A Statistical Method for Observing Personal Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes with Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Assignment of Reads to Each Haplotype for AK1 and HG002
2.3. Generating the Diploid Methylomes
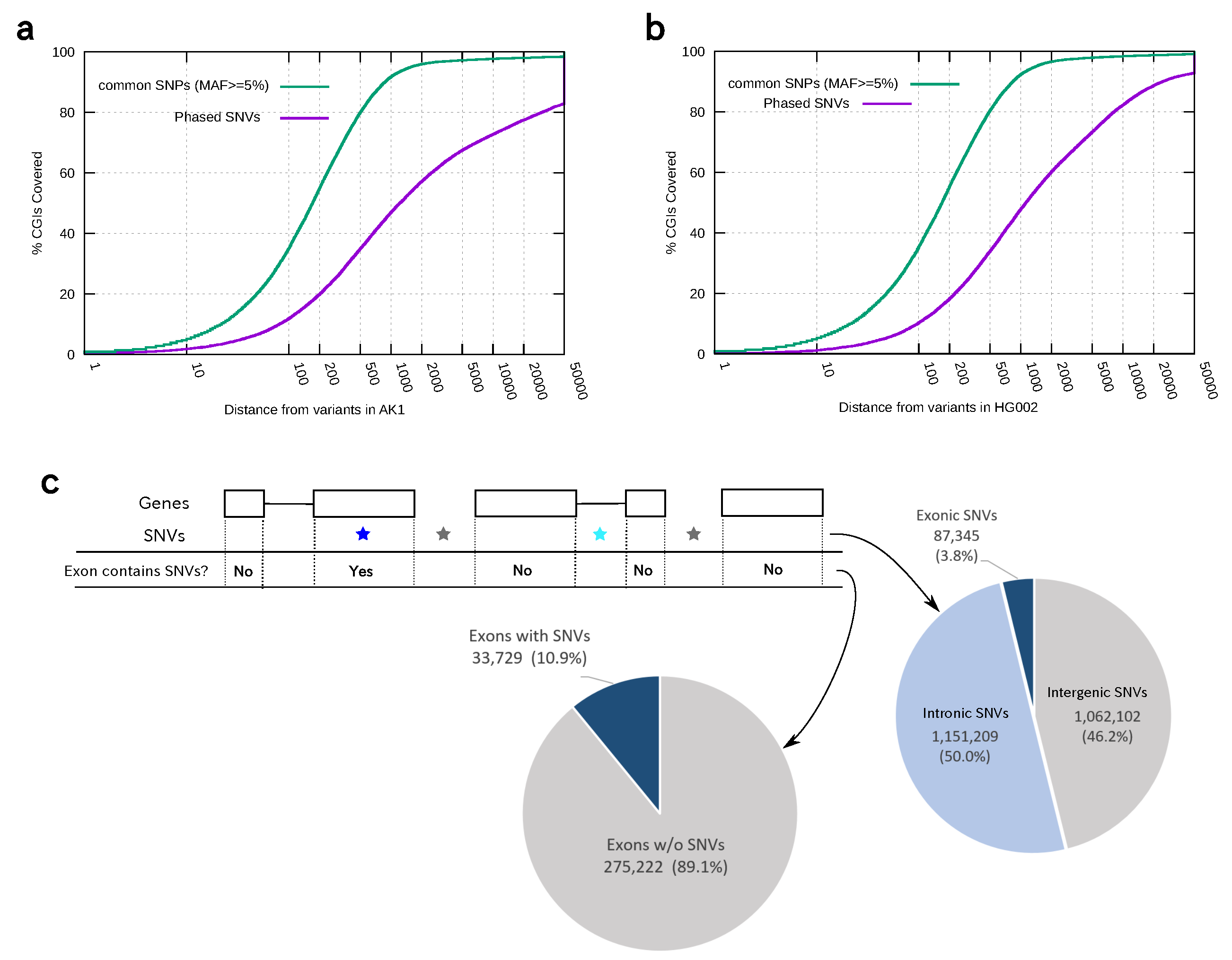
2.4. Calculating the Distribution of Phased Heterozygous Variants with Respect to CpG Islands or Exons
2.5. Allele-Specific Expression Analysis of AK1
2.6. Identifying CpG Islands with Allele-Specific Methylation
3. Results
3.1. A Statistical Model for Accurate Read Assignment
3.2. Generating Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes for the AK1 and HG002 Datasets
3.3. Distribution of Phased Heterozygous Variants in Two Personal Genomes
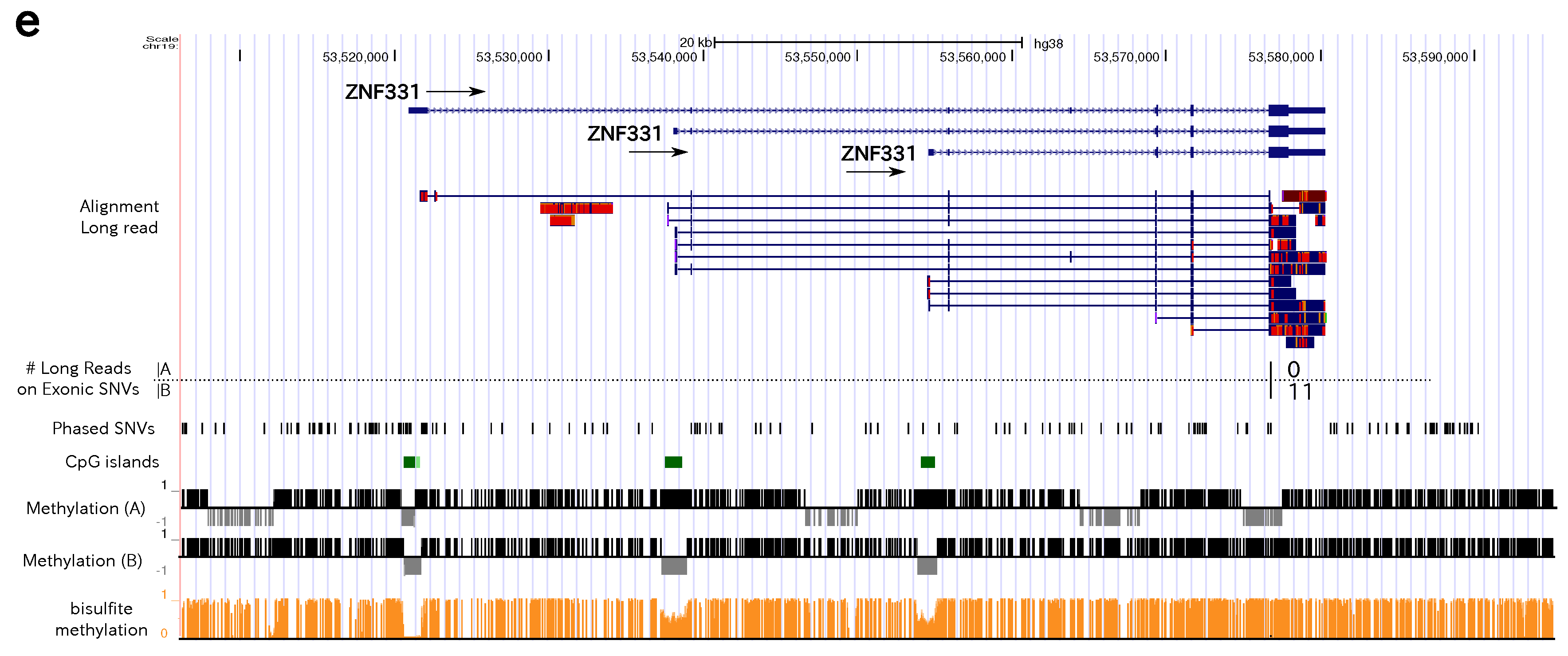
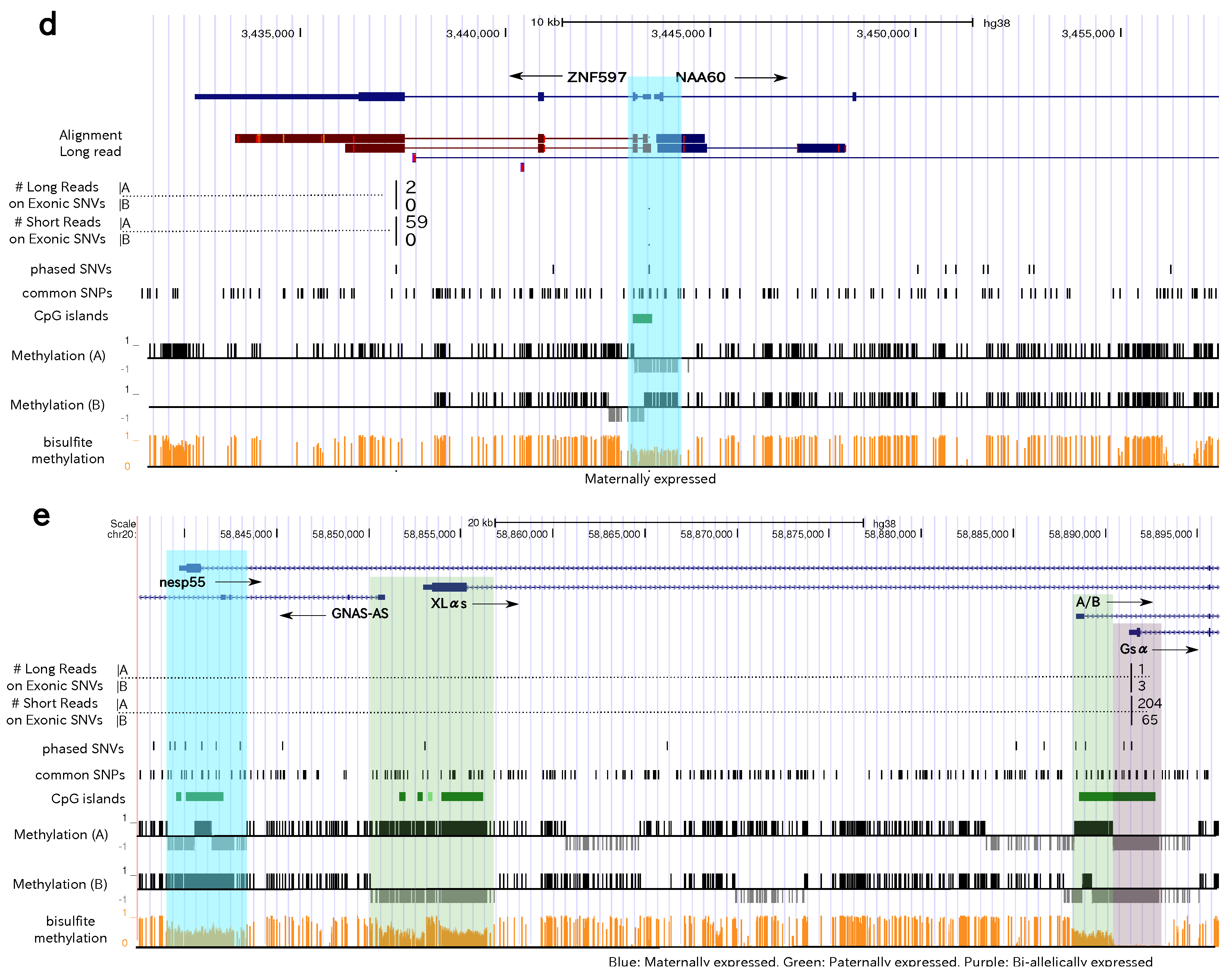
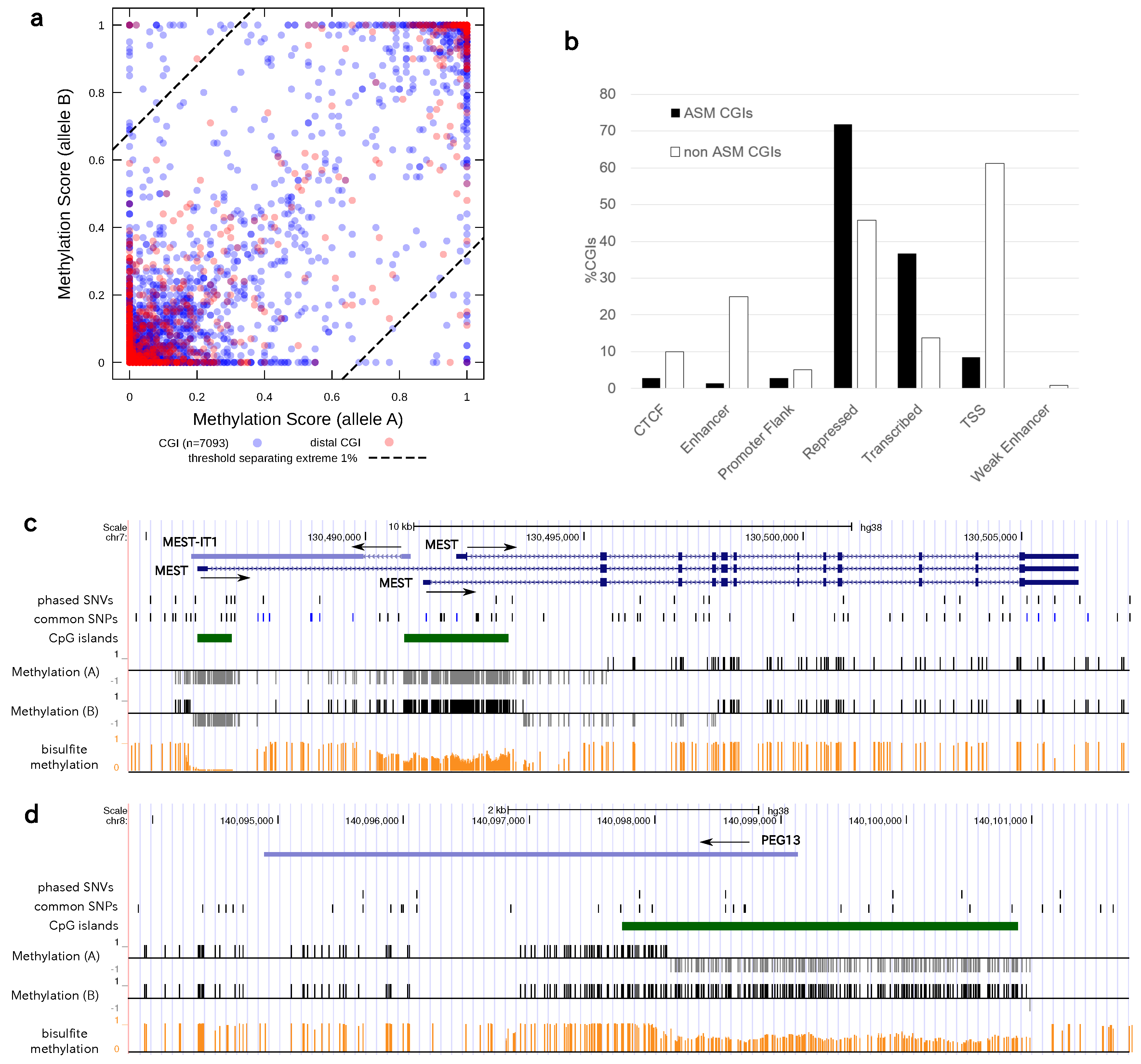
3.4. Allele-Specific Methylation of CpG Islands and Allele-Specific Expresion
3.5. Statistics of Allele-Specific Methylation CpG Islands
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASM | Allele-specific methylation |
| ASE | Allele-specific expresssion |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SNV | Single nucleotide variant |
| PHV | Phased heterozygous variant |
| IPD | Inter-pulse duration |
| CGI | CpG island |
References
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA methylation: Roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schübeler, D. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature 2015, 517, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Down, T.A.; Rakyan, V.K.; Turner, D.J.; Flicek, P.; Li, H.; Kulesha, E.; Graef, S.; Johnson, N.; Herrero, J.; Tomazou, E.M.; et al. A Bayesian deconvolution strategy for immunoprecipitation-based DNA methylome analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Dowen, R.H.; Hawkins, R.D.; Hon, G.; Tonti-Filippini, J.; Nery, J.R.; Lee, L.; Ye, Z.; Ngo, Q.M.; et al. Human DNA methylomes at base resolution show widespread epigenomic differences. Nature 2009, 462, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smallwood, S.A.; Lee, H.J.; Angermueller, C.; Krueger, F.; Saadeh, H.; Peat, J.; Andrews, S.R.; Stegle, O.; Reik, W.; Kelsey, G. Single-cell genome-wide bisulfite sequencing for assessing epigenetic heterogeneity. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gravina, S.; Dong, X.; Yu, B.; Vijg, J. Single-cell genome-wide bisulfite sequencing uncovers extensive heterogeneity in the mouse liver methylome. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Smallwood, S.A.; Kelsey, G.; Reik, W. Single-cell epigenomics: Powerful new methods for understanding gene regulation and cell identity. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Miura, F.; Soejima, H.; Uchiyama, M.; Iwasaka, T.; Mukai, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Ito, T. A comprehensive analysis of allelic methylation status of CpG islands on human chromosome 21q. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkel, K.; Spadola, A.; Yuan, E.; Kosek, J.; Jiang, L.; Hod, E.; Li, K.; Murty, V.V.; Schupf, N.; Vilain, E.; et al. Genomic surveys by methylation-sensitive SNP analysis identify sequence-dependent allele-specific DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalkwyk, L.C.; Meaburn, E.L.; Smith, R.; Dempster, E.L.; Jeffries, A.R.; Davies, M.N.; Plomin, R.; Mill, J. Allelic skewing of DNA methylation is widespread across the genome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.; Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K. Allele-specific methylation is prevalent and is contributed by CpG-SNPs in the human genome. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gertz, J.; Varley, K.E.; Reddy, T.E.; Bowling, K.M.; Pauli, F.; Parker, S.L.; Kucera, K.S.; Willard, H.F.; Myers, R.M. Analysis of DNA methylation in a three-generation family reveals widespread genetic influence on epigenetic regulation. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, F.; Enomoto, Y.; Dairiki, R.; Ito, T. Amplification-free whole-genome bisulfite sequencing by post-bisulfite adaptor tagging. Nucl. Acids Res. 2012, 40, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sebra, R.; Pullman, B.S.; Qiao, W.; Peter, I.; Desnick, R.J.; Geyer, C.R.; DeCoteau, J.F.; Scott, S.A. Quantitative and multiplexed DNA methylation analysis using long-read single-molecule real-time bisulfite sequencing (SMRT-BS). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, V.; Xie, D.; Chen, R.; Pushkarev, D.; Ma, Z.; Blauwkamp, T.; Kertesz, M.; Snyder, M. Whole-genome haplotyping using long reads and statistical methods. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W.; Tsukahara, T.; Taniguchi, J.; Qu, W.; Ichikawa, K.; Yoshimura, J.; Yurino, H.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. AgIn: Measuring the landscape of CpG methylation of individual repetitive elements. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.D.; He, Y.; Whitaker, J.W.; Hariharan, M.; Mukamel, E.A.; Leung, D.; Rajagopal, N.; Nery, J.R.; Urich, M.A.; Chen, H.; et al. Human body epigenome maps reveal noncanonical DNA methylation variation. Nature 2015, 523, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deonovic, B.; Wang, Y.; Weirather, J.; Wang, X.J.; Au, K.F. IDP-ASE: Haplotyping and quantifying allele-specific expression at the gene and gene isoform level by hybrid sequencing. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, K.F.; Sebastiano, V.; Afshar, P.T.; Durruthy, J.D.; Lee, L.; Williams, B.A.; van Bakel, H.; Schadt, E.E.; Reijo-Pera, R.A.; Underwood, J.G.; et al. Characterization of the human ESC transcriptome by hybrid sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4821–E4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genome in a Bottle Consortium. Available online: ftp://ftp-trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/giab/ftp/release (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Seo, J.S.; Rhie, A.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Sohn, M.H.; Kim, C.U.; Hastie, A.; Cao, H.; Yun, J.Y.; Kim, J.; et al. De novo assembly and phasing of a Korean human genome. Nature 2016, 538, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, G.X.; Lau, B.T.; Schnall-Levin, M.; Jarosz, M.; Bell, J.M.; Hindson, C.M.; Kyriazopoulou-Panagiotopoulou, S.; Masquelier, D.A.; Merrill, L.; Terry, J.M.; et al. Haplotyping germline and cancer genomes with high-throughput linked-read sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.D.; Watanabe, C.K. GMAP: A genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.S.; Peluso, P.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Nattestad, M.; Concepcion, G.T.; Clum, A.; Dunn, C.; O’Malley, R.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Morales-Cruz, A.; et al. Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, K.F.; Underwood, J.G.; Lee, L.; Wong, W.H. Improving PacBio long read accuracy by short read alignment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, Y.; Asai, K.; Hamada, M. PBSIM: PacBio reads simulator—Toward accurate genome assembly. Bioinformatics 2012, 29, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zook, J.; Catoe, D.; McDaniel, J.; Vang, L.; Spies, N.; Sidow, A.; Weng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mason, C.; Alexander, N.; et al. Extensive sequencing of seven human genomes to characterize benchmark reference materials. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stunnenberg, H.G.; Abrignani, S.; Adams, D.; de Almeida, M.; Altucci, L.; Amin, V.; Amit, I.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Aparicio, S.; Arima, T.; et al. The International Human Epigenome Consortium: A blueprint for scientific collaboration and discovery. Cell 2016, 167, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucl. Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastepe, M. The GNAS locus: Quintessential complex gene encoding Gsα, XLαs, and other imprinted transcripts. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.E.P. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, Y.; Subramaniam, M.; Biton, A.; Tukiainen, T.; Tsang, E.K.; Rivas, M.A.; Pirinen, M.; Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Smith, K.S.; Kukurba, K.R.; et al. The landscape of genomic imprinting across diverse adult human tissues. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porubsky, D.; Garg, S.; Sanders, A.D.; Korbel, J.O.; Guryev, V.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Marschall, T. Dense and accurate whole-chromosome haplotyping of individual genomes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Christiansen, L.; Thomas, J.; Pokholok, D.; Jackson, R.; Morrell, N.; Zhao, Y.; Wiley, M.; Welch, E.; Jaeger, E.; et al. Haplotype phasing of whole human genomes using bead-based barcode partitioning in a single tube. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Elazar, S.; Chor, B.; Yakhini, Z. Extending partial haplotypes to full genome haplotypes using chromosome conformation capture data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, i559–i566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostovoy, Y.; Levy-Sakin, M.; Lam, J.; Lam, E.T.; Hastie, A.R.; Marks, P.; Lee, J.; Chu, C.; Lin, C.; Džakula, Ž.; et al. A hybrid approach for de novo human genome sequence assembly and phasing. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzuki, Y.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F.; Morishita, S. A Statistical Method for Observing Personal Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes with Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing. Genes 2018, 9, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9090460
Suzuki Y, Wang Y, Au KF, Morishita S. A Statistical Method for Observing Personal Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes with Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing. Genes. 2018; 9(9):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9090460
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzuki, Yuta, Yunhao Wang, Kin Fai Au, and Shinichi Morishita. 2018. "A Statistical Method for Observing Personal Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes with Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing" Genes 9, no. 9: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9090460
APA StyleSuzuki, Y., Wang, Y., Au, K. F., & Morishita, S. (2018). A Statistical Method for Observing Personal Diploid Methylomes and Transcriptomes with Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing. Genes, 9(9), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9090460




