New Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps Using a Data-Driven Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Data Description
2.2. Data-Driven Approach Using Support Vector Regression and Its Modification
3. Results
4. Discussion
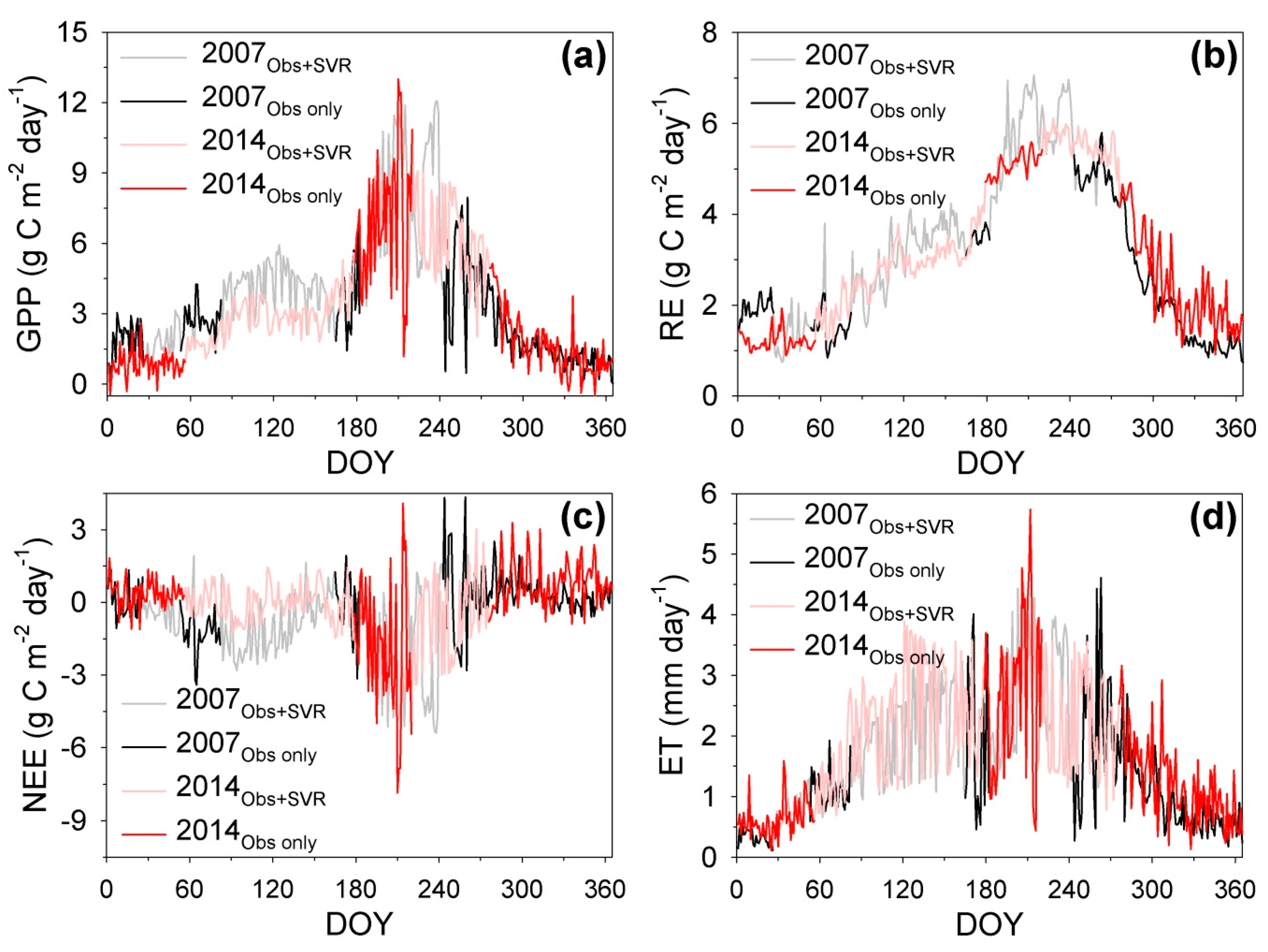
4.1. How Large is the Uncertainty Related to the Long-Period Flux-Gap-Filling?
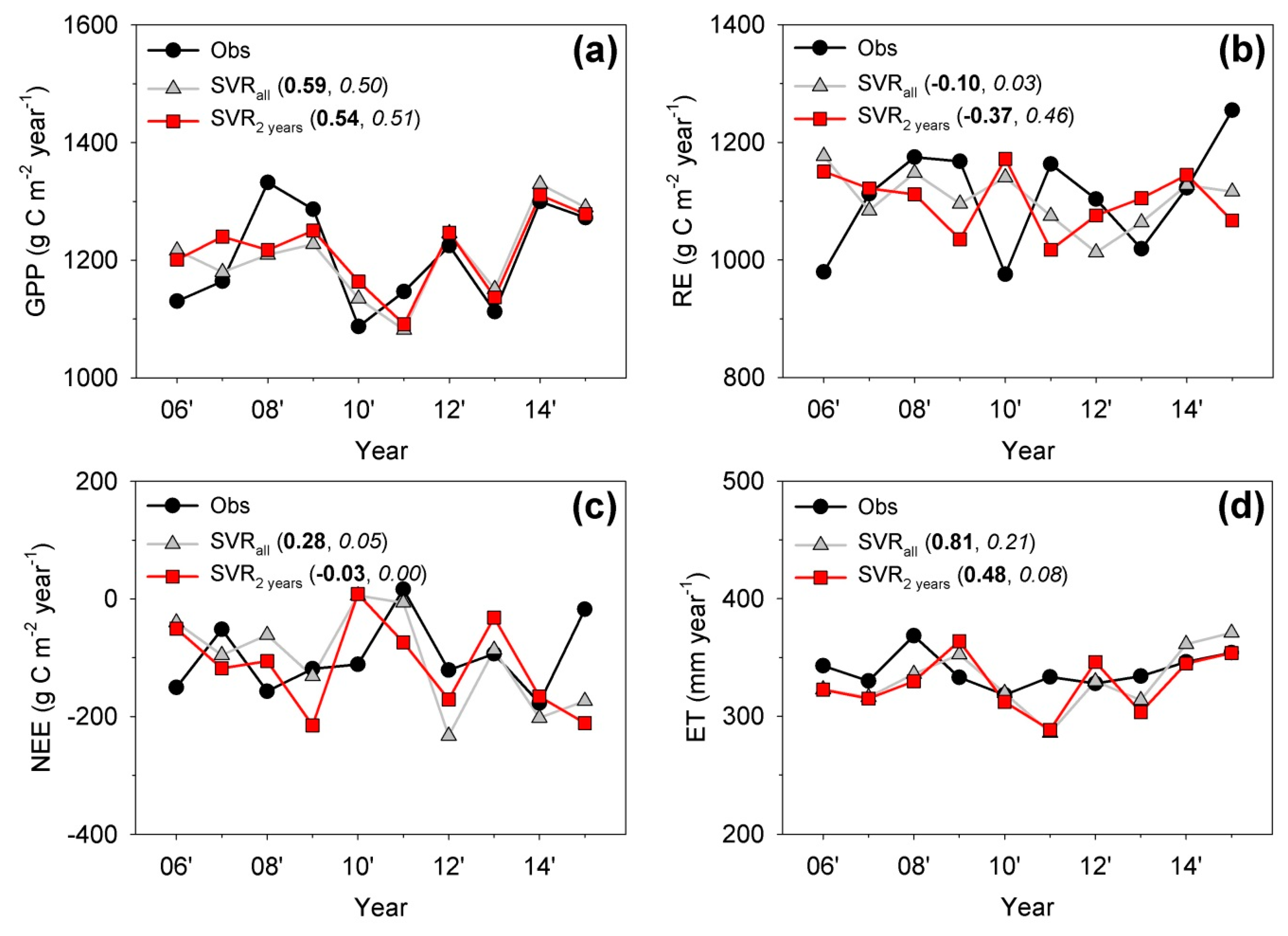
4.2. Can the Long-Period-Gap-Filled Flux Data Capture the Interannual Variability?
5. Conclusions: Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps
- In situ measurement data should be preferentially used as the input for machine learning, if available.
- Data covering as long a period as possible should be used to train the machine-learning-based model.
- If there has been a significant ecosystem state change over the study period and the primary objective of gap-filling is to quantify interannual variability rather than seasonality, multiple models should be established for each ecosystem state.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichstein, M.; Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Papale, D.; Aubinet, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Buchmann, N.; Gilmanov, T.; Granier, A.; et al. On the separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and ecosystem respiration: Review and improved algorithm. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Olson, R.; Anthoni, P.; Aubinet, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Burba, G.; Ceulemans, R.; Clement, R.; Dolman, H.; et al. Gap filling strategies for long term energy flux data sets. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Olson, R.; Anthoni, P.; Aubinet, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Burba, G.; Ceulemans, R.; Clement, R.; Dolman, H.; et al. Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, A.M.; Papale, D.; Reichstein, M.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Richardson, A.D.; Barr, A.G.; Beckstein, C.; Braswell, B.H.; Churkina, G.; Desai, A.R.; et al. Comprehensive comparison of gap-filling techniques for eddy covariance net carbon fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 147, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, D. Data Gap Filling, 2012 ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Ciais, P.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Sheffield, J.; Goulden, M.L.; Bonan, G.; Cescatti, A.; Chen, J.; De Jeu, R.; et al. Recent decline in the global land evapotranspiration trend due to limited moisture supply. Nature 2010, 467, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Schwalm, C.R.; Huntingford, C.; Sitch, S.; Ahlström, A.; Arneth, A.; Camps-Valls, G.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. Compensatory water effects link yearly global land CO2 sink changes to temperature. Nature 2017, 541, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, K.; Ueyama, M.; Kondo, M.; Saigusa, N.; Kim, J.; Alberto, M.C.; Ardö, J.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Kang, M.; Hirano, T.; et al. New data-driven estimation of terrestrial CO2 fluxes in Asia using a standardized database of eddy covariance measurements, remote sensing data, and support vector regression. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 767–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Hong, J. The simulation of water vapor and carbon dioxide fluxes over a rice paddy field by modified soil-plant-atmosphere model (mSPA). Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 44, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Park, S.; Kwon, H.; Choi, H.T.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J. Evapotranspiration from a deciduous forest in a complex terrain and a heterogeneous farmland under monsoon climate. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 45, 175–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.; Oncley, S.; Stage, S. Sonic Anemometer Tilt Correction Algorithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Kang, M.; Park, S.-B.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, J. The effect of coordinate rotation on the eddy covariance flux estimation in a hilly KoFlux forest catchment. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 9, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Kang, M.; Park, S.-B.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, J. Expansion of the planar-fit method to estimate flux over complex terrain. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 110, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Park, T.-Y.; Hong, J.; Lim, J.-H.; Kim, J. Seasonality of Net Ecosystem Carbon Exchang in Two Major Plant Functional Types in Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 45, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Kwon, H.; Lim, J.-H.; Byun, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Standardization of KoFlux eddy-covariance data processing. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 11, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Thakuri, B.M.; Chun, J.; Cho, C. New gap-filling and partitioning technique for H2O eddy fluxes measured over forests. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, D.; Reichstein, M.; Aubinet, M.; Canfora, E.; Bernhofer, C.; Kutsch, W.; Longdoz, B.; Rambal, S.; Valentini, R.; Vesala, T.; et al. Towards a standardized processing of Net Ecosystem Exchange measured with eddy covariance technique: Algorithms and uncertainty estimation. Biogeosciences 2006, 3, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Malla Thakuri, B.; Chun, J.; Cho, C. Modification of the moving point test method for nighttime eddy CO2 flux filtering on hilly and complex terrains. MethodsX 2019, 6, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ichii, K.; Wang, W.; Hashimoto, H.; Yang, F.; Votava, P.; Michaelis, A.R.; Nemani, R.R. Refinement of rooting depths using satellite-based evapotranspiration seasonality for ecosystem modeling in California. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM—A Library for Support Vector Machines. Available online: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/ (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- Myneni, R.B.; Hoffman, S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Glassy, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, G.R.; et al. Global products of vegetation leaf area and fraction absorbed PAR from year one of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhuang, Q.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Law, B.E.; Richardson, A.D.; Chen, J.; Oren, R.; Starr, G.; Noormets, A.; Ma, S.; et al. Estimation of net ecosystem carbon exchange for the conterminous United States by combining MODIS and AmeriFlux data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1827–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center, O.R.N.L.D.A.A. MODIS Collection 6 Land Product Subsets Web Service. Available online: https://daac.ornl.gov/LAND_VAL/guides/MODIS_Web_Service_C6.html (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- Papale, D.; Valentini, R. A new assessment of European forests carbon exchanges by eddy fluxes and artificial neural network spatialization. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.M. New refinements and validation of the MODIS Land-Surface Temperature/Emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, K.; Kondo, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Kim, J.; Ueyama, M.; Lim, H.J.; Shi, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, A.; et al. Site-level model-data synthesis of terrestrial carbon fluxes in the CarboEastAsia eddy-covariance observation network: Toward future modeling efforts. J. For. Res. 2013, 18, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, R.; Murakami, H. Estimating photosynthetically available radiation at the ocean surface from ADEOS-II Global Imager data. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 63, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Kang, S.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, J. Evaluation of land surface radiation balance derived from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) over complex terrain and heterogeneous landscape on clear sky days. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A. randomForest—Classification And Regression With Random Forest. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/randomForest/versions/4.6-14/topics/randomForest (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- The MathWorks, Inc. Fit Data with a Shallow Neural Network. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/gs/fit-data-with-a-neural-network.html (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- Richardson, A.D.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Burba, G.G.; Davis, K.J.; Flanagan, L.B.; Katul, G.G.; Munger, J.W.; Ricciuto, D.M.; Stoy, P.C.; Suyker, A.E.; et al. A multi-site analysis of random error in tower-based measurements of carbon and energy fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 136, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Hollinger, D.Y. A method to estimate the additional uncertainty in gap-filled NEE resulting from long gaps in the CO2 flux record. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 147, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, P.L.; Sims, P.F. Sampling error in eddy correlation flux measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 3503–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Baldocchi, D.D.; John, R.; Wolf, S.; Reichstein, M. Fluxes all of the time? A primer on the temporal representativeness of FLUXNET. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrawati, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kang, M. Assessment of Ecosystem Productivity and Efficiency using Flux Measurement over Haenam Farmland Site in Korea (HFK). Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 20, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Ruddell, B.L.; Cho, C.; Chun, J.; Kim, J. Identifying CO2 advection on a hill slope using information flow. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Hong, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, S.K.; Lim, J.H.; Son, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; et al. HydroKorea and CarboKorea: Cross-scale studies of ecohydrology and biogeochemistry in a heterogeneous and complex forest catchment of Korea. Ecol. Res. 2006, 21, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Scott, R.L.; Moore, D.J.P.; Biederman, J.A.; Smith, W.K. Understanding the relationship between vegetation greenness and productivity across dryland ecosystems through the integration of PhenoCam, satellite, and eddy covariance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
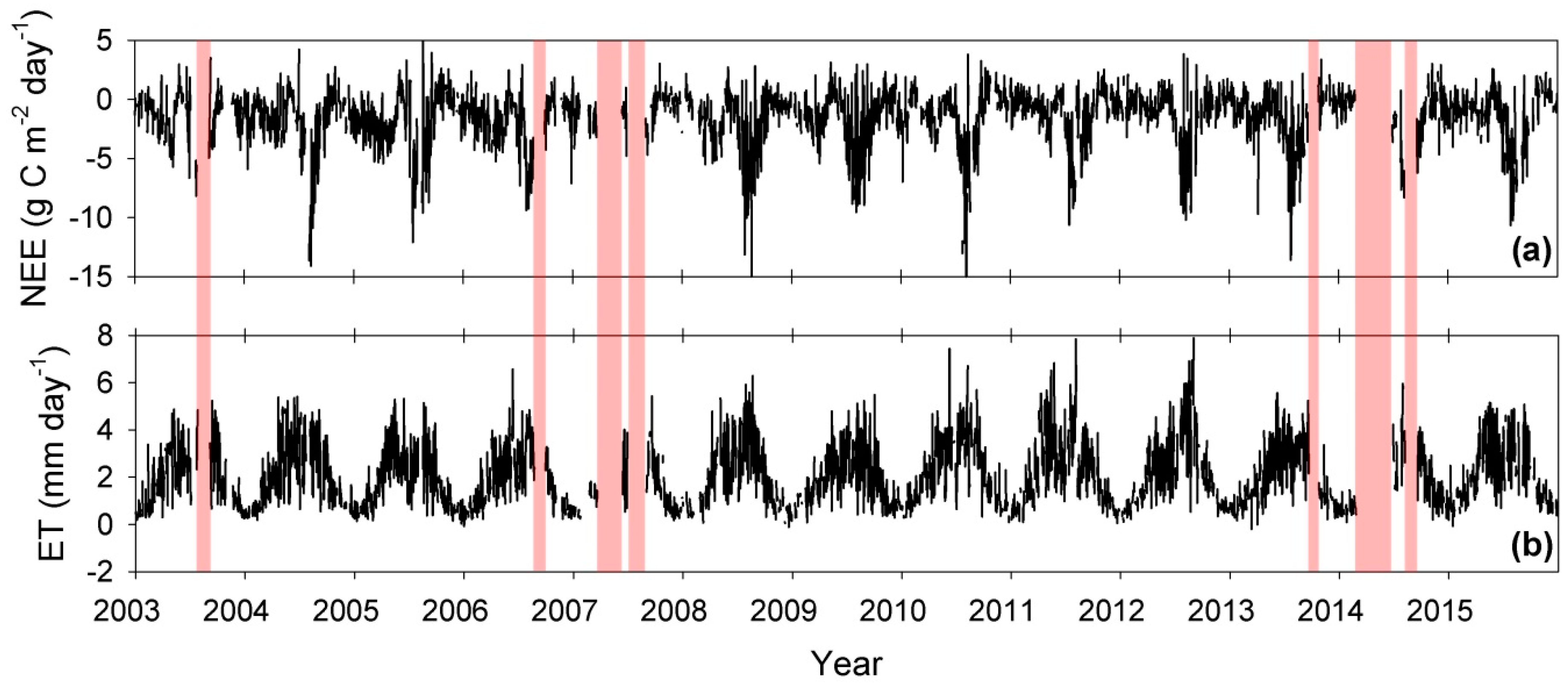
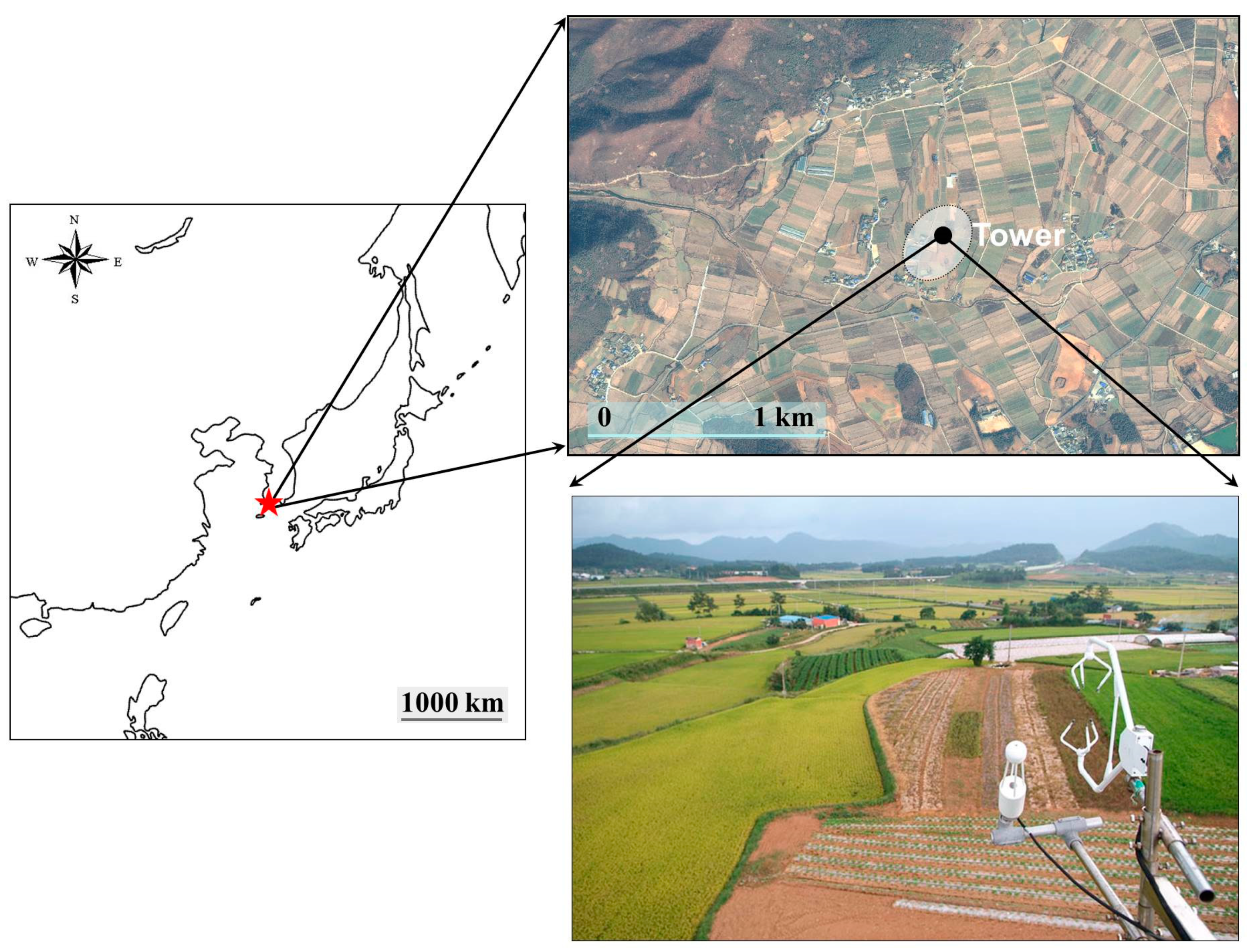
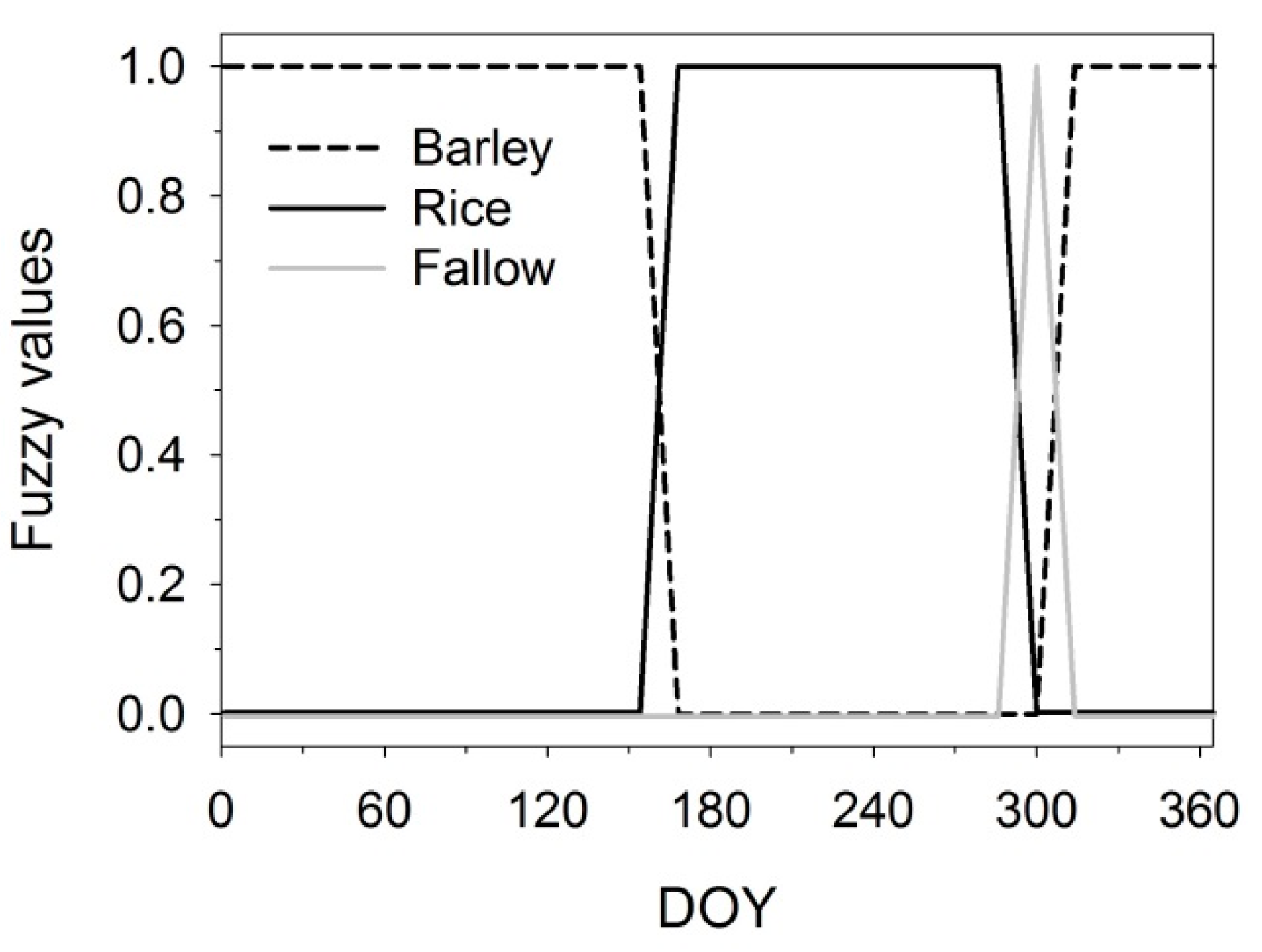
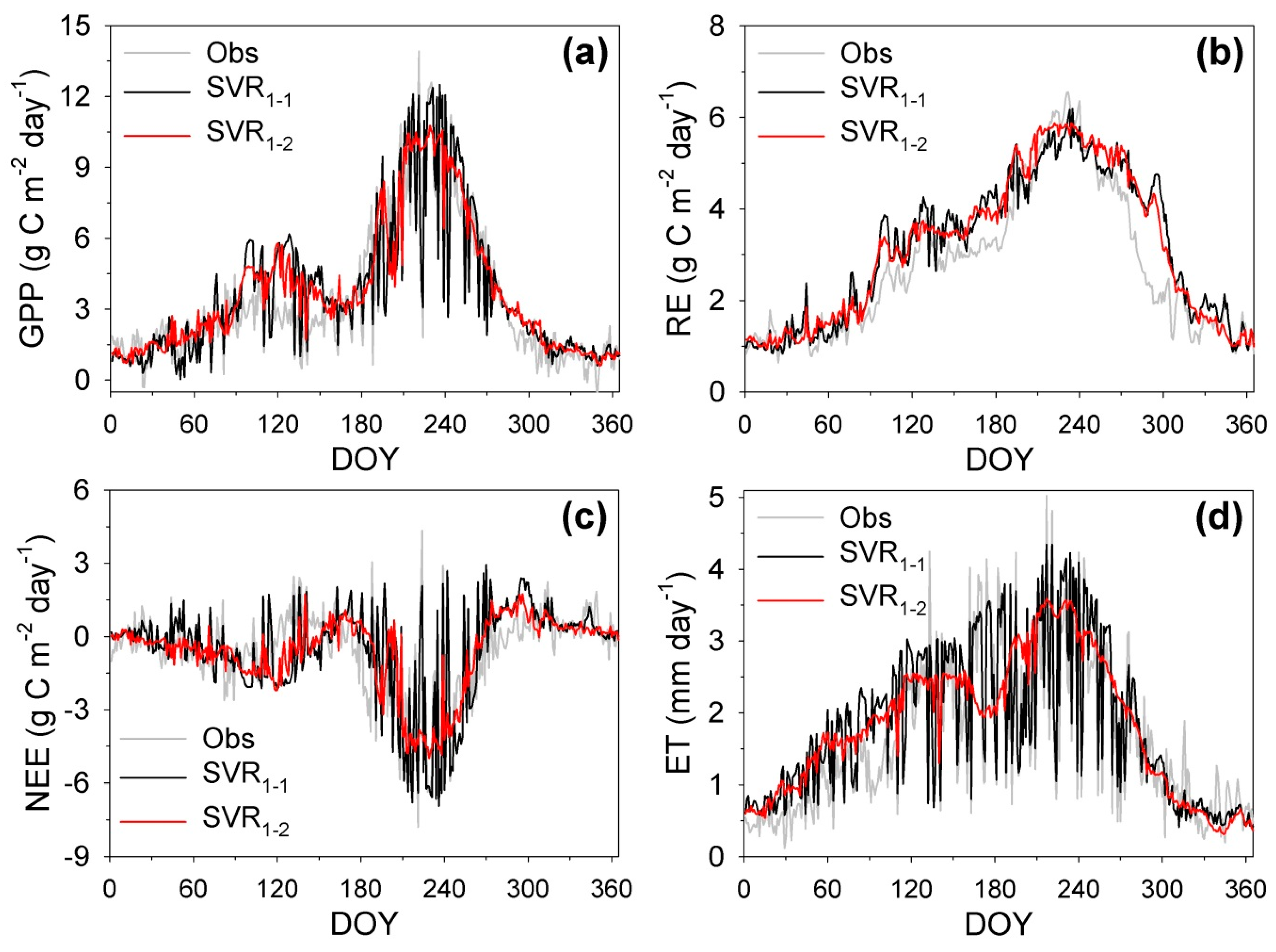
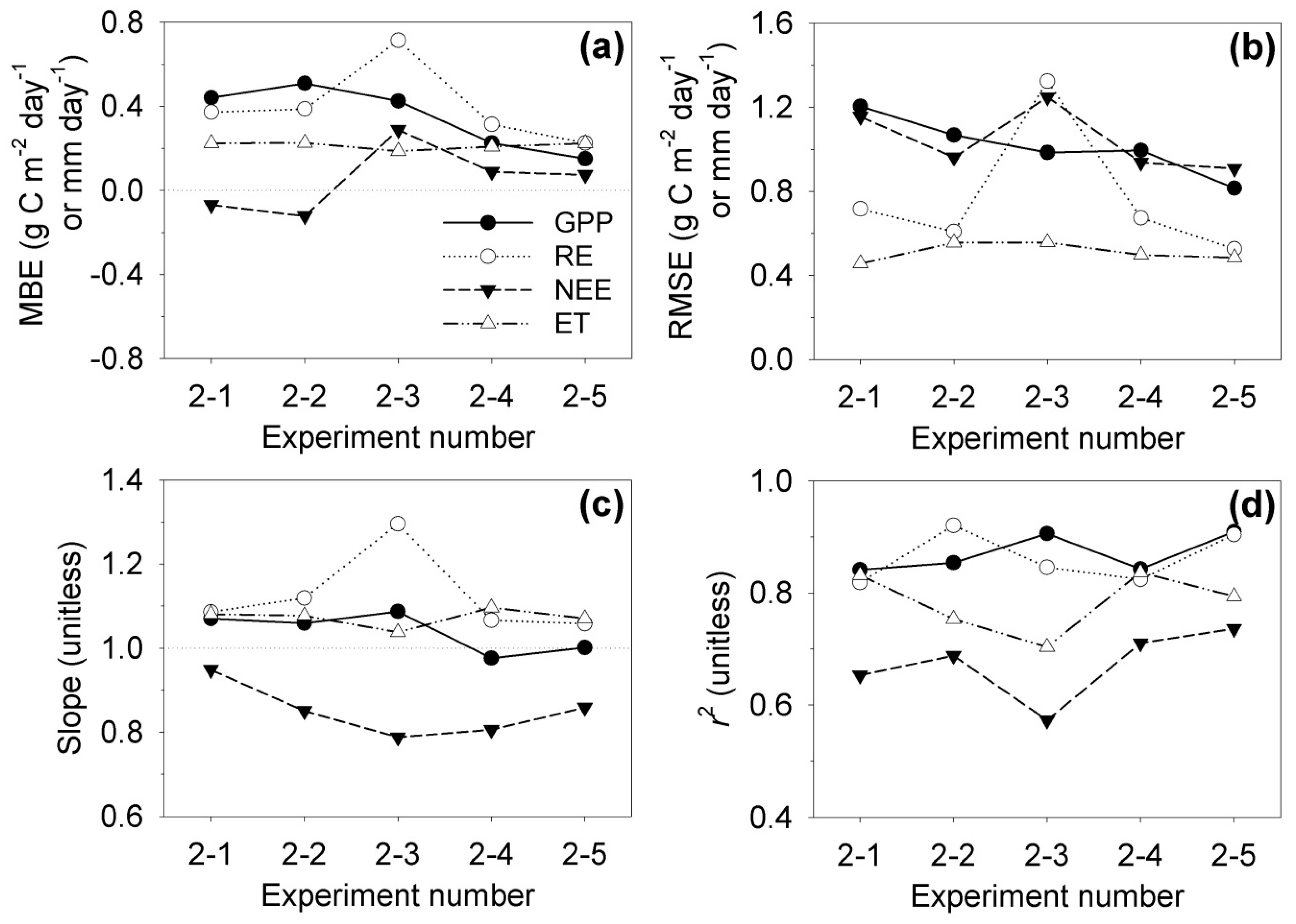
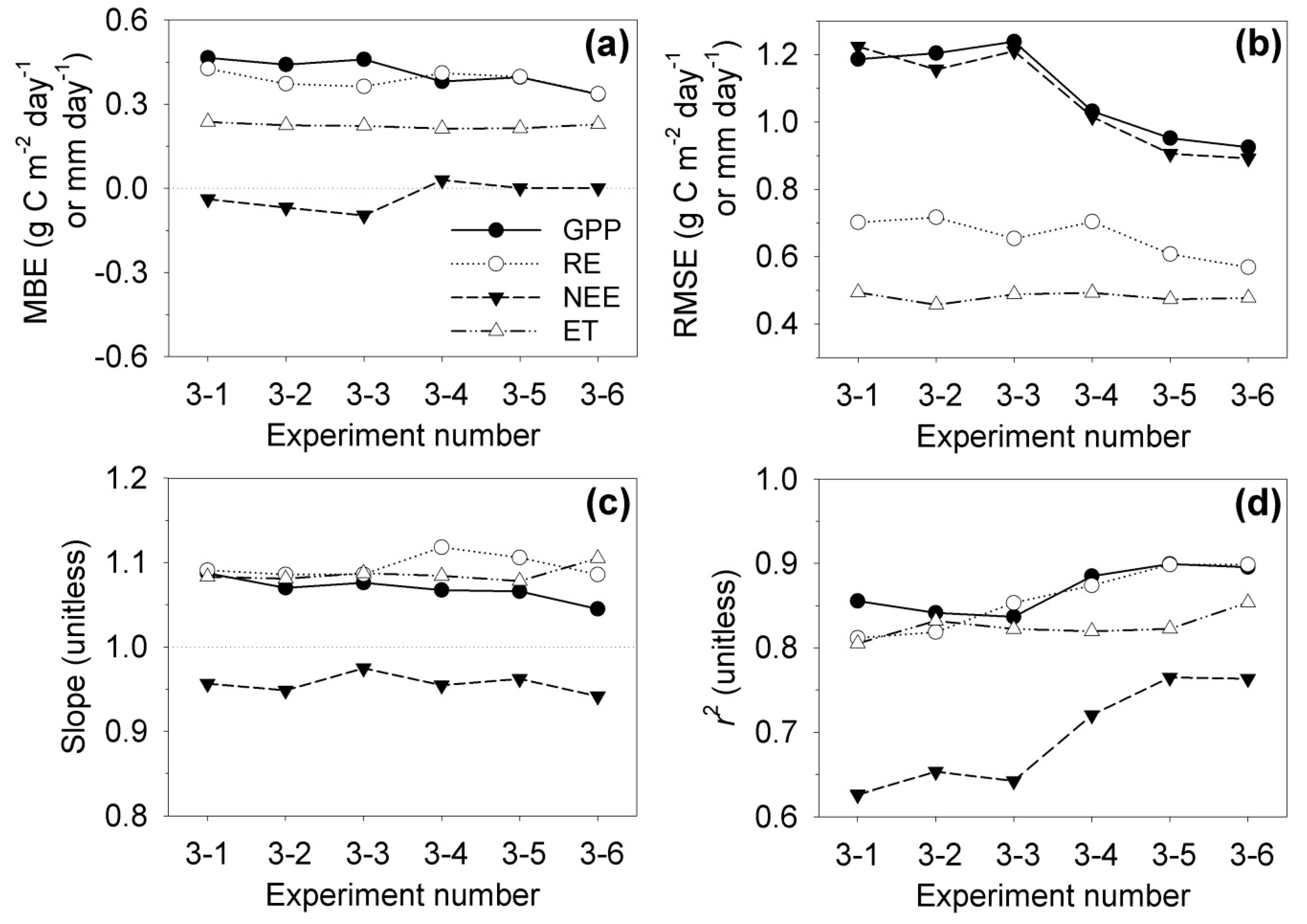
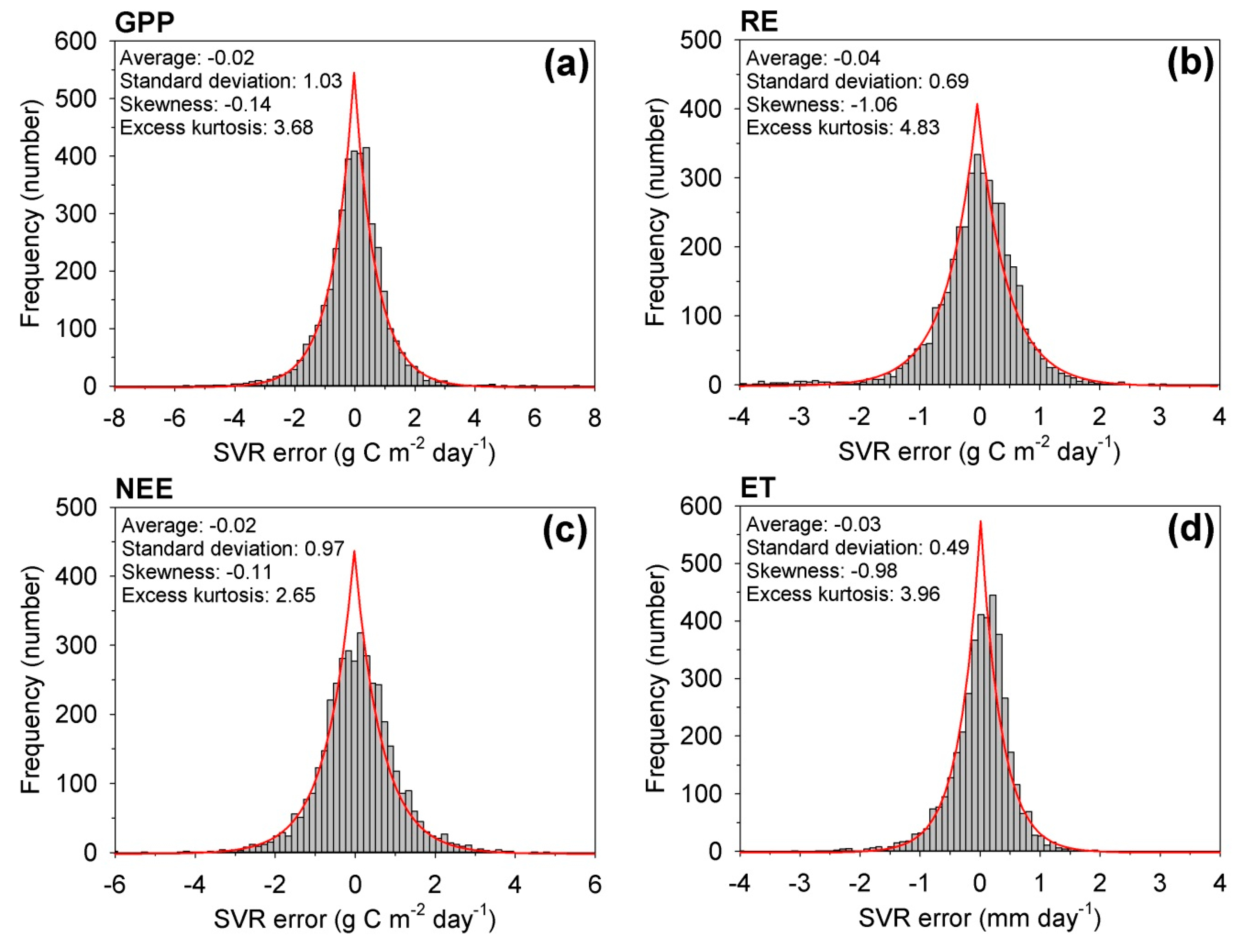
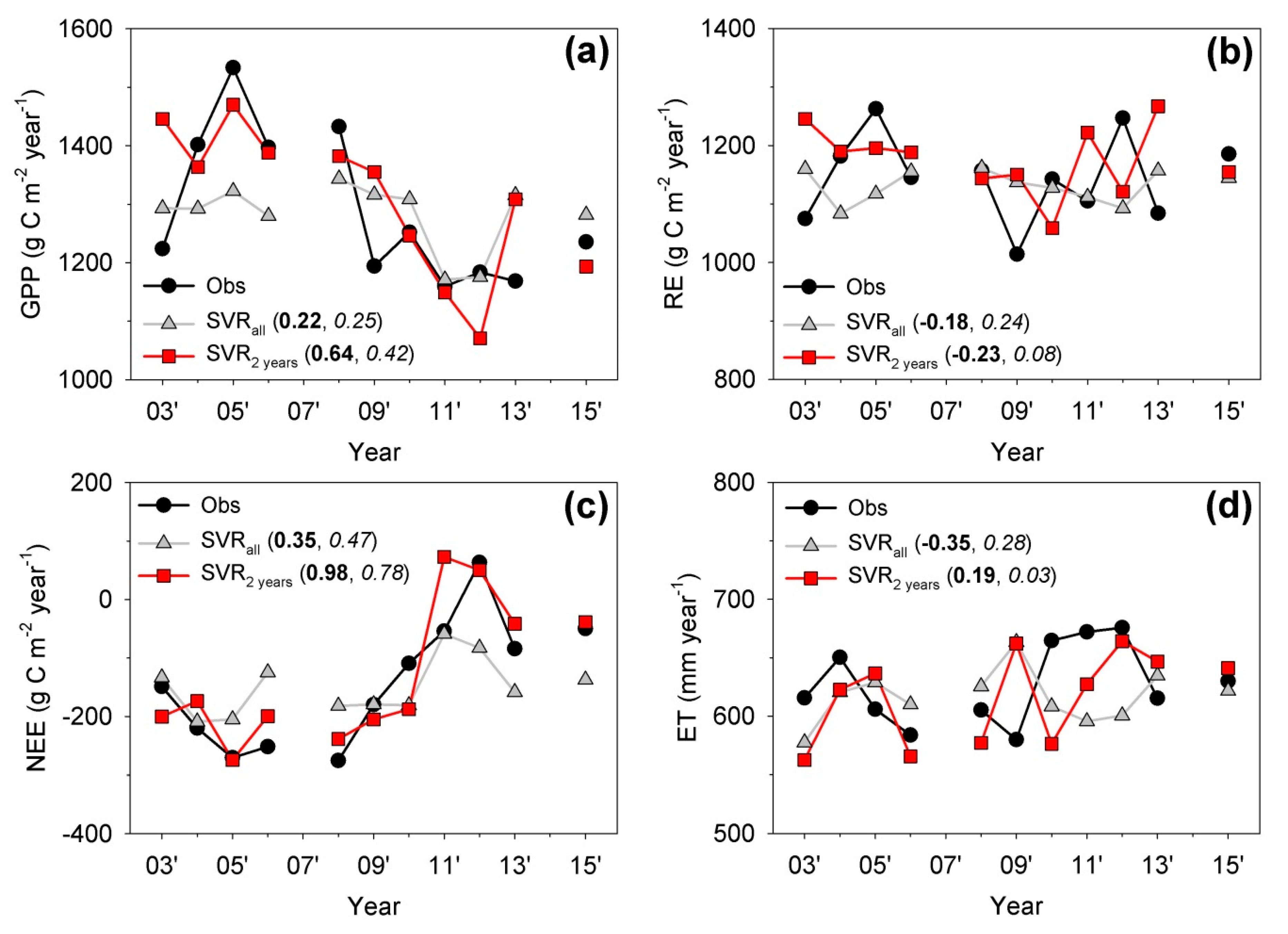
| Year | Data Retrieval Rate (%) | Length of the 1st Longest Gap (Day) | Length of the 2nd Longest Gap (Day) | Total Length of the Long Gaps (Day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCO2 | ET | FCO2 | ET | FCO2 | ET | FCO2 | ET | |
| 2003 | 52.3 | 55.9 | 34.3 | 34.3 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 34.3 | 34.3 |
| 2004 | 68.1 | 69.4 | 13.1 | 13.0 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2005 | 69.8 | 72.0 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2006 | 60.7 | 62.4 | 35.3 | 35.3 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 35.3 | 35.3 |
| 2007 | 34.6 | 35.7 | 82.5 | 81.5 | 61.4 | 61.4 | 143.9 | 142.9 |
| 2008 | 62.5 | 67.1 | 13.9 | 13.8 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2009 | 61.9 | 63.0 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2010 | 64.5 | 67.2 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2011 | 71.1 | 70.6 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2012 | 65.1 | 67.3 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 2.9 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2013 | 63.3 | 65.5 | 31.3 | 31.2 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 31.3 | 31.2 |
| 2014 | 35.5 | 36.2 | 123.1 | 123.1 | 41.1 | 41.1 | 164.1 | 164.1 |
| 2015 | 63.4 | 63.4 | 12.4 | 12.4 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AVG 2 | 59.4 | 61.2 | 29.1 | 29.0 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 31.5 | 31.4 |
| STD | 11.8 | 11.9 | 35.5 | 35.4 | 18.8 | 18.8 | 56.4 | 56.4 |
| Year | Rsdn | Tair | VPD | P | LAI | EVI | LSWI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MJ m−2) | (°C) | (hPa) | (mm) | (m2 m−2) | (Unitless) | (Unitless) | |
| 2003 | 4750 | 15.8 | 6.6 | 1740 | 0.96 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2004 | 5190 | 16.5 | 8.6 | 1594 | 0.99 | 0.30 | 0.08 |
| 2005 | 5298 | 15.8 | 7.0 | 1272 | 0.92 | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| 2006 | 4909 | 15.9 | 7.0 | 1683 | 0.89 | 0.29 | 0.09 |
| 2007 | 4833 | 16.2 | 7.3 | 1678 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 0.09 |
| 2008 | 5100 | 16.1 | 7.3 | 1098 | 0.91 | 0.28 | 0.08 |
| 2009 | 5186 | 15.9 | 7.2 | 1278 | 0.99 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2010 | 4897 | 15.2 | 6.3 | 1496 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2011 | 5147 | 14.8 | 6.2 | 1499 | 0.85 | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| 2012 | 5107 | 14.8 | 6.2 | 1695 | 0.78 | 0.29 | 0.09 |
| 2013 | 5319 | 15.4 | 6.1 | 1078 | 0.89 | 0.29 | 0.07 |
| 2014 | 5082 | 15.5 | 5.7 | 1173 | 0.93 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| 2015 | 5162 | 15.7 | 5.6 | 1158 | 0.89 | 0.29 | 0.09 |
| AVG | 5075 | 15.7 | 6.7 | 1419 | 0.91 | 0.29 | 0.09 |
| STD | 176 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 250 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Hypotheses | Exp. No. | Target Year | Training Year | Meteorological Input Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Estimation using in situ measurement data as the input for machine learning is more reasonable than that using remote-sensing and modeling data. | 1-1 | 2009 | 2008 & 2010 | In situ measurement |
| 1-2 | Remote sensing & modeling | |||
| (2) A training dataset for machine learning that is closer to the gaps results in better estimation. | 2-1 | 2009 | 2008 & 2010 | In situ measurement |
| 2-2 | 2006 & 2011 | |||
| 2-3 | 2005 & 2012 | |||
| 2-4 | 2004 & 2013 | |||
| 2-5 | 2003 & 2015 | |||
| (3) A longer training dataset for machine learning results in better estimation. | 3-1 | 2009 | 2008 or 2010 | In situ measurement |
| 3-2 | 2008 & 2010 | |||
| 3-3 | 2006, 2008, 2010, & 2011 | |||
| 3-4 | 2005, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2011, & 2012 | |||
| 3-5 | 2004, 2005, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2011, 2012, & 2013 | |||
| 3-6 | 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, & 2015 |
| Variables | Experiment No. 1-1 | Experiment No. 1-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBE | RMSE | Slope | r2 | MBE | RMSE | Slope | r2 | |
| GPP (g C m−2 day−1) | 0.441 | 1.204 | 1.070 | 0.841 | 0.518 | 1.545 | 1.028 | 0.679 |
| RE (g C m−2 day−1) | 0.373 | 0.717 | 1.086 | 0.819 | 0.376 | 0.655 | 1.100 | 0.875 |
| NEE (g C m−2 day−1) | −0.068 | 1.156 | 0.948 | 0.653 | −0.142 | 1.463 | 0.585 | 0.294 |
| ET (mm day−1) | 0.225 | 0.457 | 1.081 | 0.832 | 0.228 | 0.761 | 0.997 | 0.328 |
| Variables | Support Vector Regression | Random Forest | Artificial Neural Network | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBE | RMSE | Slope | r2 | MBE | RMSE | Slope | r2 | MBE | RMSE | Slope | r2 | |
| GPP | 0.335 | 0.925 | 1.045 | 0.896 | 0.412 | 0.940 | 1.046 | 0.885 | 0.338 | 0.938 | 1.050 | 0.895 |
| RE | 0.337 | 0.568 | 1.086 | 0.899 | 0.454 | 0.628 | 1.133 | 0.922 | 0.376 | 0.633 | 1.100 | 0.876 |
| NEE | 0.002 | 0.892 | 0.941 | 0.763 | 0.043 | 0.854 | 0.825 | 0.753 | 0.038 | 0.895 | 0.949 | 0.767 |
| ET | 0.229 | 0.477 | 1.105 | 0.854 | 0.252 | 0.474 | 1.096 | 0.831 | 0.240 | 0.477 | 1.095 | 0.833 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.; Ichii, K.; Kim, J.; Indrawati, Y.M.; Park, J.; Moon, M.; Lim, J.-H.; Chun, J.-H. New Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps Using a Data-Driven Approach. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100568
Kang M, Ichii K, Kim J, Indrawati YM, Park J, Moon M, Lim J-H, Chun J-H. New Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps Using a Data-Driven Approach. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(10):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100568
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Minseok, Kazuhito Ichii, Joon Kim, Yohana M. Indrawati, Juhan Park, Minkyu Moon, Jong-Hwan Lim, and Jung-Hwa Chun. 2019. "New Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps Using a Data-Driven Approach" Atmosphere 10, no. 10: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100568
APA StyleKang, M., Ichii, K., Kim, J., Indrawati, Y. M., Park, J., Moon, M., Lim, J.-H., & Chun, J.-H. (2019). New Gap-Filling Strategies for Long-Period Flux Data Gaps Using a Data-Driven Approach. Atmosphere, 10(10), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100568






