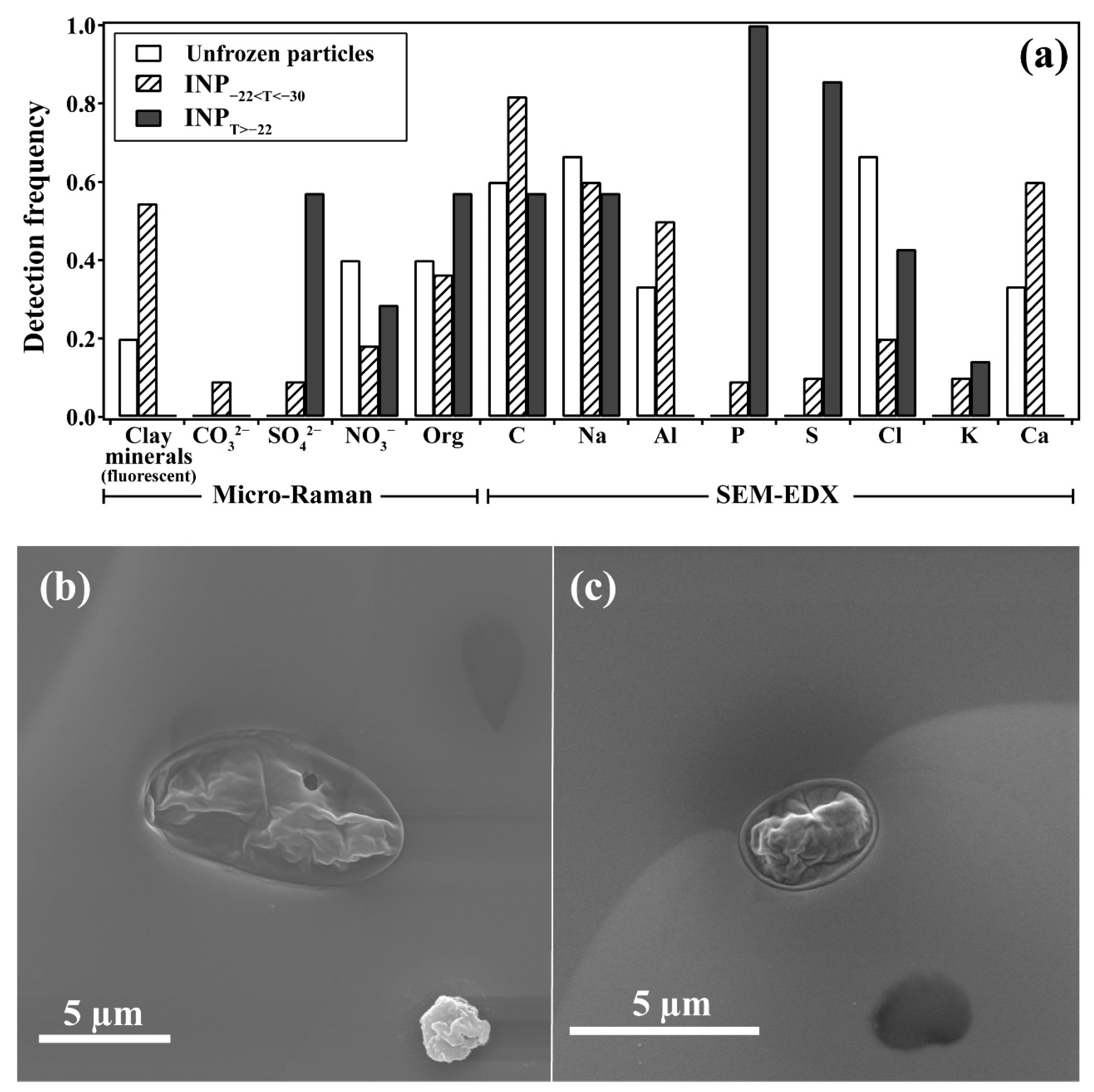
3.2. Biological Fingerprints of Efficient INPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, 2nd ed.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kanji, Z.A.; Ladino, L.A.; Wex, H.; Boose, Y.; Burkert-Kohn, M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Krämer, M. Overview of Ice Nucleating Particles. Meteorol. Monogr. 2017, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, W.; Heymsfield, A. Production of ice in tropospheric clouds: A review. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demott, P.J.; Rogers, D.C. Freezing nucleation rates of dilute solution droplets measured between −30° and −40 °C in laboratory simulations of natural clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, T.; Luo, B.; Tsias, A.; Peter, T. Water activity as the determinant for homogeneous ice nucleation in aqueous solutions. Nature 2000, 406, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.J.; Broadley, S.L.; Wilson, T.W.; Bull, S.J.; Wills, R.H.; Christenson, H.K.; Murray, E.J. Kinetics of the homogeneous freezing of water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10380–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.J.; O’Sullivan, D.; Atkinson, J.D.; Webb, M.E. Ice nucleation by particles immersed in supercooled cloud droplets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMott, P.; Prenni, A.J.; Liu, X.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Petters, M.D.; Twohy, C.H.; Richardson, M.S.; Eidhammer, T.; Rogers, D.C. Predicting global atmospheric ice nuclei distributions and their impacts on climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11217–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratt, K.A.; Demott, P.J.; French, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Westphal, D.L.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Twohy, C.H.; Prenni, A.J.; Prather, K.A. In situ detection of biological particles in cloud ice-crystals. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenni, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Sullivan, R.C.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Rogers, D.C. Biomass burning as a potential source for atmospheric ice nuclei: Western wildfires and prescribed burns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardon-Dryer, K.; Levin, Z. Ground-based measurements of immersion freezing in the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5217–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lohmann, U.; Raga, G.B.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Kulmala, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Reissell, A.; Andreae, M.O. Flood or Drought: How Do Aerosols Affect Precipitation? Science 2008, 321, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niemand, M.; Möhler, O.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Hoose, C.; Connolly, P.; Klein, H.; Bingemer, H.; DeMott, P.; Skrotzki, J.; et al. A Particle-Surface-Area-Based Parameterization of Immersion Freezing on Desert Dust Particles. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.D.; Murray, B.J.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Whale, T.F.; Baustian, K.J.; Carslaw, K.S.; Dobbie, S.; O’Sullivan, D.; Malkin, T.L. The importance of feldspar for ice nucleation by mineral dust in mixed-phase clouds. Nature 2013, 498, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worringen, A.; Kandler, K.; Benker, N.; Dirsch, T.; Mertes, S.; Schenk, L.; Kästner, U.; Frank, F.; Nillius, B.; Bundke, U.; et al. Single-particle characterization of ice-nucleating particles and ice particle residuals sampled by three different techniques. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4161–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamphus, M.; Ettner-Mahl, M.; Klimach, T.; Drewnick, F.; Keller, L.; Cziczo, D.J.; Mertes, S.; Borrmann, S.; Curtius, J. Chemical composition of ambient aerosol, ice residues and cloud droplet residues in mixed-phase clouds: Single particle analysis during the Cloud and Aerosol Characterization Experiment (CLACE 6). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8077–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boose, Y.; Sierau, B.; García, M.I.; Rodríguez, S.; Alastuey, A.; Linke, C.; Schnaiter, M.; Kupiszewski, P.; Kanji, Z.A.; Lohmann, U. Ice nucleating particles in the Saharan Air Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9067–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, A.D.; Whale, T.F.; Carpenter, M.A.; Holden, M.A.; Neve, L.; O’Sullivan, D.; Temprado, J.V.; Murray, B.J. Not all feldspars are equal: A survey of ice nucleating properties across the feldspar group of minerals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10927–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isono, K.; Komabayasi, M.; Ono, A. The Nature and the Origin of Ice Nuclei in the Atmosphere. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 1959, 37, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Temprado, J.; Murray, B.J.; Wilson, T.W.; O’Sullivan, D.; Browse, J.; Pringle, K.J.; Ardon-Dryer, K.; Bertram, A.K.; Burrows, S.M.; Ceburnis, D.; et al. Contribution of feldspar and marine organic aerosols to global ice nucleating particle concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3637–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pummer, B.G.; Bauer, H.; Bernardi, J.; Bleicher, S.; Grothe, H. Suspendable macromolecules are responsible for ice nucleation activity of birch and conifer pollen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, C.E.; Georgakopoulos, D.G.; Sands, D.C. Ice nucleation active bacteria and their potential role in precipitation. J. Phys. IV 2004, 121, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Sands, D.C.; Glaux, C.; Samsatly, J.; Asaad, S.; Moukahel, A.R.; Gonçalves, F.L.T.; Bigg, E.K. Urediospores of rust fungi are ice nucleation active at >−10 °C and harbor ice nucleation active bacteria. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.W.; Ladino, L.A.; Alpert, P.A.; Breckels, M.N.; Brooks, I.M.; Browse, J.; Burrows, S.M.; Carslaw, K.S.; Huffman, J.A.; Judd, C.; et al. A marine biogenic source of atmospheric ice-nucleating particles. Nature 2015, 525, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pummer, B.G.; Budke, C.; Augustin-Bauditz, S.; Niedermeier, D.; Felgitsch, L.; Kampf, C.J.; Huber, R.G.; Liedl, K.R.; Loerting, T.; Moschen, T.; et al. Ice nucleation by water-soluble macromolecules. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4077–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maki, L.R.; Galyan, E.L.; Chang-Chien, M.M.; Caldwell, D.R. Ice nucleation induced by pseudomonas syringae. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Möhler, O.; DeMott, P.J.; Vali, G.; Levin, Z. Microbiology and atmospheric processes: The role of biological particles in cloud physics. Biogeosciences 2007, 4, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.A.; Prenni, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Pöhlker, C.; Mason, R.H.; Robinson, N.H.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Tobo, Y.; Desprès, V.R.; Garcia, E.; et al. High concentrations of biological aerosol particles and ice nuclei during and after rain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6151–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.M.; Harrison, R.M. The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.P.; Hader, J.D.; McMeeking, G.R.; Petters, M.D. High relative humidity as a trigger for widespread release of ice nuclei. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobo, Y.; Prenni, A.J.; Demott, P.J.; Huffman, J.A.; McCluskey, C.S.; Tian, G.; Pöhlker, C.; Pöschl, U.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Biological aerosol particles as a key determinant of ice nuclei populations in a forest ecosystem. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10100–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, F.; Kakikawa, M.; Wada, M.; Matsuki, A. Variations of ice nuclei concentration induced by rain and snowfall within a local forested site in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Hill, T.C.J.; Prenni, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Franc, G.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Biogenic ice nuclei in boundary layer air over two U.S. high plains agricultural regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhlker, C.; Wiedemann, K.T.; Sinha, B.; Shiraiwa, M.; Gunthe, S.S.; Smith, M.; Su, H.; Artaxo, P.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Biogenic Potassium Salt Particles as Seeds for Secondary Organic Aerosol in the Amazon. Science 2012, 337, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobo, Y. An improved approach for measuring immersion freezing in large droplets over a wide temperature range. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whale, T.F.; Murray, B.J.; O’Sullivan, D.; Wilson, T.W.; Umo, N.S.; Baustian, K.J.; Atkinson, J.D.; Workneh, D.A.; Morris, G.J. A technique for quantifying heterogeneous ice nucleation in microlitre supercooled water droplets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwata, A.; Matsuki, A. Characterization of individual ice residual particles by the single droplet freezing method: A case study in the Asian dust outflow region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1785–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolli, C.; Nagare, B.; Welti, A.; Lohmann, U. Ice nucleation efficiency of AgI: Review and new insights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8915–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Maki, T.; Kakikawa, M.; Kobayashi, F.; Matsuki, A. Effects of different temperature treatments on biological ice nuclei in snow samples. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, B.C.; Morris, C.E.; Foreman, C.M.; Cai, R.; Sands, D.C. Ubiquity of Biological Ice Nucleators in Snowfall. Science 2008, 319, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, M.; Amato, P.; Deguillaume, L.; Monier, M.; Hoose, C.; Delort, A.-M. Quantification of ice nuclei active at near 0 °C temperatures in low-altitude clouds at the Puy de Dôme atmospheric station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8185–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouleur, S.; Richard, C.; Martin, J.; Antoun, H. Ice Nucleation Activity in Fusarium acuminatum and Fusarium avenaceum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Hill, T.C.J.; Pummer, B.G.; Yordanova, P.; Franc, G.D.; Pöschl, U. Ice nucleation activity in the widespread soil fungus Mortierella alpina. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, T.C.J.; Moffett, B.F.; DeMott, P.J.; Georgakopoulos, D.G.; Stump, W.L.; Franc, G.D. Measurement of Ice Nucleation-Active Bacteria on Plants and in Precipitation by Quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.-R.; Hodson, R.E.; Binder, B.J.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. Application of Digital Image Analysis and Flow Cytometry To Enumerate Marine Viruses Stained with SYBR Gold. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 67, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Petters, M.D.; Wright, T.P. Revisiting ice nucleation from precipitation samples. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8758–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.C.J.; Demott, P.J.; Tobo, Y.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Moffett, B.F.; Franc, G.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Sources of organic ice nucleating particles in soils. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7195–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Adams, M.P.; Tarn, M.D.; Harrison, A.D.; Vergara-Temprado, J.; Porter, G.C.E.; Holden, M.A.; Sanchez-Marroquin, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Whale, T.F.; et al. Contributions of biogenic material to the atmospheric ice-nucleating particle population in North Western Europe. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Messerer, A.; Yang, X.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopic analysis of changes in the chemical structure and reactivity of soot in a diesel exhaust aftertreatment model system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3702–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baustian, K.J.; Cziczo, D.J.; Wise, M.E.; Pratt, K.A.; Kulkarni, G.; Hallar, A.G.; Tolbert, M.A. Importance of aerosol composition, mixing state, and morphology for heterogeneous ice nucleation: A combined field and laboratory approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskina, O.; Young, M.A.; Kleiber, P.D.; Grassian, V.H. Infrared extinction spectroscopy and micro-Raman spectroscopy of select components of mineral dust mixed with organic compounds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6593–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, M.A.; Hasenkopf, C.A.; Beaver, M.R.; Tolbert, M.A. Optical properties of internally mixed aerosol particles composed of dicarboxylic acids and ammonium sulfate. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 13584–13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobanska, S.; Hwang, H.; Choël, M.; Jung, H.J.; Eom, H.J.; Kim, H.; Barbillat, J.; Ro, C.U. Investigation of the chemical mixing state of individual asian dust particles by the combined use of electron probe X-ray microanalysis and raman microspectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Eom, H.J.; Kang, H.W.; Moreau, M.; Sobanska, S.; Ro, C.U. Combined use of quantitative ED-EPMA, Raman microspectrometry, and ATR-FTIR imaging techniques for the analysis of individual particles. Analyst 2014, 139, 3949–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias-Maser, S.; Obolkin, V.; Khodzer, T.; Jaenicke, R. Seasonal variation of primary biological aerosol particles in the remote continental region of Lake Baikal/Siberia. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3805–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, F.; Morris, C.E.; Leifeld, J.; Yakutin, M.V.; Alewell, C. Biological residues define the ice nucleation properties of soil dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9643–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.F.; Lai, C.H.; Chu, H.J.; Lin, W.H. Evaluating and mapping of spatial air ion quality patterns in a residential garden using a geostatistic method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.E.; Conen, F.; Huffman, J.A.; Phillips, V.; Pöschl, U.; Sands, D.C. Bioprecipitation: A feedback cycle linking Earth history, ecosystem dynamics and land use through biological ice nucleators in the atmosphere. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwata, A.; Imura, M.; Hama, M.; Maki, T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kunihisa, R.; Matsuki, A. Release of Highly Active Ice Nucleating Biological Particles Associated with Rain. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100605
Iwata A, Imura M, Hama M, Maki T, Tsuchiya N, Kunihisa R, Matsuki A. Release of Highly Active Ice Nucleating Biological Particles Associated with Rain. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(10):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100605
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwata, Ayumi, Mayu Imura, Moeka Hama, Teruya Maki, Nozomu Tsuchiya, Ryota Kunihisa, and Atsushi Matsuki. 2019. "Release of Highly Active Ice Nucleating Biological Particles Associated with Rain" Atmosphere 10, no. 10: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100605
APA StyleIwata, A., Imura, M., Hama, M., Maki, T., Tsuchiya, N., Kunihisa, R., & Matsuki, A. (2019). Release of Highly Active Ice Nucleating Biological Particles Associated with Rain. Atmosphere, 10(10), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100605






