Synteny-Based Development of CAPS Markers Linked to the Sweet kernel LOCUS, Controlling Amygdalin Accumulation in Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Isolation
2.2. Simple Sequence Repeat Marker Analysis
2.3. Development of Sk-Linked CAPS Markers
2.4. Linkage Analysis
2.5. CAPS Assay on a Cultivar Collection
2.6. Bioinformatic Characterization of the Peach Sk Synthenic Region
3. Results
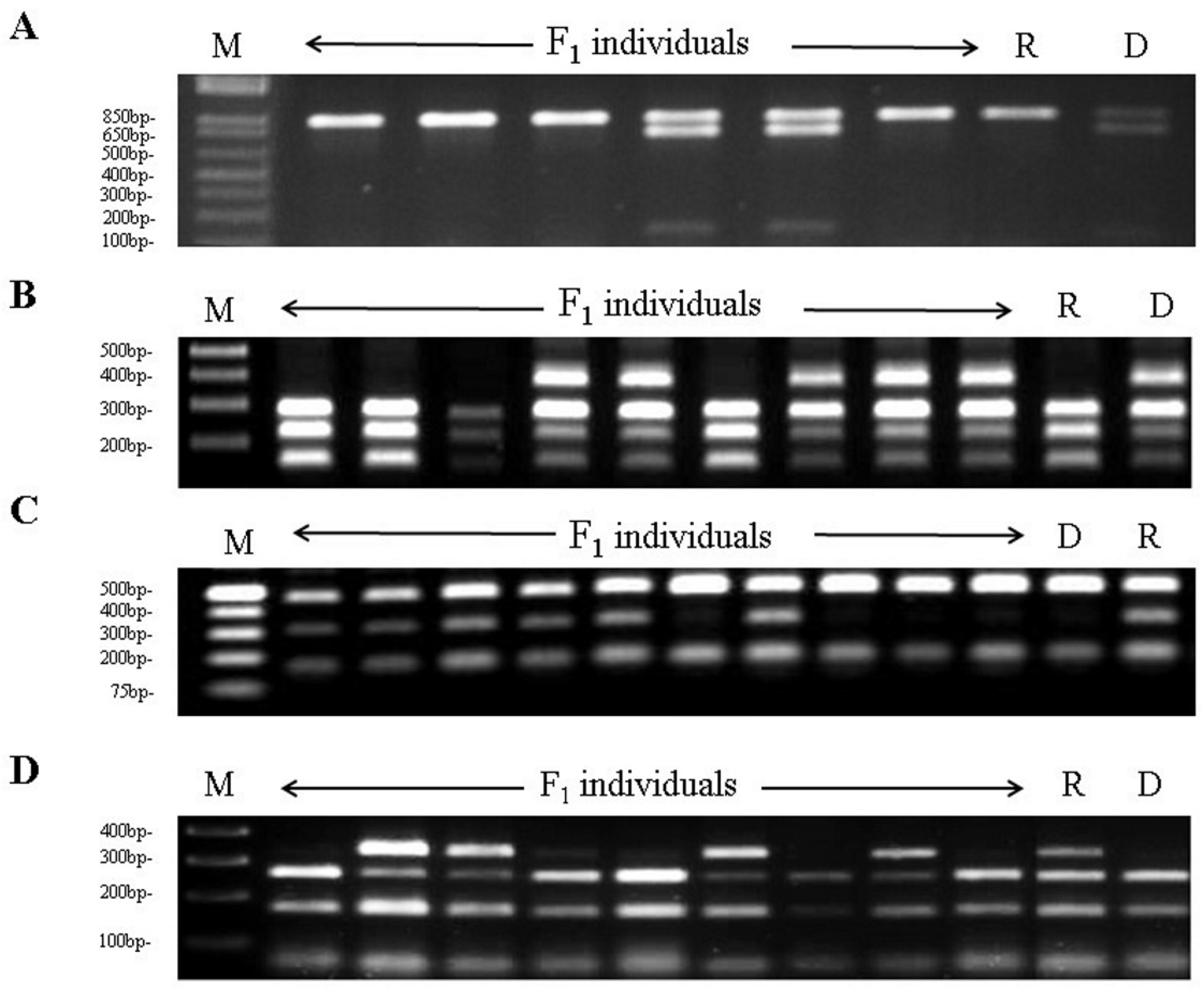
3.1. Development of Sk-Linked CAPS Markers
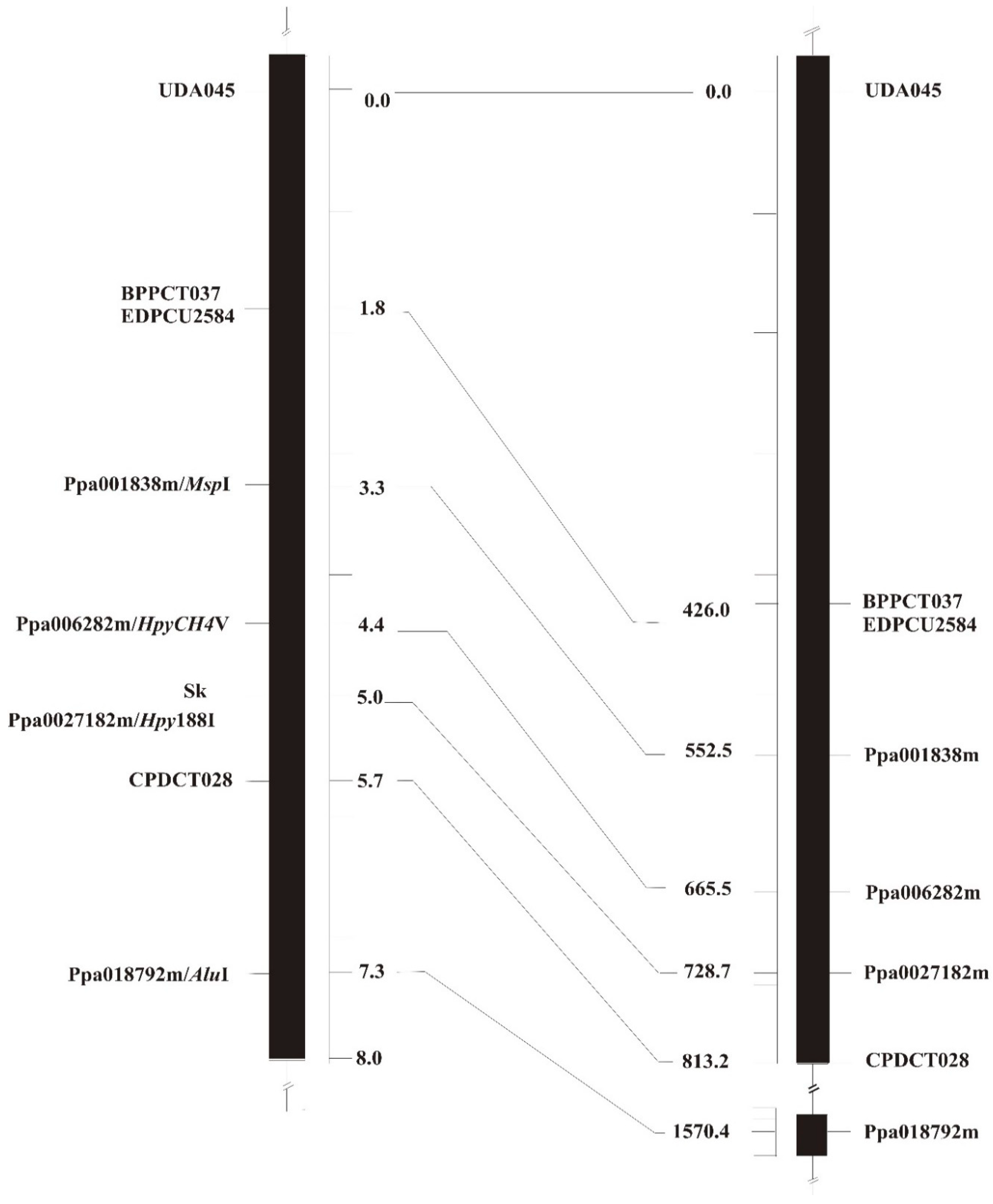
3.2. Sk Mapping and Syntenic Relationships with the Peach Genome
3.3. Marker Validation in An Almond Germplasm Collection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S.; Rasmussen, A.V.; Jørgensen, B.; Naumann, C.M.; Møller, B.L. Cyanogenic glucosides and plant-insect interactions. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicenta, F.; Ortega, E.; Martìnez-Gòmez, P. Use of recessive homozygous genotypes to assess the genetic control of kernel bitterness in almond. Euphytica 2007, 153, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicenta, F.; Martìnez-Gòmez, P.; Ortega, E.; Duval, H. Cultivar pollinizer does not affect almond flavour. HortScience 2000, 35, 1153–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Howad, W.; Dicenta, F.; Arùs, P.; Martìnez-Gòmez, P. Mapping major genes and quantitative trait loci controlling agronomic traits in almond. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicenta, F.; García, J.E. Inheritance of the kernel flavour in almond. Heredity 1993, 70, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Jørgensen, K.; Olsen, C.E.; Dicenta, F.; Møller, B.L. Bitternes in almond. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Belmonte, F.S.; Borch, J.; Dicenta, F.; Møller, B.L.; Jørgensen, K. Prunasin hydrolases during fruit development in sweet and bitter almonds. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1916–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro Vieira, M.L.; Santini, L.; Diniz, A.L.; de Freitas Munhoz, C. Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, S.; Schiavulli, A.; Lotti, C.; Ricciardi, L. CAPS technology as a tool for the development of genic and functional markers: Study in peas. In Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences (CAPS) Markers in Plant Biology; Shavrukov, Y., Ed.; Nova Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, S.; Schiavulli, A.; Appiano, M.; Miacola, C.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y.; Lotti, C.; Ricciardi, L. Identification of a complete set of functional markers for the selection of er1 powdery mildew resistance in pea. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, S.; Zheng, Z.; van den Berg, P.; Lotti, C.; De Giovanni, C.; Borisova, M.; Lindhout, P.; de Jong, H.; Ricciardi, L.; Visser, R.G.F.; et al. Map vs. homology-based cloning for the recessive gene ol-2 conferring resistance to tomato powdery mildew. Euphytica 2008, 162, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Howad, W.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Arús, P.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Dicenta, F. Molecular markers for kernel bitterness in almond. Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Cosson, P.; Howad, W.; Capdeville, G.; Bosselut, N.; Claverie, M.; Voisin, R.; Poizat, C.; Lafargue, B.; Baron, O. Microsatellite genetic linkage maps of myrobalan plum and an almond-peach hybrid—Location of root-knot nematode resistance genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Crosson, A.; Tavaud, P.; Aranzana, M.J.; Poizat, C.; Zanetto, A.; Arús, P.; Laigret, L. Development of microsatellite markers in peach and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnejja, M.; García-Mas, J.; Howad, W.; Arus, P. Development and transportability across Prunus species of 42 polymorphic almond microsatellites. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke, M. An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Pozo, N.; Menda, N.; Edwards, J.D.; Saha, S.; Tecle, I.Y.; Strickler, S.R.; Bombarely, A.; Fisher-York, T.; Pujar, A.; Foerster, H.; et al. The Sol Genomics Network (SGN)—From genotype to phenotype to breeding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. JoinMap 4.0: Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage Maps in Experimental Populations; Kyazma B.V.: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Agy, S.; Poczai, P.; Cernák, I.; Gorji, A.M.; Hegedűs, G.; Taller, J. PICcalc: An online program to calculate polymorphic information content for molecular genetic studies. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InterPro: Protein Sequence Analysis & Classification. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Smith, S.M.; Maughan, P.J. SNP genotyping using KASPar assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1245, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cultivar | Origin |
|---|---|
| Del Cid | Spain |
| Ramillete | Spain |
| Atocha | Spain |
| Desmayo Largueta | Spain |
| Marcona | Spain |
| Vivot | Spain |
| Peraleja | Spain |
| Antoñeta | Spain |
| Ferragnès | France |
| Lauranne | France |
| Marta | Spain |
| R-1000 | France |
| Mono | USA |
| Tioga | USA |
| Titan | USA |
| Wawona | USA |
| Nonpareil | USA |
| Tardy-Nonpareil | USA |
| Achaak | Tunisia |
| Ardechoise | France |
| Chellaston | Australia |
| Primorskii | Russia |
| Garrigues | Spain |
| Genco | Italy |
| Tuono | Italy |
| Marker | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | PCR Product (bp) | SNP | Digestion Products (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppa001838m/MspI | F: GGTTGTTCTGGGAGATGGAA R: ACTTGACCGCAACCAAAATC | 800 | T→G | D: 800, 650, 150 |
| R: 800 | ||||
| ppa006282m/HpyCH4V | F: GTTTCGCTCGATTGGGTCTC R: ATCATTTCCCGCCTGAATGC | 700 | G→A | D: 400, 300, 250, 150 |
| R:300, 250, 150 | ||||
| ppa027182m/Hpy188I | F: AAAGAAGATTGGGGCCTTGT R: TGGTTAAGCTTCTCGCGTCT | 600 | C→T | D: 450, 150 |
| R: 450, 300, 150, | ||||
| ppa018792m/AluI | F: ACGTTGTCTCGTTCGTGGTT R: AGGTGCTGCAAAGACACTGA | 540 | T→C | D:280, 180, 80 |
| R:340, 280, 180, 80 |
| GDR ID | Interval on Scaffold 5 | InterPro Putative Function |
|---|---|---|
| ppa006282m | 12.547.702-12.551.295 | Uncharacterised protein family UPF0017, hydrolase-like, conserved site |
| ppa005470m | 12.555.940-12.558.349 | Cys/Met metabolism, pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme |
| ppa003882m | 12.562.194-12.564.053 | Cytochrome P450 |
| ppa011942m | 12.576.856-12.578.103 | Mediator complex, subunit Med10 |
| ppa023406m | 12.587.426-12.589.276 | Glyoxal oxidase |
| ppa022201m | 12.597.330-12.598.918 | Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding-Transcription factor MYC/MYB |
| ppa025417m | 12.603.688-12.605.325 | Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding-Transcription factor MYC/MYB |
| ppa027182m | 12.612.821-12.614.522 | Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding-Transcription factor MYC/MYB |
| ppa015634m | 12.625.785-12.627.695 | Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding-Transcription factor MYC/MYB |
| ppa005343m | 12.636.946-12.638.591 | Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding-Transcription factor MYC/MYB |
| ppa005388m | 12.644.406-12.646.982 | Alpha/beta hydrolase fold-1 |
| ppa021506m | 12.649.801-12.651.659 | GDSL lipase |
| ppa010428m | 12.662.679-12.664.291 | Domain of unknown function DUF4033 |
| ppa004653m | 12.666.017-12.668.186 | Glycoside hydrolase, family 9 |
| ppa005847m | 12.669.378-12.670.953 | Transmembrane receptor, eukaryota |
| ppa022759m | 12.673.586-12.675.114 | Unknown |
| ppa019752m | 12.677.592-12.679.579 | WRC domain protein |
| ppa021141m | 12.680.973-12.682.964 | IQ motif, EF-hand binding site |
| ppa019815m | 12.687.460-12.688.443 | Glutaredoxin |
| ppa006801m | 12.695.757-12.697.169 | No apical meristem (NAM) protein |
| CPDCT028 | 12.699.037-12.699.598 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricciardi, F.; Del Cueto, J.; Bardaro, N.; Mazzeo, R.; Ricciardi, L.; Dicenta, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Pavan, S.; Lotti, C. Synteny-Based Development of CAPS Markers Linked to the Sweet kernel LOCUS, Controlling Amygdalin Accumulation in Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb). Genes 2018, 9, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9080385
Ricciardi F, Del Cueto J, Bardaro N, Mazzeo R, Ricciardi L, Dicenta F, Sánchez-Pérez R, Pavan S, Lotti C. Synteny-Based Development of CAPS Markers Linked to the Sweet kernel LOCUS, Controlling Amygdalin Accumulation in Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb). Genes. 2018; 9(8):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9080385
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicciardi, Francesca, Jorge Del Cueto, Nicoletta Bardaro, Rosa Mazzeo, Luigi Ricciardi, Federico Dicenta, Raquel Sánchez-Pérez, Stefano Pavan, and Concetta Lotti. 2018. "Synteny-Based Development of CAPS Markers Linked to the Sweet kernel LOCUS, Controlling Amygdalin Accumulation in Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb)" Genes 9, no. 8: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9080385
APA StyleRicciardi, F., Del Cueto, J., Bardaro, N., Mazzeo, R., Ricciardi, L., Dicenta, F., Sánchez-Pérez, R., Pavan, S., & Lotti, C. (2018). Synteny-Based Development of CAPS Markers Linked to the Sweet kernel LOCUS, Controlling Amygdalin Accumulation in Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb). Genes, 9(8), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9080385






